Nervous System
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
functions of nervous system
sensory input, integration, motor output
the nervous system utilizes
electrical energy
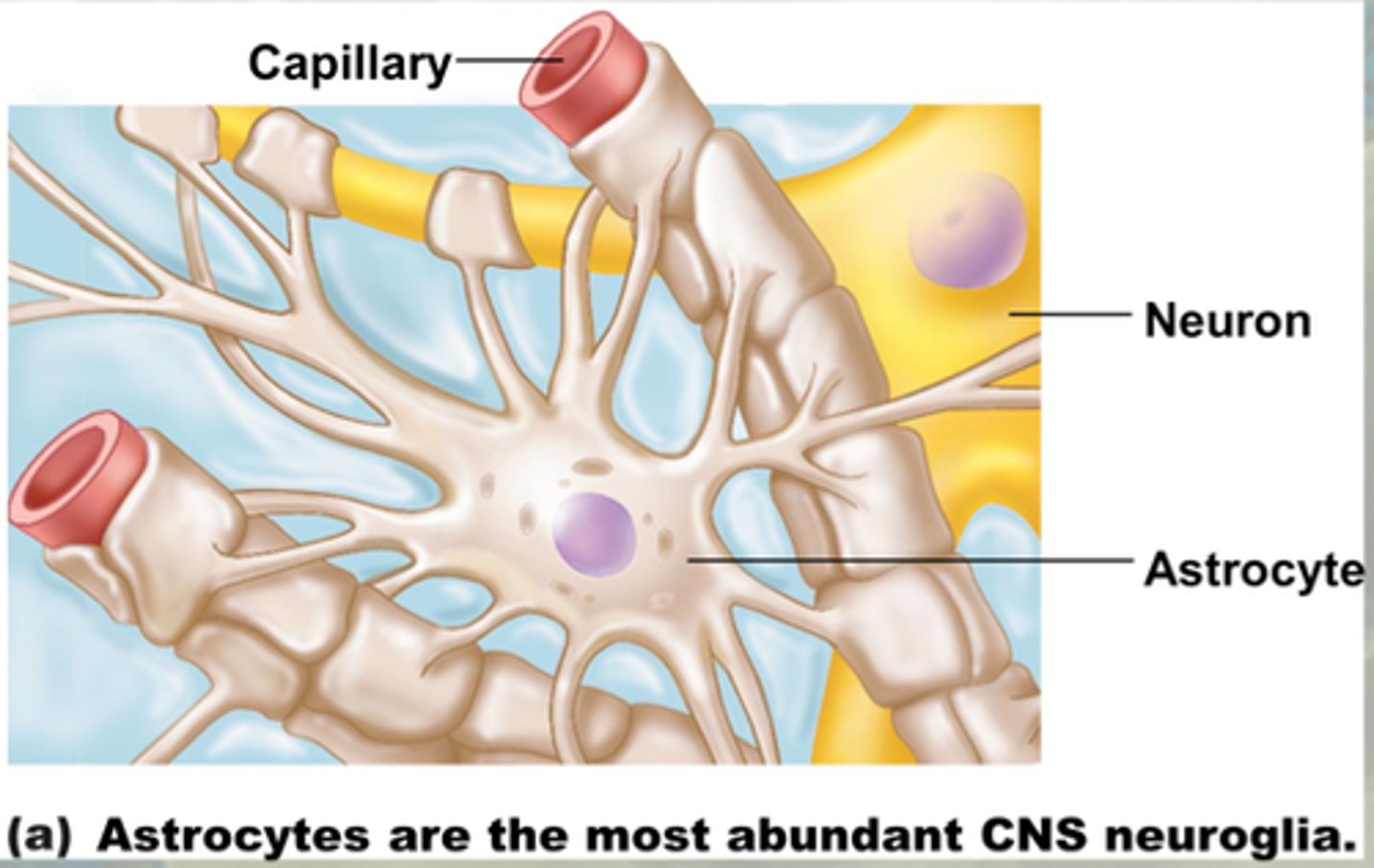
astrocytes
star cell
most abundant and versatile
1. brace neurons and blood vessels
2. formation of blood brain barrier
3. hold on to glucose
4. store potassium ions
5. mop up neurotransmitters
what can cross blood brain barrier
ethanol
glucose
insulin
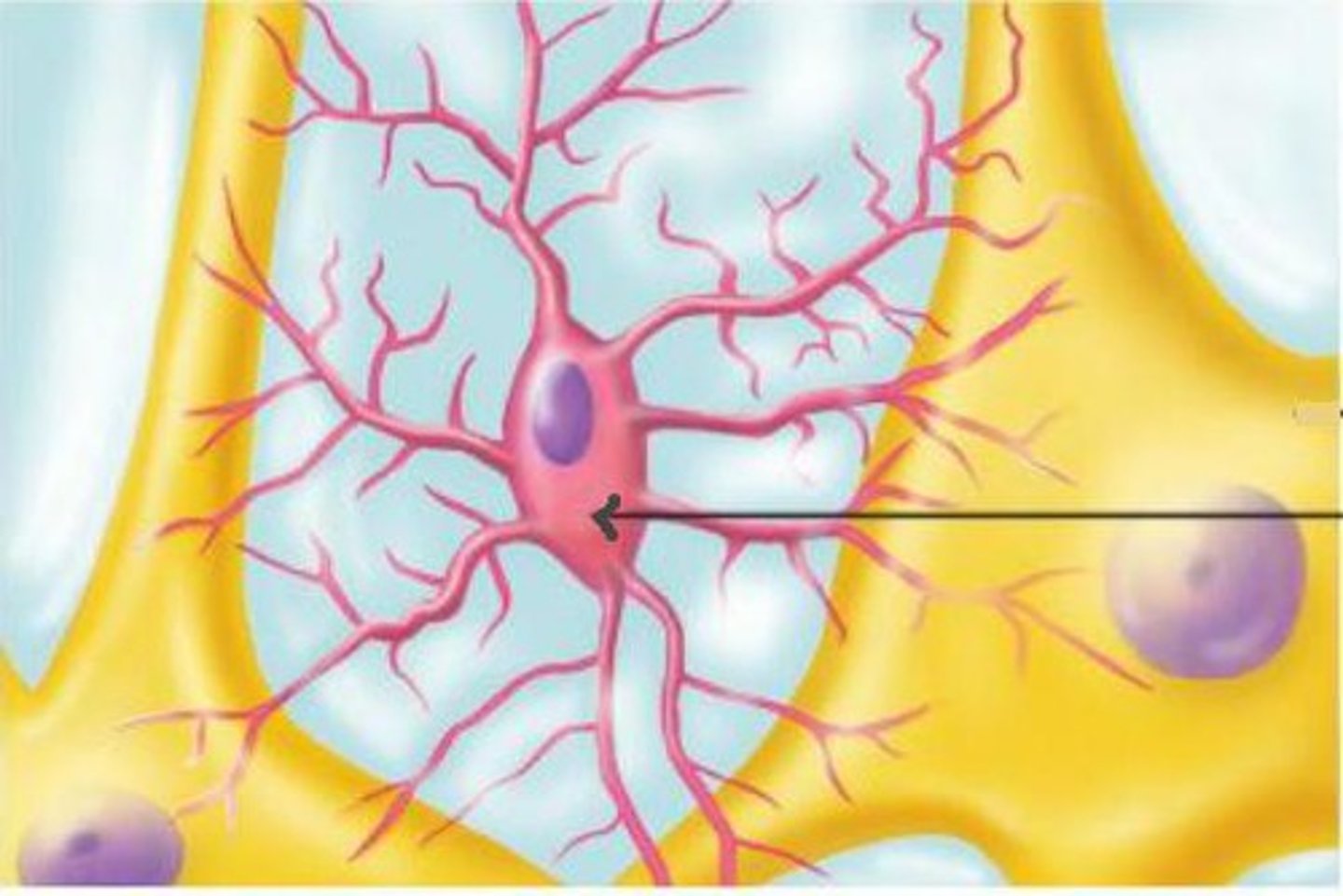
microglial cells
phagocytes
part of immune system
protect neurons from oxidative stress
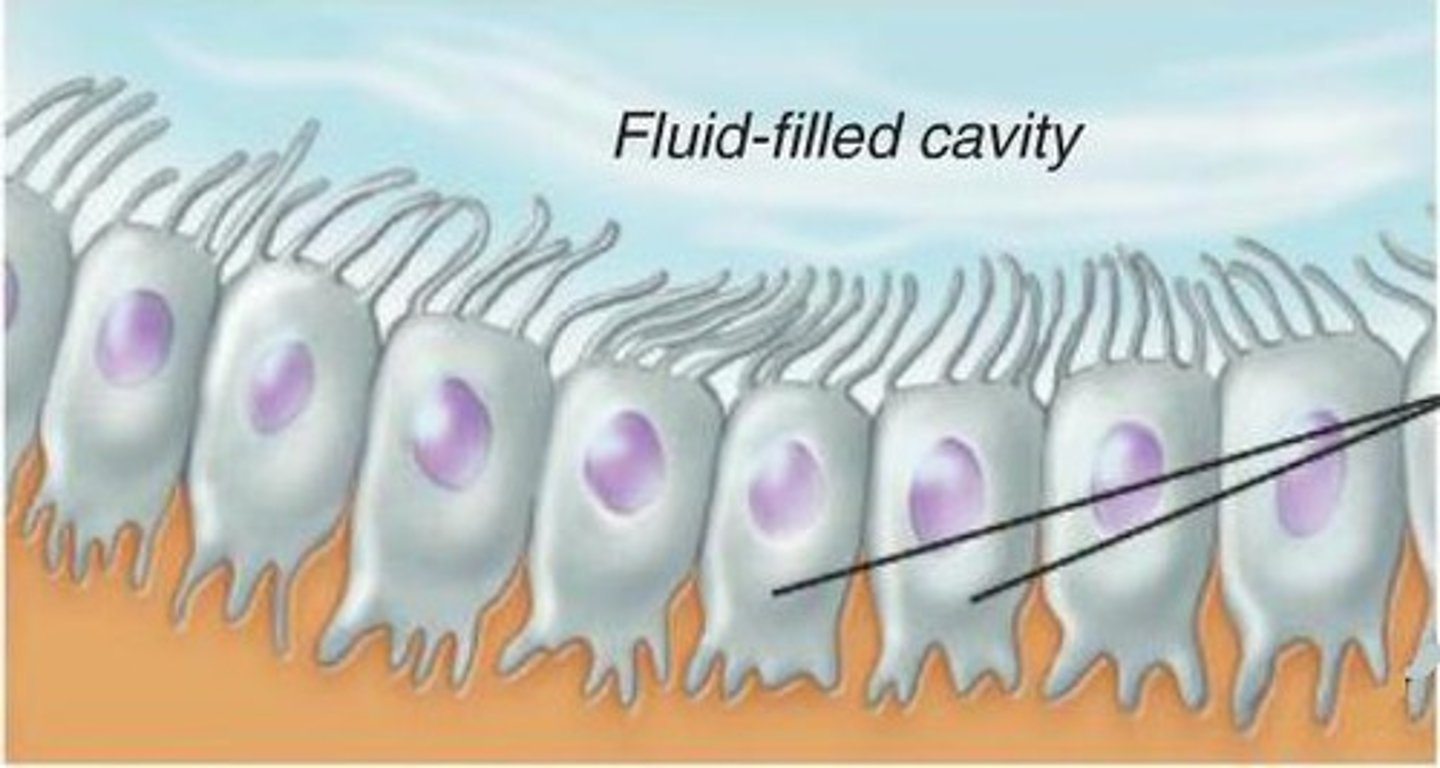
ependymal cells
epithelial cell that does not rest upon basement membrane
line ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid
-cushions/protects
-cilia propel CSF
-vitamin C mops up damaging oxygen species
oligodendroctyes
form myelin sheath (insulating fat)
wrap around CNS nerve fibers
white matter vs gray matter
white matter: axons
gray matter: lacks myelin, primarily cell bodies
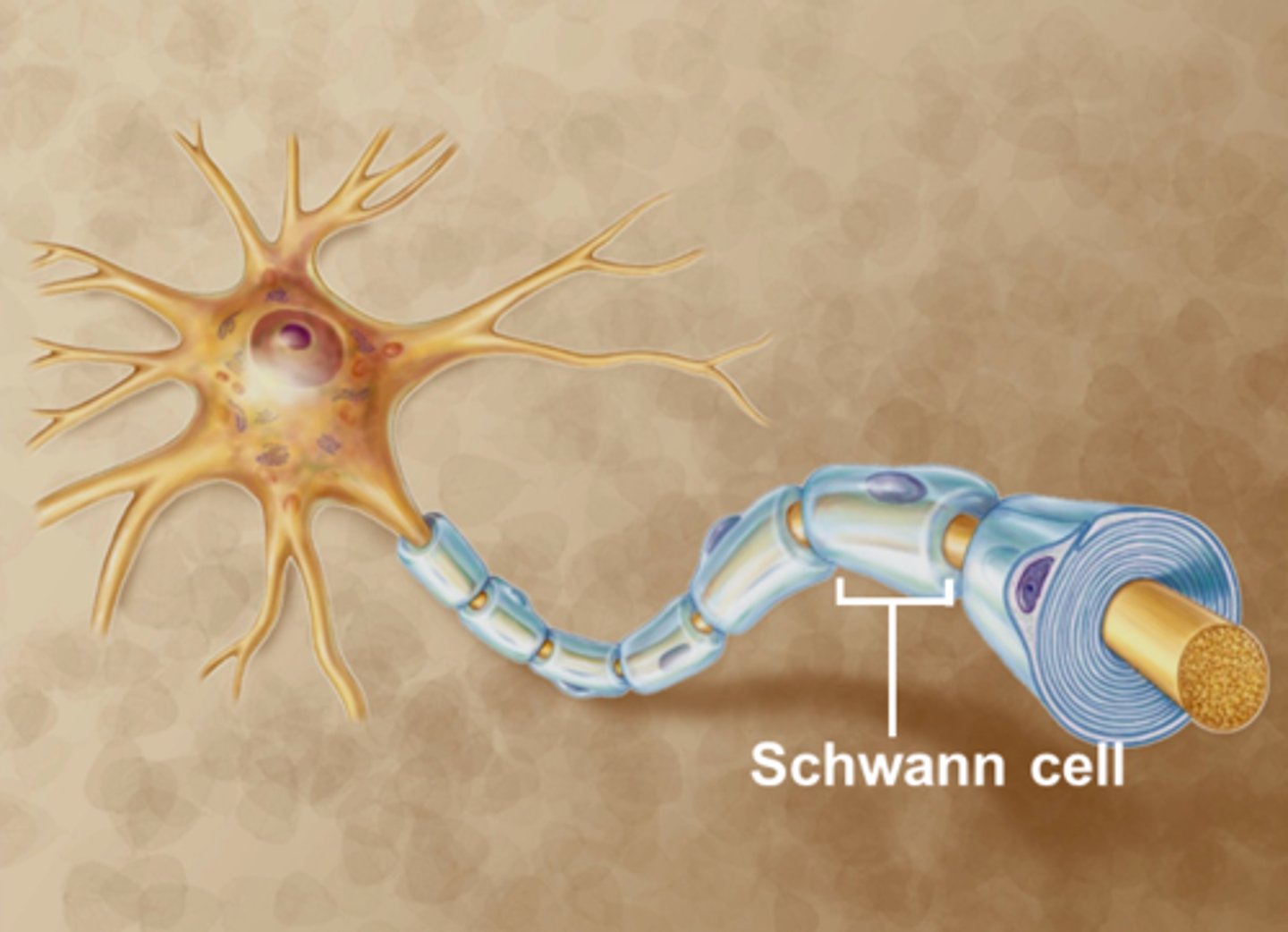
schwann cells
form myelin sheath in PNS
each cell wraps part of only 1 axon
acts as splint to allow regeneration for damage to PN fibers
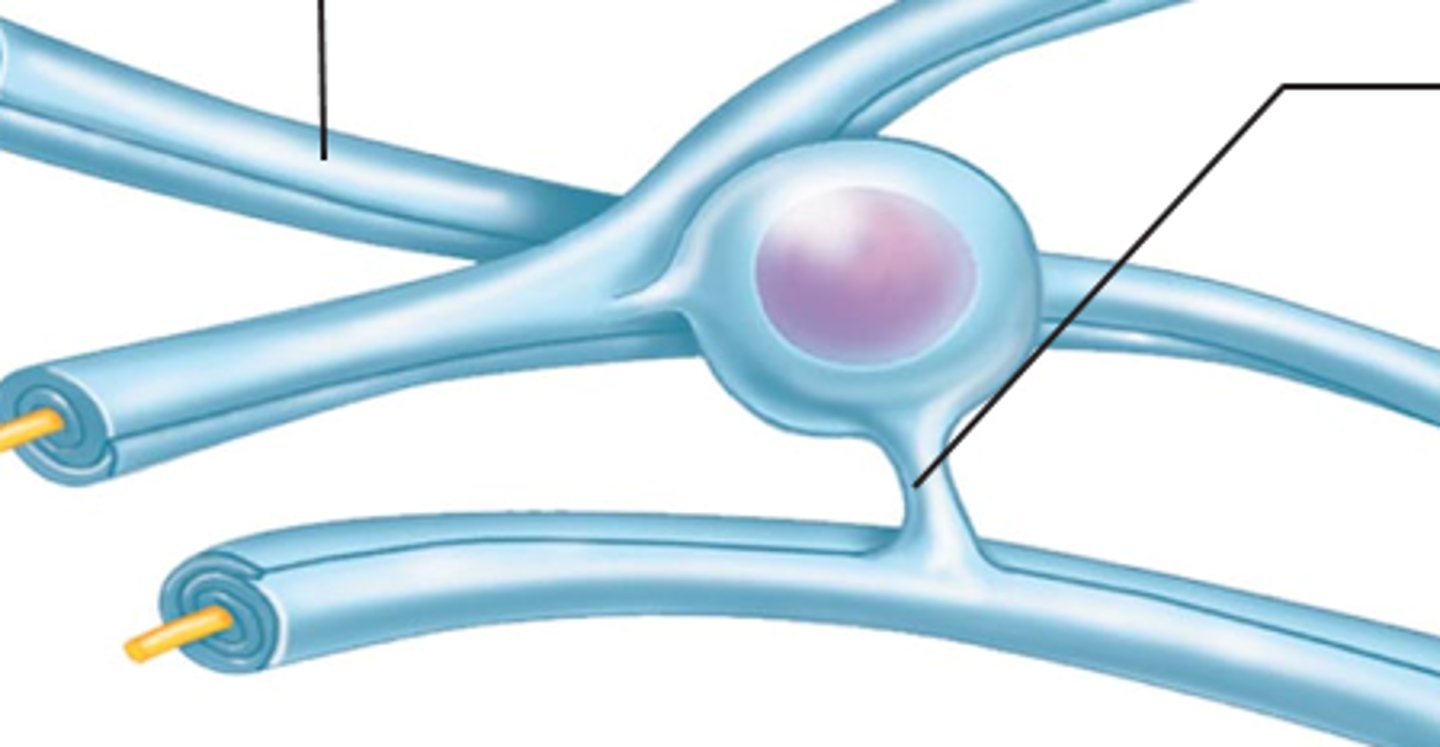
satellite cells
-cushions/protects cell bodies
-mops up damaging oxygen species
-surround cell bodies in PNS
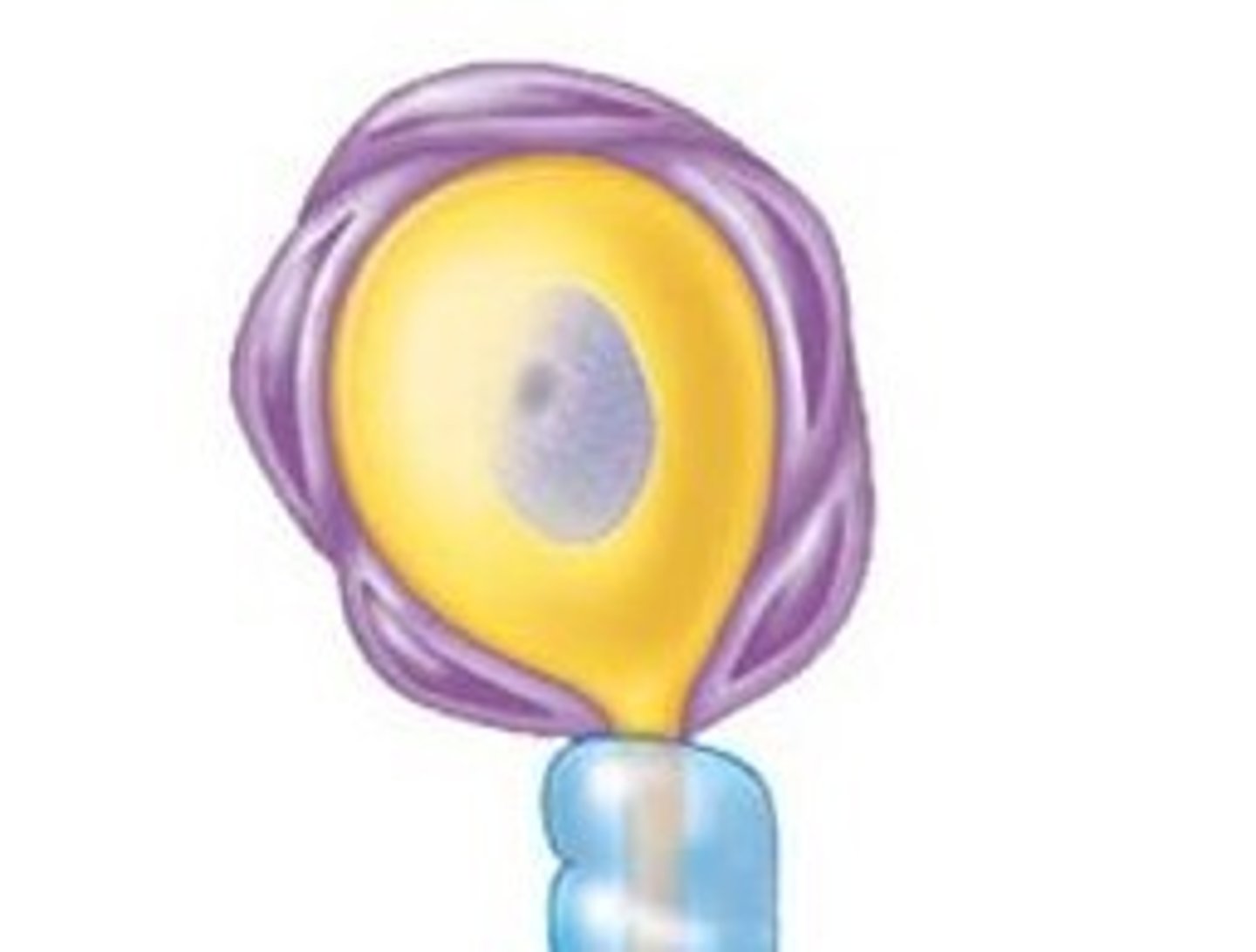
neuron structures
cell body: metabolic center
nissl bodies: rough ER
neurofibrils: intermediate filaments
types of sensory receptors
-pain and temp receptors: free nerve endings
-touch receptor: Meissner's corpuscle
-deep pressure receptor: Lamellar corpuscle
-proprioceptor: muscle spindle, golgi tendon organ
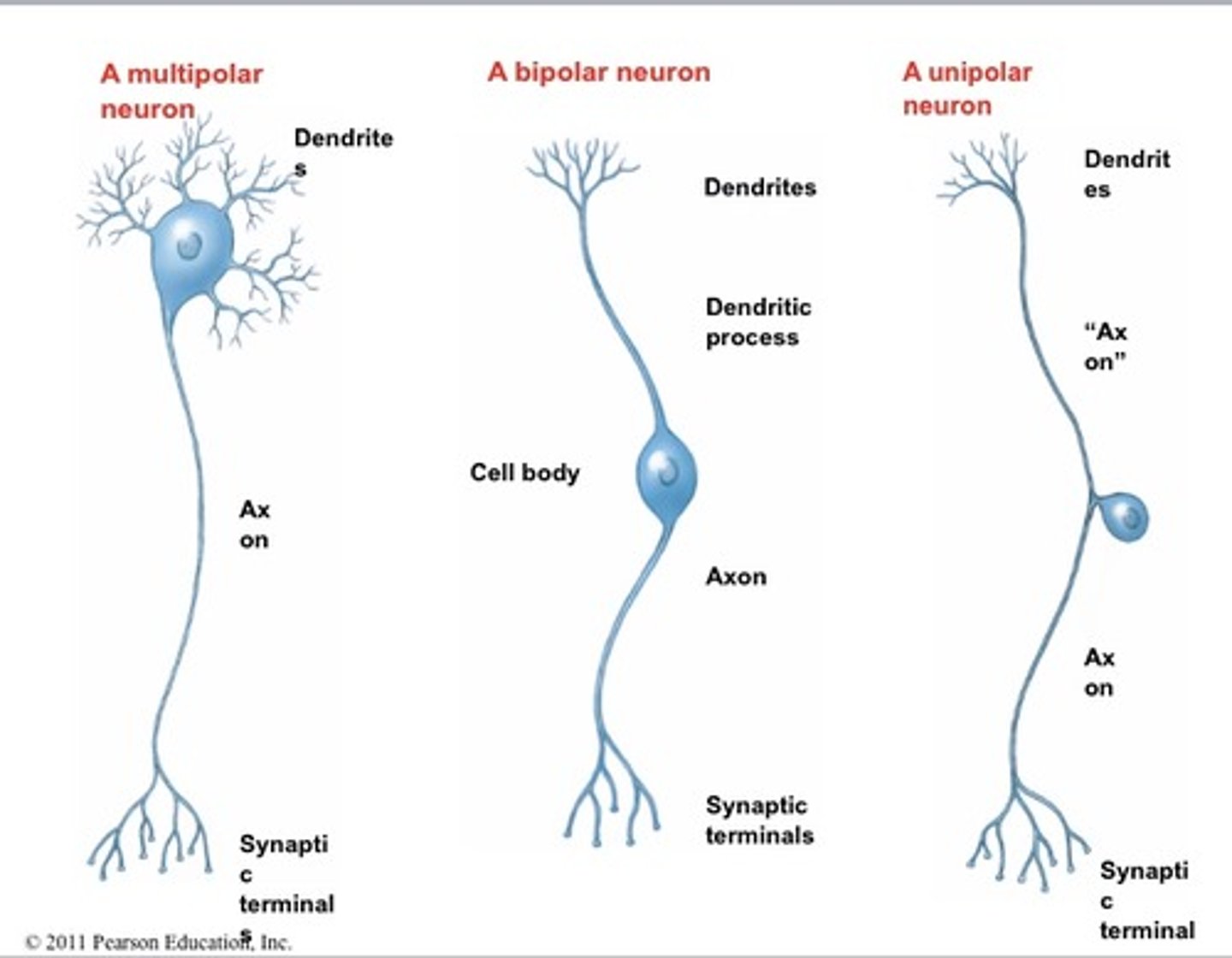
multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons
graded potential
a shift in the electrical charge in a tiny area of a neuron
-local depolarization
ventral vs dorsal horn
anterior vs posterior
cervical plexus
C1-C5
phrenic
diaphragm, skin and muscles of shoulder and neck
damage could result in respiratory paralysis
brachial plexus
C5-C8 and T1
brachial plexus nerves
axillary, radial, median, musculocutaneous, ulnar
axillary nerve
deltoid muscle and skin of shoulder and muscles/skin of superior thorax
damage could result in paralysis or atrophy of deltoid muscle
radial nerve
triceps and extensor muscles of forearm and skin of posterior upper limb
damage could cause wristdrop
median nerve
flexor muscles, some muscles and skin of hand/fingers
damage can cause decreased ability to flex and abduct hand, thumb, and cant pick up small objects
muscultaneous nerve
flexor muscles of arm
skin of lateral forearm
damage could cause decreased ability to flex forearm at elbow
ulnar nerve
some flexor muscles of forearm, wrist, hand
damage could cause clawhand
lumbar plexus
L1-L4
lumbar plexus nerves
femoral and obturator
femoral nerve
lower abdomen and thigh muscles
damage could cause inability to extend leg and flex hip and loss of cutaneous sensation
obturator nerve
adductor muscles of thigh and small hip muscles
skin of thigh and hip and knee joints
damage could cause inability to adduct thigh
sacral plexus
L4-L5 and S1-S3
sacral plexus nerves
sciatic, common fibular, tibial, superior and inferior gluteal
sciatic nerve
lower trunk and posterior thigh
hip extensors and knee flexors
damage could cause: inability to extend hip and flex knee, sciatica
common fibular nerve
leg and superior foot
damage: foot drop
tibial nerve
posterior leg and sole of foot
damage could cause inability to plant flex and invert foot-shuffling gait
superior and inferior gluteal
gluteus muscles of hip
damage could cause inability to extend hip or rotate thigh
preganglionic neuron
CNS → Preganglionic neuron → (ACh released in ganglion) → Postganglionic neuron → Target organ
functional classifcation
sensory and motor division
motor division consists of
somatic and autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system
controls skeletal muscle
autonomic nervous system
controls smooth/cardiac muscle and glands
autonomic division contains
sympathetic and parasympathetic
glial cells in central vs peripheral nervous system
CNS: microglia, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, astrocytes
PNS: Schwann cells, satellite cells
tracts
clusters of neuron cell bodies in the CNS
nerves
bundles of nerve fibers in the PNS
motor and interneurons are
multipolar
most sensory neurons are
unipolar, but some are bipolar
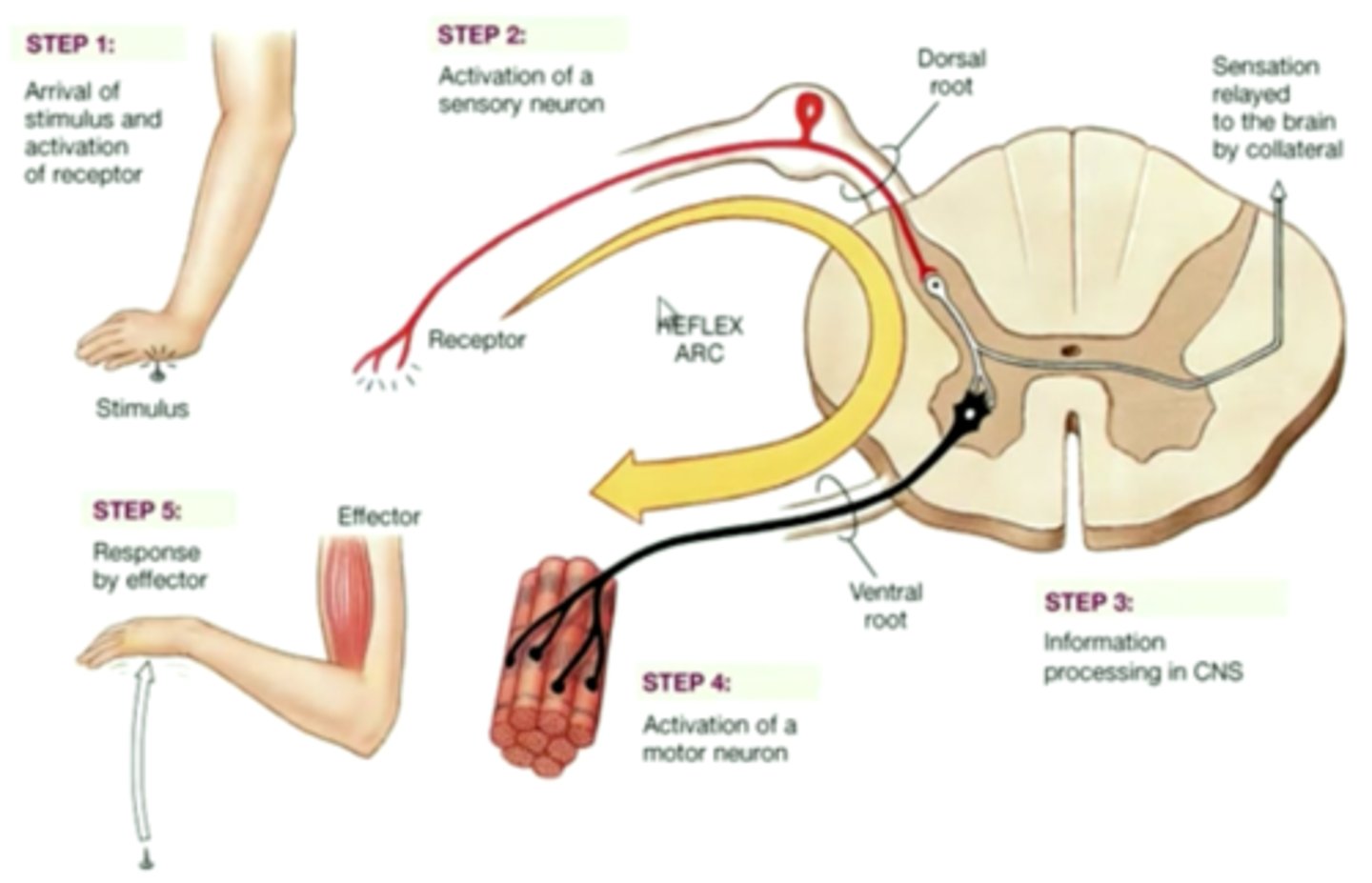
reflex arc
sensory receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, and effector that are involved in a quick response to a stimulus
gyri
Sulci (sulcus)
fissures
basal nuclei
regions of gray matter deep within white matter that modify voluntary motor activity
parkinsons and huntgions are disease of these
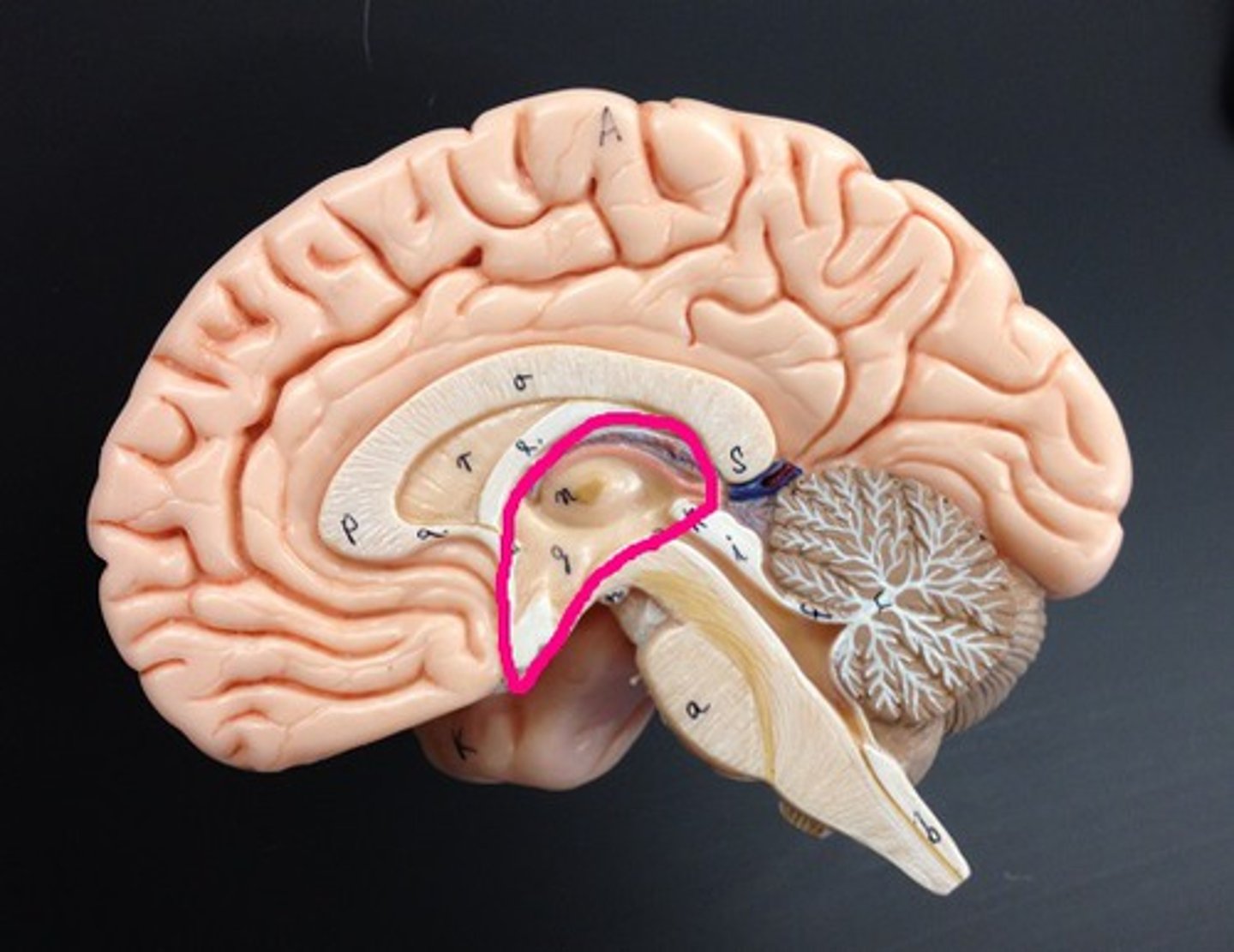
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
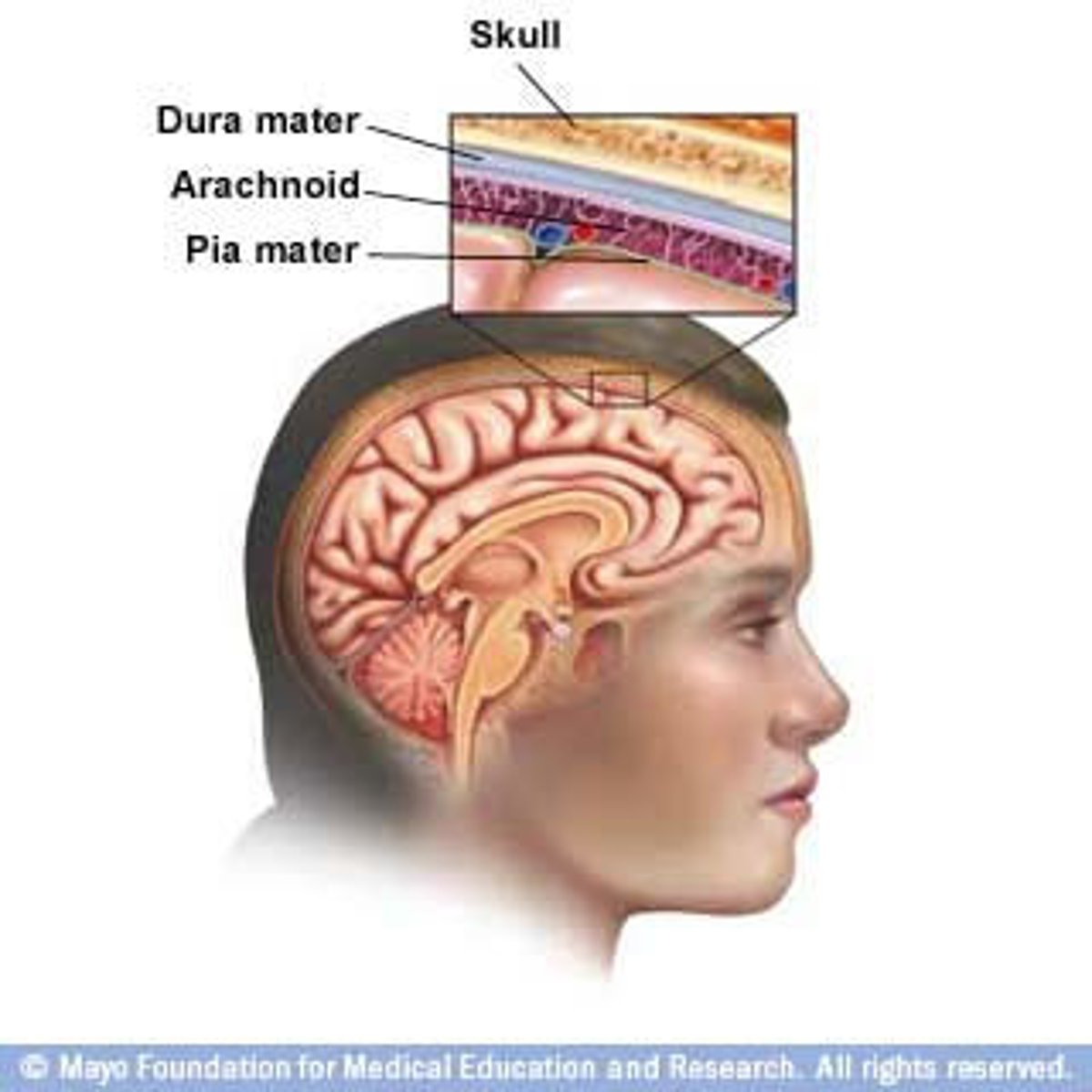
meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
CSF
formed by choroid plexuses
found in subarachnoid space, ventricles, and central canal
dorsal rami
serve the skin and muscles of the posterior trunk
ventral rami
form a complex of networks (plexus) for the anterior and limbs
parasympathetic parts
terminal ganglia are where the second motor neurons close to organ served
sympathetic parts
preganglionic neurons
ganglionic in sympathetic trunk or in collateral ganglia
postganglionic axons secrete norepinephrine
saltatory conduction
Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane.
resting potential
-70
levels that affect action potential
ATP
K
Na
Ca
the ventral root contains
axons
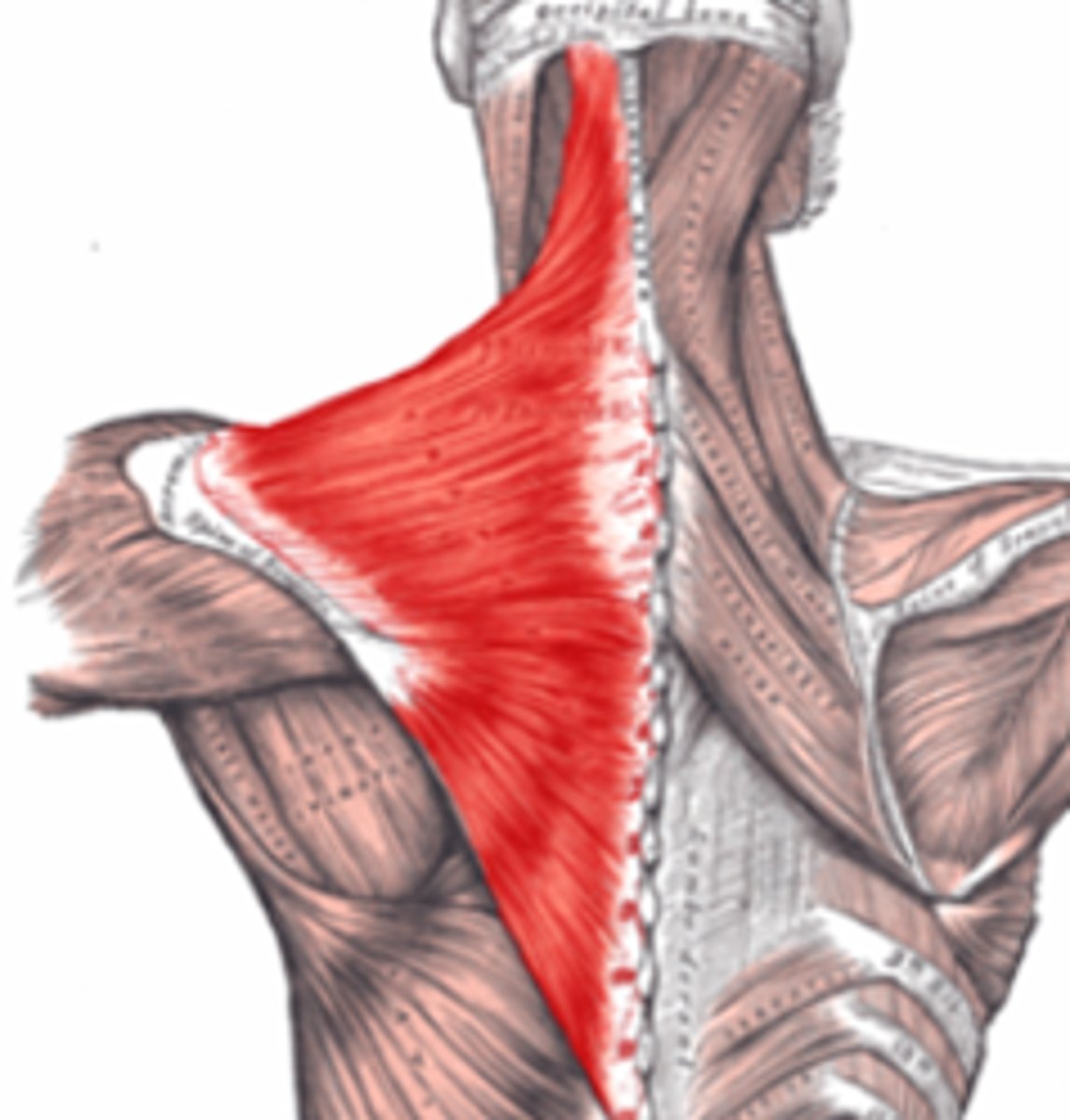
trapezius
Elevates, depresses, retracts, and rotates the scapula; rotates the arm
deltoid
abducts arm
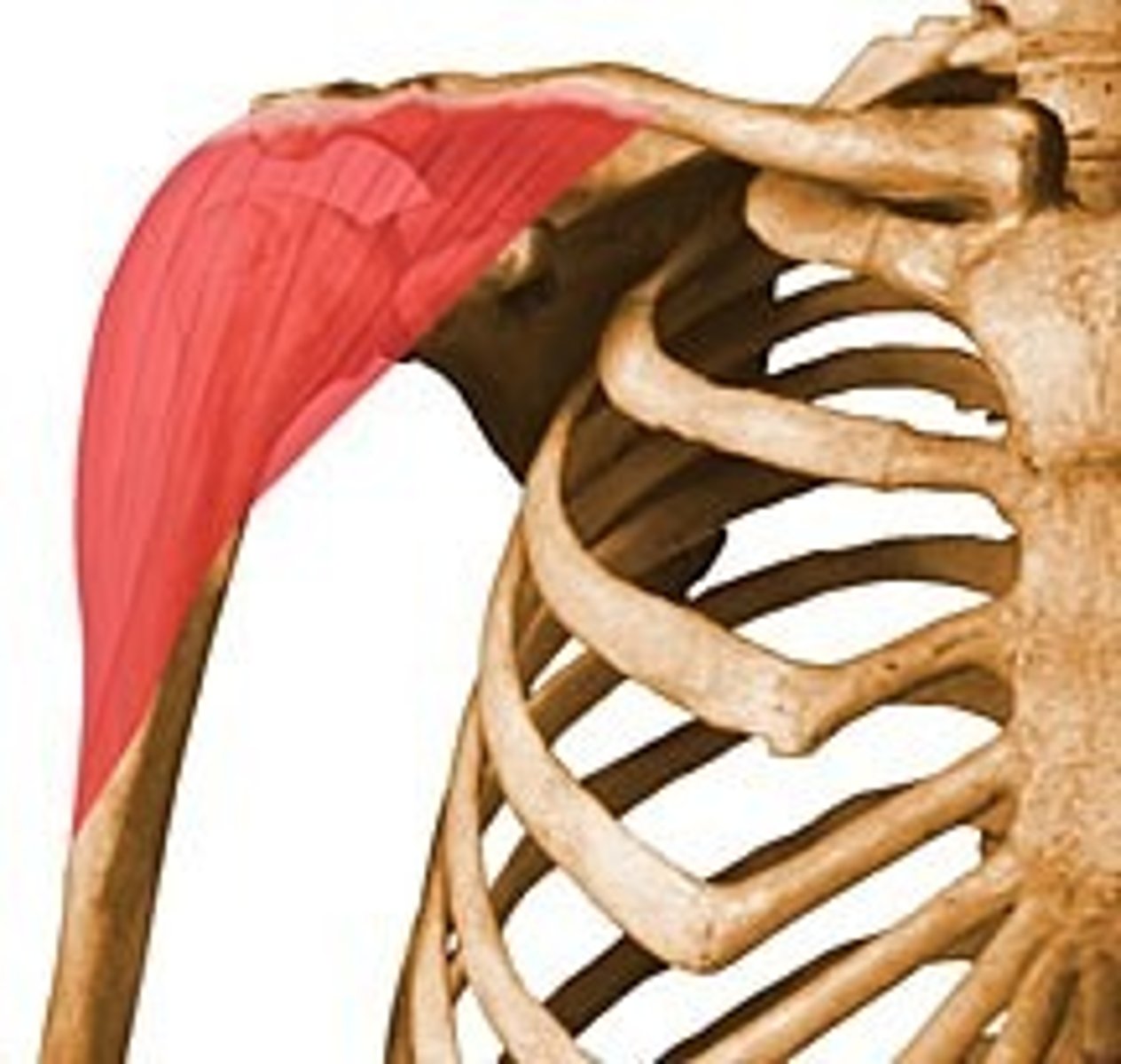
rectus femoris
extends leg and flexes thigh
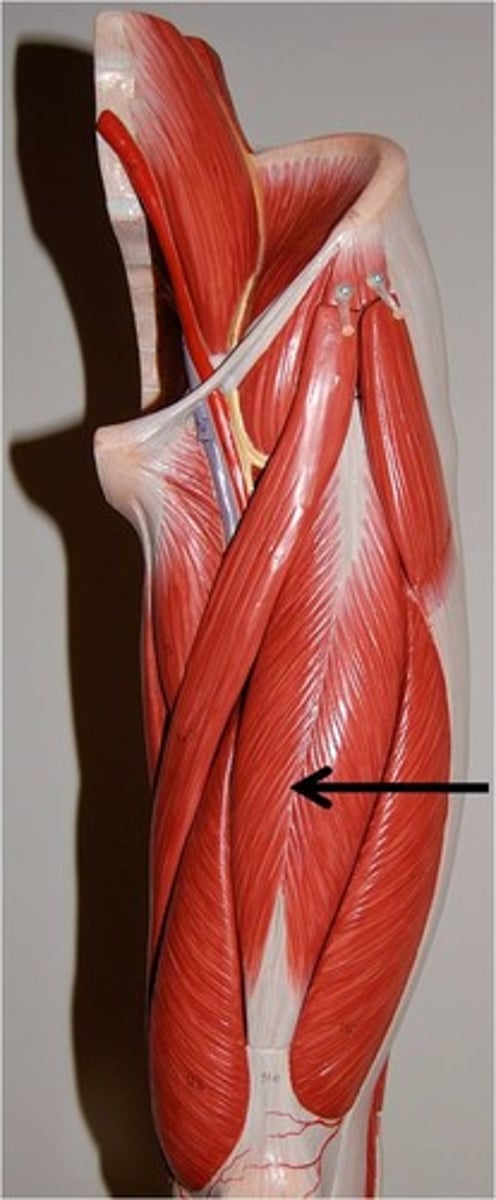
gracilis
adducts thigh, flexes and medially rotates leg
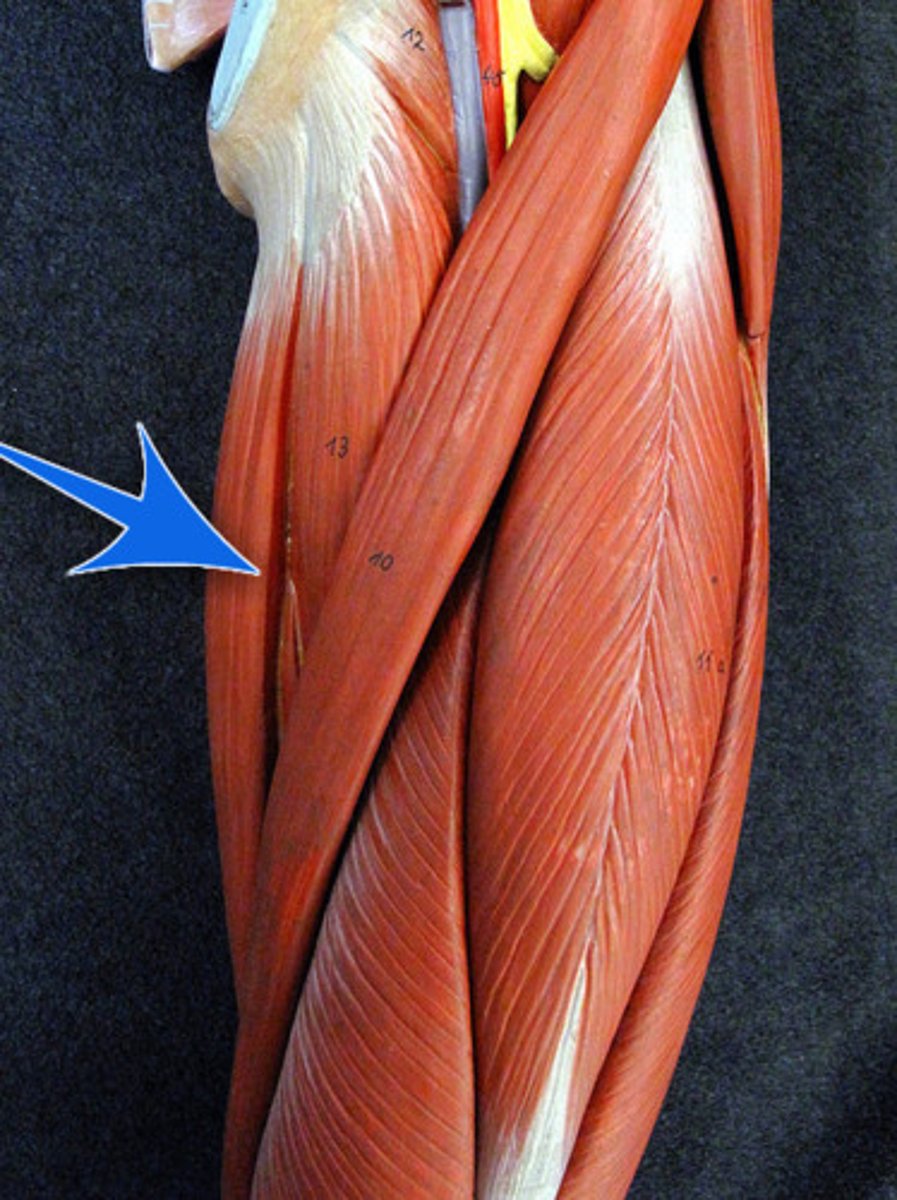
pectoralis major
Adducts and flexes humerus
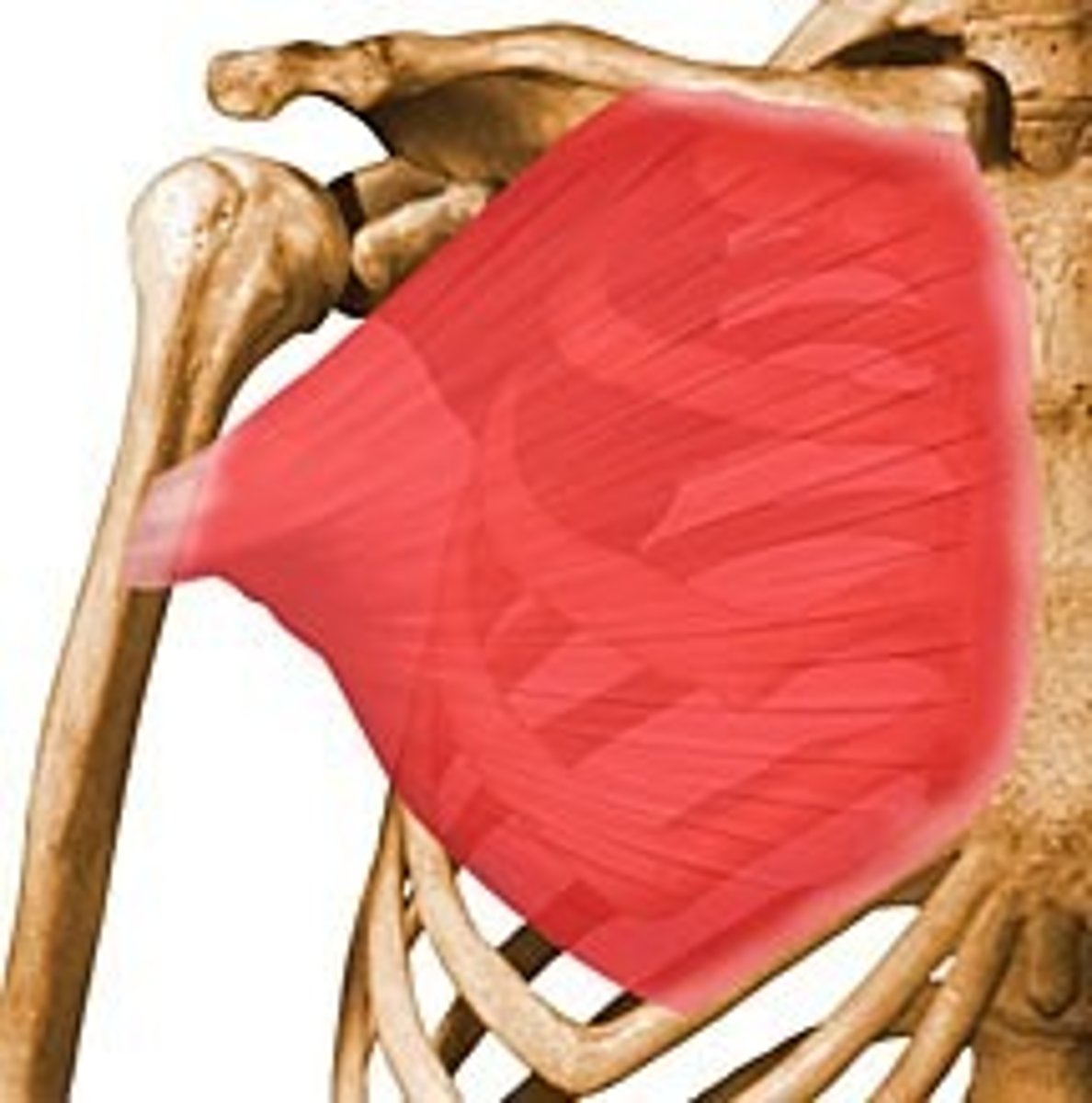
pectoralis minor
protracts and depresses scapula
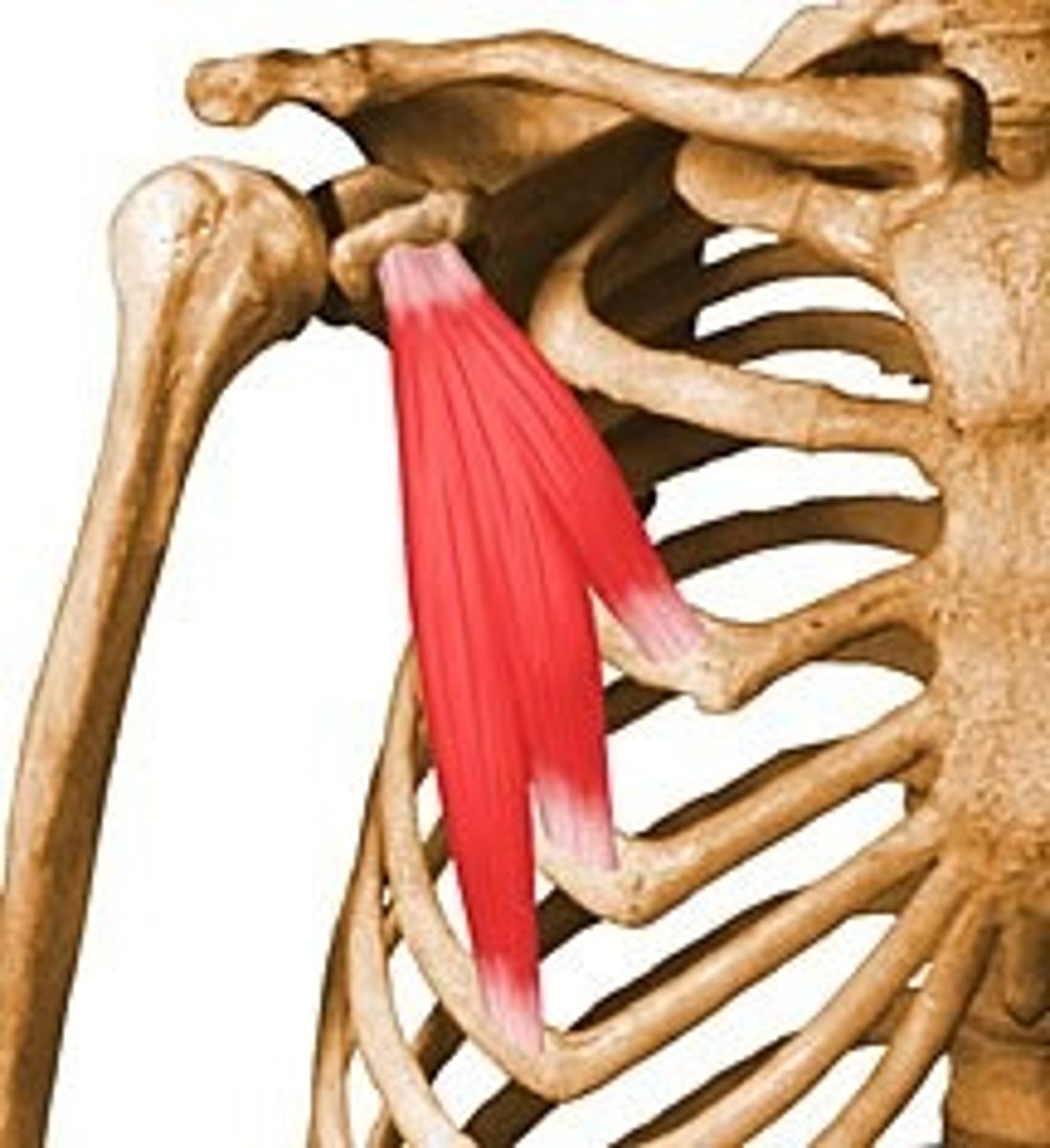
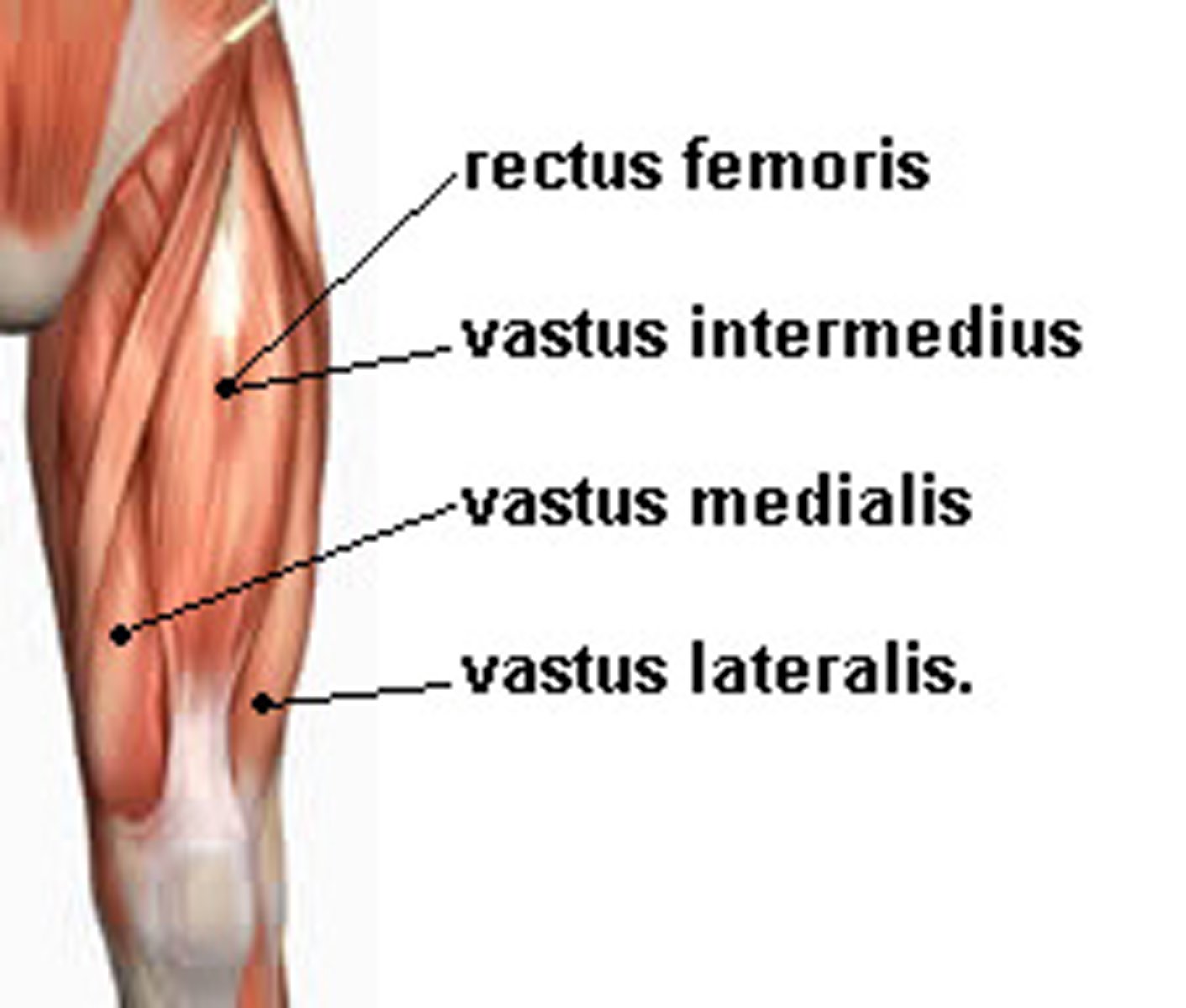
quadriceps femoris group
extends leg at knee
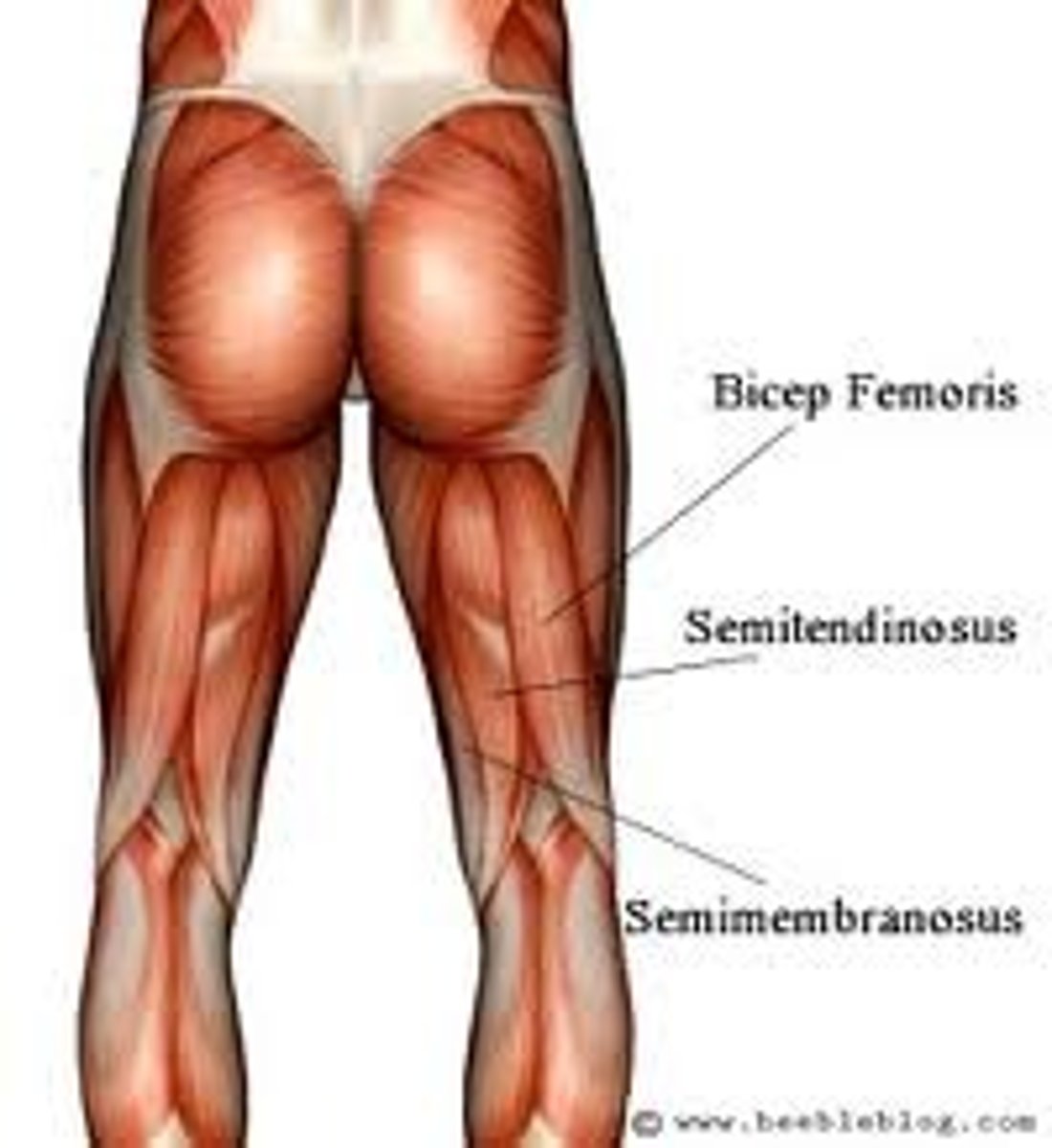
hamstring group
involved in knee flexion and hip extension
Sartorius
Flexes thigh on hip
longest muscle
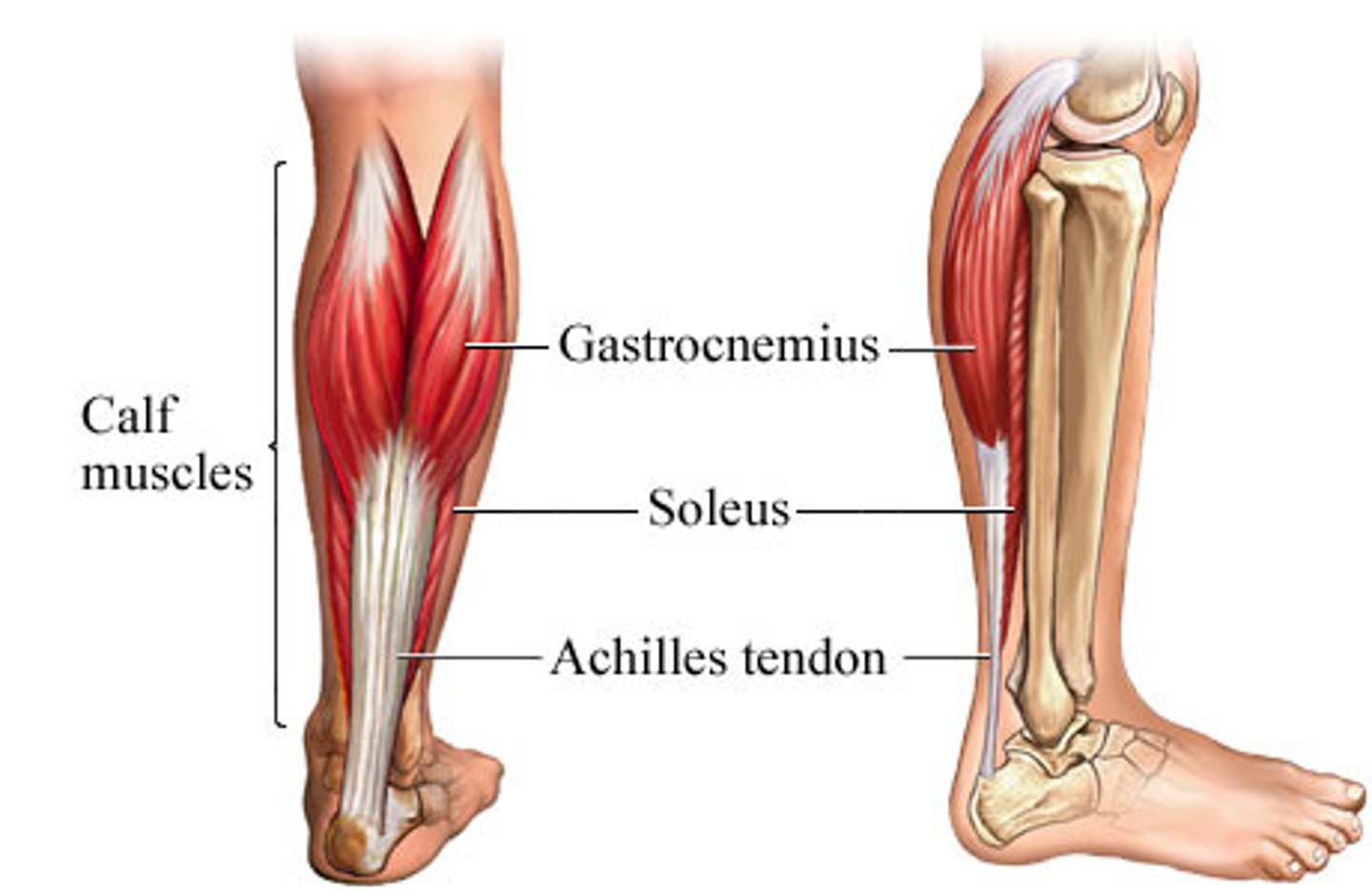
soleus
plantar flexes foot
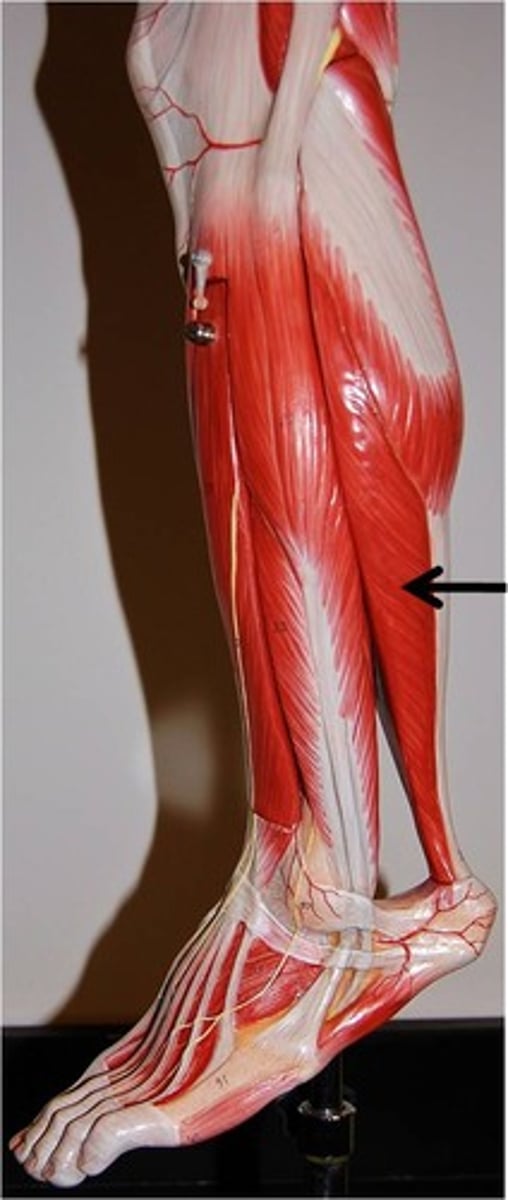
Gastrocnemius
plantar flexes foot
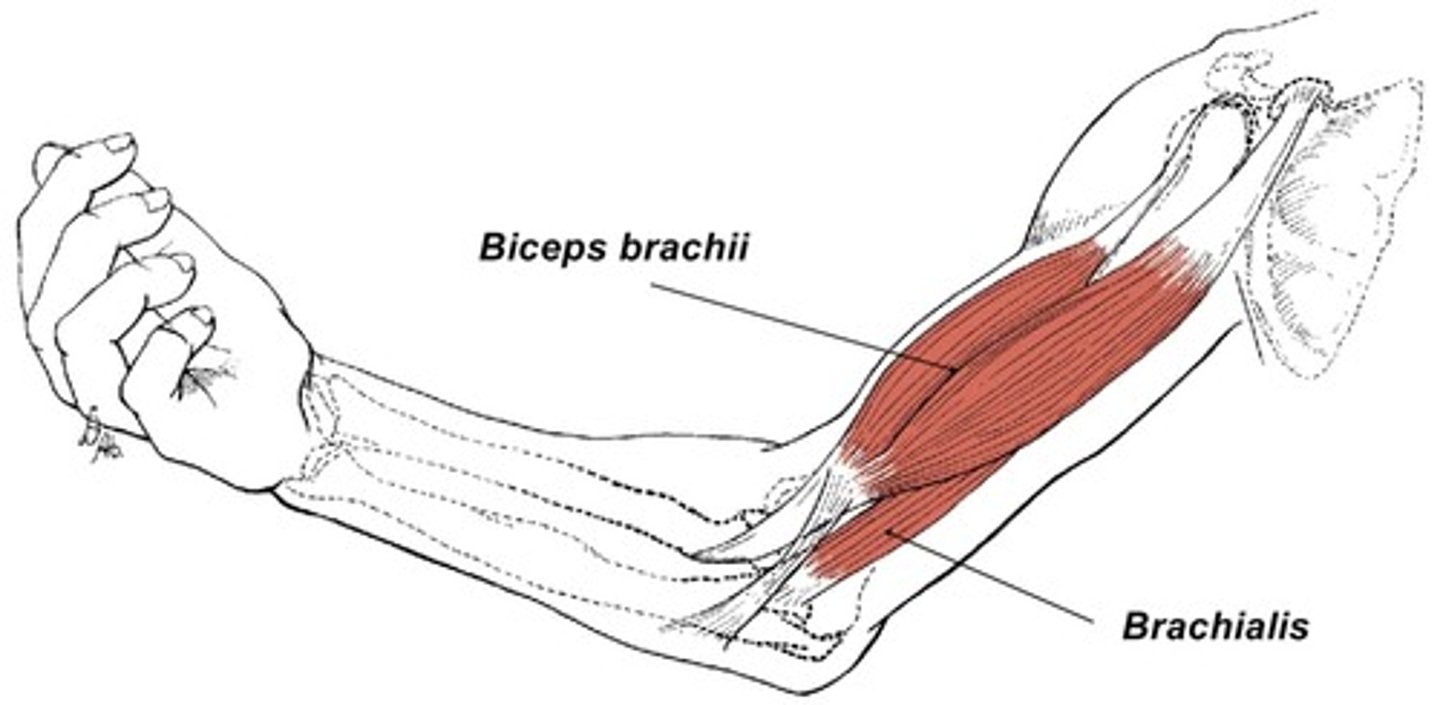
brachialis
elbow flexion
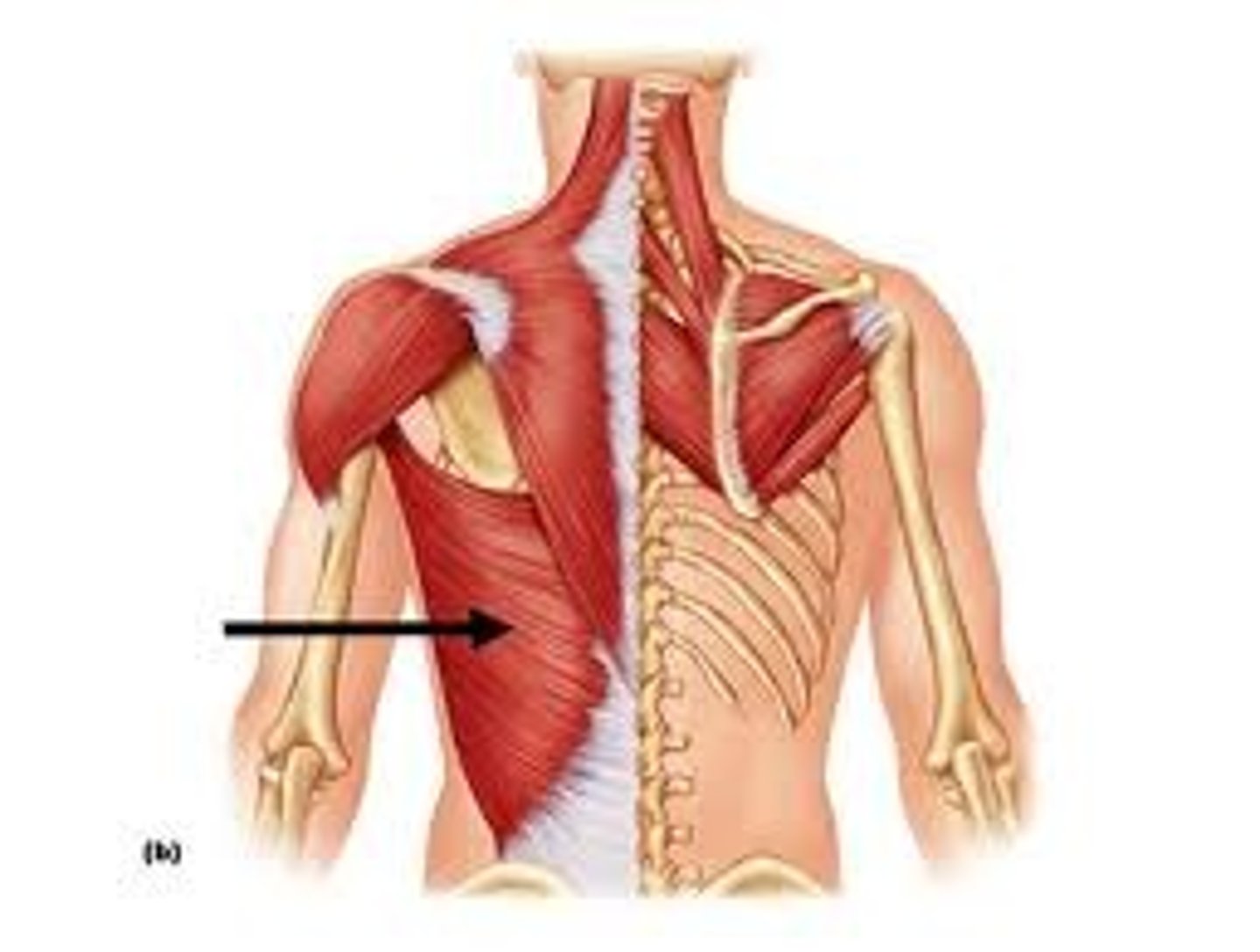
latissmus dorsi
extends and adducts humerus
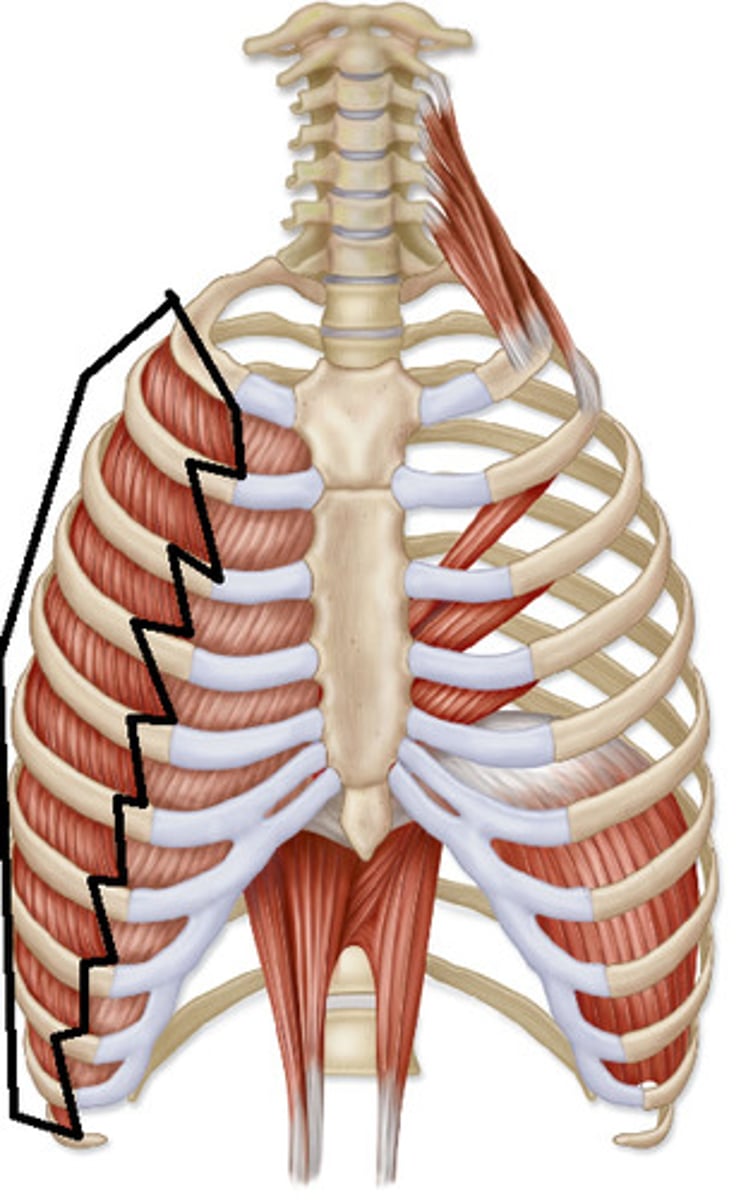
intercostals
between ribs; moves ribs for breathing
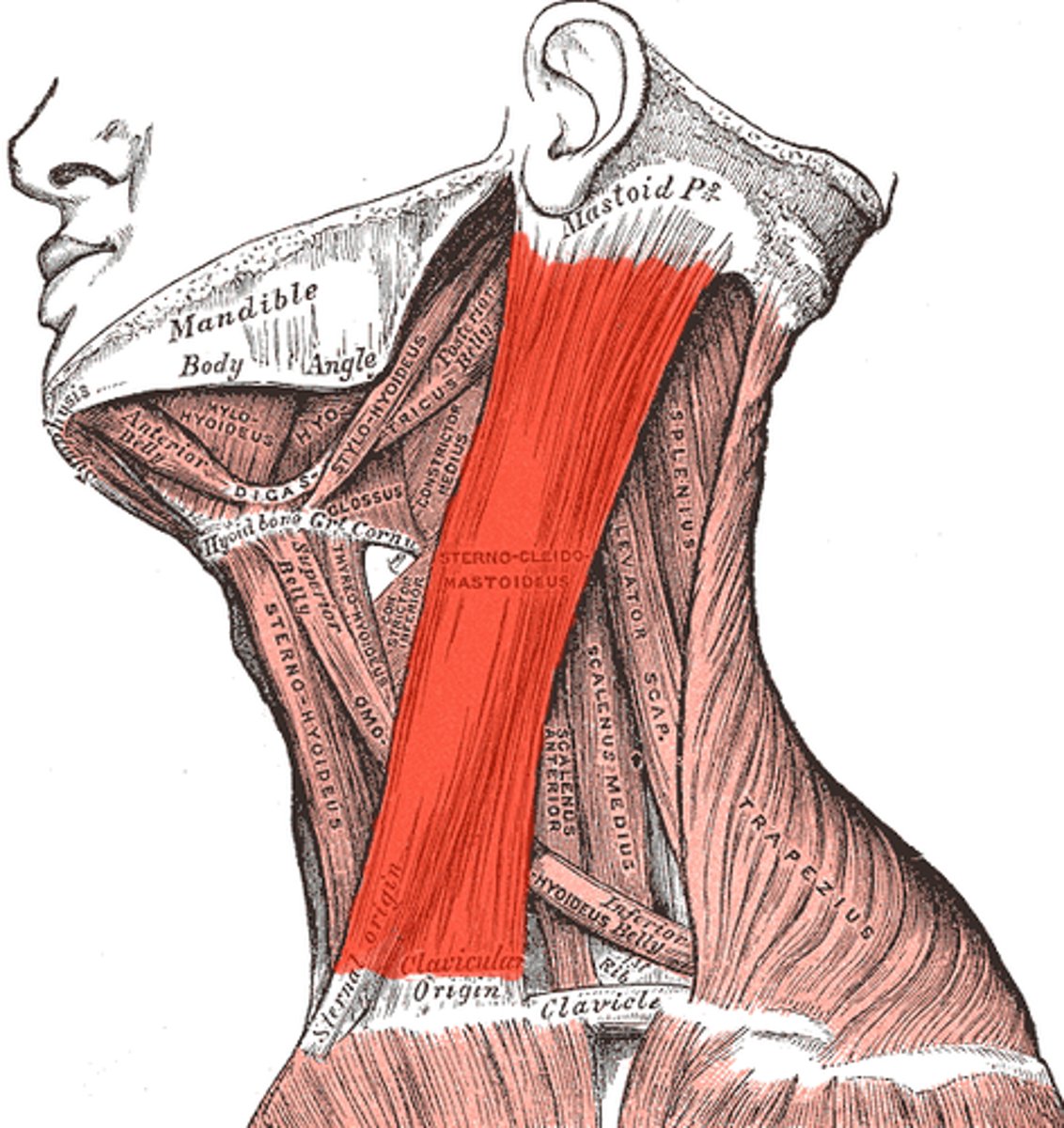
Sternocleidomastoid
Rotates head side to side and flexes neck.
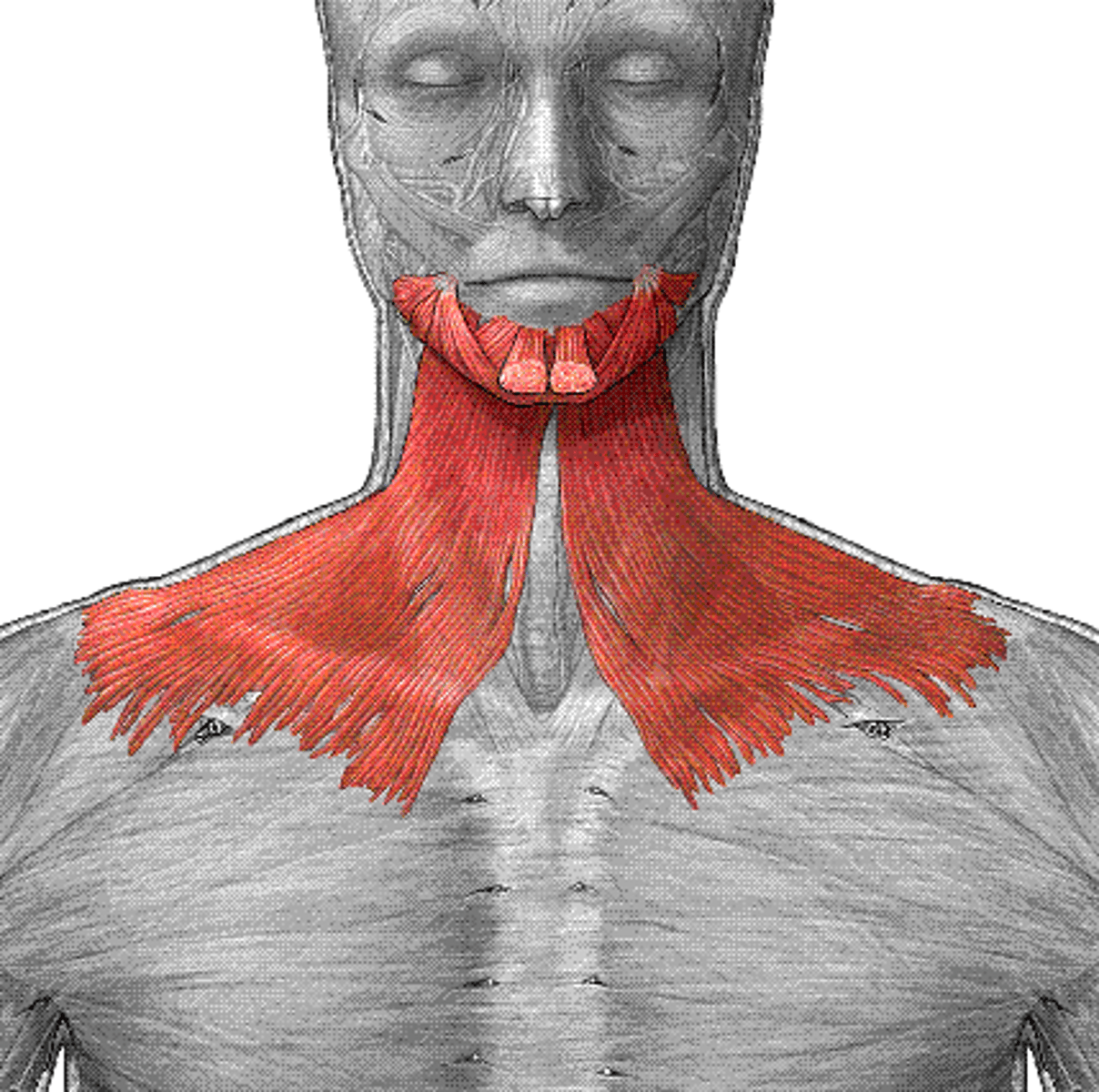
Platysma
Tenses skin of neck, depresses mandible.
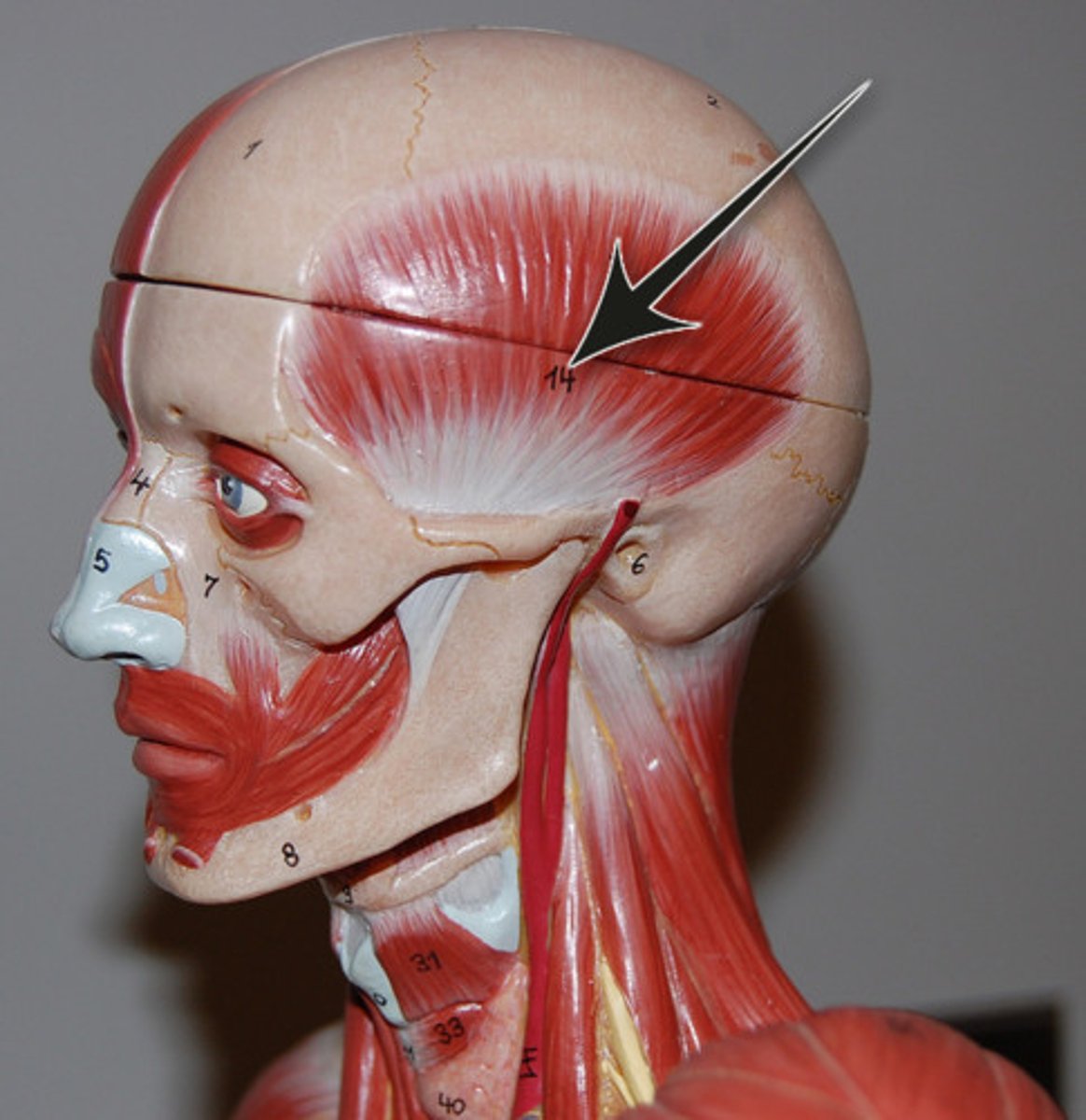
Temporalis
Elevates and retracts mandible (chewing).
Masseter
Closes jaw, elevates mandible.