UA 4A (Crystals)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is the recommended volume?
10-15 ml (12 ml preferred)
What is the centrifugation time?
5 minutes
What is the centrifugation speed for microscopic urinalysis?
400-450 g (in our lab this is 1800 rpm)
How to properly prepare a sediment for microscopic examination
- Mix specimen and pour aliquot of 10-12 mL into urine centrifuge tube
- Centrifuge for 5 minutes at 400-450 g
- After the specimen comes to a complete stop, decant the tube with a smooth but quick tilting motion
- Mix the remaining sediment well (approx.. 0.4 ml)
- Deliver the well mixed sediment to the slide using a disposable pipet
enumerating casts
Low 10x -> 40x may be used for ID
Mucous
Low 10x
Crystals
high 40x
WBCs
high 40x
RBCs
high 40x
Yeast
high 40x
Other particles that compose urine sediment
high 40x
RBCs in Hypertonic urine
Crenated cells
RBCs in hypotonic urine
Swelled, lysed, or ghost cells (pale outline of plasma membrane)
What happens to RBCs in Acetic Acid
They will lyse
What is pyuria?
WBCs in urine
WBCs in hypertonic urine will
Shrink but will not crenate
WBCs in Hypotonic urine will
enlarge and may lyse
Evidence of WBC degeneration
Lysing and bleb formation
Clinical significance of WBCs
- Infections, autoimmune, lupus, TB
- Pyuria seen with WBC casts, cellular casts, or granular casts then an upper urinary tract infection is suspected. Protein is usually positive.
- If pyuria is seen without casts and low protein (0-10 mg/dl) a lower urinary tract infection is suspected
- Proportion of types of WBC can be indictive of disease process
o Neutrophils are the most common type of WBC seen in urine
o Predominance of eosinophils
Drug induced acute interstitial nephritis
Renal transplant rejection
o Predominance of lymphs = early renal transplant rejection
Clinical Significance of RBCs
- Hematuria indicates damage to the kidney or urinary tract
o RBCs with RBC casts and protein indicate renal origin; either glomerular or tubular
Glomerulonephritis
Pyelonephritis
Tumors
Calculi
Trauma
o RBCs without casts and without clinical proteinuria indicate bleeding “below” the kidney (inflammation due to cystitis) or contamination (menstrual or hemorrhoidal)
Squamous epithelial cells are…
- Most common and largest epi cells found in urine
o Often evidence of vaginal contamination
- 30-50 um in diameter
- Flat with irregular shapes
- Central round nucleus
- Rarely have diagnostic significance report as #/hpf
Transitional epithelial cells are…
- Urothelial cells
- Round, pear-shaped, or with tail like projection
- 20-30 um diameter
- Central round nucleus
- Originate in the renal pelvis, calyces, ureter, urinary bladder
o And upper part of urethra in males
- Report as #/hpf
- Normal: few per entire microscopic evaluation
- Expect to see increased numbers
o UTI
o Viral infections
o Catheterization: sheets of transitional epis (syncytia)
o Malignancy
Transitional cell carcinoma- clue is the presence of sheets of transitional epis without recent catheterization; may also be vacuolated
Renal tubular epithelial cells are…
MOST SIGNIFICANT
- Polyhedral-flat, cuboidal, columnar
- Eccentric nucleus
- BIG nucleus (2/3 size of the cell)
- 20-30 um in diameter
- Do not swell in water (used to extreme environments, not impacted by hyper/hypo)
- Originate in the lining of renal tubules and collecting ducts
- Most significant of epithelial cells
- Report as #/hpf
- Normal – a few per entire microscopic evalutation
- May be more prevalent in healthy infants than helathy adults
- May be pathogenic
o Pyelonephritis
o Kidney damage from medications or toxins
o Tubular necrosis
o Renal Transplant Rejection
o Viral Infections (Hep B)
- RTE absorbs solutes in the filtrate
o Bilirubin may be absorbed uring viral hepatitis; look for deep yellow color
o Hemoglovin may be absorbed following hemoglobinuria; look for yellow-brown hemosiderin grnaules in RTE and free floating
Use Prussian Blue for confirmation
What is the origin of an oval fat body
RTE cells with absorbed lipids/fats
Cholesterol is…
birefringent
Neutral fats such as triglycerides and fatty acids are…
not birefringent but can be stained for ID with Sudan Red or Oil Red O (cholesterol does not stain)
What do oil fat bodies look like?
RTE cells with absorbed lipids
What do air bubbles look like
floating most in focus; black edges (you introduce)
What do starch granules look like
Maltese cross pattern under polarized light.
Under normal light → no spherical, but highly refractile, and has a dimple in center (you introduce with powder gloves)
ID spermatozoa in urine
Head with a tail
What is the significance of spermatozoa in MALES
indicates recent ejaculation or nocturnal emission
What is the significance of spermatozoa in FEMALES
vaginal contamination
If sperm is found in a female under ____ years old, follow protocol of institution
16
Is sperm mostly dead or alive in our urine specimens
Dead 💀
Define Glitter cells
when neutrophils swell in a hypotonic solution; refractile cytoplasmic granules move by Brownian movement and “glitter”
Define lipiduria
fat in urine
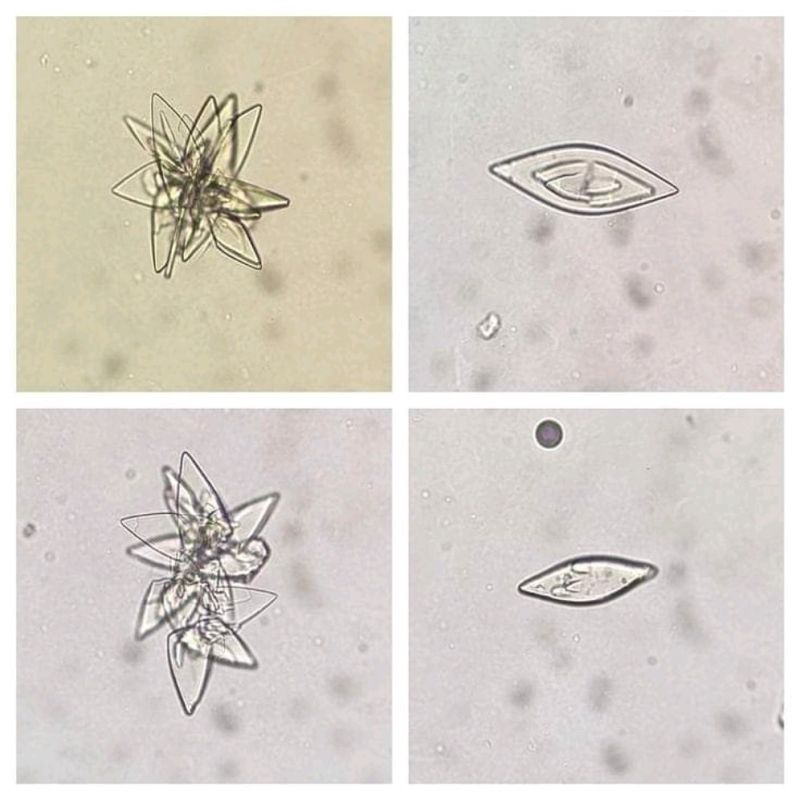
Uric acid (Rhomboid/Rossette) yellowish brown

Uric acid (Barrel) yellowish brown
Acidic normal crystals
Uric Acid
Amorphous urates
Monosodium Urate
Calcium oxalate
Hippuric Acid
Acidic Abnormal Crystals
Tyrosine
Leucine
Bilirubin
Cystine
Cholesterol
Sulfonamide
Radiographic dye
Alkaline normal crystals
Amorphous phosphates
Triple phosphates
Calcium carbonates
Calcium phosphates
Ammonium biurates
Uric acid clinical significance
normal but…
Chemotherapy
Gout
Acute febrile conditions
Chronic renal disease
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
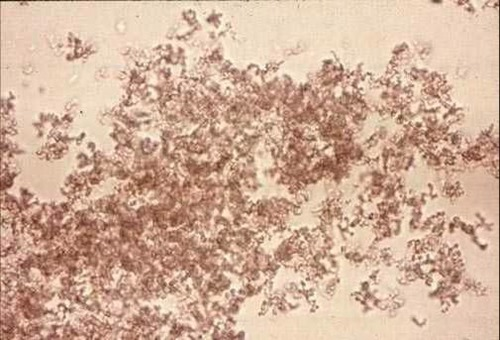
Amorphous urates (yellow brown, pink sediment “brick dust”) junk looking
Amorphous urates clinical significance (hint: what do you do to the specimen)
No clinical signifcance, but…
Soluble in heat (warm it up)
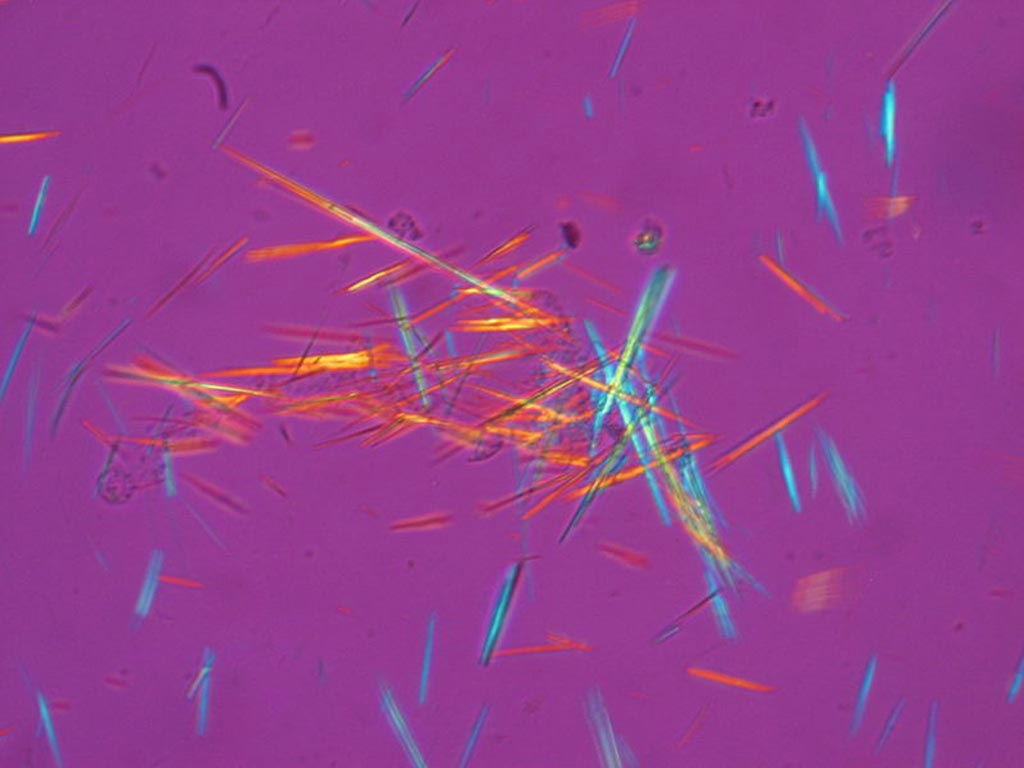
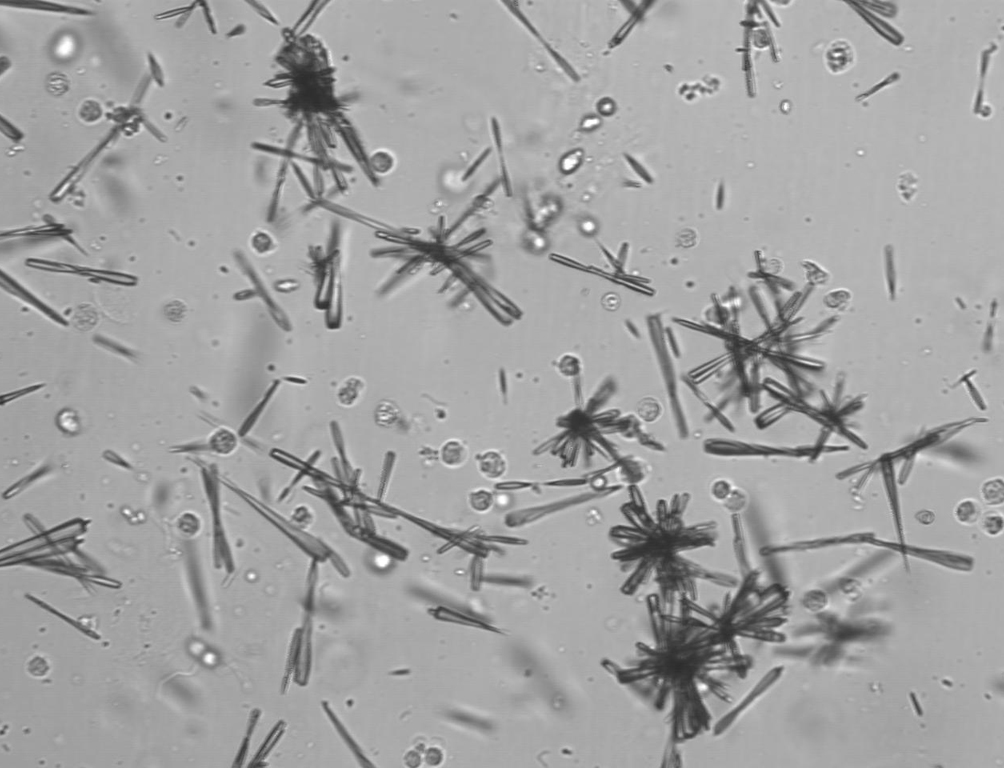
Monosodium urates (colorless to light yellow) needle like prisms
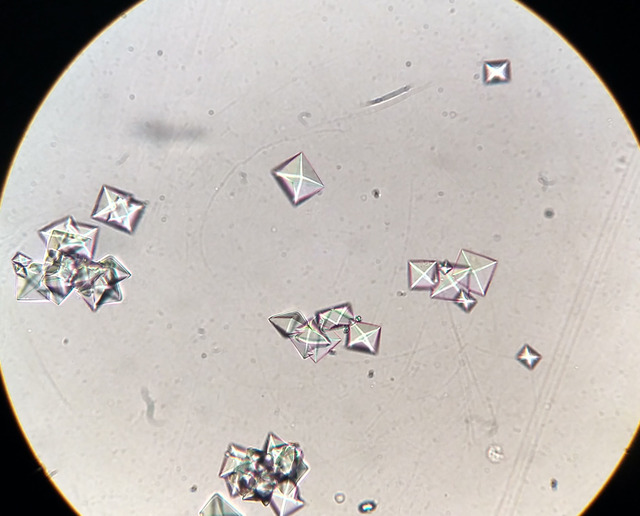
Calcium oxalate (Dihydrate envelope)
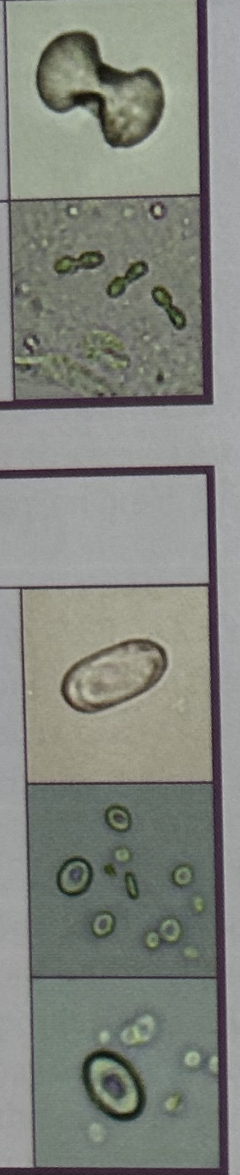
Calcium oxalate (Monohydrate form; smaller and ovid or dumbbell shaped)
Calcium oxalate clinical significance (pathologic)
ingestion of ethylene glycol (antifreeze) usually monohydrate
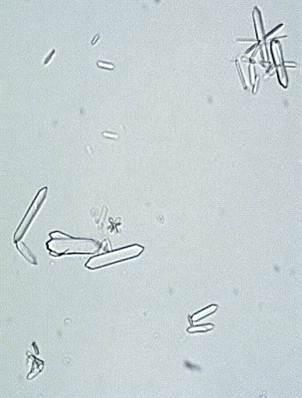
Hippuric acid (six sided prisms, needles, diamonds) fat needles
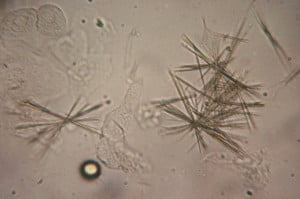
Tyrosine (needle-like, thin, usually clustered) yellow
Tyrosine crystals are normally seen with
leucine crystals
Tyrosine clinical significance
Severe liver disease, urine stirp will often indicate the presence of bilirubin as well
Significant
Tyrosinemia
Severe liver disorder
o Viral hepatitis, hepatocellular poisons
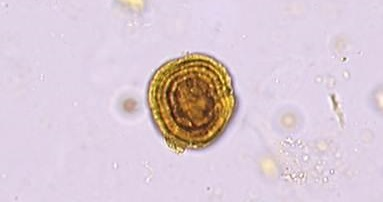
Leucine (sphere with concentric striations → bullseyes)
Clinical significance of leucine
Sever liver disorder
liver disease, viral hepatitis, hepatocellular poisons
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
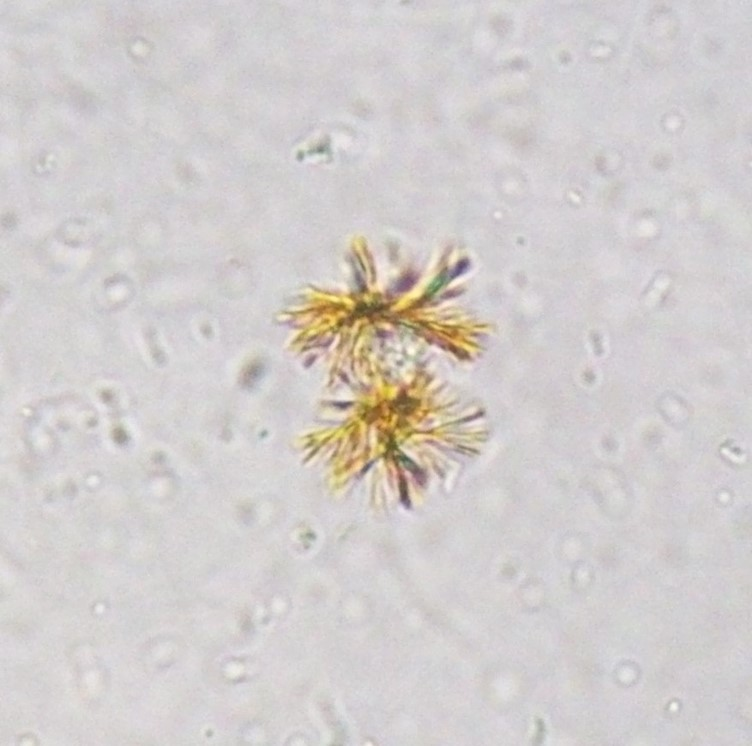
Bilirubin (small clusters of fine needles) yellow-brown
Clinical significance of bilirubin crystals
liver disease that leads to jaundice
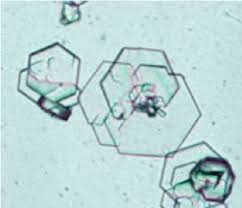
Cystine (colorless, thin hexagonal plates; sometimes with two sides shorter or longer than the other four sides)
Clinical significance of cystine crystals
Metabolic disorders: cystinosis, cystinuria

Cholesterol (notched corner “Utah” flat plate)
Clinical significance of cholesterol crystals
Nephrotic syndrome
Renal disease
Deposition of lipids in the kidneys (chyluria)

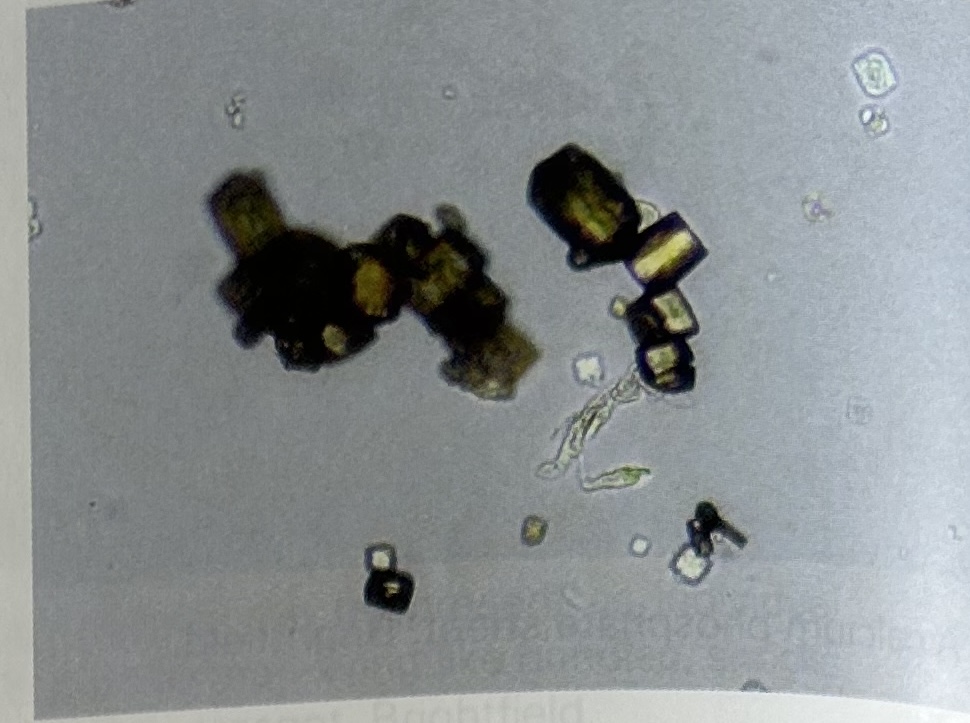
Sulfanomide (varies from granules to plates)
Sulfmethoxazole → brown rossettes or spheres with irregular radial striations
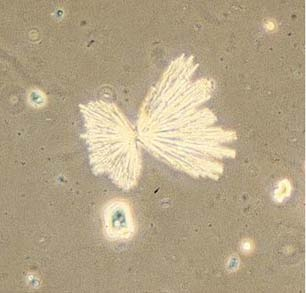
Sulfanomide (varies from granules to plates)
Sulfadiazine → shocks of wheat, needles, fans
clinical significance of sulfanomide crystals
Medication → sulfanomides
Crystals may cause renal tubular damage
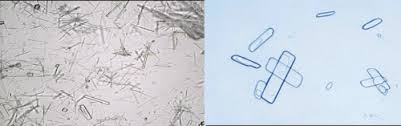
Radiographic Dye (pleomorphic needles, single or in sheaths, or in long flat rectangular plates)
What is the specific gravity when there are radiographic dyes
>1.040 (often >1.050) by refractometer
Clinical significance of radiographic dye
Patient history will indicate recent administration of radiographic dye or contrast media

Amorphous phosphates (fine, colorless to slt brown granules) white precipitate when centrifuged
Acetic acid good for clearing
Significance of amorphous phosphates
alkaline tide after eating

Triple phosphate (coffin lids, colorless)
Significance of Triple phosphate
May cause calculi
Infection with urea splitting bacteria
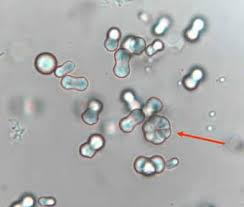
Calcium carbonate (colorless granules; often form in pairs to give appearance of dumbbells)
significance of calcium carbonate
May be seen after ingesting a large amount of vegetables

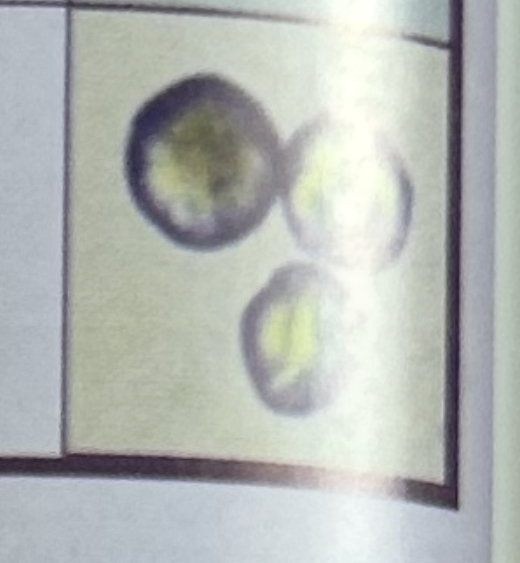
Calcium phosphates (granular, amorphous, or crystalline prisms with one pointed end; “foam finger”)
Significance of calcium phosphates
more likely found in patines with cystitis
may form calculi
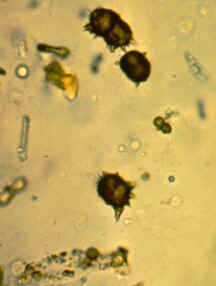
Ammonium biurates (yellow brown spheres with radiating spicules; “thorny apples”)
significance of ammonium biurates
May be seen with ammonia producing bacteria