QA, QC, lab math, specimen processing
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is percent concentration?
an expression of concentration that does not give MW info
What is the formula for percent concentrations?

What is molarity?
concentration of a solute within a solution, or relative number of reactant particles
What is the equation to calculate molarity?
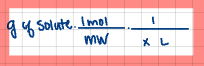
What is inverse proportion?
The determination of a working solution from a stock solution
What is the equation for inverse proportions?
C1V1 = C2V2
what is statistics?
the mathematical analysis and evaluation of collected data
What is a statistic?
a number that summarizes data
What is descriptive statistics?
summary of features from a single group of data (example: mean)
What is inferential statistics?
inferring findings from a small group to a large population
what is the equation of standard deviation?
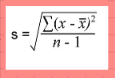
What is mode?
the number value in a dataset that occurs most frequently
What is median?
The value that occurs in the middle of all values
What is the coefficient of variation?
comparison of relative ability between two sets that do not have the same units
What is the equation for coefficient of variation?

What comprises whole blood?
plasma, cells, platelets
What is serum?
the remainder of whole blood after the blood has clotted, there is no anticoagulant present
What is plasma?
Whole blood that has been treated with anticoagulant, it contains fibrinogen and other clot factors
What are some factors that affect test result quality?
anticoagulant use, collection technique, diet, health status, specimen handling
What does normal serum look like?
clear, pale to medium yellow
What does hemolyzed serum look like?
pink/orange/red tinged serum, still clear
What does icteric serum look like?
bright yellow or green
What does lipemia serum look like?
cloudy or turbid
what are four factors in specimen handling?
maintain an ID
specimen preservation
specimen separation
specimen transport
What are some controllable factors for specimens?
posture, bed rest, exercise, circadian rhythm, diet, smoking, alcohol
What are some non-controllable factors for specimens?
sex, age, ethnicity, environment, medical conditions
What is quality?
a degree of excellence
What are some analytical variables for specimens?
statistics for QC, reagent deterioration, and bad calibration
What is statistical QC?
the monitoring and performance of analytical methods utilizing control material and charts
what is the most common control chart used for QC?
Levey-Jennings chart
What are Westgard multirules?
rules to detect subtle changes in QC that warrant warnings, re-runs, or rejections
What is the 12s rule?
One control value that exceeds the mean ± 2 stdev.
What is the 22s rule?
Two consecutive control values that exceeds the mean ± 2 stdev.
What is the 13s rule?
One control value that exceeds the mean ± 3 stdev.
What is the 41s rule?
Four consecutive control values that exceeds the mean ± 1 stdev.
What is the R4s rule?
One control value that exceeds the mean + 2 stdev AND one control value that exceeds the mean - 2 stdev.
What is the 10x rule?
10 consecutive controls that fall on the same side of the mean, either (-) or (+)
Which of the westgard multirules are considered a systematic issue?
22s, 41s, and 10x because they are all consecutive
Which of the westgard multirules are considered a random issue?
13s, R4s because they are isolated events
Which of the westgard multirules is considered a warning?
12s because it could just be some variation in QC
What are some procedures for non-statistical QC?
delta check, or correlation of test results from the same patient
avg. of normal, or assessment of all patient values
pattern recognition, or combinations of trends in test values
What is QA?
quality assurance is an assurance practice that the laboratory meets standards