4.2 Amorphous Solids - polymers
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Polymers are just a chain of repeat molecular units called…
monomers
n represents…
the amount of monomers in the polymers
What is molecular weight impacted by?
Temperature, reactant ratios, catalysts, inhibitors, polymer chemistry
A high molecular weight =
high elastic modulus, tensile strength, service temp, toughness, chemical resistant to dissolution
a low molecular weight =
low elastic modulus, tensile strength, service temp, toughness, chemical resistant to dissolution
more vanderwaals bonds between chains means…
a higher molecular weight
The monomer molecular weight…
gets skewed towards heavier molecules
What are homopolymers?
They have the same repeat unit
What are copolymers?
They have different repeat units
What do side groups do?
Hang off the polymer backbone
Rigid/bulky styrene side group means
a denser polymer property, higher Tg
Polar side group
higher Tg (stronger bonding)
Flexible side group
lower Tg (easier to pack/slide)
What is tacticity?
The way side groups are arranged along the backbone
What does atactic mean?
Randomly arranged, less dense, harder to crystallize
What does isotactic mean?
Same side arranged, more dense & easier to crystallize
What does syndiotactic mean?
Every other arranged
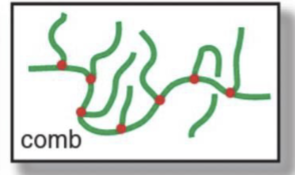
What’s a signature feature of a comb polymer?
The branches don’t have branches
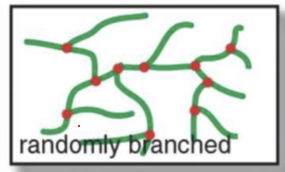
What’s a signature feature of a randomly branched polymer?
The branches have branches
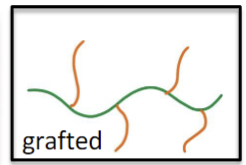
What do the different colors in a grafted polymer structure mean?
The side branch is one type of polymer, and the main chain is one type of monomer
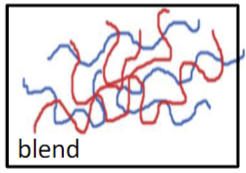
What’s a defining feature of a blend polymer?
A physical mixture of 2 types of polymers
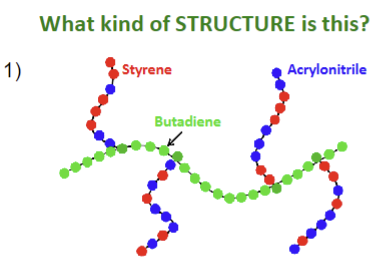
What kind of structure is this?
A grafted copolymer
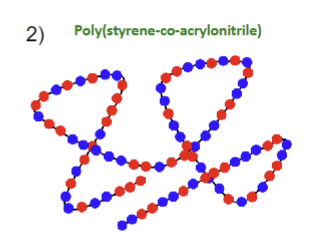
What type of structure is this?
A random linear copolymer
What do chemical cross links involve?
Covalent bonds between 2 polymer chains
What do physical cross links involve?
Ionic or vanderwaals bonds between 2 polymer chains
What’s an example of a chemical cross link?
Tires
What’s an example of a physical cross link?
Slime
What happens when you increase cross-links?
Strength and rigidity increases as well
What are some cross linking methods?
Catalysts (vulcanization or photo-curing) and network formers
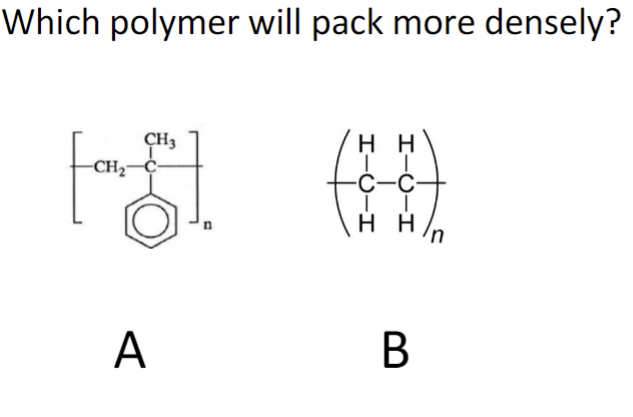
Which polymer will pack more denser?
Polymer B because there’s no side group in the way
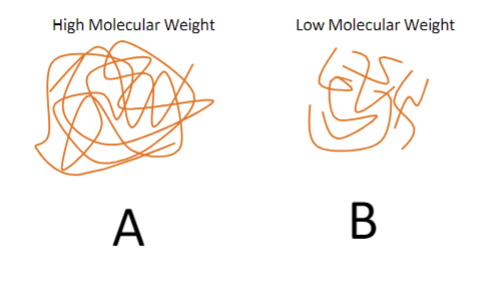
Which polymer will be mechanically stronger?
Polymer A because there’s more secondary bonds between chains
What happens when you increase chain length?
It increases 2nd degree bonding between chains, which leads to increased strength
What is visco-elasticity?
Time dependent behavior between stress and strain
What is the deborah number?
time of relaxation/time of observation
What does it mean if you have a smaller deborah number?
the material changes faster
What deborah numbers do liquids have?
0
What deborah numbers do solids have?
infinity (much > 1 is a solid)
What is creep?
Constant stress is applied
What is stress?
Constant strain is applied
What’s an example of a viscoelastic polymer?
Slime
True/False: Polymers have a glass transition
True
What is Tg influenced by?
Molecular weight, types of side groups, % crystalinity
What happens if your polymer is above Tg?
It’s rubbery, moldable, and flowable
What happens if your polymer is below Tg
The polymer is glassy and brittle
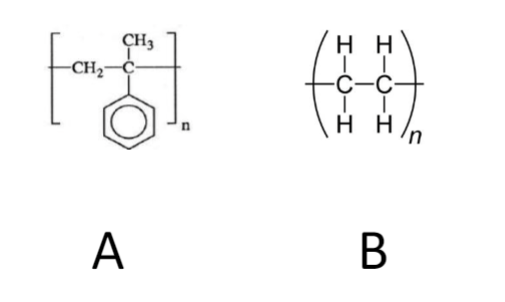
Which polymer will have a higher Tg?
Polymer A because the side group makes it harder for the chains to move past each other
True/False: Thermosets have a high degree of crosslinks compared to thermoplastics
true
True/False: Thermoplastics are stronger/tougher but also more brittle than thermosets
True
Why can’t thermosets be melted and remelted?
Because they degrade
What is special about thermoplastics?
They can be recycled and be shaped using more different processing methods
How does the thermoplastic change as the temperature gets hotter?
glassy (below Tg) —> rubbery moldable <—> Melt
How does the thermoset polymer change as the temperature increases?
glassy (below Tg) —> rubbery tough —> degrade before they ever melt
How can you change polymers so they don’t dissolve in water?
By adding crosslinks to the structure
True/False: Hydrogels are soluble in water
False, they are not soluble instead they absorb water
Are solid state polymers 100% crystalline?
No, they can be completely amorphous, partially crystalline, or almost completely fully crystalline
What are crystalline regions of polymers called?
Crystallite
What are crystallites composed of?
Chains folded onto themselves called lamellae which organize into spherulite
What structural features make a polymer more likely to crystallize?
Smaller side groups, lower branching density, isotactic or syndiotactic, fewer repeat units, hydrogen bonding or polar side groups
What does higher crystallinity lead to?
Higher elastic modulus, melting (service) temp, opacity, difficulty of dyeing, better vapor barrier properties
Where do semiconducting polymers charge transport?
Along the conjugated backbone
what’s a defining feature of a semiconducting polymer?
Alternating double bonds or aromatic cycles
What is significant about electron mobility in semiconducting polymers?
They have much lower electron mobility than traditional conductors
Why are semiconducting polymers useful?
Flexibility, biocompatibility, cheaper, better for enivronment
True/False: You can use thermosets in the extrusion process or in injection molding
False, you can only use thermoplastics because you’re melting it
True/False: Compression molding can be done with thermosets
True because you’re not melting them
What happens in chain growth?
Growth only happens from one side
What happens in step growth?
2 or more reactive functional groups where growth can happen from either side
If it has double bonds what can we conclude about the synthesis route?
It will proceed via chain growth
If it has 2+ function groups what can we conclude about the synthesis route>
It will proceed via step growth
What is the route if there are 3+ functional groups?
The route is able to make a network polymer
Addition reactants have…
no byproducts
Condensation reactions have…
a byproduct