Approach to GI disease and localization
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are the different anatomic localizations of GI disease?
Primary vs secondary GI disease
Oropharyngeal vs esophageal vs gastric vs SI vs LI vs mixed
What are the temporal classifications of GI disease?
Acute or chronic
What are mechanisms of diarrhea?
Osmotic, secretory, dysmotility, exudative
What do you want from a history?
Signalment, vax/deworming, duration, frequency, diet, travel history
If a patient is vomiting what are some followup questions?
Associated with eating or drinking?
Time of last bowel movement?
Concurrent diarrhea?
What do you want to to find on PE for GI dz?
Dehydration, fever, abdominal pain, BCS, signs of systemic dz (oral ulcer, icterus)
Where is a primary GI disease located?
Oral/pharngeal, esophageal, gastric, intestinal, rectoanal
What are some signs of oral disease?
Difficult prehension, food bolus formation, chewing abnormalities
What is pharyngeal/cricopharyngeal disease?
Impaired passage of food through oropharynx
What happens during esophageal disease?
Impaired passage of food through body of esophagus into stomach
What are signs of pharyngeal/cricopharyngeal disease?
Gagging and immediate food reflux
Regurgitations points you to what part of the GI tract?
Esophagus
What is regurgitation?
Passive process without vomiting movements like lip-licking, retching, contractions
Silent
Inability to predict timing
Undigested food
No bile
Vomiting 8-10 hours after eating suggests what?
Delayed gastric emptying
What are signs of gastric disease?
Vomiting
Also nausea, ptyalism, dysrexia, belching, abdominal distention, cranial abdominal pain, weight loss w/ decreased intake
What are signs of intestinal disease?
Diarrhea
Also nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss
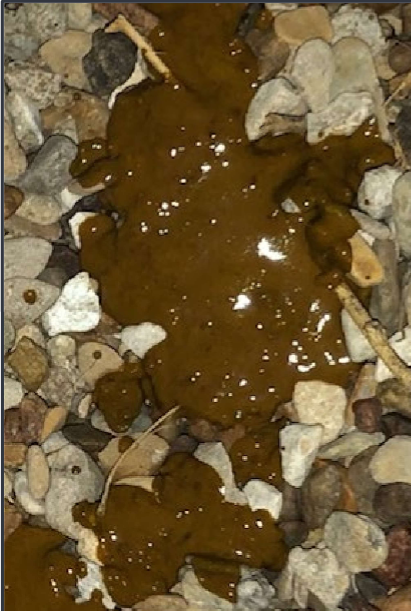
Diarrhea that is normal to slightly increased frequency of defecation, large volume, and lack of urgency indicate?
SI diarrhea
What can SI diarrhea also have visually?
Melena, flatulence, steatorrhea, concurrent vomiting, weight loss
Diarrhea that has increased frequency, small volume, urgent, tenesmus is what?
LI diarrhea
What can LI diarrhea also have visually?
Hematochezia and or mucus

SI diarrhea
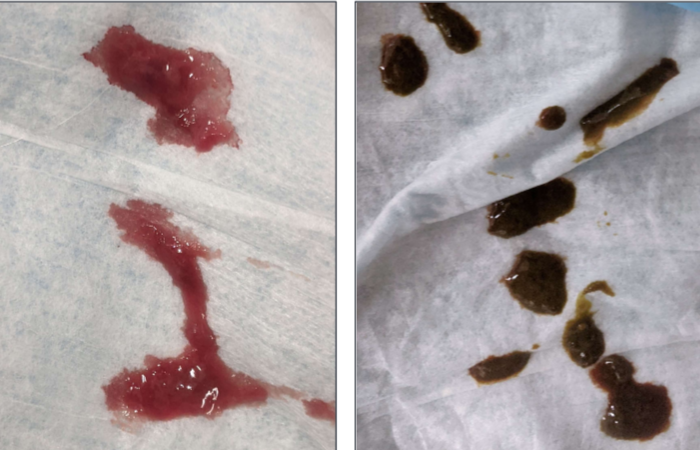
LI Diarrhea
What does rectoanal disease look like?
Dyschezia, tenesmus, mucoid or hemorrhagic discharge
Ribbon like stool
Blood on outside of feces
What is dyschezia?
Difficult or painful defecation
What is your diagnostic approach for acute GI disease with mild C/S?
Nothing if you think it was a one time thing
Check hydration, fecal float, rule out other things like foreign body
When do you do radiographs for an acute animal with mild C/S signs?
Lack of bowel movement
Foreign body
Non-productive retching
Abdominal distension
When do you always want additional diagnostics for an acute vomiting/diarrhea animal?
Dull/depressed, fever, tachy or brady cardia, abdominal pain, melena, severe signs, mild case that was unresponsive to symptomatic therapy
What are some rapid initial tests for an acute animal with moderate or severe or systemic signs?
Hydration (PCV/TS)
POC electrolytes
CBC, chem, urinalysis
Radiographs to determine if surgery is needed
What are some tests that you do on a case-by-case basis depending on presentation?
Parvovirus SNAP
Fecal float
Blood pressure
Cortisol ± ACTH stim
Coag test
What is an important thing when diagnosing chronic disease?
Exclusion of non-GI disease
Rule out infectious disease
Usually will do abdominal imaging
What are some good tests to exclude non-GI disease?
CBC/chem, urinalysis, baseline cortisol (dogs), T4 in cats, spec PL, bile acids
How can you exclude infectious diseases?
Fecal float and deworming
Describe the value of abdominal imaging in chronic cases?
Non-specific, can get decreased serosal detail if effusion or thin, gas or fluid distension if decreased motility
Describe the value of abdominal ultrasound with chronic cases
Very good, can evaluate intestinal wall changes, lymph nodes, GI masses or chronic FB, effusion gas/fluid GI distension
What are some intestinal wall changes with chronic GI disease?
Increased thickness
Decreased layering
Mucosal hyperchogenicity
How often is abdominal ultrasound normal in patients with idiopathic chronic enteropathies?
30%
What does the GI panel establish?
Rules out pancreatic disease
Localizes to GI
Defines disease severity
Determine need for supplement
What are the tests in a GI panel?
Cobalamin
Folate
Pancreatic specific lipase
Trypsin-like immunoreactivity
What does hypocobalaminemia indicate?
Ileum malabsorptive disease
R/o exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
What does decreased folate indicate?
Proximal SI disease
When do you biopsy the GI tract?
Typically chronic diseases with clinical parameters of inappetence, lethargy, progressive weight loss, treatment trial failure
Diagnostic indicators for biopsy are hypoalbuminemia, hypocobalaminemia, suspicion of infectious or neoplastic cause
Why should you always biopsy prior to steroids?
Steroids can alter biopsy results
What can you definitively diagnose with a biopsy?
Needed for idiopathic inflammatory enteropathies
Usually get lymphoplasmacytic
What can you find on a biopsy to point you in other directions?
Neoplasia concern
Neutrophils can make you consider FISH, campylobacter in cats
Eosinophils can make you repeat deworm or a food trial
Pyogranulomatous can make you search for fungal or atypical bacteria
Low fat diet in yorkies
What are some limitations of GI biopsies?
All inflammatory patterns can be seen with idiopathic chronic dz
Do not differentiate between treatment responses
histopath does not correlate with C/S seveity
Microscopic changes do not resolve with treatment