Chapter 6 Anatomy Muscular System
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
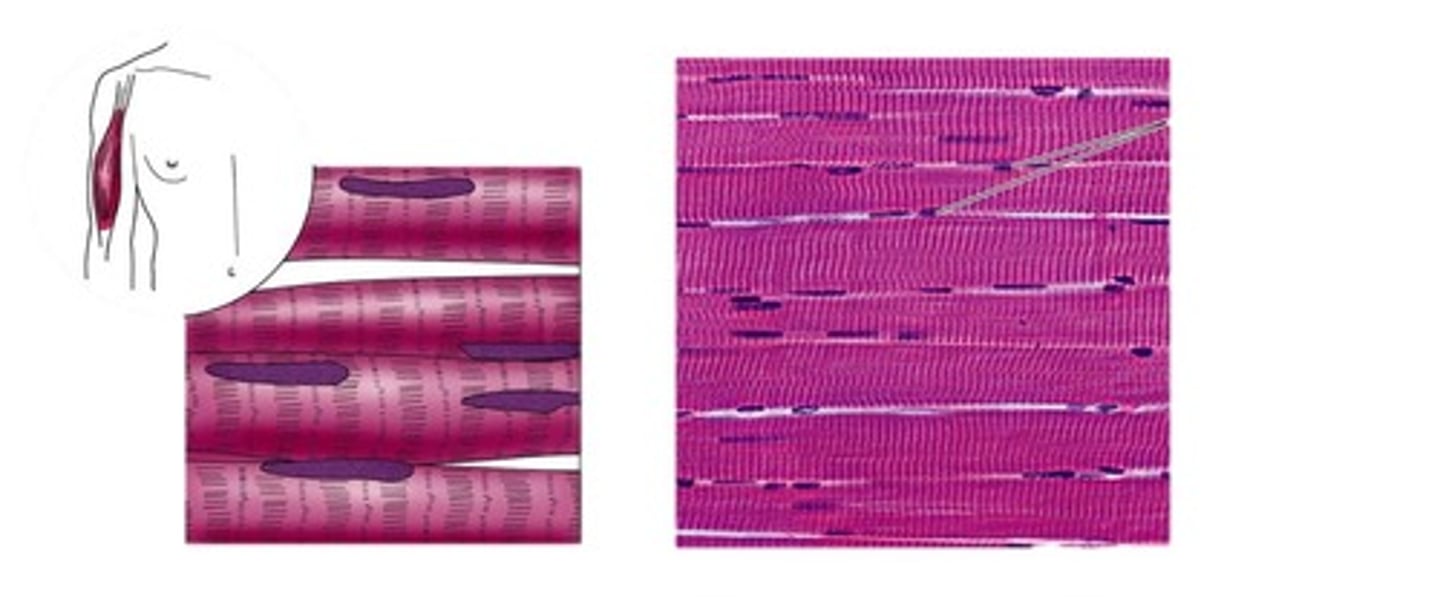
Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle
- Striated
- voluntary
-Attached to bones by tendons (strong cord-like structures made of collagen)
-Large, cigar-shaped cells are multinucleate (having multiple nuclei)
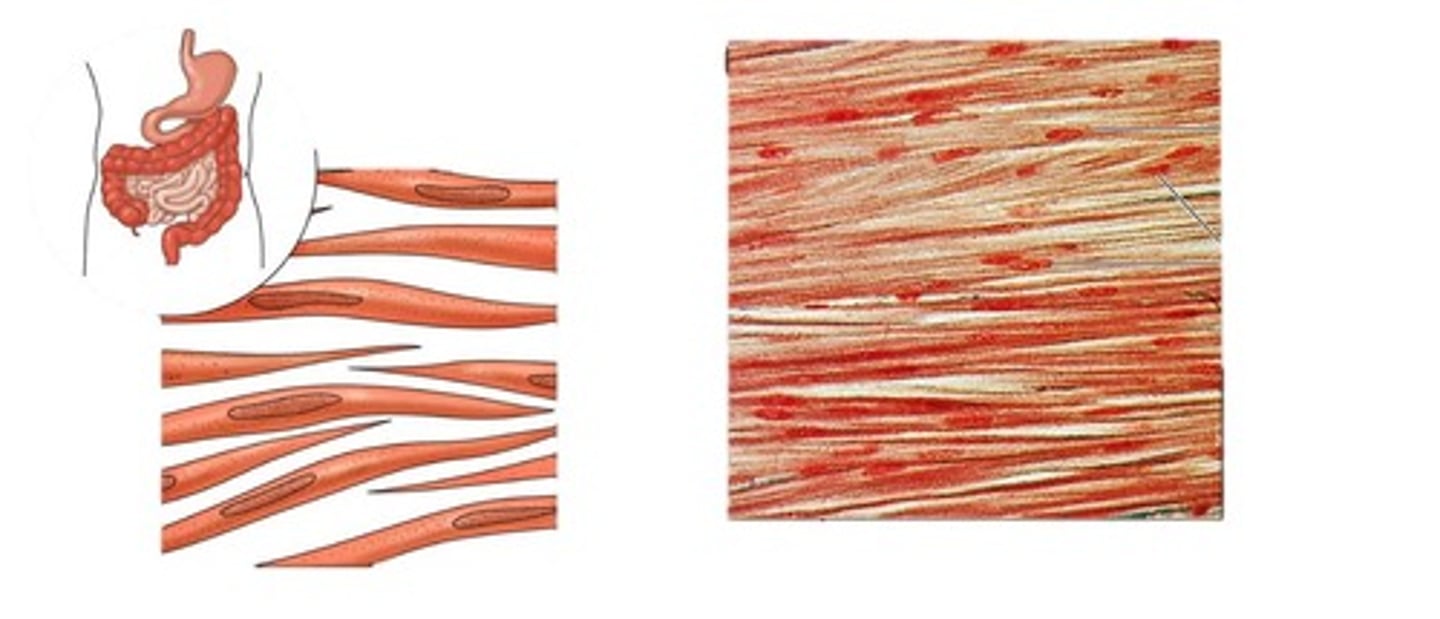
Characteristics of Smooth Muscle
-Lacks striations
-Involuntary
-Located in the walls of hollow organs (stomach, bladder, etc.)
-Spindle Shaped
-Uninucleate (has one nucleus)
-Allows for slow, sustained contraction that helps regulate blood flow
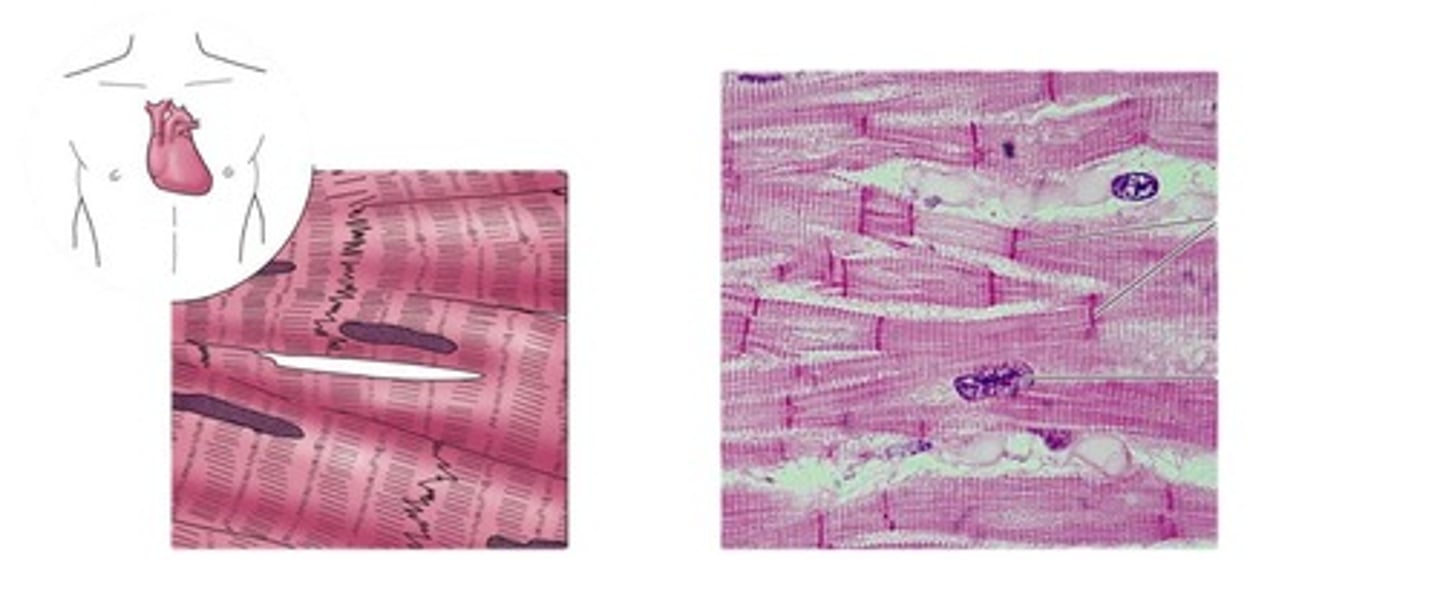
Characteristics of Cardiac Muscle
-Straited
-Involuntary
-Cells are branching and interconnected by intercellular discs, which include gap junctions that facilitate rapid electrical activity signal conduction
- Cardiac muscle contracts at a steady rate set by pacemaker cells, ensuring that the heart pumps blood efficiently.
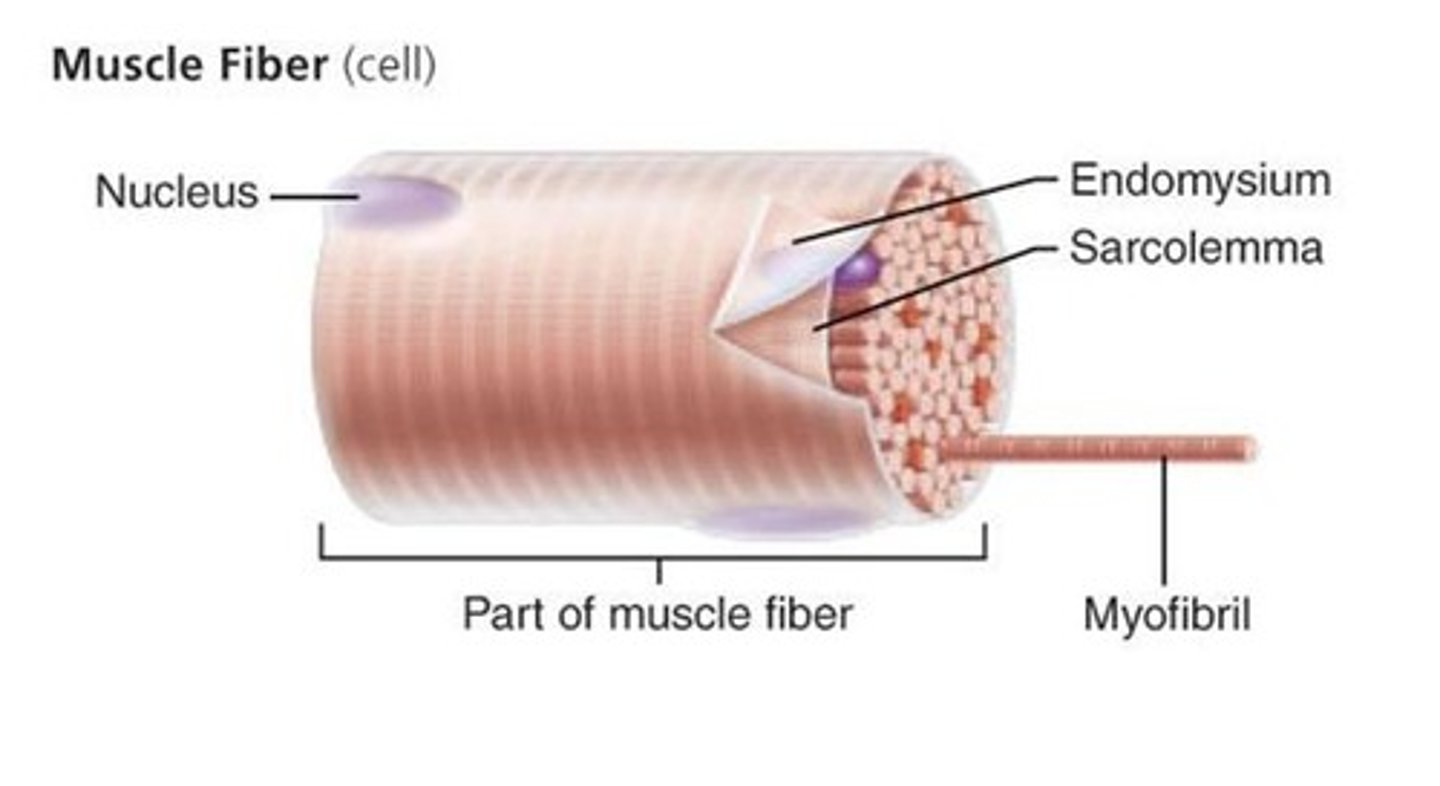
Sarcolemma
The specialized plasma membrane of a muscle fiber that conducts electrical impulses
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in muscle cells that store and releases calcium during muscle contraction
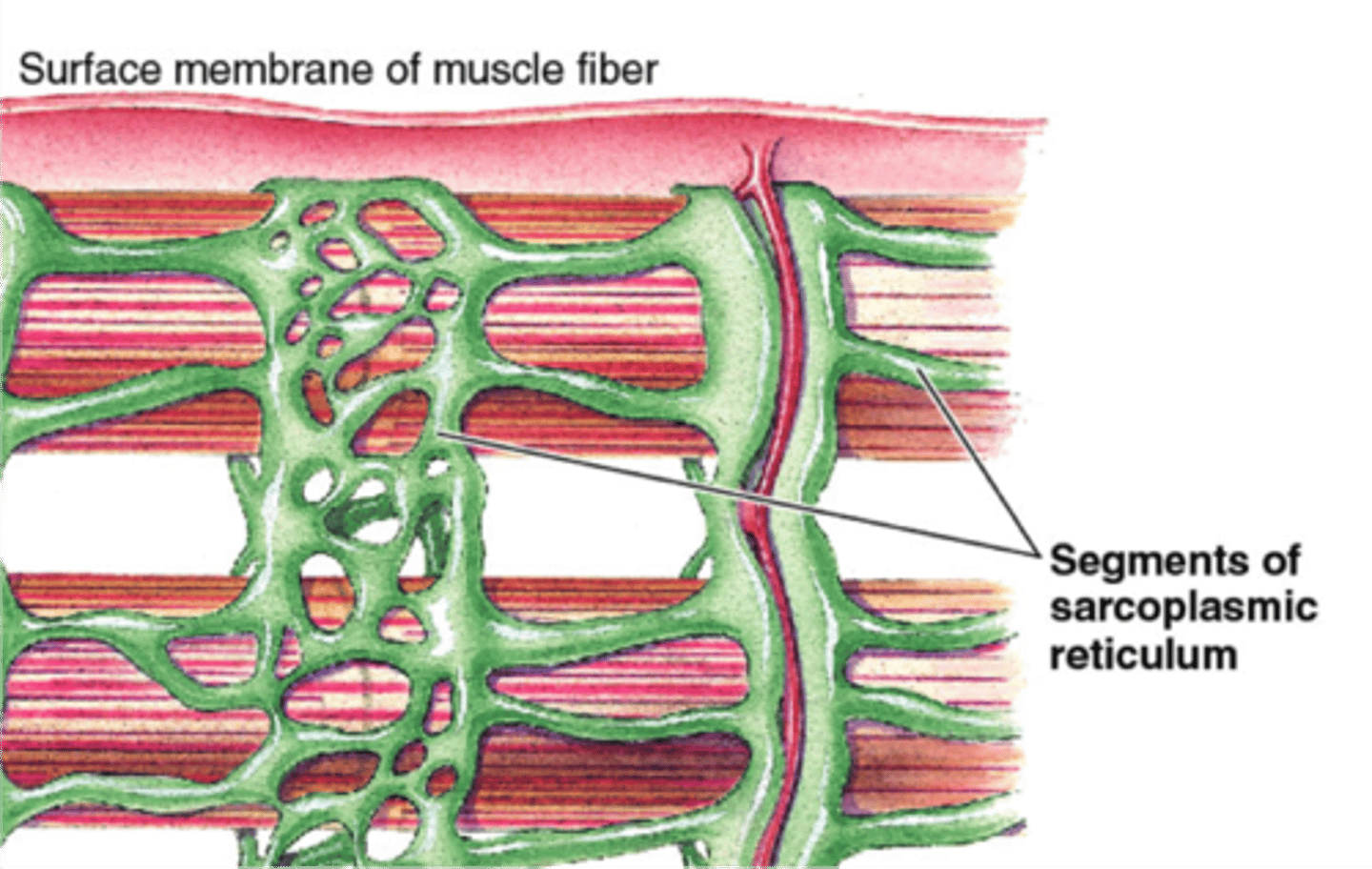
Myofibril
-long, rod-like organelles
-fills the muscle cell
-consist of repeating units (sarcomeres) creates straited appearance through their arrangement of light (I) and dark (A) bands
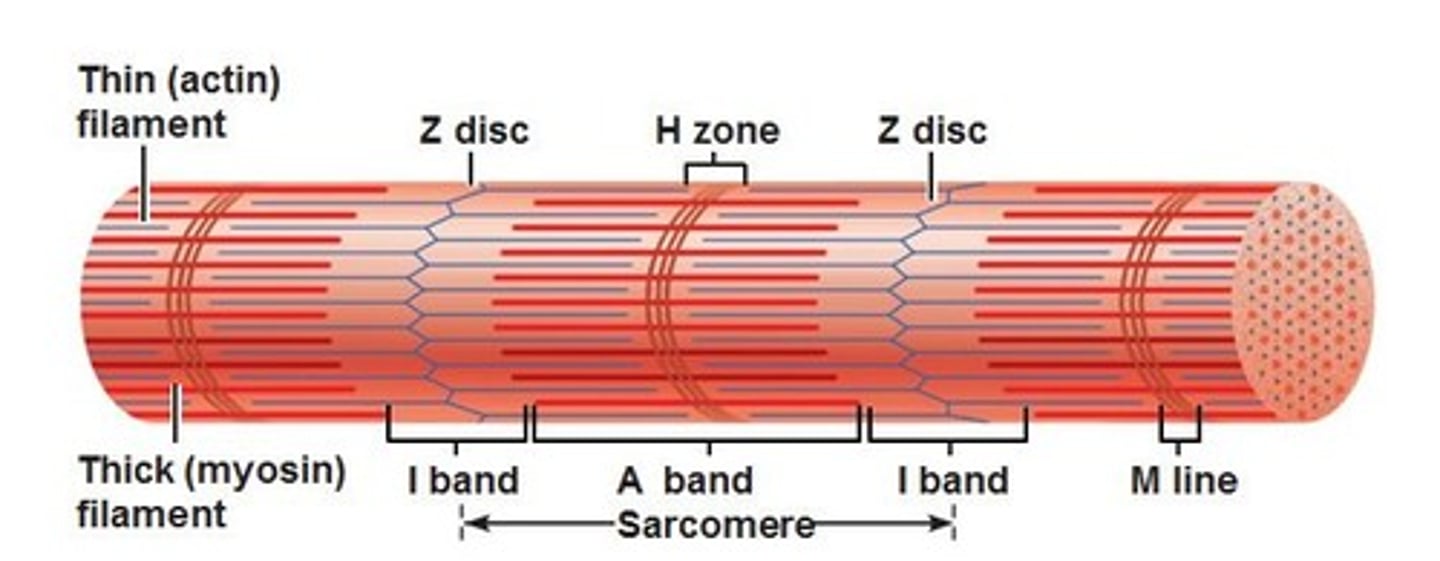
Dark (A) bands
one of the cross striations in striated muscle that contain myosin filaments and appear dark under the light microscope and light in polarized light.
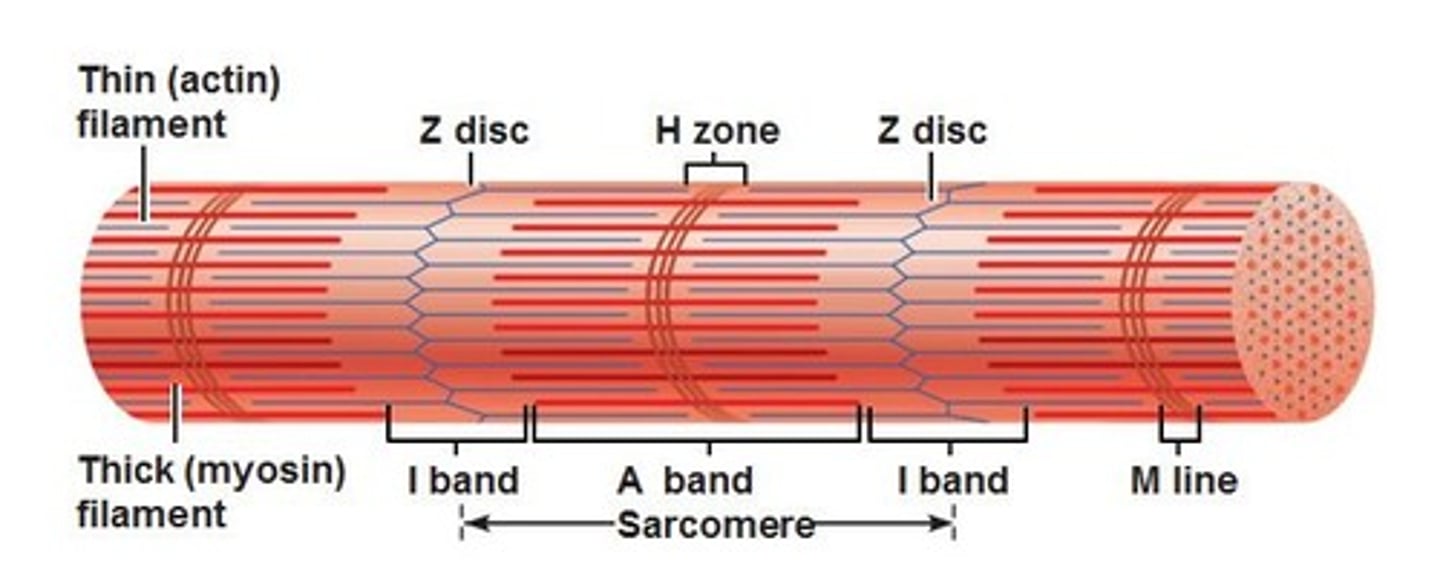
Light (I) band
section of the sarcomere containing only thin filaments, flanks both ends of the A band.
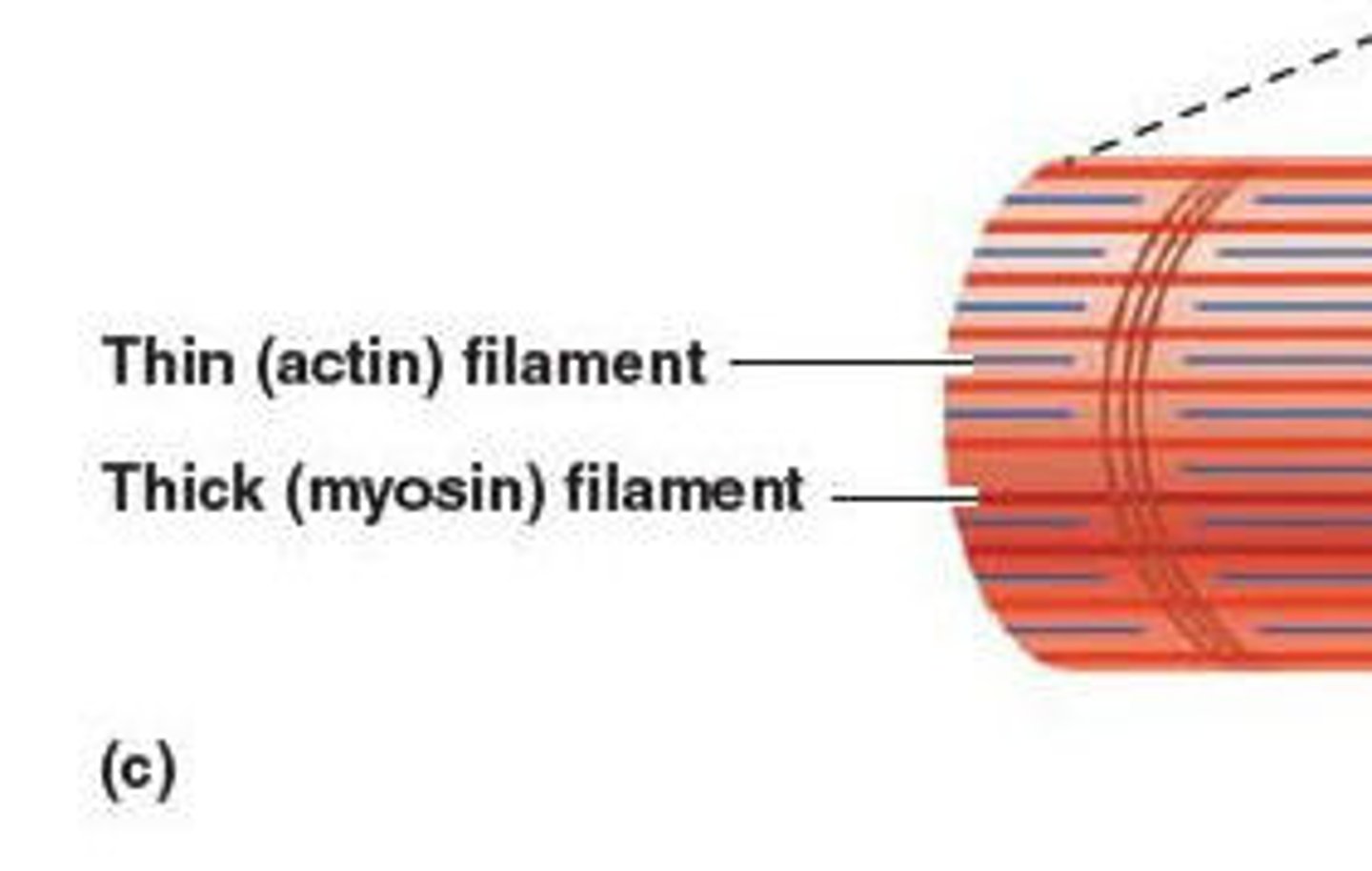
Thin Filaments
made of actin; these filaments are anchored to the Z disc, providing structure to the sarcomere and aiding to contraction
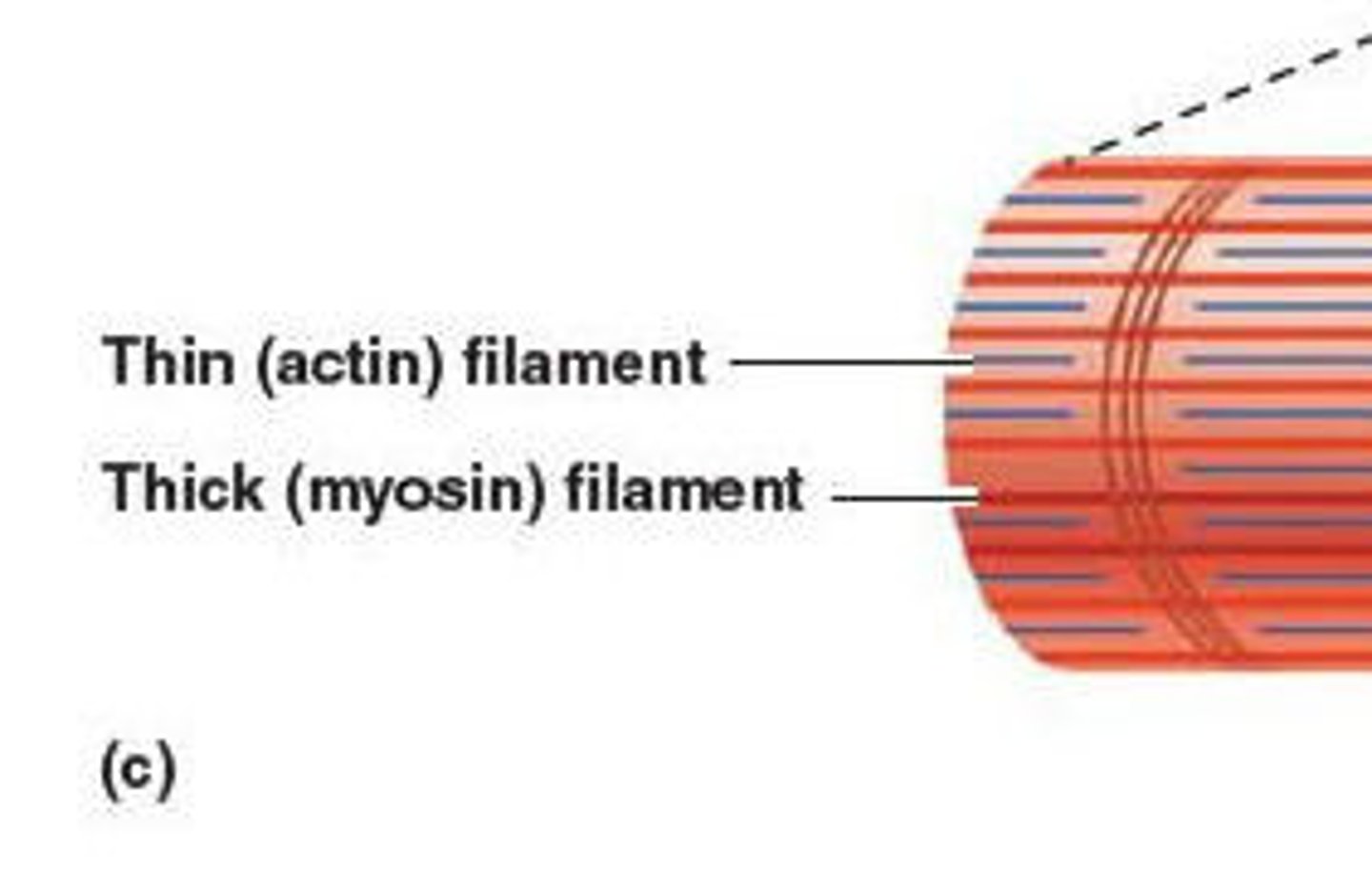
Thick Filaments
composed of myosin; these filaments contain ATPase enzymes that are crucial for muscle contraction
Acetylcholine (ACh):
A neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction that initiates muscle contraction by stimulating the muscle fiber.
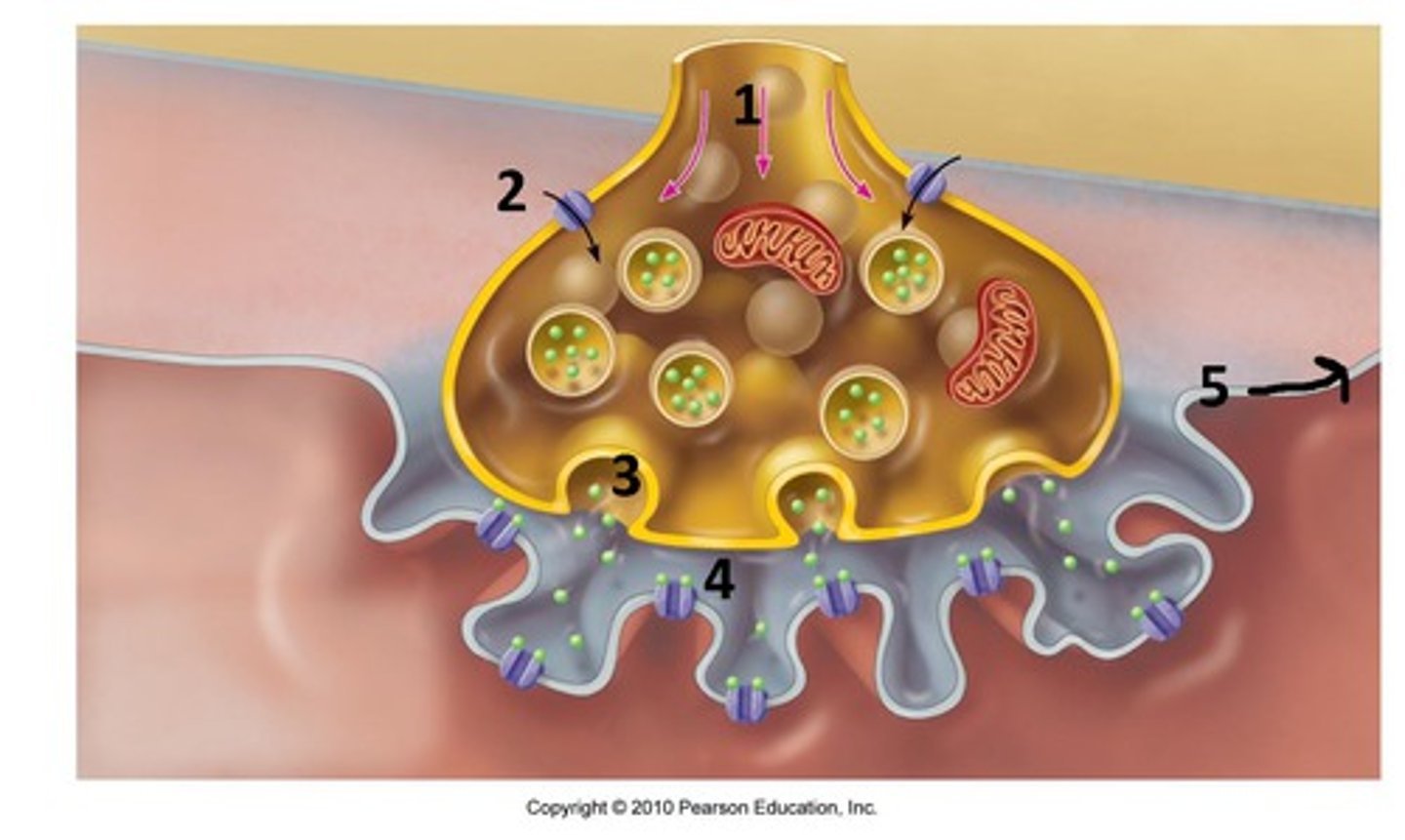
Action Potential
The movement of ions generates an electrical current
Motor Unit:
Consists of one motor neuron and all the skeletal muscle cells it stimulates, enabling coordinated muscle contractions.
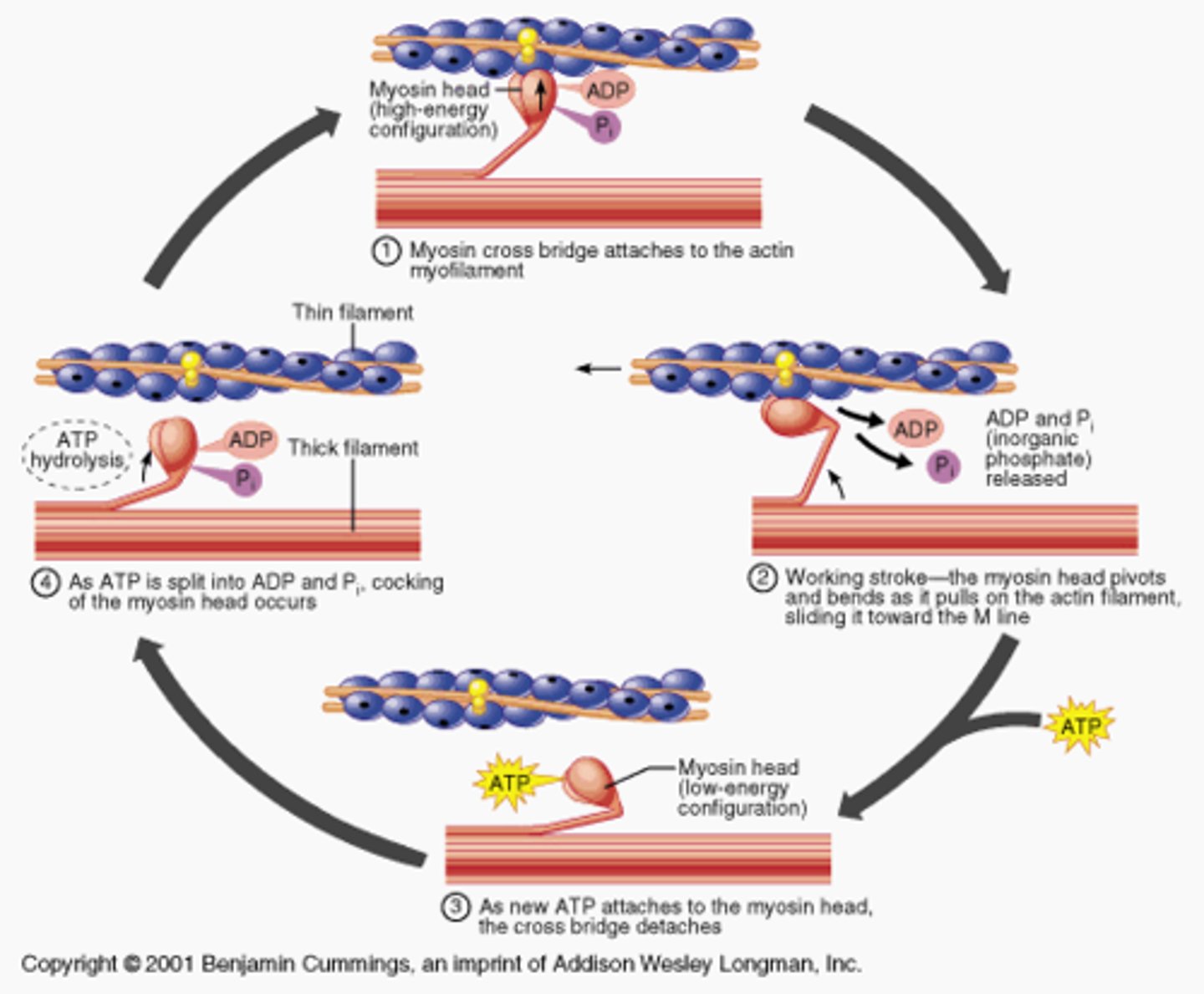
Sliding Filament Theory
-Calcium ions bind to proteins on thin filaments, exposing myosin-binding sites.
-Myosin heads attach to actin, pivoting to pull thin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere.
-Contraction continues as long as calcium ions are present, and ATP supplies the necessary energy.
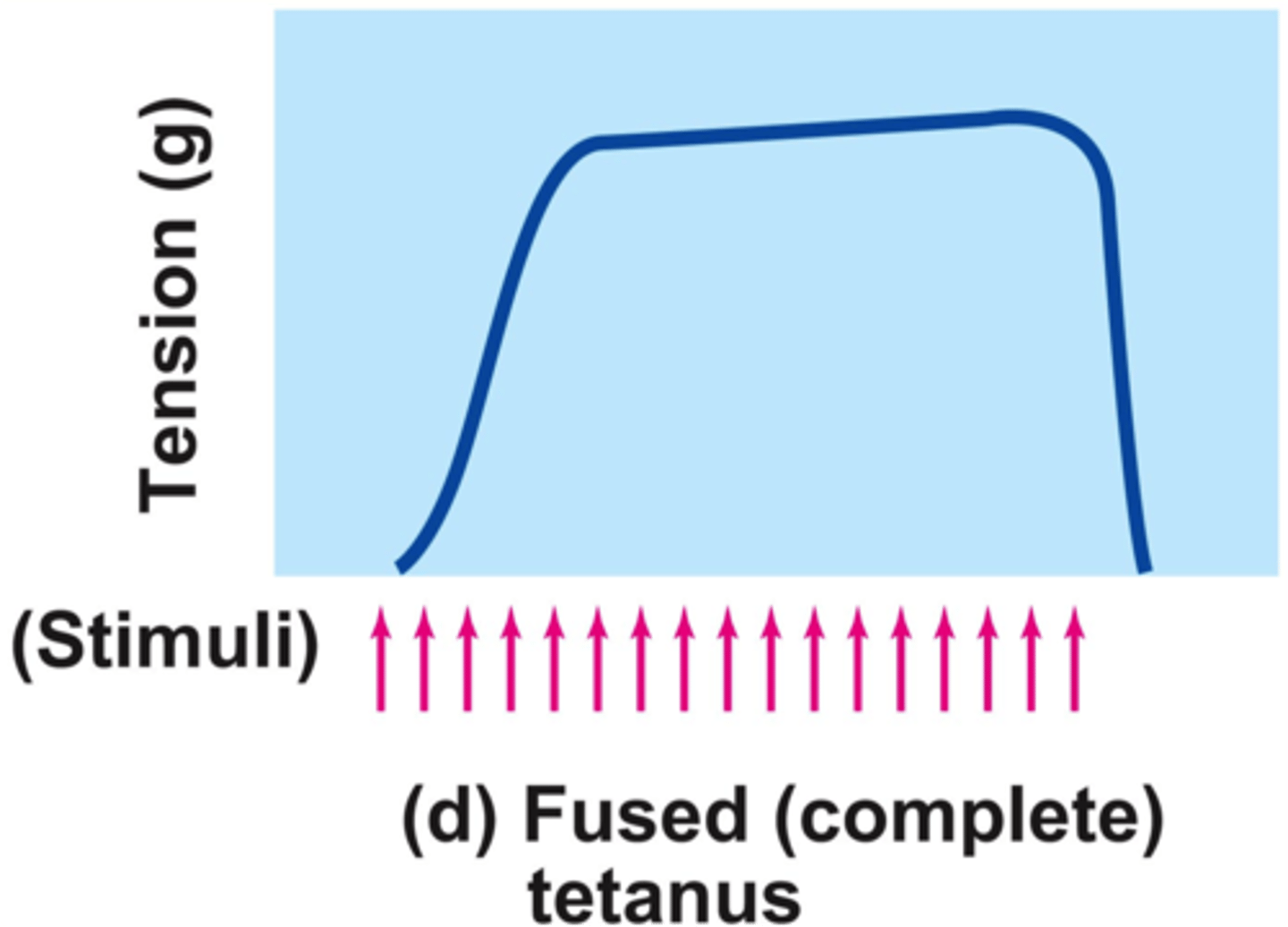
fused tetanus (complete)
when stimulus frequency is so high that no muscle relaxation takes place between stimuli
3 pathways for regeneration of ATP in working muscles
1. Direct Phosphorylation of ADP by Creatine Phosphate: The fastest method, providing immediate energy.
2. Aerobic Respiration: A slower process that requires oxygen, generating more ATP for extended activity, primarily occurring in mitochondria.
3. Anaerobic Glycolysis: Breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing ATP quickly but resulting in lactic acid and lower energy yield.
Muscle Fatigue
Muscle fatigue occurs with prolonged or intense activity, characterized by:
-Ion imbalances that disrupt normal cellular function.
-Oxygen deficits and lactic acid accumulation, leading to discomfort and reduced muscle performance.
-A decrease in energy supply (ATP) that impairs muscle contraction.
Isotonic vs. Isometric Contractions
Isotonic Contractions: Occur when the muscle shortens and movement happens (e.g., bending the knee).
Isometric Contractions: Involves muscle tension increase without shortening (e.g., pushing palms together).
Origin
Attachment to an immovable or less movable bone.
Insertion
Attachment to a movable bone.
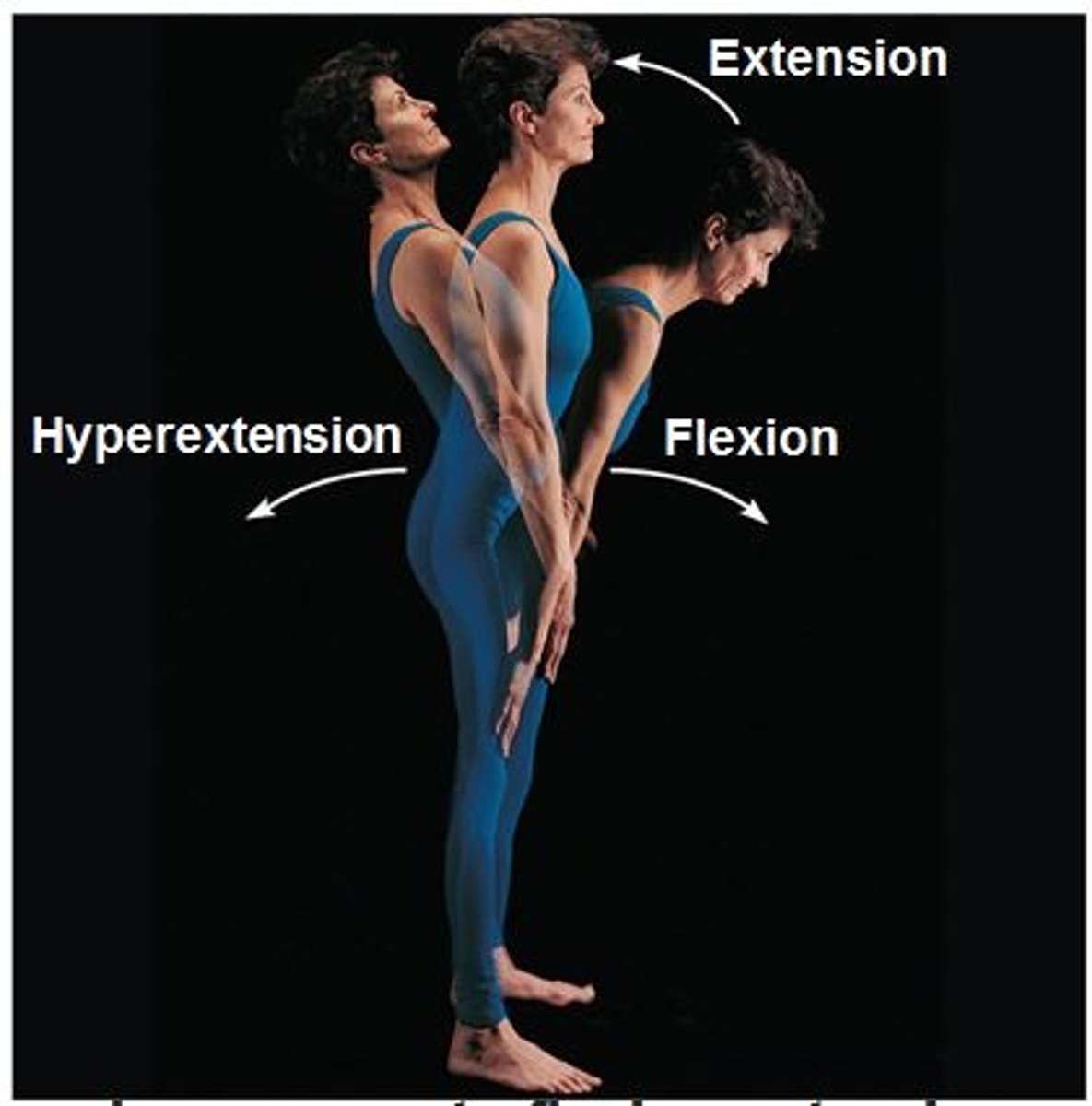
Flexion
Decreases the angle of the joint; brings two bones closer (e.g., bending the elbow).
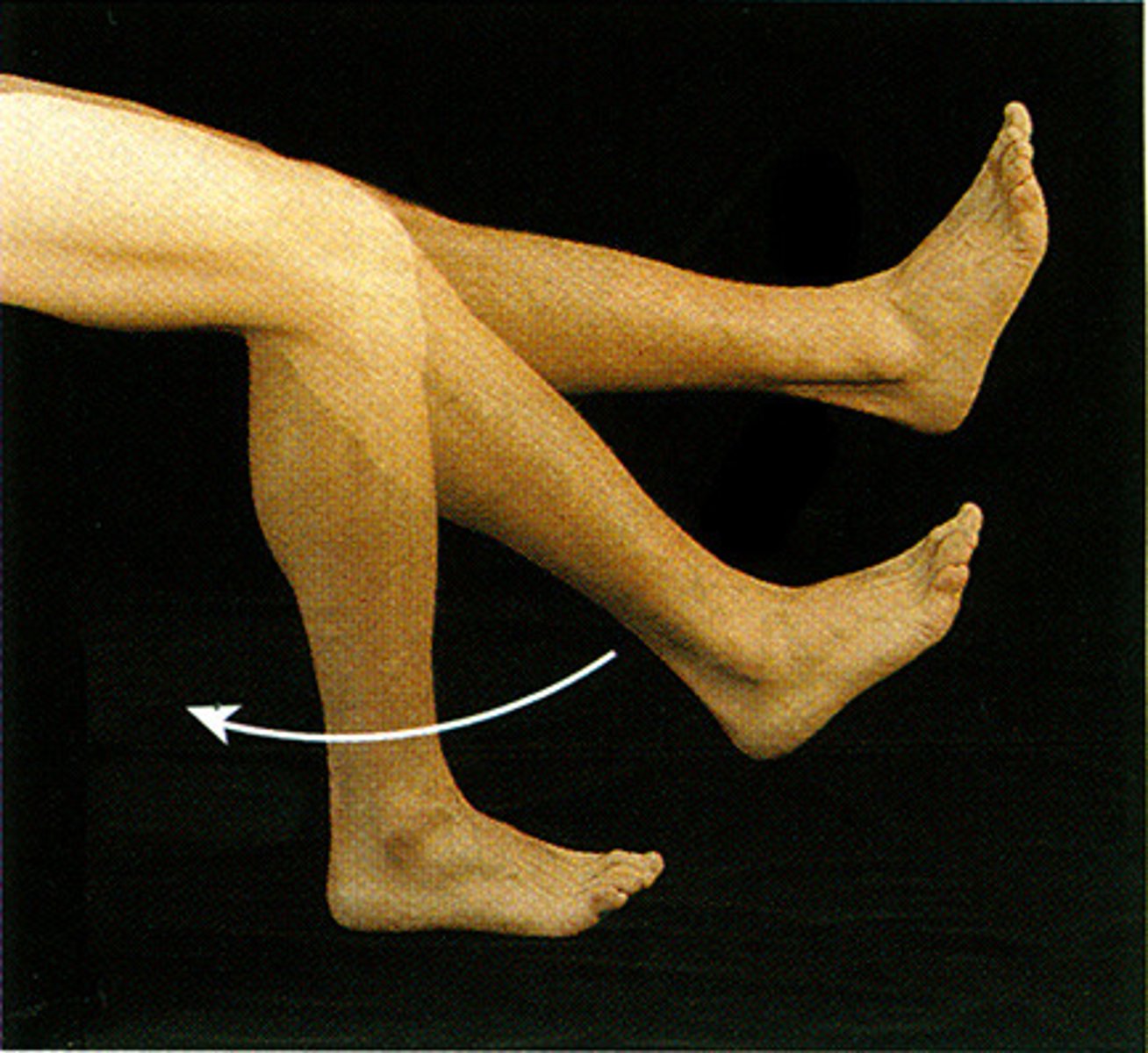
Movement Dynamics
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves toward the origin.
Extension
Increases the angle between two bones; straightening the elbow or knee.
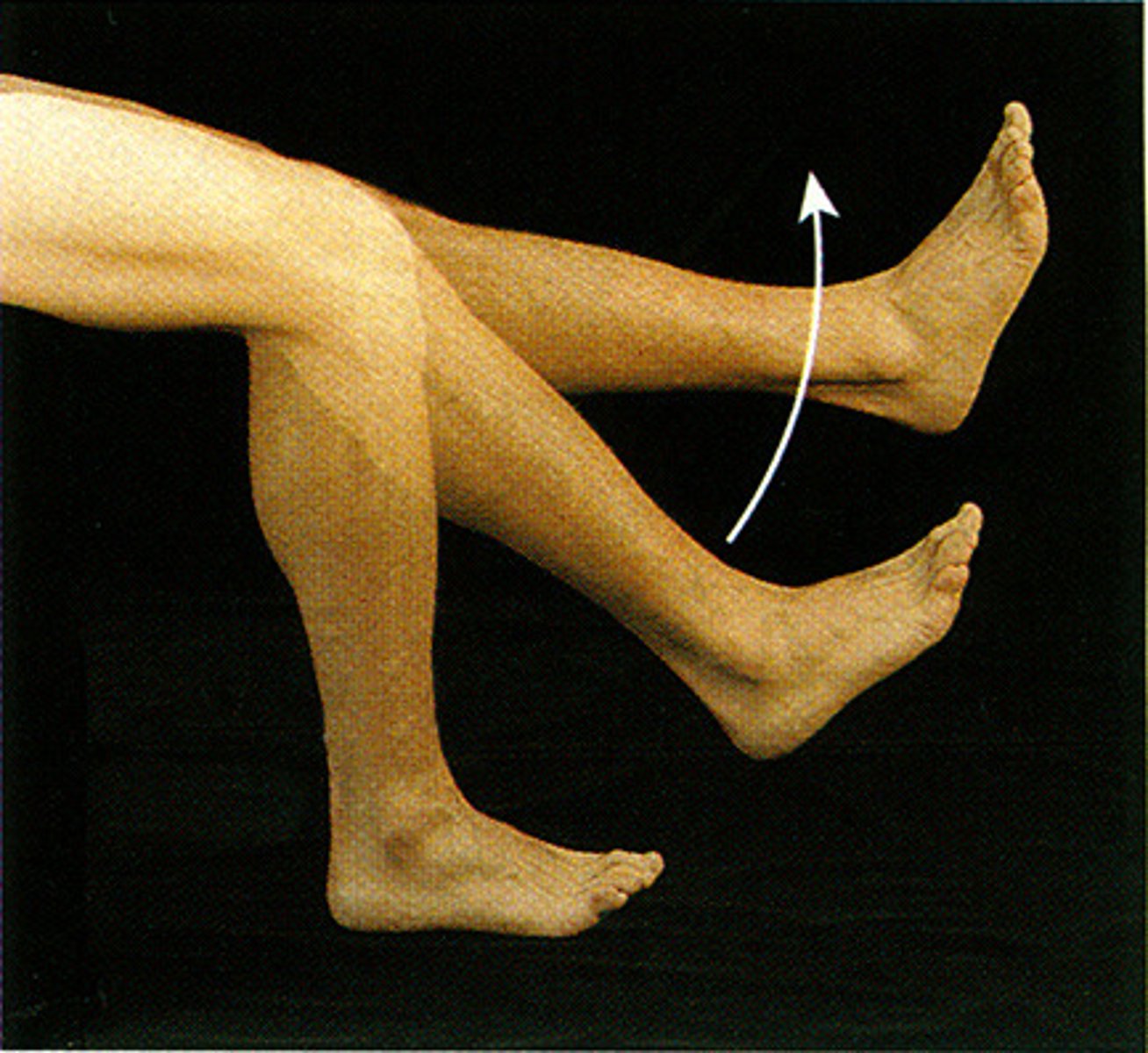
Hyperextension
Extension beyond 180°
Rotation
Involves the movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis (e.g., shaking the head 'no').
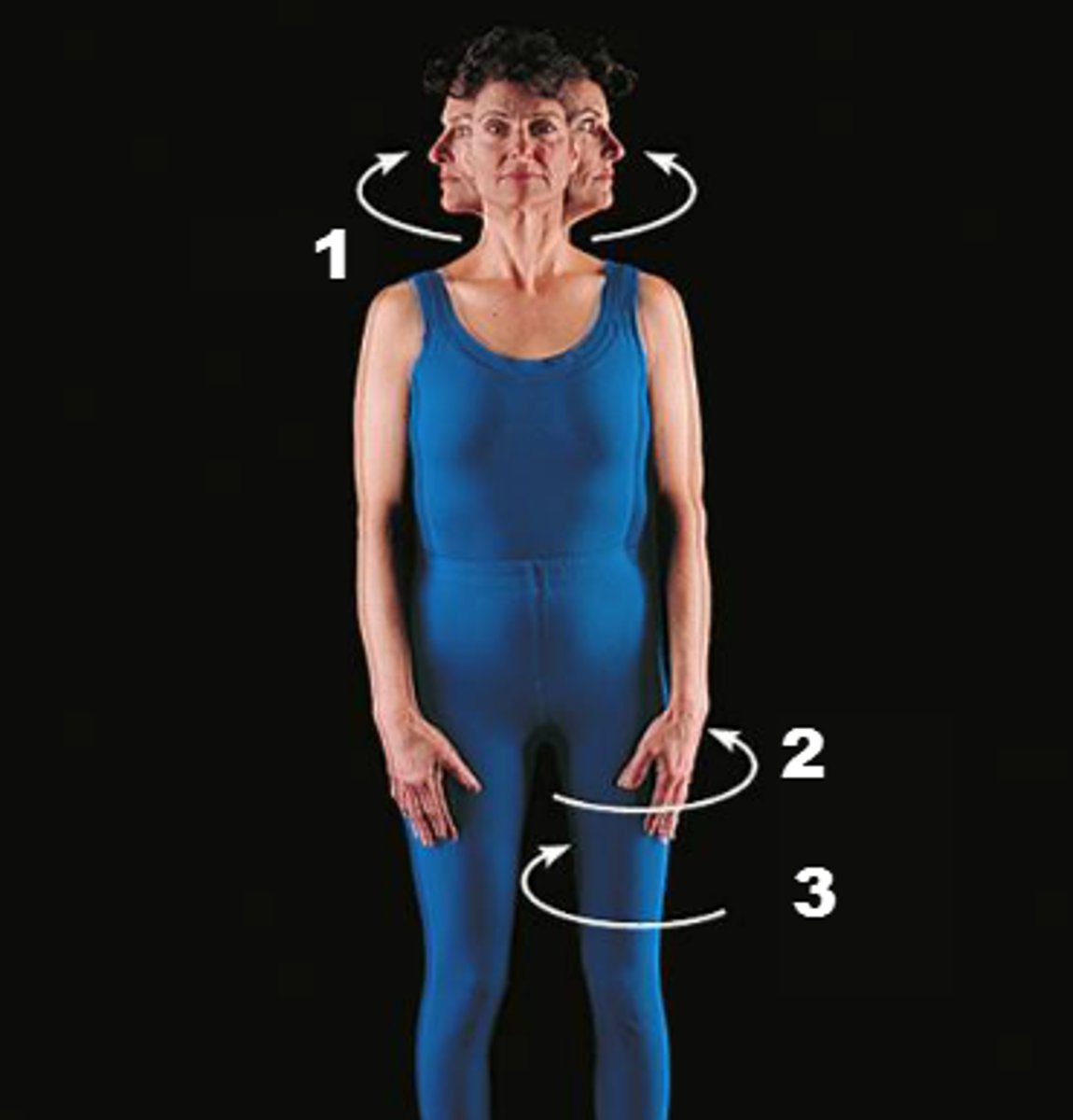
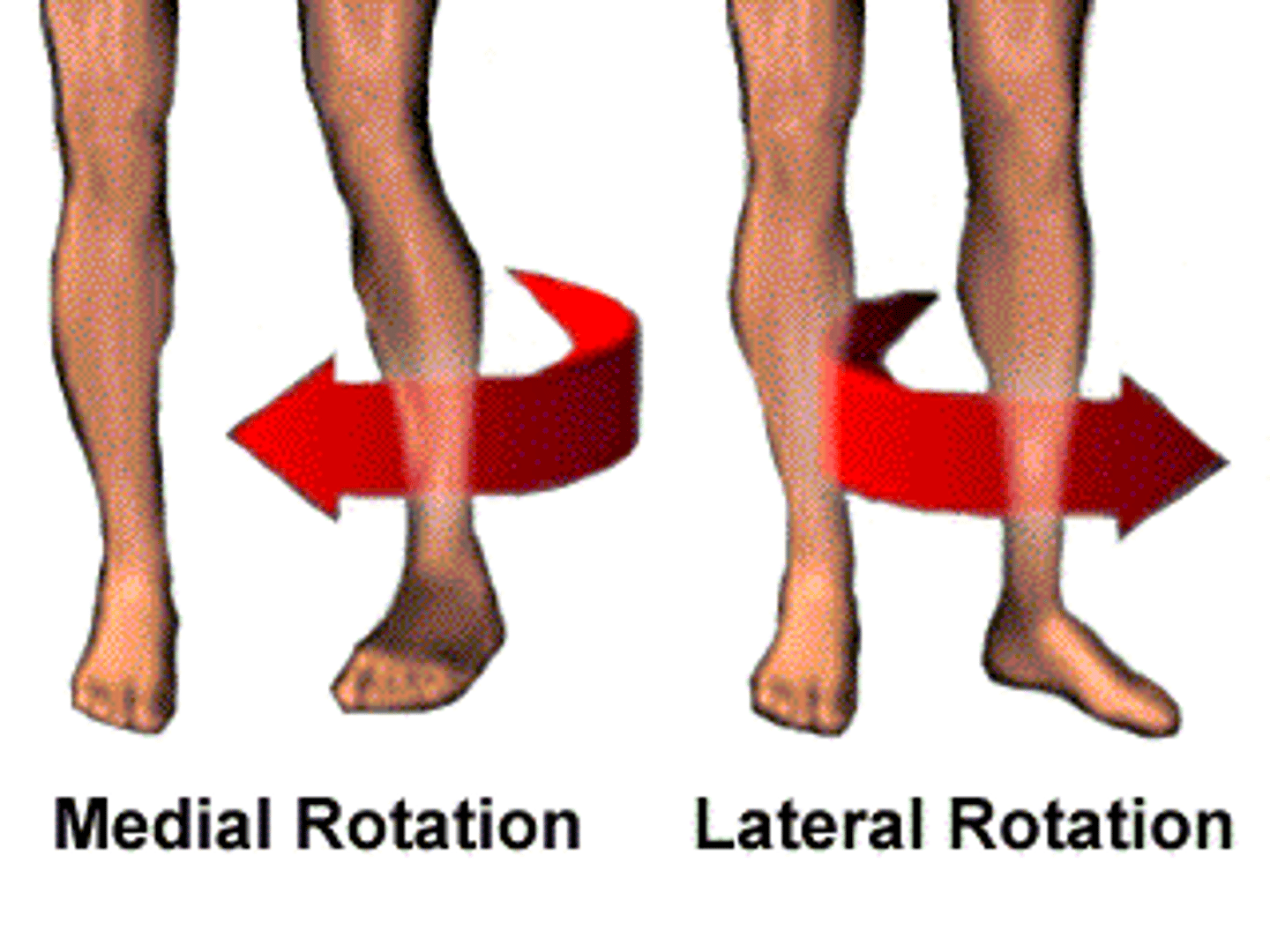
Medial Rotation
Rotation toward the midline
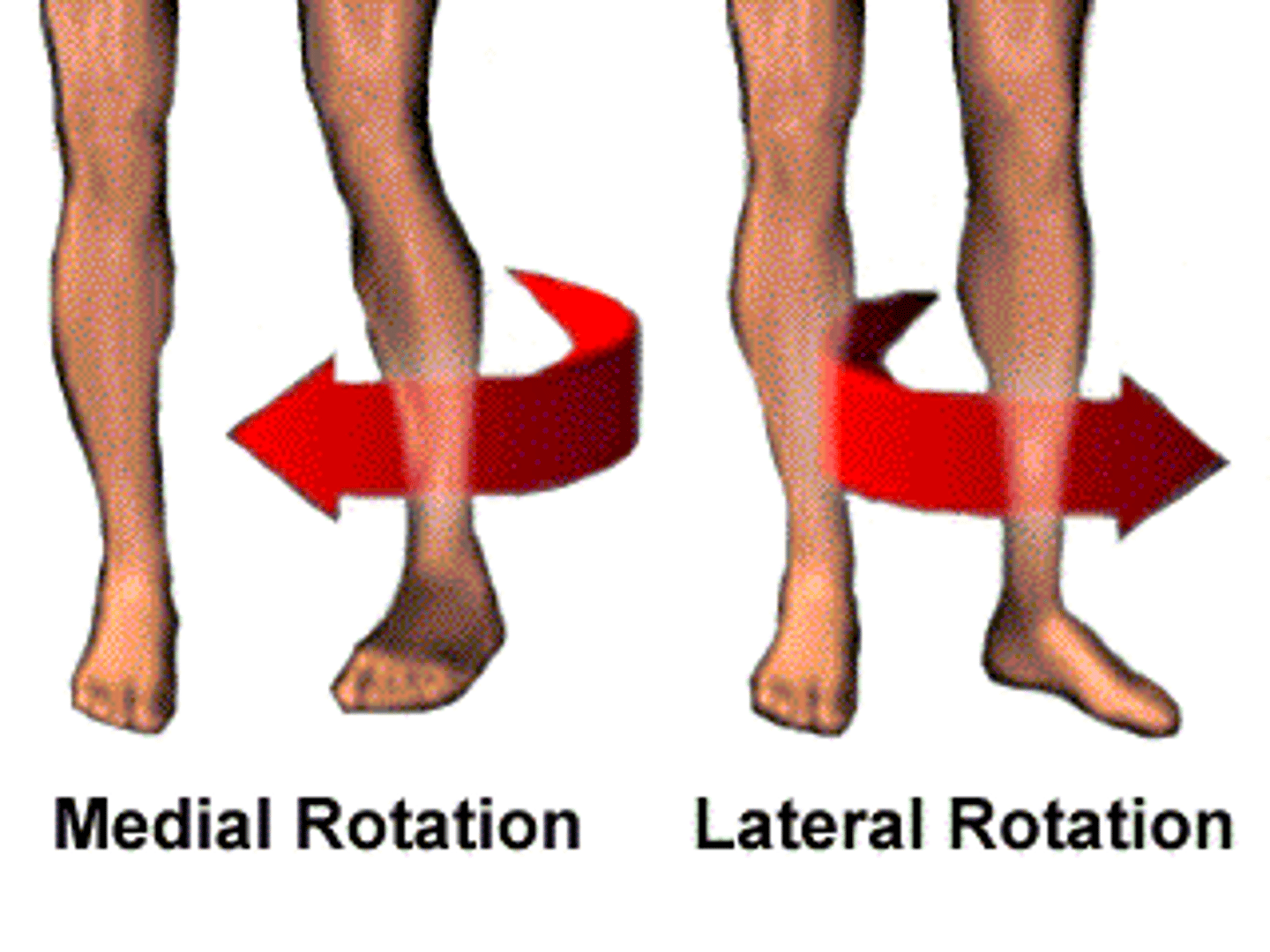
Lateral Rotation
rotation away from the midline
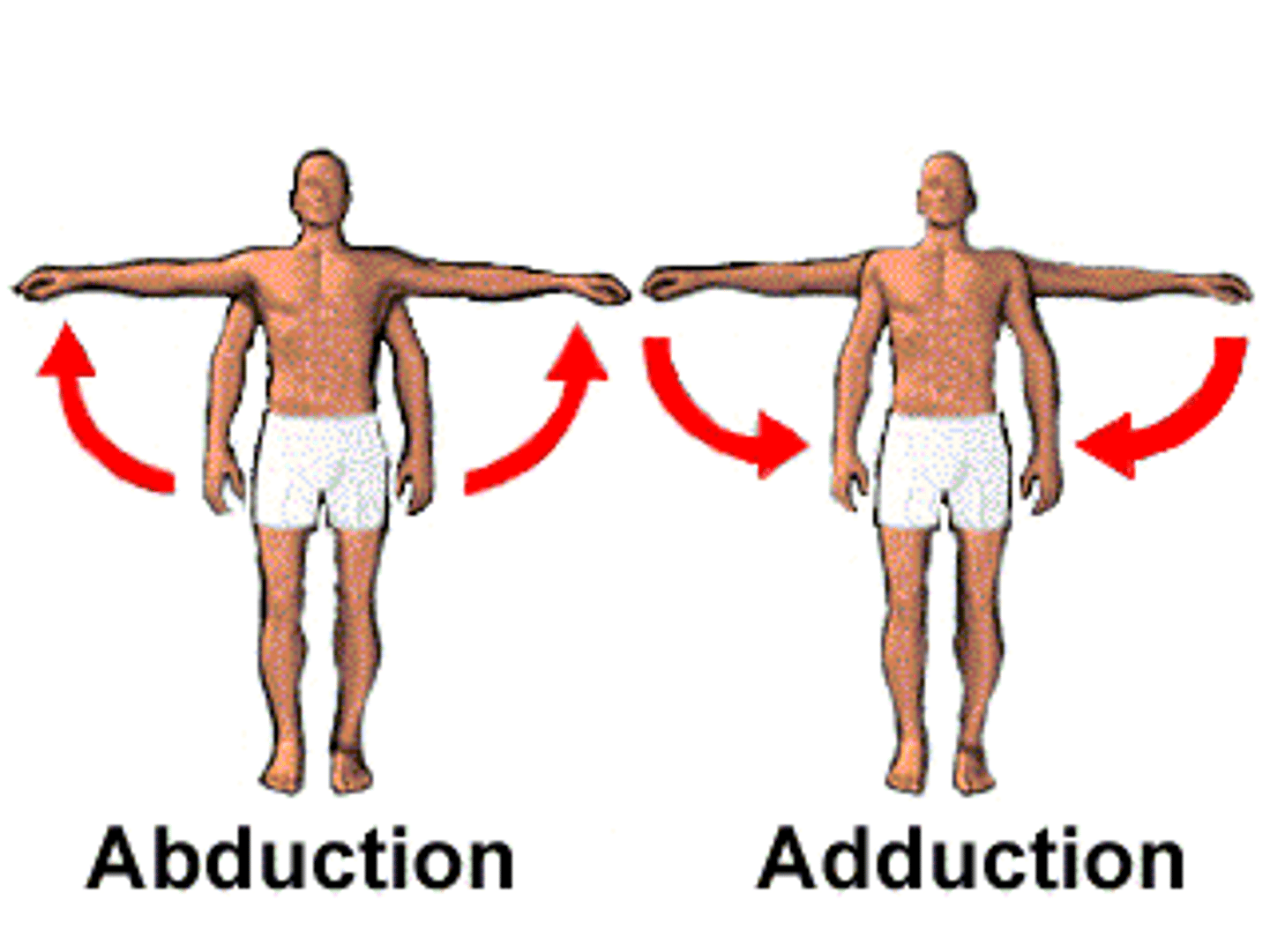
Abduction
Moves a limb away from the midline of the body.
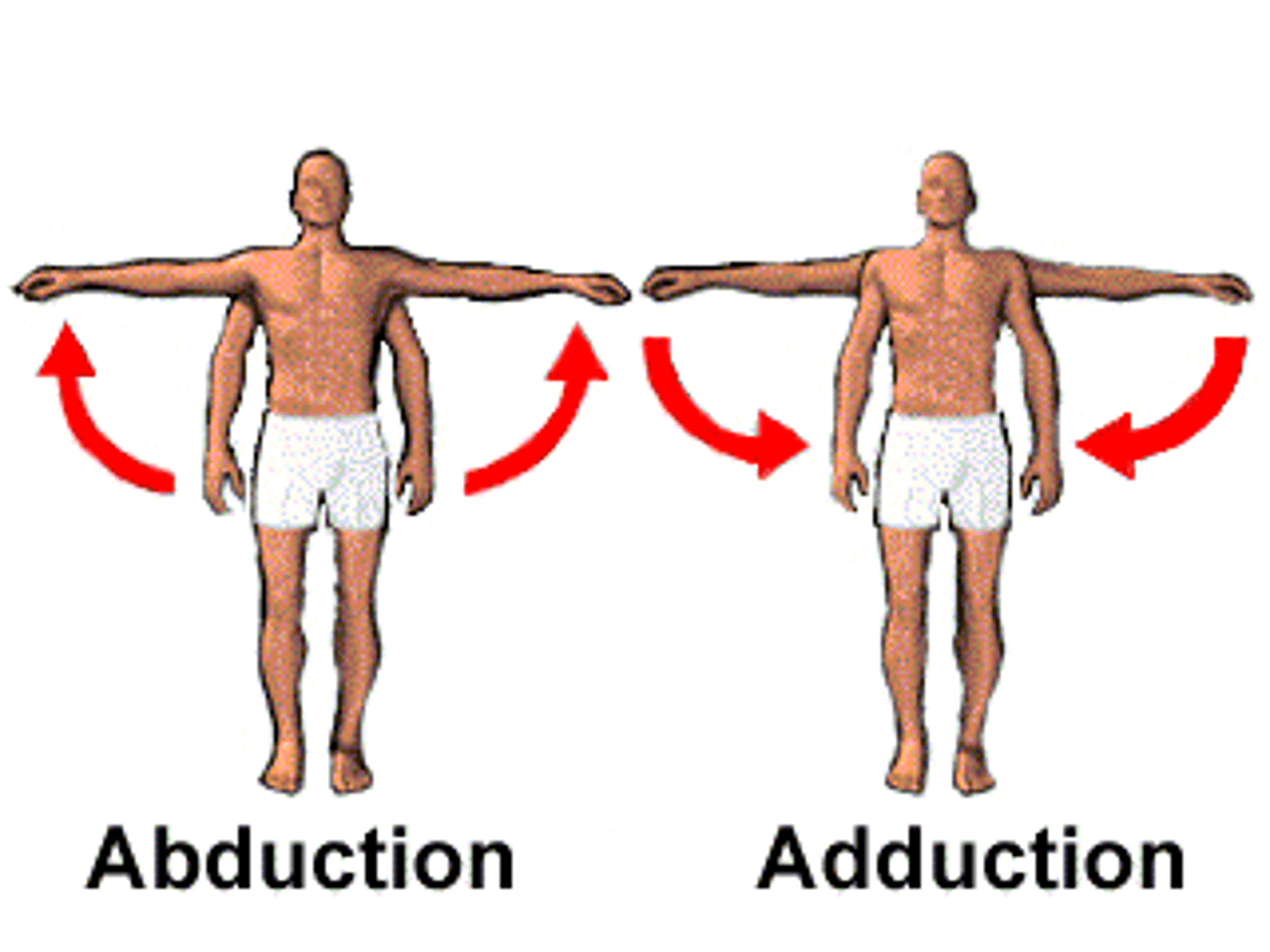
Adduction
Moves a limb toward the midline.
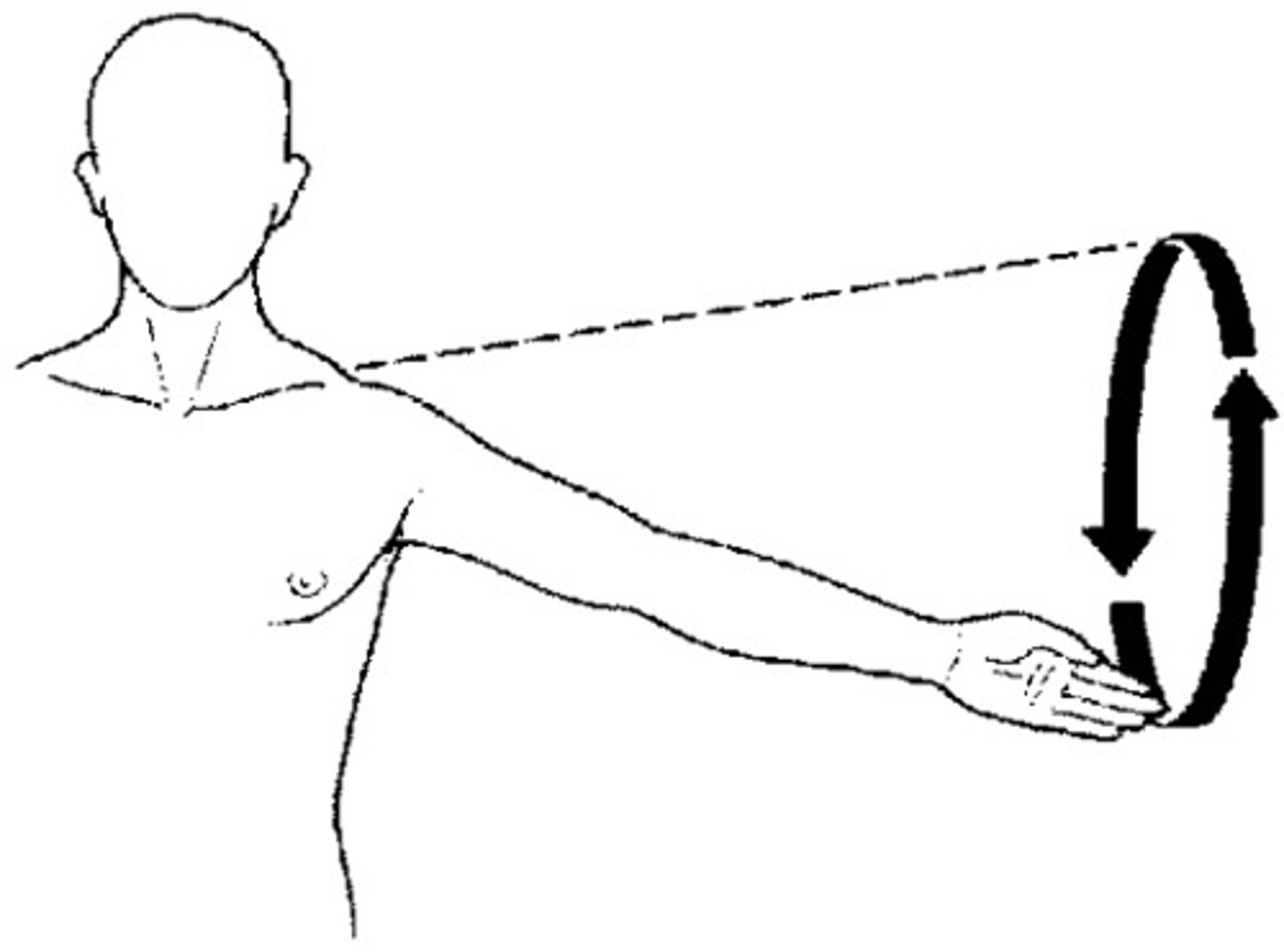
Circumduction
A circular movement combining flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction, with the proximal end stationary and the distal end moving in a circle.
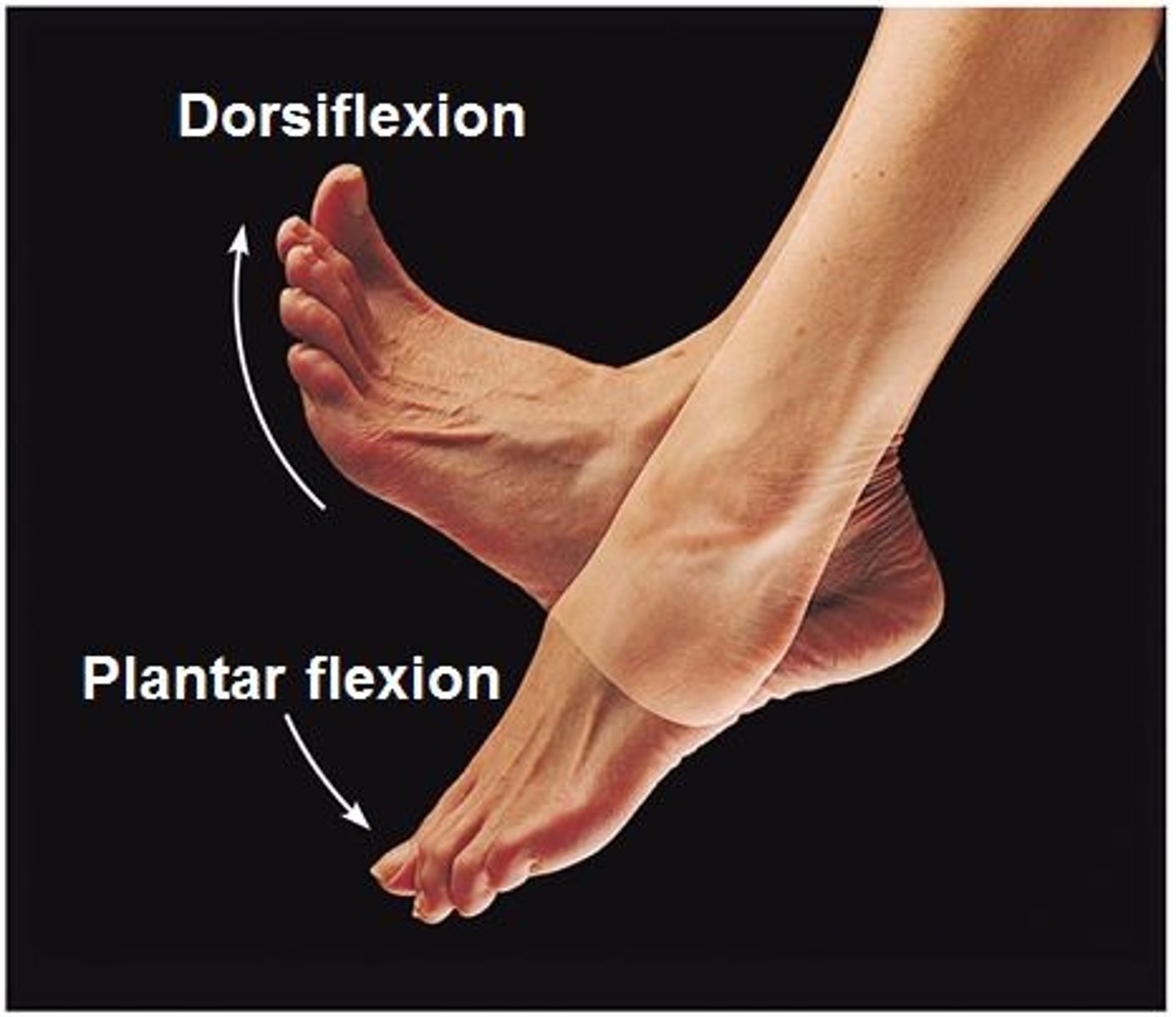
Dorsiflexion
Lifting the foot so that the superior surface approaches the shin.
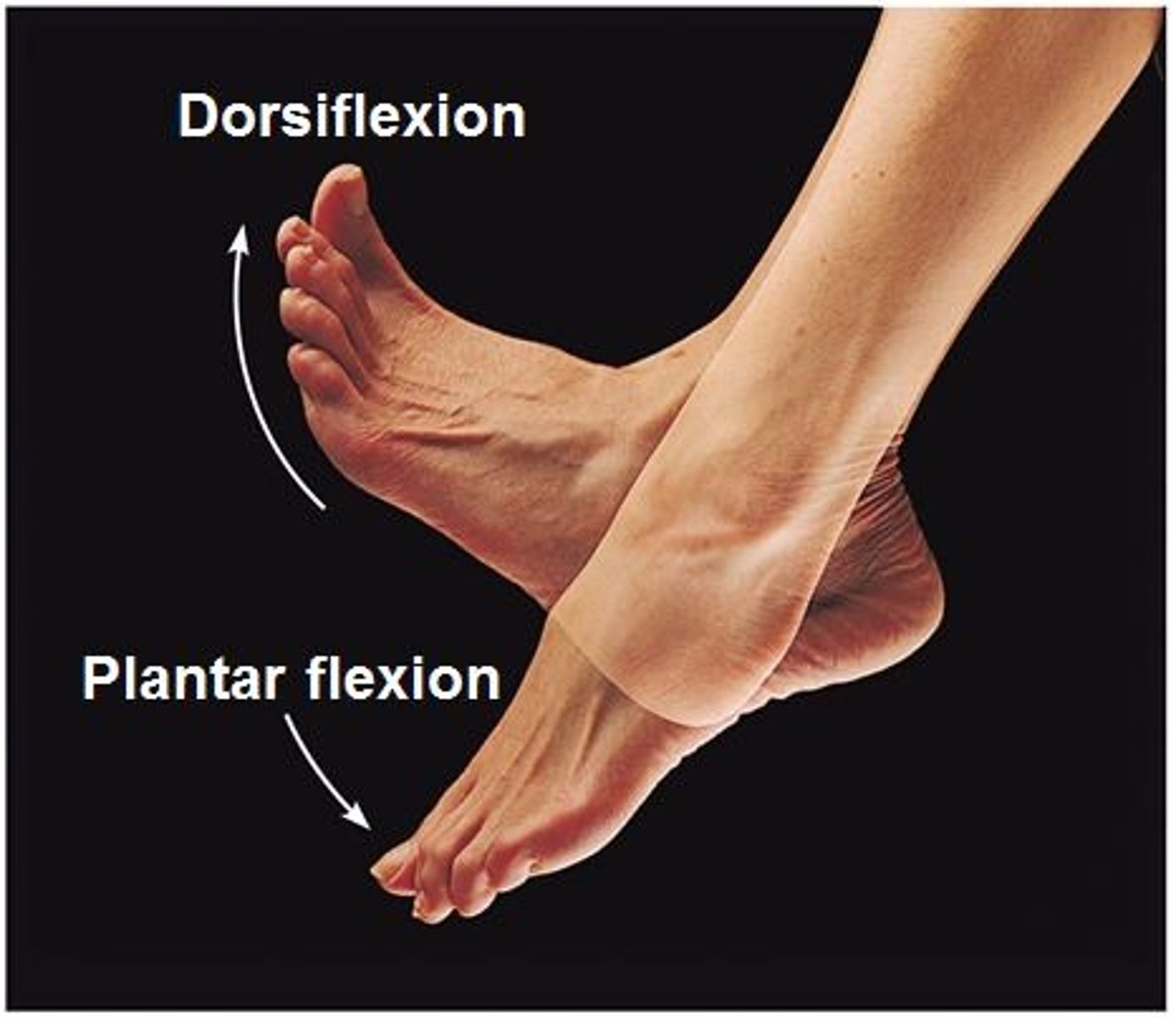
Plantar Flexion
Pointing the toes away from the head.
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot medially.
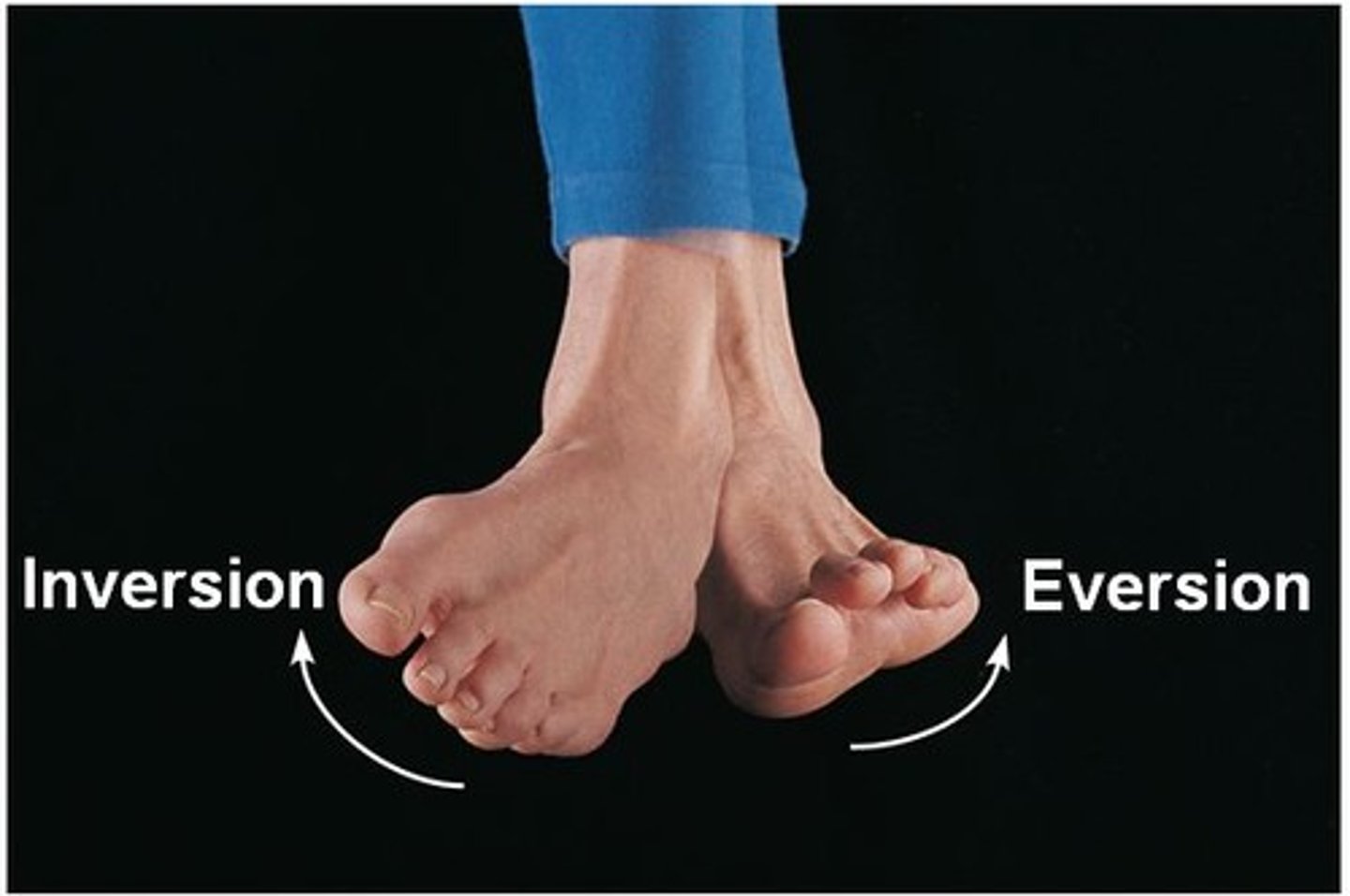
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot laterally.
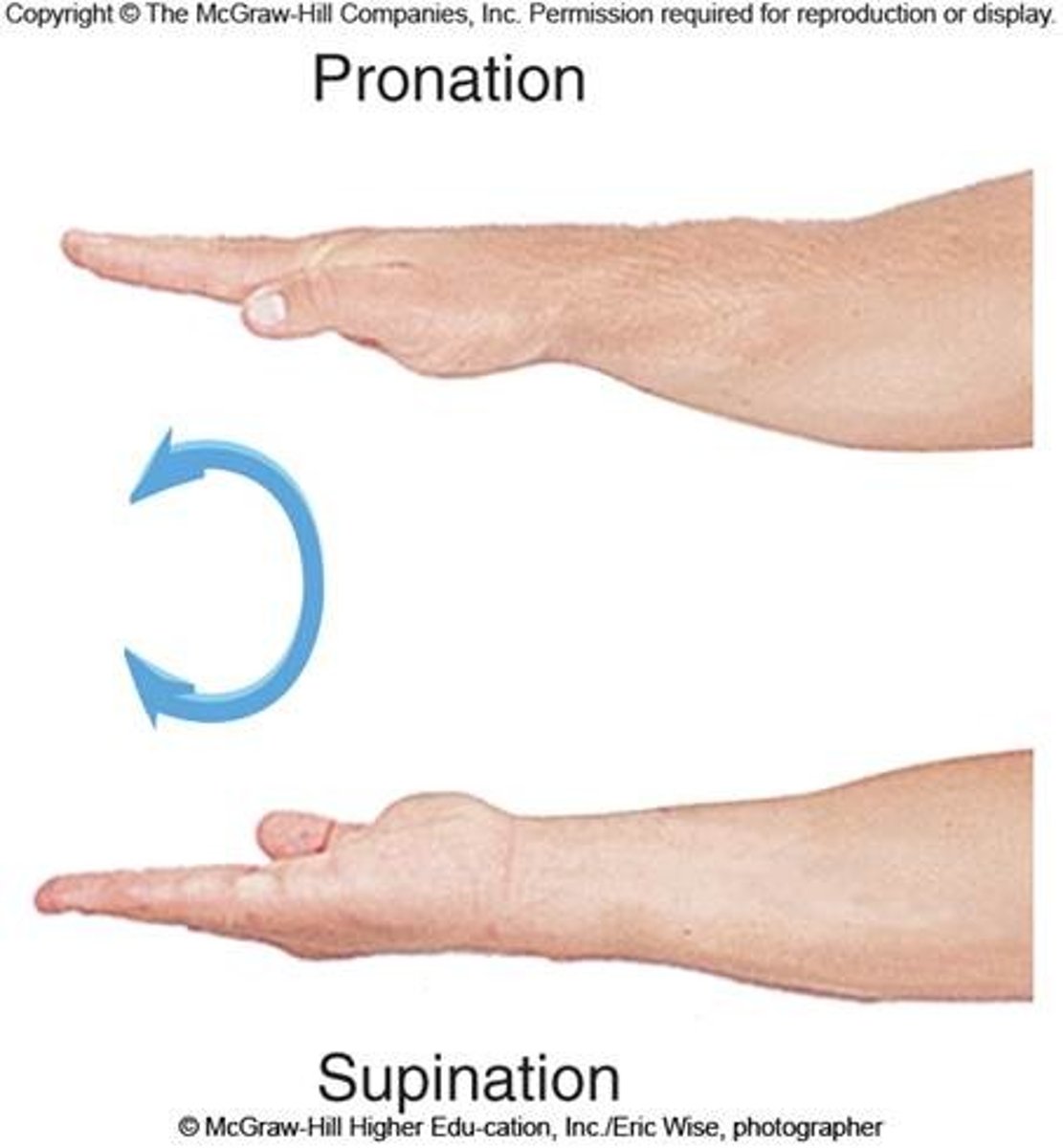
Supination
Forearm rotates laterally; palm faces anteriorly.
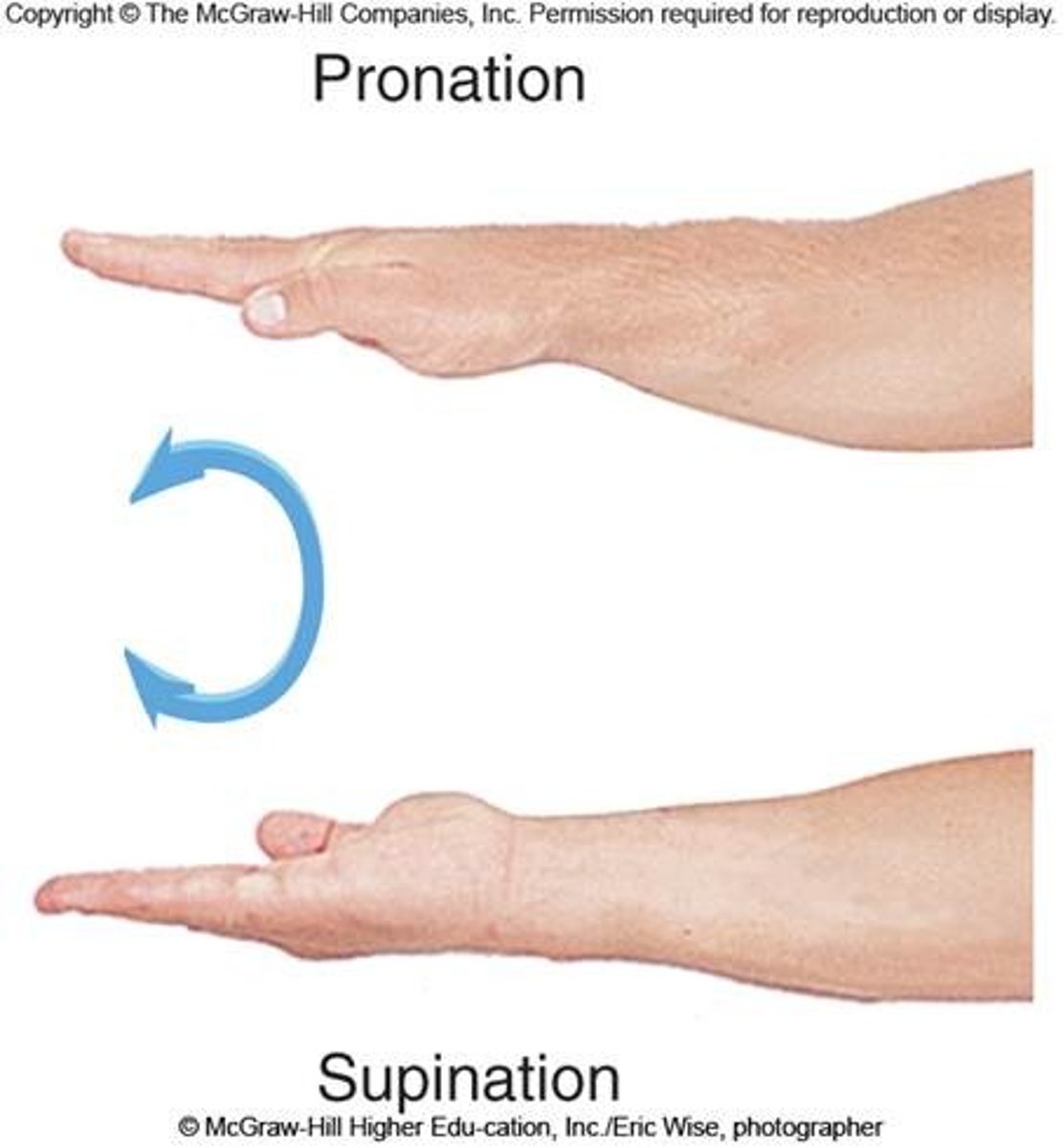
Pronation
Forearm rotates medially; palm faces posteriorly.
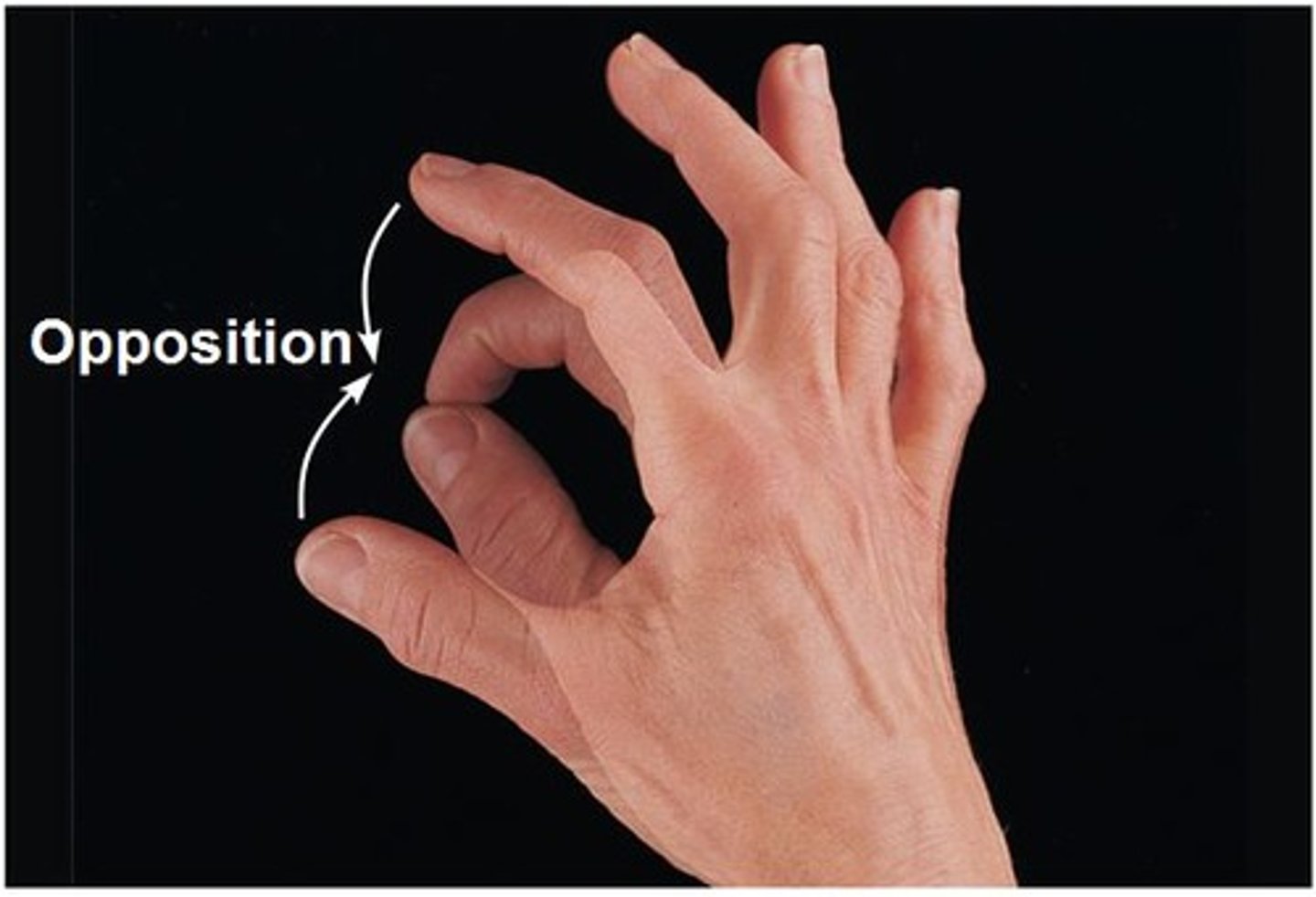
Opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the other fingers on the same hand.
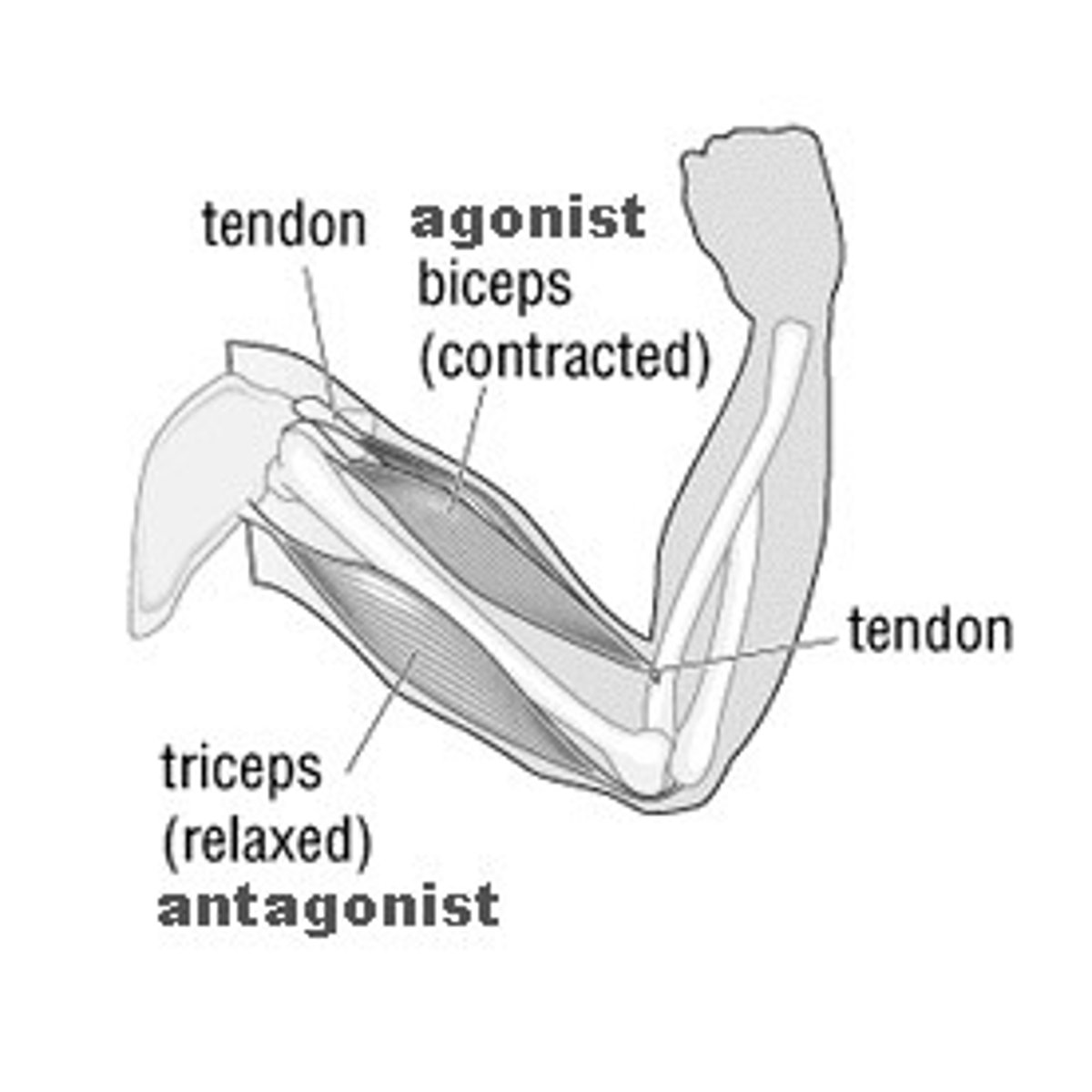
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles
Muscles can only pull; they do not push.
Prime Mover: Muscle primarily responsible for a movement.
Antagonist: Opposes or reverses the action of a prime mover.
Synergist: Assists a prime mover; reduces undesired movements.
Fixator: Stabilizes the origin of a prime mover.
Naming Skeletal Muscles
Muscles are named based on several criteria:Direction of fibers: Example: rectus (straight).Size: Example: maximus (largest).Location: Example: temporalis (temporal bone).Number of origins: Example: triceps (three heads).Shape: Example: deltoid (triangular).Action: Example: flexor (flexes a bone).
Muscle Terminology
Prefixes "myo-" and "mys-" refer to "muscle."
Prefix "sarco-" refers to "flesh."
Endomysium
A thin connective tissue wrapping that encloses a single muscle fiber, providing support and insulation.
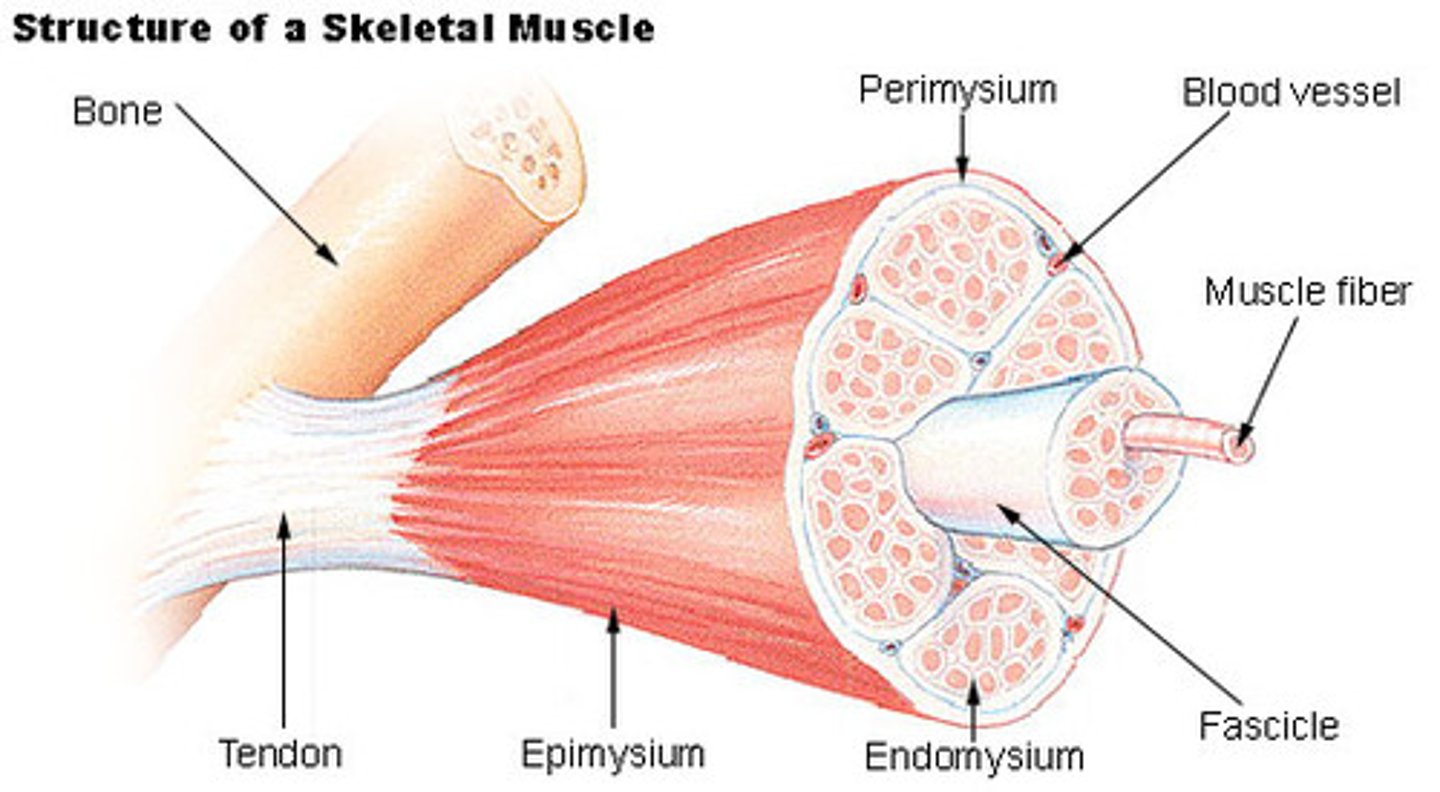
Perimysium
Connective tissue that wraps around a fascicle (bundle) of muscle fibers, containing blood vessels and nerves that supply the fibers.
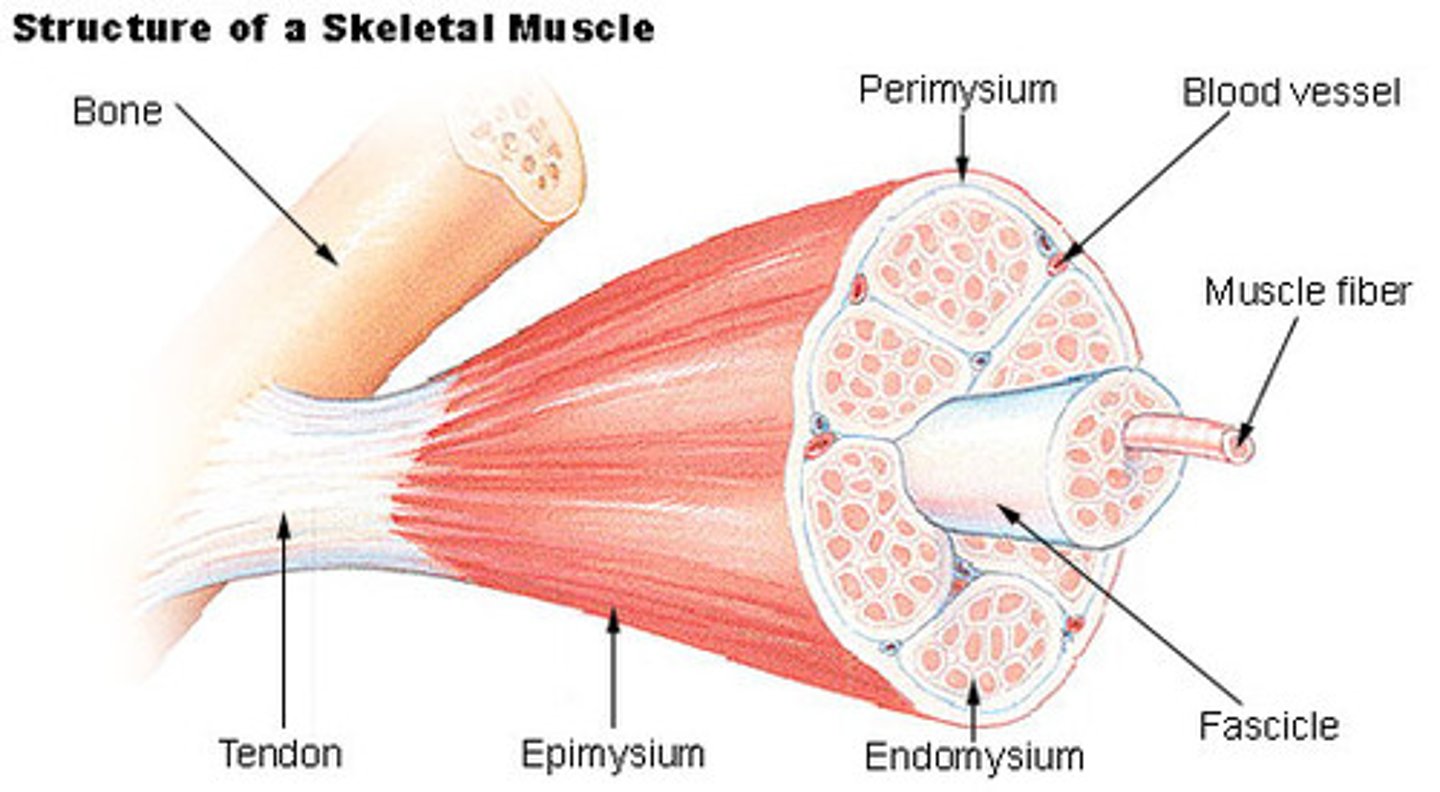
Epimysium:
The outer layer that covers the entire skeletal muscle, helping to protect and shape it.
Fascia:
A connective tissue layer that surrounds the muscle outside of the epimysium, which may connect with surrounding tissues or muscles.
Direct Phosphorylation of ADP by Creatine Phosphate
The fastest method, providing immediate energy.
Aerobic Respiration
A slower process that requires oxygen, generating more ATP for extended activity, primarily occurring in mitochondria
Anaerobic Glycolysis
Breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing ATP quickly but resulting in lactic acid and lower energy yield