MCB 150 Exam 1
1/111
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
nucleoid
not surrounded by a membrane, usually one chromosome
eukaryotic cell
animal cell
The 3 domains of life are?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Cell theory
Cells are the fundamental units of life, all organisms are composed of one or more cells, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
some cells(plants and most prokaryotes have a relatively________ providing shape and protection
rigid cell wall
every cell is surrounded by plasma membrane
that controls the movement of substances in and out. It is selectively permeable. is an interface for cells where information is received from adjacent cells and extracellular signals.
4 major types of biological polymers (macromolecules )
Carbohydrates(polysaccharides) [sugars], lipids [fats], proteins, nucleic acids.
macromolecules (polymers) are made up of monomers
Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Polysaccharides, (membrane) lipids
proteins are composed of
amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
nucleic acids are composed of
nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds.
polysaccharides are composed of
monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds.
(membrane) Lipids are composed of
fatty acids and usually glycerol.
condensation (dehydration synthesis)
monomer, in water out.
hydrolysis
water in, monomer out
Macromolecules (carbohydrates)
large molecules made up of sugar units, serving as energy sources and structural components in cells, or insects such as exoskeletons.
General formula of a carbohydrate
(H2O)n, where n is the number of carbon atoms. a 1:2:1 ratio.
Monosaccharides are typically found with
3, 5, or 6 carbons
Archea
single-celled organisms that are distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes, often found in extreme environments. closer realted to us than prokaryotes
Every cell is surrounded by a
plasma membrane that regulates entry and exit of substances. cell membrane.
plasma membrane
Allows cells to maintain a constant internal environment
- Acts as a selectively permeable barrier
- Is an interface for cells where information is received from adjacent
cells and extracellular signals
- Has molecules that are responsible for binding and adhering to
adjacent cells
Some monosaccharides have identical formulas but
different structures
isomers
Two monosaccharides can be brought together to form a very
simple polysaccharide called a
disaccharide. It consists of two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond.
The chemical formula for a disaccharide
of hexose sugars is
C12H22O11
One monomer is a
monosaccharide
Two monomers are a
disaccharide
Several monomers are called an
oligosaccharide (oligo=several)
Hundreds or thousands of monomers are a
polysaccharide (poly=many)
Carbohydrates can be modified
by adding functional groups or altering their structure. Linkage of oligosaccharides to other macromolecules
- When covalently linked to membrane proteins or lipids, carbohydrates act as identification and recognition molecules (chemical markers), as in blood typing.
Polysaccharides serve as chemical sources of energy
Polysaccharides serve as chemical sources of energy
or structural compounds
Cellulose
Starches
Glycogen
Cellulose
The most abundant carbon-containing (i.e., organic) compound on
Earth
Cellulose
found in plant cell walls
Cellulose
Linear, unbranched polymer of glucose
- monomers covalently linked by β-1,4 glycosidic linkages
- linear polymers held together by hydrogen bonding with
neighboring strands
Starches
Found chiefly in seeds, fruits, tubers, roots and stems of plants;
energy storage
Starches
Helical, unbranched or loosely branched polymers of glucose
- monomers within chains covalently linked by α-1,4 glycosidic
linkages
- chains branch by connecting with other chains by α-1,6 glycosidic
linkages
Glycogen
Found in muscle and liver cells of animals; energy storage
glycogen
Helical, highly branched polymers of glucose
- monomers within chains covalently linked by α-1,4
glycosidic linkages
- chains branch by connecting with other chains by α-1,6
glycosidic linkages
Lipids
Defined by a physical property, not a chemical structure
• Vary widely in structure
Energy Storage
Triglycerides
Biomembrane Composition
Phospholipids & Glycolipids form the structural basis of cell membranes, providing a barrier and enabling compartmentalization.
Chemical Signaling
Steroids
The monomers of (biological membrane) lipids
are fatty acids and glycerol, which combine to form various lipid structures essential for membrane integrity.
3 Fatty Acids + Glycerol =
Triglyceride
2 Fatty Acids + Glycerol + Phosphate =
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are (hydrophobic and hydrophilic)
amphipathic molecules that form biological membranes, with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads.
Phospholipids in water will spontaneously form
micelles or bilayers that create a barrier between the inside and outside of cells.
Bilayers have exposed edges, and will fold into
vesicles to minimize exposure to water. (liposomes)
Some membrane lipids are
glycolipids or cholesterol, which contribute to membrane structure and function.
The fourth type of lipids are
Steroids
Steroids
Can be used as circulating hormones like estrogen and
testosterone, or as membrane components
Animal cells have ________ in their biomembranes
cholesterol for fluidity and stability.
Biomembranes are (shape)
Asymmetrical
Membrane-associated proteins
are proteins that are attached to or associated with cell membranes, playing key roles in signaling, transport, and maintaining cell structure.
Lipid-linked proteins
Are attached to the membrane via lipid tails, which anchor them to the lipid bilayer.
Peripheral proteins
are loosely attached to the membrane surface and can be removed without disrupting the membrane structure.
Transmembrane proteins
Span the entire membrane, with regions exposed to the cell's interior and exterior. They facilitate the transport of substances across the membrane.
proteins serve a variety of functions
Transport, Enzymatic activity, Signal transduction, Cell-cell recognition, Intercellular joining, Attachment to, the cytoskeleton
and extracellular, matrix (ECM) for support.
Biomembranes are
selectively permeable barriers that separate cellular compartments and regulate the movement of substances.
does it go through?
small polar molecules can pass through easily, while larger or charged molecules require specific transport mechanisms.
Biological membranes are (shape)
fluid
If biomembranes are fluid, in what ways can the lipids
move around within the membrane?
They can move laterally, rotate, or flex their tails.
Membrane fluidity is temperature-dependents
and can be affected by the presence of unsaturated fatty acids and cholesterol.
_________ fats take up less space and are closer packed together
Saturated
fluidity and stability in phospholipid membranes have a _____ relationship
inverse
Nucleic Acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic
Acid (RNA) are the two main types of nucleic acids, essential for storing and transmitting genetic information.
The monomers of Nucleic Acids are
nucleotides, which consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
Numbering, labeling, and naming conventions:
Base + Sugar =
Nucleoside
Nucleoside + 1 Phosphate
nucleoside monophosphate
Nucleoside + 2 Phosphates
nucleoside diphosphate
Nucleoside + 3 Phosphates
nucleoside triphosphate
Pyrimidines
a class of nucleobases that includes cytosine, thymine, and uracil, characterized by a single six-membered ring structure.
Purines
a class of nucleobases that includes adenine and guanine, characterized by a two-ring structure.
The nucleotides (abbr. nts) of DNA and RNA differ in two
important ways:
DNA contains deoxyribose, while RNA contains ribose, DNA uses thymine (T) as one of its four nitrogenous bases, whereas RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine
Biomembranes have associated proteins,
Membrane-associated, Transmembrane proteins, Peripheral proteins, Lipid-linked proteins
In ________ inhibition, the inhibitor molecule binds
to the enzyme in a place other than the active site
noncompetitive
In _______ inhibition, the inhibitor molecule physically
resembles the natural substrate, and occupies active site
competitive
Irreversible Inhibitors
molecules that permanently bind to an enzyme, preventing its activity.
_______ inhibition is a demonstration of the
important point that enzymes must ultimately be
unchanged if they are to be used over and over
Irreversible
Most tend to be near body temperature and Ph?
(37 °C) and neutralpH (7.0)
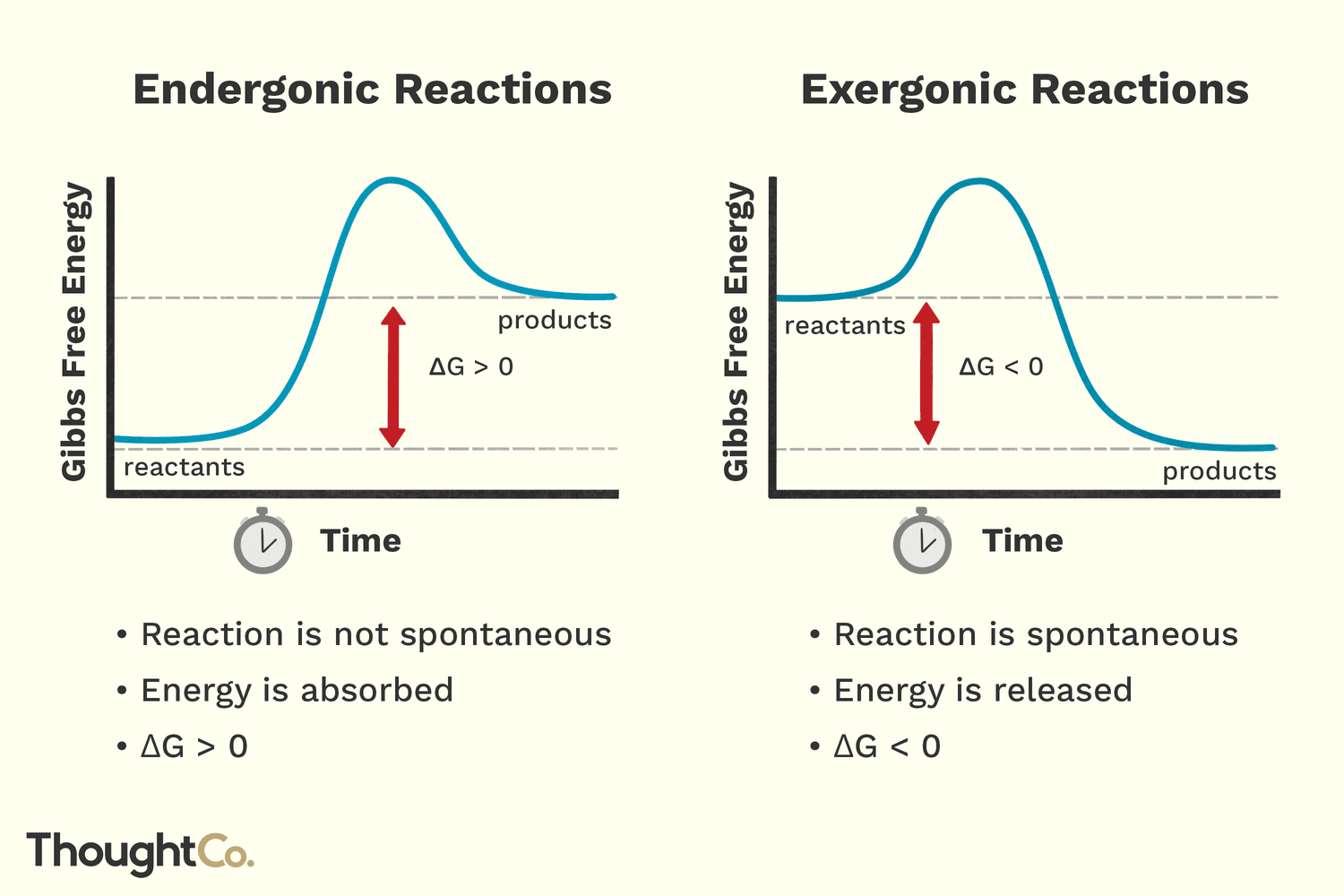
positive Gibbs free energy
endergonic
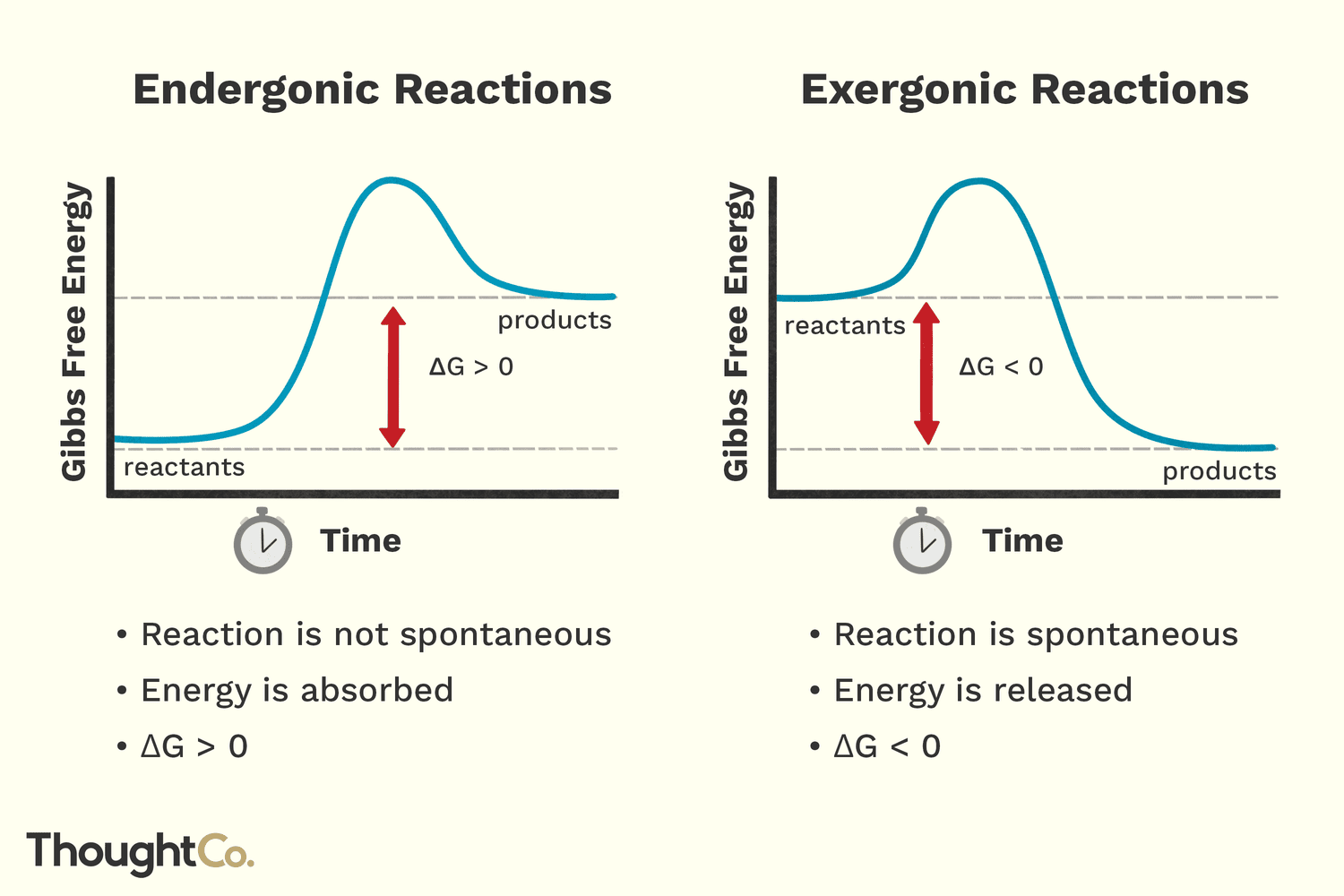
negative Gibbs free energy
exergonic
Enzymes will most likely cause some conformational
change in the substrate molecule(s), but they themselves
usually change shape upon binding substrate
Called induced fit and return to normal afterwardsafter the reaction is complete.
Enzymes bind substrates with extremely high specificity
into their
active sites, facilitating biochemical reactions.
___ = activation energy, which converts substrates into unstable transition states
Ea
2 different meanings for the word spontaneous
Typical meaning: happens automatically.
Biology meaning: a reaction that releases energy, much of
which is lost as heat
Reactions that require energy are called
biosynthetic or anabolic
Reactions that release energy are called
catabolic or also referred to as spontaneous reactions.
Many proteins are _____: biological catalysts; they
facilitate biological reactions
enzymes
If denaturing agent is removed
some proteins will resume properly folded 3D structure
instructions” are in ______ structure
the primary 1*
Removal or inactivation of stabilizing forces unfolds
(_____) the protein to 1° structure, but no peptide
bonds are broken
denaturing
if a protein is denatured
All 2° and 3° structure is lost
Disulfide linkages →
Covalent
Relative stabilities of biomolecular forces:
Disulfide linkages → Covalent
• Ionic bonds → Easily made and broken
• Hydrogen bonds
• Hydrophobic clusters
• Van der Waals forces
Quaternary Structure (4°)
Found in proteins with multiple polypeptide chains (subunits)
Subunits can be same or different(for quaternary structure 4*)
- 2 identical subunits = homodimer
- 2 different subunits = heterodimer
Tertiary Structure (3°):
Unique 3D folded structure
• Final conformation of some proteins
• Due to interactions between R-groups with each other and
with backbone
tertiary structure is Stabilized by:
- H-bonds between polar (or charged) side chains
- H-bonds between hydrophilic side chains and backbone
- Ionic bonds between acidic and basic amino acids
- Hydrophobic clustering of non-polar side chains
- Van der Waals forces
- Disulfide linkages
Prions
Infectious agents composed of misfolded proteins that can induce abnormal folding of normal proteins.
________ the only part that differs—is what
makes one amino acid different from another
The R group
________ is a covalent chemical bond that links two amino acids together, forming the backbone of proteins
peptide bond