module 12: cell maturation, activation, & differentiation
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
status: unfinished
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
T cell maturation involves
expression of various membrane markers. T-cell receptor rearrangement. positive & negative selection. maturation with CD4 or CD8 co-receptors
thymocytes or thymus-settling progenitors (TSPs)
precursor cells from bone marrow/fetal liver that are directed to thymus by chemokine receptors. give rise to B-cells, NK cells, dendritic cells. takes 1-3 weeks to mature into T cells
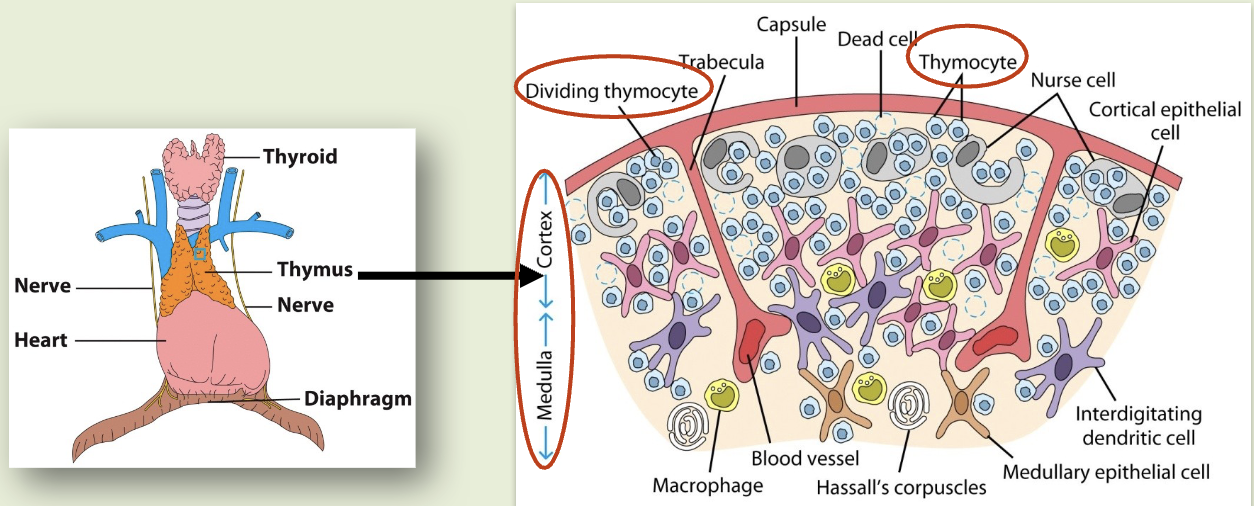
pathway of thymocytes
arrive in corticomedullary region & their Notch receptors bind to Notch ligands in thymic epithelium. leads to T cell commitment & migration to thymic cortex. proliferate in thymic cortex & express T cell receptors. cells that survive stringent selection mature, migrate into thymic medulla, & exit thymus as mature T cells.
double negative cells (DN)
T cells that lack detectable CD4 & CD8. divided into 4 subsets (1-4) based on presence or absence of cell surface molecules: C-Kit, CD44, CD25
C-kit (CD117)
a pro T (DN) cell. receptor for stem cell growth factor
CD44
a pro T (DN) cell. adhesion molecule. homing
CD25
a pro T (DN) cell. alpha chain for IL-2 receptor
DN1 stage
thymocytes are CD25-, but C-kit++ & CD44+. once they receive notch signaling, they start expressing CD25 and move into the next stage of being a thymocyte
DN2 stage
thymocytes start undergoing gamma delta receptor & beta-chain rearrangement. alpha chain locus does not rearrange. at the late stage, cells reduce the expression of C-kit & CD44. decision about gamma delta or alpha-beta lineage of T-cells depends on how correctly rearranged genes encode them. correctly rearranged gamma delta cells mature & exit as double negative cells
DN3 stage
cells are C-kit- or low (+), CD44-, & CD25+. if cells successfully rearrange the beta chain, they become committed to alpha beta lineages, lose CD25 expression, and enter into the next stage
DN4 stage
cells with rearranged beta chains associate with pre-T alpha chains and express pre-T cell receptor phenotype. pre-T cell receptors are associated non-covalently w/ CD3 and are expressed on the surface
pre-T cell receptor function
pre-T cell receptors expressed on late DN3 & DN4 thymocytes gives an intracellular signal that leads to rapid proliferation and allelic exclusion of the beta chain
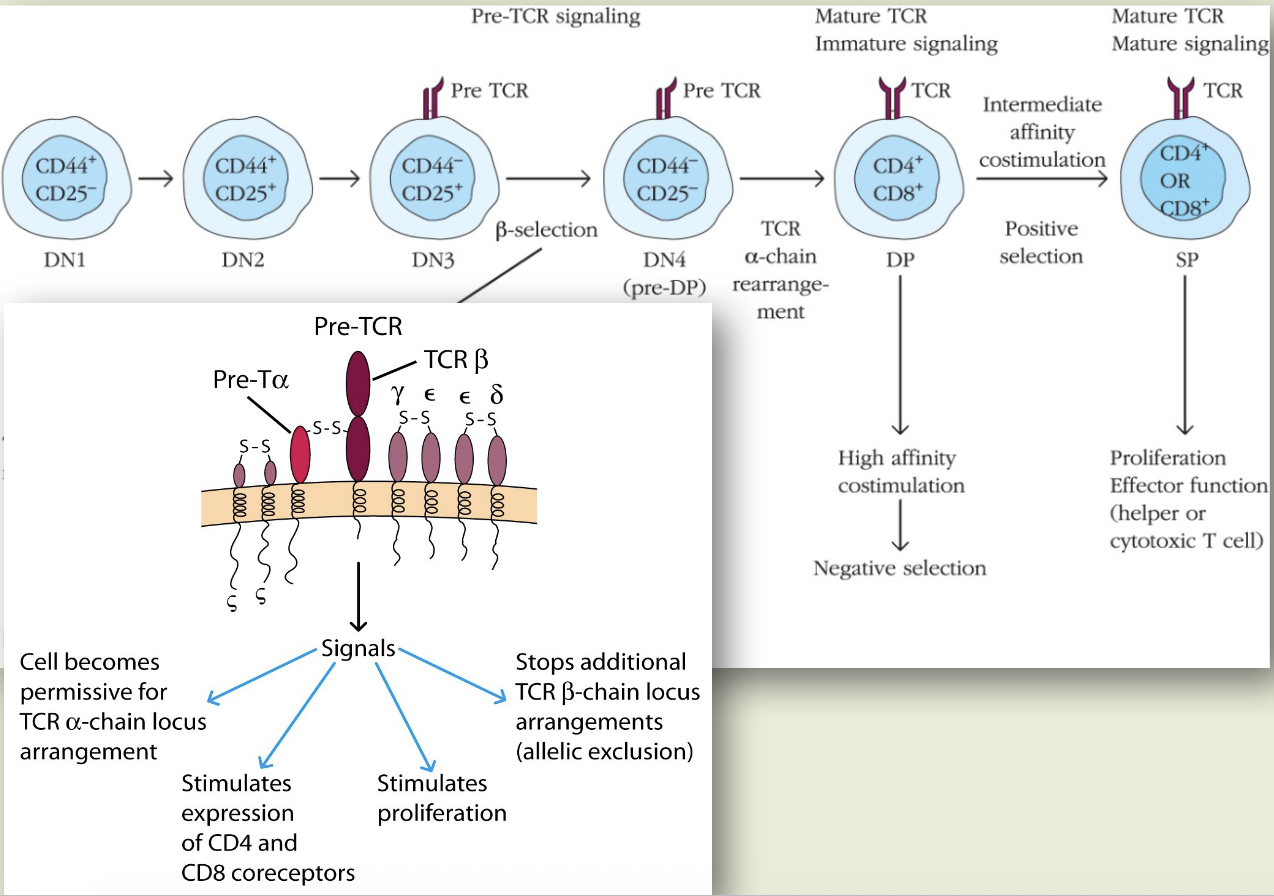
late DN4 stage
cells start expressing pre-TCR, CD4+ & CD8+, and the cell becomes a double-positive (DP) thymocyte. the DP cells now express T cell receptors and are associated with CD3. cells proliferate before TCR-alpha chain rearrangement occurs. results in DP w/ TCR
after beta-chain rearrangement in the DN4 stage, why do the cells proliferate before rearranging the alpha chain?
increases diversity of the T cell repertoire by generating a clone of cells with a beta chain that will associate with different alpha chains
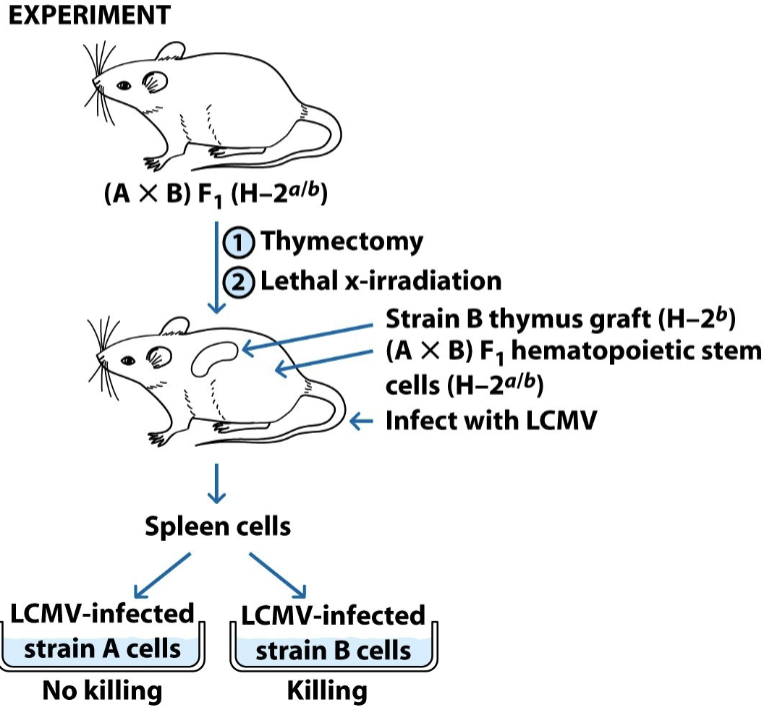
positive selection
immature thymocytes with receptors that bind weakly (low affinity) to self-MHC survive. receptors that don’t bind self-MHC are eliminated. leads to MHC restriction

negative selection
immature thymocytes with high affinity receptors for self-MHC alone or self antigen presented by self MHC are eliminated. leads to self-tolerance (unresponsiveness to self-antigen
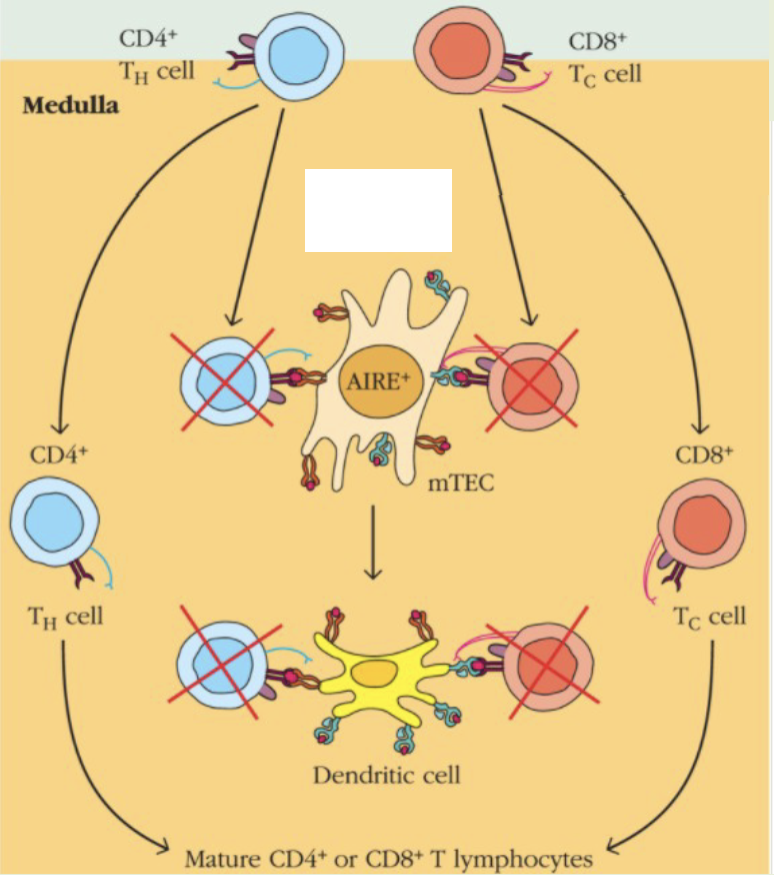
purpose of positive & negative selection
responsible for preserving useful cells and eliminating harmful ones. after selection process, matured T cells recognize foreign antigens presented by self-MHC molecules