Membrane proteins + Intracellular Transport
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Proteins that span a plasma membrane must contain ____ where they cross the membrane
Hydrophobic amino acids
How does a protein distinguish between a membrane-spanning hydrophobic domain and a hydrophobic domain that is folded into a pocket of the protein?
It is coded for in the primary sequence
What does the inside of the ER =
Outside of the cell
What are microtubules?
They are parts of the cytoskeleton that provide a track for transport
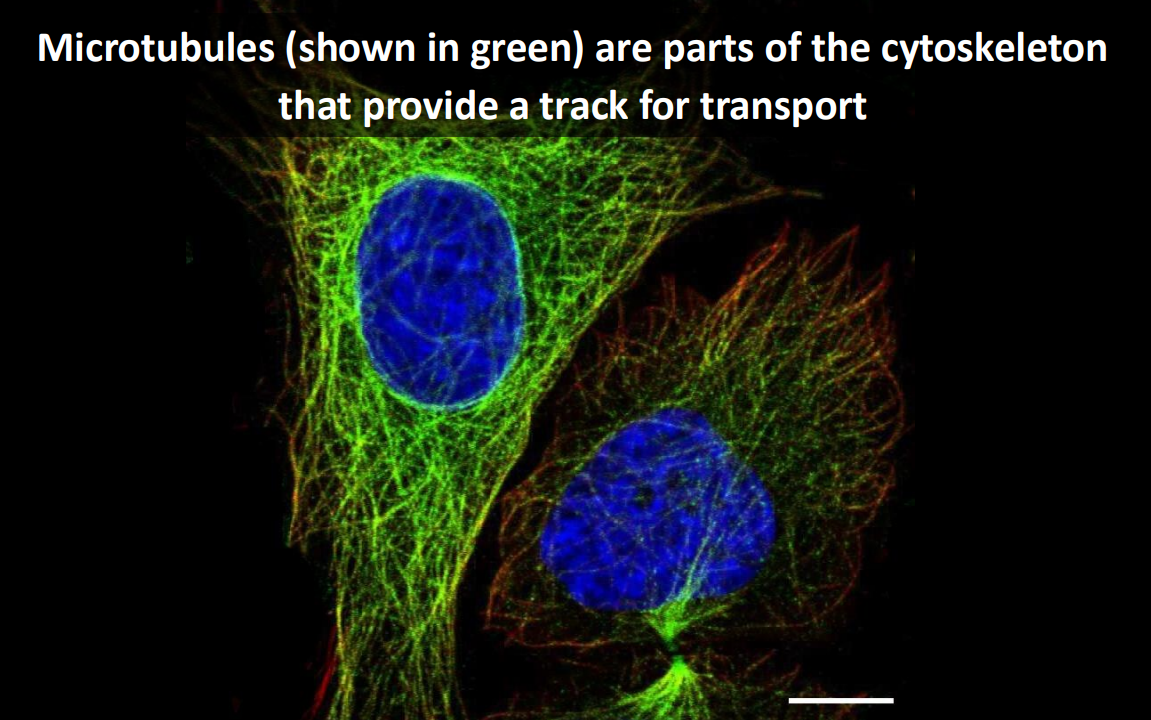
What are the building blocks of microtubules?
alpha and beta tubulin
This gives the dimer polarity, meaning it has distinct ends
What is a tubulin dimer
alpha and beta tubulins stacked together
microtubule subunit
What are protofilaments
A stack of tubulin dimers
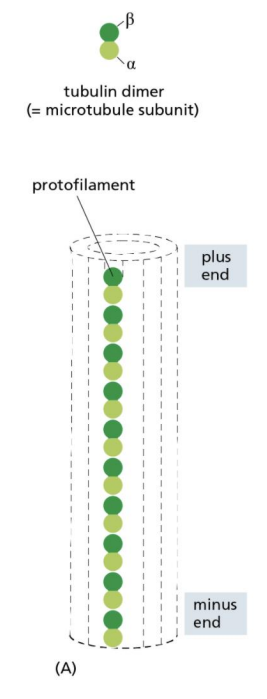
What is the plus end of a microtubule?
Where new dimers are added more rapidly
Not charges
What kind of dimers are added to the plus end of a microtubule?
GTP-bound dimers
What is a B-tubulin
a GTPase: it hydrolyzes GTP to GDP
What are the differences between GDP and GTP?
GDP and GTP have different numbers of phophates and thus different charges
Different charges = different shape
What does hydrolyzing GTP do
Hydrolyzes to GDP
adds to the microtubule strand, leads to GTP Cap
What is dynamic instability?
when b-tubulins hydrolyzes GTP faster than new dimers can be added
will fall apart
What does the polarity of microtubules allow for
directional trafficking that can happen along their length
what “motor” moves towards the minus end of a microtubule
dynein
what “motor” move towards the plus end?
Kinesin
What do motor proteins do?
They bind to vesicles and move them
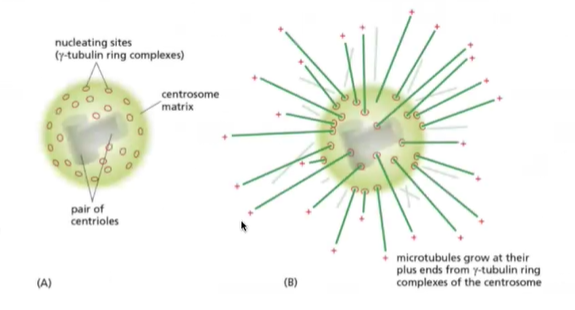
Where do microtubules grow from?
grow from centrioles that contain gamma tubulin rings
Nucleating sites increases a the chance microtubules will grow, also stabilizes it
True or false: Microtubules help organelles stay in place
True