Chapter 5: Integumentary System
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
233 Terms
The integument is?
the skin that covers your body
What is the integument also known as?
cutaneous membrane
The integumentary system is?
the skin and its derivatives
What are the two layers of the integument?
epidermis
dermis
What is the epidermis?
superficial layer
What kind of tissue is the epidermis made up of?
stratified squamous epithelium
What is the dermis?
deeper layer of skin
What kind of tissue is the dermis made up of?
areolar and dense connective tissue
Is the subcutaneous layer part of the skin?
no
Where is the subcutaneous layer located?
under dermis
What is the subcutaneous layer made up of?
areolar and adipose tissue
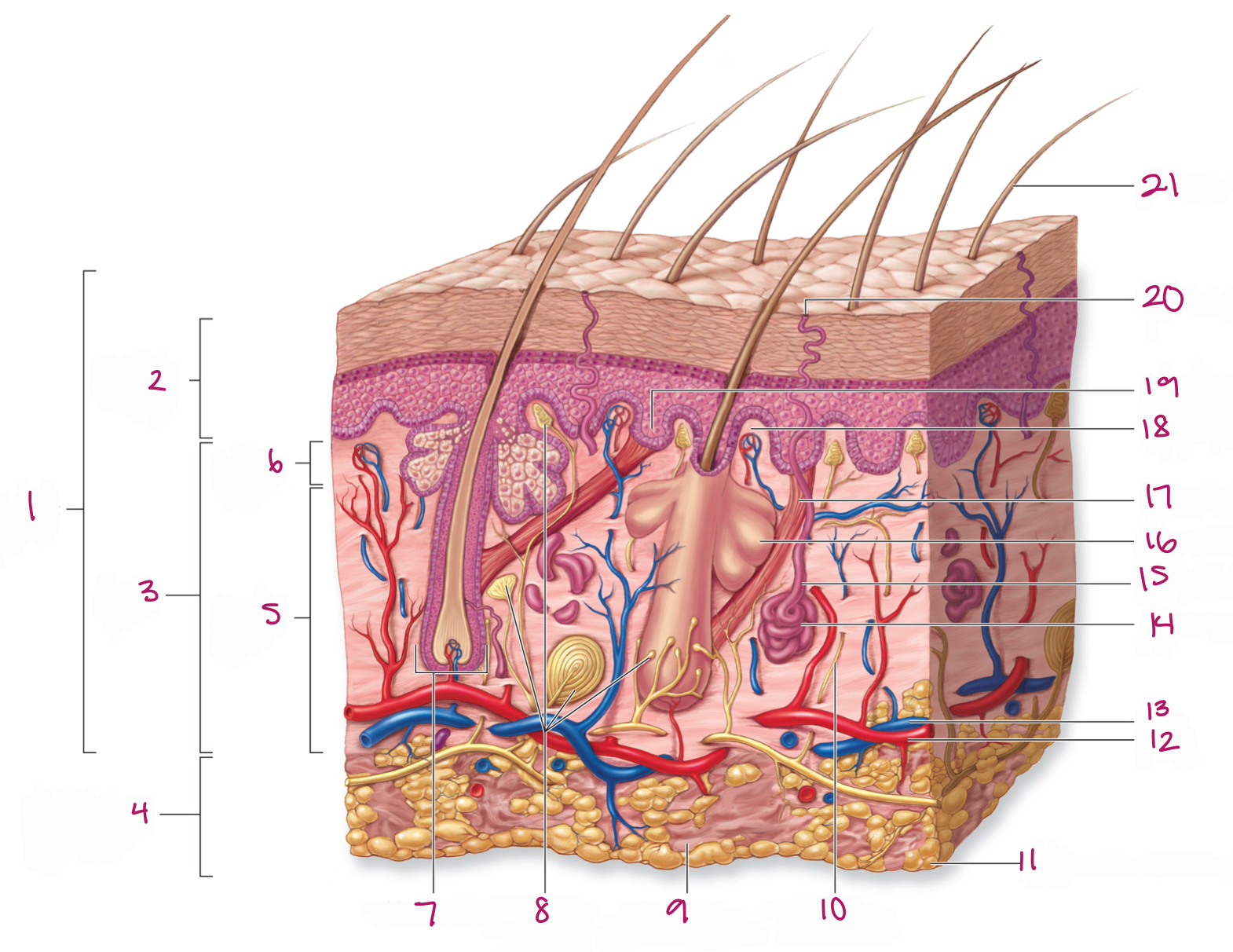
Label figure 1.
integument
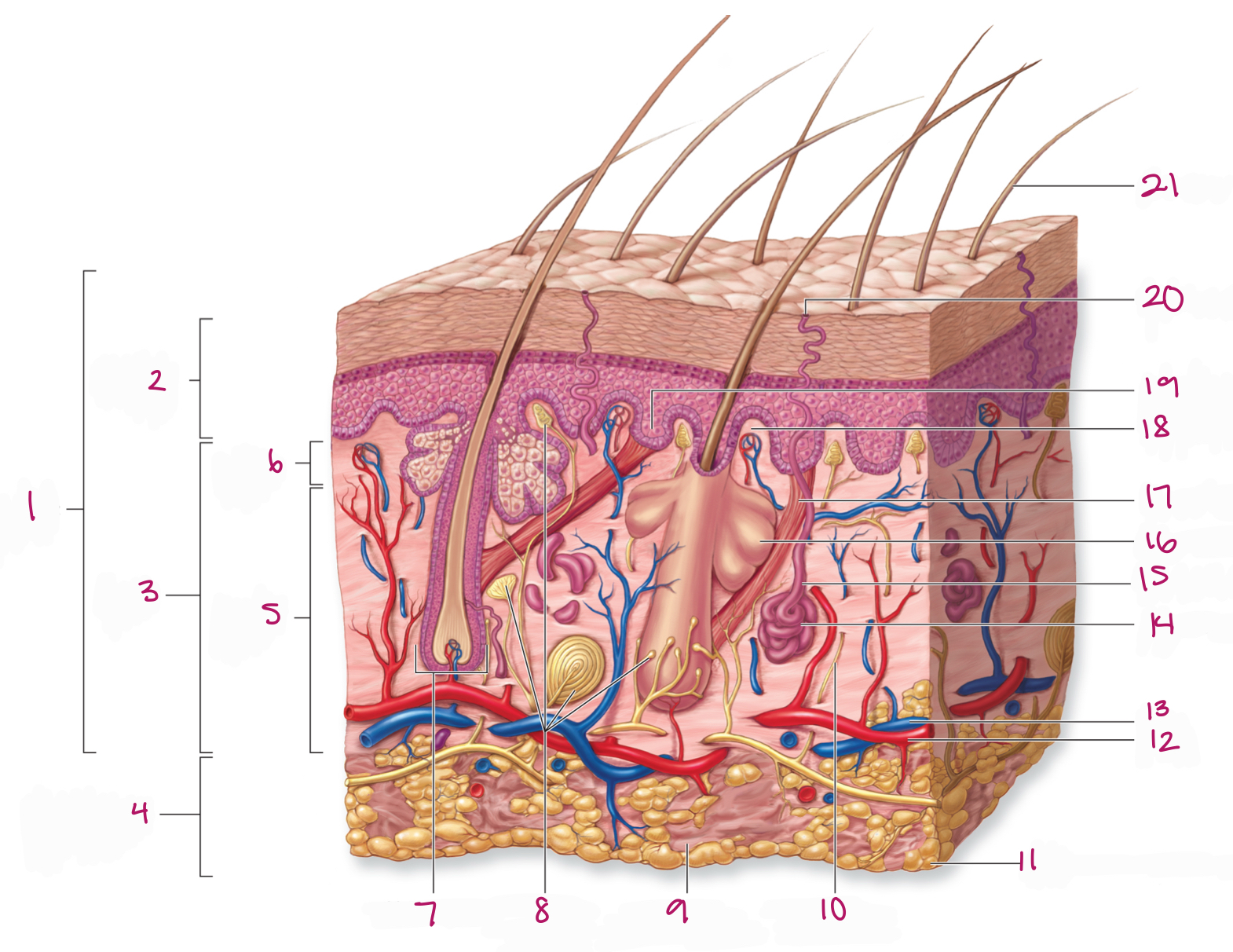
Label figure 2.
epidermis
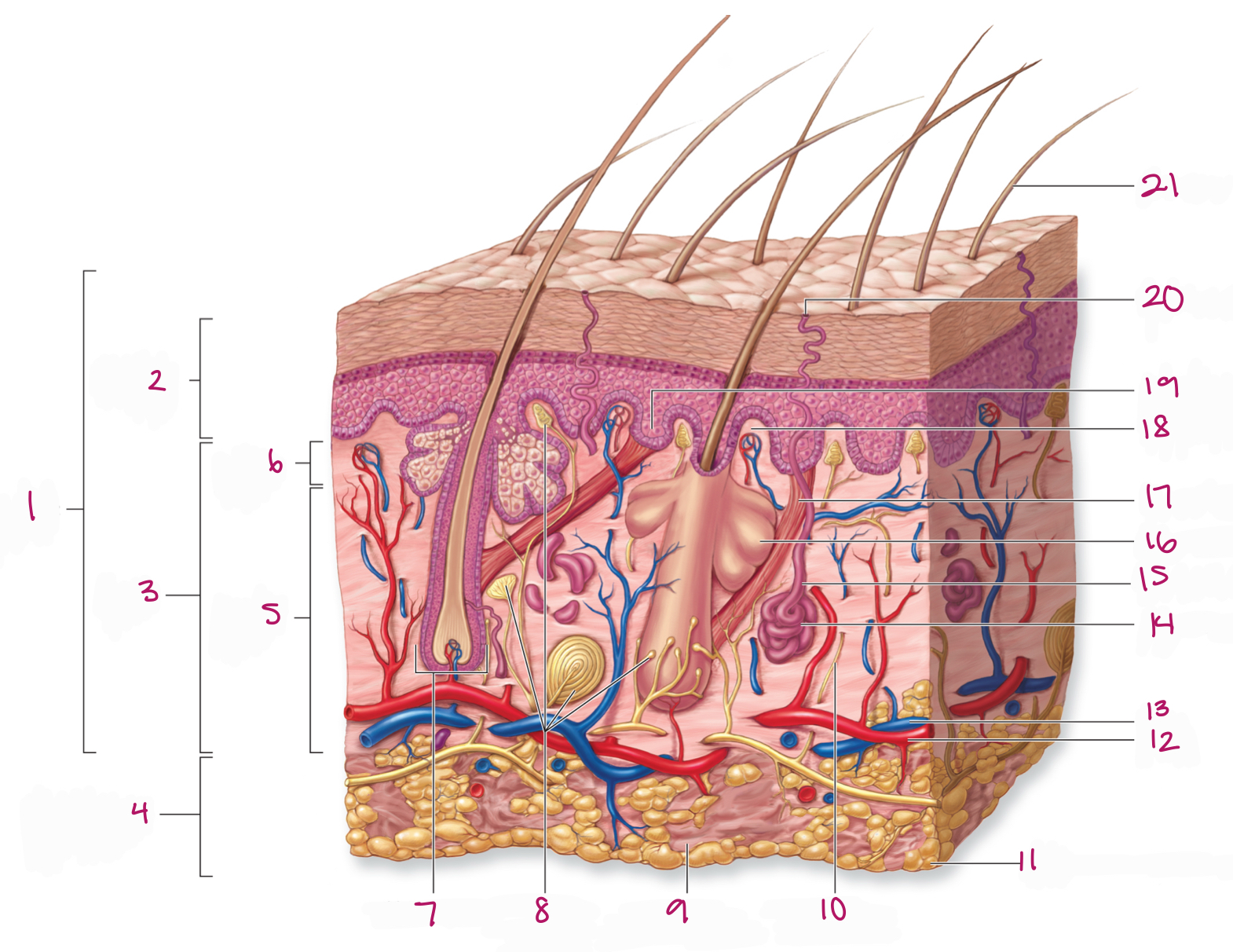
Label figure 3.
dermis
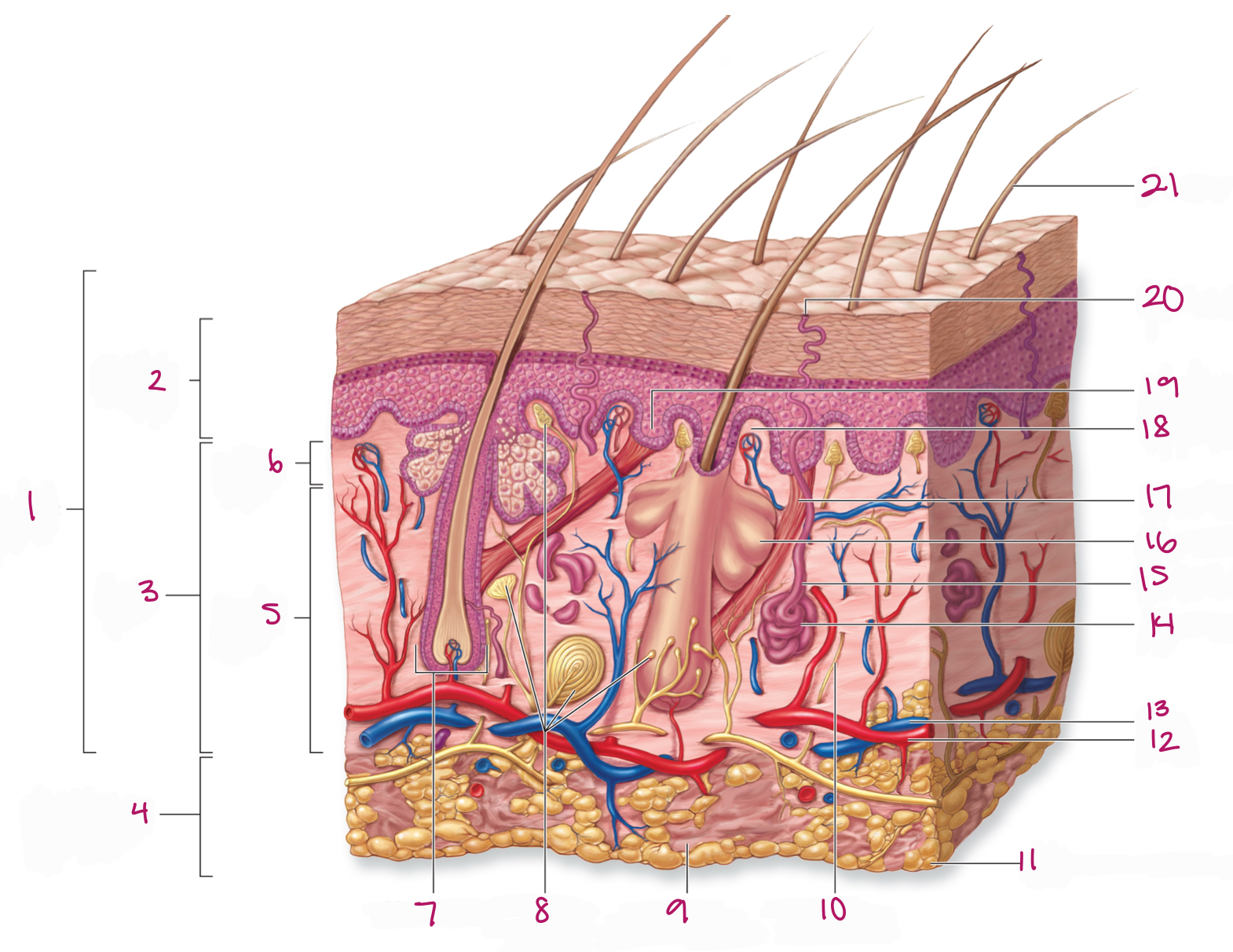
Label figure 4.
subcutaneous layer
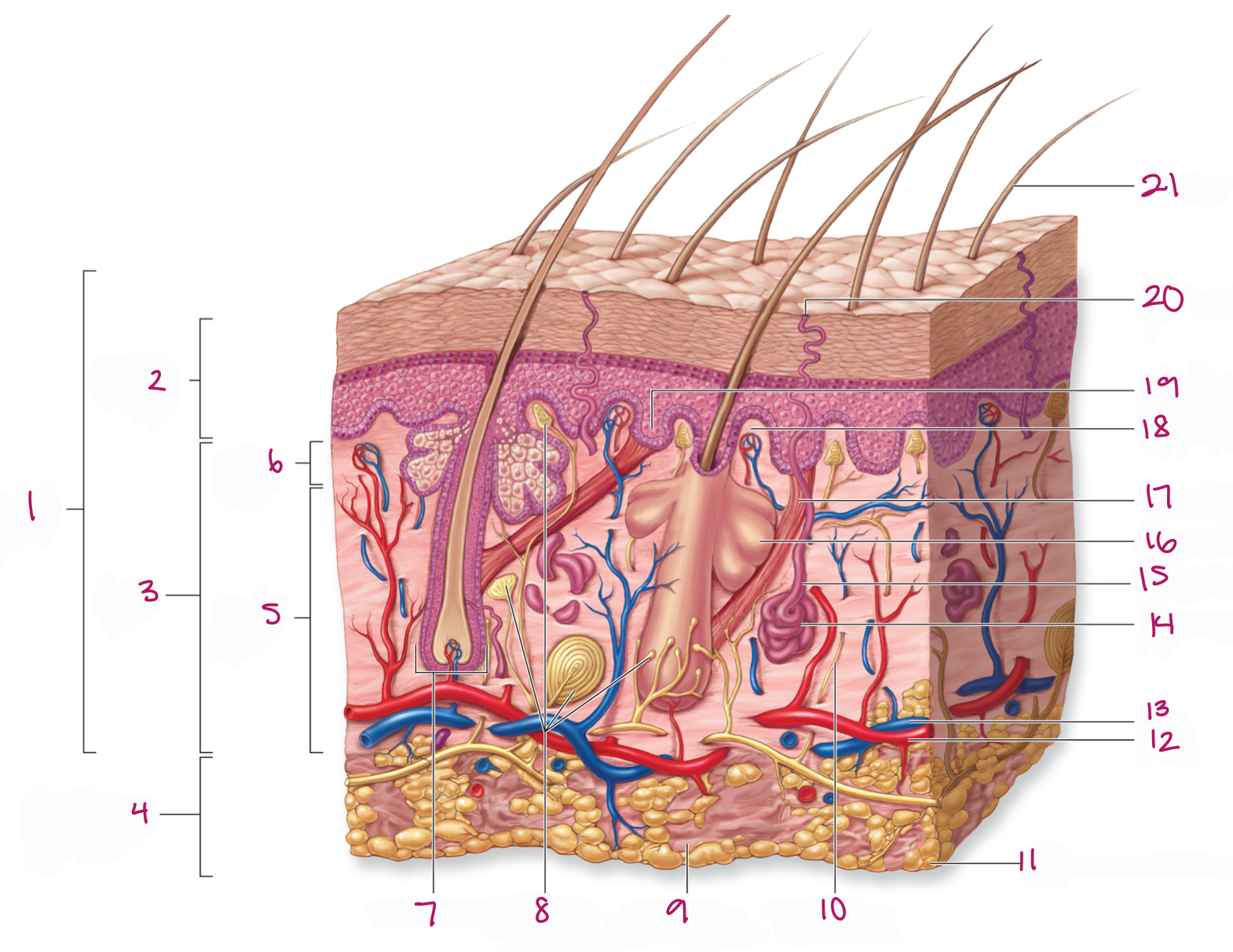
Label figure 5.
reticular layer
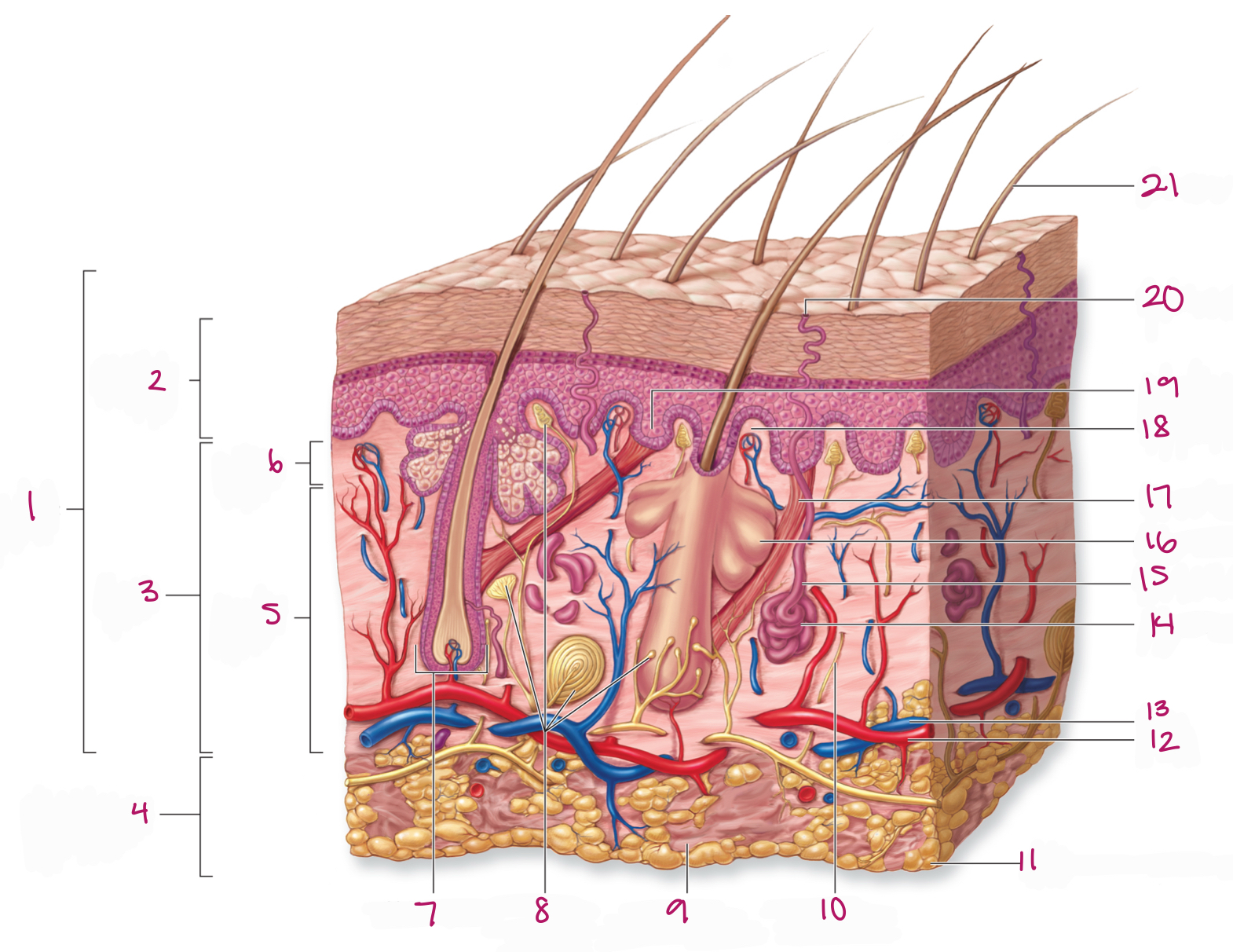
Label figure 6.
papillary layer
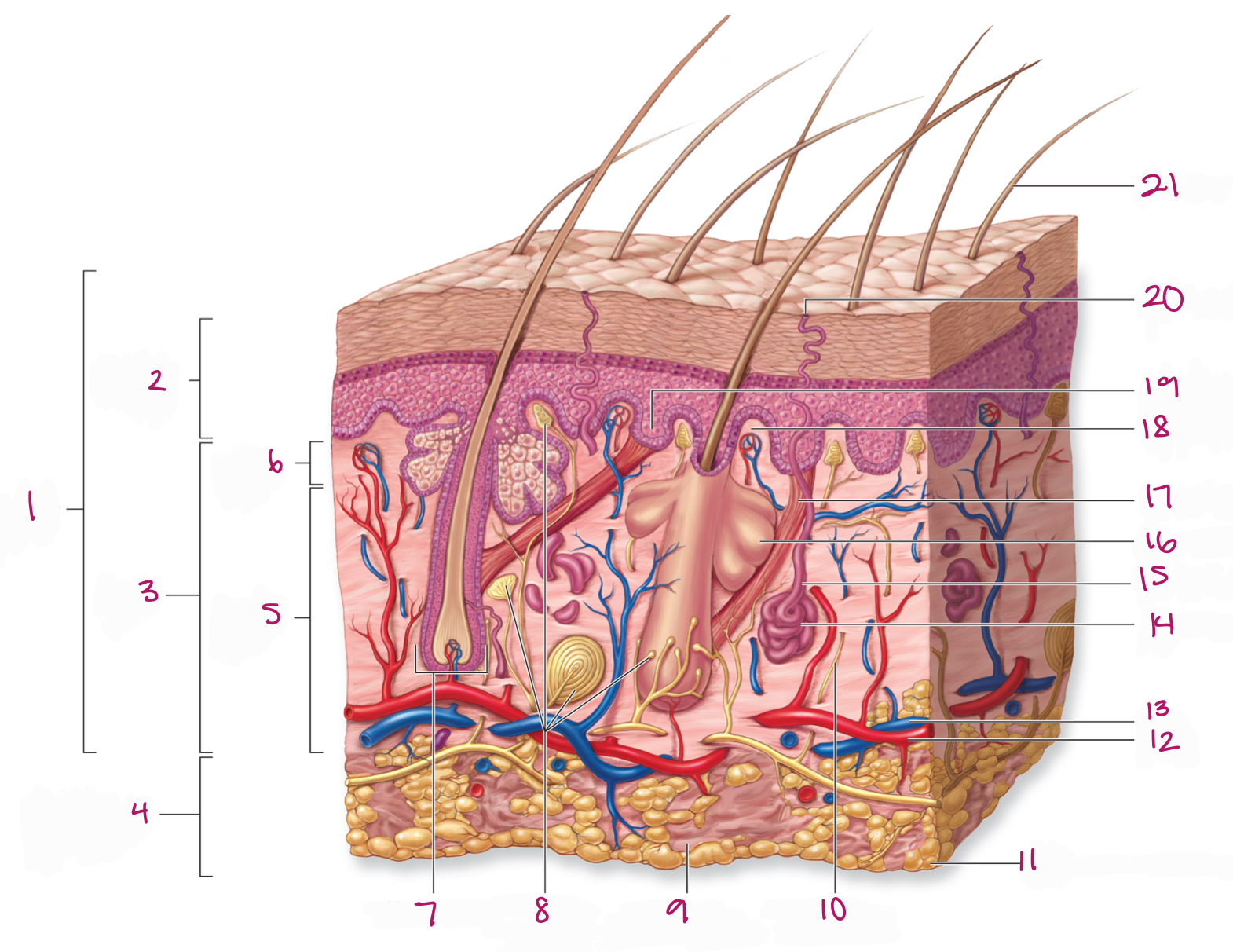
Label figure 7.
hair follicle
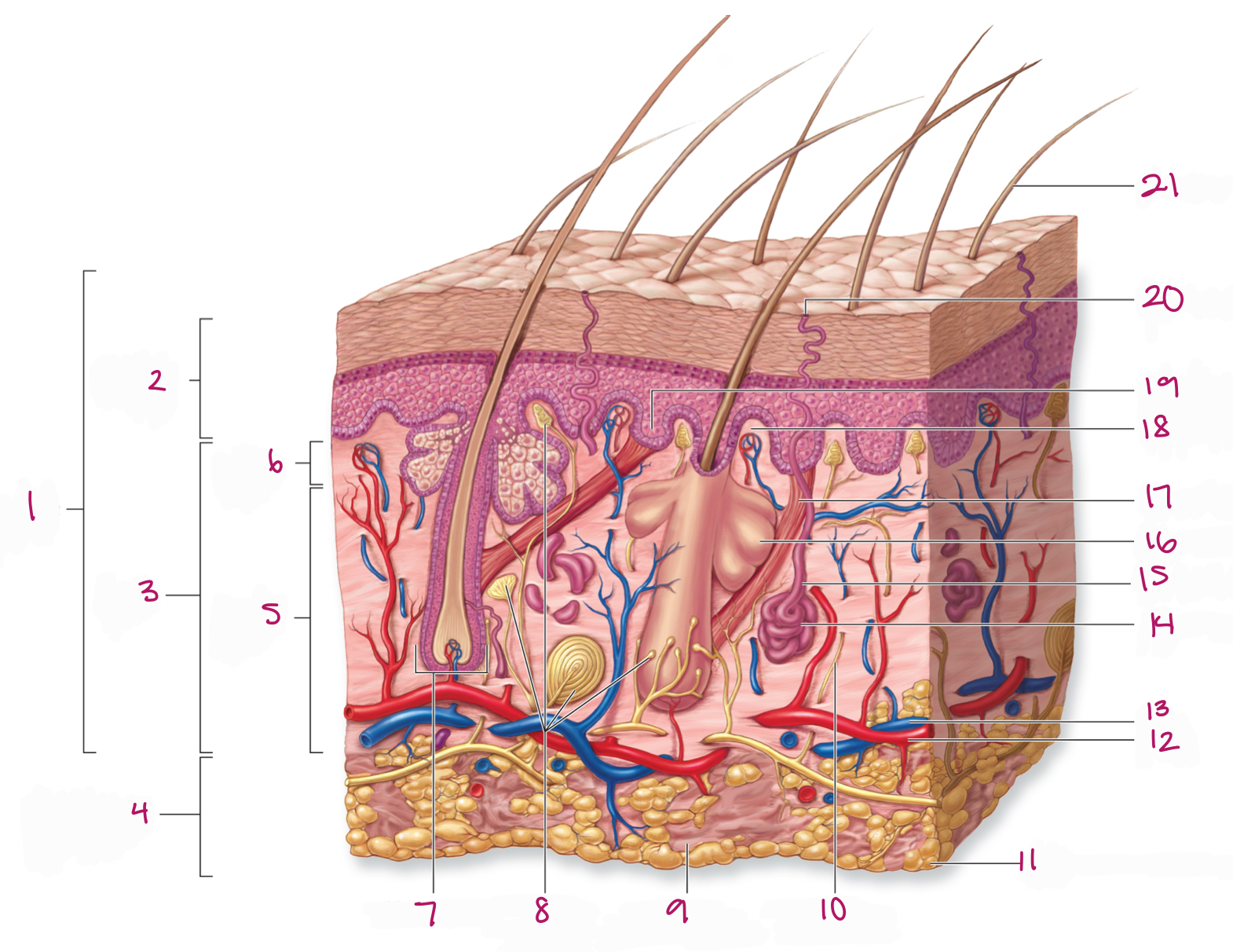
Label figure 8.
tactile (sensory) receptors
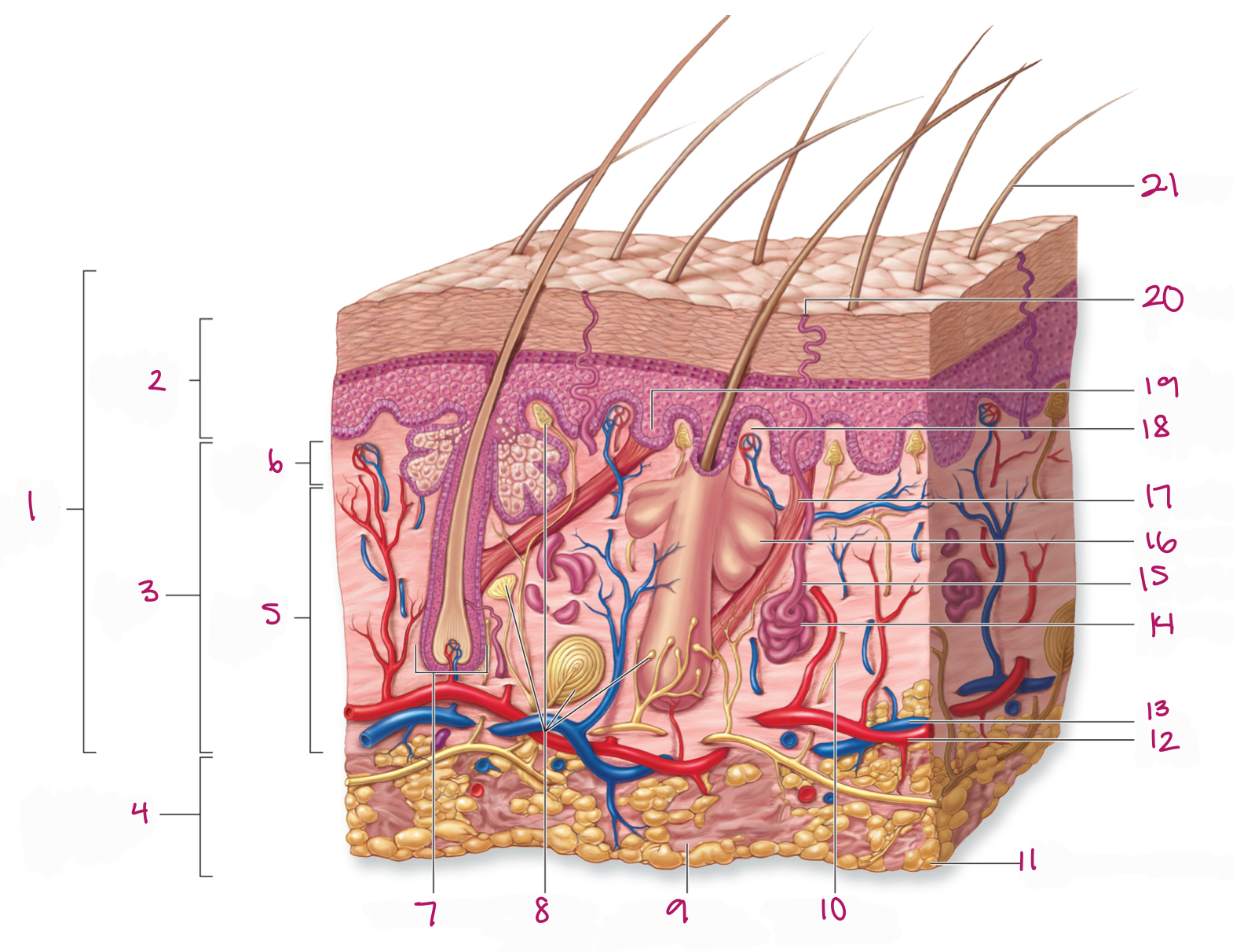
Label figure 9.
areolar connective tissue
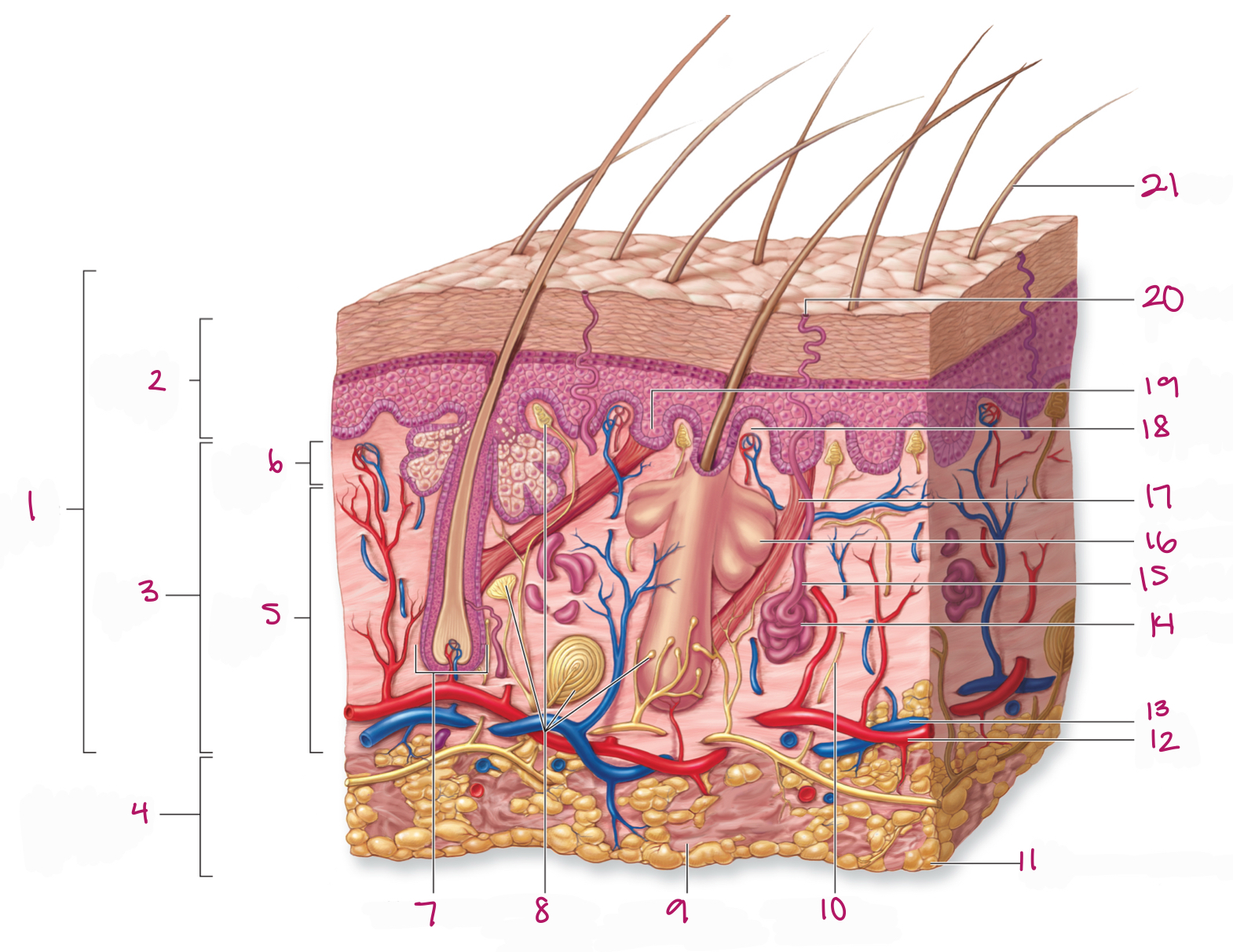
Label figure 10.
sensory nerve fiber
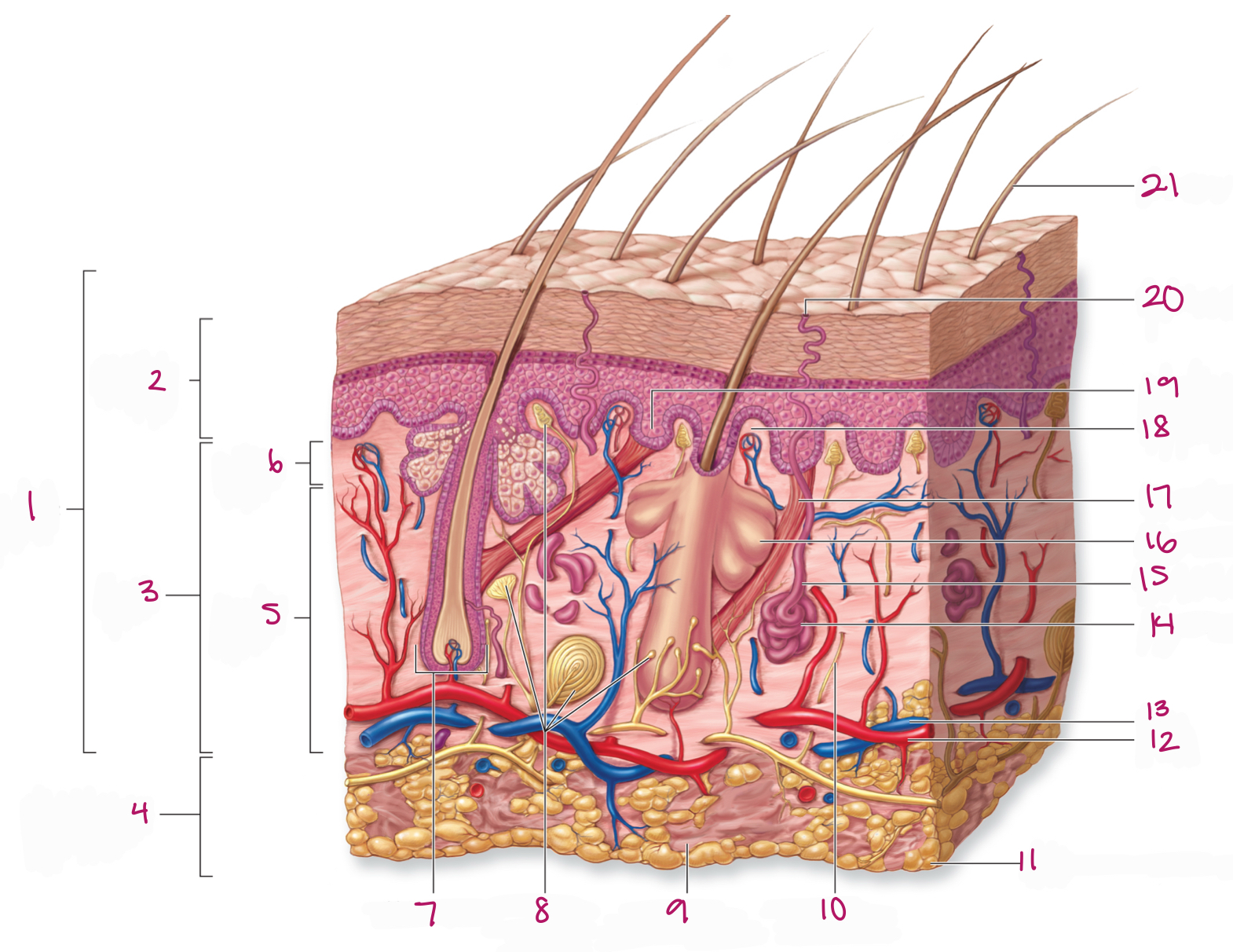
Label figure 11.
adipose connective tissue
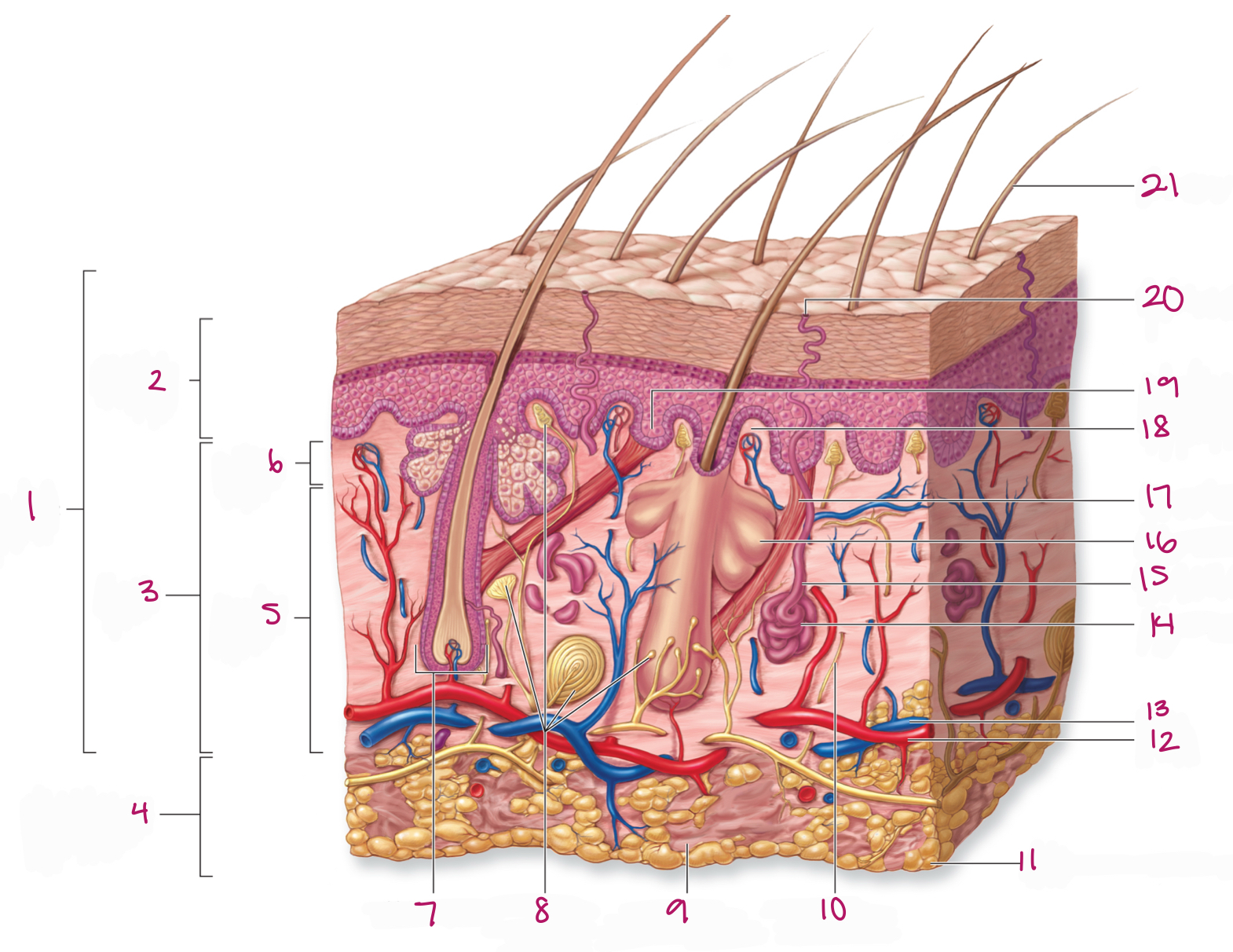
Label figure 12.
artery
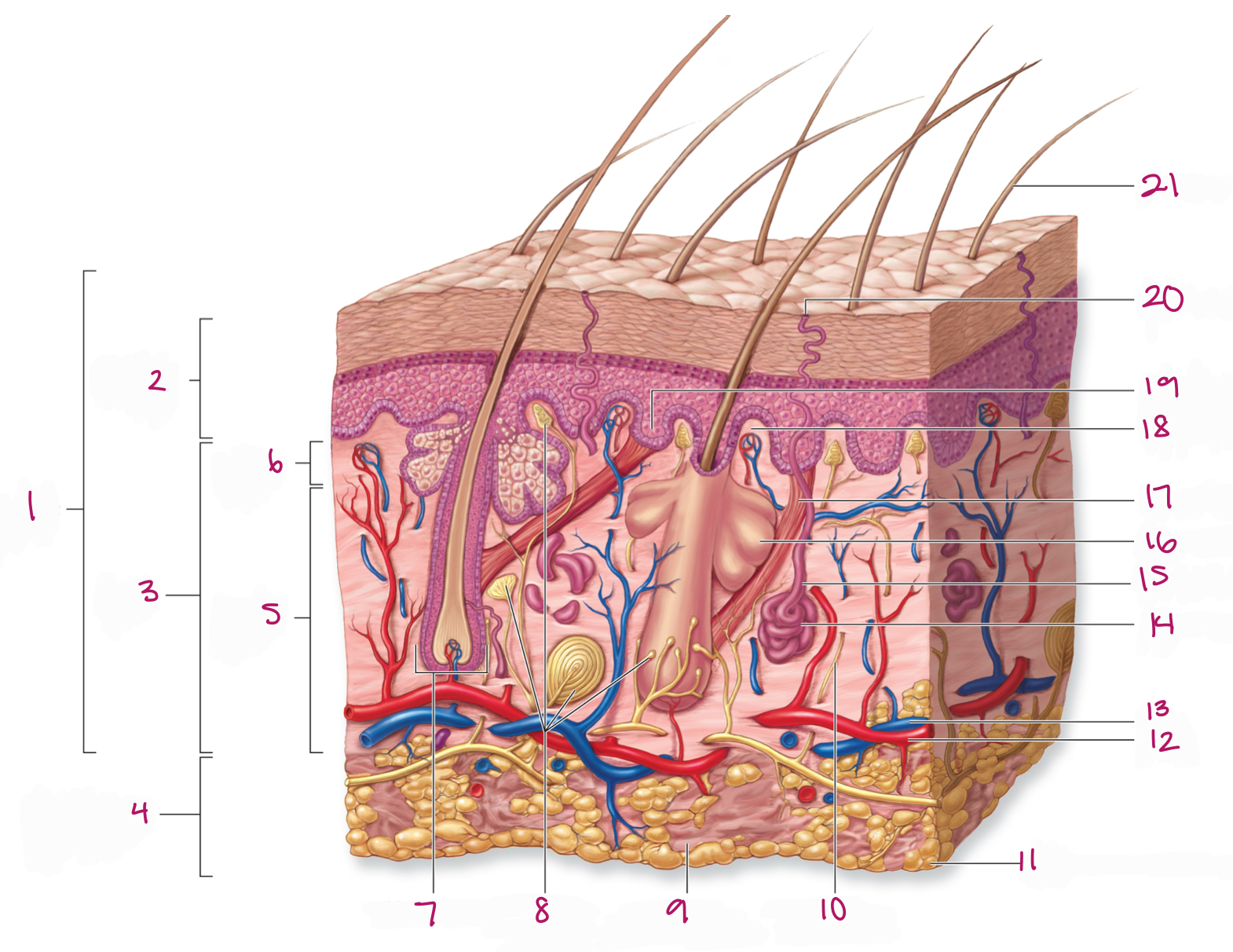
Label figure 13.
vein
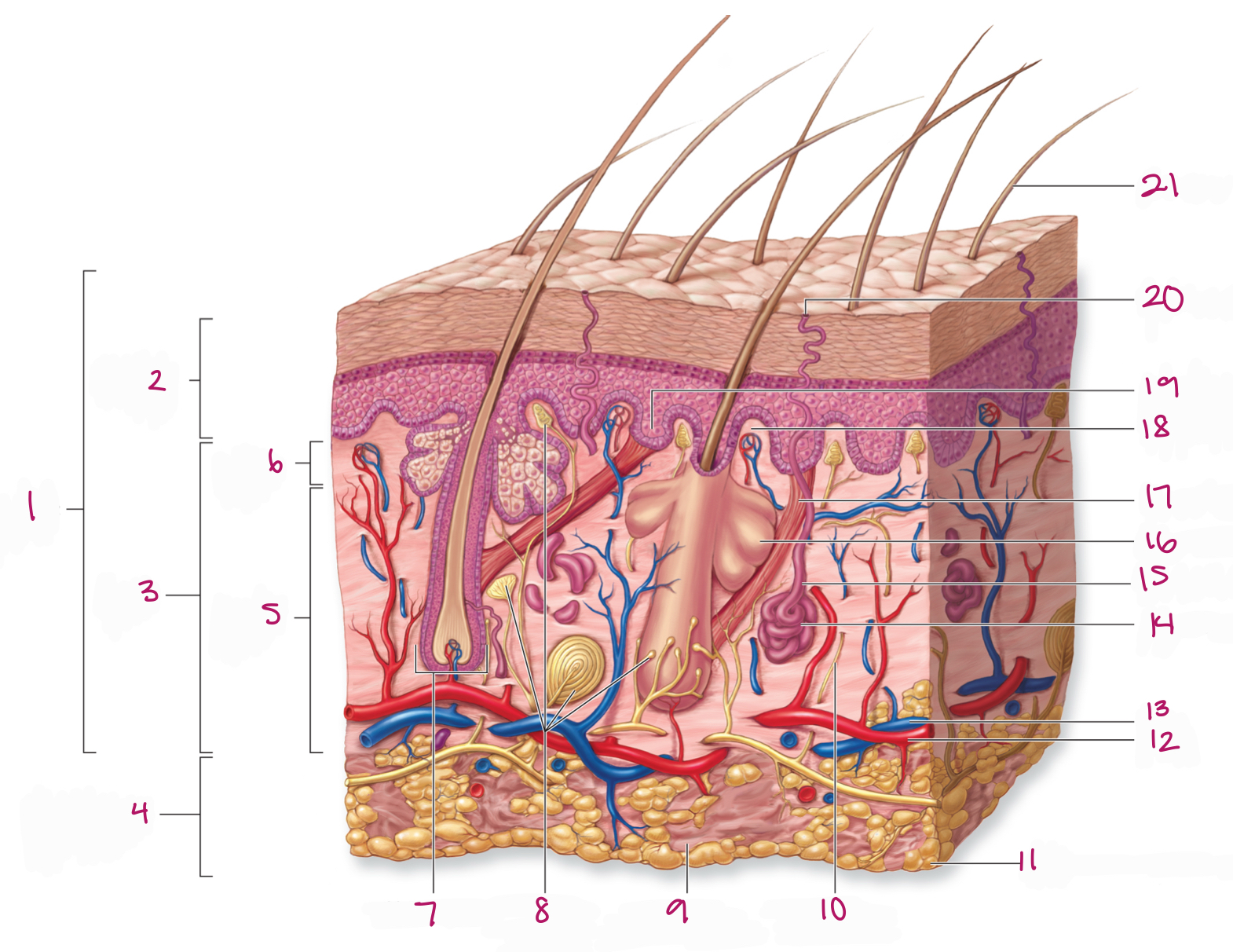
Label figure 14.
merocrine sweat gland
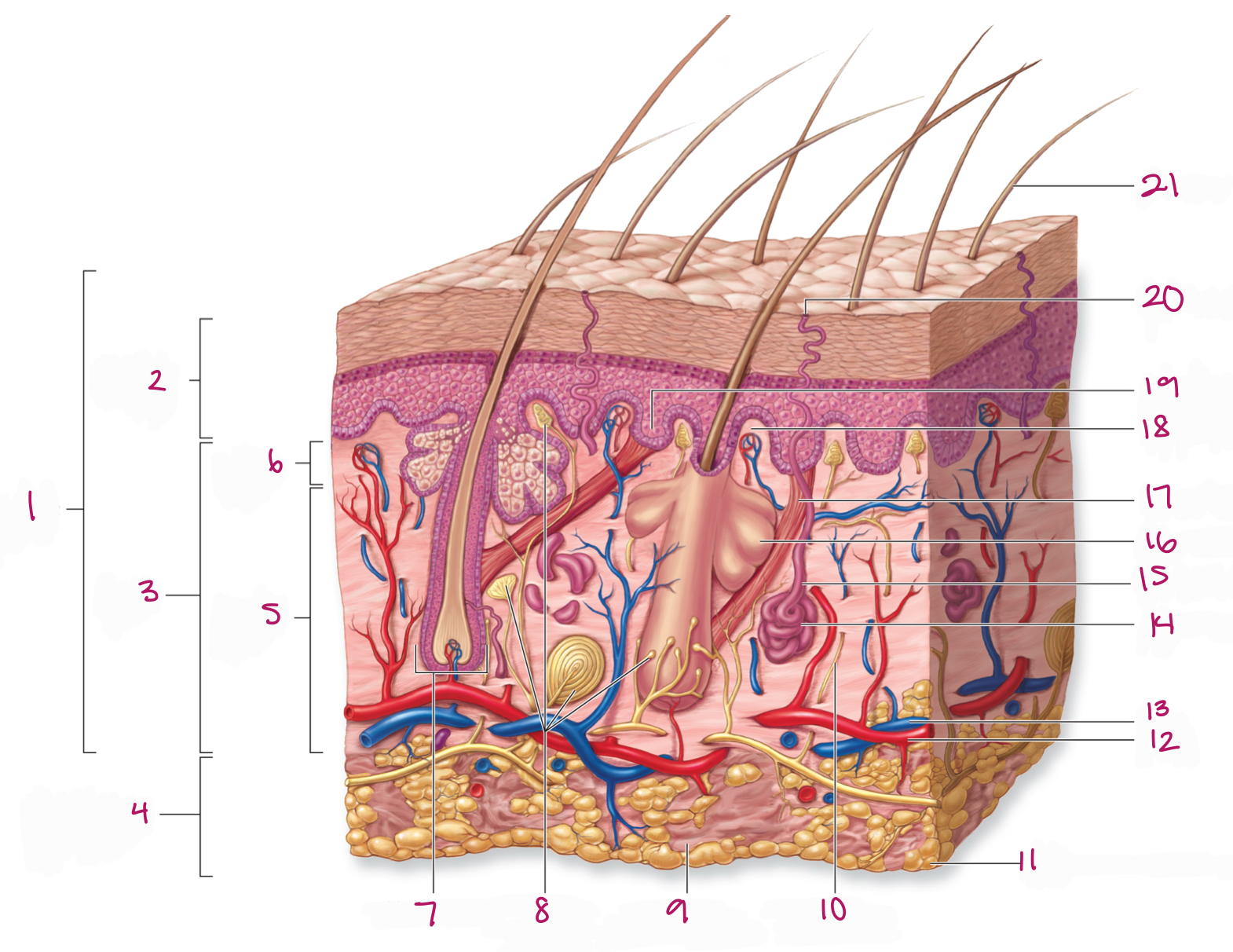
Label figure 15.
sweat gland duct
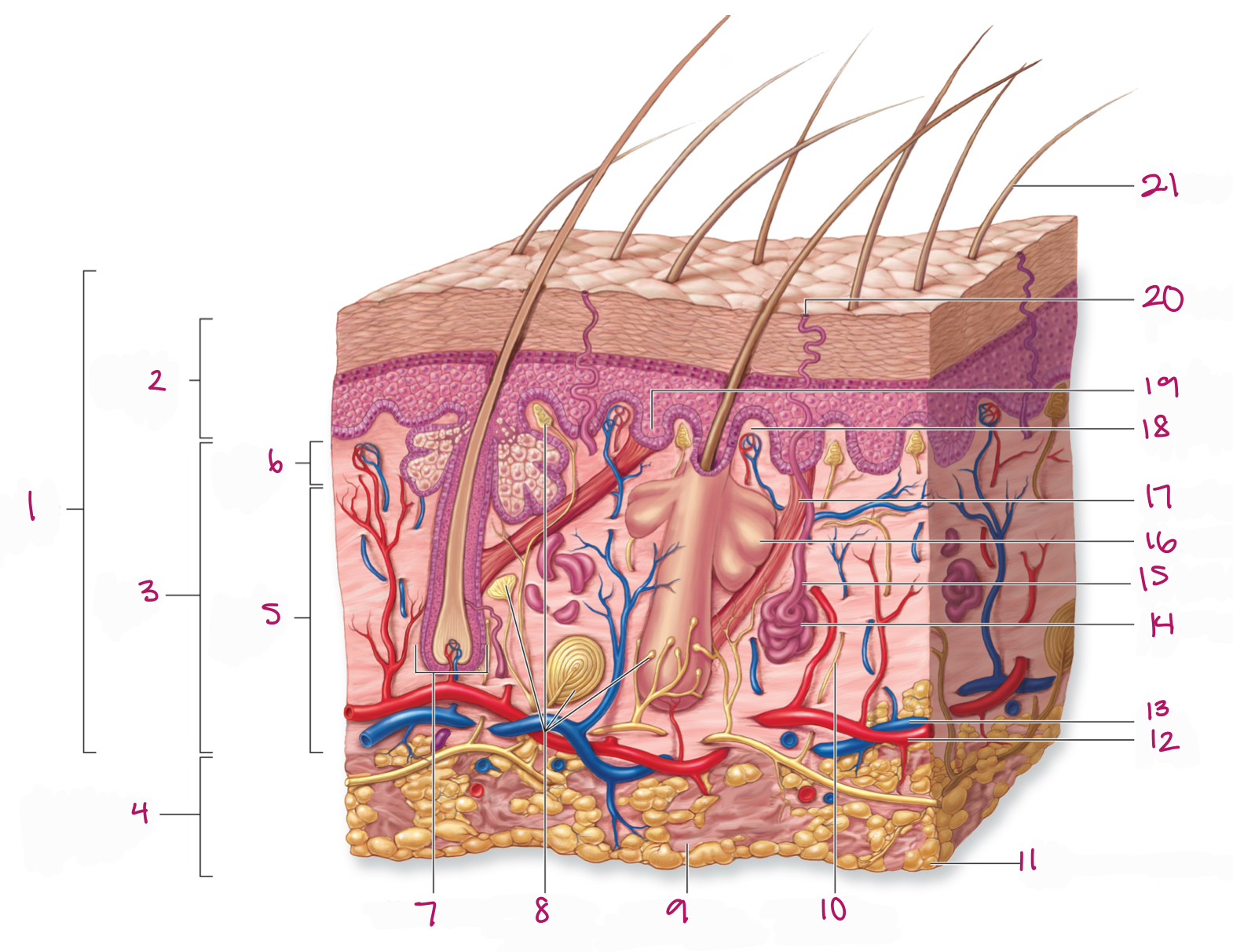
Label figure 16.
sebaceous (oil) gland
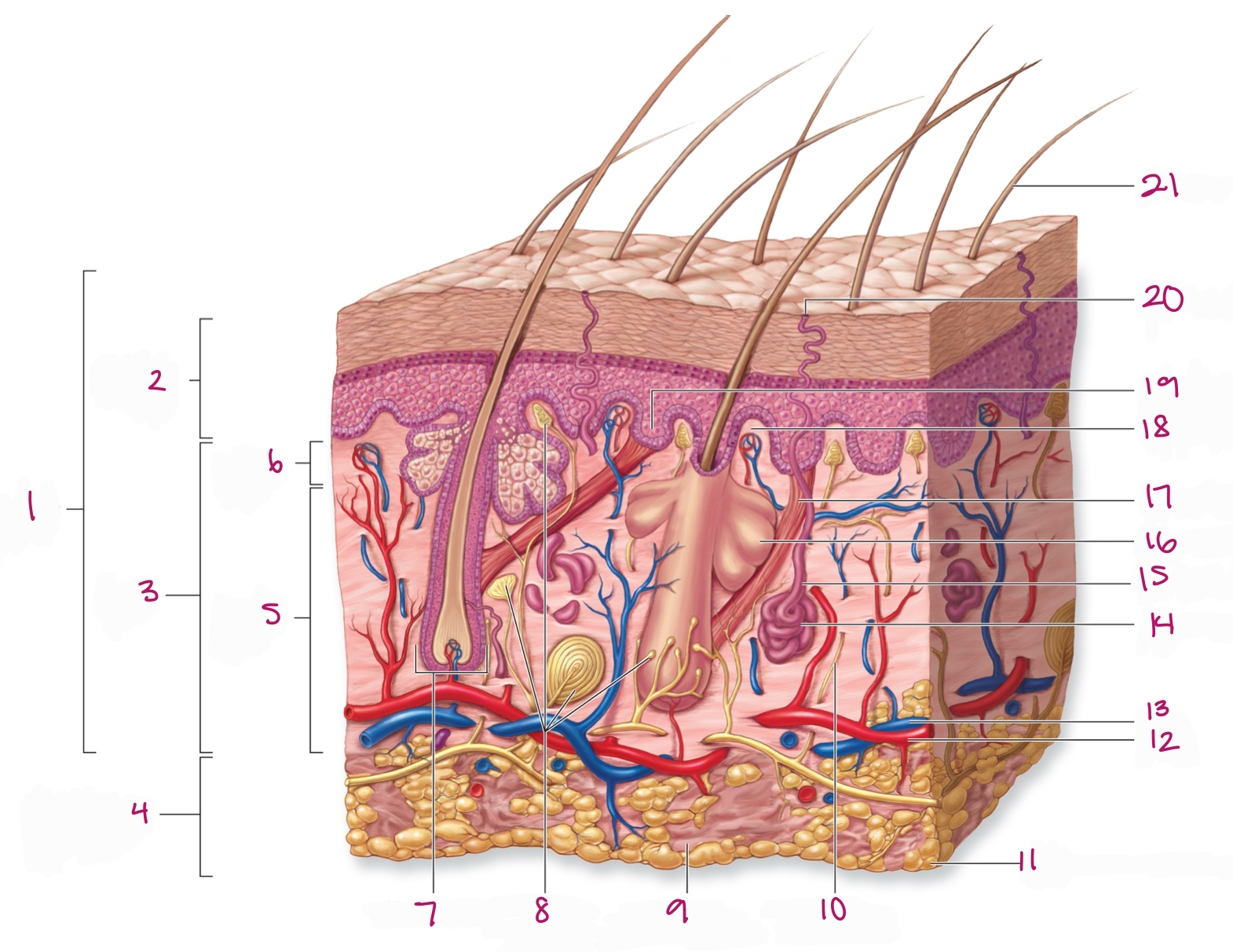
Label figure 17.
arrector pili muscle
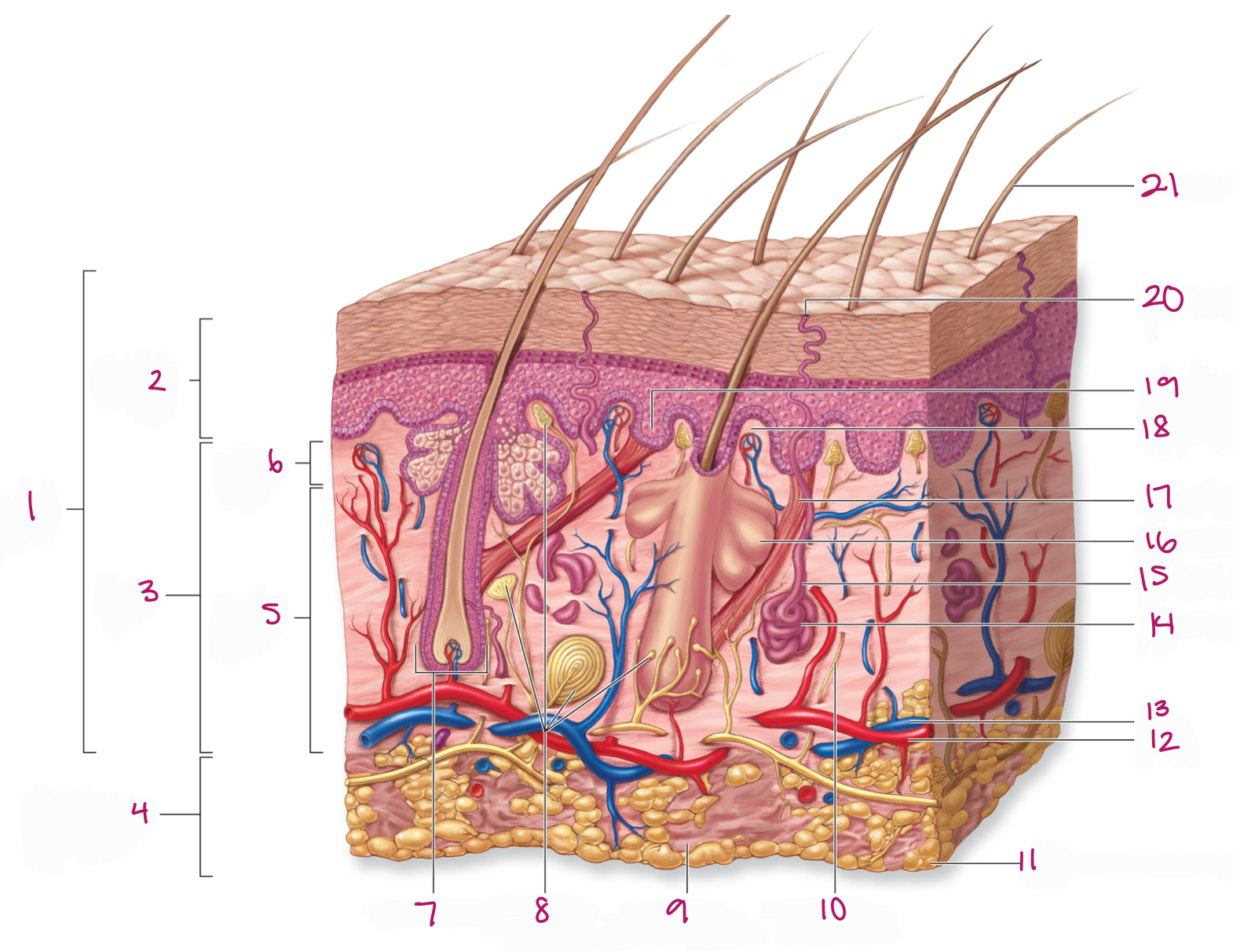
Label figure 18.
dermal papilla
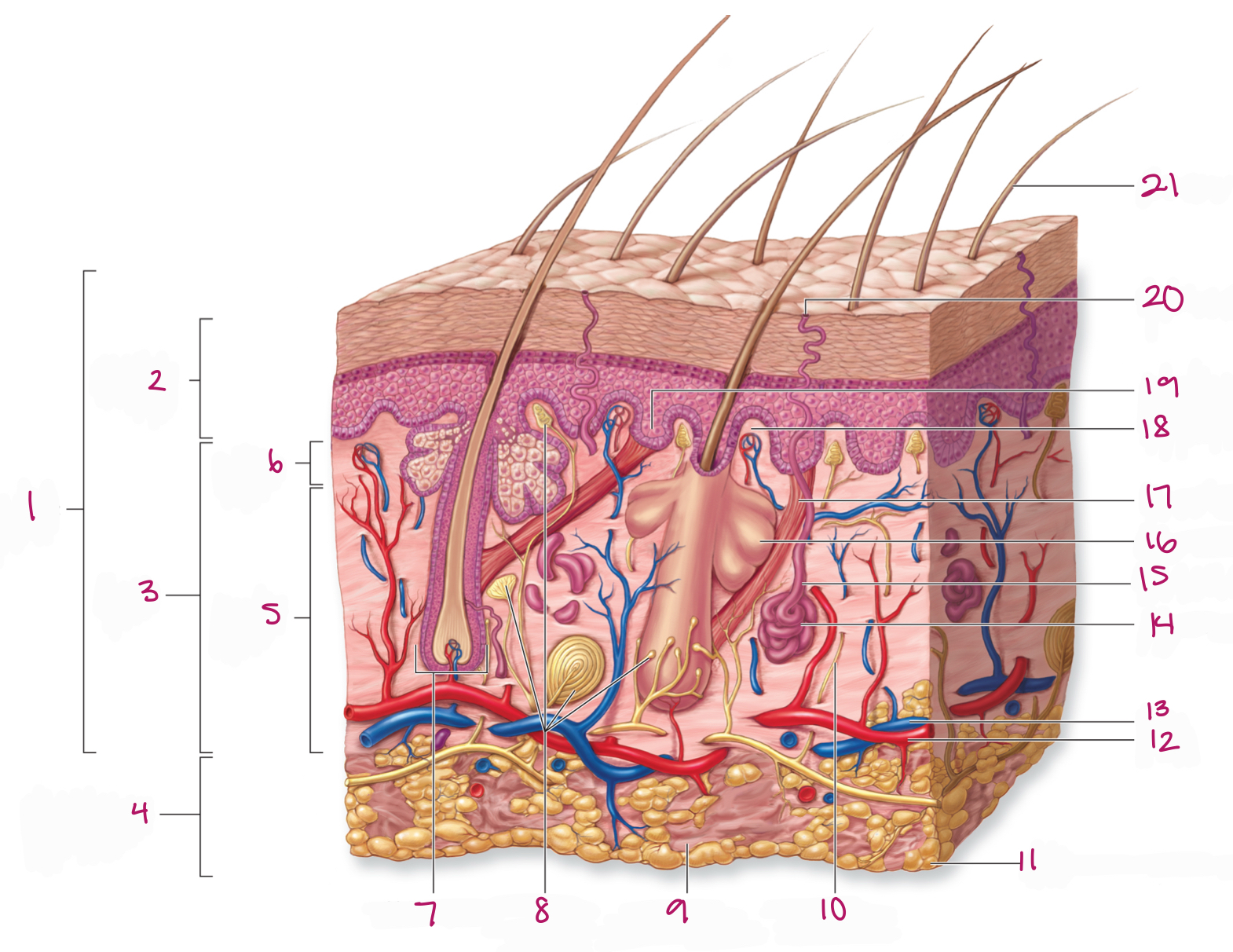
Label figure 19.
epidermal ridge
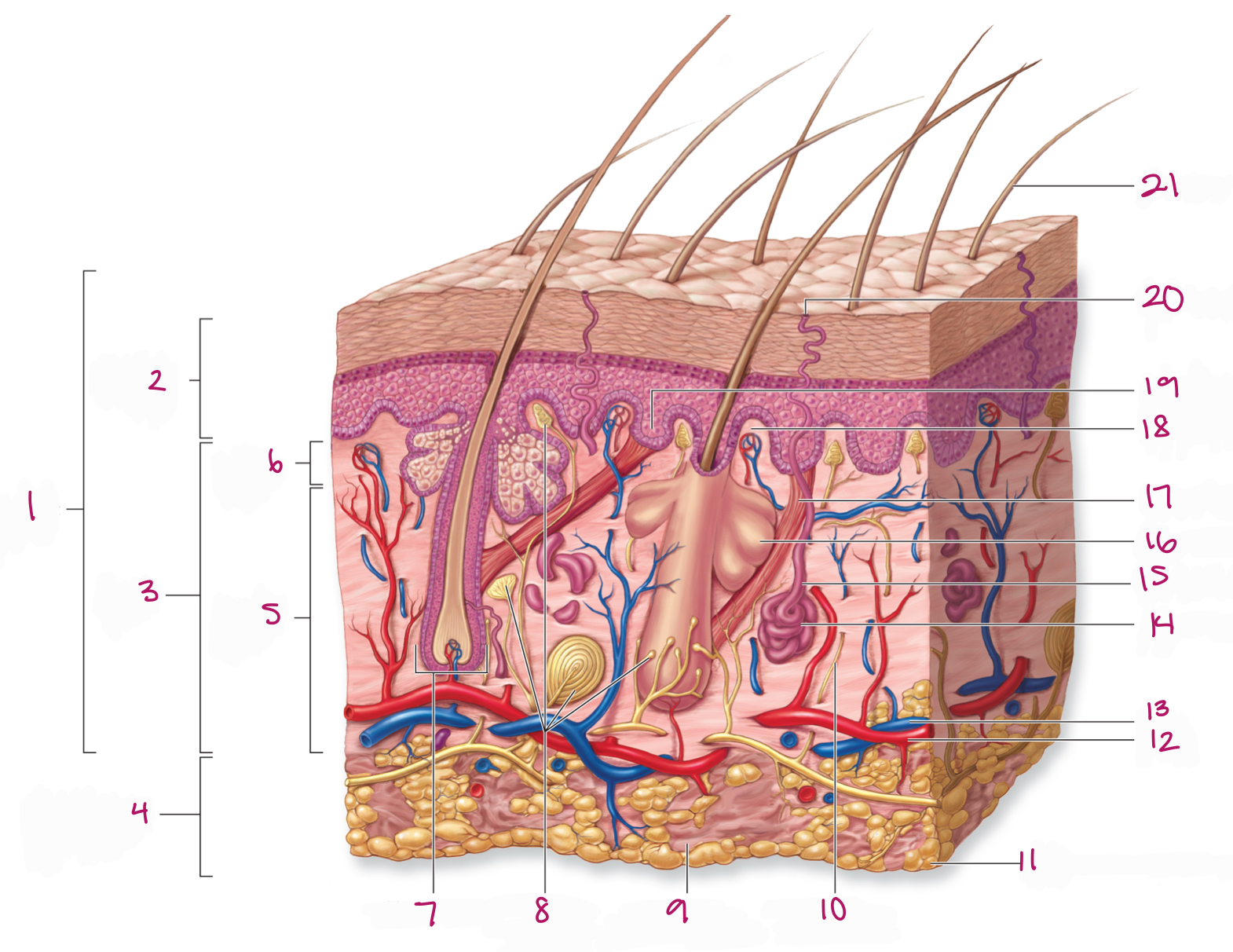
Label figure 20.
sweat pore
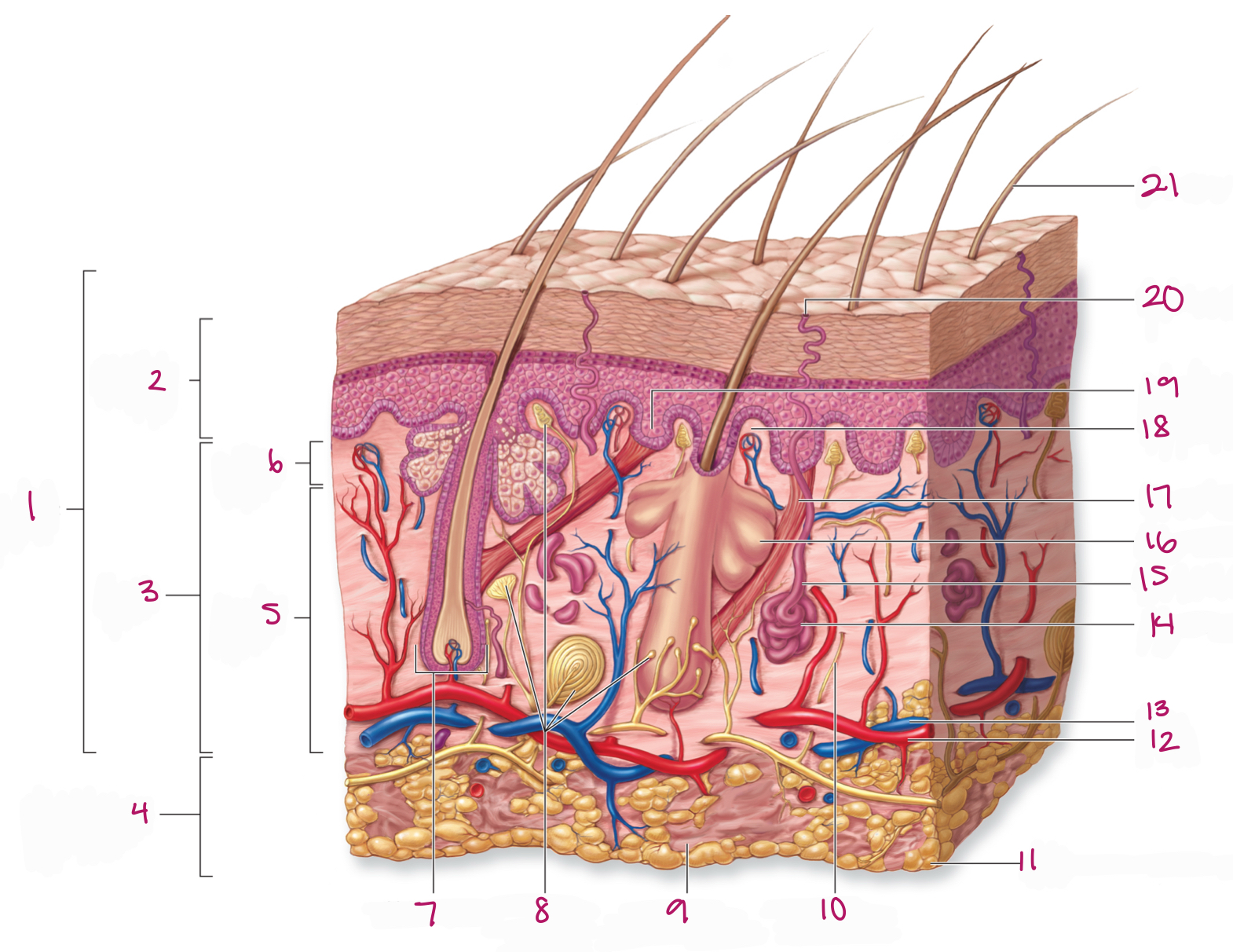
Label figure 21.
hair shaft
What are the functions of the integument?
protection
prevention of water loss and gain
temperature regulations
metabolic regulation
immune defense
sensory reception
secretion
Are certain substances absorbed into the integument? Why?
yes because of selective permeability
Why is skin water-resistant but not completely waterproof?
due to transepidermal water loss (TEWL)
What falls under transepidermal water loss (TEWL)?
insensible perspirations (non-visible sweating)
sensible perspiration (visible sweating)
How does the integument regulate temperature?
dilation of dermal vessels release heat, constriction conserves heat
How is the integument involved in metabolic regulation?
vitamin D3 produced by skin cells and converted into calcitriol by kidneys
calcitriol is a hormone involved in calcium homeostasis
How is the integument involved in immune defense?
epidermal dendtritic cells help initiate immune response
How is the integument involved in sensory reception?
skin receptors help detect changes in temperature, touch
What are tactile cells?
stimulate nerve endings in response to touch
How is the integument involved in secretion?
sweating; lubrication of hair and skin with sebum
the epithelium of the skin is the ?
epidermis
What are some characteristics of the epidermis?
avascular
composed of several layers (strata)
What are the 5 epidermal strata? in order of superficial to deep
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
What strata is only found in thick skin?
stratum lucidum
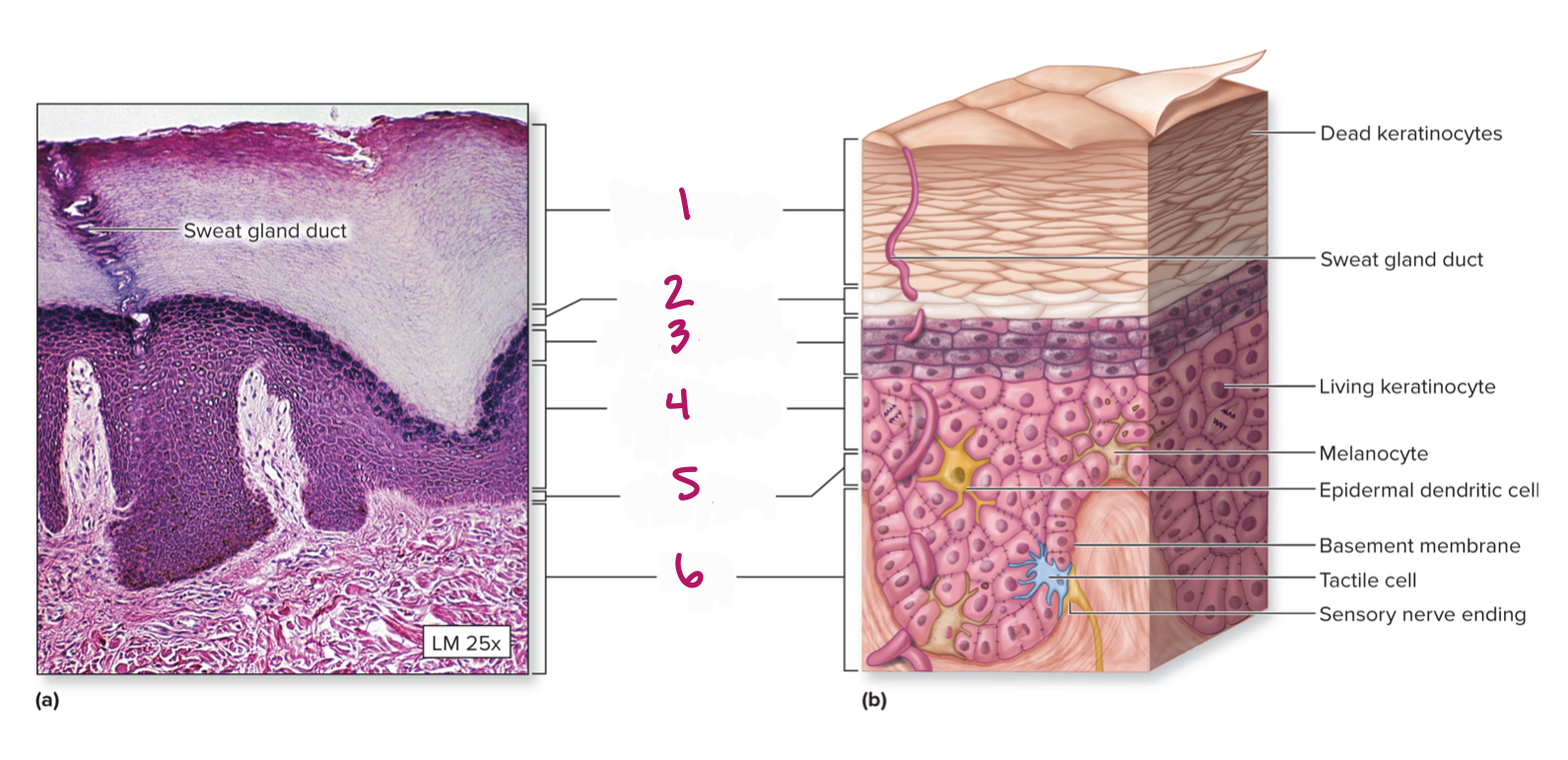
Label figure 1.
stratum corenum
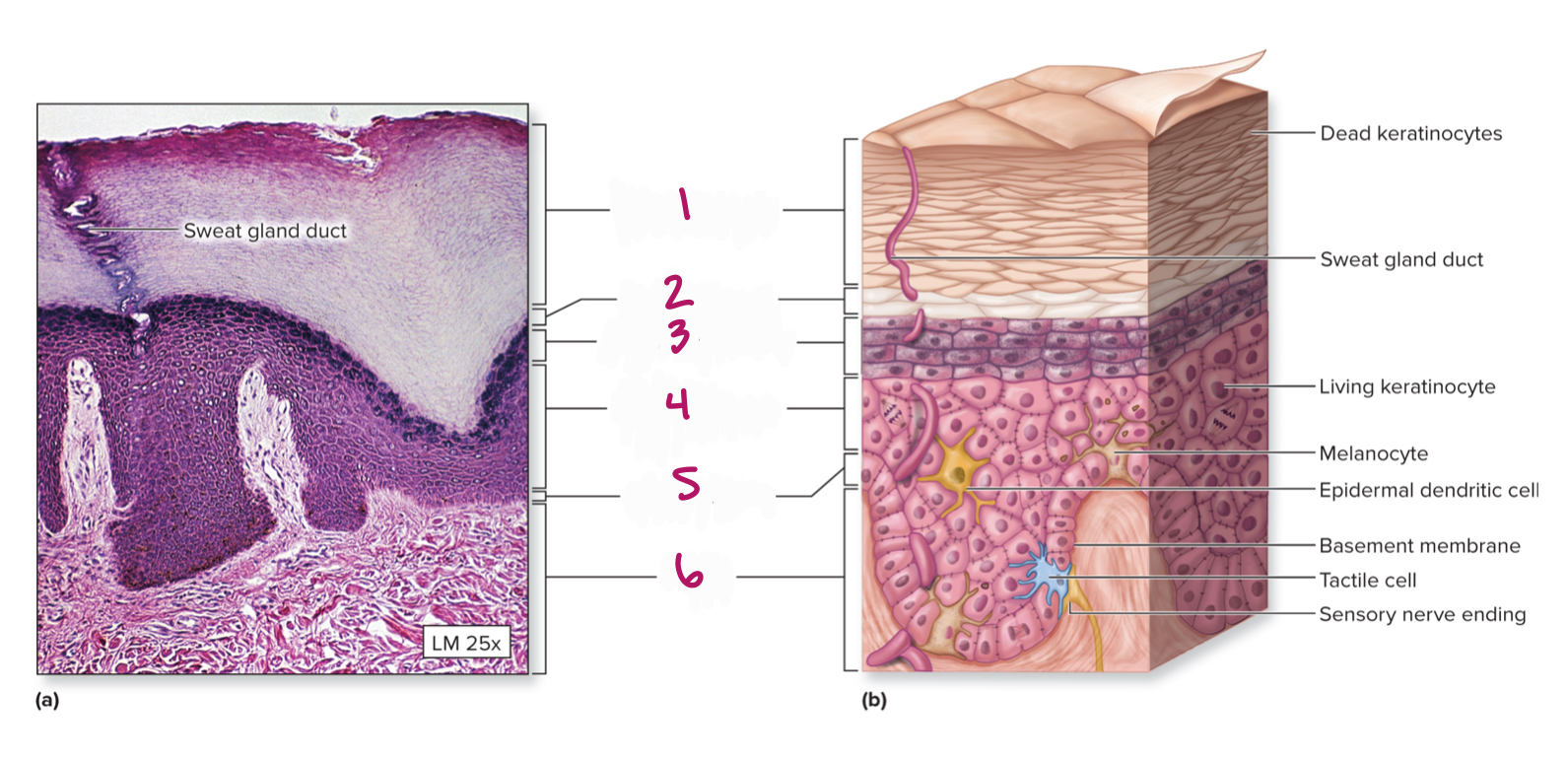
Label figure 2.
stratum lucidum
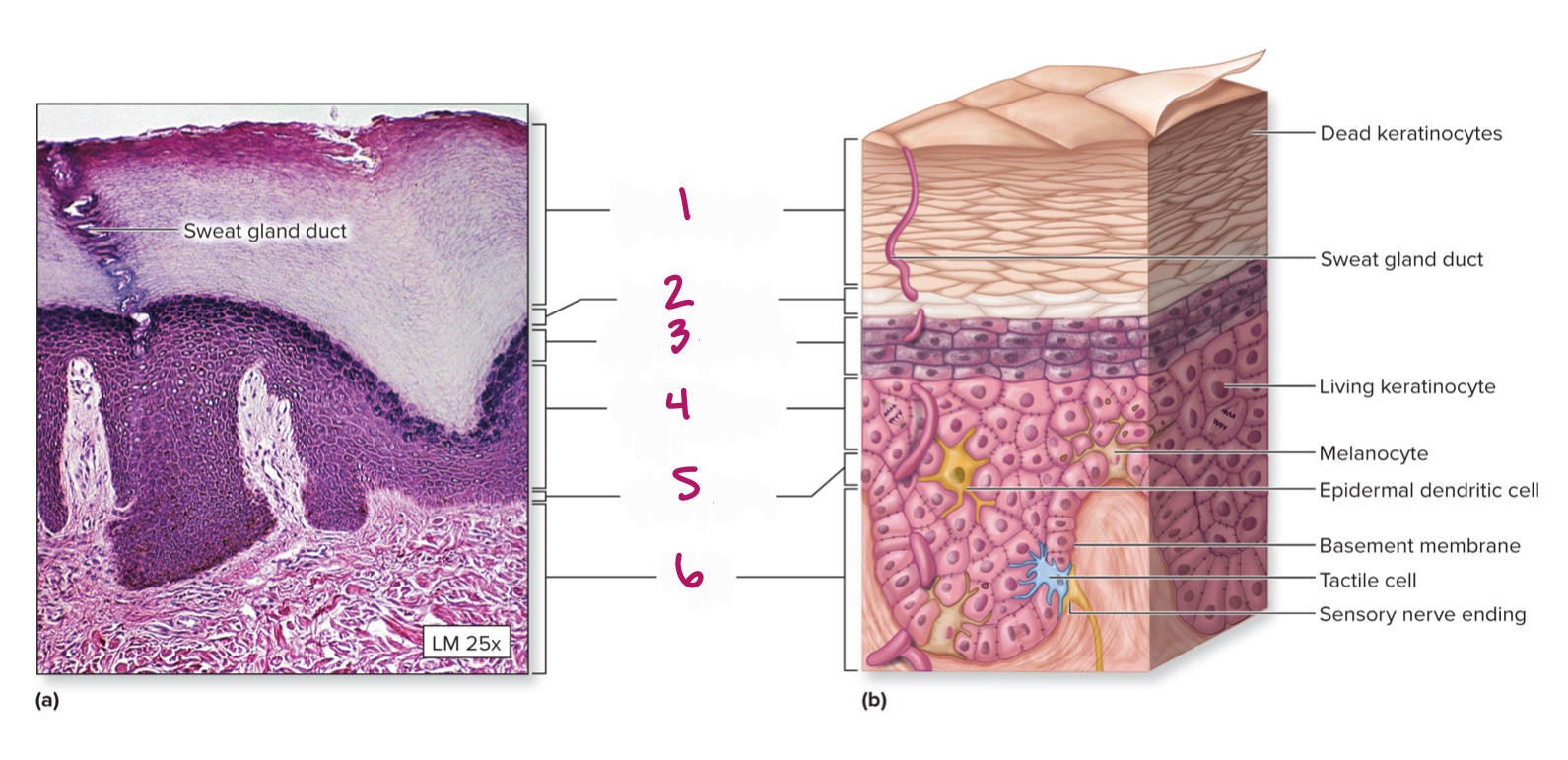
Label figure 3.
stratum granulosum
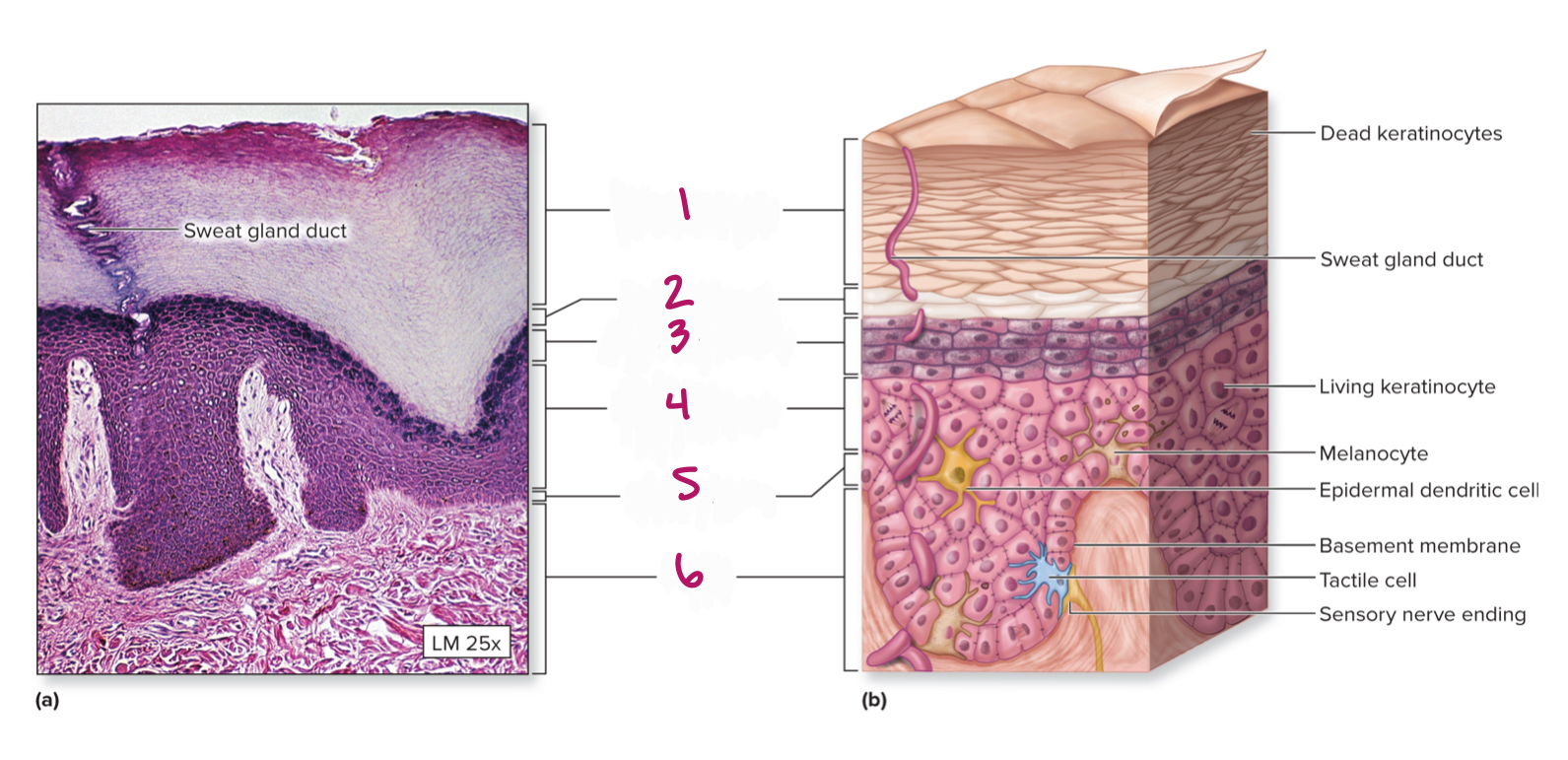
Label figure 4.
stratum spinosum
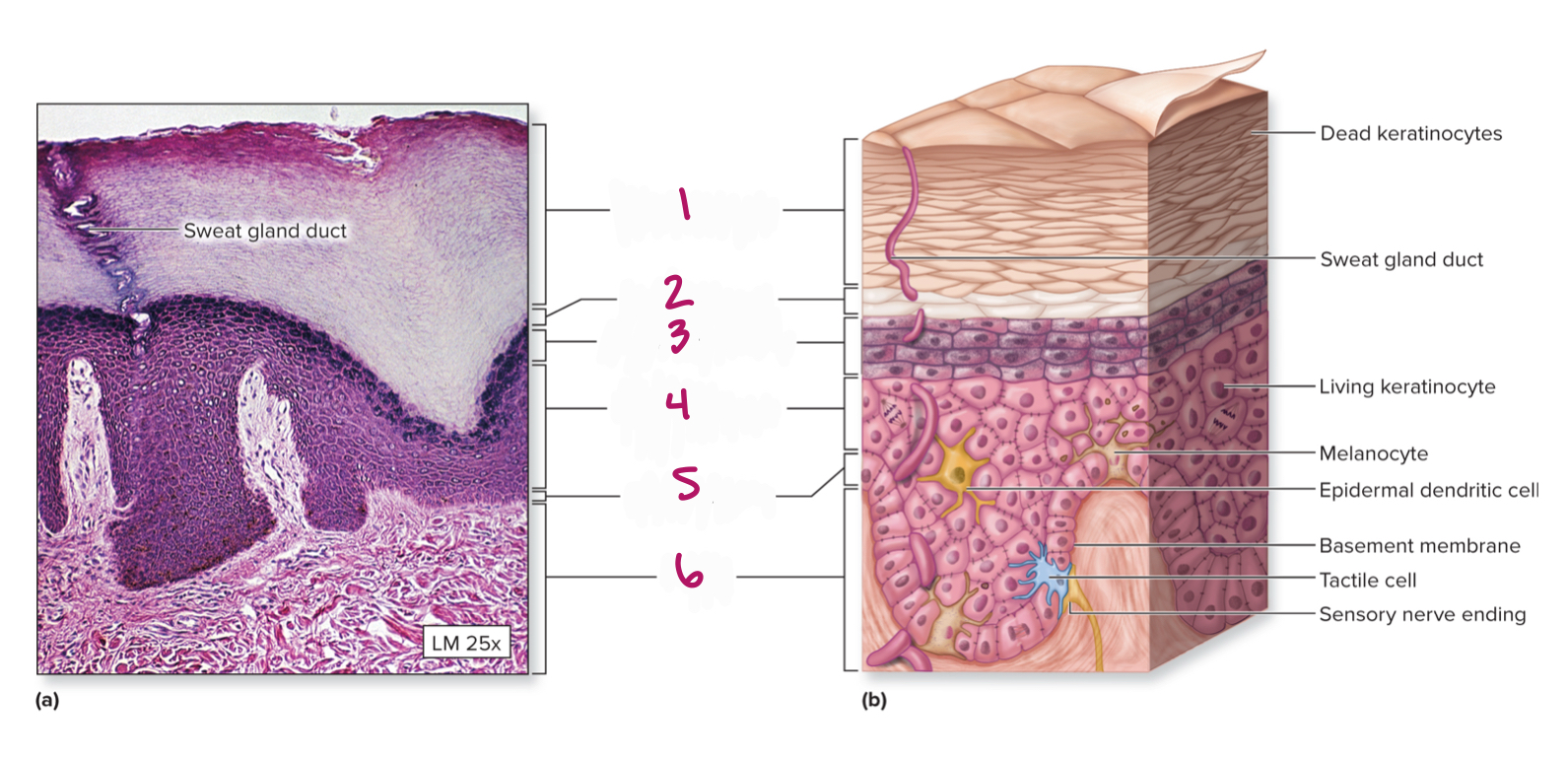
Label figure 5.
stratum basale
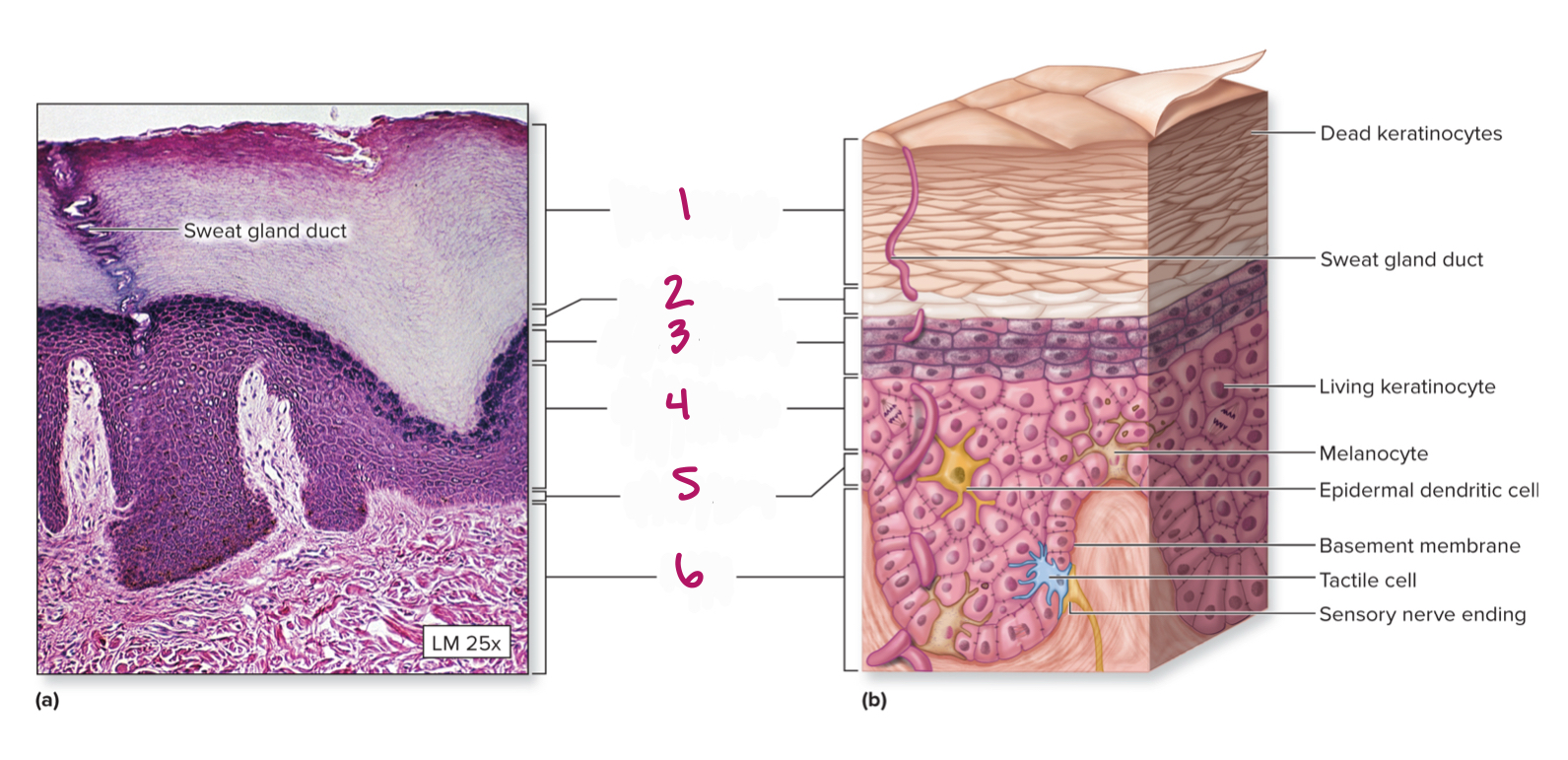
Label figure 6.
dermis
What is the arrangement/ cell type in stratum basale?
single layer of cells
cuboidal to low columnar
cells attached to basement membrane and adjacent to dermis
What are the cell types present in stratum basale?
keratinocytes
melanocytes
tactile cells
what is the most abundant cell in stratum basale?
keratinocytes
What are keratinocytes?
cells that produce keratin
______________________ predominate main cell of stratum basale; divide to replace keratinocytes shed at epidermal surface
kertinocyte stem cells
What are melanocytes?
produce pigment melanin
What does melanin do?
absorbs UV light to prevent DNA damage
melanin packed into _____________ for incorporation into keratinocytes
melanosomes
tactile cells are sensitive to?
touch
What is the arrangement/ cell type in stratum spinosum?
several layers of polygonal keratinocytes
What cell types are found in stratum spinosum?
daughter cell of stratum basale → specialized keratinocytes
epidermal dendritic cells
immune cells
How do keratinocytes in stratum spinosum attach to each other?
via desmosomes
immune cells act as _________ to fight infection and initiate immune response
phagocytes
What is the arrangement/ cell type in stratum granulosum?
three to five layers of keratinocytes undergoing keratinization
What occurs during keratinization?
cytoplasm fills w/ keratin degrading filaments
organelles begin to degrade
What are the types of keratin granules in cells of stratum granulosum?
keratohyalin granules
lamellar granules
What granules are involved in the keratinization process?
keratohyalin granules
what granules release contents (primarily lipids) into extracellular space; help form water barrier?
lamellar granules
What is the arrangement/ cell type in stratum lucidum?
thin, translucent region, two to three cell layers thick
In stratum lucidum, the cell lack organelles and are filled with?
eleidin
What is the arrangement/ cell type in stratum corneum?
thickness varies from 20-30 layers of corneocytes
What are corneocytes?
dead, scaly, interlocking keratinized cells
The cells in stratum corenum are?
anucleate (lack nucleus) and tightly packed
About how long do cells take to migrate from stratum basale to stratum corneum?
2 weeks
How long do cells remain in stratum corneum to protect deeper layers?
2 weeks
what happens to cells in stratum corenum?
eventually shed from epidermal surface
Thick skin contains how many layers and which layer specifically does it include?
five layers including stratum lucidum
Where is thick skin typically found?
palms and soles of feet
Does thick skin contain hair follicles or sebaceous glands?
no
How many layers does thin skin have, what does it exclude?
4 layers, excludes straum lucidum
Where is thin skin found?
covers most of body
about how thick is the epidermis?
0.4-0.6 mm thick
skin color is determined by what pigments?
hemoglobin
melanin
carotene
hemoglobin
blood pigment
melanin
pigment produced by melanocytes
carotene
yellow-orange pigment from foods such as carrots; it builds up in the skin
appearance of skin due to melanin is influenced by what?
hereditary
exposure to UV light
what are the subtypes of melanin?
eumelanin
pheomelanin
T/F all people have about the same number of melanocytes?
true
what is also known as a mole?
nevus
what is a mole?
localized overgrowth of melanocytes
what are freckles?
yellow or brown spots of high melanocyte activity
What are folds of epidermis and dermis on fingers, palms, soles and toes; increase friction for grasping?
friction ridges
what are the types of friction ridges?
arch
whorl
loop
where is the demis located?
deep to the epidermis
about how thick is the dermis?
0.5 mm to 3.0 mm
what is the dermis composed of?
areolar and dense irregular connective tissue
What are the two layers of the dermis?
papillary layer
reticular layer