neuroscience B, fungi
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
who were making early attempts at working out neural code? found the relationship between measurable qualities of stimulus e.g. heat & attributes of sensory experience?
Psychophysicists e.g. Wundt
what did Weber find?
-sensitivity of sensory system to differences in intensity depends on absolute strength of stimuli
-e.g. easy to see difference between 1kg and 2kg rather than 50kg and 51kg
dS=K x S
dS= min difference in strength between stimuli, K is a constant, S is reference stimulus
what is sensory threshold?
minimum amount of energy /stim needed for conscious detection
what did Lord Edgar Adrian introduce? (20th century)
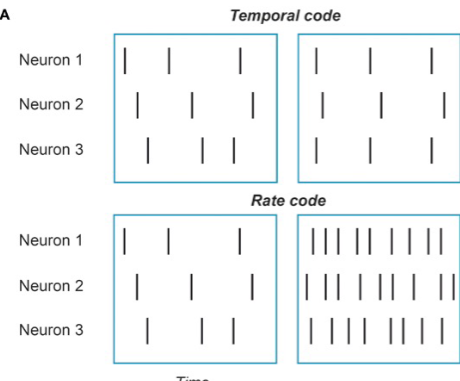
-idea of rate code to neuroscience (essences of analogue to digital code)
rate code= frequency of firing- varies w strength of stimulus, stronger stimuli evoke larger receptor potentials-generated at higher frequency of AP
what did Hubel and Wiesel find?
rate coding is found in brain not just periphery sensory neurons , it is energetically expensive
what did Bruno suggest of rate coding?
-energetically expensive
-self-selecting -once u think its the code, u only record from neurons that use it
-should focus more on temporal code (simplest)- precise and looks at relative timing of APs, rate code- mean rate of APs is most important
who discovered brain waves?
Hans Berger-1926 when he invented the EEG, can be measured at single neuron or population lvl
controversy around what each band linked to
what are the best ways to do an EEG of brain waves?
whole brain scan- to understand direction of movement fully, and origin of oscillation
what are some ‘decoding’ methods of humans?
EEG and PET (worse spatial resolution), fMRI and MEG (better spatial resolution)
how do MRI work?
-uses magnetism to image
-patient placed in large static magnet & smaller magnets change fields in different directions at right-angles to one another
-can do different contrasts- gives diff type info
what is BOLD contrast?
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent (increased local flow of blood=increased MR signal)
how does MRI/ fMRI work?
-brains have high conc. of hydrogen nuclei
-protons will Orient their magnetic fields when placed in external magnetic field, and rotate
-arrangement is disrupted when radio-frequency waves are applied
-as protons return to equilibrium they emit signal which is detached by MR scanner
BOLD tell u relative ratios of deoxygenated blood:oxygenated blood
-tracks neurons that r working harder (such as involved in certain kinds of experimental tasks)
what is fMRI useful for?
-structural imaging lacks spatial resolution
-progression of injury of interest
-insurances where organic nature of injury is questioned
who were the first big names in zapping fish?
-Scribonius Largus: torpedo fish on scalp for headache(43-48AD)
-Galen (131-410AD)
-Ibn-Sidah 11th century-electric catfish
-Walsh (1773): beginned electrophysiology
-Galvani (next his son Giovanni Aldini)
-Volta
what did Fritsch and Hitzig discover?
1870- electrical stimulation of the cortex can produce movements, had exposed surface of dogs brain- observed which parts produced different places of movement
what was McIntosh Physician’s Faradic battery for?
headaches/ migraine (very weak evidence base)
what did Creutzfeldt find?
1962- applied DC to the cortex -found increased strength increases frequency, doesn’t matter if anode or cathode is above, effects outlast stimulation period
negative current inhibited it
what was Aldinis work
suggest dc applied to the scalp can modulate human brain function (depression)
what is tES, tDCS, tACS, tRNS?
tES: transcranial electrical stimulation
tDCS: transcranial direct current stimulation
tACS: transcranial alternating current stimulation
tRNS: trancranial random noise stimulation
what are some issues with tES?
-limited outcome measures in humans
-unknown transfer functions from cellular effects to behaviour
-poorly mapped interindividual confounding factors
what are the steps between membrane excitability and cognition/ behaviour?
population activity→ network activity & plasticity→ motor evoked-potential & neuroimaging (all unknown transfer functions)
how can you visualise the brain in tES?
do an anatomical MRI→ do tissue segmentation→ do FEM modelling→ do visualisation w optimal montage→ neruonavigation→ place stimulating pads in correct place!
how can you tell which region of hypha is oldest?
no or less cytoplasm remaining (chitin wall still there)
in hyphae, what is the organising centre for growth and morphogenesis?
Spitzenkörper
what species of fungi have septa?
Ascomycota and Basidiomycota (unless sealing off injured parts or delimiting sexual structures)
Trichomyectes (zygomycota) & M. hiemalis (when young colony) have septa (quite complex in Zygomycota)
what are dolipore septa
specialised septa, repair damage to hyphae
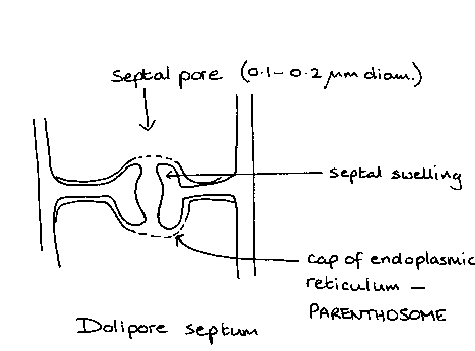
how are septa formed? why are they formed?
centripetally- narrowing diaphragm (opposite of plants), strengthen, can block off injured parts, restrict cytoplasmic continuity-allows differentiation
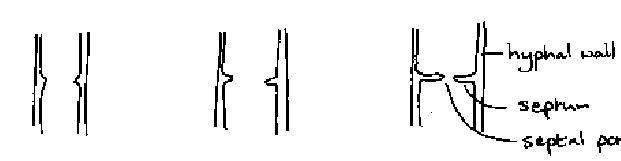
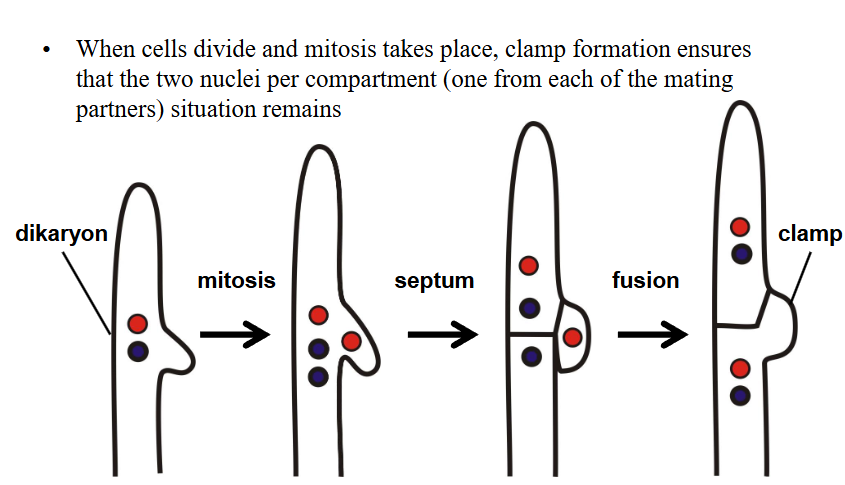
what happens in clamp formation in basidiomycetes
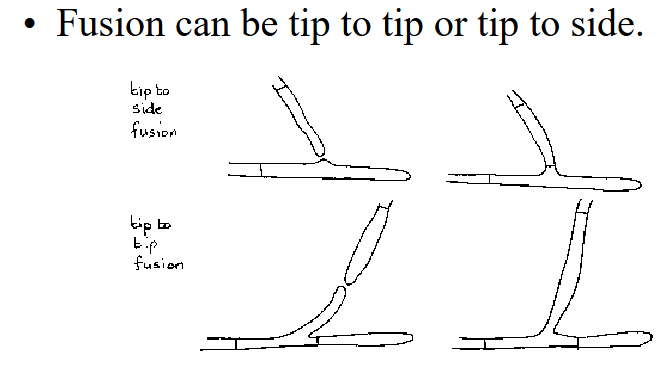
what are anastomoses?
what are the different hyphal types in fruiting bodies?
1. Generative: thin walled; give rise to other types of hyphae
2. Skeletal: unbranched, thick-walled, narrow lumen.
3. Binding: much-branched, narrow, thick-walled, of limited growth
what does monomitic, dimitic and trimitic mean?
Monomitic - just generative e.g. Bjerkandera adusta
Dimitic - (i) generative and binding Laetiporus sulphureus
(ii) generative and skeletal Heterobasidion annosum
Trimitic - all three types Trametes versicolor
what are some of the ways in which fungi trap (e.g. nematodes for nitrogen)
Constrictng rings
Adhesive rings
Adhesive knobs
Adhesive spores
Hooked conidia
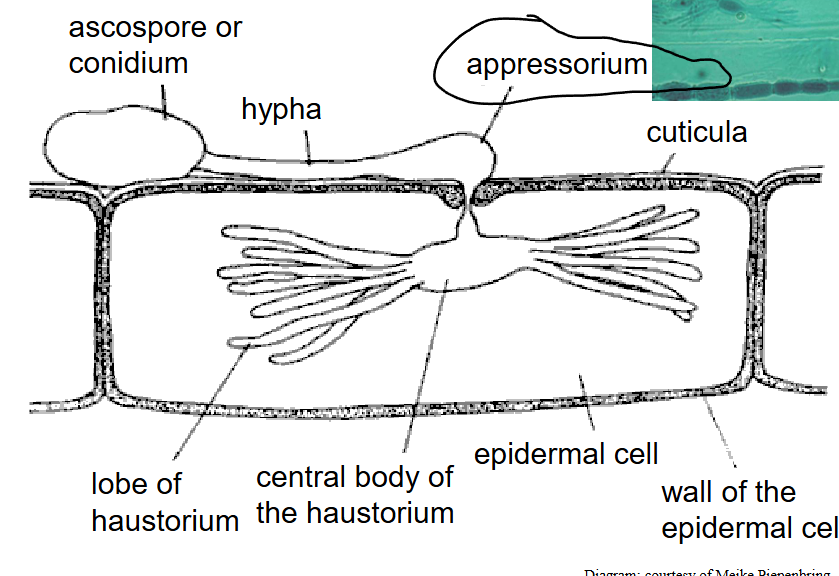
how does this work?
like a peg, applies physical activity, pressure and enzymes
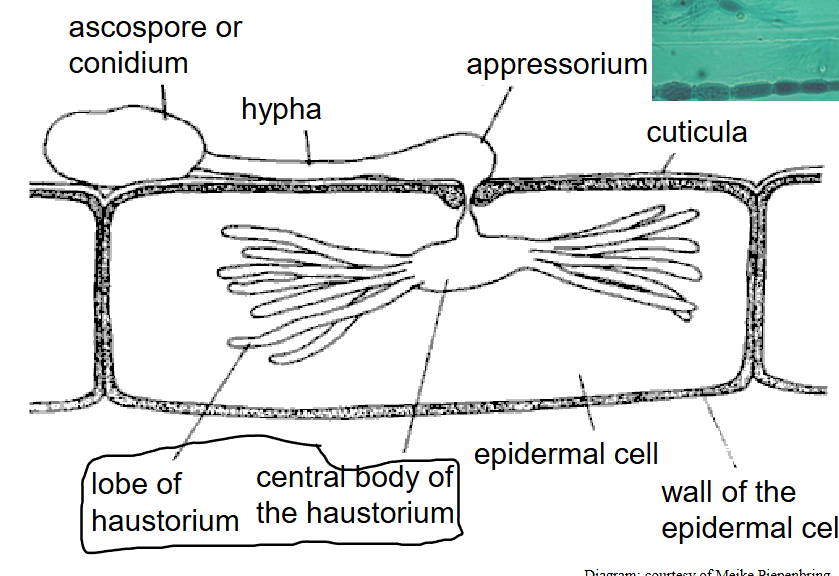
how does this work?
extract nutrient from cell
what are arbuscles and pelotons?
arbuscle- ‘dwarf tree’ inside the cell
peleton- coils within the cell
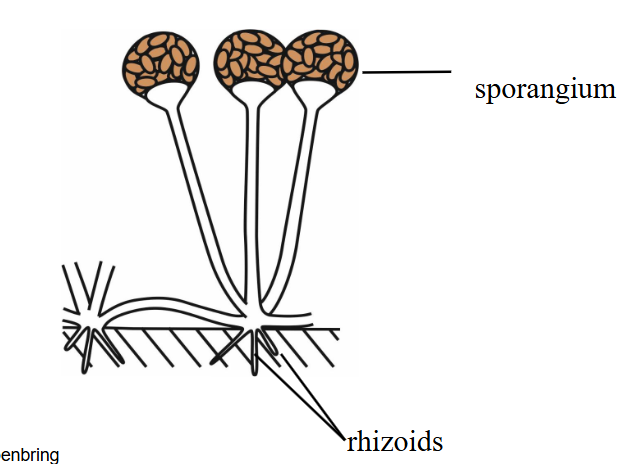
what do rhizoids do?
anchor the fruiting body
what do cords and rhizomorphs look like?
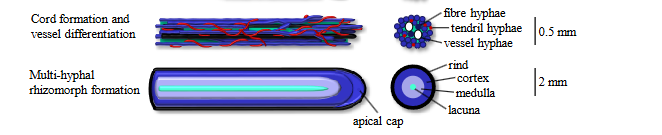
what is plectenchyma tissue?
any tissue organized from hyphae
what is prosenchyma?
loosely woven hyphae
what is pseudoparenchyma?
hyphae form short
'cells' rounded by mutual pressure, thin-walled
what is pseudosclenrenchyma?
thick-walled and dark,
rounded
what do sclerotia look like?
rounded, flattened or elongated masses

what could germination give rise to?
mycelium, outer or inner fruiting bodies
what are psedosclerotia?
look like sclerotia, but are on inside and outside of a different organism, can form plates (resistant to fluid/mycelium penetration)
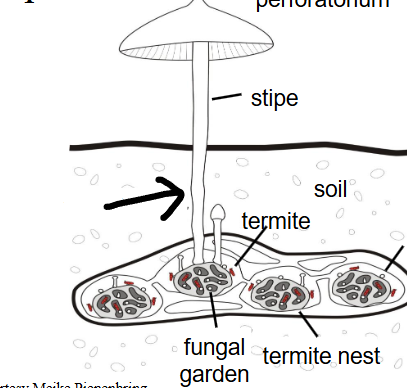
what is missing
pseudorhiza
what are stromata?
they are plates or solid
masses, Fruiting structures are
borne in or on them
what is a coremia
aggregated sporophores, stalked structures
what is plasmogomy and karyogamy?
plasmogamy - joining of thalli
•karyogamy - joining of nuclei
what are the names of the reproductive structures of each of these: Mucoromycotina, Chytridiomycetes, Glomeromycotina, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota?
Mucoromycotina-zygospore with suspensors
Chytridiomycetes- flagellate cell
Glomeromycotina- no sex reproduction?
Ascomycota-ascus w ascospores
Basidiomycota-basidium w basidiospores
in chytridiomycetes, zygomycetes, (haploid) what has the biggest gap?
mitosis and plasmogamy
in oomycetes (diploid) what has the biggest gap?
karyogamy and mitosis
what are the different types of plasmogamy?
Gametic copulation, Gametangial copulation, Gametangial conjugation, Spermatization, Somatogamy
what is anisogamy?
both gametes are motile, different sizes
what is the difference between gametangial copulation & conjugation?
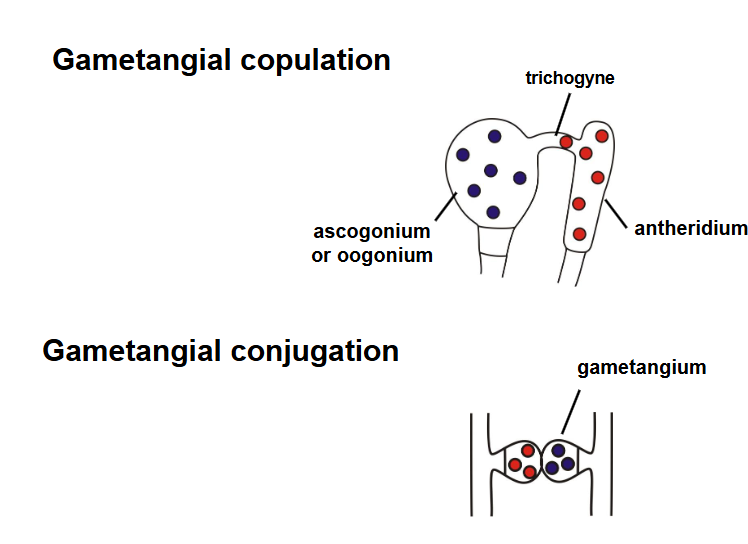
where does karyogamy occur in chytrids?
zygotes
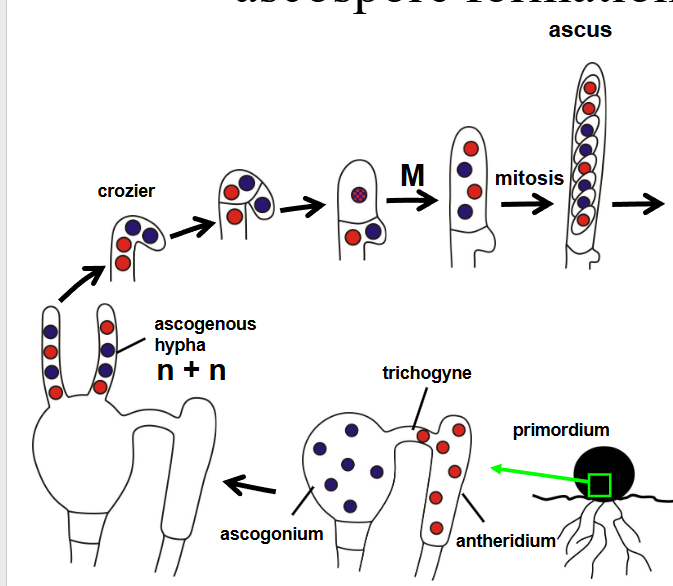
what types of cell does karyogamy and meiosis in ascomycetes?
crozier cells (become dikaryotic)
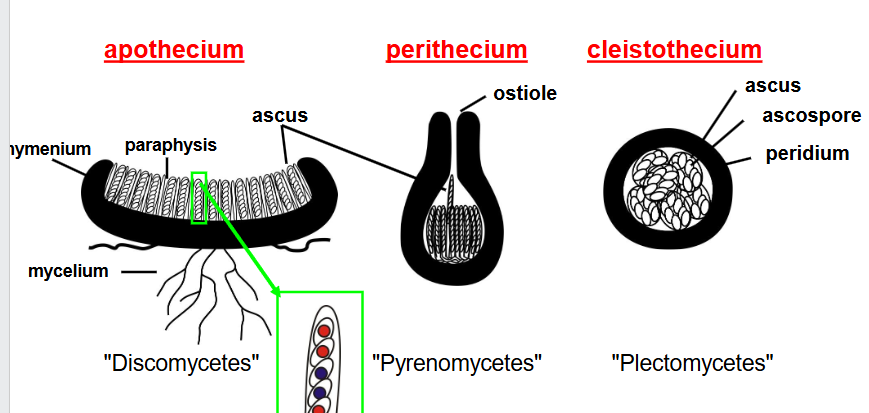
what are the different shapes of Ascomycota fruit bodies?
how are ascospores formed?
how are basidiospores formed?
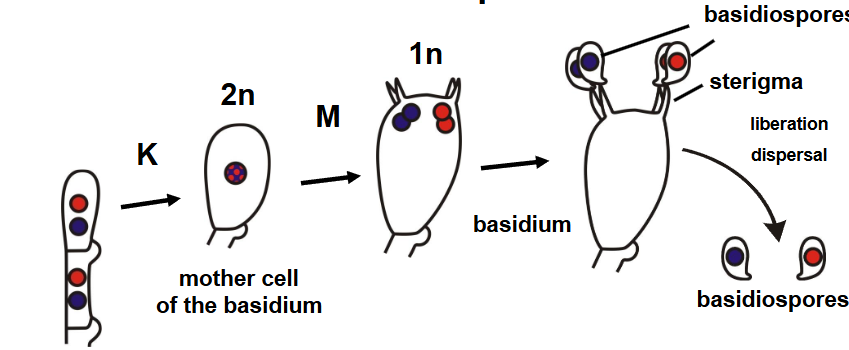
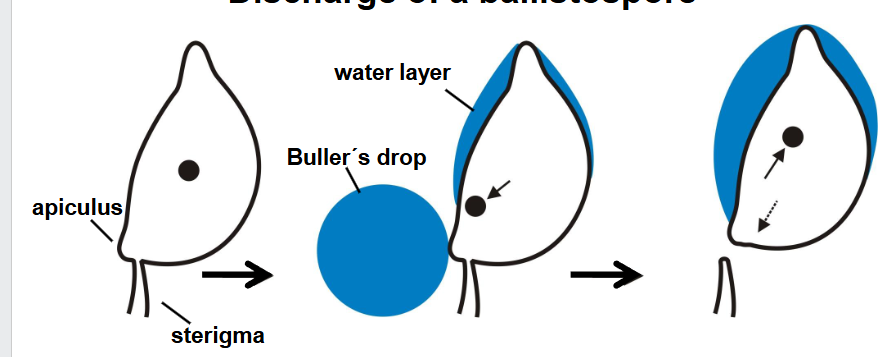
how are ballistospores discharged?
water droplet- changes spore centre of gravity allowing it to shoot off, leave sterigma behind