Lab 9: The Skeletal System
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
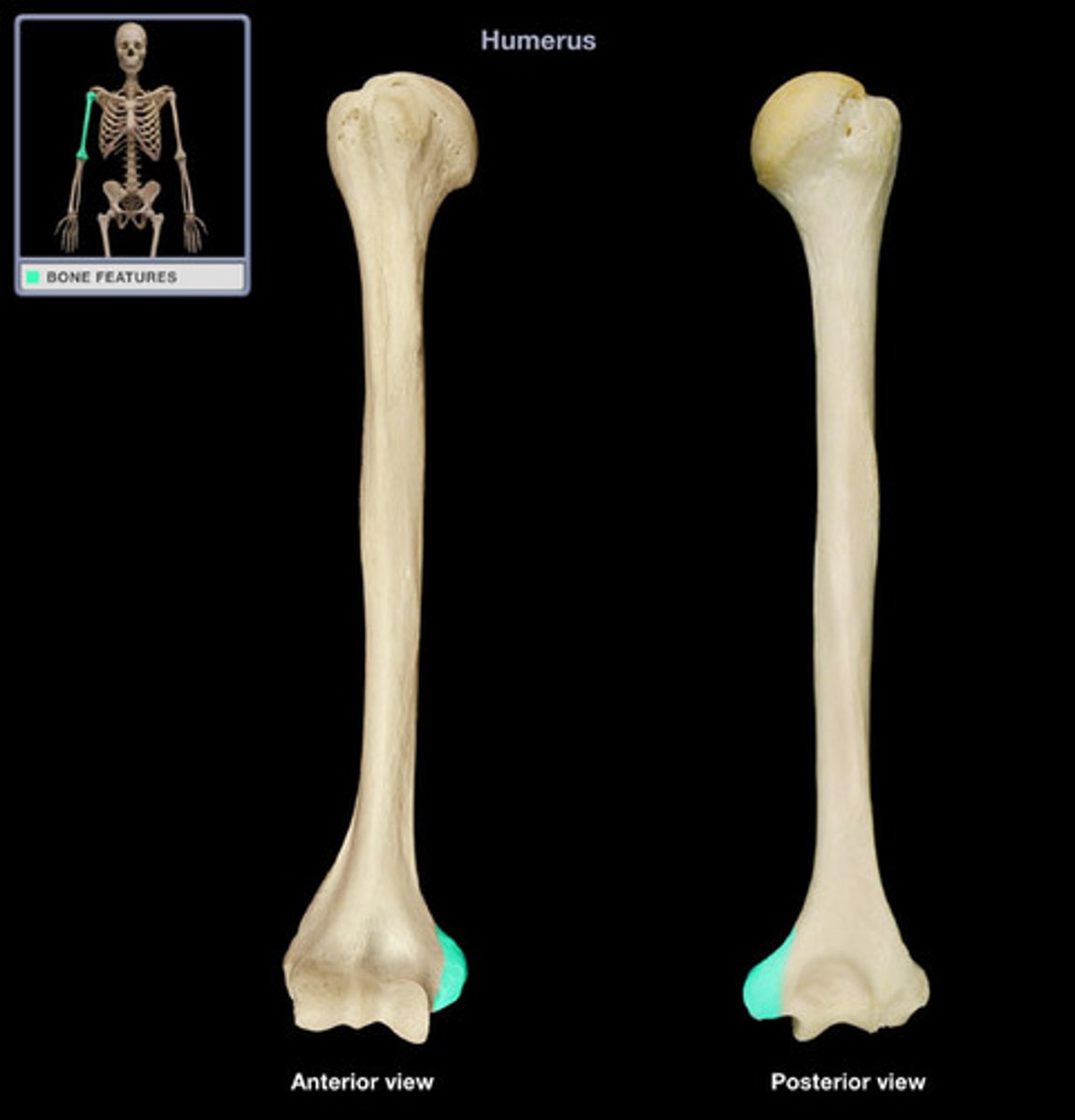
lateral epicondyle of humerus
How many bones are there in the human body
206
axial skeleton
The portion of the skeleton that supports and protects the head, neck, and trunk
appendicular skeleton
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
long bones
bones that are longer than they are wide
compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
short bones
Roughly cuboidal in shape, include the ankle and wrist bones.
flat bones
These bones are thin, flat, and curved. They form the ribs, breastbone, and skull.
irregular bones
Complicated shapes
Vertebrae and hip bones
sesamoid bones
round bones found near joints bound in a tendon (patella)
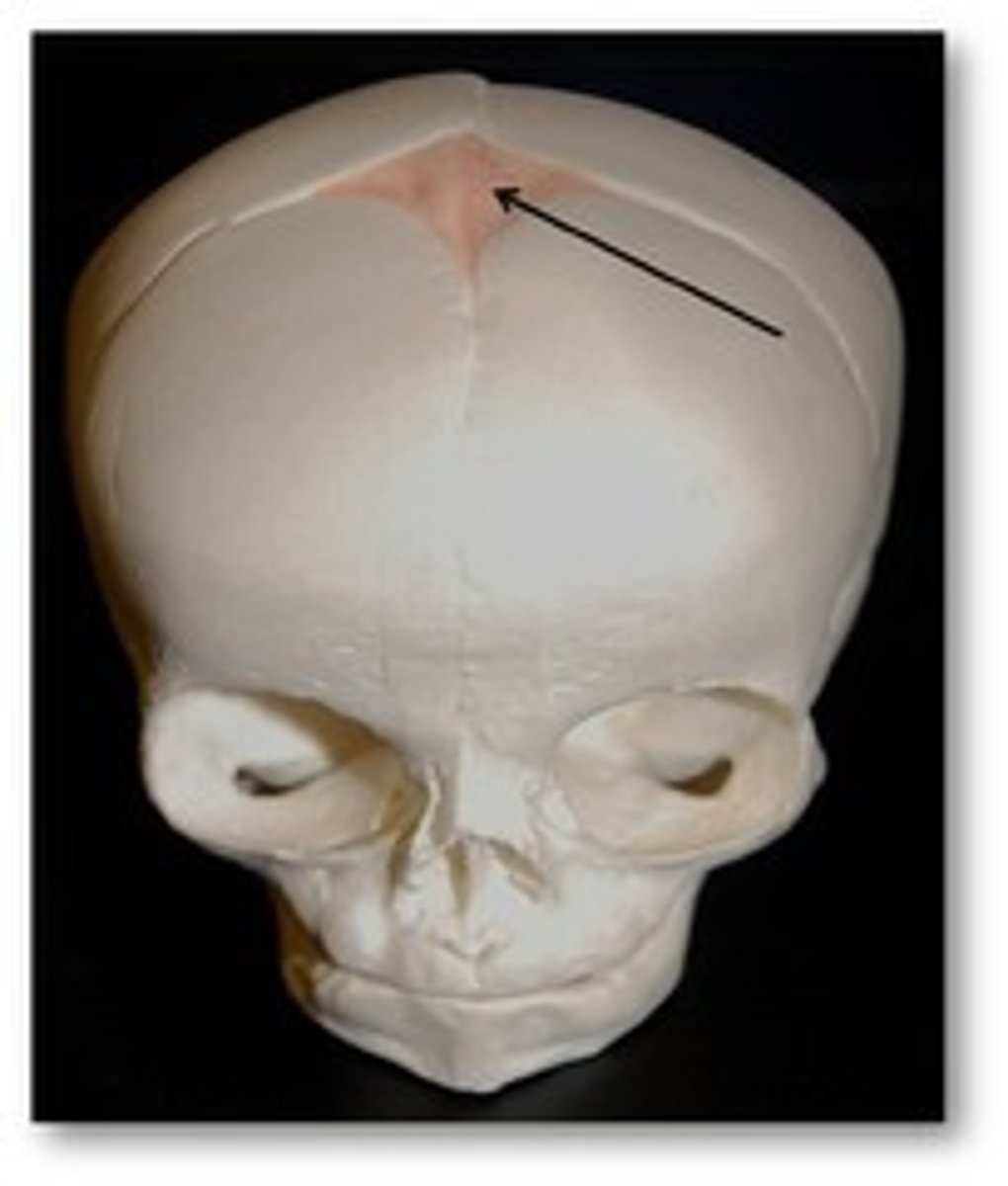
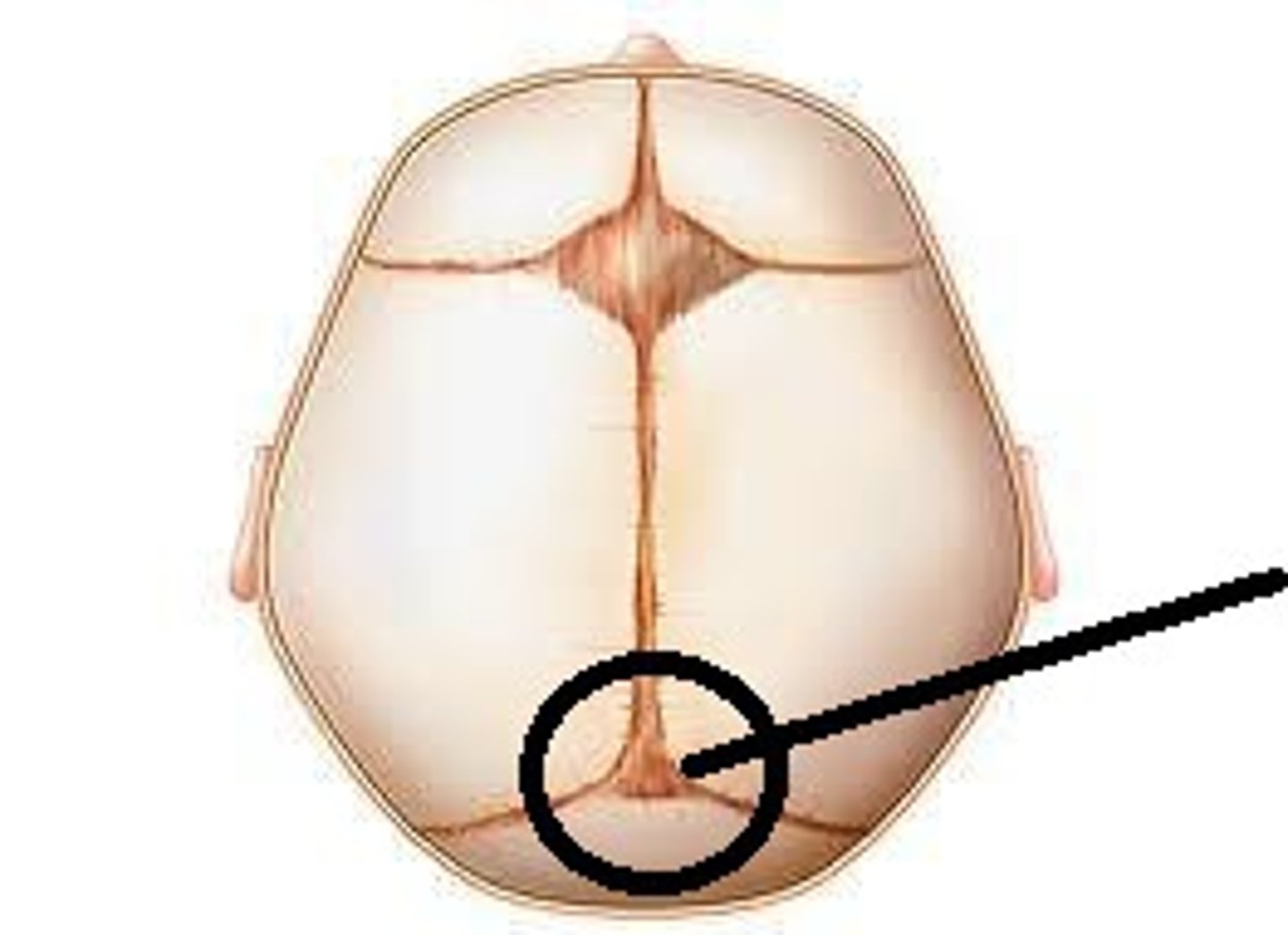
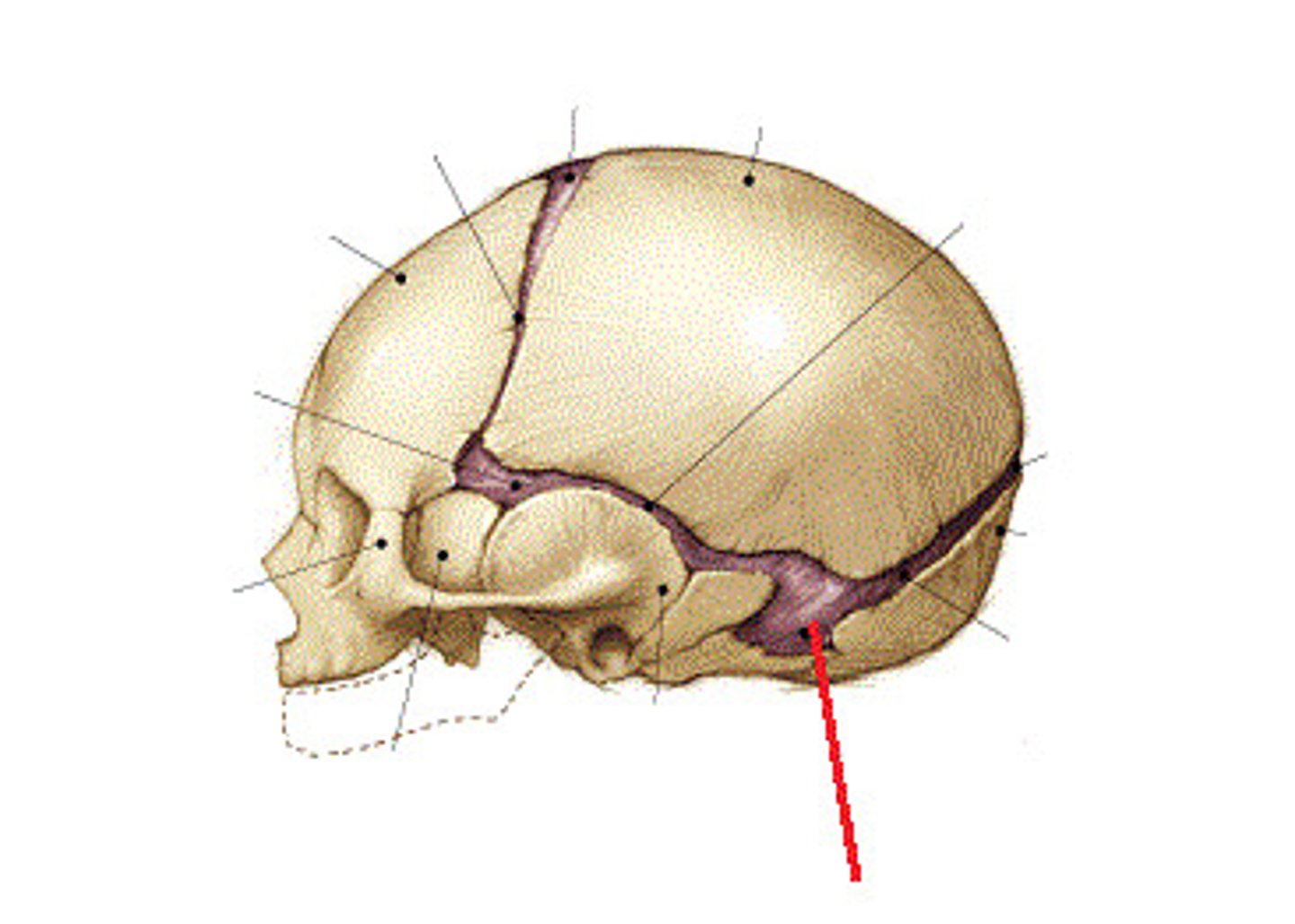
fontanels
fibrous membranes connecting the cranial bones
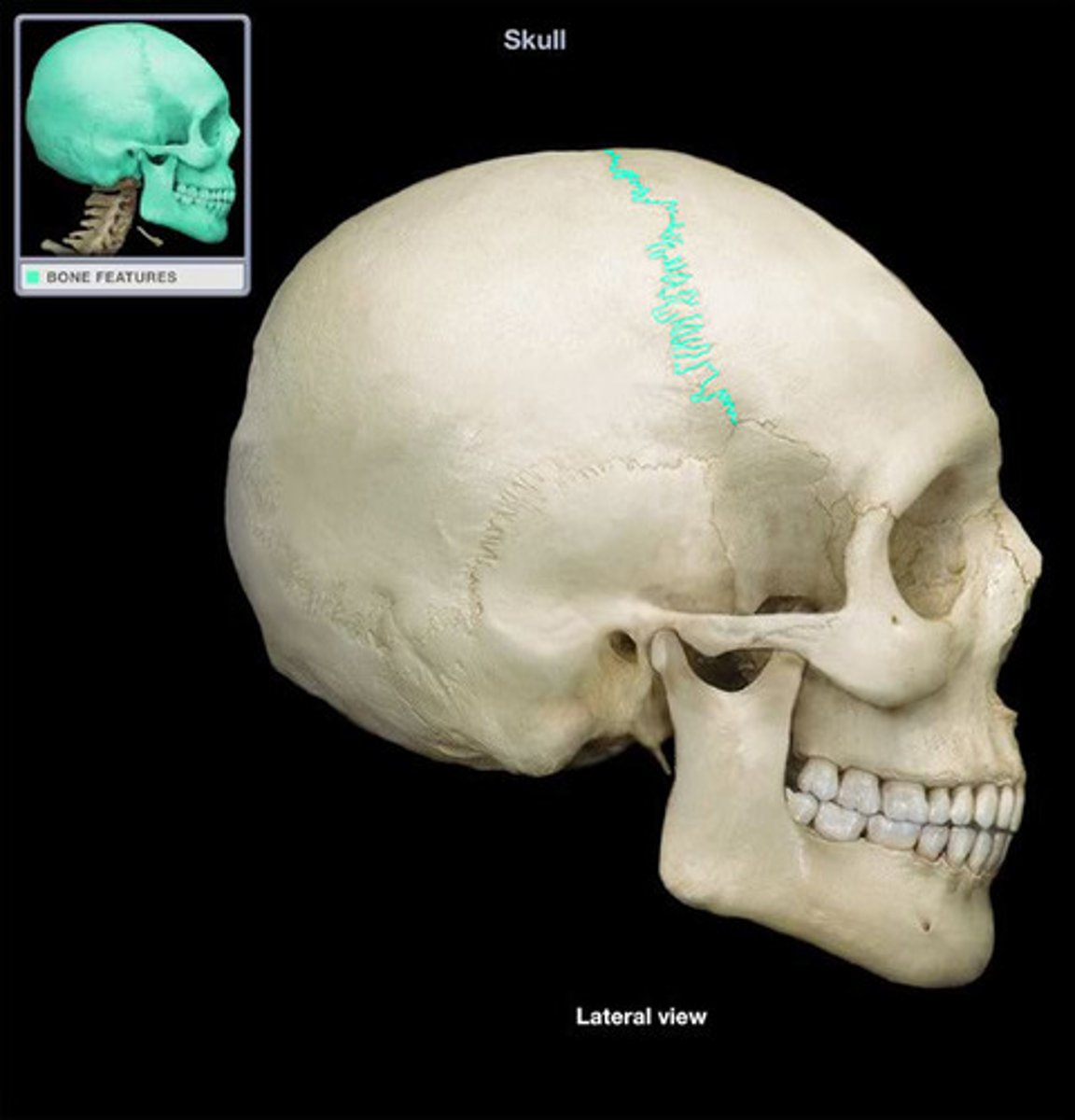
coronal suture
Sphenoid fontanelle
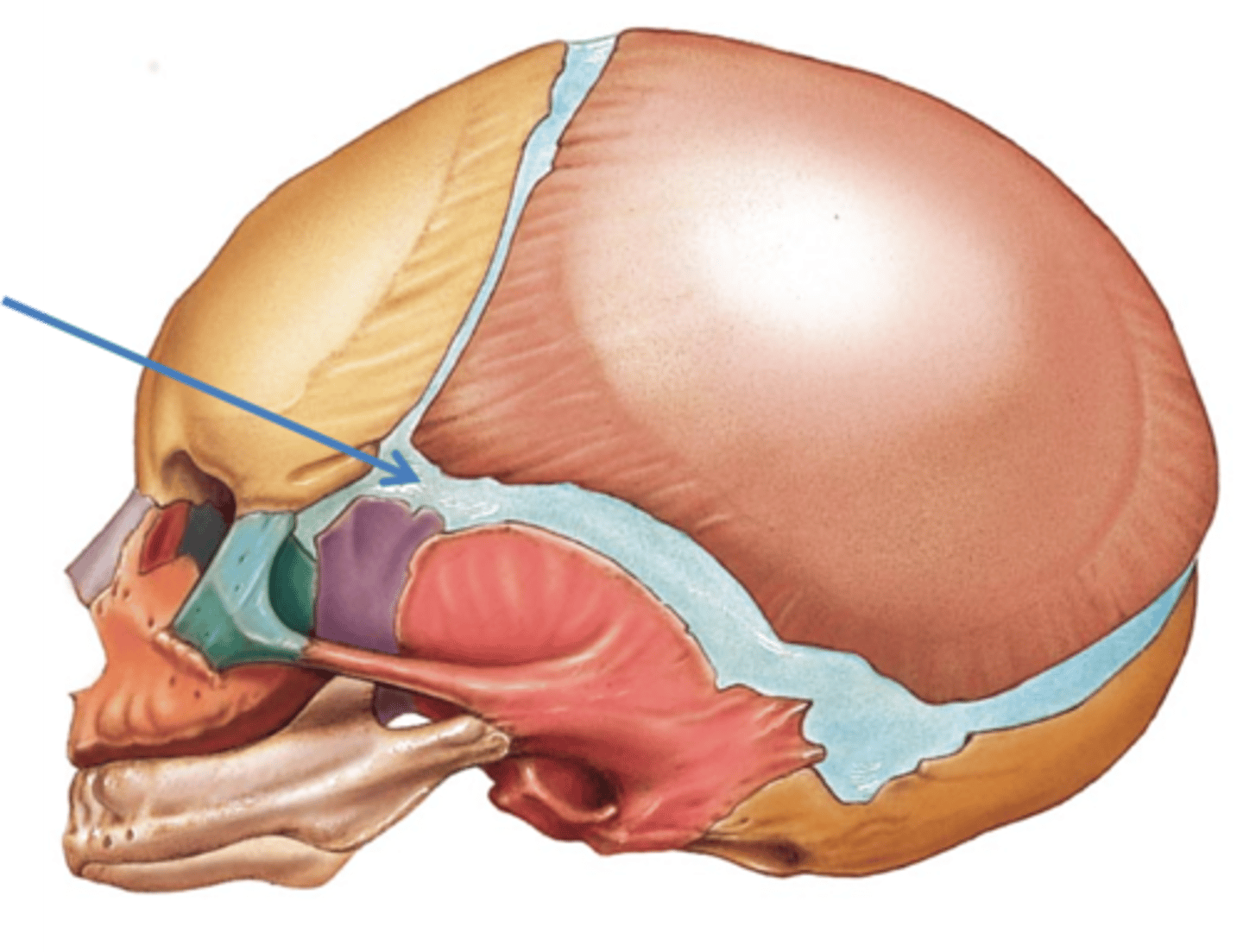
frontal fontanel
Occipital fontanelle
mastoid fontanelle
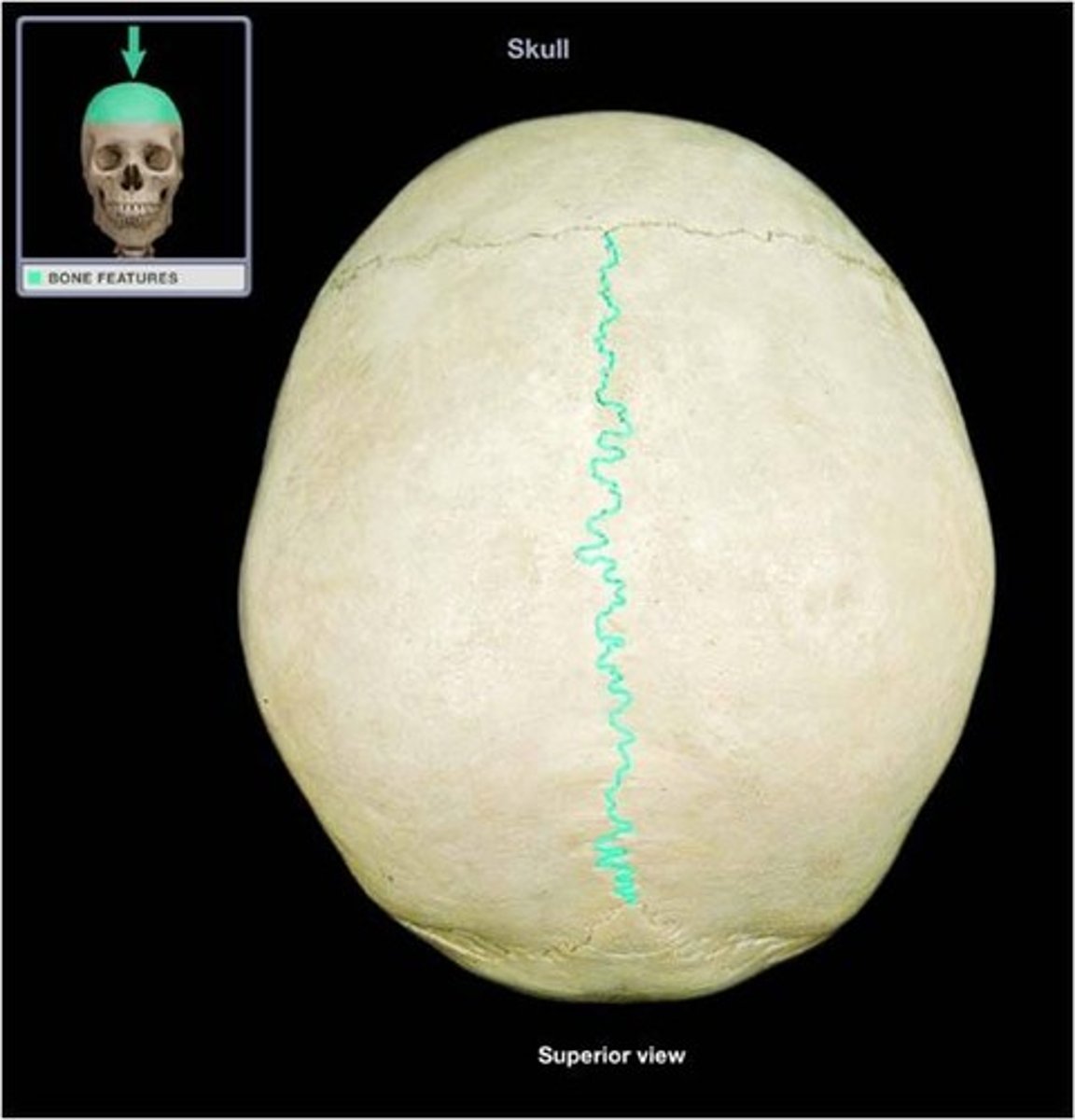
sagital suture
how many bones in adult skull
22
frontal bone
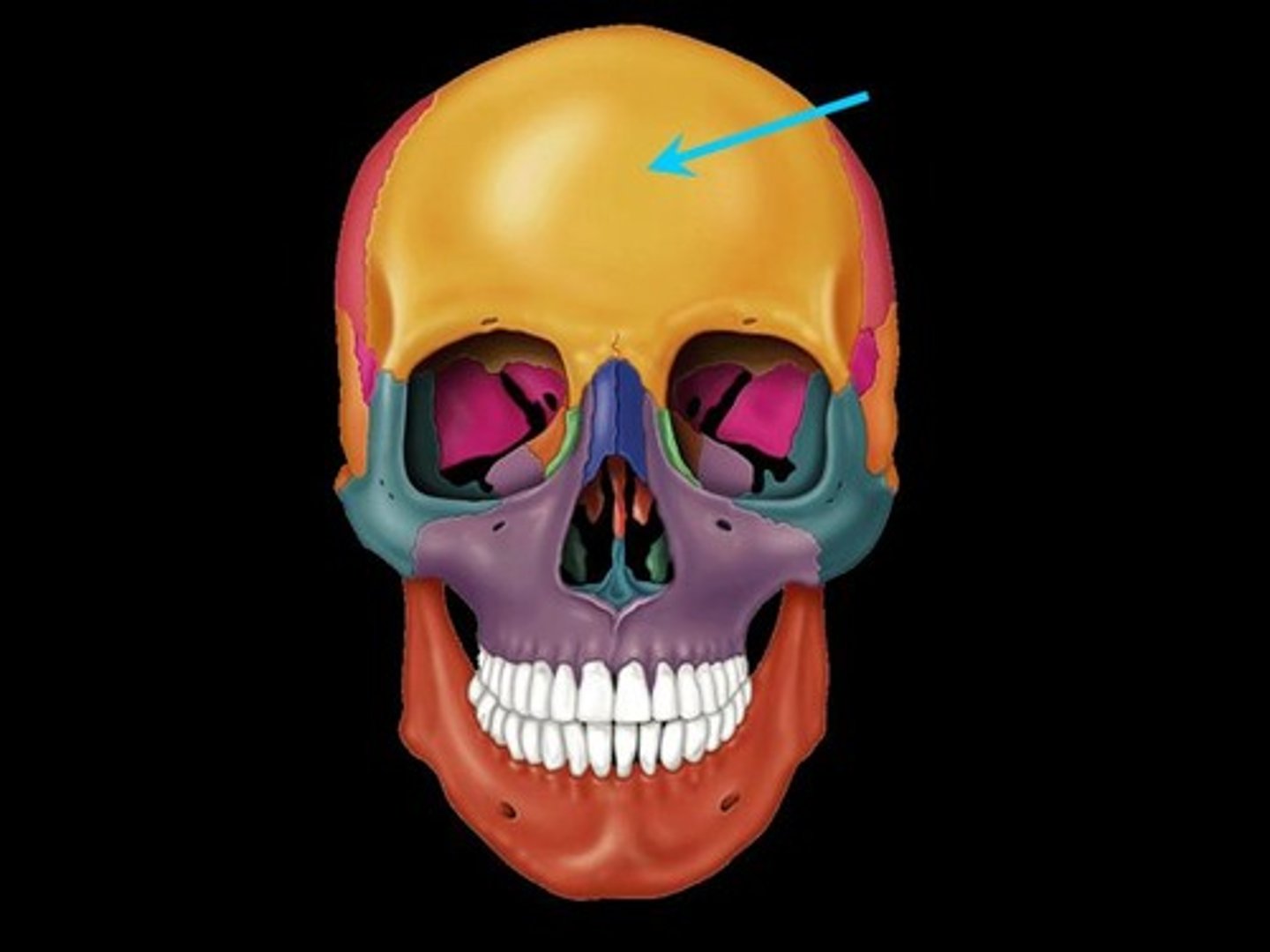
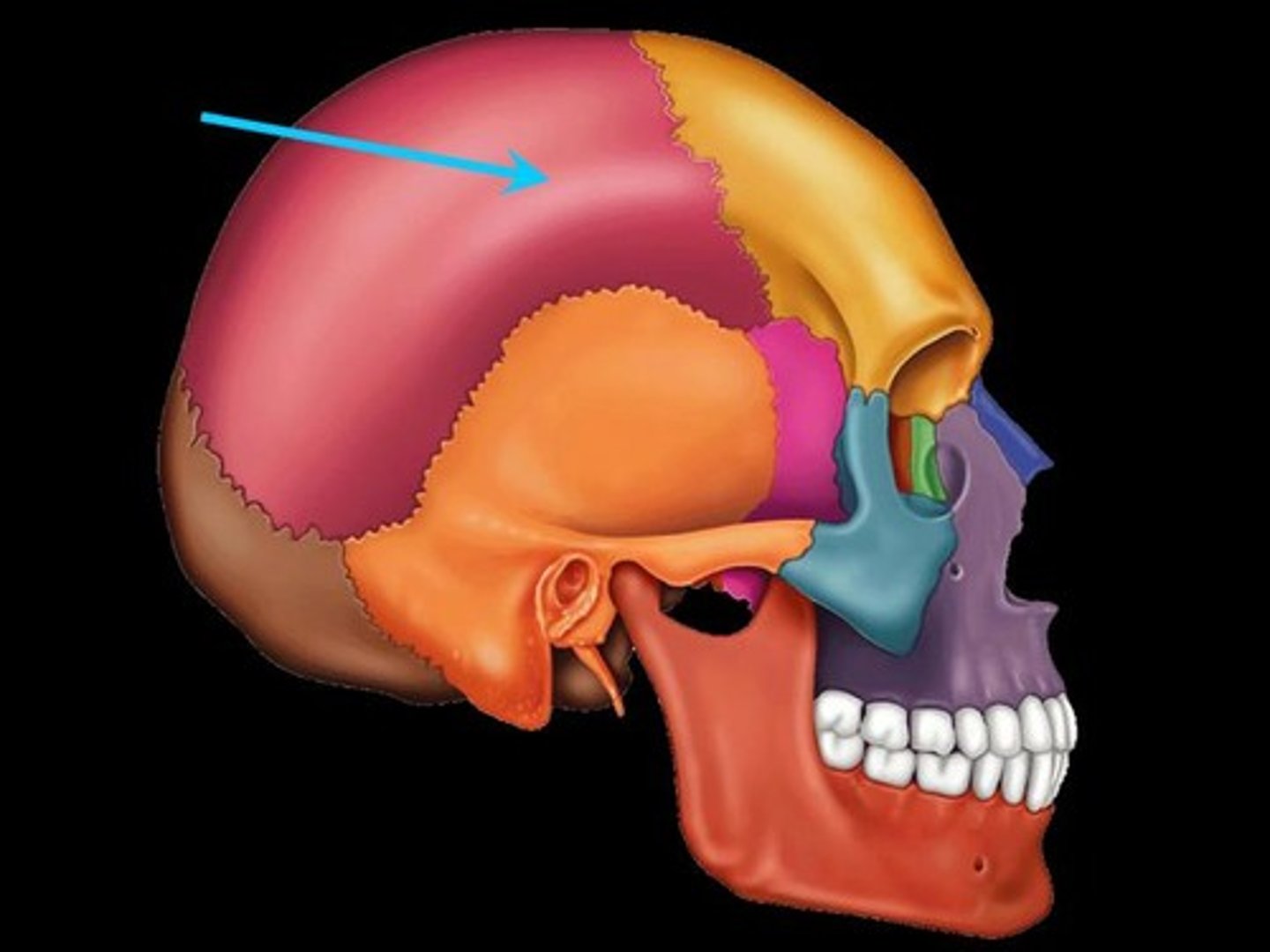
parietal bones
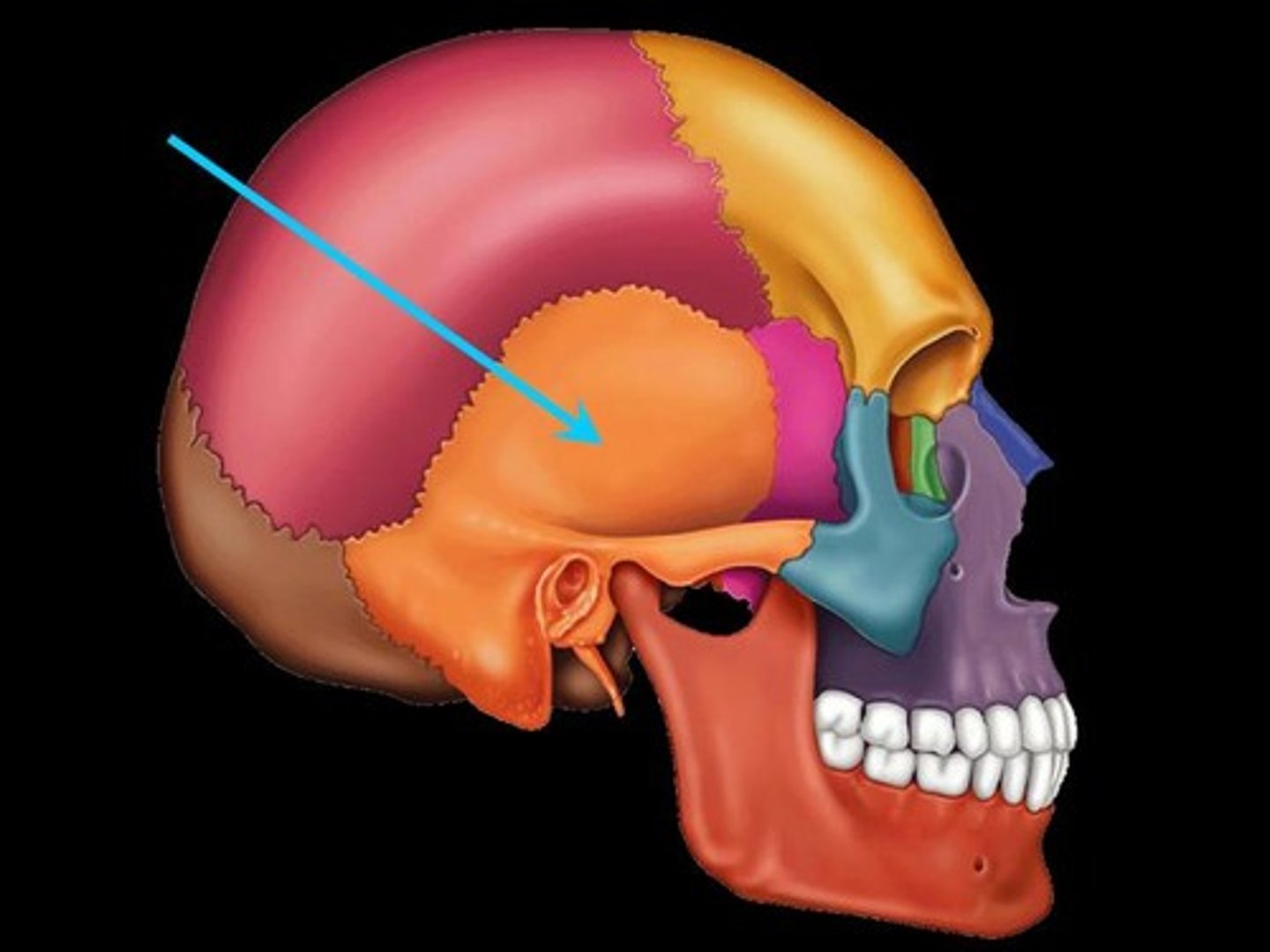
temporal bone
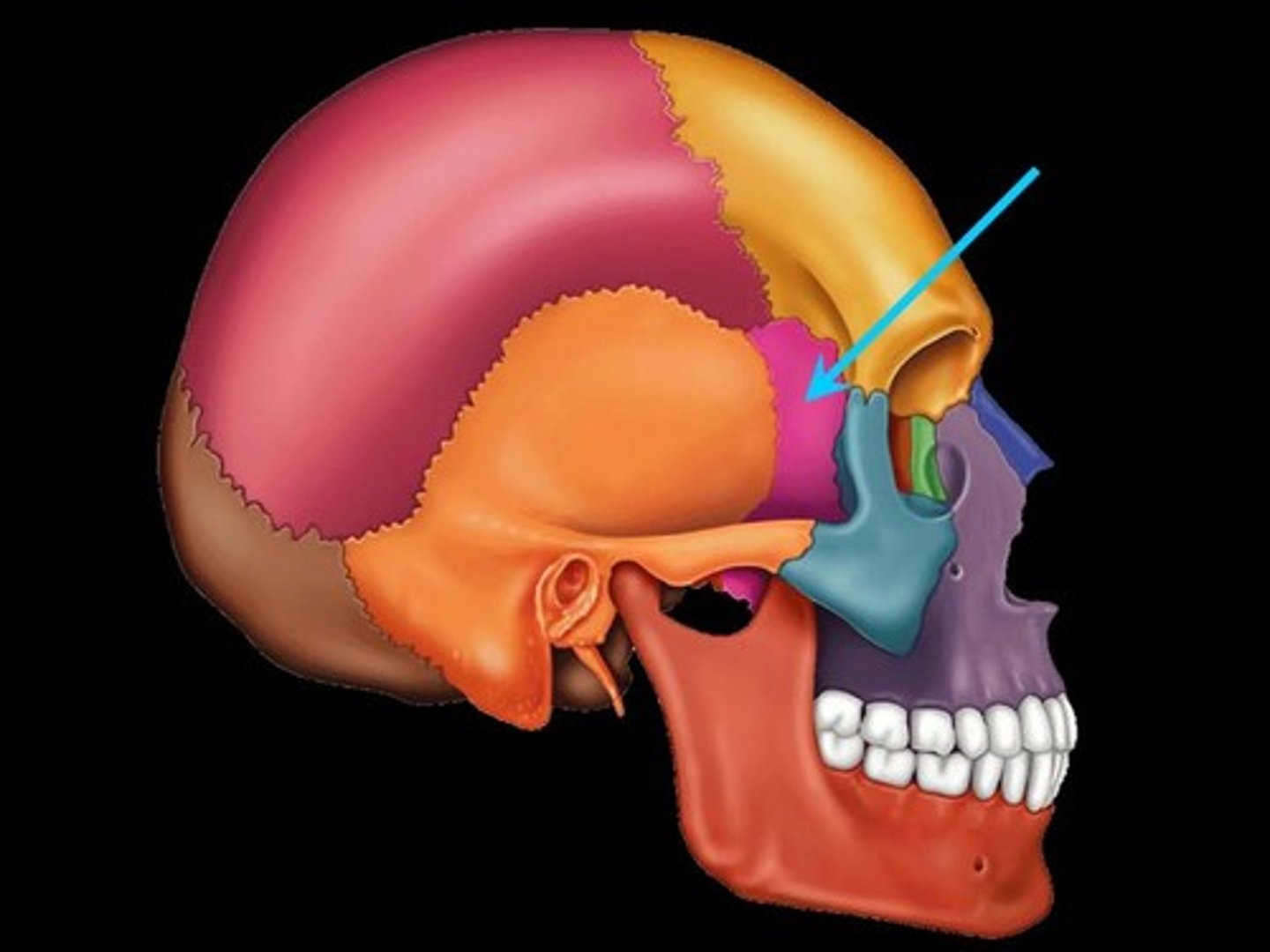
sphenoid bone
nasal bone
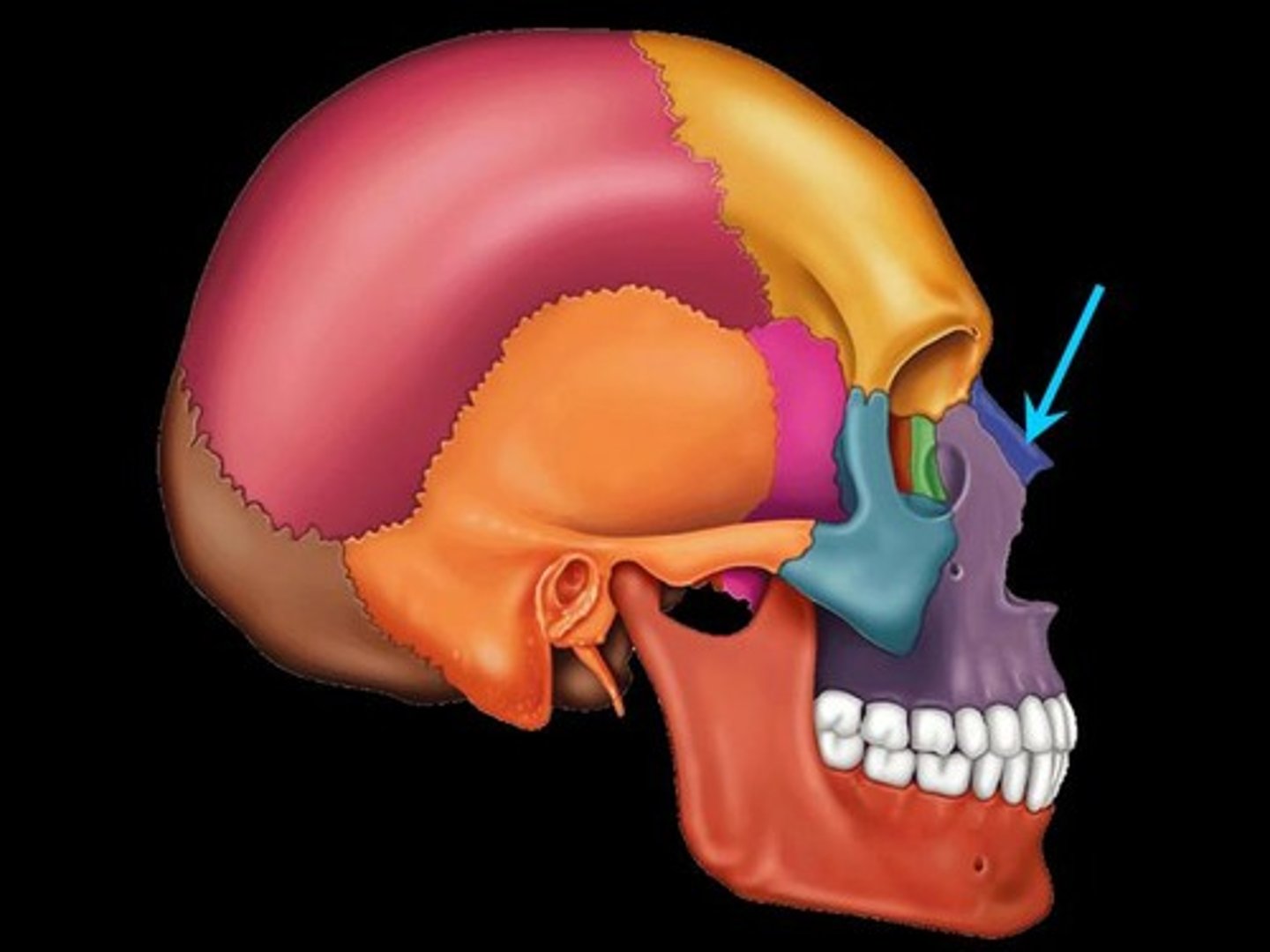
lacrimal bone
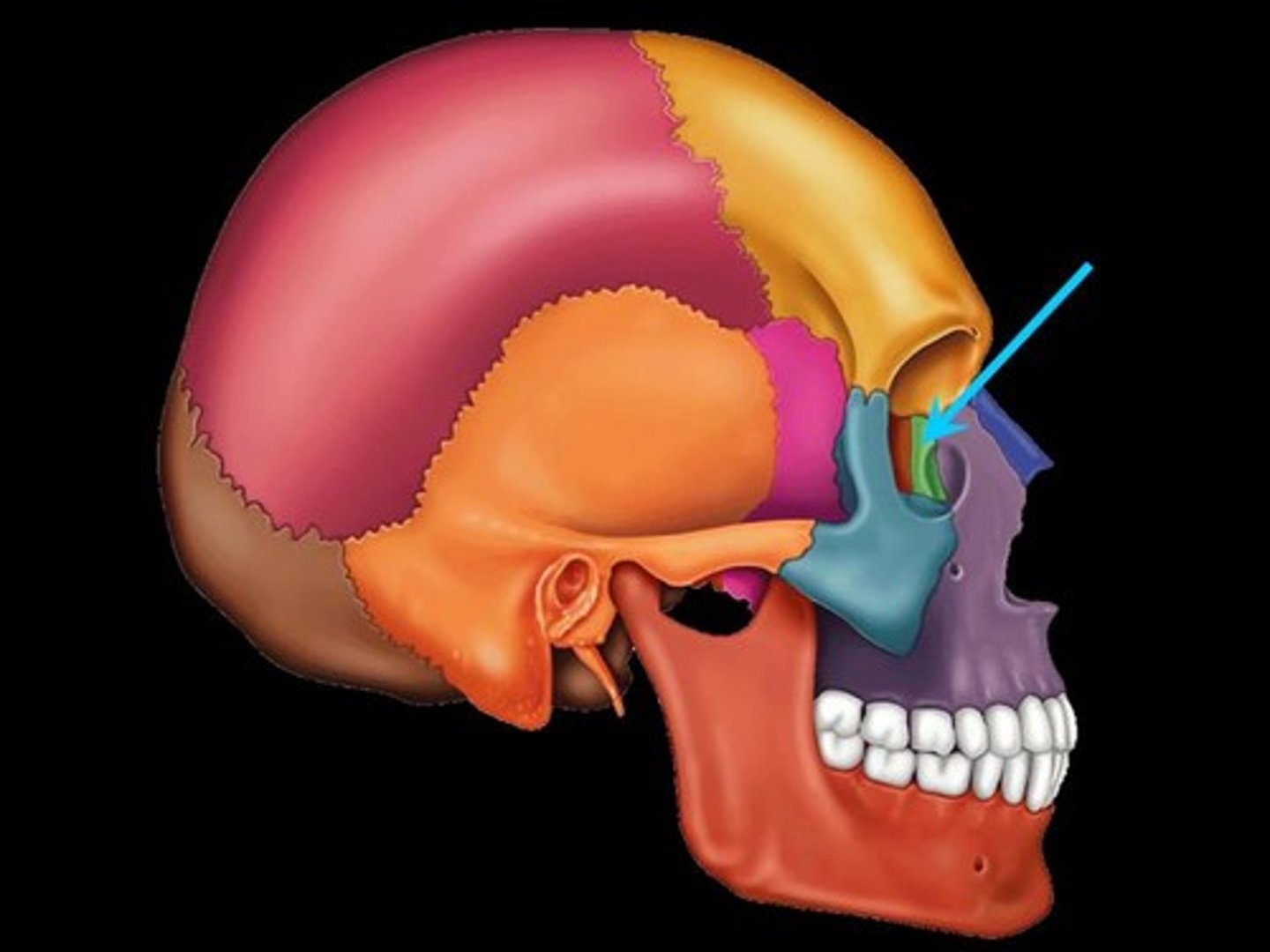
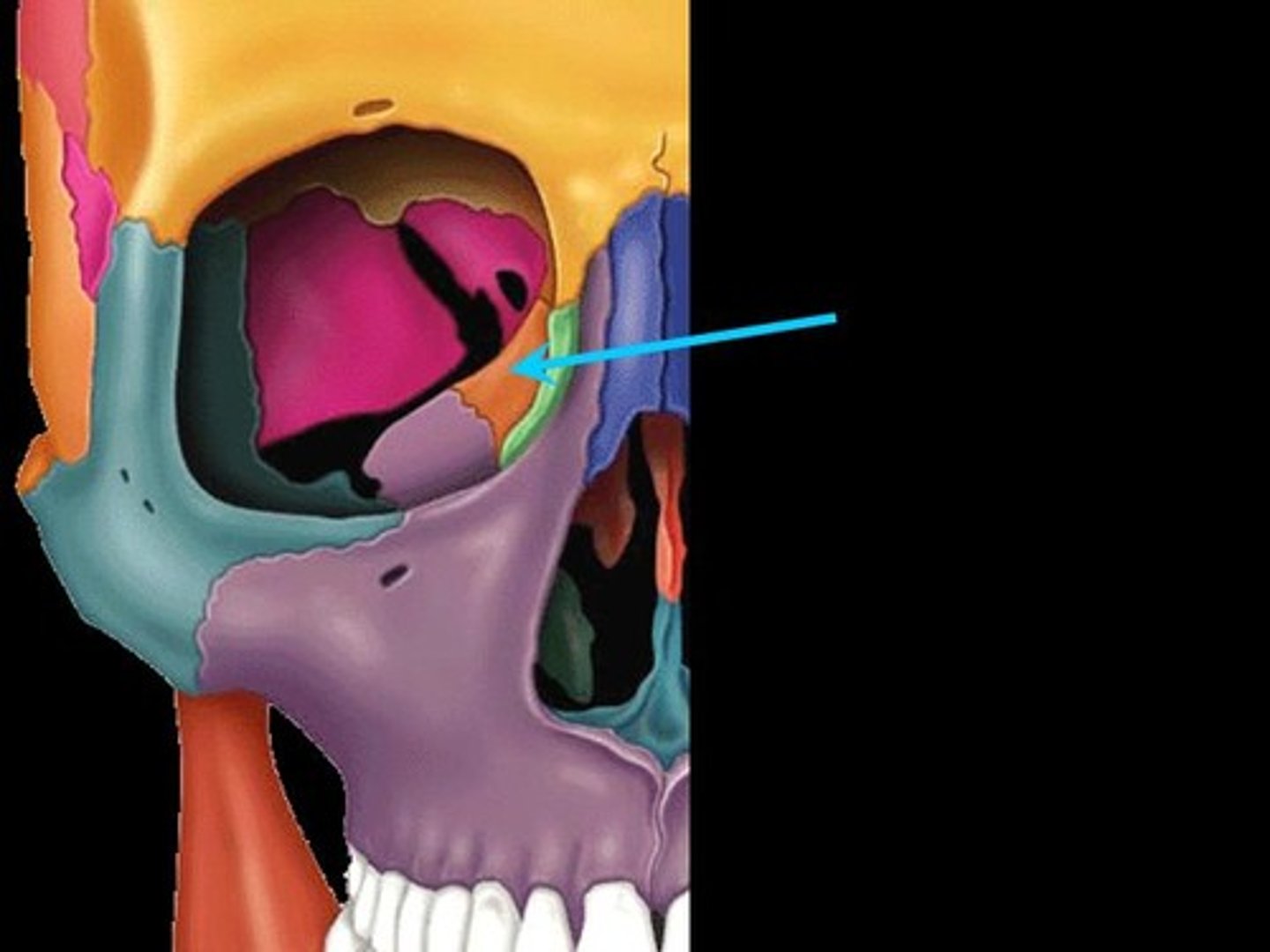
ethmoid bone
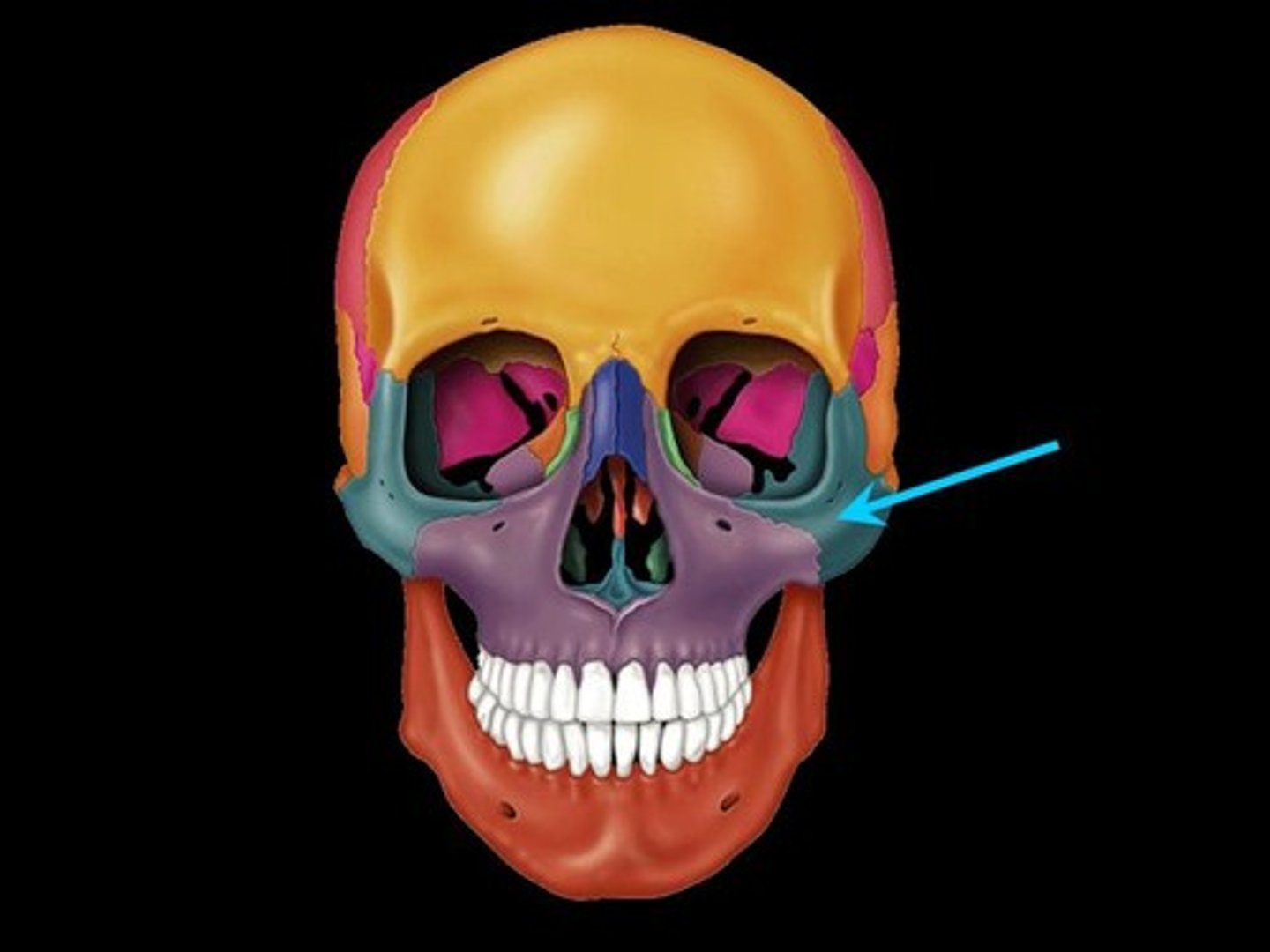
Zygomatic bone
nasal conchae
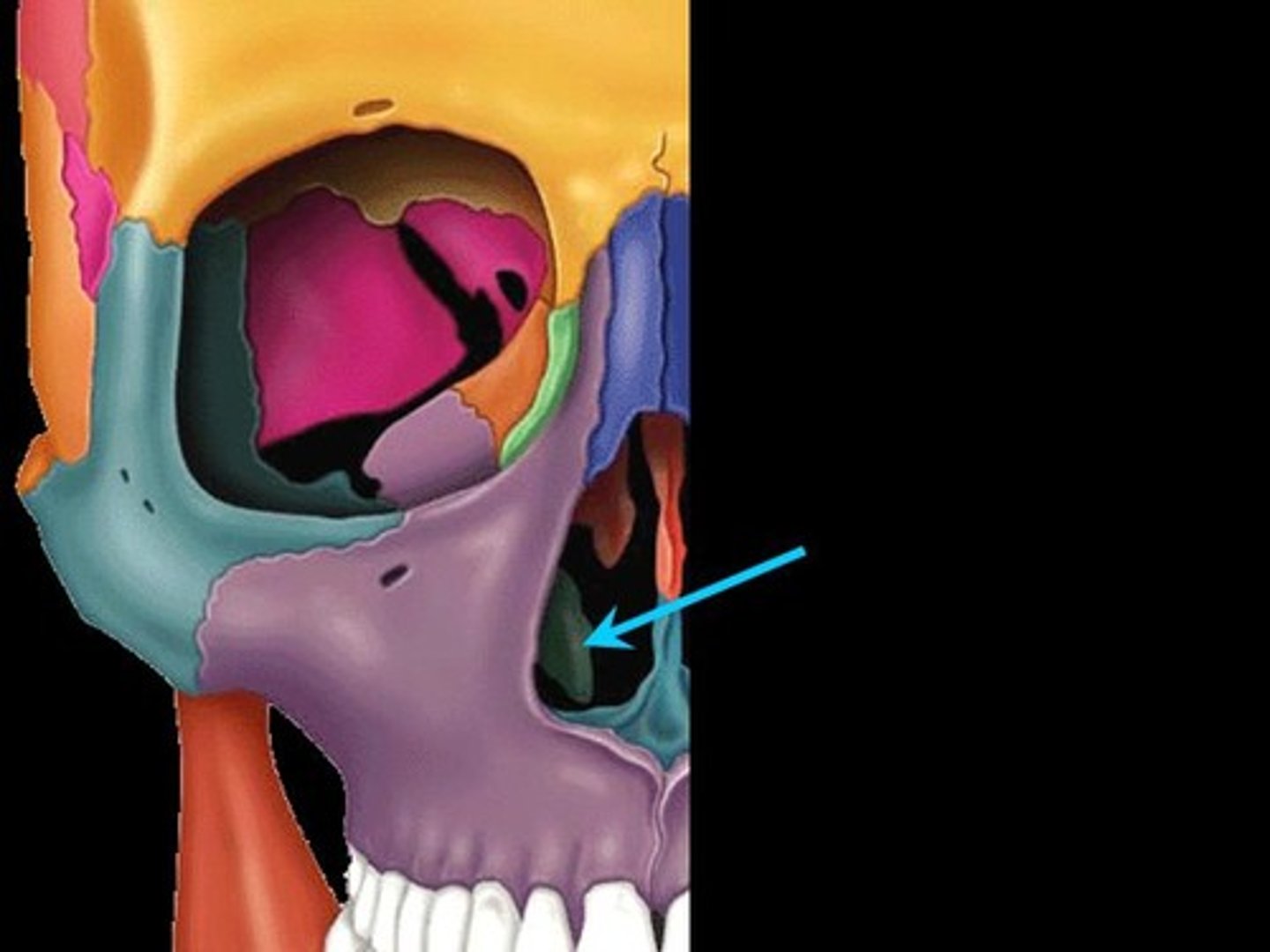
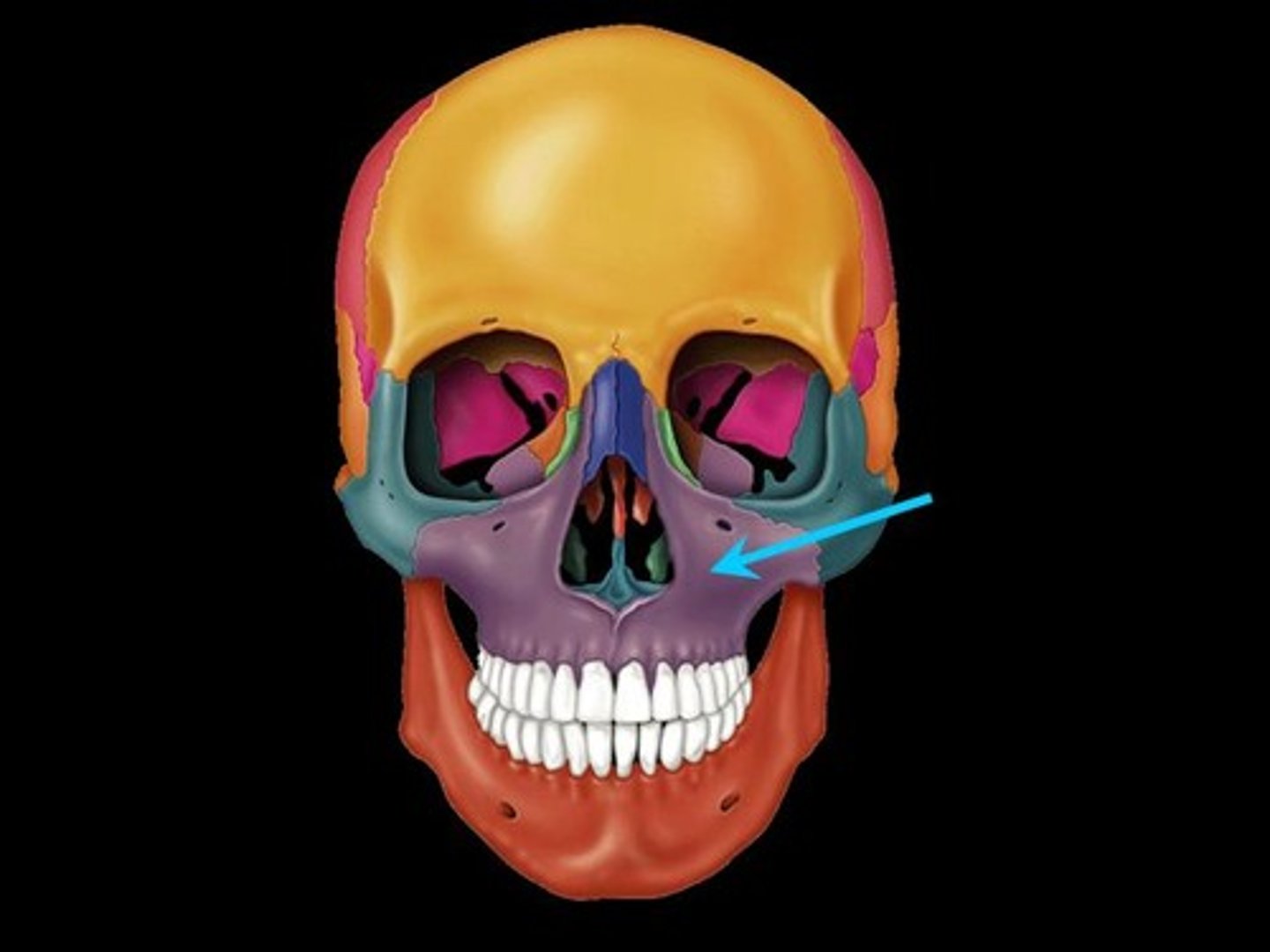
maxiallary bone
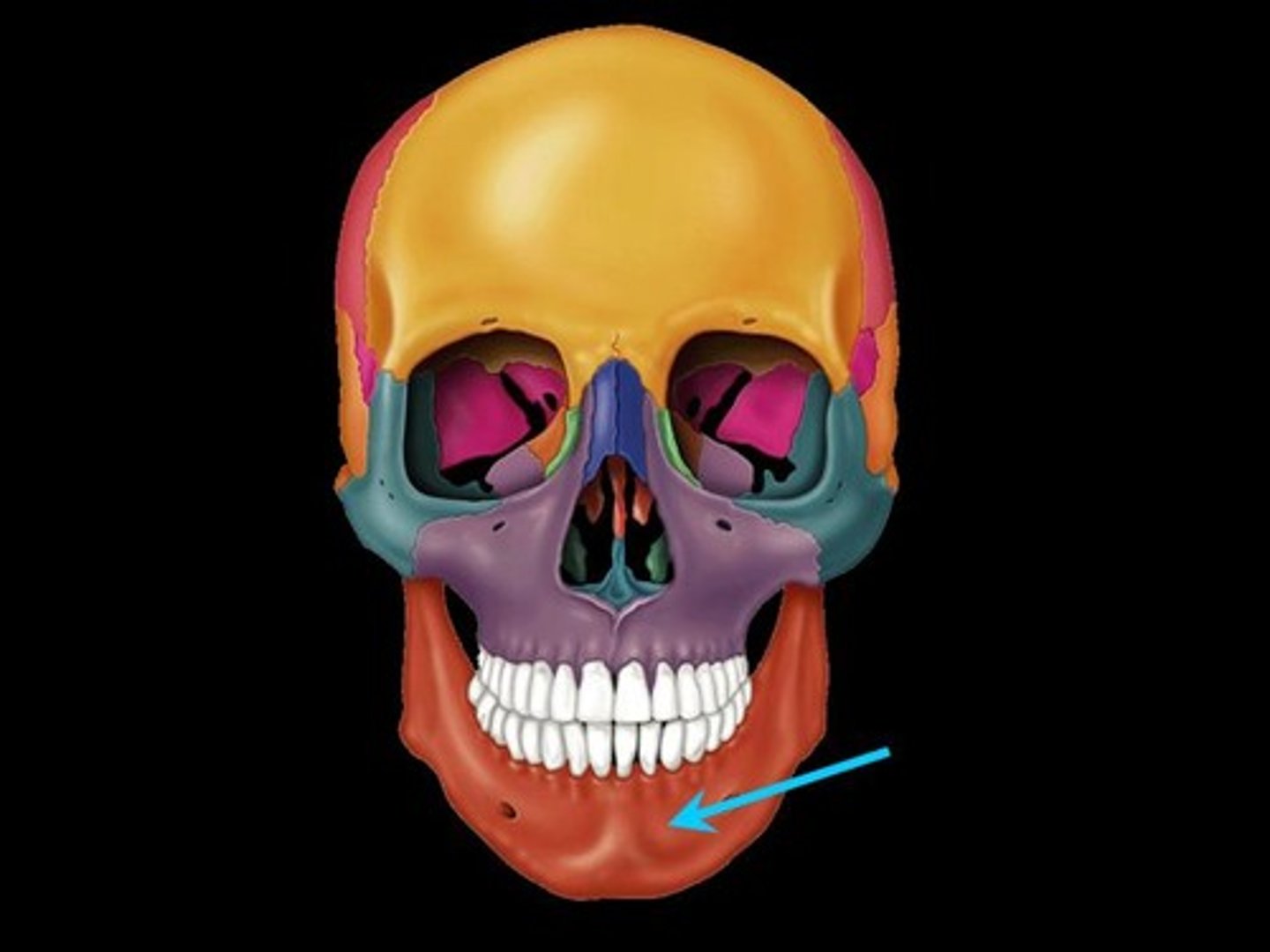
mandible
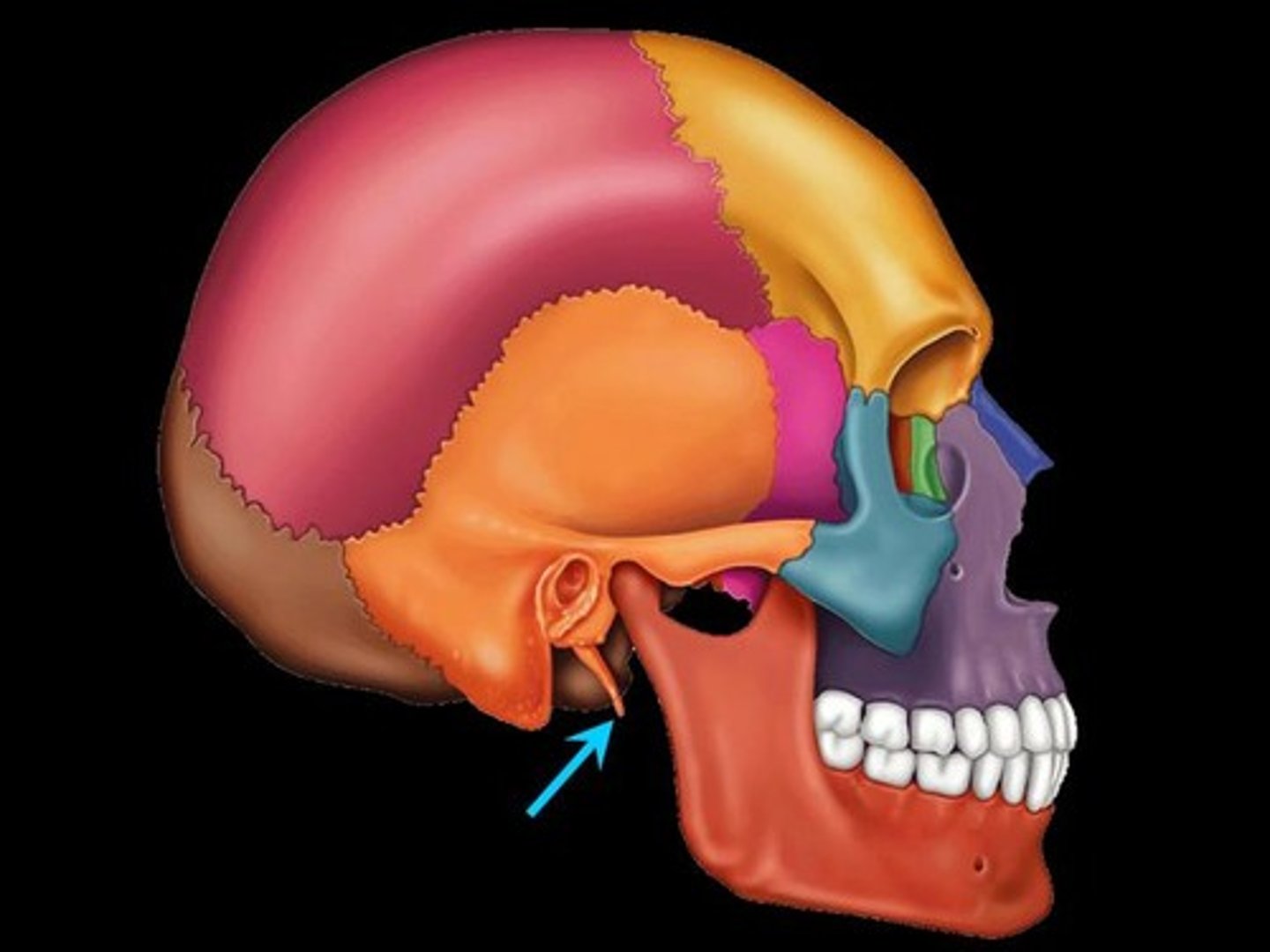
styloid process
mastoid process
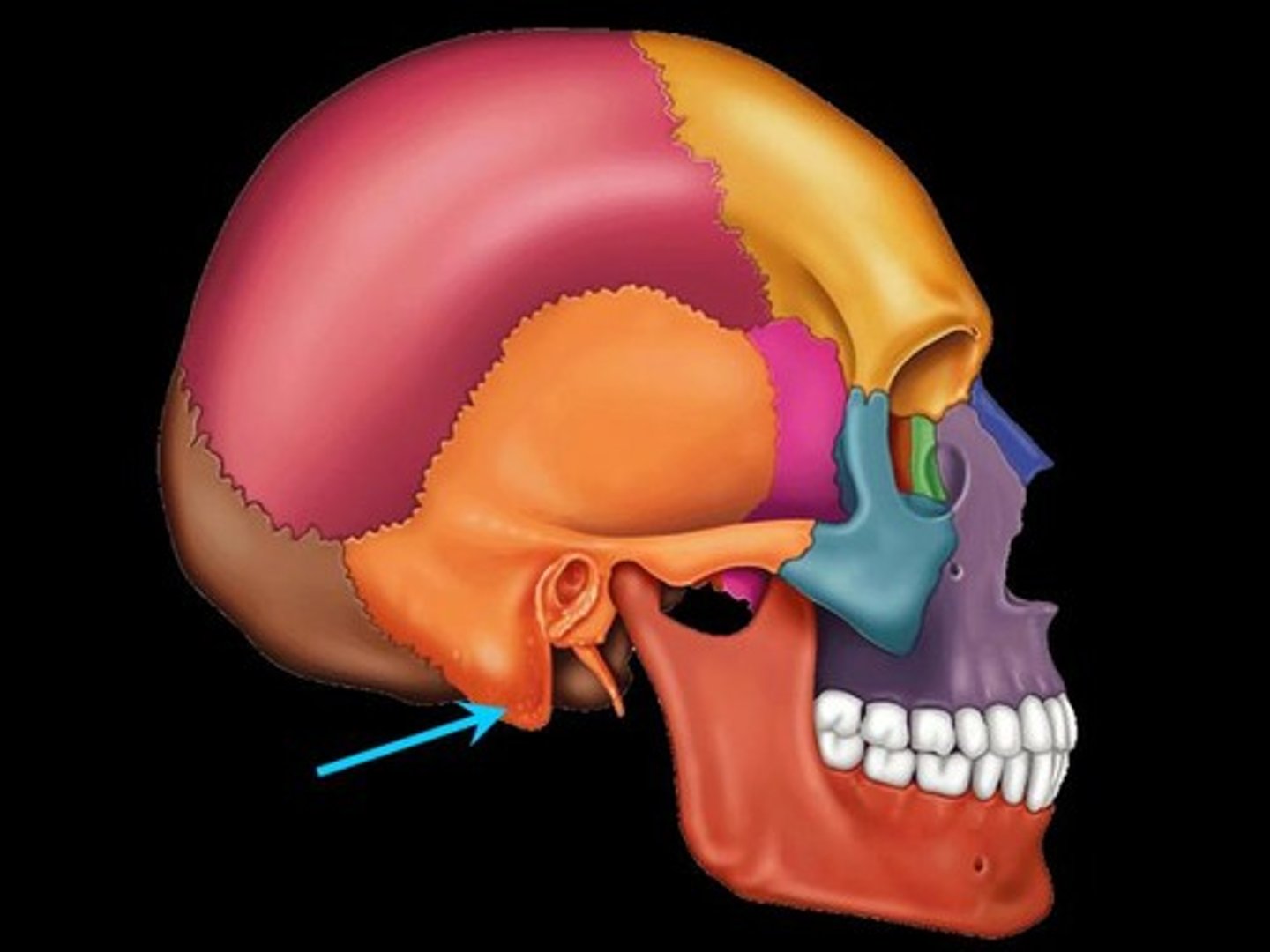
external auditory meatus
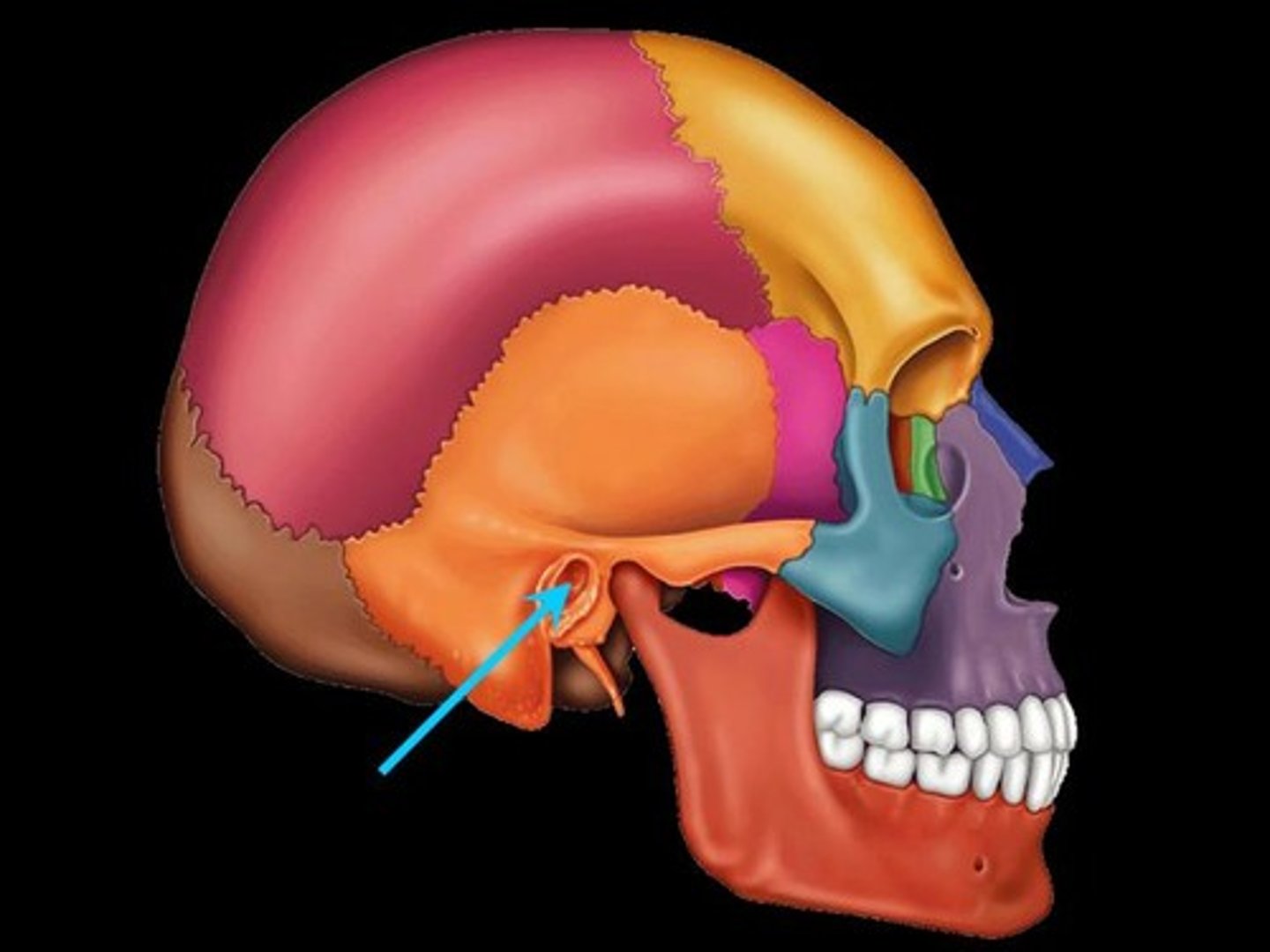
mandibular condyle
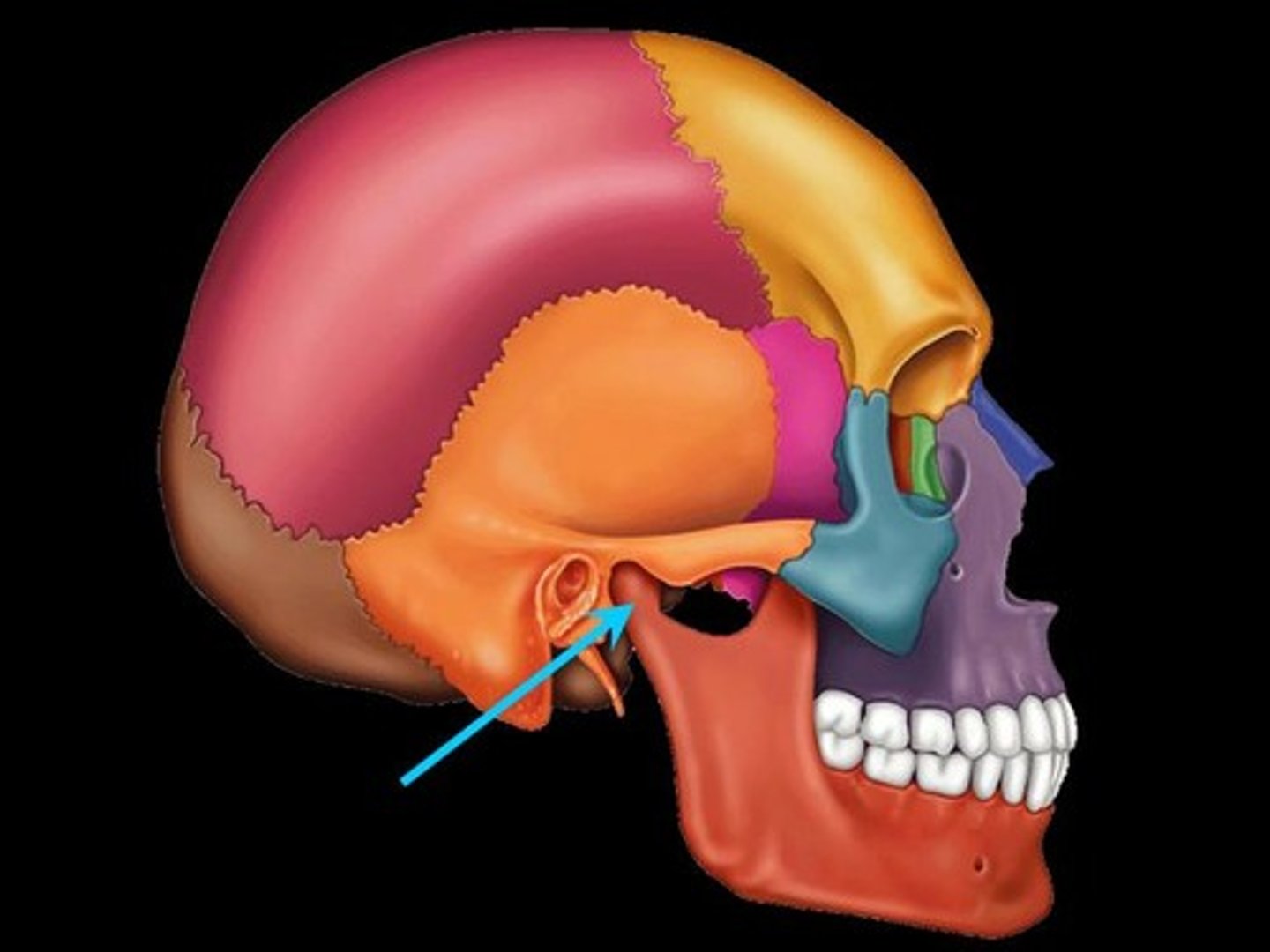
what is the only movable bone in the skull
mandible
what is the practical purpose of frontanels
provide flexibility
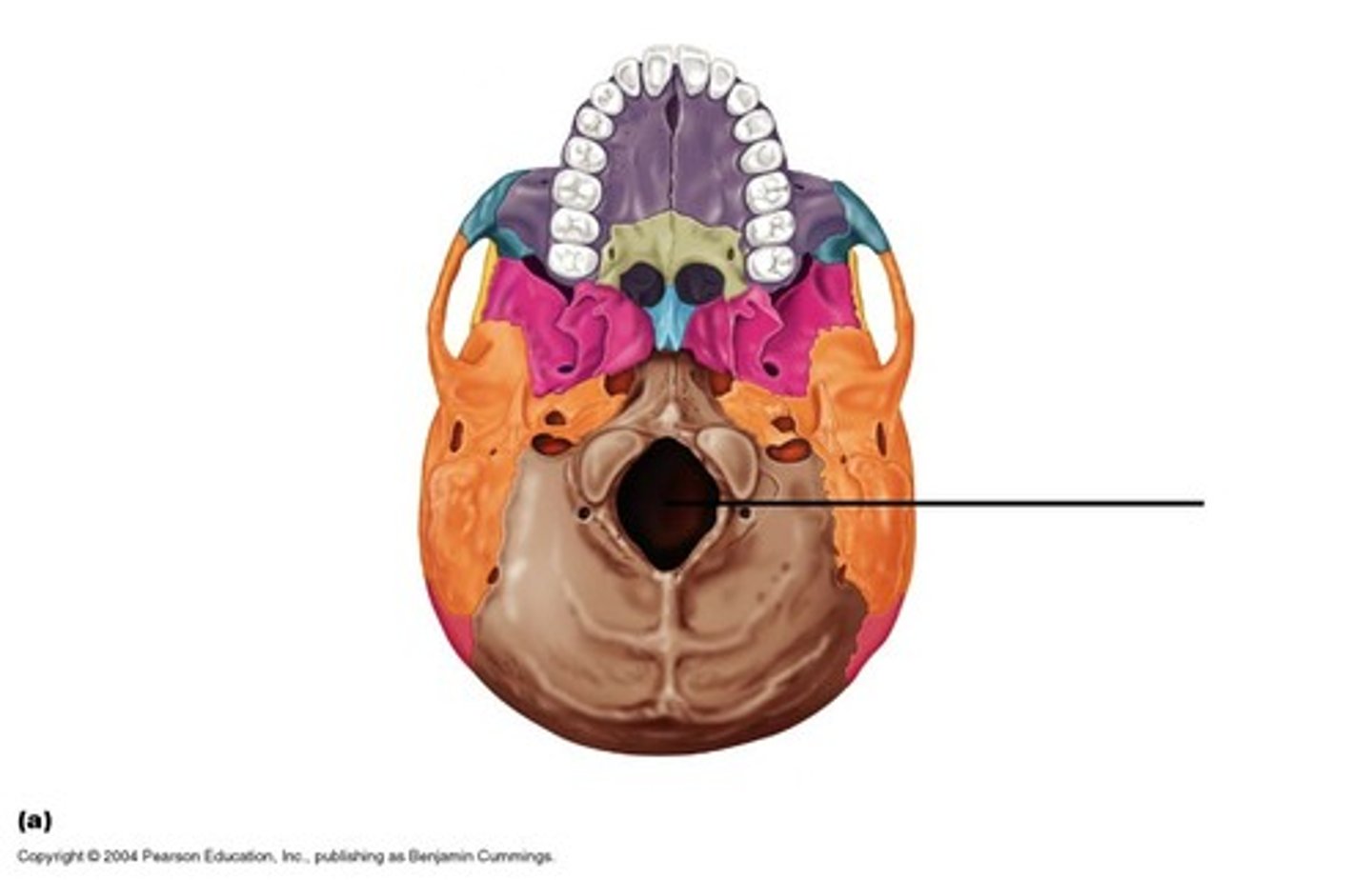
what structure passes through the foramen magnum
spinal cord
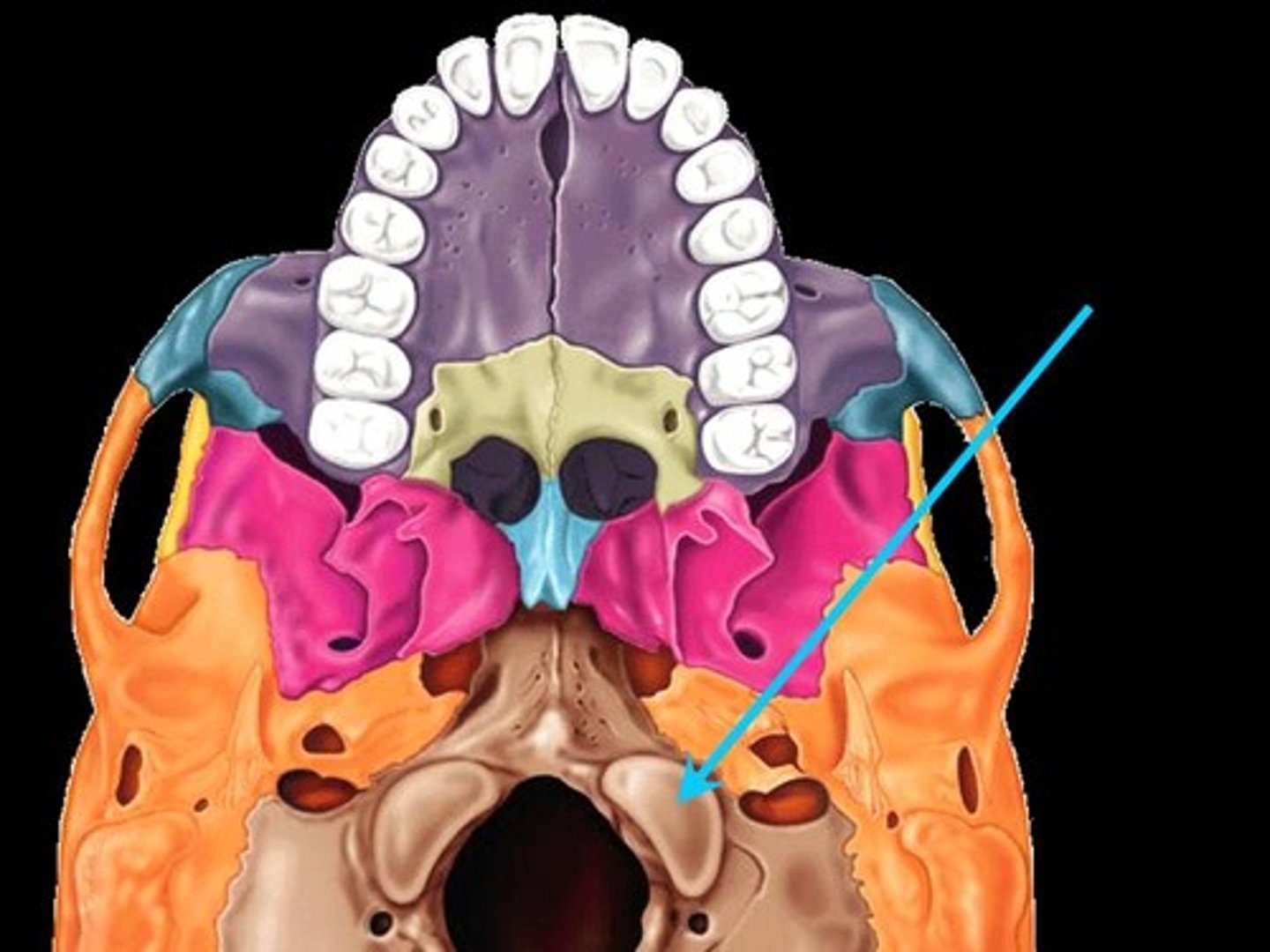
the occipital condyles rest upon
C1 - atlas
how many bones form the face
14
how many bones form the eye orbit
7
vomer
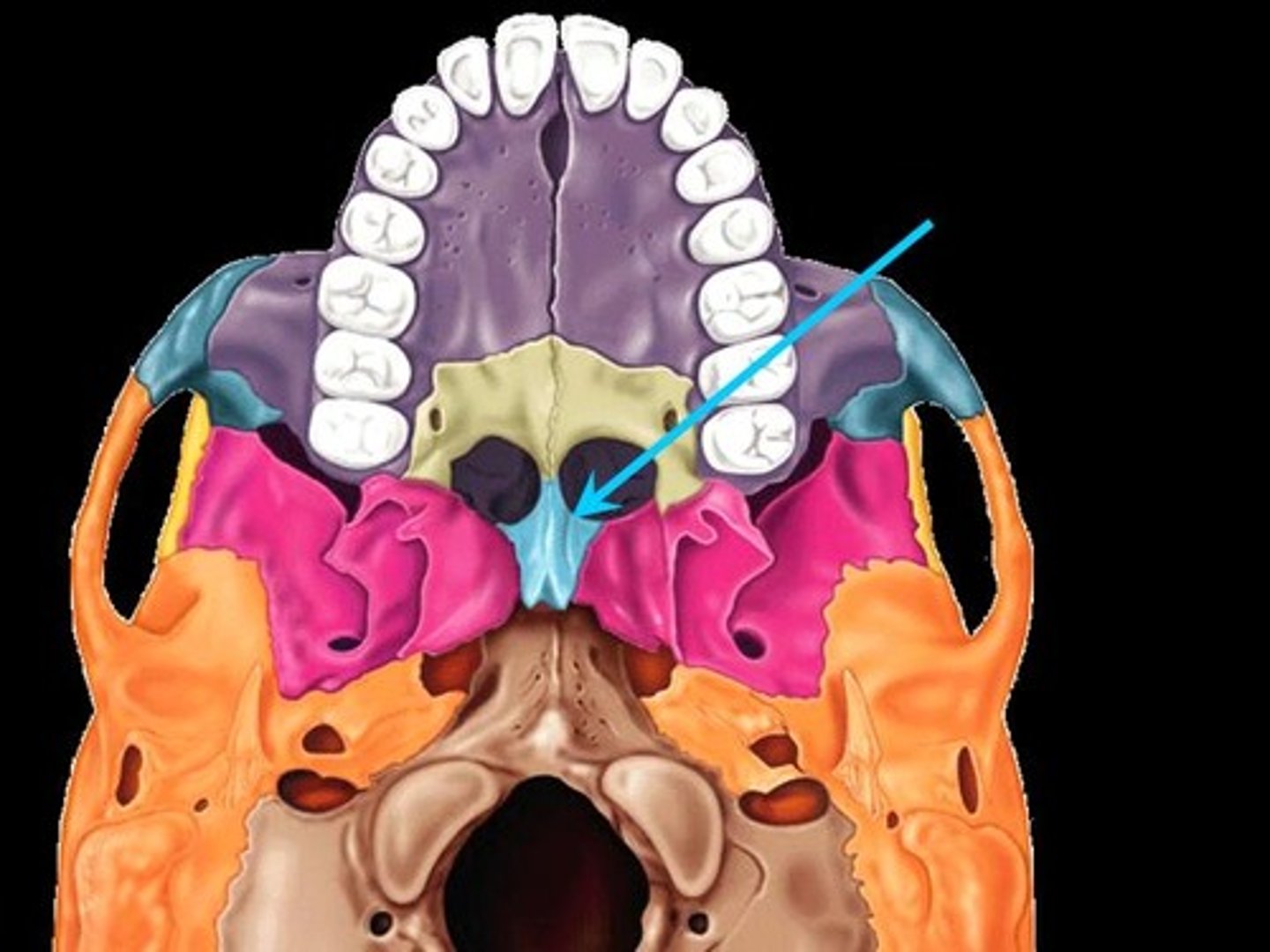
palitine
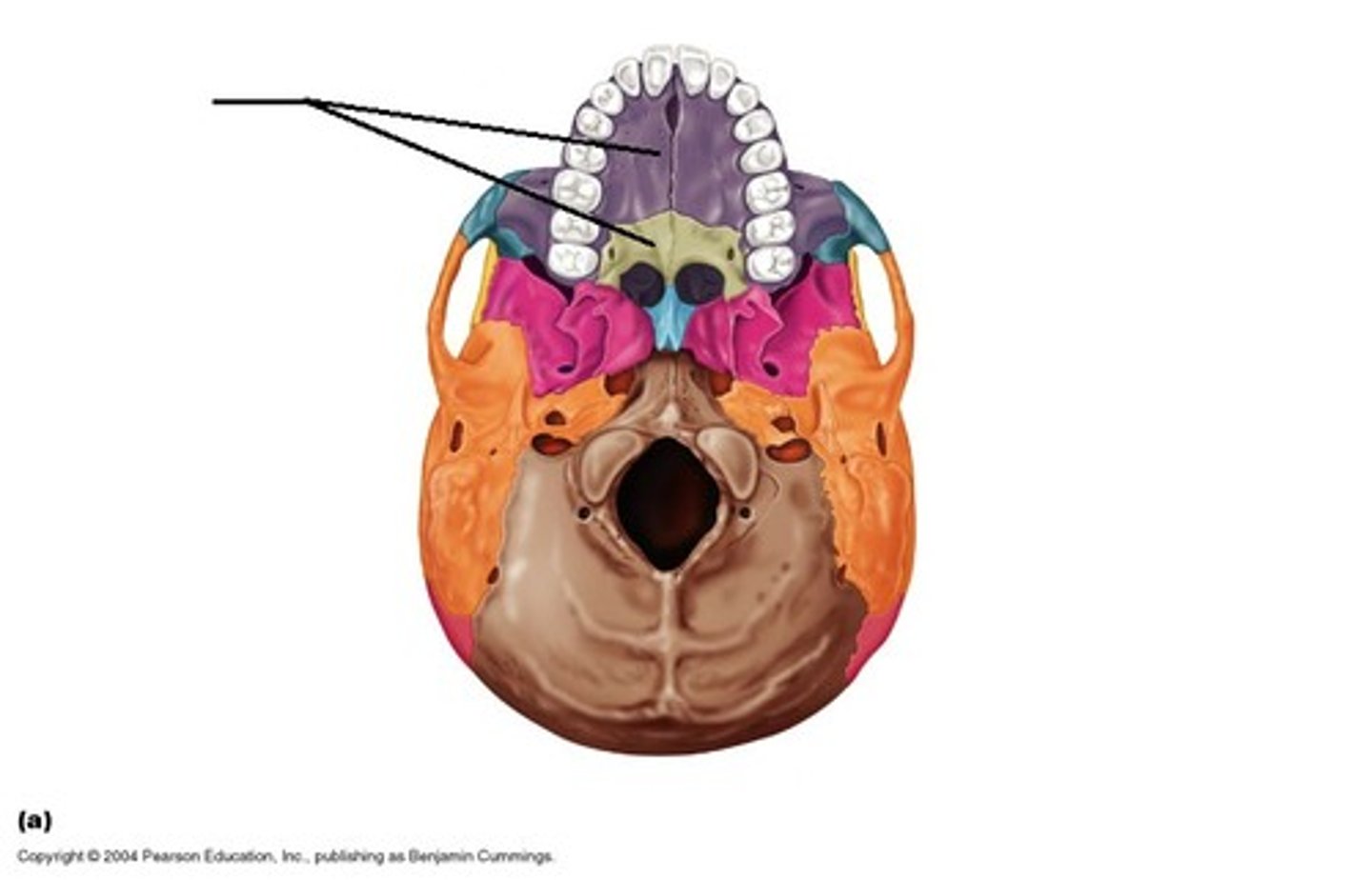
foramen magnum
occipital condyles
hyoid bone
U-shaped bone at the base of the tongue that supports the tongue and its muscles.
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
cervicle vertebrae
C1-C7
smallest and lightest
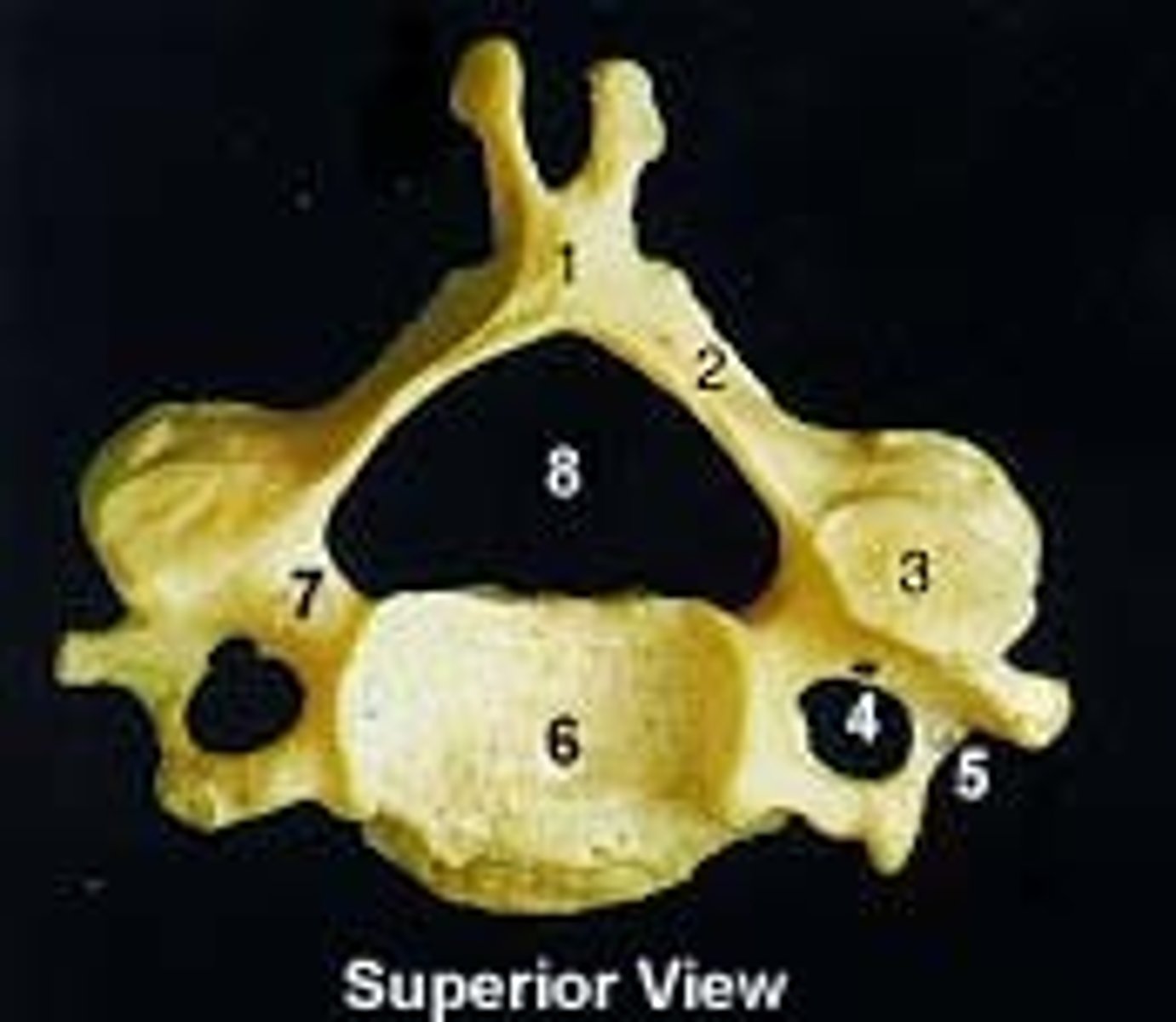
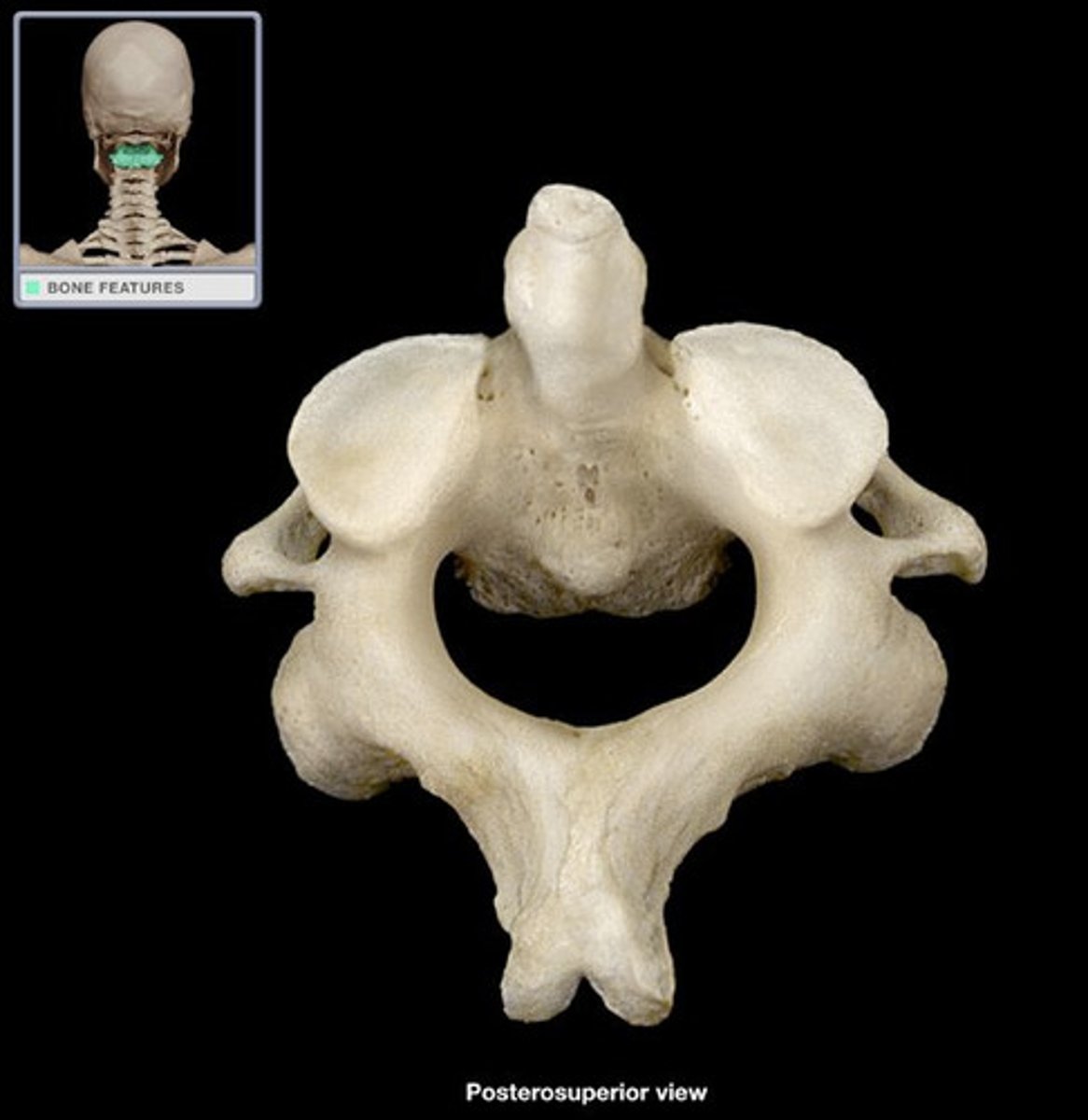
atlas - C1
axis - C2
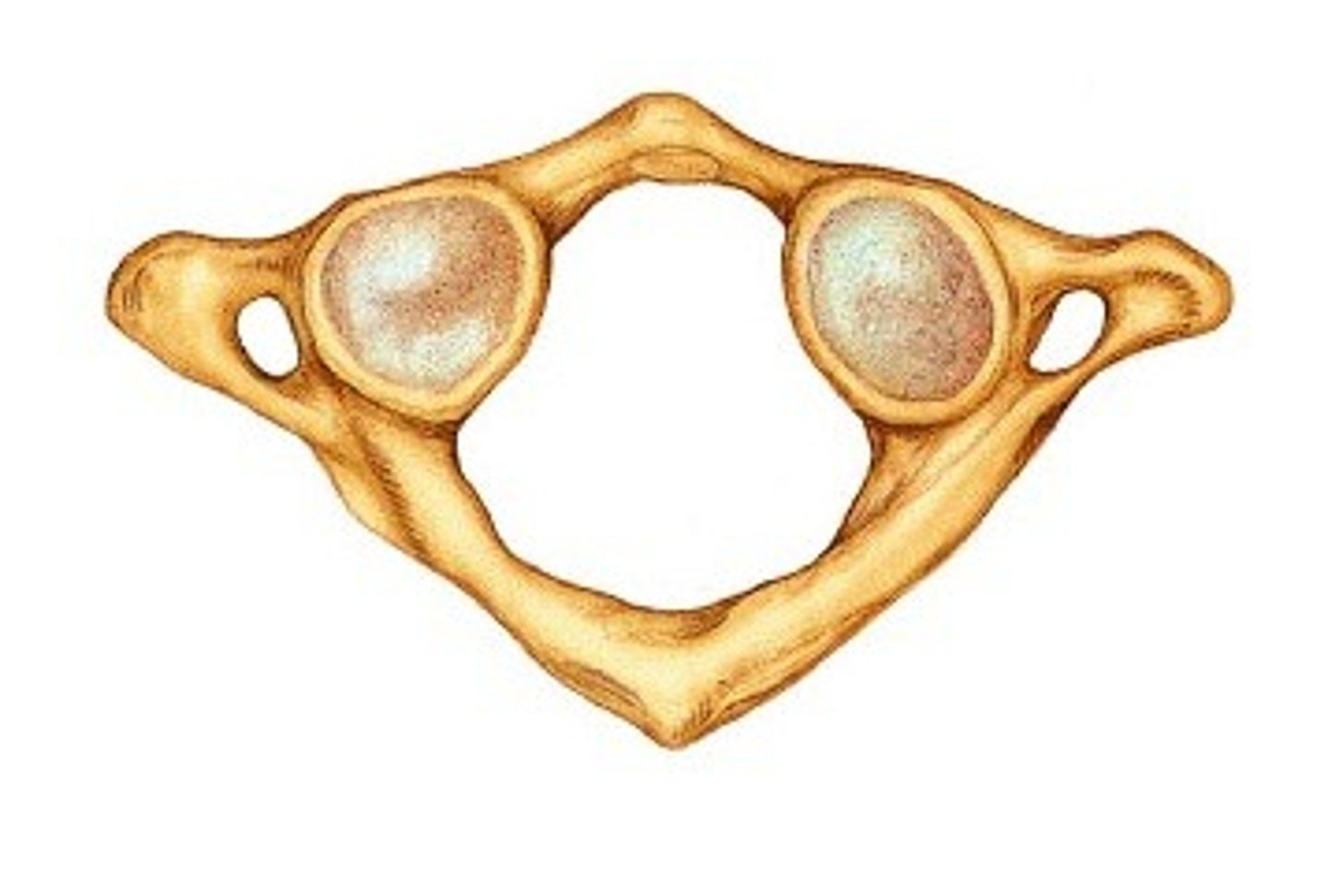
thoracic vertebrae
T1-T12
heart shaped body, circular vertebral foramen, long spinous process
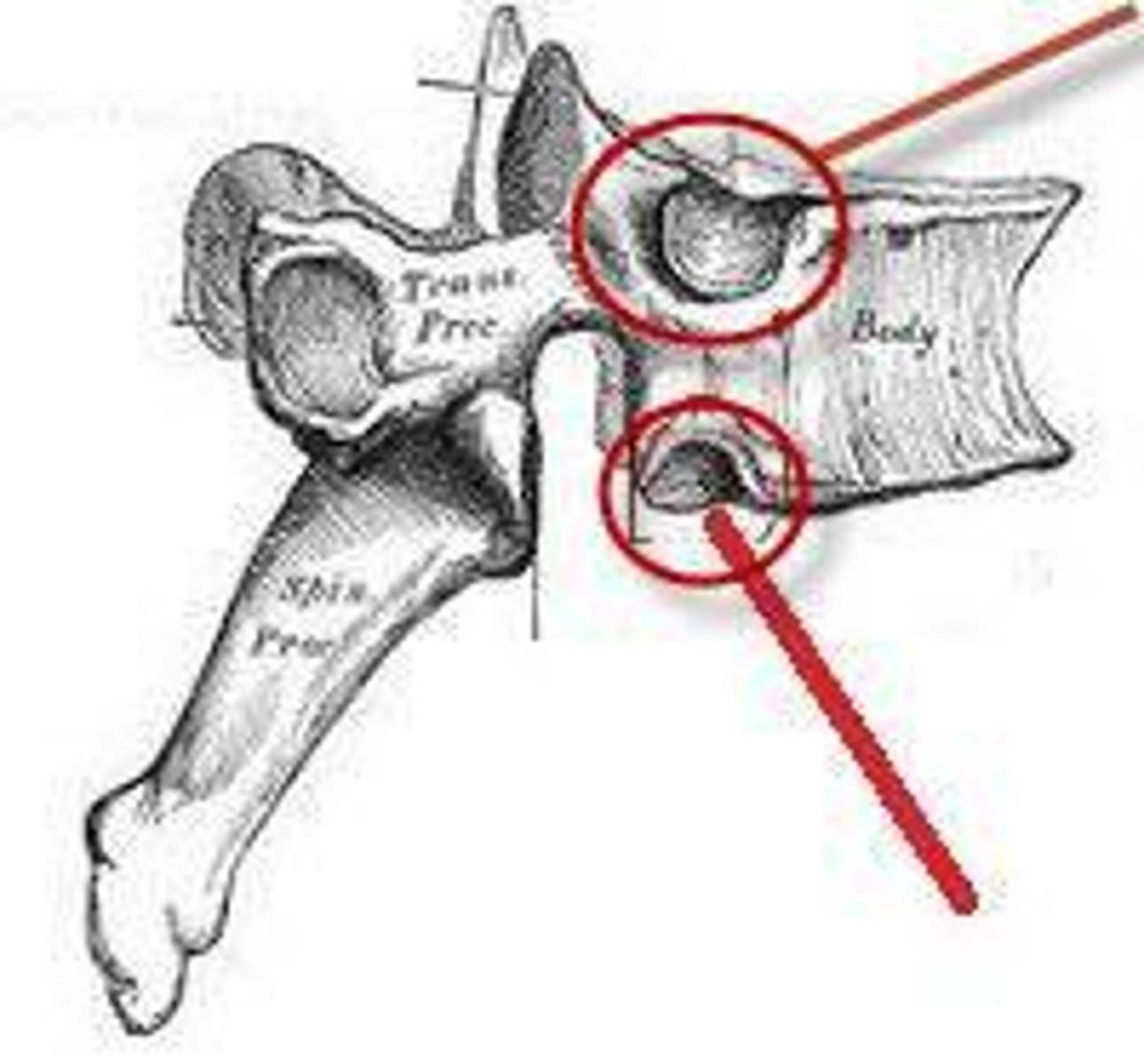
facets and demifacets
the structures on a thoracic vertebra called that articulate with ribs at costovertebral joints
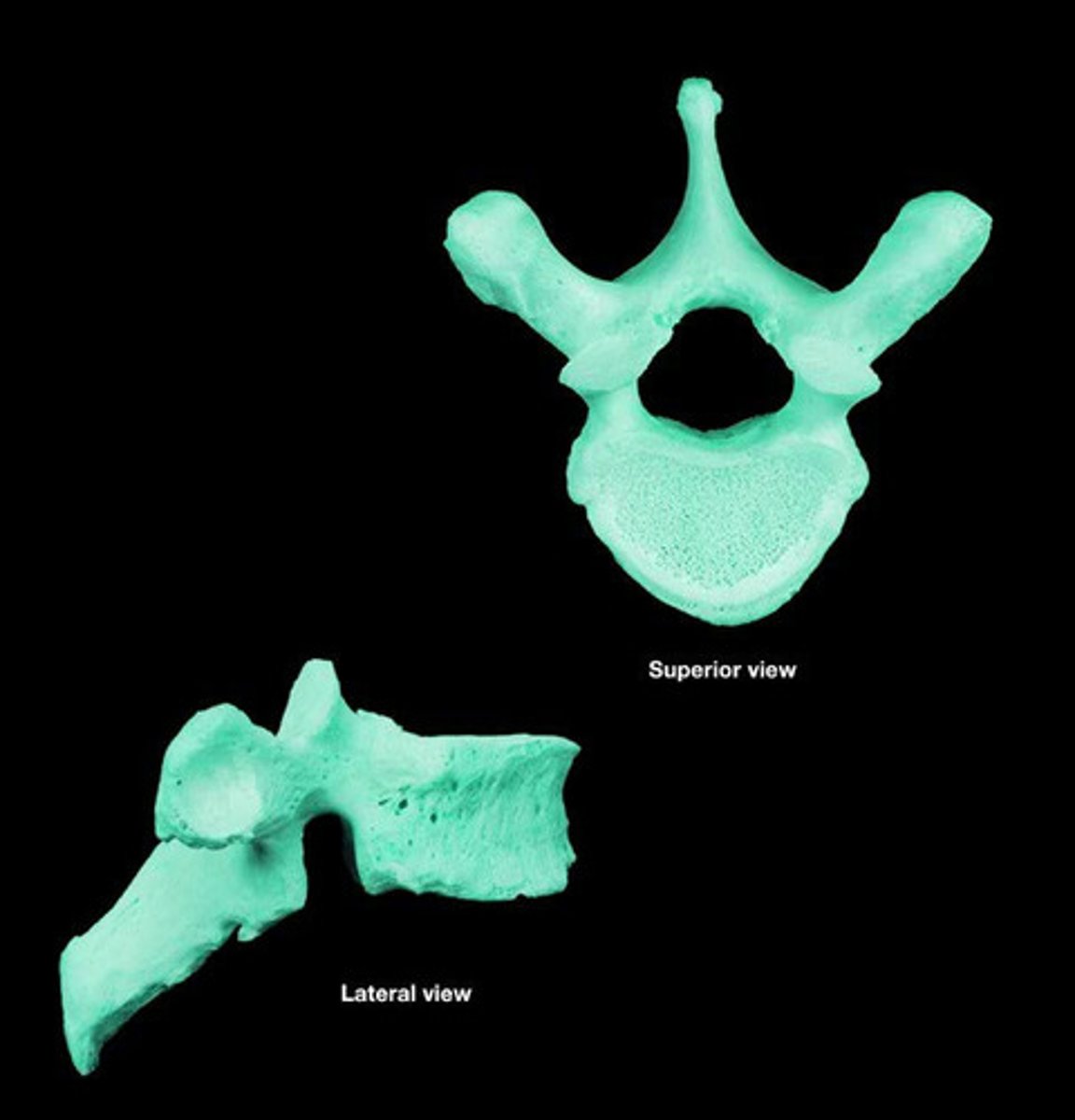
lumbar vertebrae
L1-L5
biggest because most weight bearing
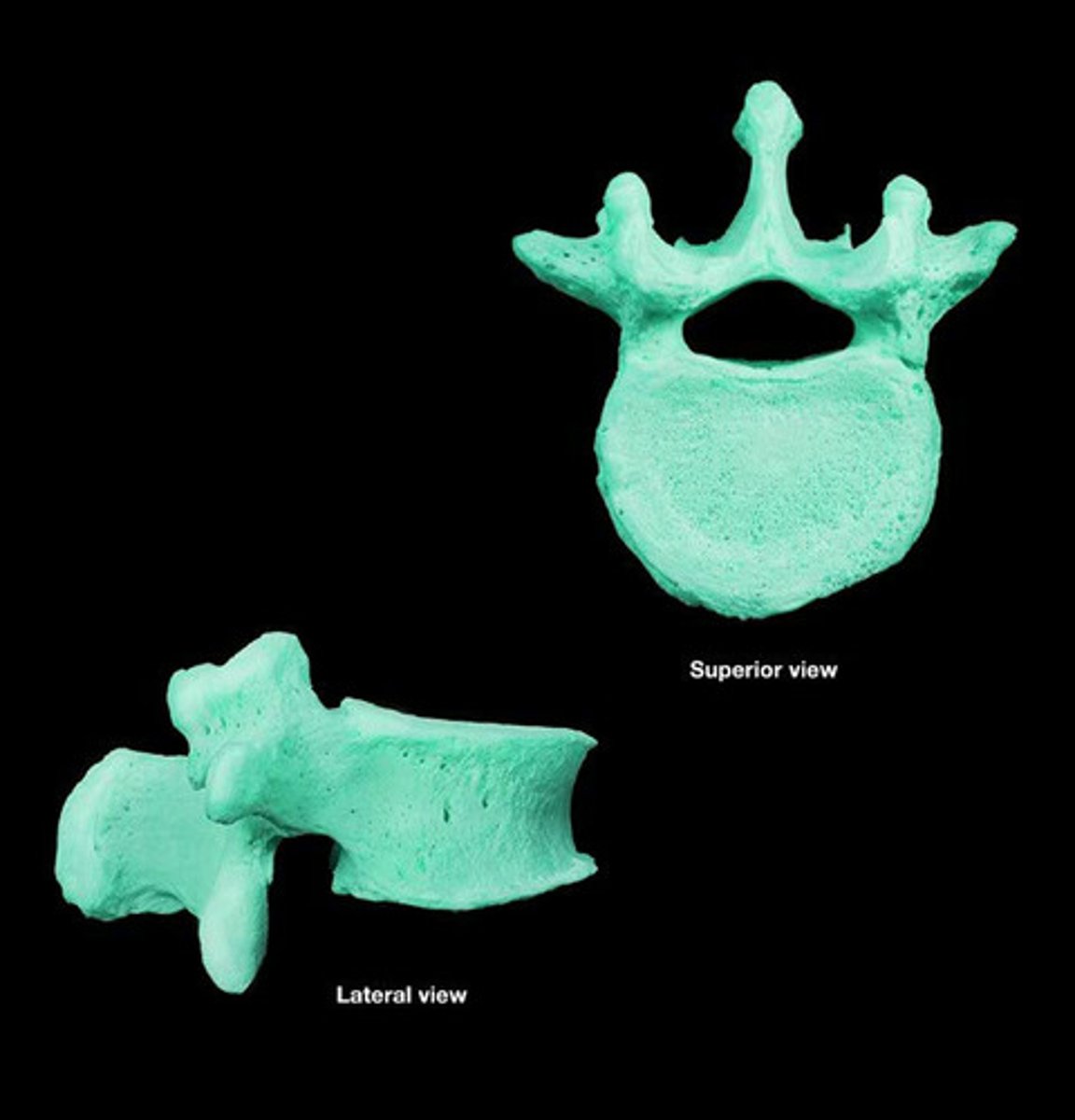
sacrum
bone formed from five vertebrae fused together near the base of the spinal column
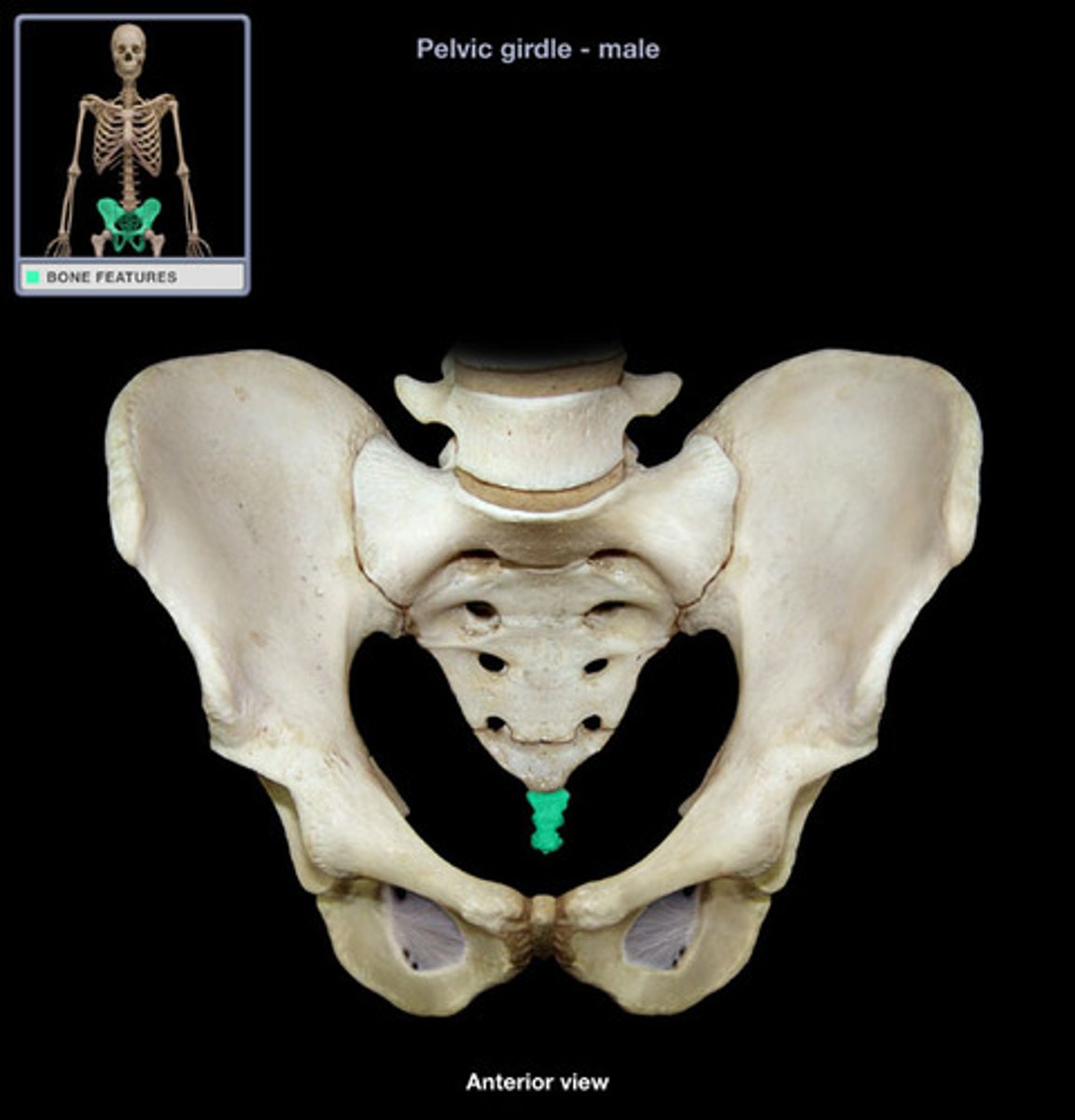
coccyx
four vertebrae fused together to form the tailbone
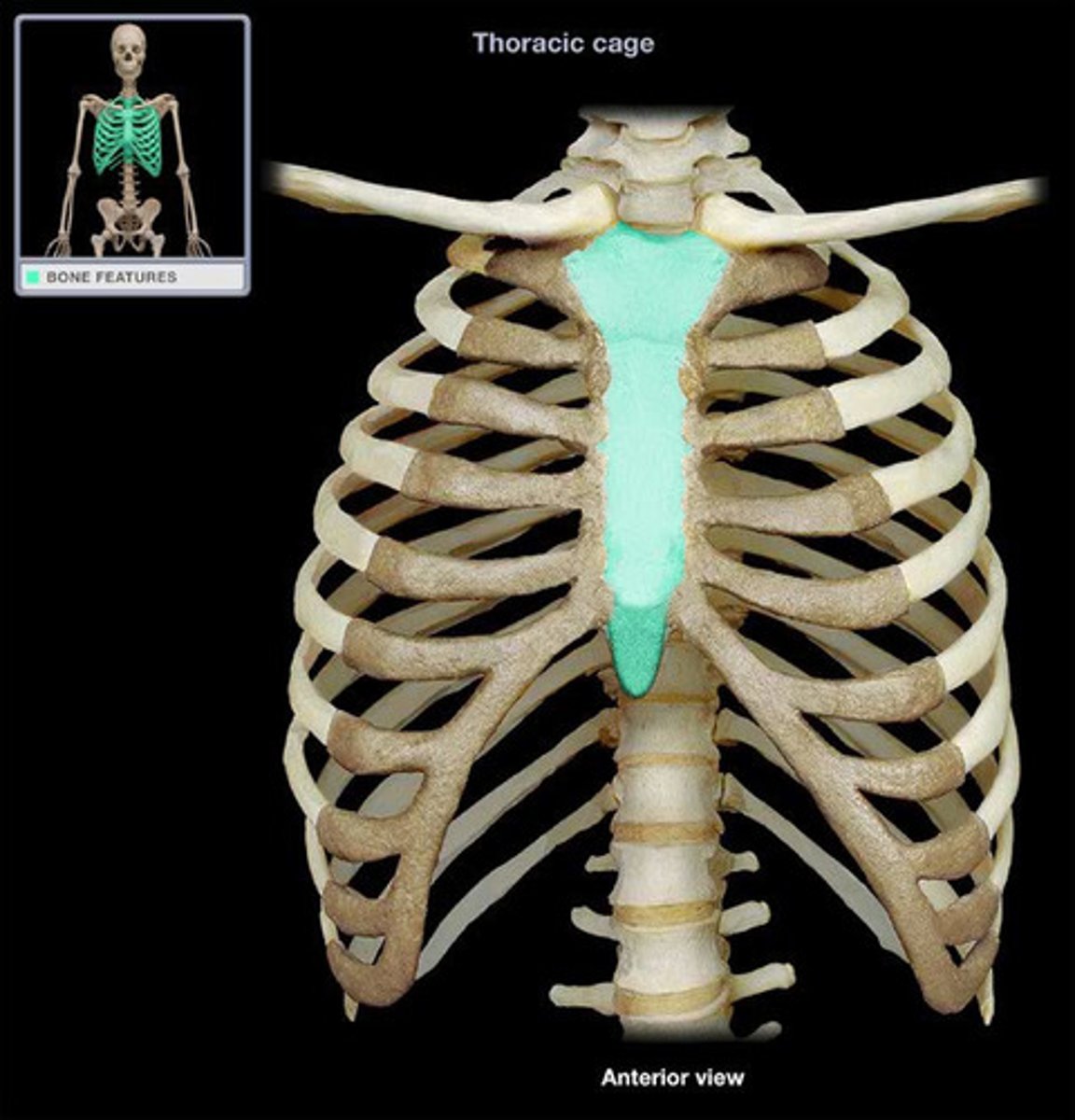
Sternum
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
true ribs
first 7 pairs of ribs; attach directly to sternum
false ribs
ribs 8 - 10; attach indirectly to sternum (costal cartilage)
floating ribs
ribs 11-12 ; do not attach to sternum
which bone is U-shaped and located anteriorly in the upper neck
rib 1
which vertebrae do the ribs articulate with
thoracic vertebrae
what is kyphosis
Slouch back (shoulders roll forward)
what is scoliosis
lateral curvature of the spine
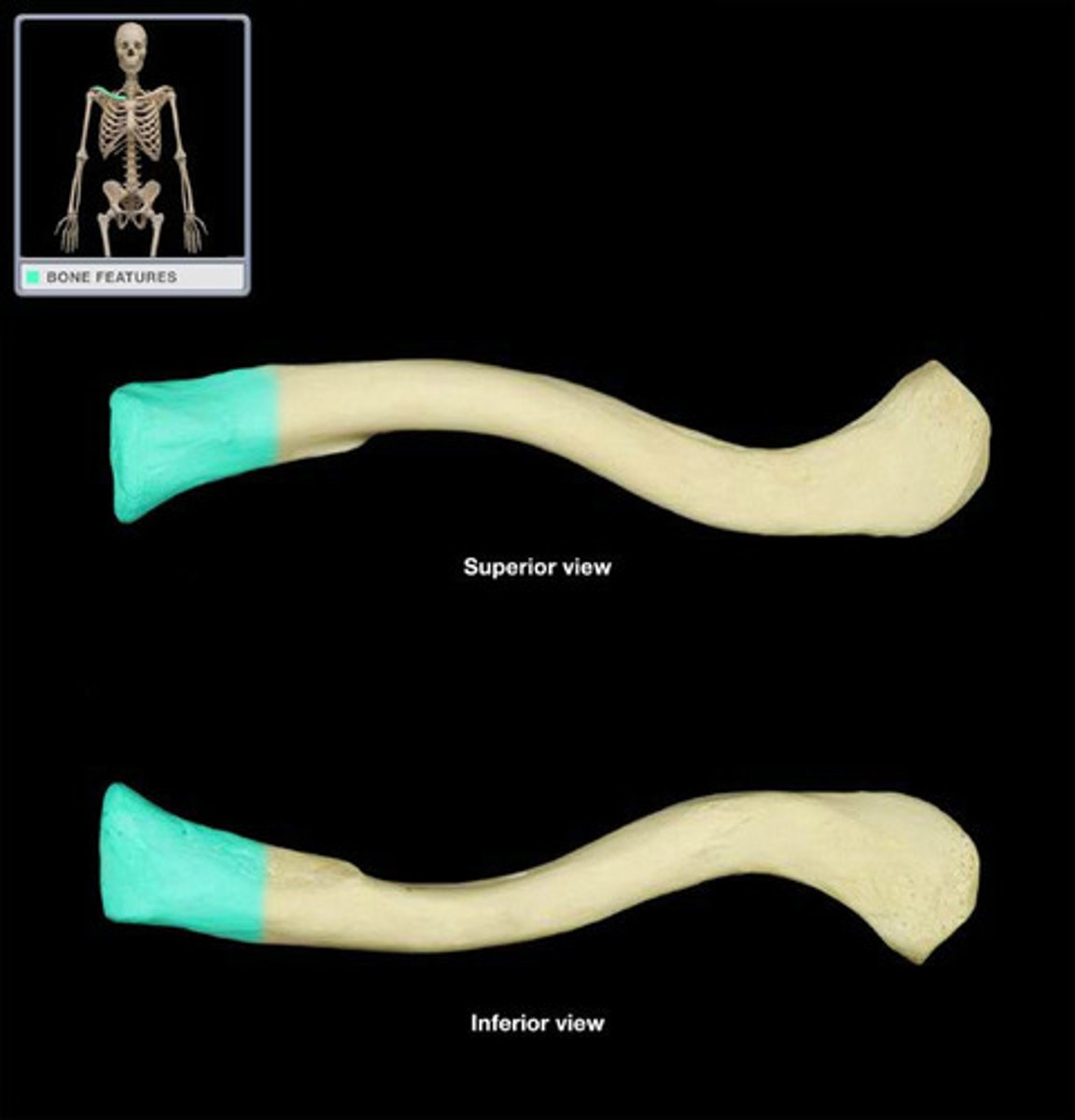
medial clavicle
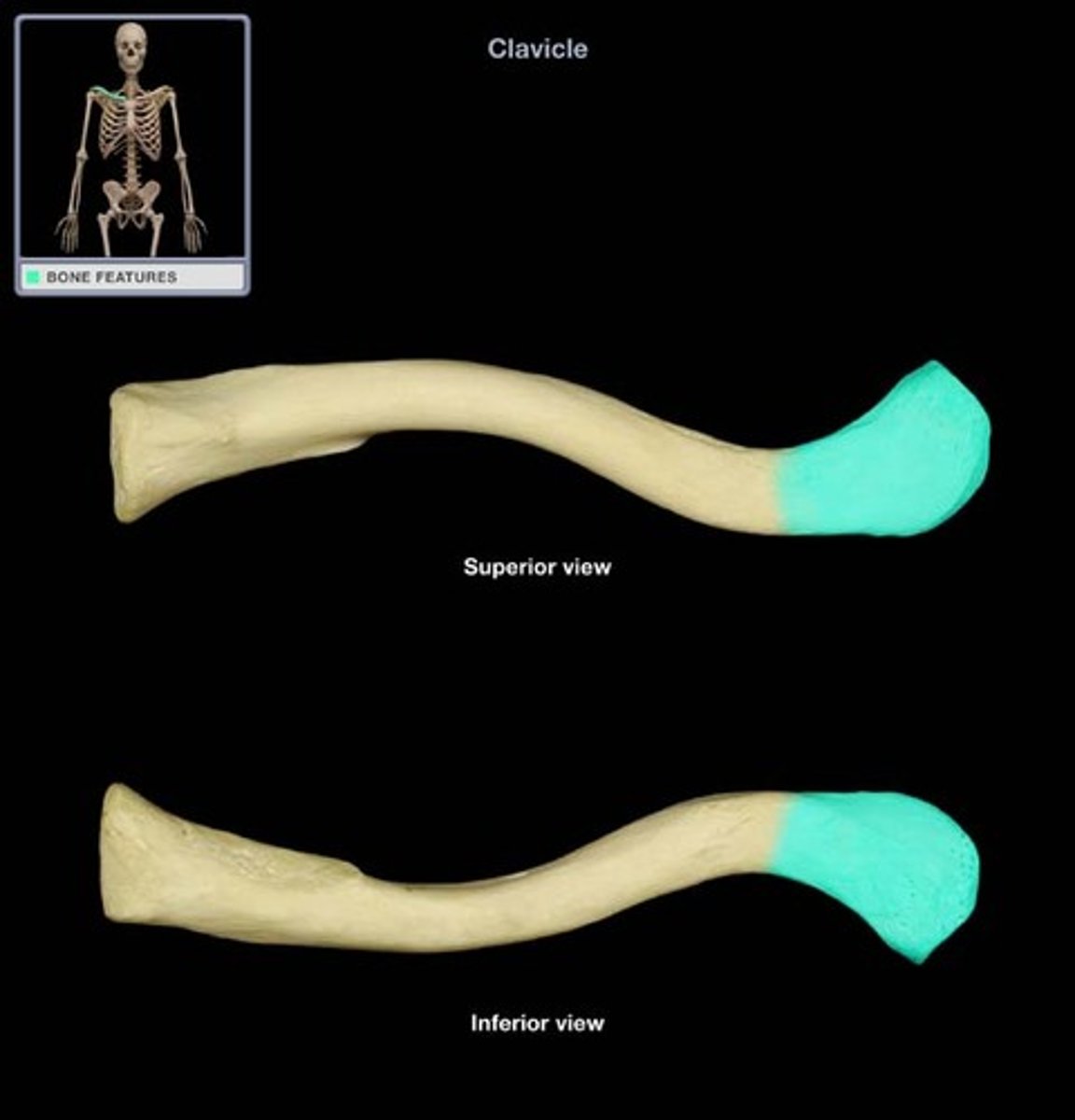
lateral clavicle
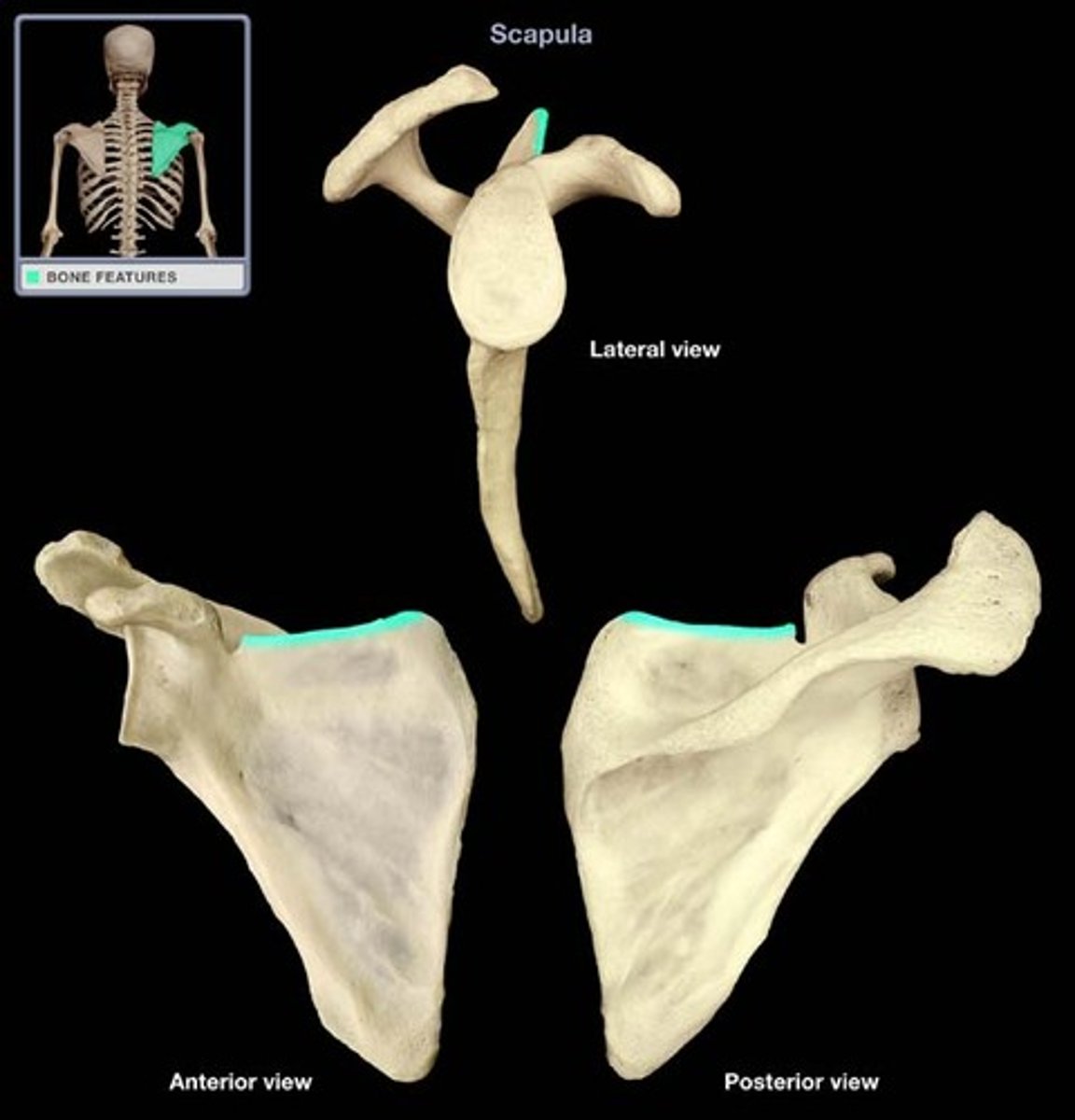
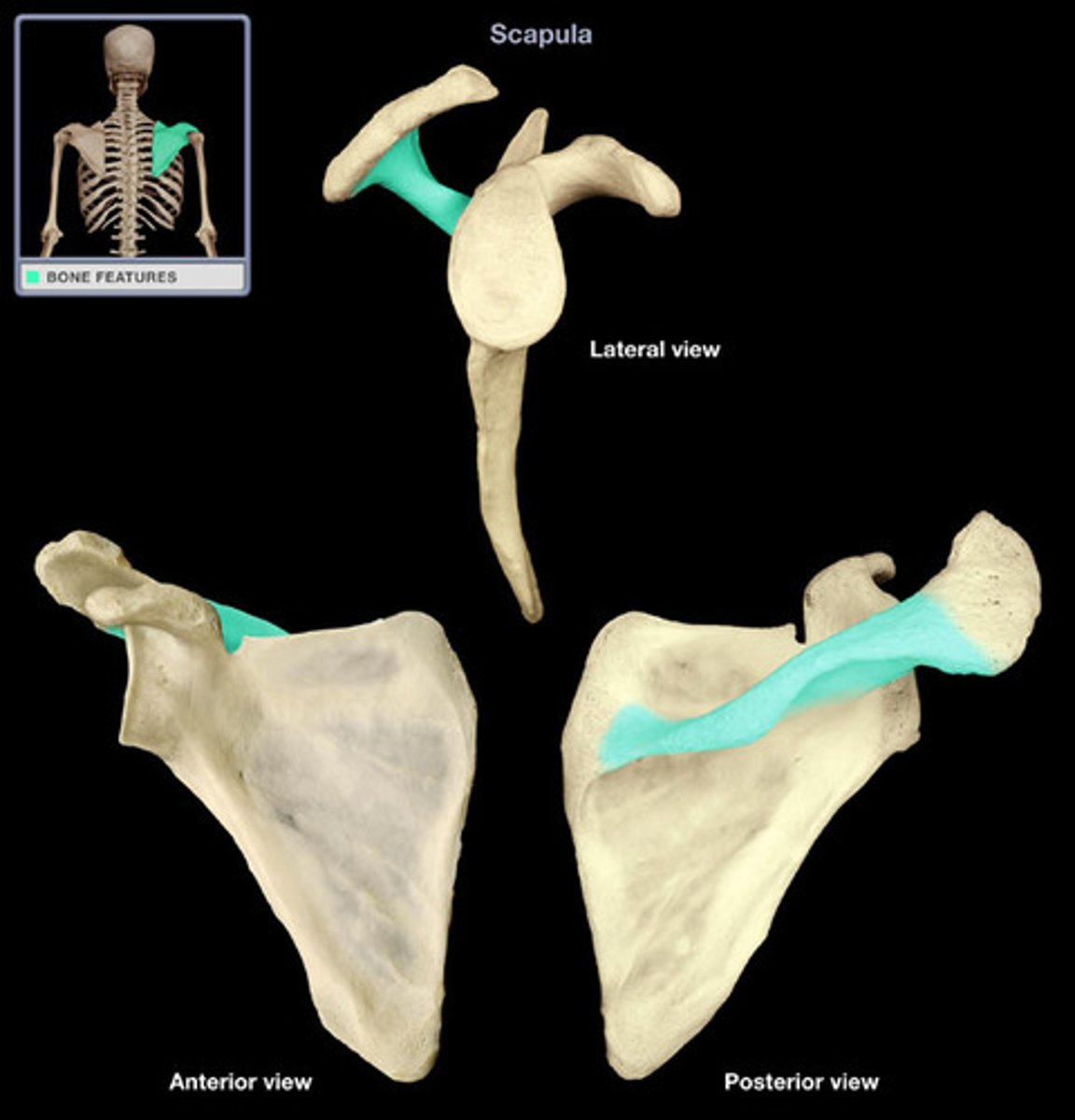
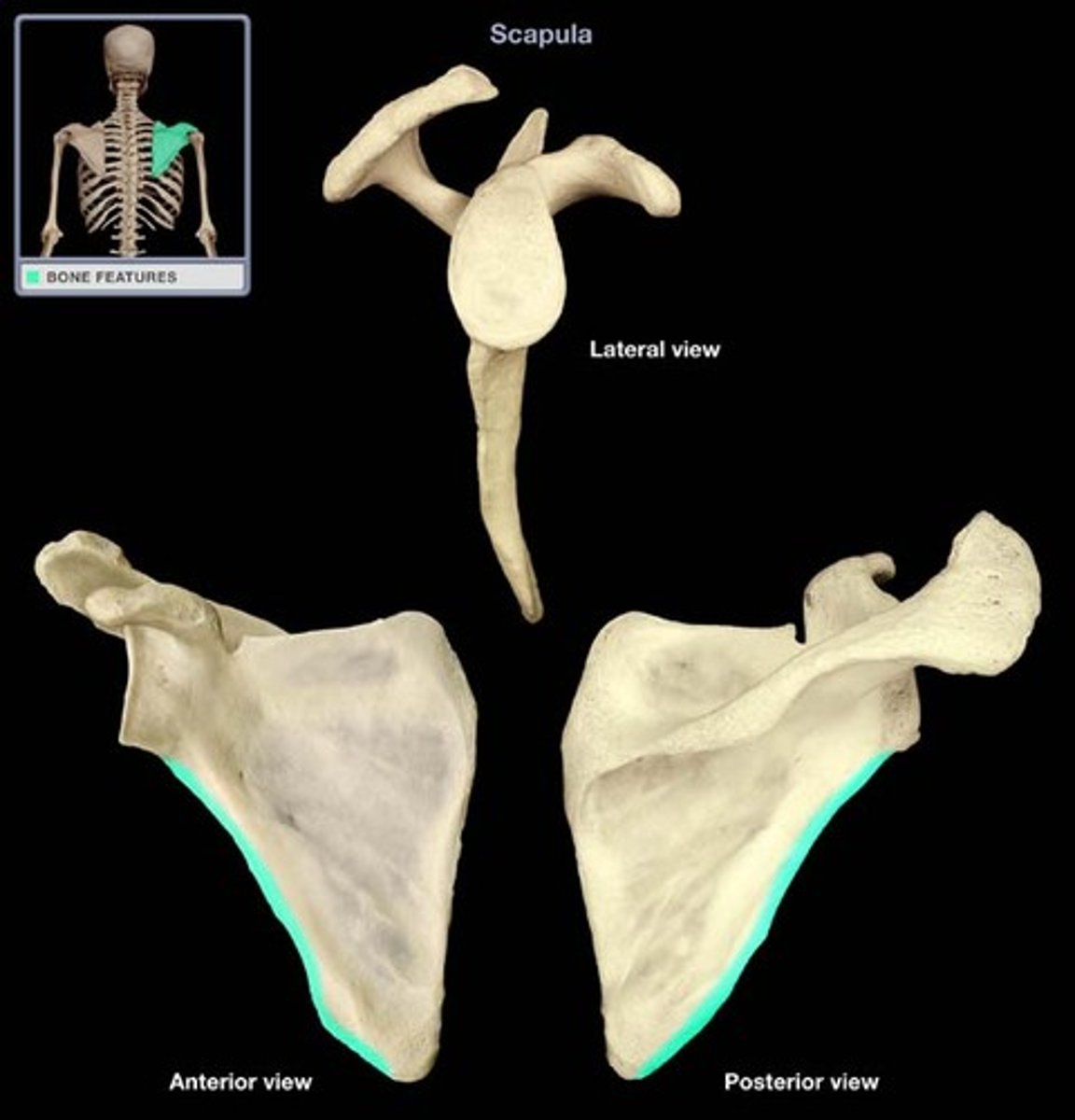
superior border of scapula
coracoid process
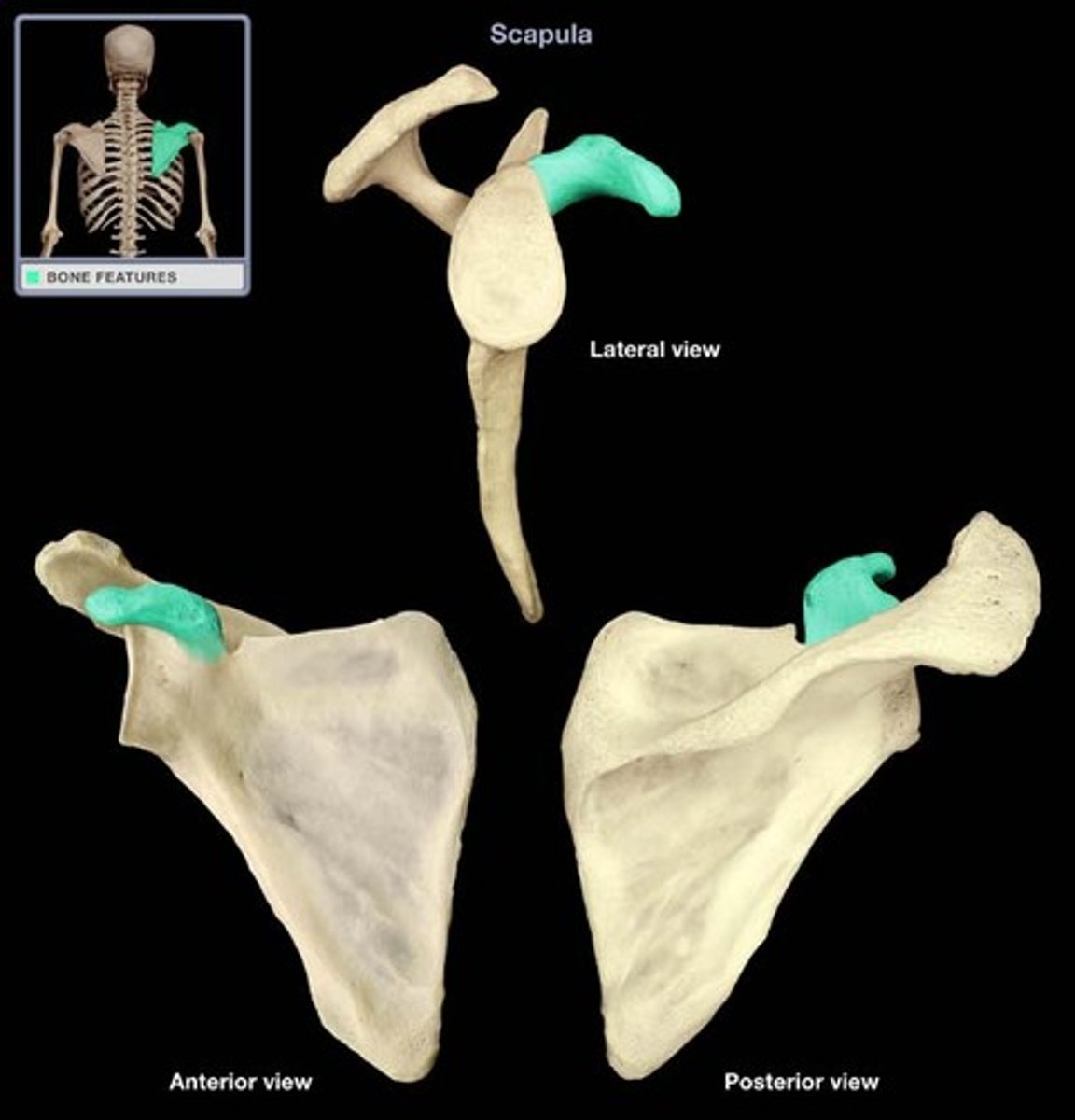
acrominon process
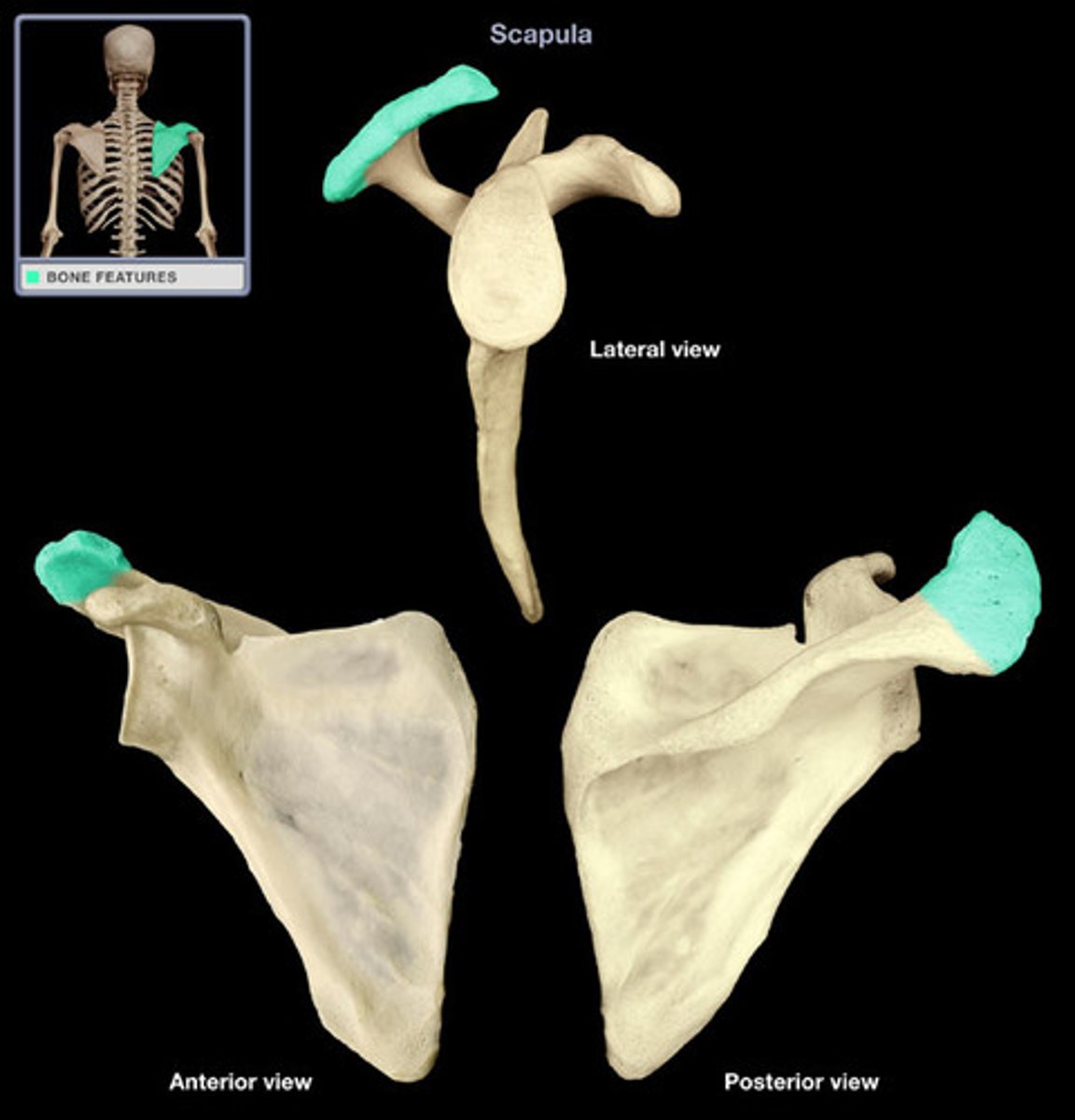
glenoid cavity
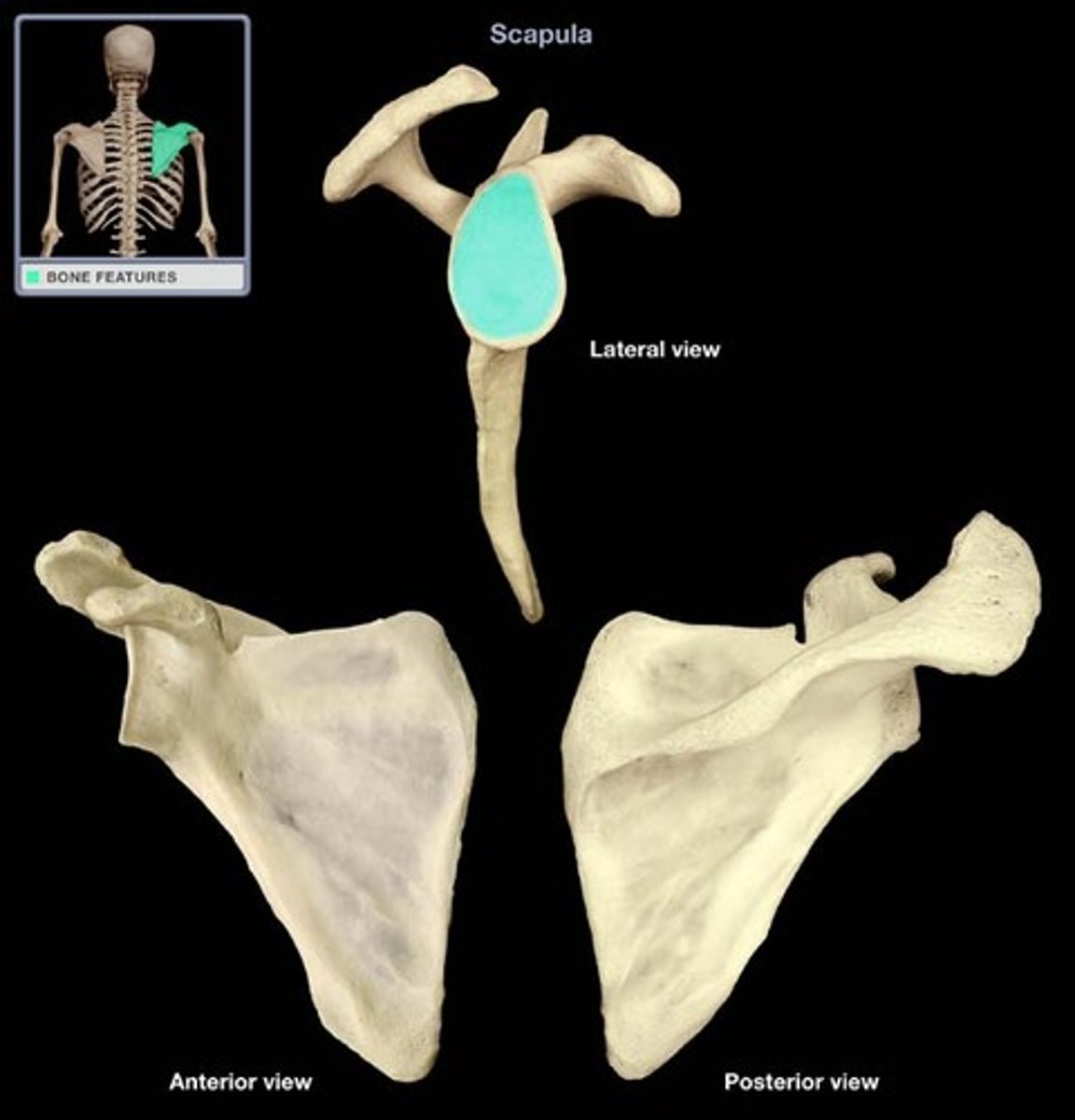
spine of the scapula
medial border of the scapula
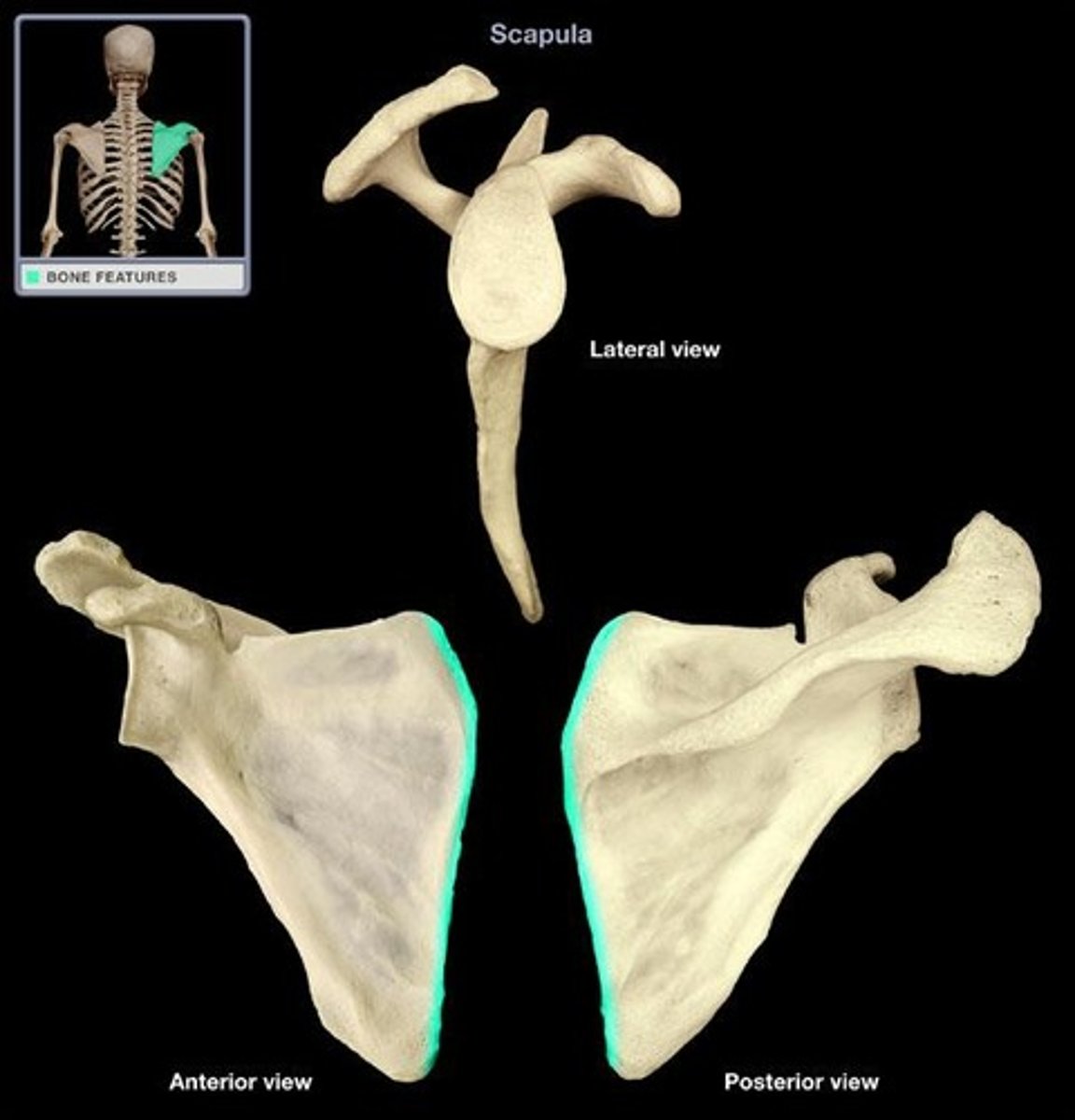
lateral border of scapula
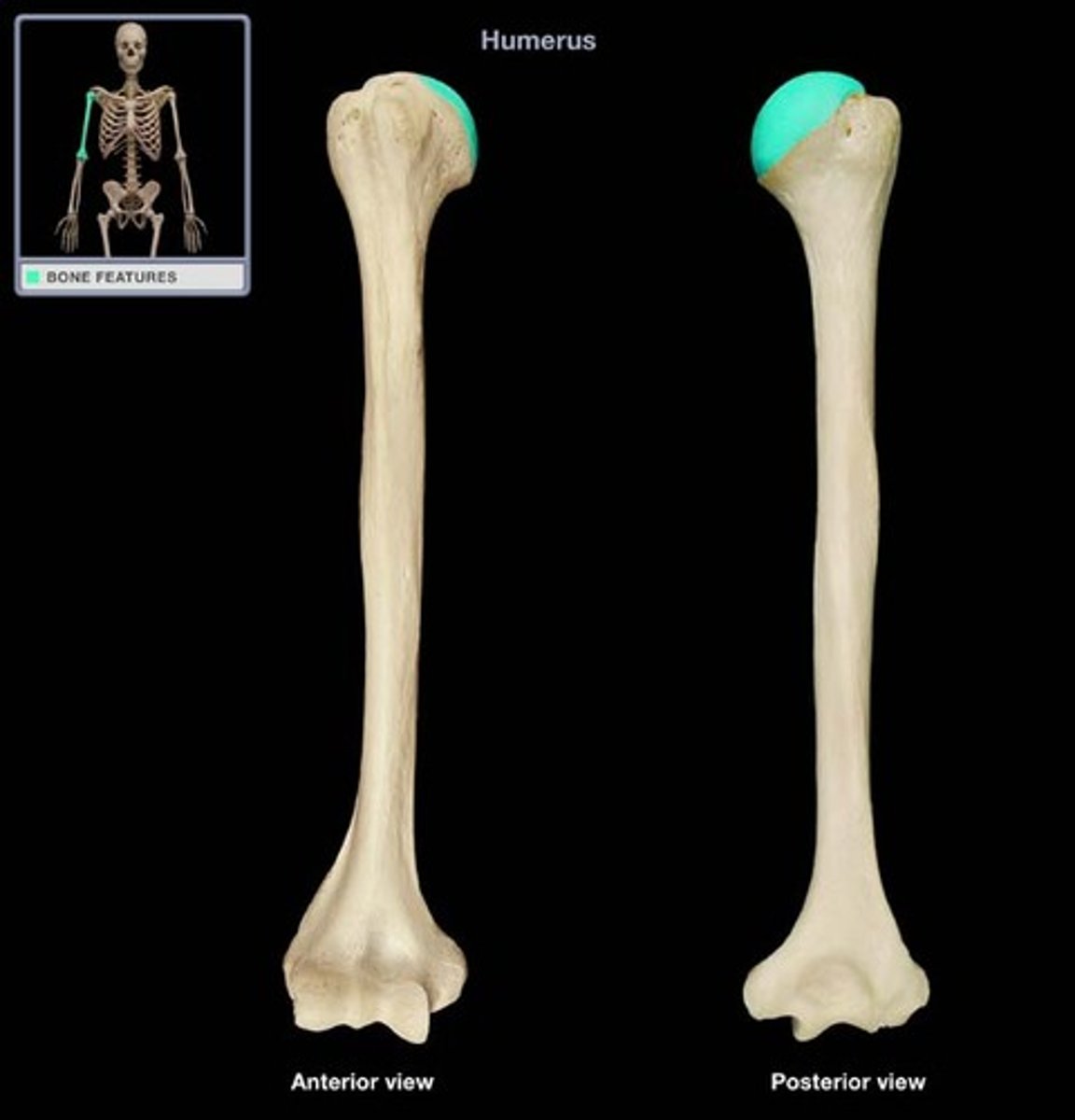
head of humerus
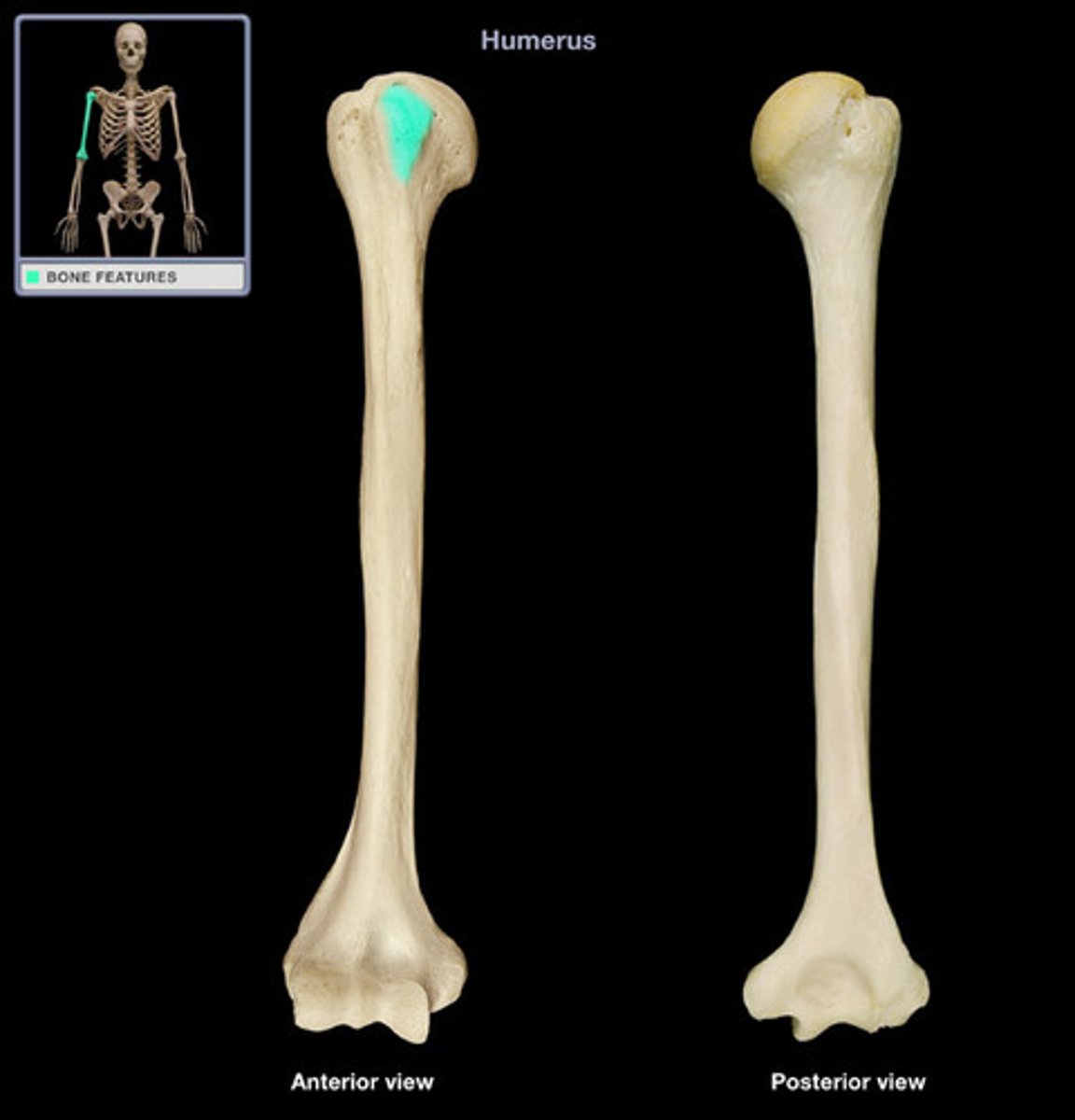
lesser tubercle of humerus
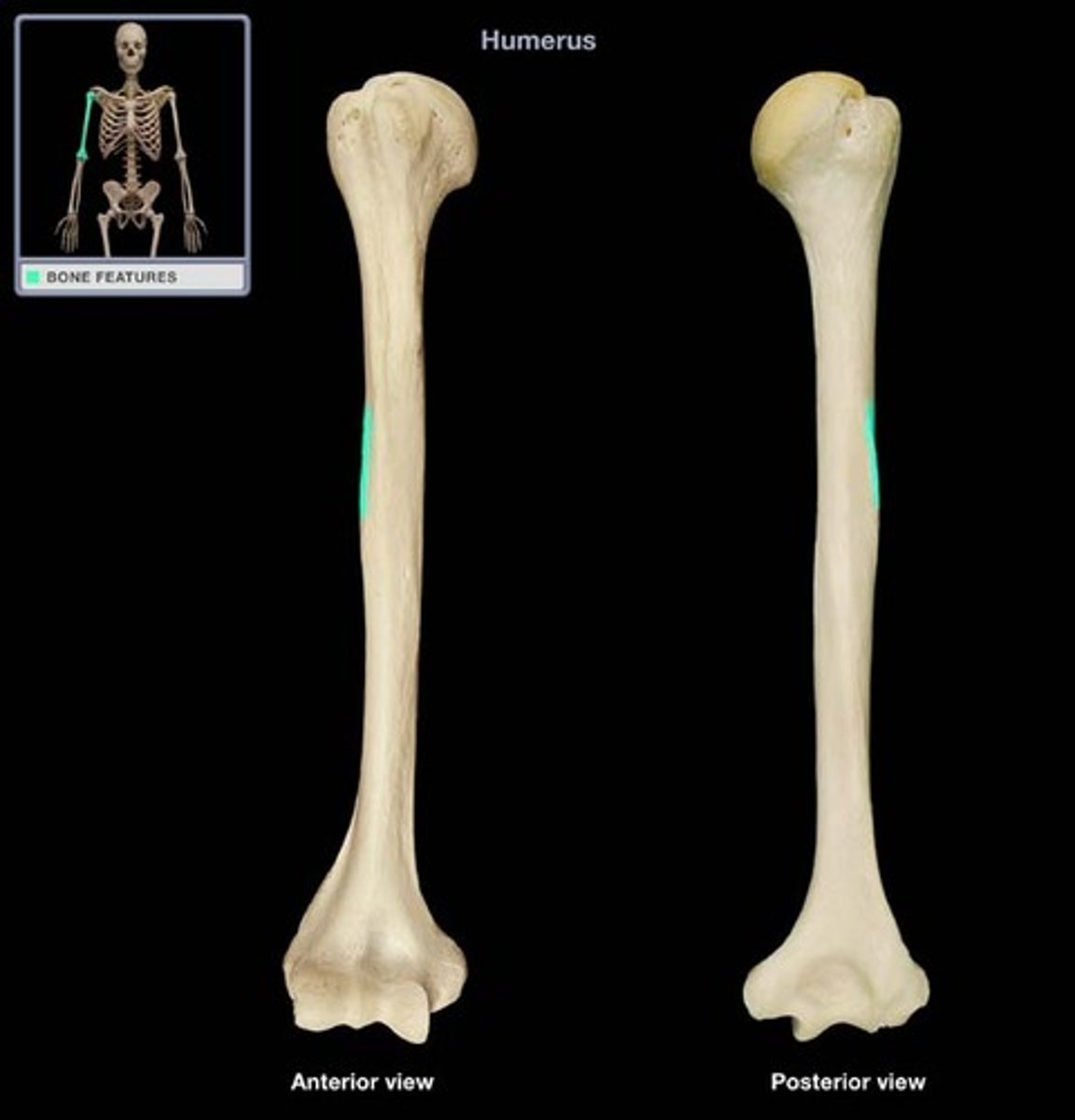
deltoid tuberosity of humerus
capitulum of humerus
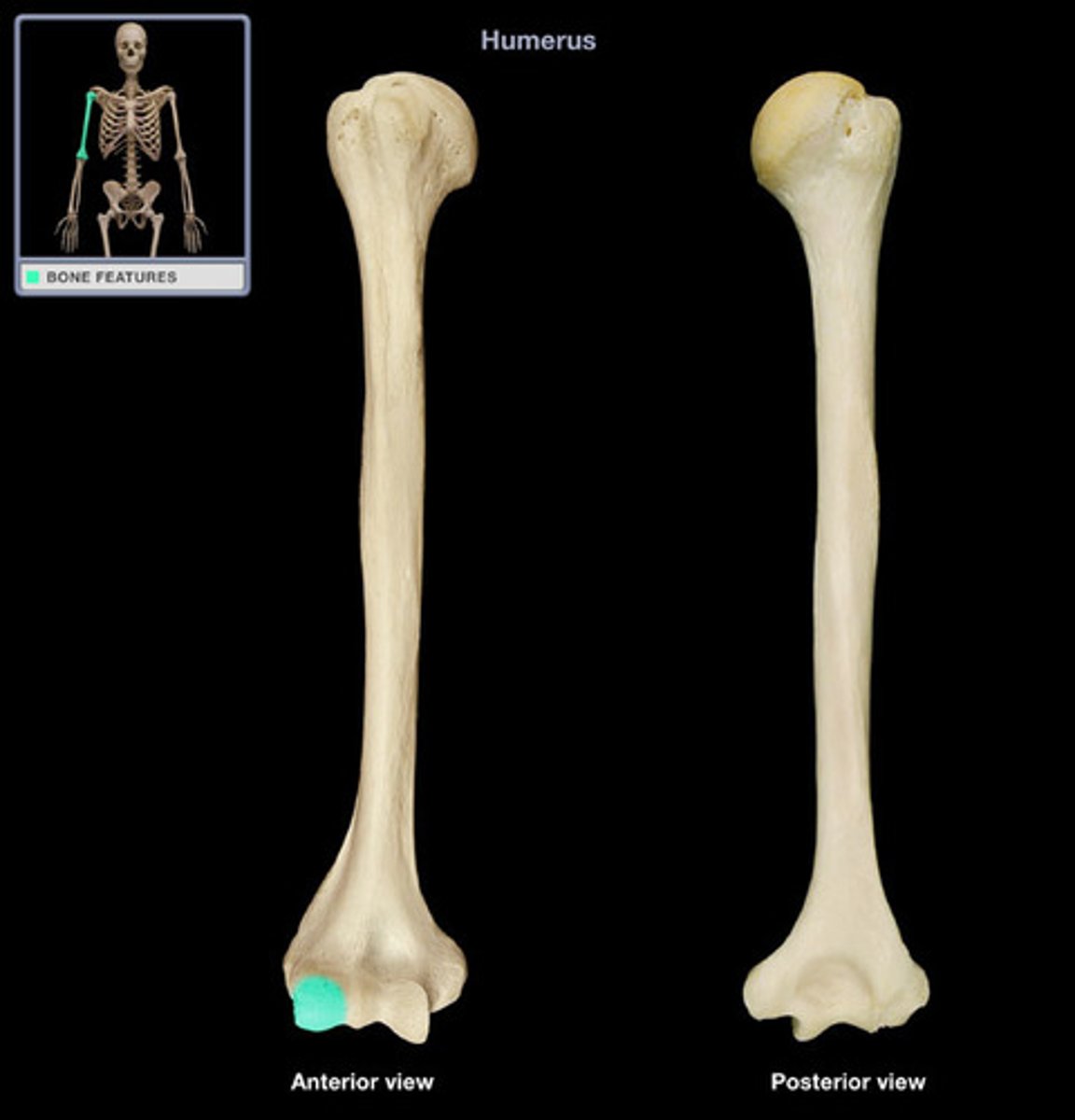
medial epicondyle of humerus
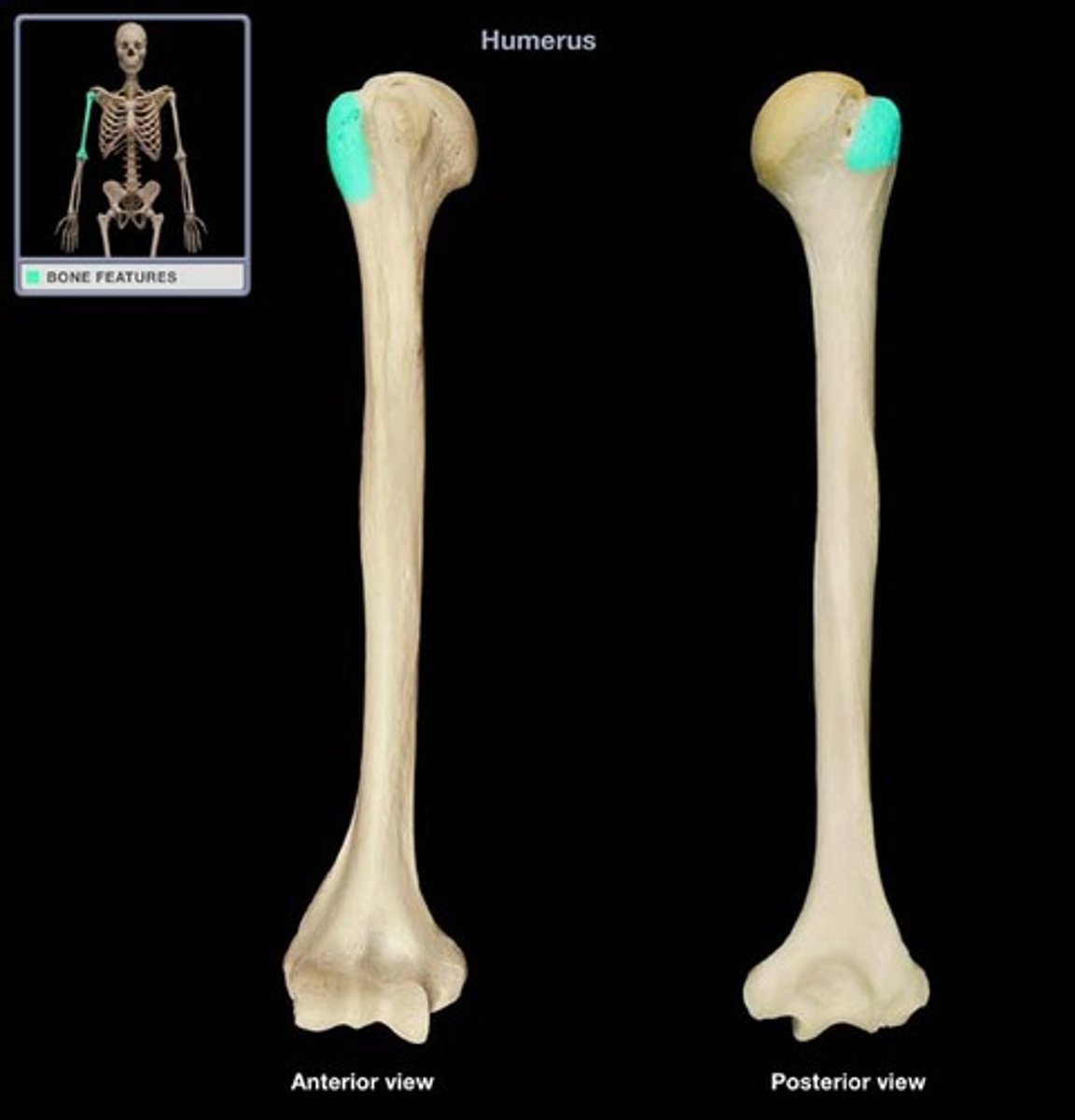
greater tubercle
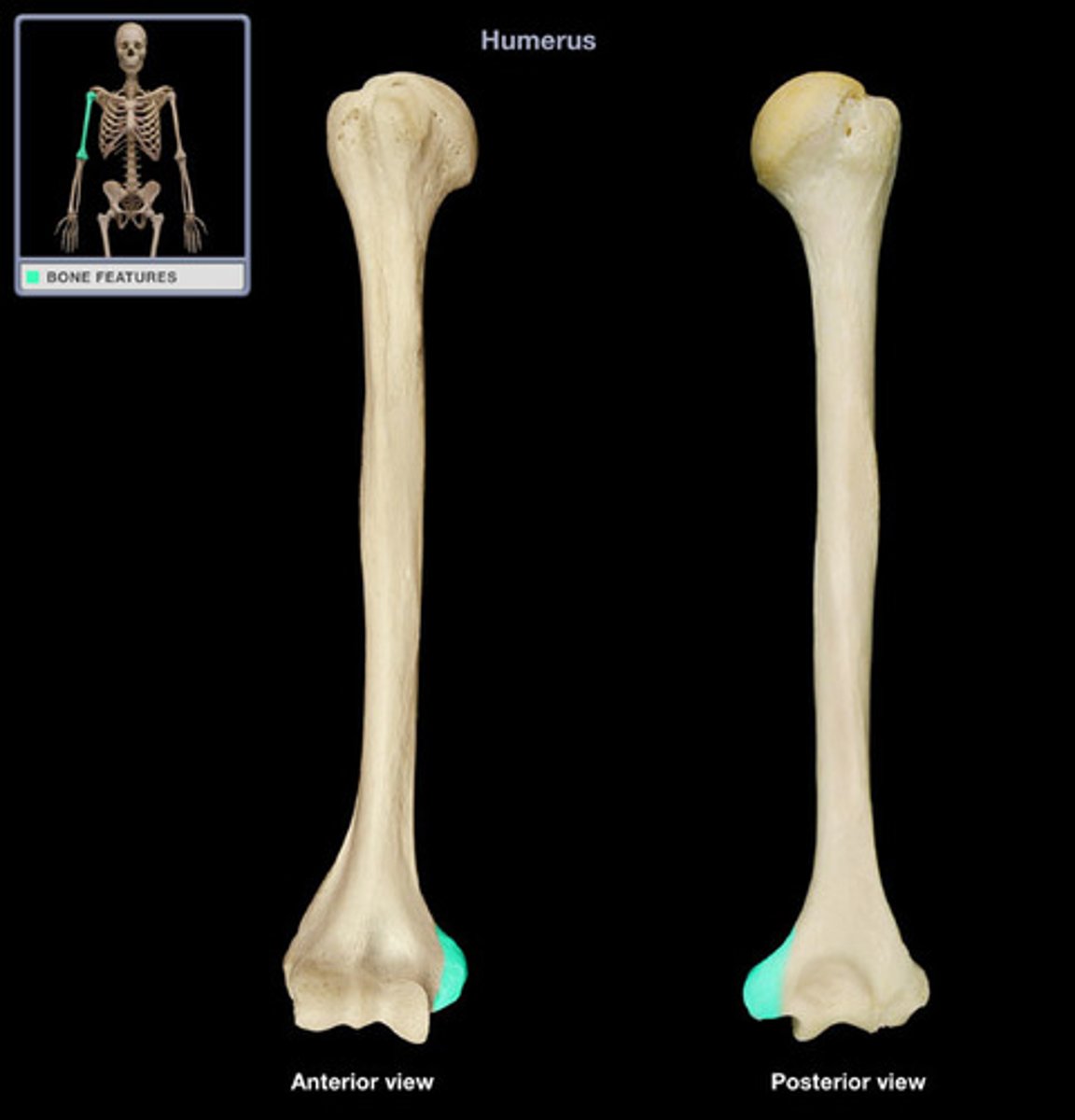
olecranon fossa
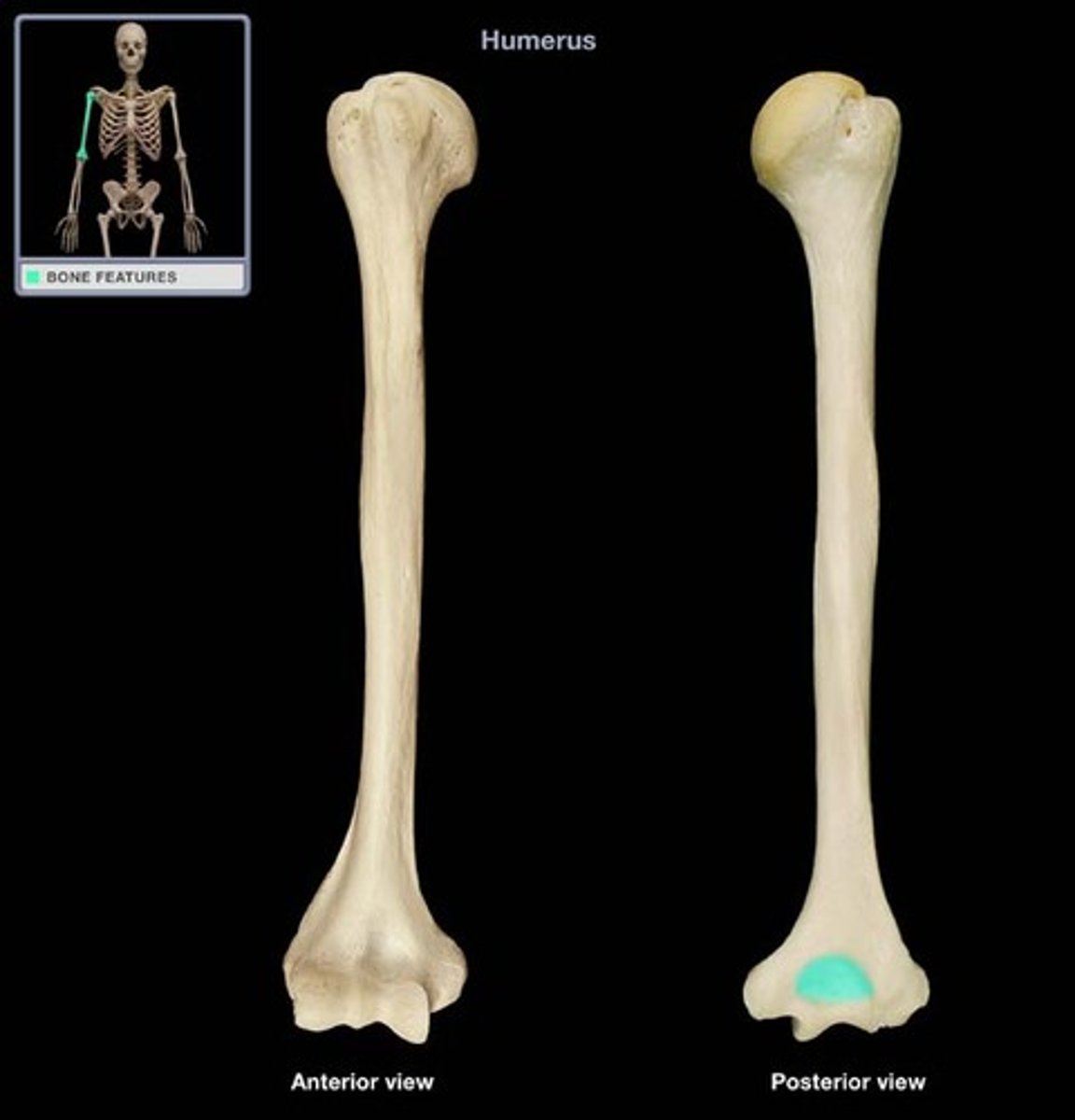
head of radius
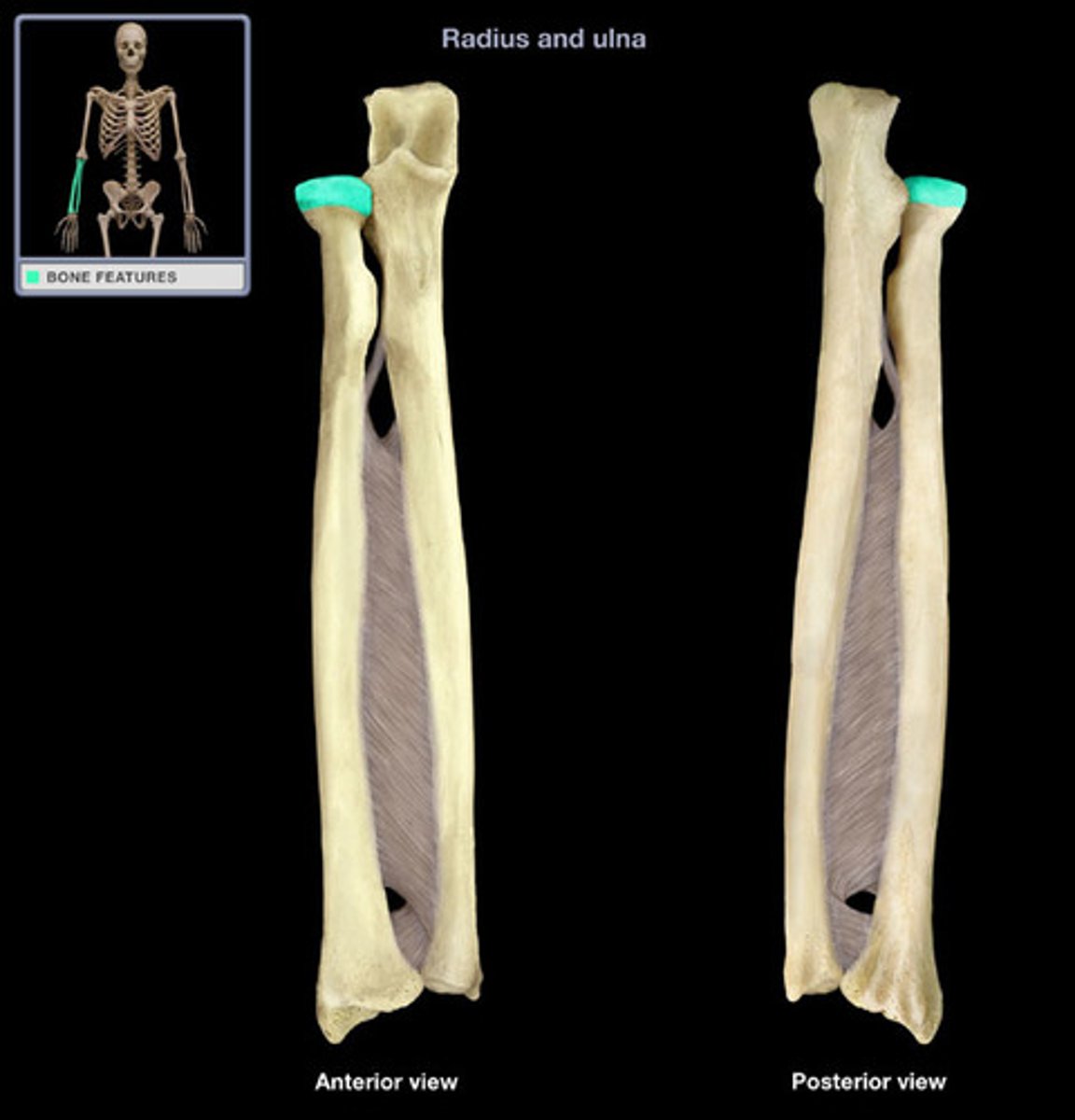
radial tuberosity of radius
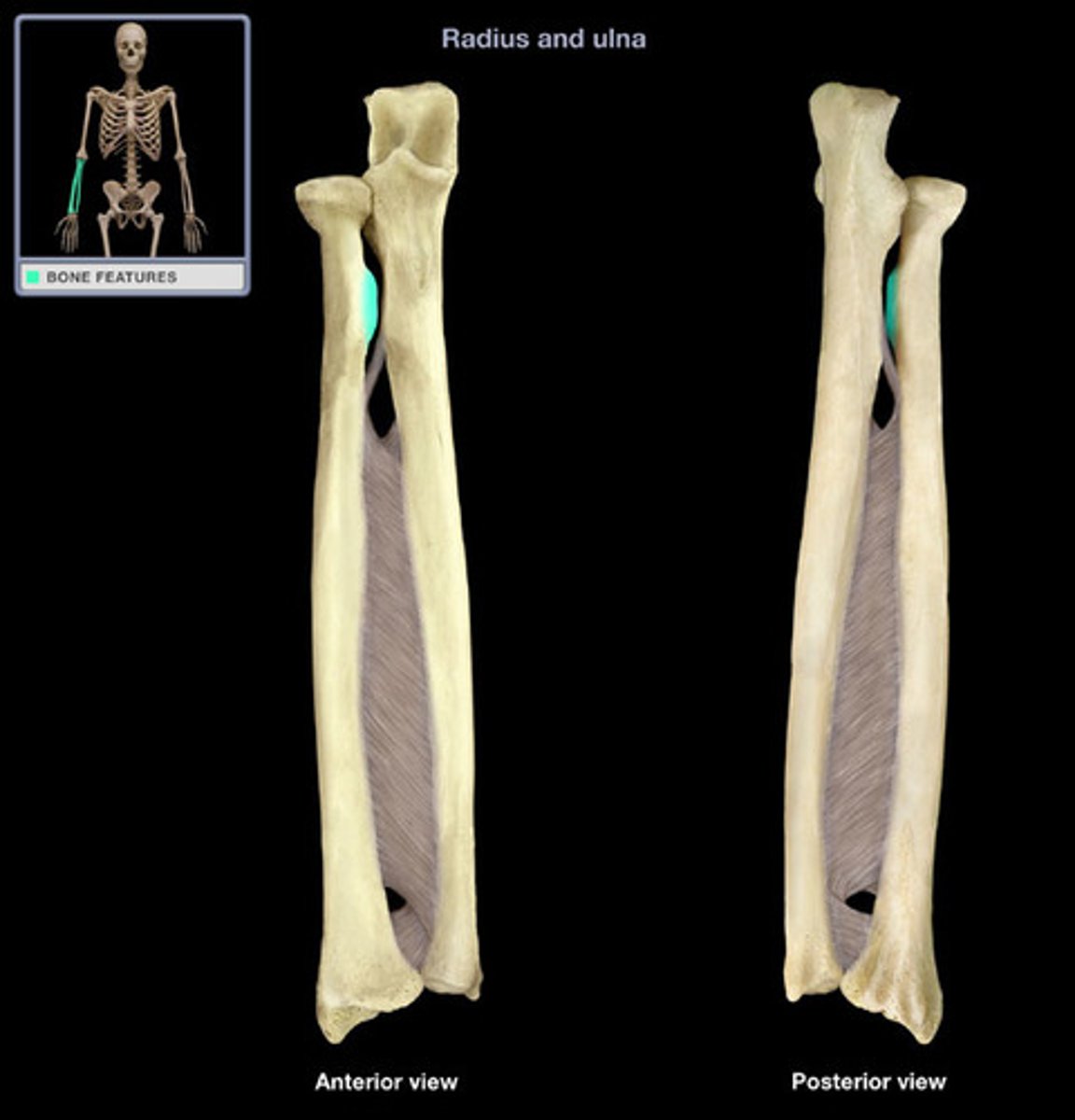
styloid process of radius
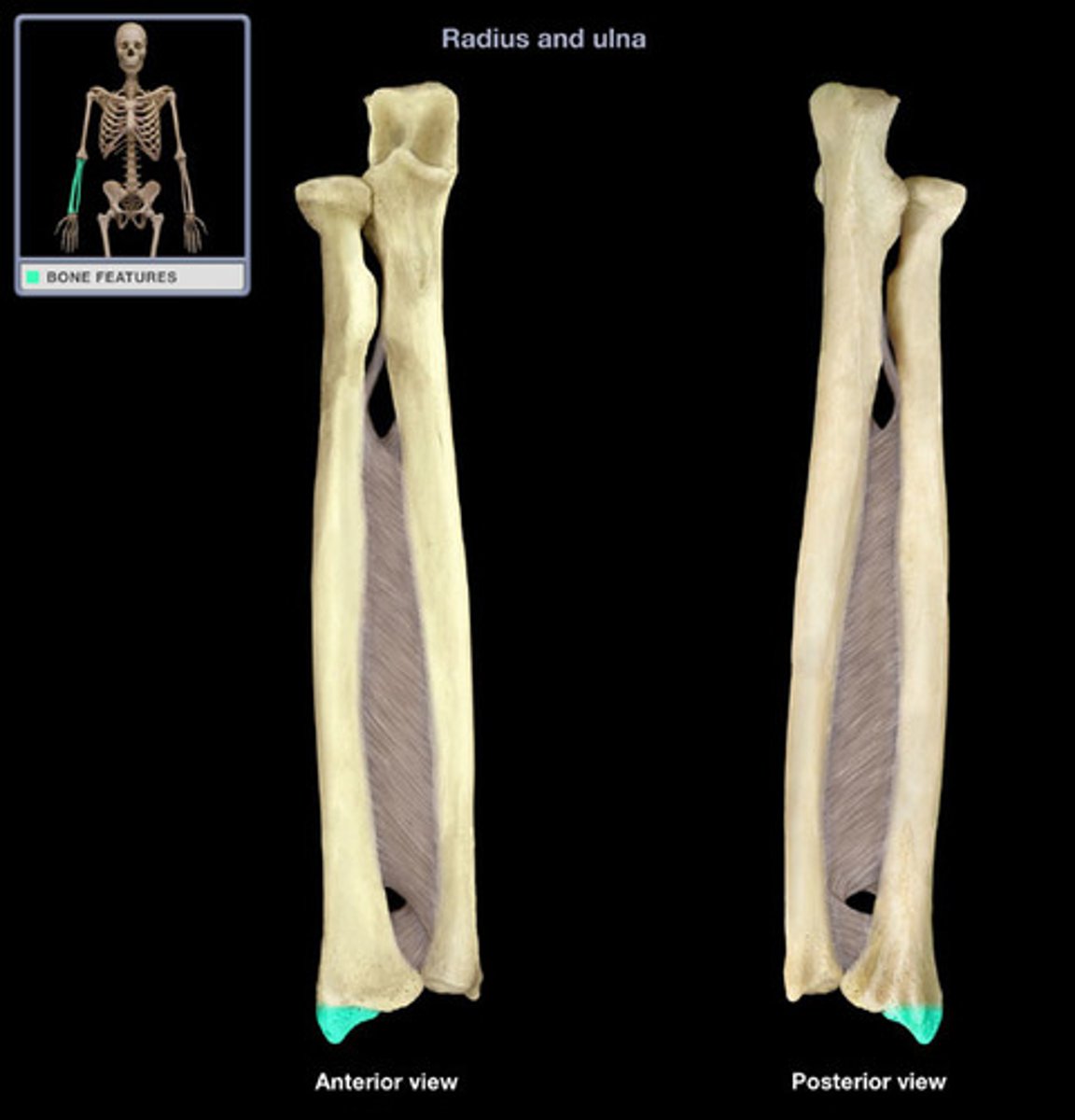
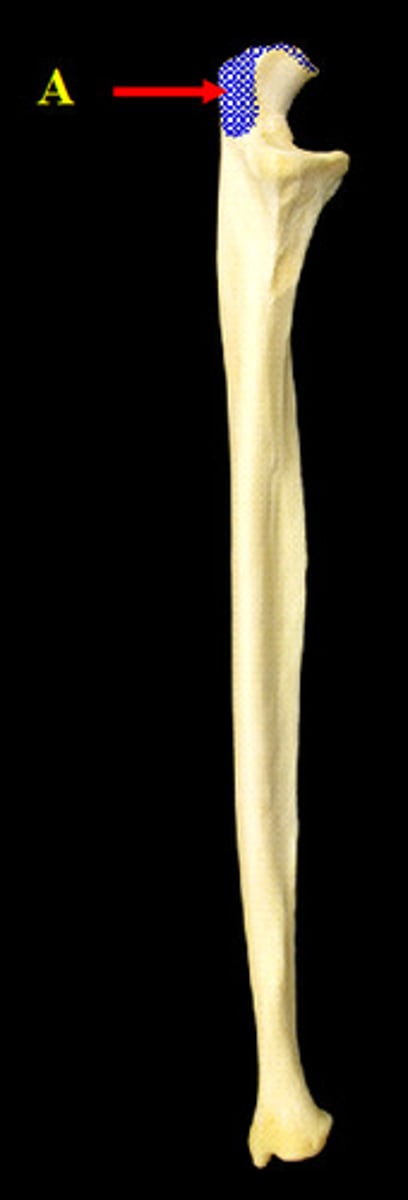
olecranon process of ulna

trochlear notch of ulna
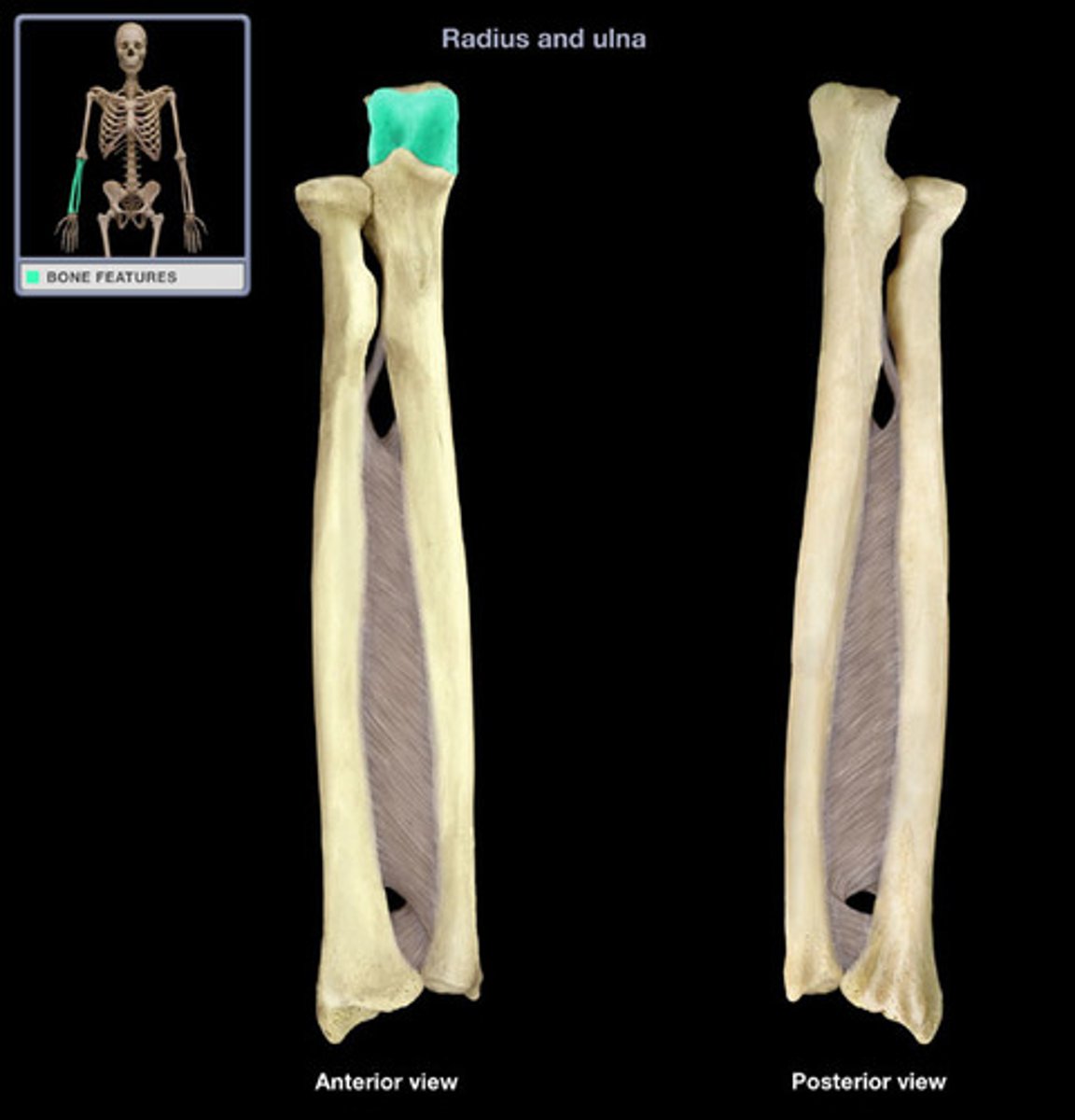
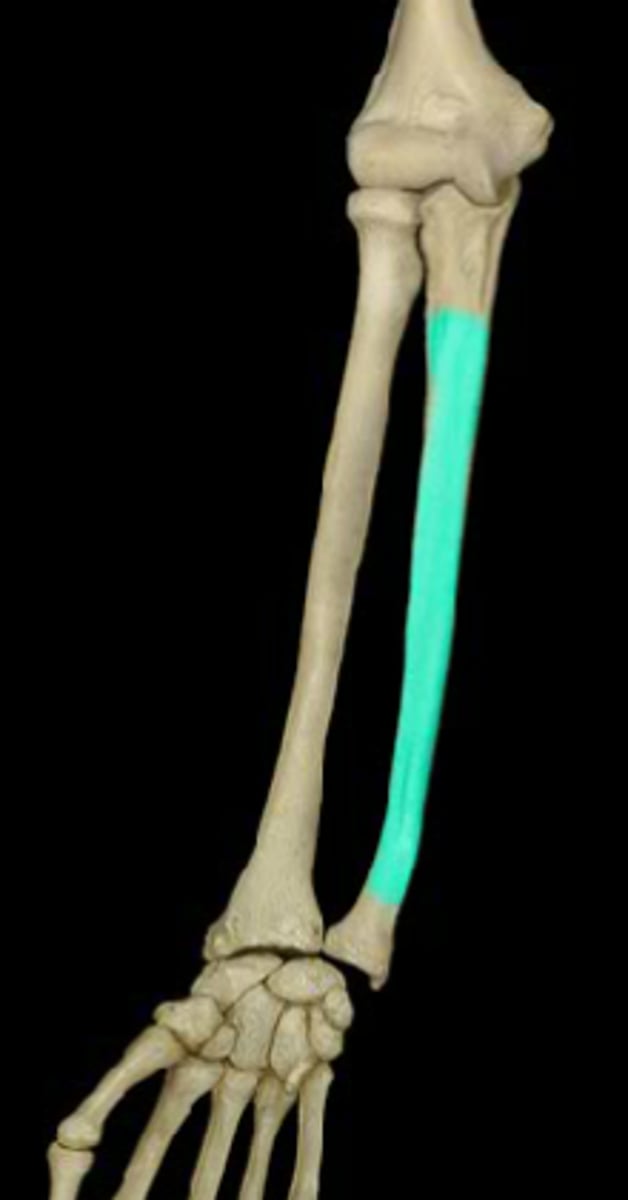
shaft of ulna
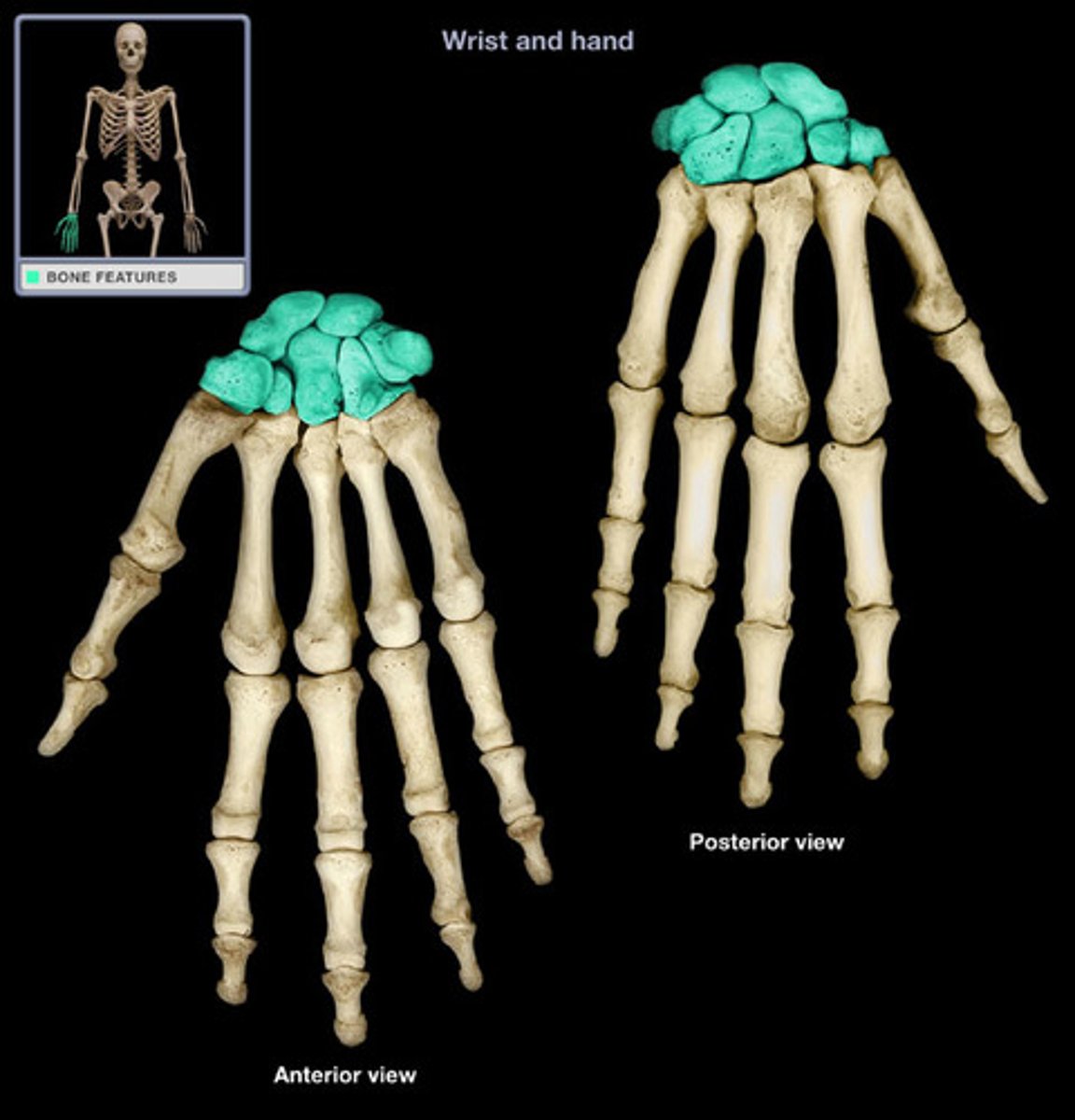
carpal bones
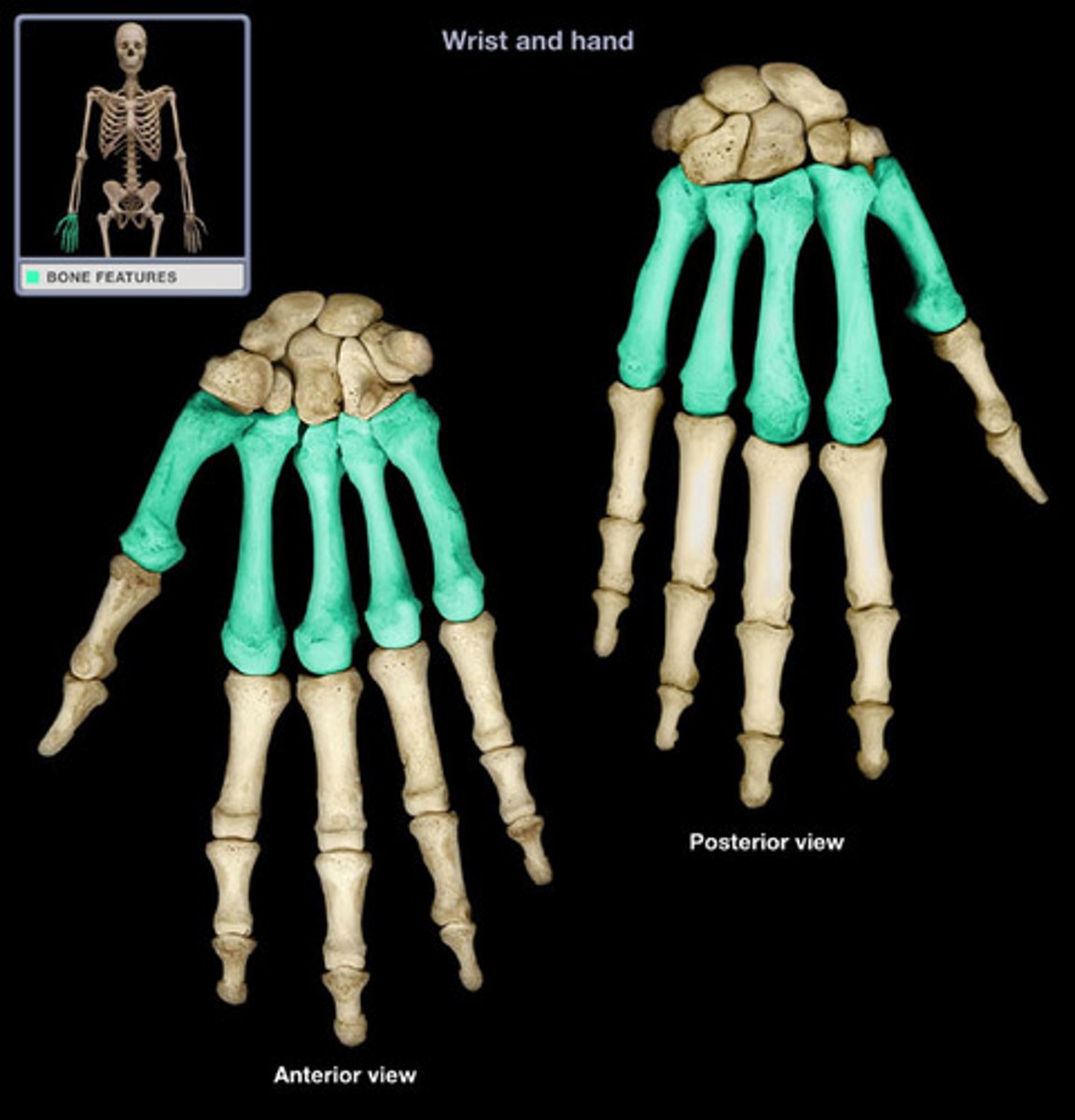
metacarpal bones
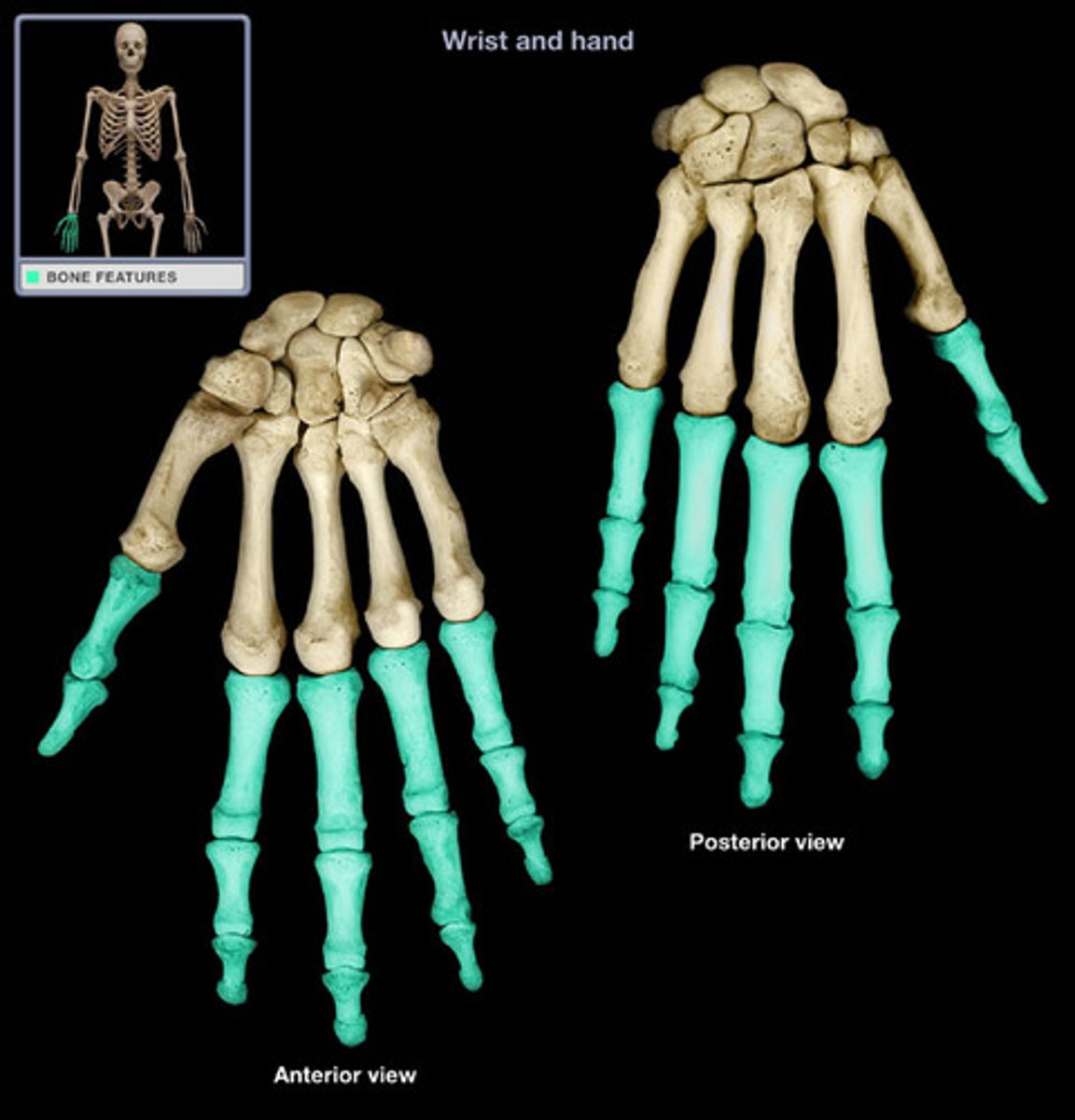
Phalanges of hand
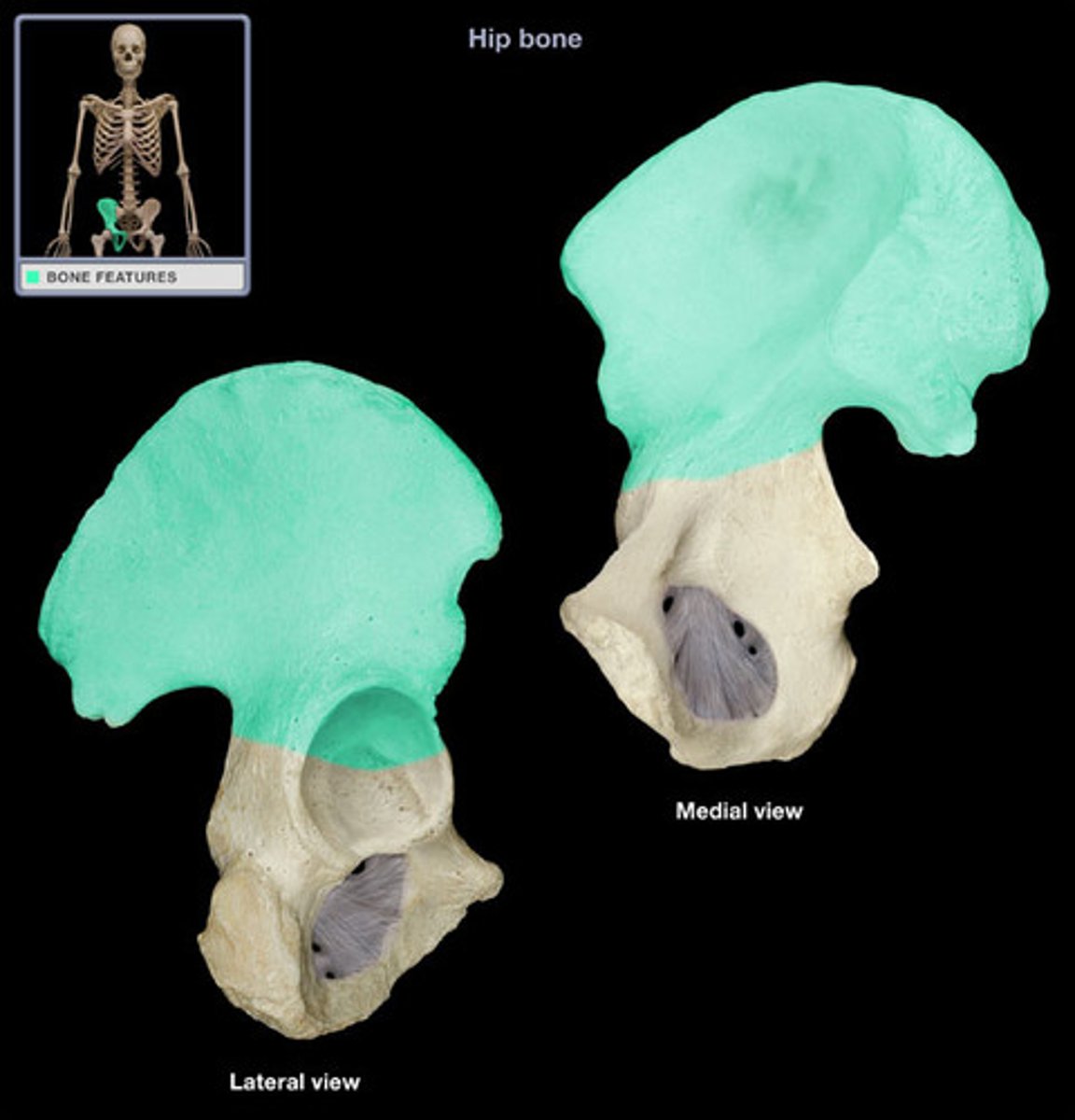
os coxae
the hipbone; formed by the union of the ilium, ischium, and pubis
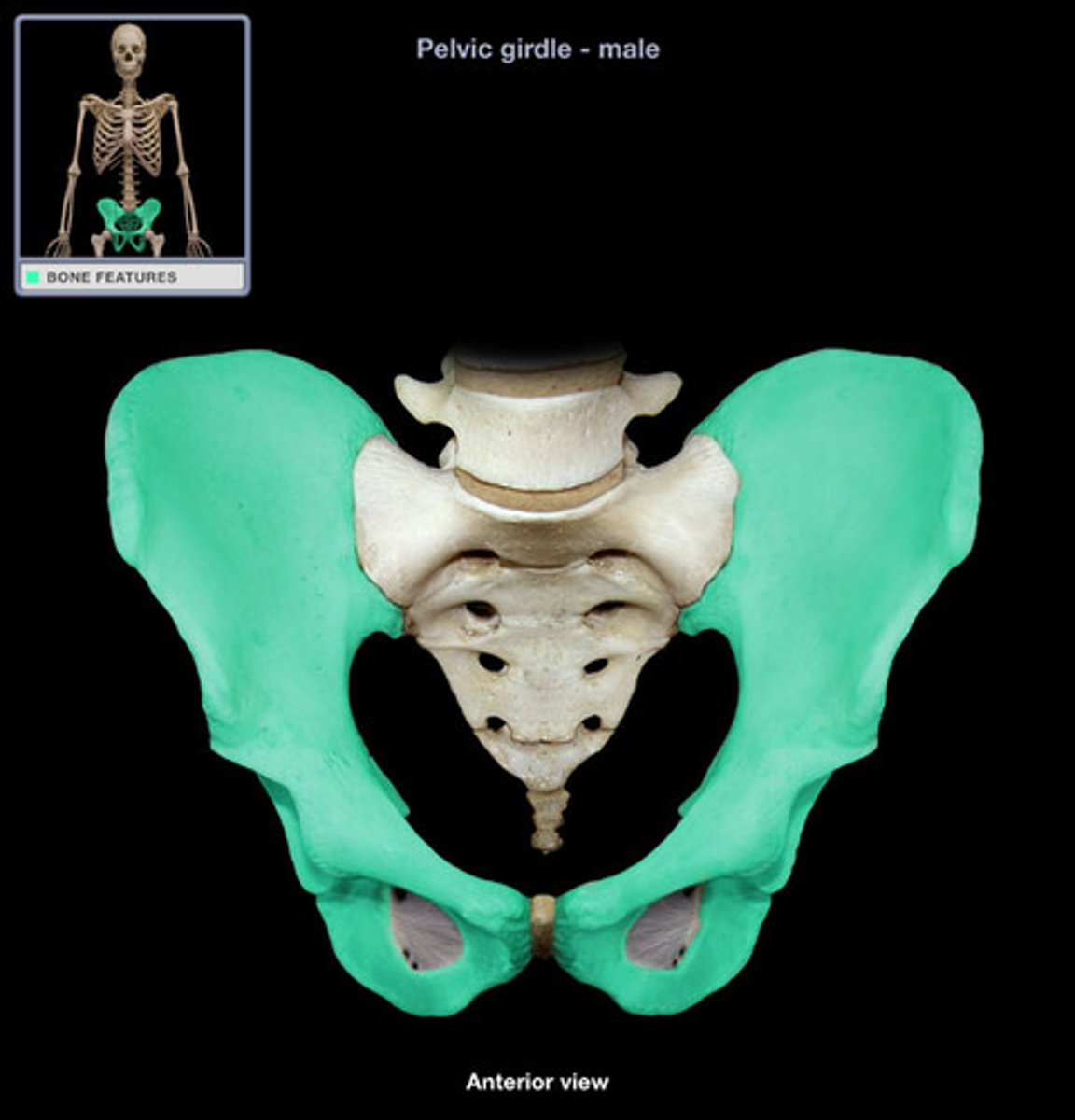
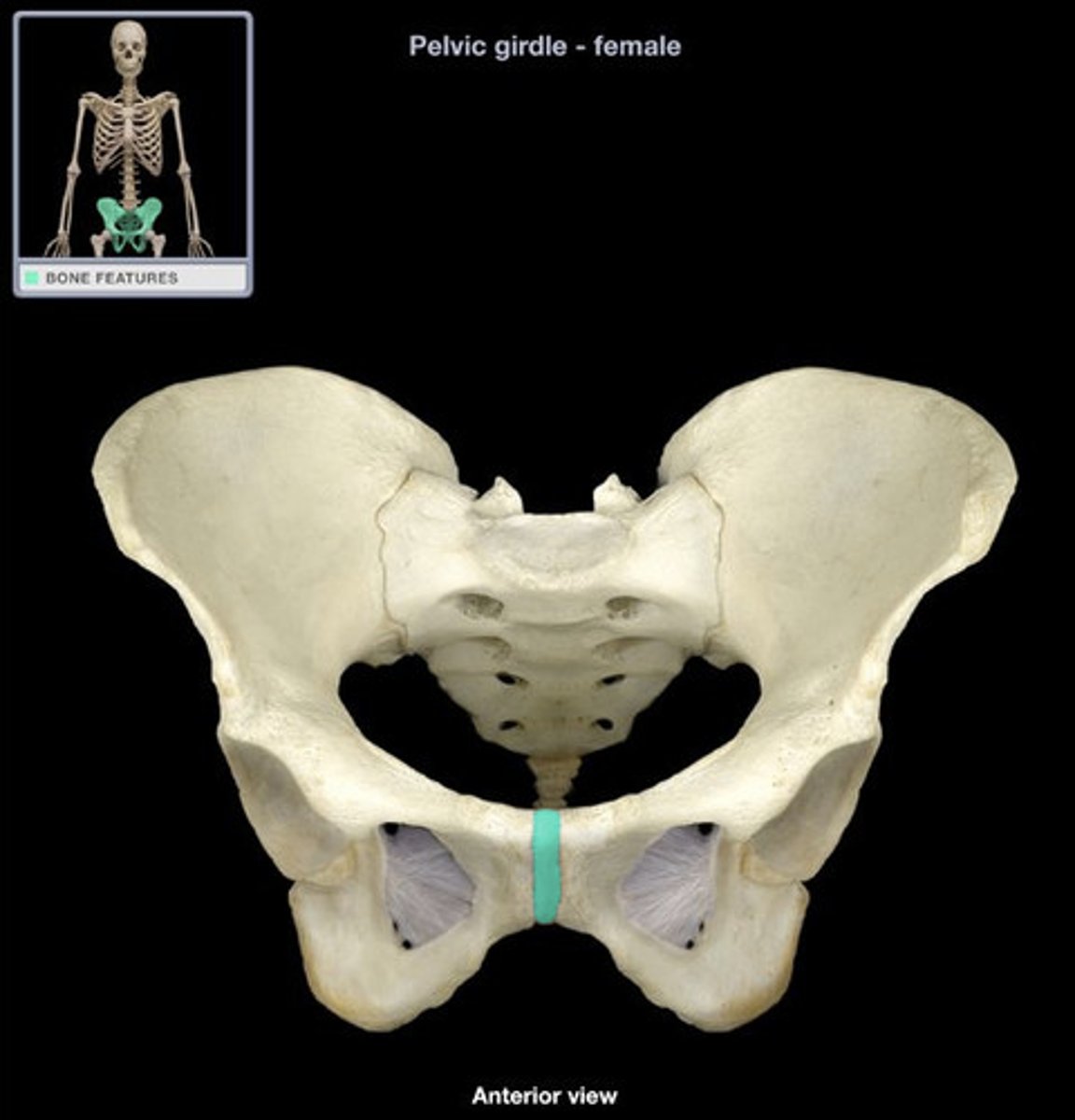
pubic symphysis
Illium
ischium
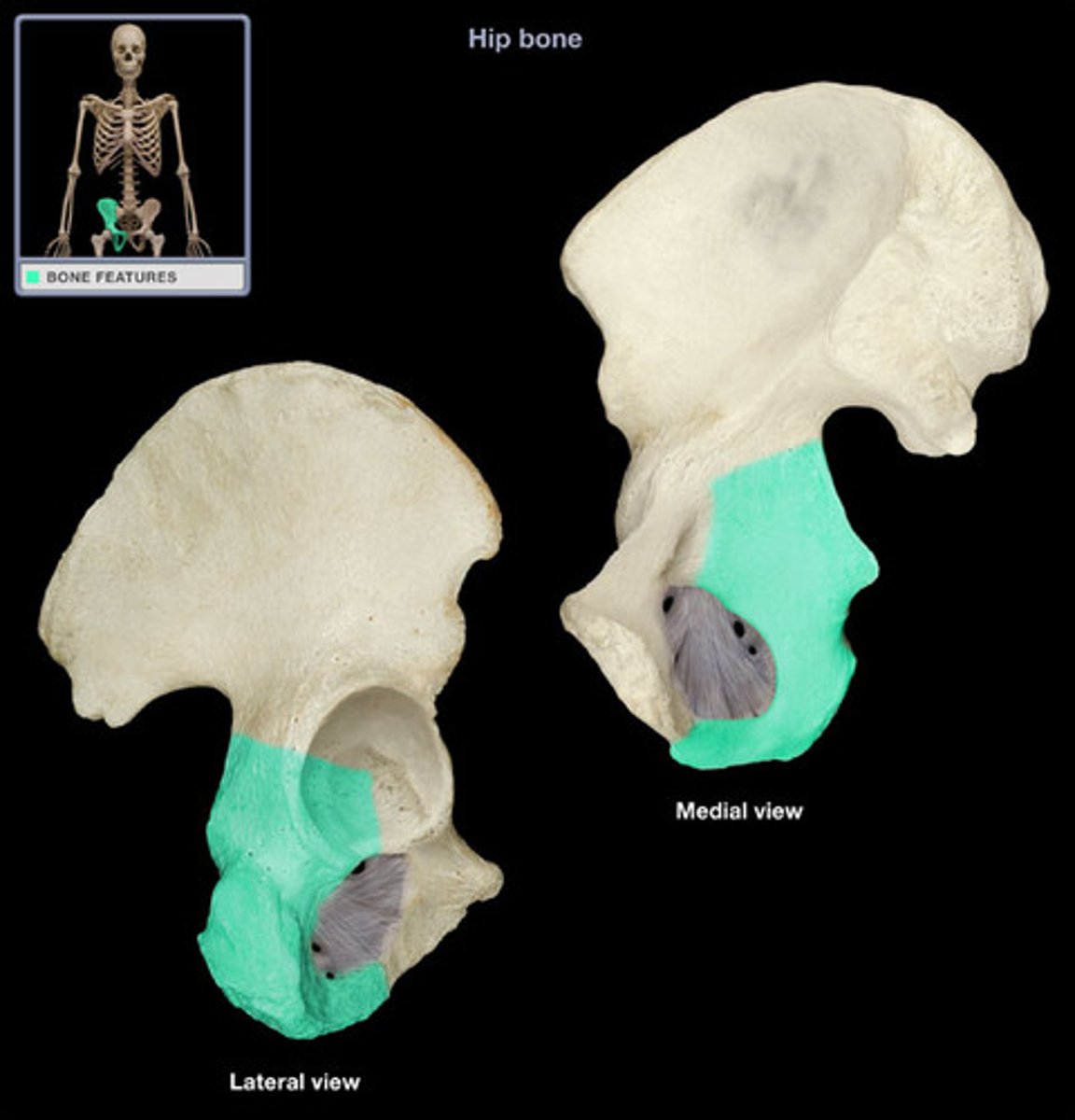
pubis
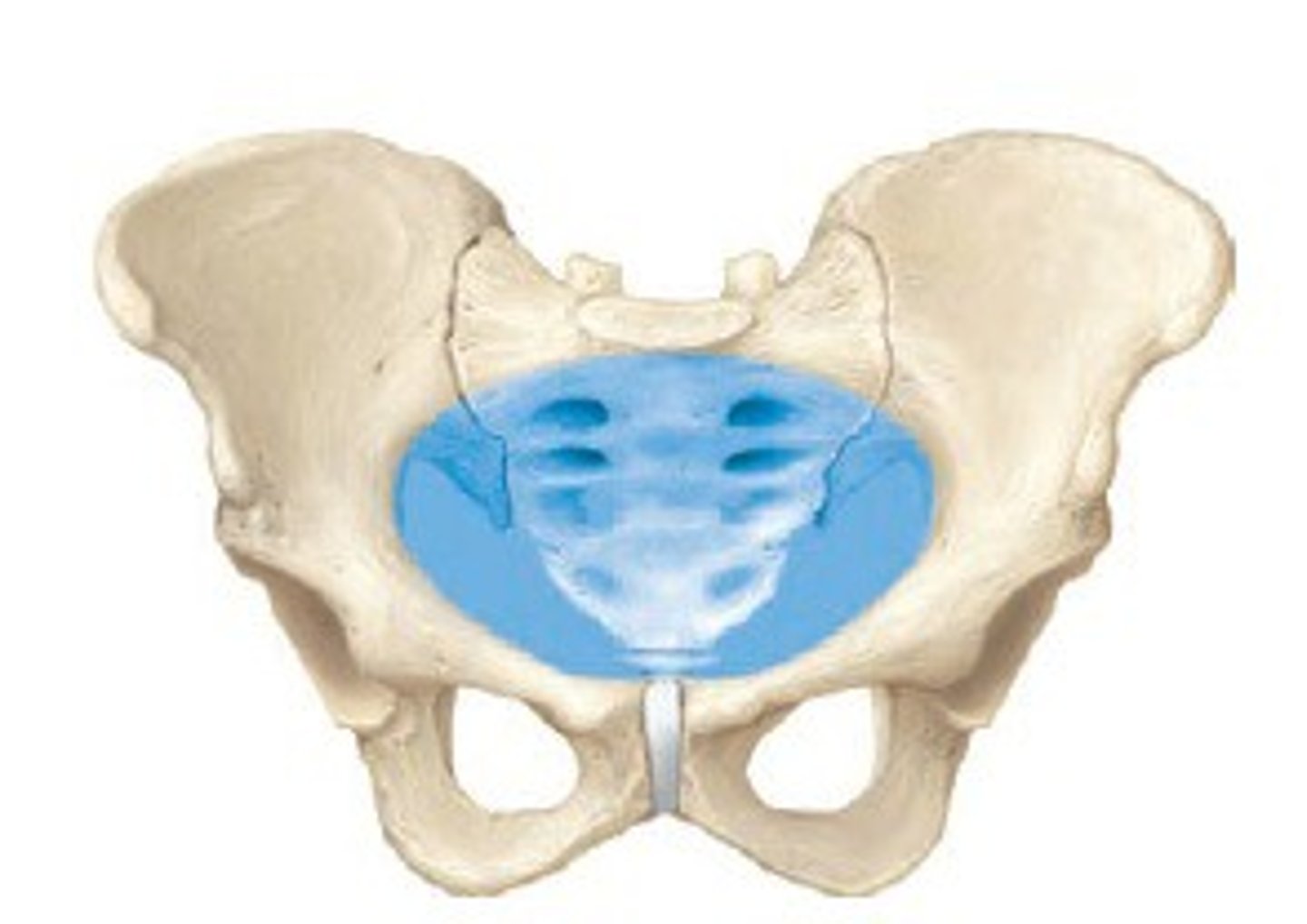
true pelvis
inferior to pelvic brim; defines birth canal
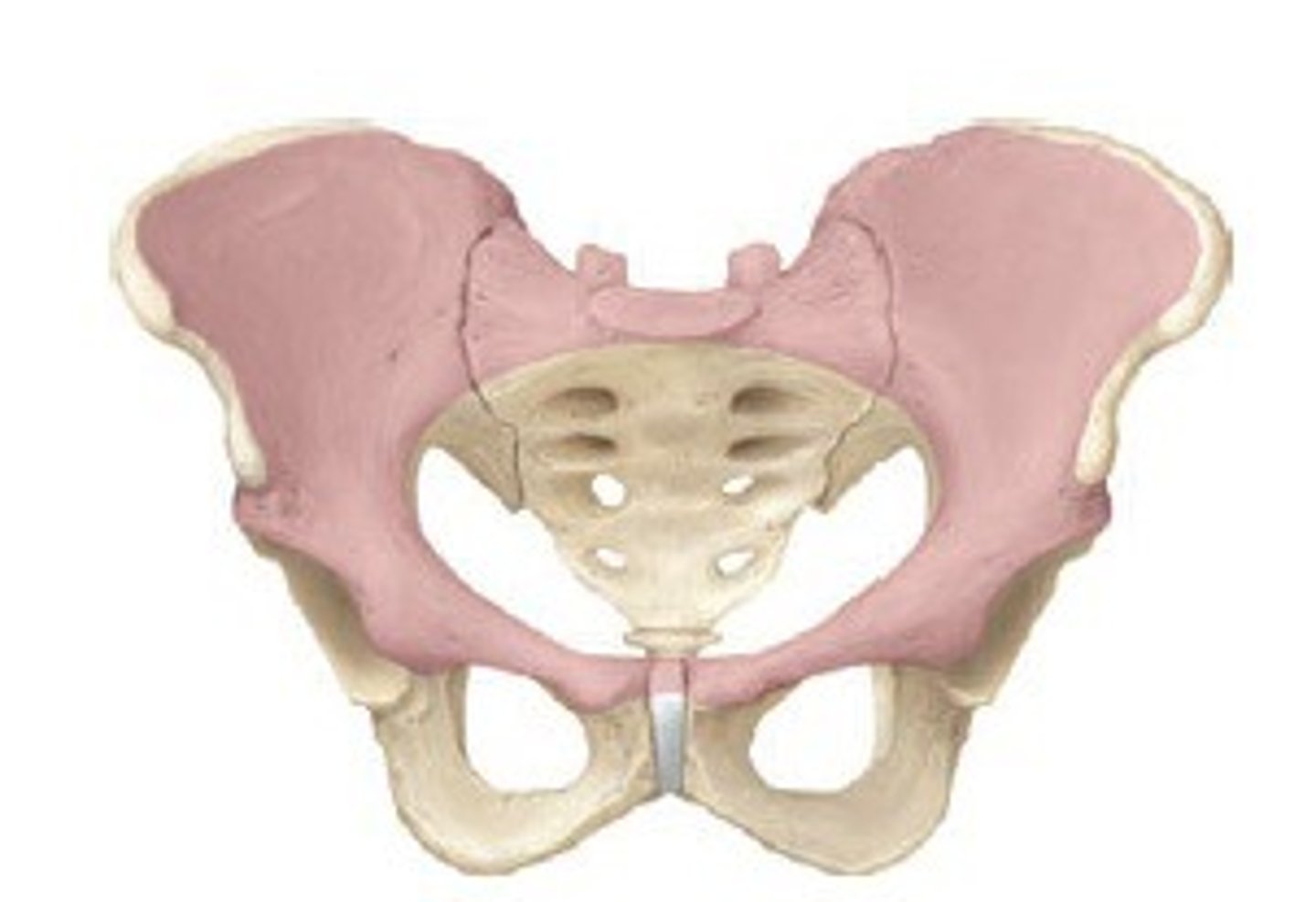
false pelvis
Superior to pelvic brim, houses inferior abdominal organs
male pelvis
-Tilted less forward
-Adapted for support of heavier male build and stronger muscles
-Cavity of true pelvis is narrow and deep
female pelvis
tilted forward, adapted to childbearing, broad, shallow, pubic angle lightweight
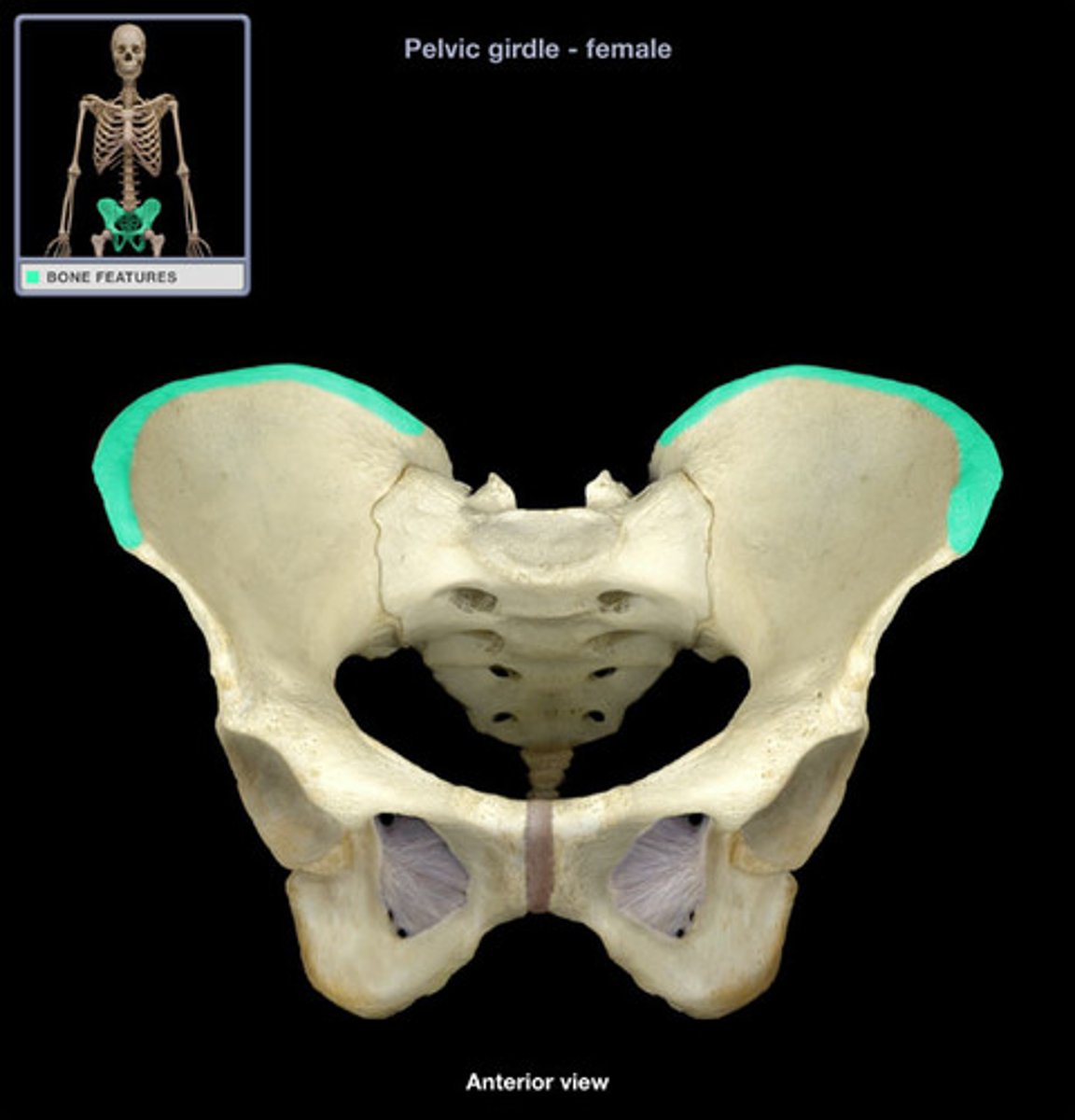
iliac crest
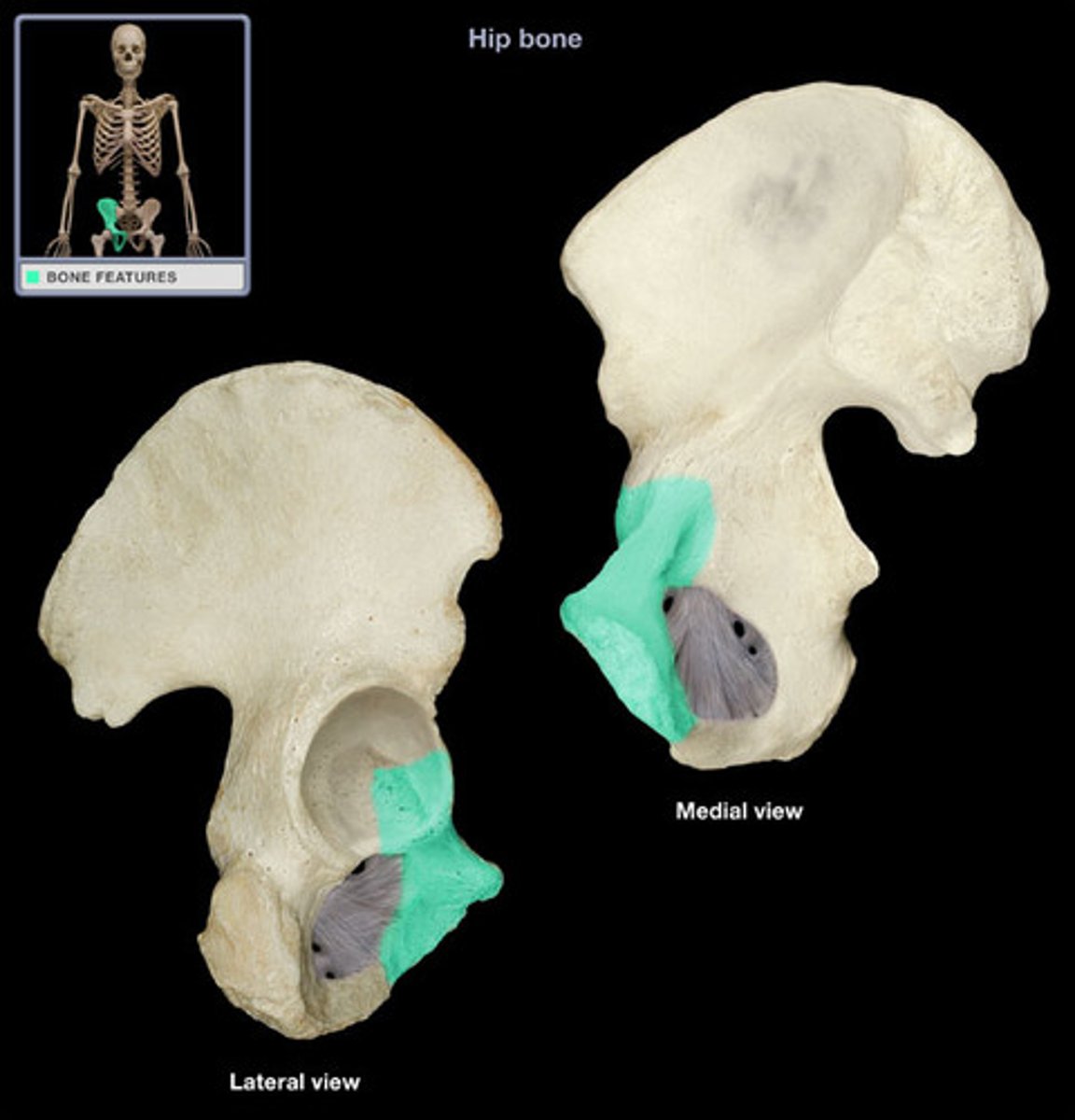
Acetabulum
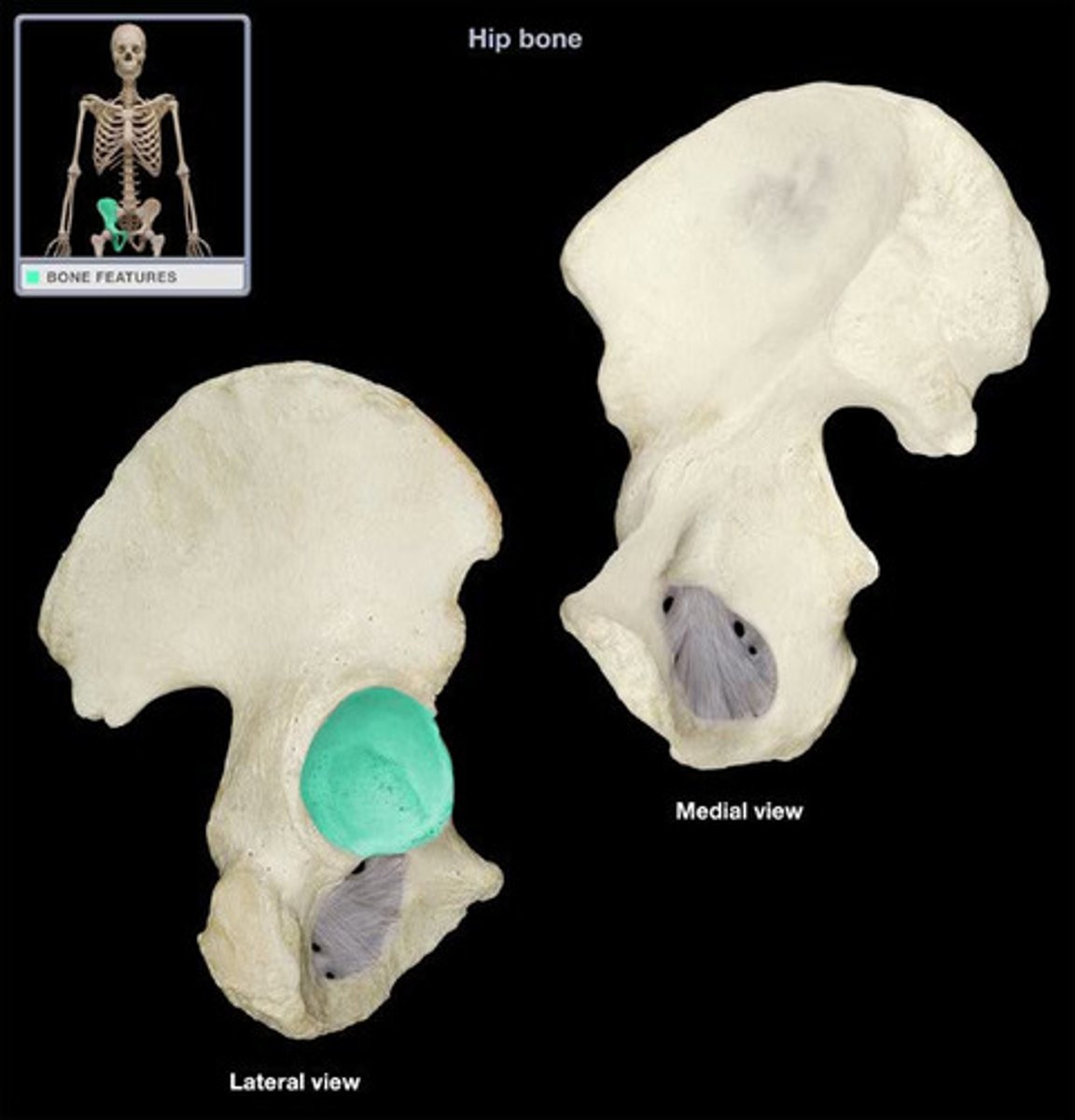
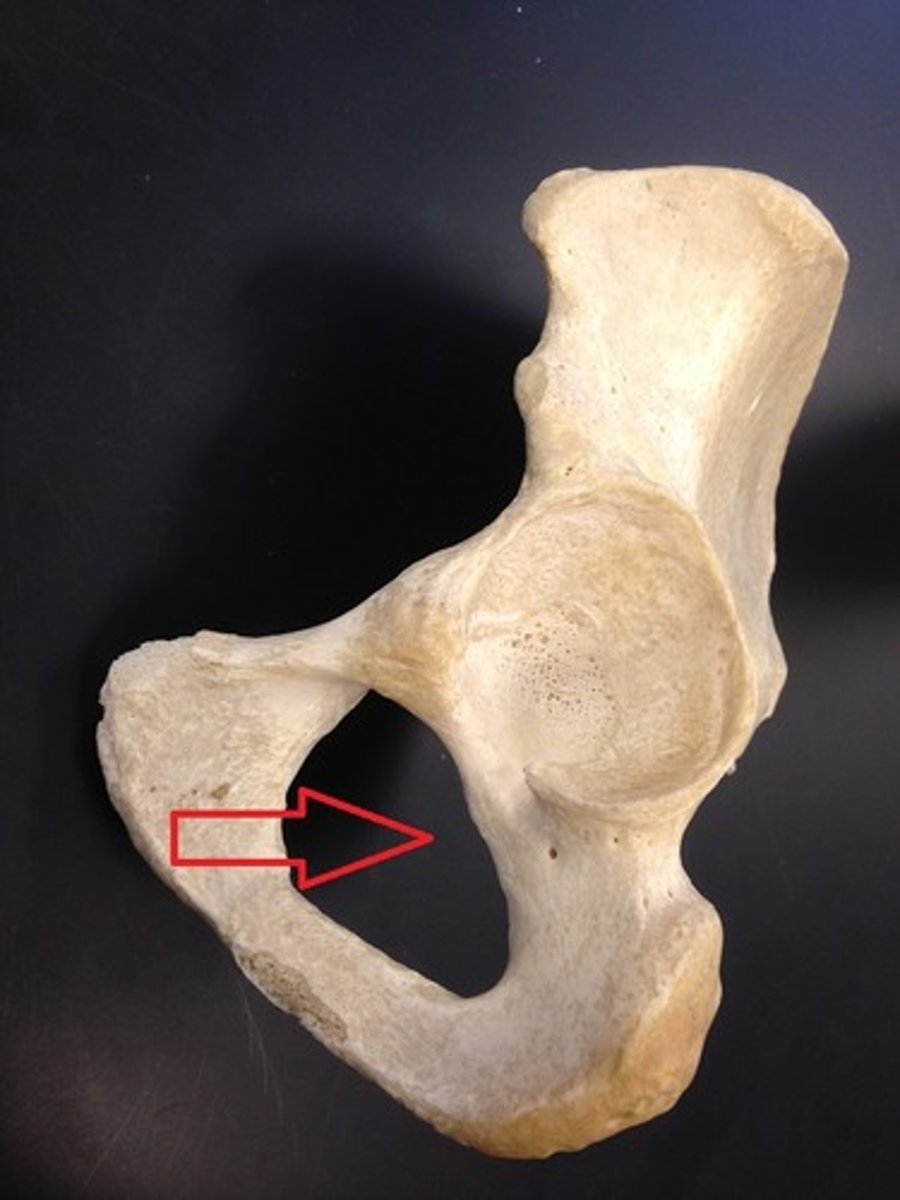
oburator foramen