Types of Communication Models (copy)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
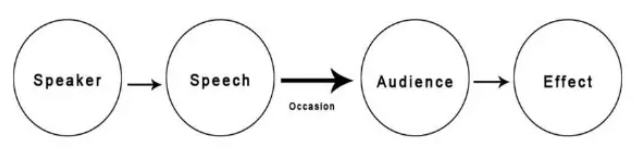
Aristotles communication model
Considered as the first model of communication and is a widely accepted model
Communication
It is a process by which information is transmitted and understood between two or more people
Rhetoric
In order to attain the effect or achieve the purpose of communication, people should be able to master the art of ______________
Aristotles communication model
This model focuses on the speaker and its speech
Aristotles communication model
This model is used to develop public speaking and to create a propaganda
Speaker, speech, audience, effect
These are the 4 components of Aristotles communication model
Logos, ethos, pathos
These are the 3 rhetorical appeals
Persuasive
Aristotle and the rhetorical appeals focuses on the ______________ perspective
Logos
Refers to logical appeal
Logos
Appealing to one logical side often backed up by facts, statistics, charts, and graphs
Ethos
Refers to credibility appeal
Ethos
Establishes that the persuader is trustworthy, by showing where one’s information came from or by using an expert or testimonial
Pathos
Refers to emotional appeal
Pathos
Refers to creating an emotional response/personal connection with the audience
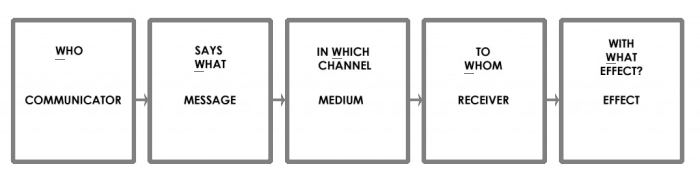
Lasswell’s communication model
He believes that a convenient way to describe an act of communication is to answer the questions: who, says what, in which channel, to whom, with what effect
Lasswell’s communication model
This models intention is for MASS COMMUNICATION
Communication, medium, receiver, result
Who: _________
Says what: Message
In which channel: ___________
To whom: ______________
With what effect: _______________
Control analysis, content analysis, media analysis, effect analysis
Who: _____________
Says what: _______________
In which channel: _________________
To whom: Audience analysis
With what effect: ______________
Lasswell’s communication model
This model uses the concept of effect
Lasswell’s and Aristotle’s communication models
Both of these models have no concept of feedback
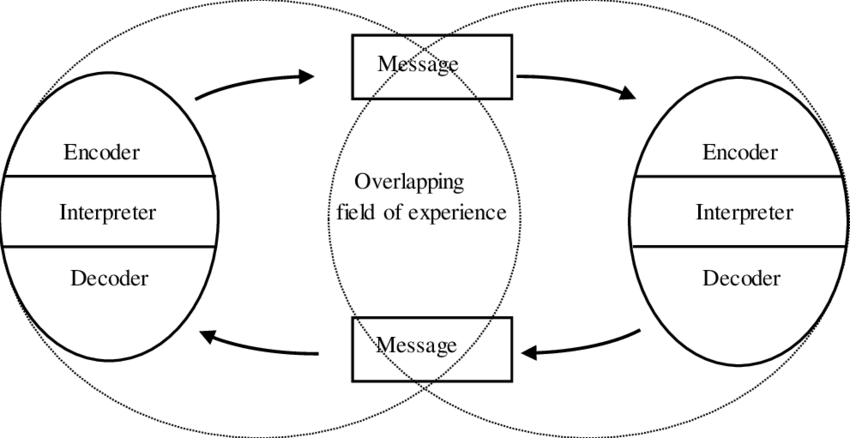
Osgood-Schramm’s communication model
This model highlights that communication is reciprocal and equal, a two-way street
Osgood-Schramm’s communication model
This model highlights that the sender and the receiver can be the same person
Cyclical
Communication is a ___________ process, not a simultaneous process
Semantic barrier
These are OBSTACLES in communication that DISTORT or misinterpret the meaning of the message
These are misunderstandings between the sender and receiver
Encoder
Refers to the one who does the encoding or sends the message
Decoder
Refers to he/she that receives the message
Interpreter
Refers to the person trying to understand or interpret the message
Message
Refers to the information or content being communicated between the sender and receiver. These can be verbal or non-verbal.
Field of experience, message, encoder, decoder, interpreter, and feedback
These are the components of Osgood-Schramm’s model
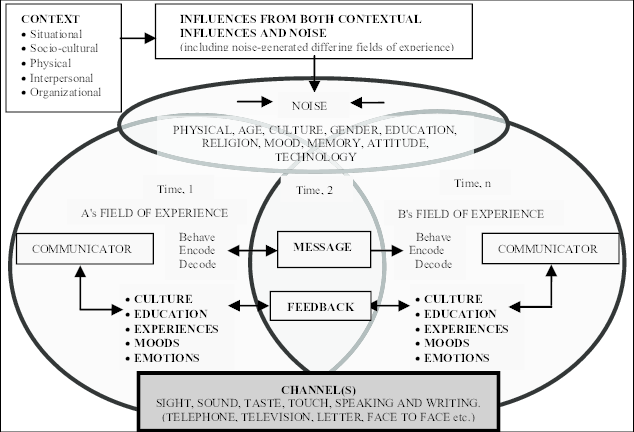
Wood, Adler, and Towne communication model
It is a model of communication that emphasizes INTERPERSONAL communication and focuses on the interactive nature of how people communicate
Wood, Adler, and Towne communication model
This model highlights how people build relationships, negotiate meaning, and manage communication challenges in their interactions
Communicator, message, feedback, noise, channel, and context
These are the components of Wood, Adler, and Towne’s communication model
Channel
The MEDIUM through which the message is transmitted, such as face-to-face conversation, phone calls, written text, etc.
Wood, Adler, and Towne communication model
This model highlights the importance of CONTEXT (Situational, sociocultural, physical, interpersonal, organizational)
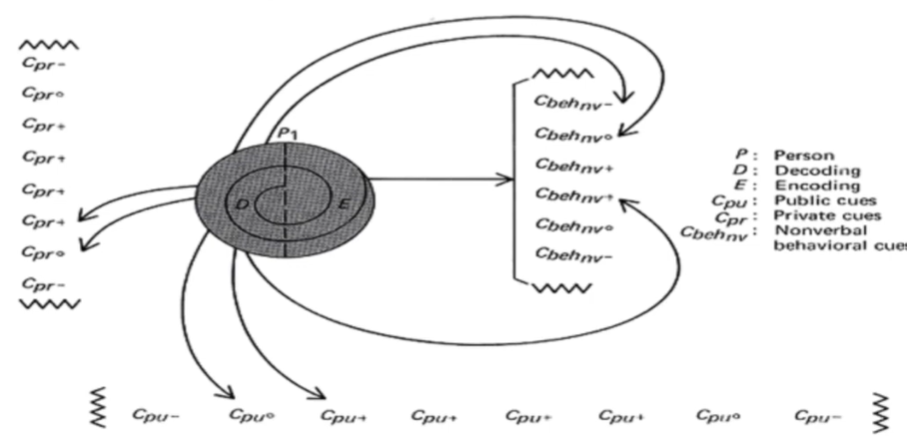
Barlund’s transactional communication model
The model states that giving and receiving messages is reciprocal. Both communicators are responsible of the effect and effectiveness of the communication. They need to build a SHARED MEANING of the message
Barlund’s transactional communication model
In this model, verbal and non verbal behavioral cues are introduced
Encoder/Decoder, noise/jagged lines, private cues, public cues, behavioral cues, arrows
These are the components of Barlund’s transactional communication model
Interpersonal and intrapersonal
According to Barlund there are two (2) types of communication which are?
Intrapersonal
Refers to encoding and decoding messages within ONES SELF
Interpersonal
Refers to encoding and decoding messages with ONE ANOTHER
Noise/Jagged Lines
A component in Barlund’s model that refers to the problem that arises in communication flow and disturbs the message flow
Private cues
A component in Barlund’s model that refers to (cue) the personal thoughts based on the background on the person (intrapersonal)
Public cues
A component in Barlund’s model that refers to (cue) that refers to the [physical] environment that affects communication
Filters
A component in Barlund’s model that refers to the REALITIES of people engaged in communication. Here the senders’ and receivers’ personal filters might differ according to cultures, traditions, content of the message, etc.
Arrows
A component in Barlund’s model that shows the message is intentional
Jagged Lines
A symbol in Barlund’s model that show that the availability of cues can be unlimited and are denoted as VVVV
Positive, negative, and neutral
These are the three (3) types of valence signs in Barlund’s model
Positive valence
This valence sign shows that the other person agrees/supports with your statements
Negative valence
This valence sign shows that the other person disagrees/anti with your statements
Neutral valence
This valence sign shows that the other person neither agrees or disagrees with your statements
Wood, Adler, and Towne communication model
Identity this communication model
Aristotle’s communication model
Identity this communication model
Lasswell’s communication model
Identity this communication model
Osgood-Schramms communication model
Identity this communication model
Barlund’s transactional communication model
Identity this communication model