quantum mechanics part 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what phase is rotational spectroscopy usually done in?
why?
gas phase
solids inhibit rotation, and in a liquid, too many collisions cause rapid energy transfer
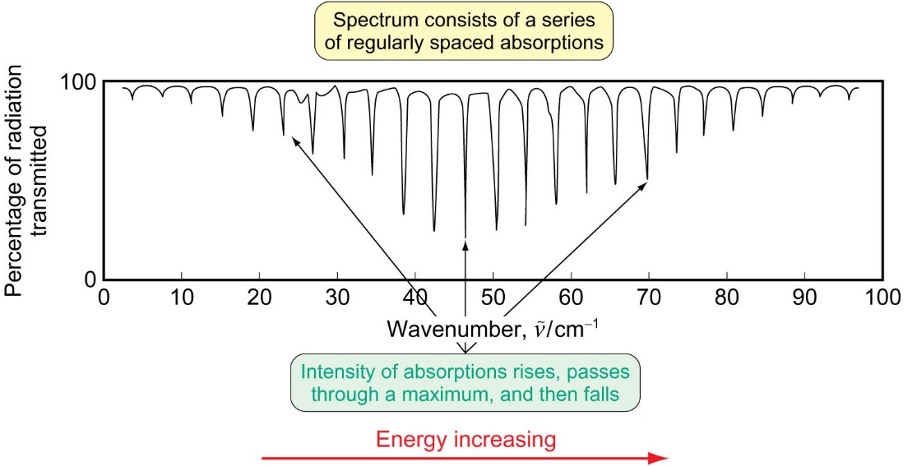
what does rotational spectrum look like?
absorptions are regularly spaced
intensity of abs rises, reaches a max then falls
what is the rigid rotor model?
what does it assume?
assumes fixed bond length between two atoms in molecule
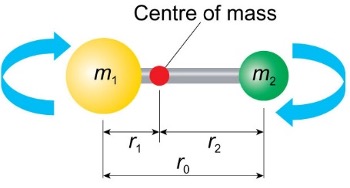
what does the moment of inertia tell us?
how easy it is to spin the diatomic molecule about its centre of mass
how does speed of rotation change for heavier masses of molecules and longer bond length?
rotor spins more slowly for a given magnitude of push
when calculating reduced mass ,what should you remember?
multiply by atomic mass unit to calculate in kg
what is J?
rotational quantum number
how to calculate EJ?
EJ = hBJ(J+1) (B has units s-1)
what are the conditions needed for rotational spectroscopy?
the molecule must have a permanent electric dipole
why must a molecule have a permanent electric dipole to have a rotational spectrum?
the oscillating electric dipole during rotation can interact with oscillating electric and magnetic fields of the EM radiation at the same frequency
which molecules cannot be probed for a rotational spectrum?
homonuclear molecules have no permanent electric dipole
what is the specific selection rule for rotational spectroscopy?
transitions can only take place between adjacent energy levels
ΔJ = ± 1
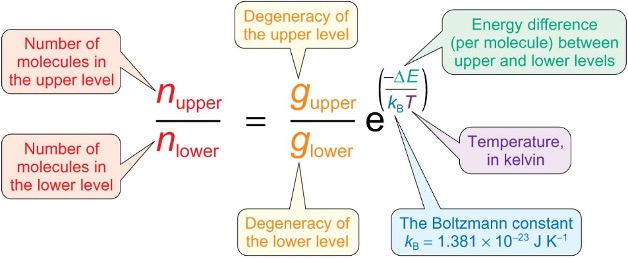
what is the equation to calculate the ratio of populations in energy levels?
what is the wavefunction for J=0?
spherical symmetric
similar to s orbital
how many wave functions for J=1?
what are they like?
three wave functions
similar to p orbitals of H atom
how many wavefunctions for J=2?
what are they like?
five wave functions
similar to d orbitals of H atom
why are higher rotational energy levels more populated than lower?
higher energy levels have higher degeneracy (2J+1)
higher potential for higher occupancy
how does population change as you go up rotational energy levels?
increases until energy gaps eventually become ≥ kBT and then population drops off
how can you find ΔE from microwave spectrum?
find from wavenumbers of spectral peaks
peak intensities means energy level occupancies can be calculated
assigning peaks to ELs means can find degeneracy
temperature is only unknown
what is centrifugal distortion?
rotational energy increases, molecule spins faster, bond length increases
what is the equation for EJ accounting for centrifugal distortion?
EJ = hBJ(J+1) - DJ2(J+1)2
how does the gaps between ELs change as rotational energy increases for non-rigid rotors?
as rotational energy increases, the gaps between the energy levels get smaller
how does vibrational spectroscopy probe molecular motions?
due to movement of atoms in individual chemical bonds
how are chemical bonds modelled for IR spec?
what is the equation?
bonds modelled as mechanical springs
F = -kx
k is bond force constant
x is displacement
F is restoring force
how to calculate displacement from equilibrium position (bond length)?
x = r - r0
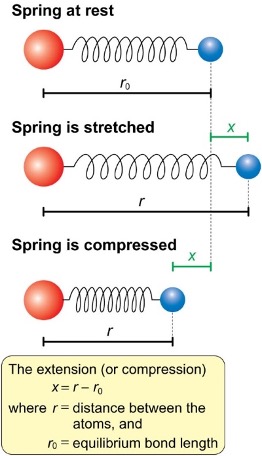
how does the force work when the atoms are pushed farther apart? if displacement is inwards (pushed together?)
the more you push the atoms further apart, the greater the force pushing back together
if pushed inwards, the force is pushing them back out
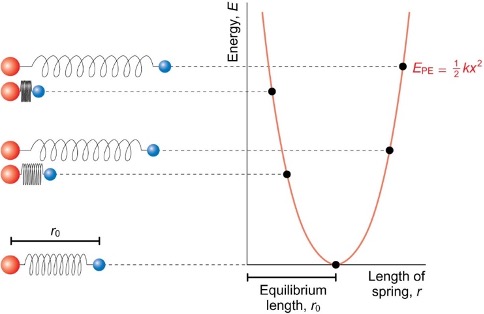
what is the graph for potential energy of bond vibrations?
how to calculate force?
force is negative gradient
what does vibrational frequency depend on (2)?
the mass of the atoms (heavier atoms vibrate at a slower frequency)
the bond force constant (stiffer springs vibrate at higher frequency)
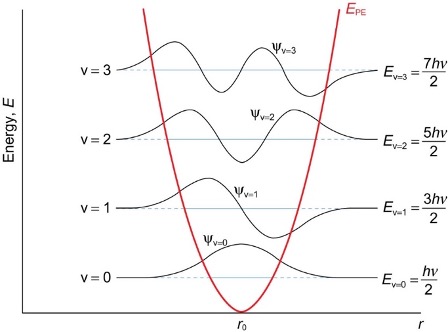
what is the equation for EV?
EV = (v + ½ )hv
how do the wavefunctions change in and out of the parabolic well?
finite outside of the parabolic well
= quantum mechanic tunnelling
finite probability of particle penetrating this region even though classically should not exist outside well
what two rules pertain to infrared spectroscopy?
gross selection rule (must be change in dipole moment)
specific selection rule Δv=±1.
what does +1 and -1 values of Δv mean (vibrational spec)?
+1 is adsorption
-1 is emission
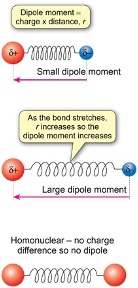
how to calculate dipole moment of vibration of bond?
charge x distance (r)
how does dipole moment change as bond stretches?
r increases so dipole moment increases
when is there no change in dipole moment for CO2?
when is there?
for symmetric (vibrate both inwards/outwards), there is no change
for asymmetric there is a change as the electrons are pulled towards O differently
dipole moment for bending modes
why do you only expect one peak for diatomic molecules in a vibrational spectrum?
energy levels are evenly spaced
only one frequency that a diatomic molecule absorbs at
what is the bond force constant a measure of?
stiffness and therefore strength of the bond
why is k independent of isotopes?
doesn’t change significantly by adding neutrons to nucleus
why is the shift in infrared spectra most significant for H→D isotopic substitution?
lightest atom moves much more than the heavy atom and dominates the value of the reduced mass
how is anharmonic oscillation different from harmonic oscillation?
real energy levels aren’t equally spaced
potential energy curve isn’t a parabola
if the atoms are pulled far enough apart, the bond breaks
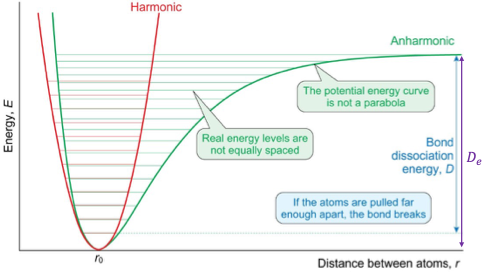
how does the spacing between energy levels change as you go up (anharmonic)?
spacing gets smaller
what transitions are observed in real molecules (vibrational)? why?
what are these called? when do they occur?
selection rule is only for harmonic
transitions v = 0 → v = 2 and v = 0 → v - 3
overtone bands (occur at twice and three times the fundamental frequency)
how many vibrational modes do linear molecules have?
3N-5 (N is number of atoms)
how many vibrational modes do non-linear molecules have?
3N-6 (N is number of atoms)
how does number of modes of vibration change with number of atoms?
more atoms means more possible modes of vibration
how many degrees of freedom do N atoms have?
3N
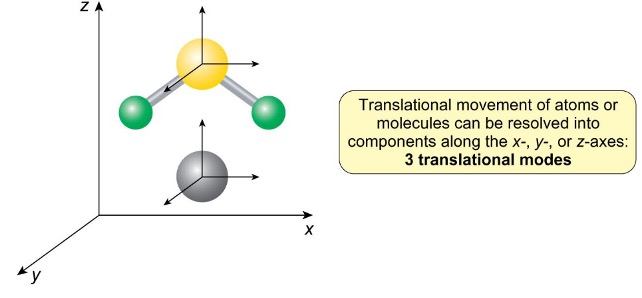
how many translational modes are there for molecules?
3
along the x, y, z axes
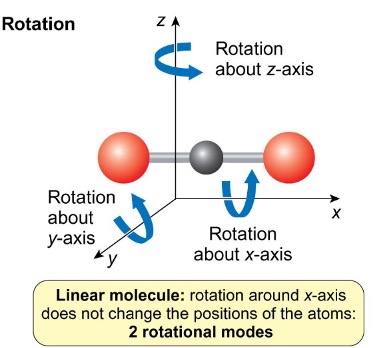
how many rotational modes do linear molecules have?
2
rotation around the x axis doesn’t change the positions of the atoms
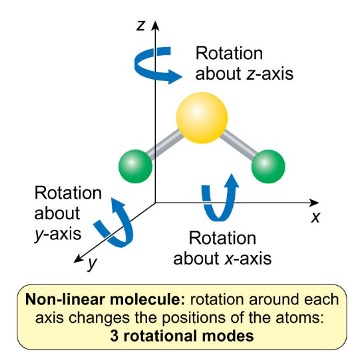
how many rotational modes do non linear molecules have?
3
rotation around each axis changes the position of the atoms
how many degrees of freedom do monoatomic molecules have?
how many translational, rotational and vibrational modes?
3 degrees of freedom
3 translational, 0 vibrational and rotational
how many degrees of freedom do diatomic molecules have?
how many translational, rotational and vibrational modes?
six degrees of freedom
3 translational, 2 rotational, 1 vibrational
how many degrees of freedom do triatomic linear molecules have?
how many translational, rotational and vibrational modes?
9 degrees of freedom
3 translational, 2 rotational, 4 vibrational
how many degrees of freedom do triatomic non linear molecules have?
how many translational, rotational and vibrational modes?
9 degrees of freedom
3 translational, 3 rotational, 3 vibrational
what causes UV/vis spectroscopy?
lower occupied molecular orbital to a higher unoccupied or partially occupied molecular orbital
what causes the colour in compounds?
absorption of light due to transitions between electronic energy levels
if KMnO4 is purple, what is it absorbing and what is it transmitting?
absorbs green
transmits blue and red
what are bonds like in excited state?
weaker and longer
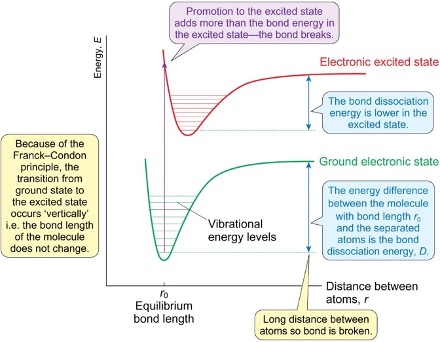
electronic spectra diagram
where do transitions occur to and from?
what is the energy minimum like in the excited state? what does this mean about the bond?
occur from ground state to a number of vibrational energy levels in electronic excited state
energy minimum is at a longer distance as bond is longer
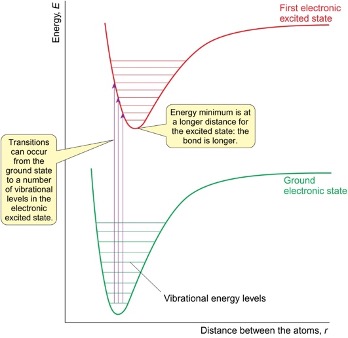
what causes broad spectral bands in electronic spectra?
if vibrational energy levels are close together they merge to give broad band
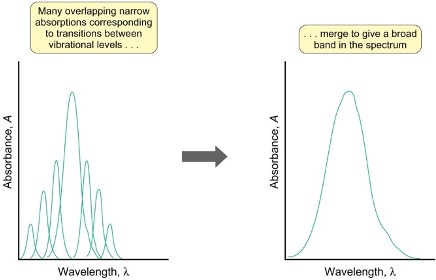
what does the frank-condon principle state about electronic spectra?
absorption of photons happens on much shorter timescale than for nuclear motions
which way do transitions from ground to excited state occur?
what does this mean about bond lengths?
vertically
bond lengths of molecule do not change
what causes photodissociation?
photon adds enough energy to exceed bond dissociation energy and bond breaks
how is bond dissociation energy different for ground state vs excited?
greater distance for ground state
therefore lower dissociation energy for excited state
what happens when molecular length (chromophore) is increased?
what is this similar to?
wavelength of absorption increases and molecular extinction coefficient increases
similar to increasing length of box in which delocalised electrons are confined
can predict energy levels with particle in a box model