Microbio lec3 Prokaryotic Cell Walls, Staining Techniques, and Archaeal Structures
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Lysozyme cleaves the β1-4 glycosidic bonds between ________ and ________ in peptidoglycan.
NAM and NAG
Note: Lysozyme is and antibacterial defence in our tears, saliva, and mucus
attach slide 13 w3p1
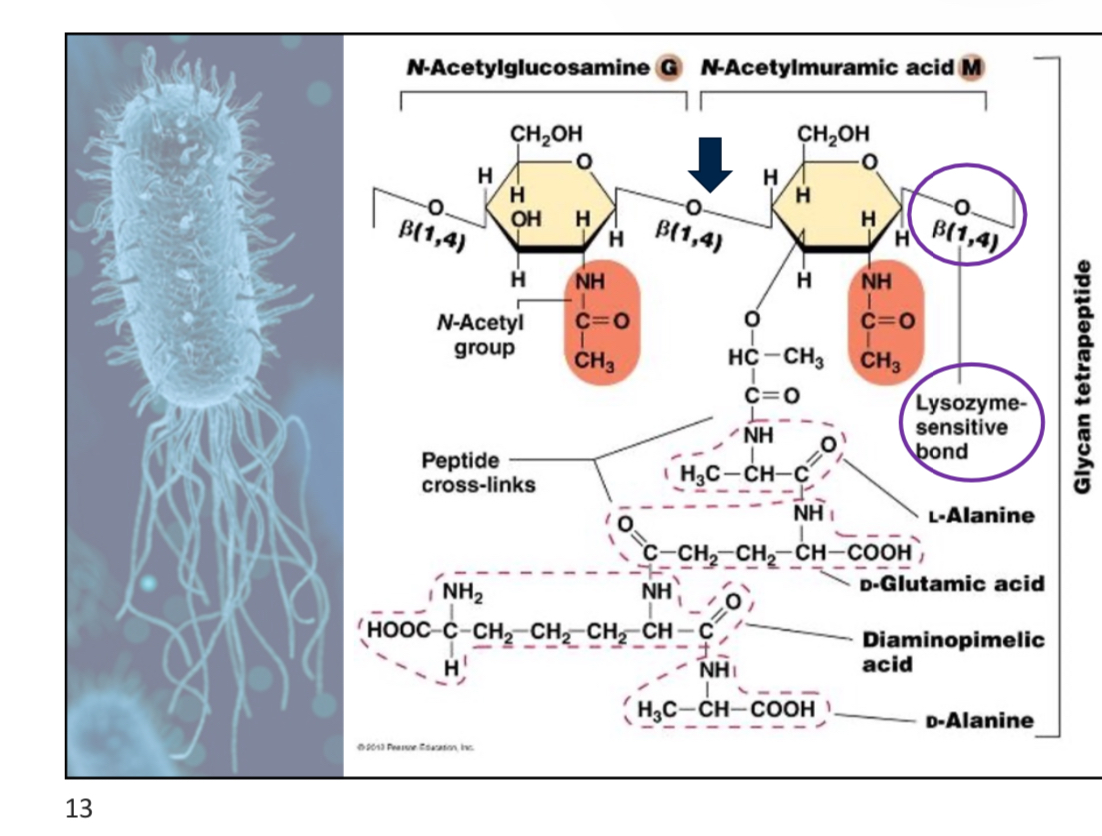
____ contain lysozyme that punch holes in bacteria to infect it
Bacteriophages (Virus)
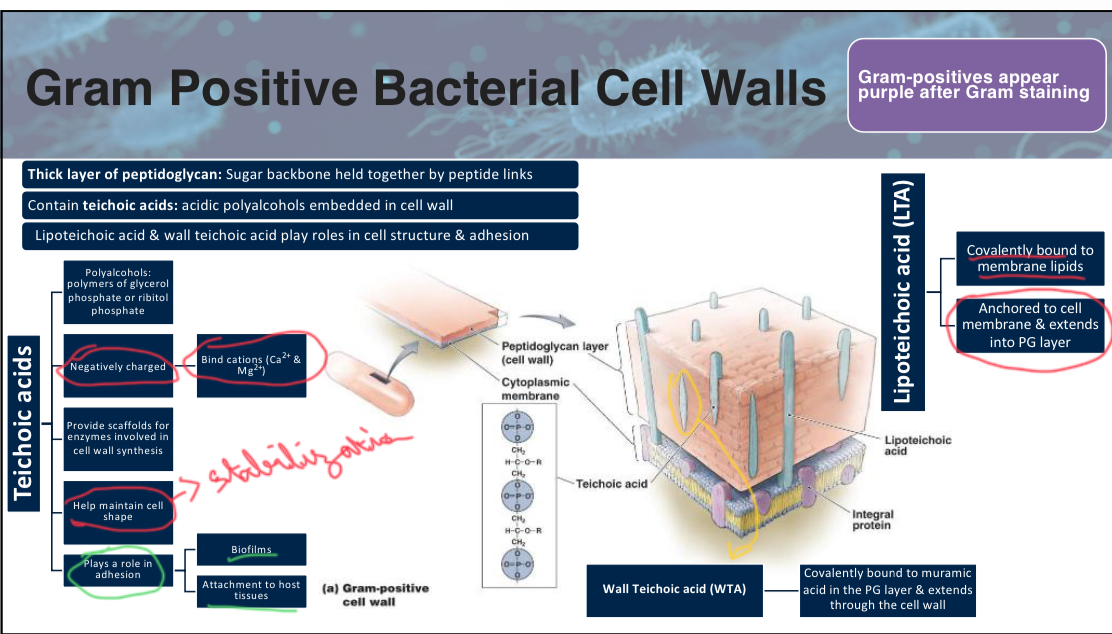
If a bacterium has a thick peptidoglycan layer and teichoic acids, it is likely:
A) Gram-negative
B) Acid-fast
C) Gram-positive
D) A virus
C
note; there’s 2 styles of teichoid acid in gram positive bacteria. Wall teichoic acid, and lipoteichoid acid
attach slide 7 w3p1
The space between the inner and outer membranes in Gram-negative bacteria is known as the ________ space.
Periplasmic
What color do Gram-positive bacteria appear after Gram staining?
A) Pink
B) Purple
C) Blue
D) Green
B
G- stain pink/red
Which of the following antibiotics inhibits the transport of peptidoglycan subunits across the cell membrane?
A) Bacitracin
B) Penicillin
C) Vancomycin
D) Cephalosporin
A
Note: Bacitracin binds/inhibits bactoprenol. Inhibition of bactoprenol blocks transport of new PG subunit across cell membranes.
attach slide 19 of w3p1
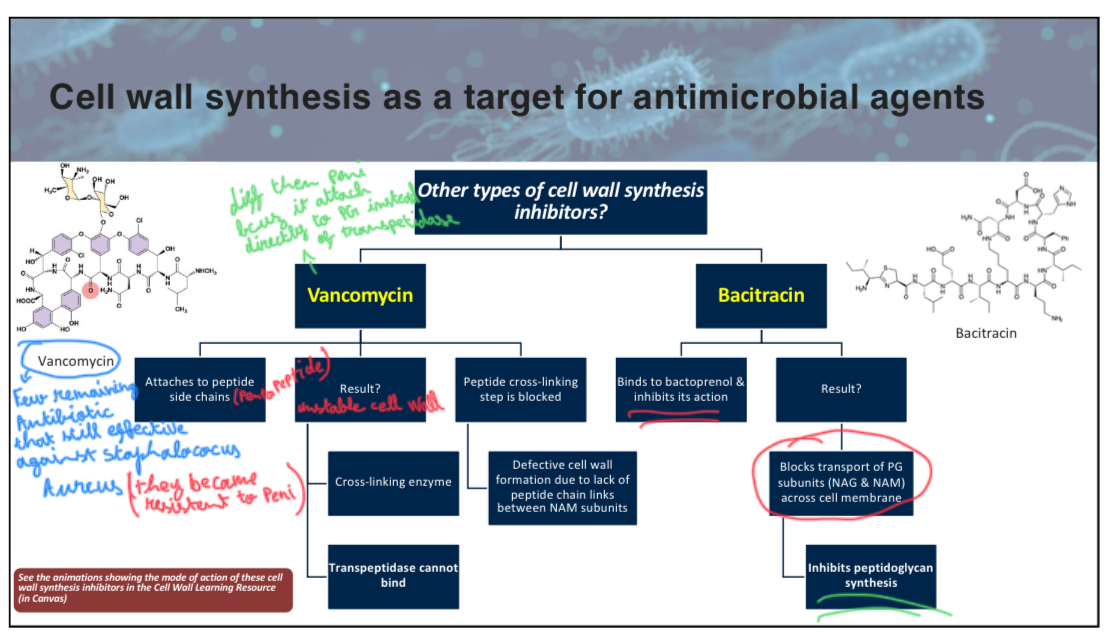
If a bacterium is resistant to penicillin, which of the following might be a reason?
A) It has a thick outer membrane.
B) It lacks teichoic acids.
C) It has a cell wall.
D) It can produce lysozyme.
A (penicillin cannot cleave the β-1,4 glycosidic bond in Gram-negative bacteria because they have a protective outer membrane that prevents penicillin from accessing their peptidoglycan layer)
What role do porins play in Gram-negative bacteria?
A) They provide structural support for the outer membrane.
B) They bind and transport ions such as Ca2+ and Mg2+.
C) They synthesize components of the bacterial cell wall.
D) They facilitate selective transport across the outer membrane.
D
True/False: Gram-negative bacteria can be distinguished from Gram-positive bacteria based on their ability to retain crystal violet during staining.
True
G+ retain the crystal violet during the staining process while G- lose it during the staining process
True/False: Vancomycin inhibits bacterial growth by blocking transglycosylation during cell wall synthesis.
False
Vancomycin attach to the pentapeptide side chain to block peptide cross linking resulting in unstable/defective cell walls
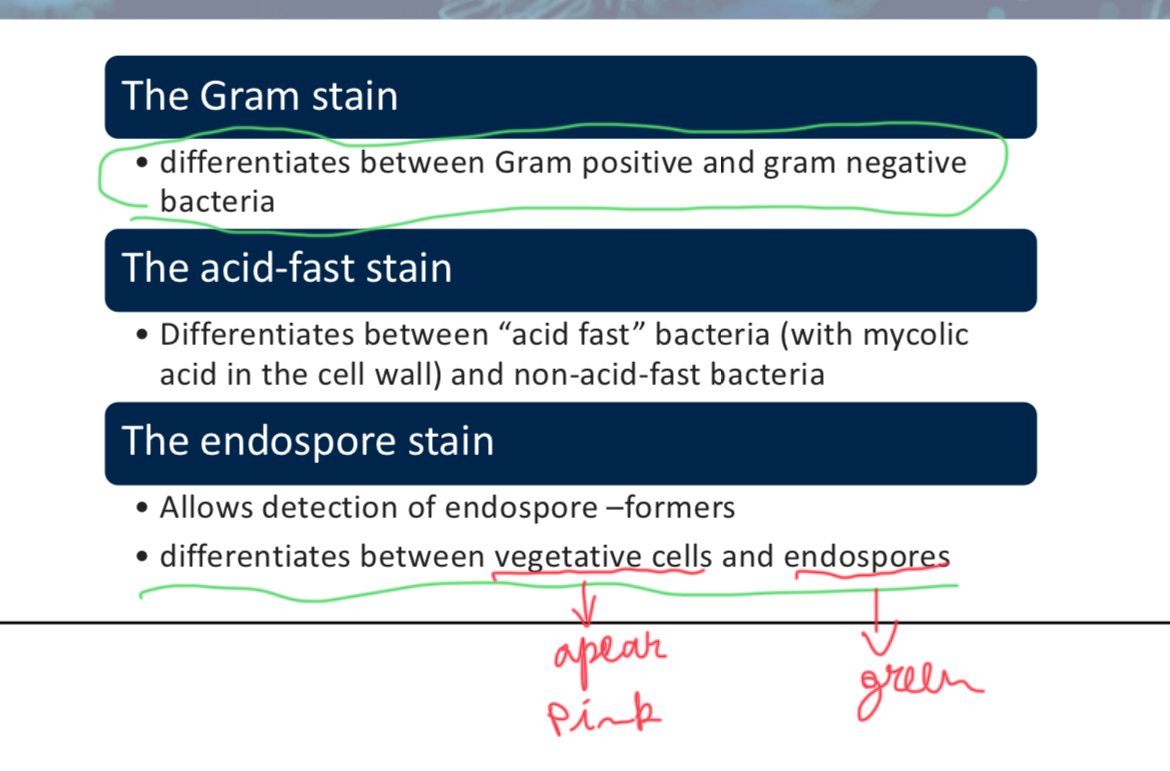
What is the primary purpose of staining bacteria?
To increase contrast and resolution by coloring specimens with stains/dyes
What are charged chromophores?
they provide particular colour to stain specimen. Microbiological stains contain these charged chromophores
Which of the following is NOT a type of differential stain?
a) Gram stain
b) Acid-fast stain
c) Crystal violet stain
d) Endospore stain
C
attach slide 6 of w3p2

The ________ stain differentiates between bacteria with mycolic acid in the cell wall and those without.
Acid fast
What is the purpose of heat-fixing a bacterial smear on a glass slide?
To adhere the bacteria to the slide
True or False: Basic dyes are more commonly used for staining cells because they stain acidic structures.
True (also bcuz cells are typically negatively charged so they are more efficiently bound by cationic chromophores of simple stains)
What is the function of iodine in the Gram staining procedure?
It acts as a mordant to increase the intensity of staining
Which step in the Gram staining procedure causes Gram-negative bacteria to lose the crystal violet-iodine complex?
the alcohol/acetone decolorization phase
What is the purpose of the counterstain in the Gram staining procedure?
To make Gram-negative bacteria visible after they lose the crystal violet-iodine complex
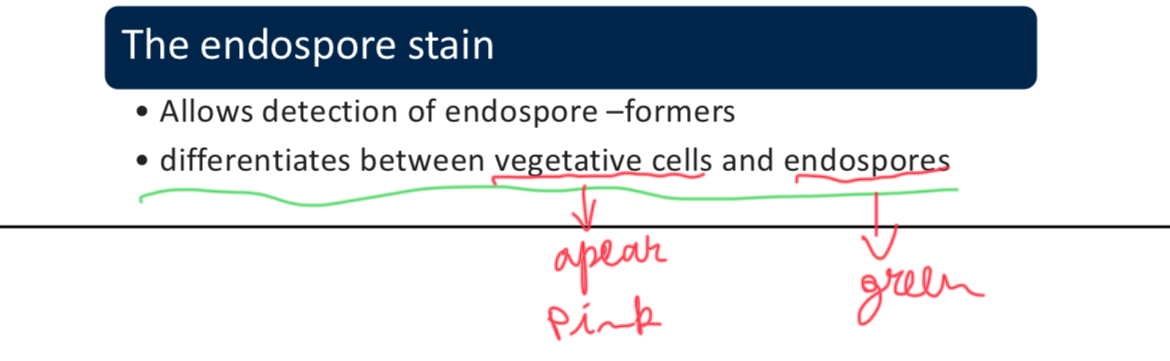
The ________ stain allows detection of endospore-formers and differentiates between vegetative cells and endospores.
Endospore stain (uses heat to drive the dye malachite green into endospore)
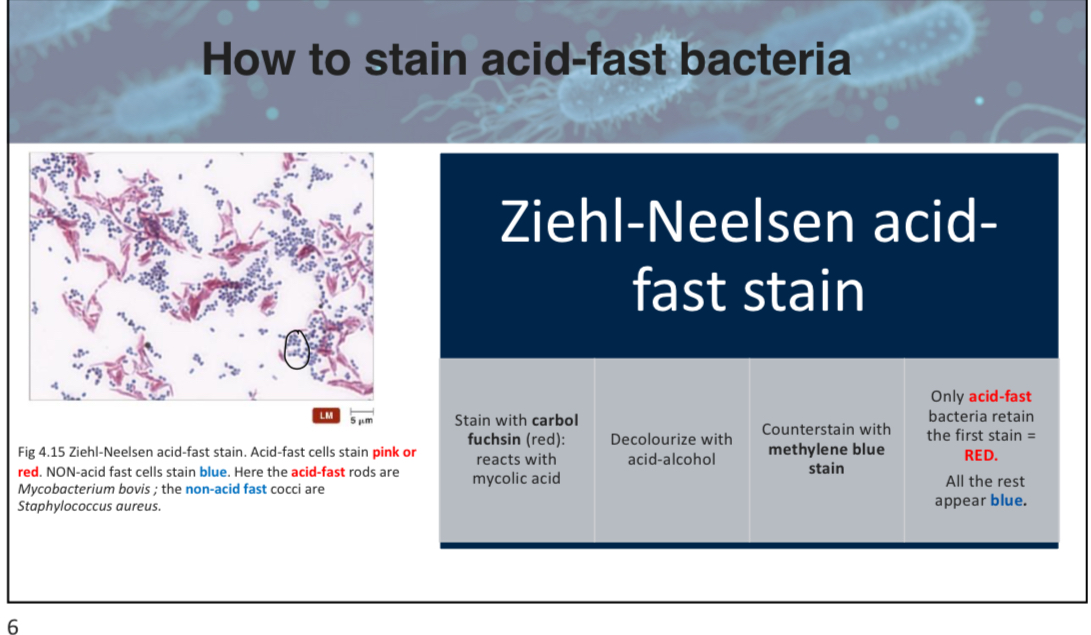
If a bacterium does not retain the carbol fuchsin stain during the Ziehl-Neelsen method, what color will it appear after counterstaining?
A) Red
B) Blue
C) Green
D) Yellow
B (in acid fast stains, the carbol fuchsin (red) is the stain, the decolorizer is acid alcohol and the counter stain is methylene blue.)
attach image on slide 6 w3p3
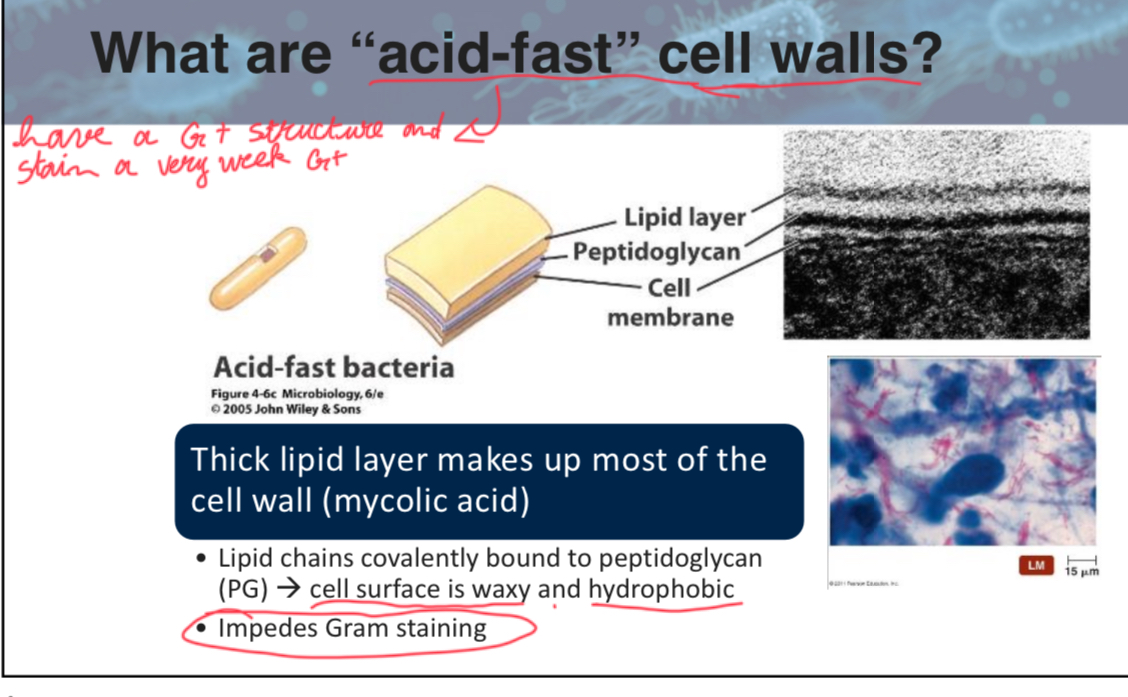
The presence of ________ in the cell membrane of Mycoplasma species allows them to survive without a traditional cell wall.
Sterols
note; the mycolic acid is the thick cell wall (waxy/hydrophopbic lipid layer with unusual peptidoglycan)
If a sample contains pink/red rods after staining, what can be concluded about these bacteria?
A) They are Gram-negative.
B) They are non-acid-fast.
C) They are acid-fast.
D) They have no cell wall.
A
non-acid-fast— stain blue
acid-fast— stain red
Gram-positive— stain purple
Which of the following is NOT an example of an acid-fast bacterium?
A) Mycobacterium leprae
B) Nocardia
C) Staphylococcus aureus
D) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C
acid-fast bacterium are typically from the phylum Mycobacteria or Nocardia.
Staphylococcus aureus is gram positive
The two key genre that are known for forming endospores are __________ and __________
Clostridium and Bacillus
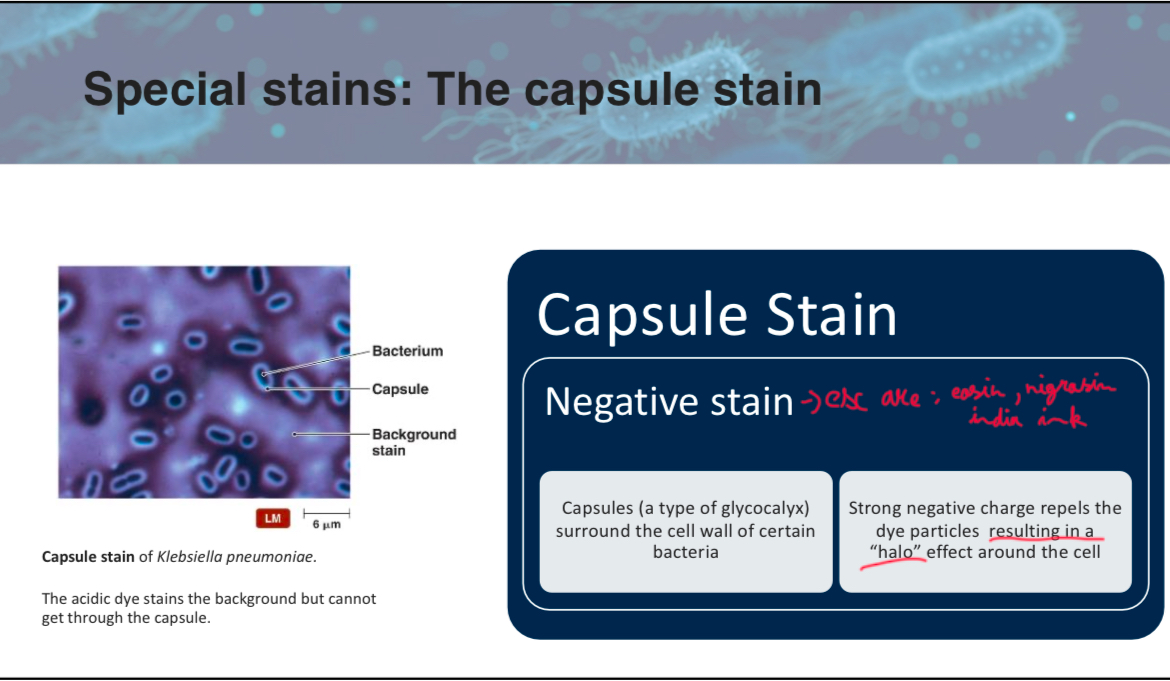
If a microbiologist observes a "halo" effect around a bacterial cell under a microscope, which type of stain was likely used?
A) Endospore stain
B) Capsule stain
C) Flagellar stain
D) Gram stain
B
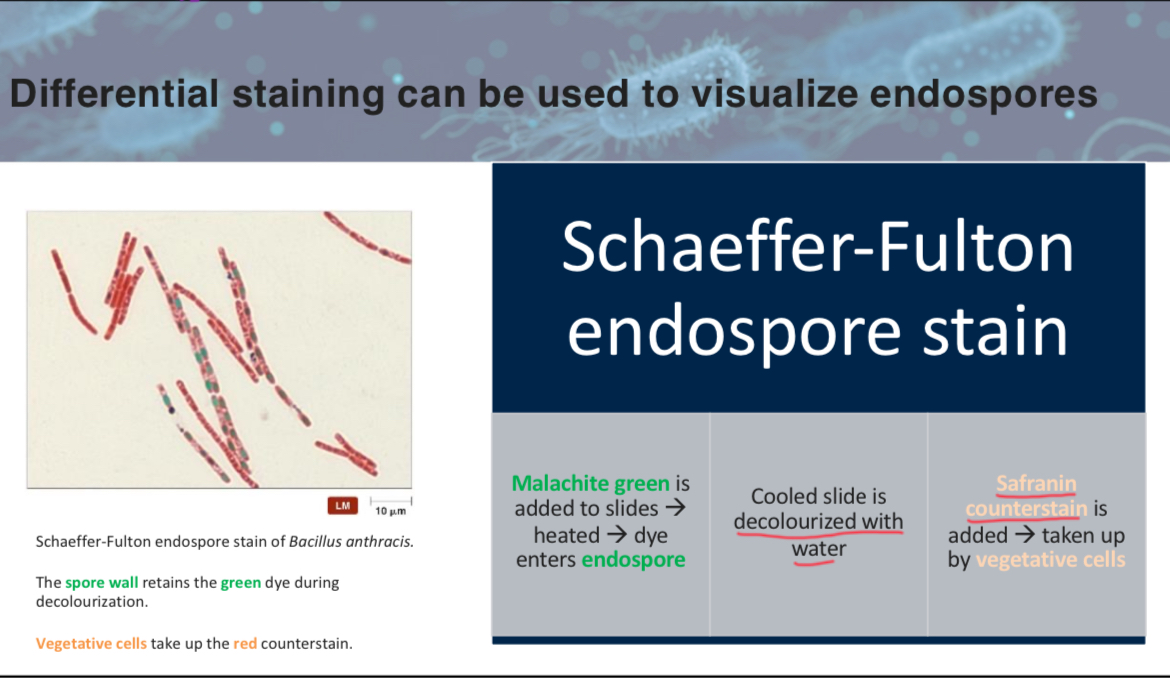
What color does the safranin counterstain impart to vegetative cells in the Schaeffer-Fulton endospore staining process?
A) Green
B) Blue
C) Red
D) Yellow
C
attach slide 4 w3p4
In the flagella staining process, dyes bind to flagella, resulting in an increase in __________ and a change in __________, making them visible.
Diameter and color
True/False: The acidic dye used in the capsule stain can penetrate the capsule and stain the bacteria within.
False
it stains everything around the it (background) leaving a halo affect on the capsule
During a lab experiment, if a student fails to decolorize properly after applying malachite green, what is likely to happen?
A) All cells will appear red
B) Endospores will not be visible
C) Both endospores and vegetative cells will appear green
D) The slide will be ruined
C
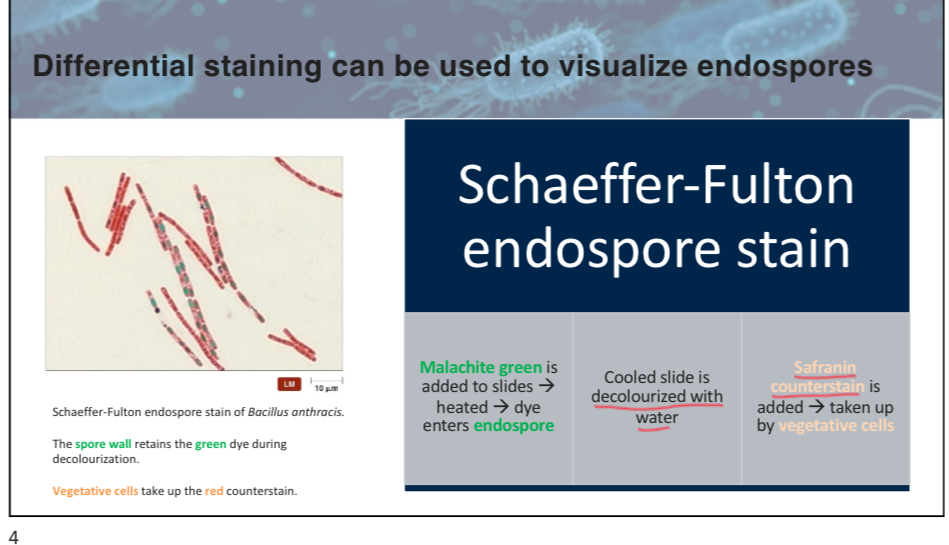
What are the primary differences between prokaryotic cells in the domains Archaea and Bacteria?
A) Archaea have peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
B) Bacteria can survive in extreme environments.
C) Archaea have unique lipid structures in their membranes.
D) Bacteria have a stronger membrane structure.
C
attach slide 4 w3p5
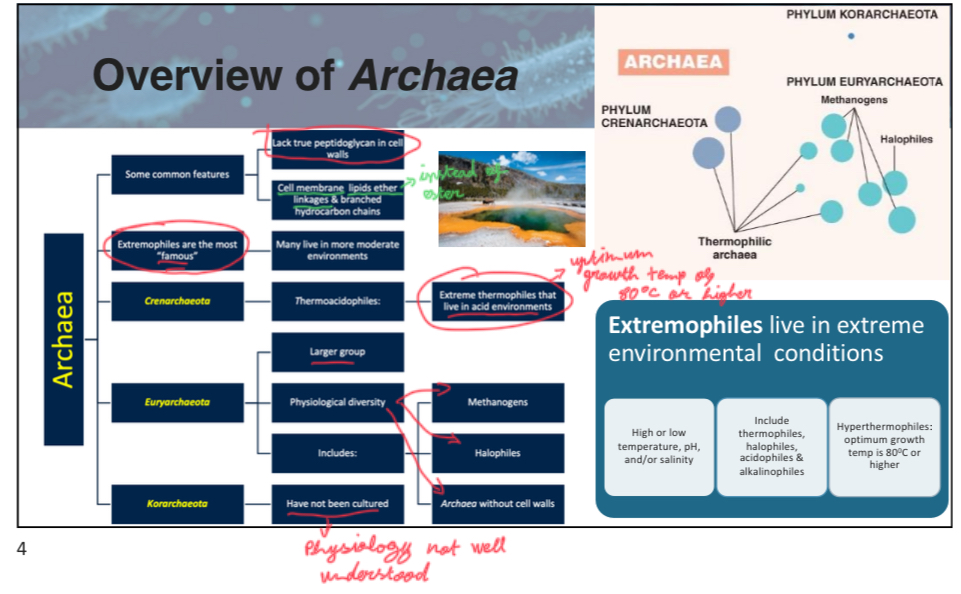
The optimum growth temperature for hyperthermophiles is __________ degrees Celsius or higher.
80
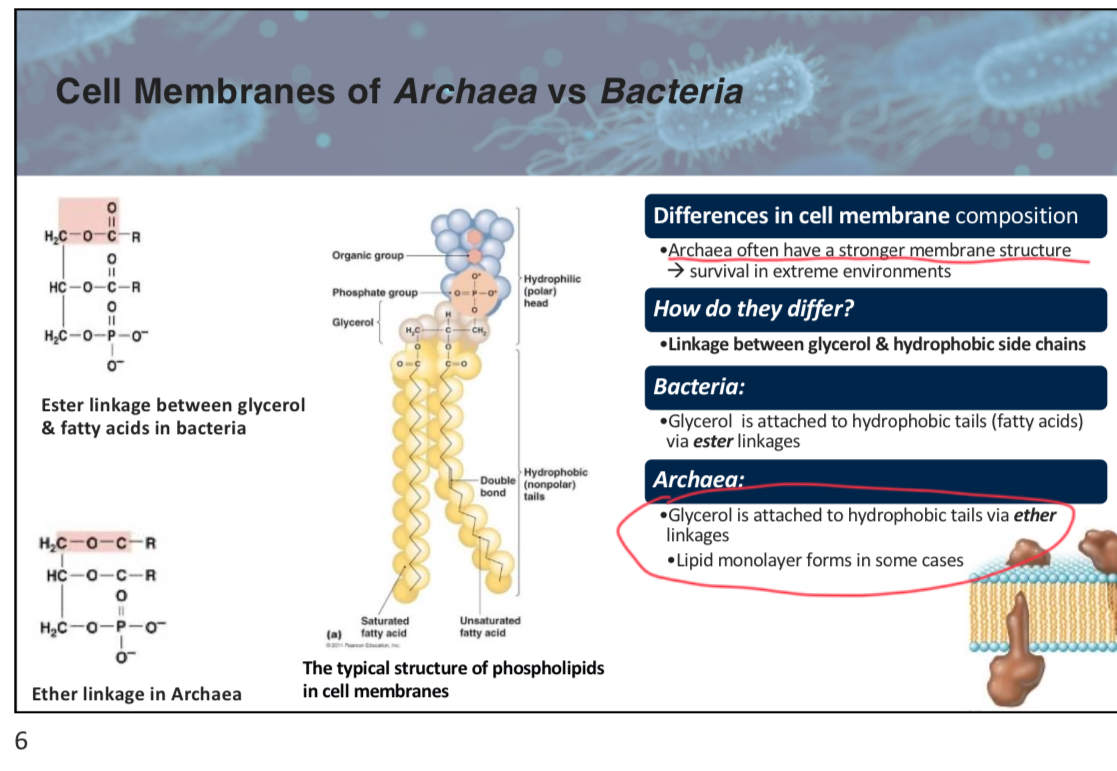
True or False: Archaeal membranes typically use ester linkages to connect glycerol to hydrophobic tails.
False (uses ether linkages. This difference allows them to have a stronger membrane to survive in extreme environment)
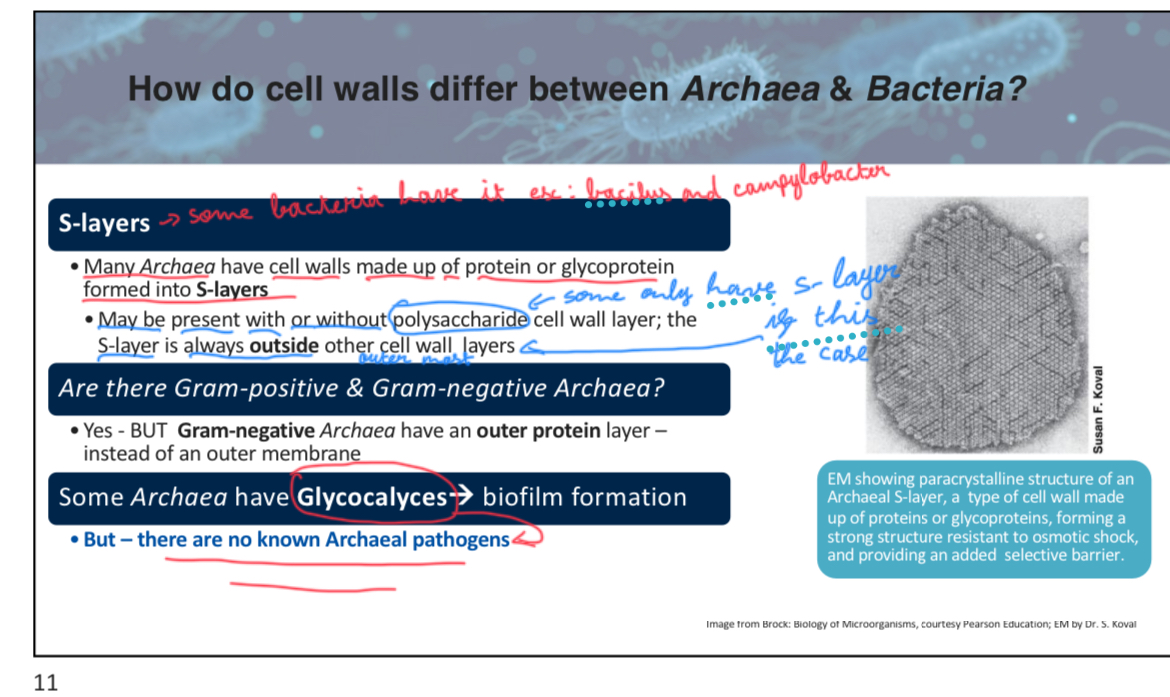
Many Archaea have cell walls made up of __________ or glycoprotein formed into S-layers.
Protein
attach slide 11 w3p5
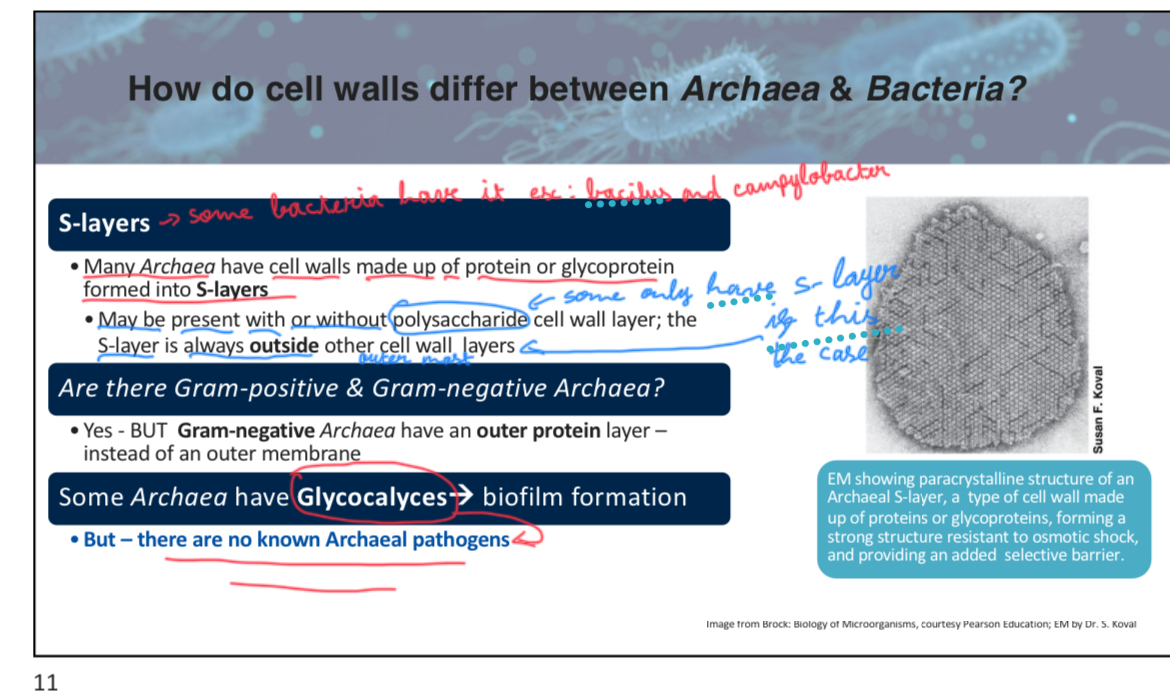
True or False: Some Archaea lack cell walls entirely.
True (Some archaea that lack a typical cell wall have a protein-based layer called an "S-layer" to maintain their cell shape and provide protection. The S-layer can also be part of their cell wall structure if they have one)
attach slide 11 week3p5
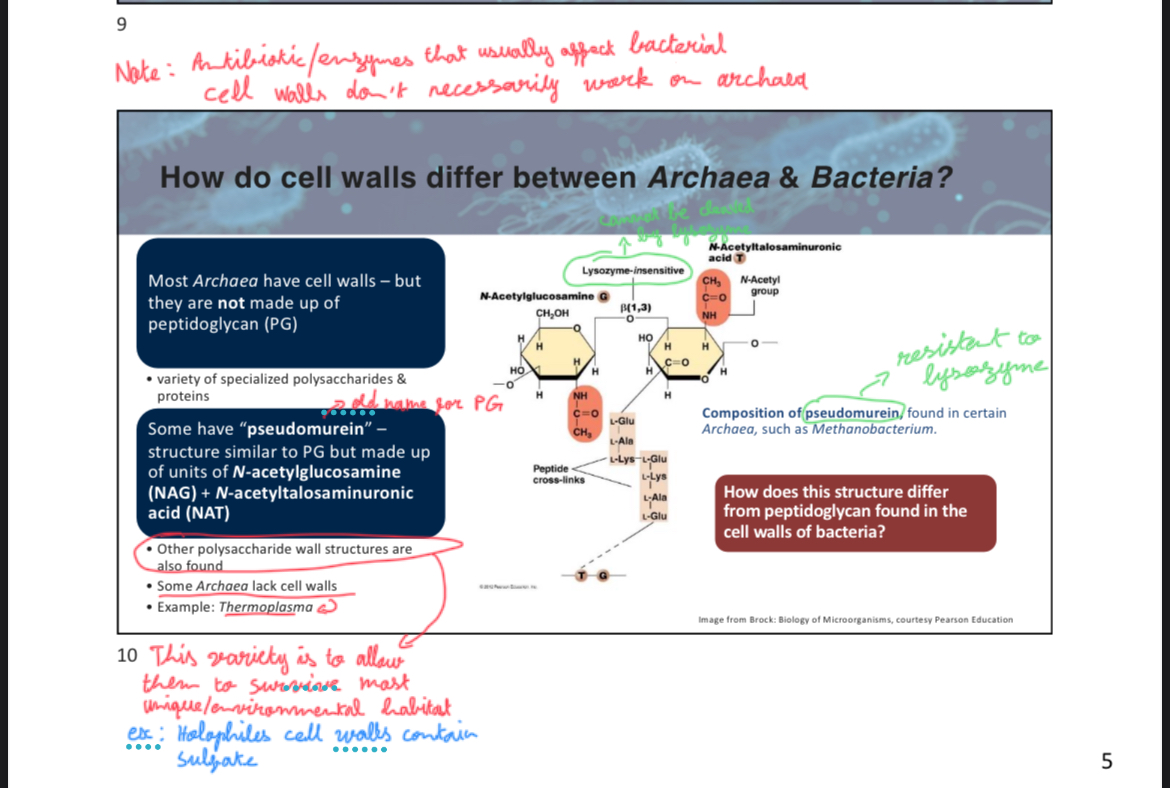
Which structure is similar to peptidoglycan but made of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid?
A) Pseudomurein
B) Cellulose
C) Chitin
D) Glycocalyx
A
attach slide 10 w3p5
The ribosomes of Archaea are classified as __________ ribosomes.
70S
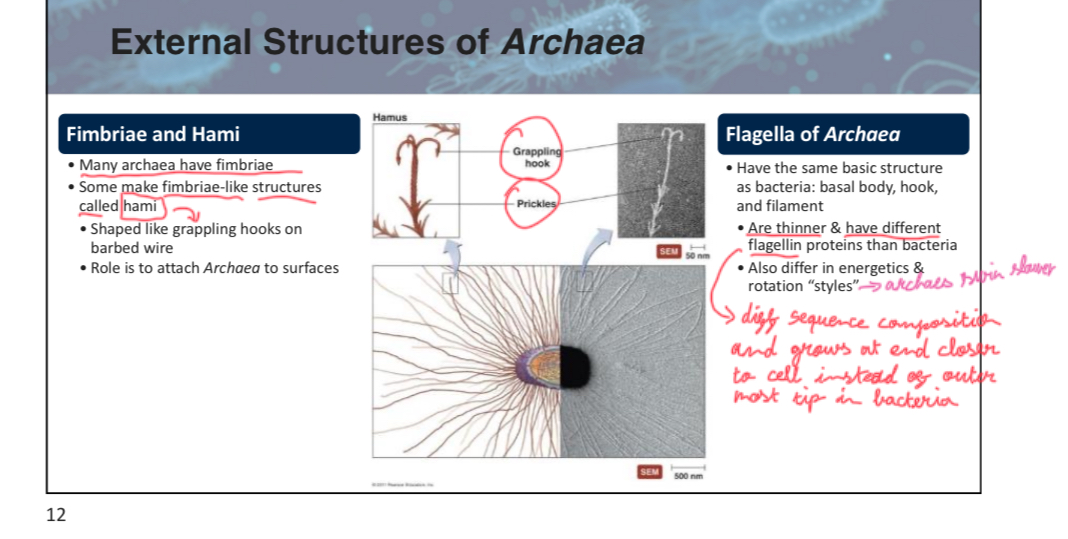
True or False: The flagella of Archaea and Bacteria are structurally identical.
False
attach slide 12 w3p5
True or False: There are known Archaeal pathogens that affect humans.
there are no known Archael pathogens
Which of the following best describes hami?
A) Structures used for energy storage and adhesion to surface.
B) A type of fimbriae shaped like a grappling hook for attachment.
C) Components of archaea flagella that allows archaea move.
D) None of the above.
B
The composition of archaeal cell walls varies but does not include __________.
peptidoglycan