3.2.1 - 3.2.2 - 3.2.3 (Transport in animals)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What 3 things make an effective transport system
A fluid or medium to carry nutrients, oxygen wastes round the body - This is the blood
A pump to create pressure that will push the fluid around the body - This is the heart
Exchange surfaces that enable substances to enter the blood and leave it again where they are needed - These are capillaries
What 2 things make an efficient transport?
Tubes or vessels to carry the blood by mass flow
Two circuits - One to pick up oxygen and another to deliver oxygen
What are the 4 types of of circulatory system?
Single
Double
Open
Closed
What is a single circulatory system and where are they present?
It is a circulatory system where the blood flows through the heart once for each circuit of the body
They are present in fish
What is the route that blood takes in a fish?
Heart → Gills → Body → Heart
Why do fish have an single circulatory system?
Because they are not as metabolically active as mammals, as they do not need to maintain body temperature and therefore need less energy
The single circulatory system supplies sufficient oxygen and nutrients for respiration
What is the a double circulatory system and where are they present?
It is a circulatory system where the blood flows through the heart 2 times each circuit of the body
They are present in all mammals
What are the 2 circuits in a double circulatory system in a mammal?
Pulmonary circulation:
Carries blood to the lung to pick up oxygen
Systemic circulation:
Carries oxygen and nutrients around the body to the tissues
What is the route that blood takes in a double circulatory system?
Heart → Body → Heart → Lungs → Heart
What are the advantages of a double circulatory system?
The blood pressure
What is an open circulatory system and what is an example where it is found?
It is circulatory system in which the blood is not held in blood vessels, instead the blood fluid circulates through the body cavity, so that tissues and cells are bathed in blood directly
An examples where it is found is in insects
Why is movement in some animals which have an open circulatory system important?
In some animals movement helps to circulate the blood around the body and so if movement is stopped then blood will stop moving
Therefore, movement is required in order to circulate blood in order to supply oxygen and nutrients for respiration
Describe the open circulatory system in an insect?
They have a long muscular pumping organ much like the heart that lies just under the dorsal(top) surface of the body#
Blood like fluid enters the “heart” from the body through pores called ostia
The heart then pumps the blood towards the head by peristalsis and empties into the body cavity
What are disadvantages of having an open circulatory system?
Blood pressure is low and blood flow is slow
Circulation of blood may be affected by body movements or lack of body movements
What is a closed circulatory system what is an example of where its found?
It is where blood is held in vessels
An example is in mammals and fish
What bathes the tissue and cells in a closed circulatory system organism?
Tissue fluid
What are advantages of a closed system over an open system?
Higher pressure, so blood flows more quickly
More rapid delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissue which allows animals to be more active
More rapid removal of CO2 and other wastes
Transport is independent from body movements
What circulatory system does fish, mammals and insects have?
Fish
Closed single circulatory system
Insects:
open circulatory
Mammals:
Closed double circulatory system
What are similarities or differences between the circulatory system in a fish and in mammals?
Similarities:
Both are closed systems with blood which is contained in vessels
Both have a heart
Both carry oxygen and haemoglobin
Both have arteries, veins and capillaries
Differences:
Fish have a single circulatory system and mammals have a double circulatory system
The fish’s heart has a 2 chambers which the mammal heart has 4 chambers
The blood pressure in fish is maintained lower than in mammals
Fish’s circulatory system is less efficient at supplying oxygen than mammals
What are the 5 blood vessels that we need to know about?
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Arterioles
Venules
What is the common tissue in all blood vessels?
The endothelium
A single layer of cells that is particularly smooth in order to reduce friction with the flowing
What is the function of elastic tissue in blood vessels?
Allows the expansion of the lumen without causing damage
Allows the elastic recoil and smooths the out the flow of flow blood
What is the function of smooth muscle
Can contract and vessels - vasoconstriction - therefore reducing rate of blood flow
It can relax to widen vessels - Vasodilation - therefore increasing rate of blood flow and distribution
What is the function of Collagen?
A fibrous protein that provides strength to vessels so they don’t burst
What tissues are present in the Arteries?
Lumen
Endothelium
Elastic fibres
Smooth muscle
Collagen fibres
What is the structure of the arteries?
They have a narrow lumen
They have a thick layer of elastic fibres, smooth muscle tissue and collagen
Why do arteries have their structure?
A narrow lumen-in order to maintain a high blood pressure
A Thick layer of collagen to be able to withstand high pressure of blood flow
A thick layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres to maintain high blood pressure
Why do arteries have folded endothelial cells in the lumen?
This is in order to prevent damage of the artery as it stretched due to high pressure in the artery
What are the 3 layers of the artery and what are they made of?
Tunica intima - A think layer of elastic tissue which allows the wall to stretch and then recoil to help maintain high blood pressure
Tunica media - A thick layer of smooth muscle
Tunica Adventitia - A thick layer of collagen and elastic tissue. This provides strength to withstand high pressure and recoil to maintain the pressure
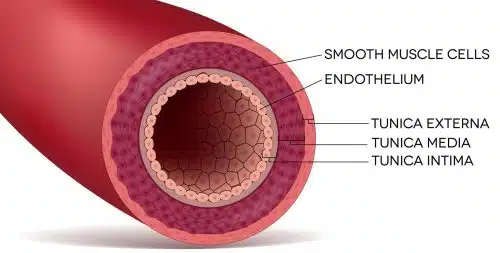
What are arterioles?
They are smaller blood vessels which connect to the arteries that distribute blood from an artery to the capillaries
How can the arterioles be contracted and why does that help?
The arterioles can be constricted by contracting the layer of smooth muscle on the wall of arteriole
This can reduce the rate of flow of blood which can be used to divert the flow of blood to regions of the body that are demanding more oxygen for respiration
What tissues are present in the capillaries?
Lumen
Endothelium
What is the strcuture of the capillaries?
It has a very narrow lumen - diameter is similar of a red blood cell.
The walls are a single layer of flattened endothelial cells
The walls are leaky
How does the structure of the capillaries help it do its function?
A very narrow lumen means that red blood cells and other nutrients in the blood plasma are closer to tissue fluid which means that there is a shorter diffusion distance and therefore a higher rate of diffusion
One cell thick layer means that there is a short diffusion distance which means that there is a higher rate of diffusion
What tissues are present in veins?
Lumen
Endothelium
Elastic fibres
Smooth muscle
Collagen
What is the structure of the veins?
They have a wider lumen than arteries
They have a valve
They have a thinner layer of collagen, elastic fibres and smooth muscle
How does the structure of veins help them preform their function?
Wider lumen:
This is order to decrease the pressure and do reduce blood flow
Valve:
This is help to prevent the back flow of blood so the blood can flow to the heart properly
Thinner wall:
This is because they do not to stretch and recoil in order to withstand with the high pressure
They do not need to stretch and recoil actively to maintain high blood pressure
How do veins move blood back to the heart?
Around the veins there are skeletal muscles
Because the vein wall is very thin this means that veins can be flattened by the contraction of skeletal muscles
This contraction causes pressure to be applied on the blood which forced the blood move in a direction determined by the valves
What are venules and what are their functions?
After the blood goes through the capillaries, to be sent to veins, they have to go through venules
which collect the blood from the capillary bed and lead to the veins
What are the tissues present in venules?
The venule wall consists of a thin layer of muscle and elastic tissue outside the endothelium and a thin outer layer of collagen
What is the blood made of?
It is made of a liquid called plasma which contains many blood cells and other dissolved substances
Cells:
Red blood cells - erythrocytes
White blood cells - leucocytes
Fragments called platelets
Dissolved substances:
Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide
Minerals
Glucose
Amino acids
Hormones
Plasma proteins
What is tissue fluid and how is formed?
It is a liquid which is produced by the plasma leaking out of the capillaries and surrounds the the cells in the tissue
What s the function of tissue fluid?
It supplies tissues and cells with oxygen and nutrients which they require
What is the name of movement of dissolved substances in the tissue fluid out of the capillaries?
Mass flow
What happens to waste products in the tissue fluid?
They will be carried back into the capillaries as some of the tissue fluid will return back to the capillary
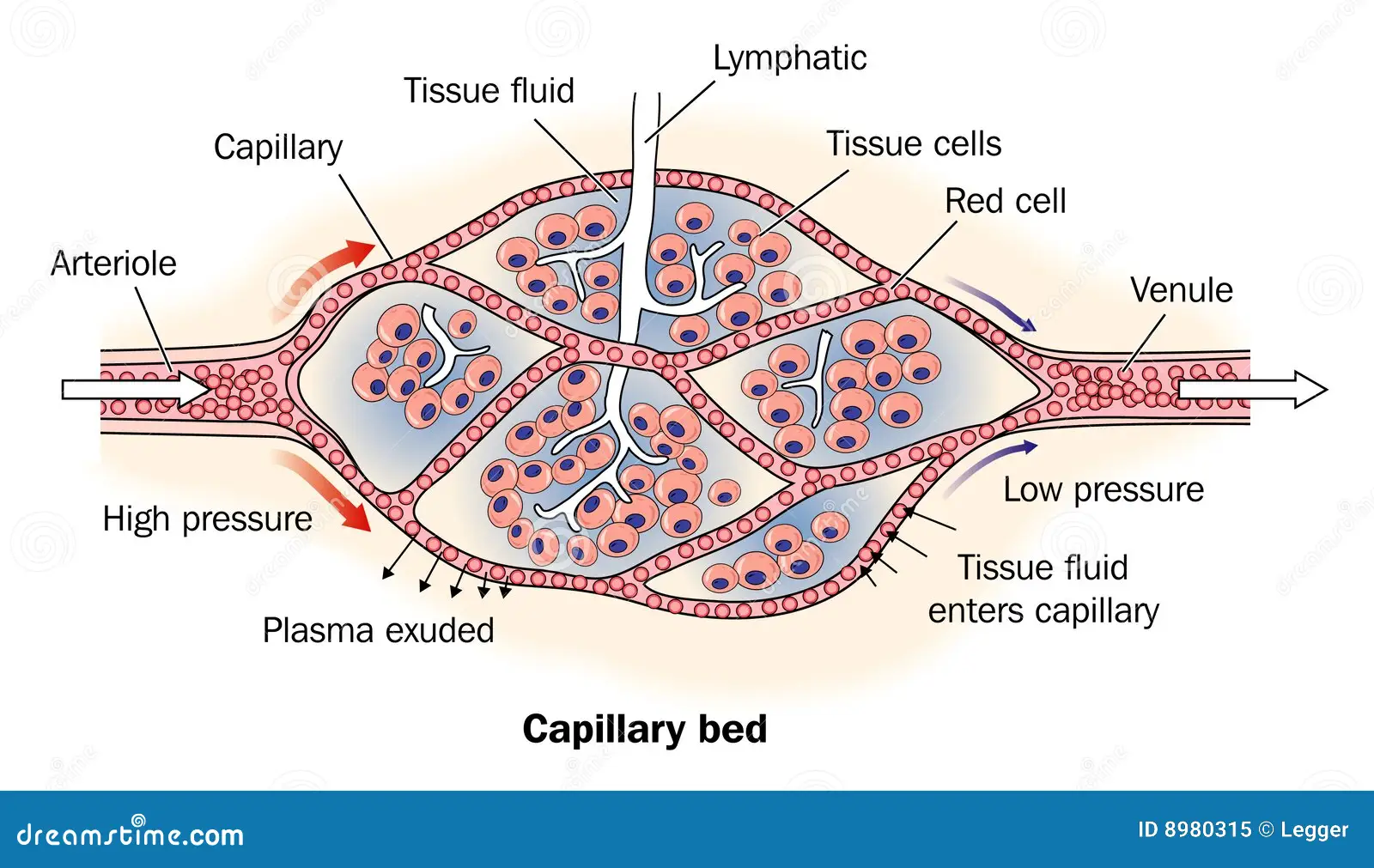
What is the name of a network of capillaries called?
A capillary bed
What is the water potential of the capillaries in a capillary bed at all times?
-3.3kPa
Why does the blood have a negative water potential at all times?
This is because plasma proteins in the blood cannot diffuse out of the capillaries into the tissue fluid through the pores of the capillaries
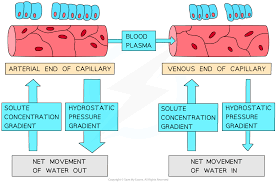
What is generally the hydrostatic pressure at the arteriole end of the capillary?
4.6kPa
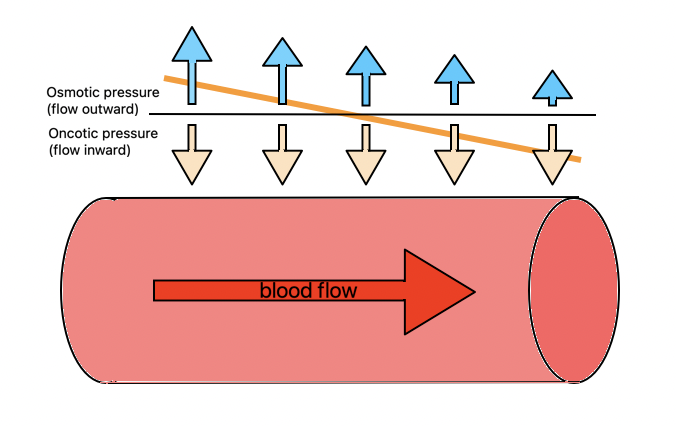
What is meant by oncotic pressure?
The pressure created by the osmotic effects of the solutes
What is meant by hydrostatic pressure?
The pressure that a fluid exerts when pushing against the sides of a vessel or a container
Describe how blood plasma becomes tissue fluid and is recycled back to the blood
When the blood is flowing in the capillaries, at the arteriole end of the capillary the hydrostatic pressure is higher than the oncotic pressure and therefore there is a net movement of plasma out of the capillaries via pores and gaps between cells
This fluid is no longer plasma due to it losing some substances that were in it to become tissue fluid
The fluid then bathes the cells and tissue so substances are able to diffuse into the cells
At the end of the capillary - the venule end - the hydrostatic pressure decreases which causes water and some tissue fluid to move back into the blood
The tissue fluid that does not enter the blood again is directed to a tubular system called the lymph/lymphatic system
The lymph which is the excess tissue fluid travels through the lymphatic system to lymph nodes where they are checked for pathogens
After the lymph has travelled through lymph nodes, it is then moved back into the blood in the subclavian vein in the chest where it is recycled
When do lymph nodes swell up and why?
They swell when they are producing lymphocytes as an immune response. These are WBCs which are used to fight of infections
What is the net movement of tissue fluid at the arteriole end of the capillary?
It has a positive net movement outflow of 1.5kPa (osmotic pressure is the same as hydrostatic)
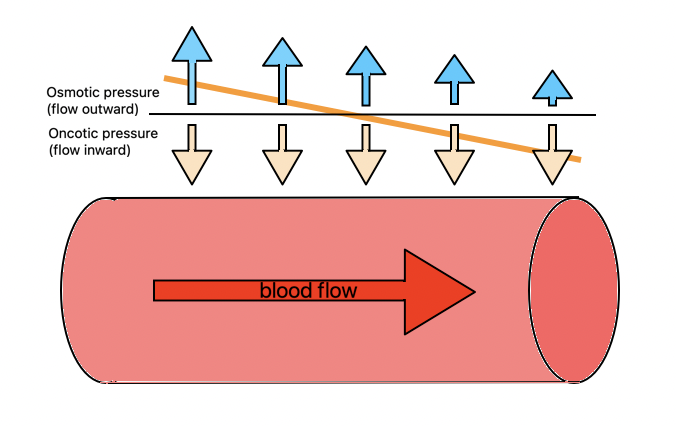
What is the net movement of tissue fluid at the venule end of the capillary?
It has a negative net movement inflow of -1.5kPa (osmotic pressure is the same as hydrostatic)
What substances can and cannot move out of the capillaries?
Can:
Minerals and ions
CO2
O2
Lipid soluble substances
Glucose
Amino Acids
Can’t:
Plasma proteins
Red Blood Cells