Test 3
1/286
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
287 Terms
angi/o
vessel
aort/o
aorta
arter/o or arteri/o
artery
arther/o
fatty plaque
atri/o
atrium
cardi/o or coron/o
heart
phleb/o or ven/o
vein
thromb/o
blood clot
varic/o
dilated vein
vas/o or vascul/o
vessel
ventrocul/o
ventricle
cardia
heart condition
stenosis
narrowing or stricture
brady
slow
endo
in, within
epi
above, upon
peri
around
anatomy of the heart and great vessels
2 chambers: atrium and ventricles
right side: blood from body- from superior and inferior vena cava
left side: blood from pulmonary vein - to aorta → systemic circulation
base: top part of heart
apex: point of heart
great vessels: pulmonary arteries and aorta
anatomy of pericardium and cardiac muscles
pericardium: encases heart, shield heart from infection and trauma
myocardium: thick muscular tissue, contracts → eject blood from ventricles
endocardium: most innerpart
coronary arteries: supply blood to the pericardium and cardiac muscles - supply O2
blood flow through the heart
superior/ inferior vena cava
right atria
tricuspid valve
right ventricle
pulmonary valve → pulmonary arteries
lungs
pulmonary veins
left atria
mitral valve
left ventricle
aortic valve → aorta
body
heart valves
regulate blood flow through heart
tricuspid valve
A/V valve
pulmonary valve
semilunar valve
mitral valve
A/V valve
aortic valve
semilunar valve
electric conduction of the heart
SA node: electric impulse originates here. superior aspect of right atrium. also known as the cardiac pacemaker. 60-100 beats per minute. stimulates atrial contraction
AV node: impulse then travels here. if SA node fails the AV node can generate 40-60 impulses per minute
bundle of His and Purkinje fibers in the myocardium: results in ventricular contraction. if both the SA and AV nodes fail they can create 20-40 impulses per minute
cardiac cycle
systole: first heart sound (S1)
ventricles contract, creating pressure to close the AV valves, preventing backflow of blood
semilunar valves open and blood is ejected into the aorta and pulmonary arteries. when the blood is ejected the pressure in the ventricle decreases and semilunar valves close
the ventricles then relax and diastole starts over
diastole: second heart sound (S2) indicates start of diastole
ventricles are relaxed and fill with blood from atria
blood moves when the pressure of blood in the atria becomes hgiher than in the ventricles
at the end of diastole, the ventricles are filled with blood
pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
shows the condition of the blood vessels
low/ narrow: poor cardiac output
normal: 40-60
high/wide: stiff vessels, narrowing/clogged arteries
Mean arterial pressure
Average amount of pressure in the arteries walls
low: Poor profusion to the organs
normal: 70 to 100
high: too much pressure
preload
Volume in the right Atria at the end of diastole
Afterload
The pressure in the great vessels against which the left ventricle contracts
cardiac output
The amount of blood injected from the left ventricle each minute
If the SA node of the heart is properly functioning, what heart rate should we expect to assess on a client
60-100 bpm
venous system vs arterial system
venous system
veins
low pressure
valves
towards heart
usually unoxegenated
arteries
away from heart
usually oxygenated
pulses
temporal
carotid
brachial
radial
femoral
popliteal
posterior tibial
dorsalis pedis
arteries
take freshly oxygenated blood from the heart to all body tissues
arterioles
tiny branch of artery
venules
tiny branch of veins
capillaries
fine branching blood vessels that form a network between arterioles and venules
veins
take the deoxygenated blood and waste products from the tissues and return into the heart
thrombosis
formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing flow
bruit
abnormal sound that occurs when blood flows turbently through an artery
thrill
a vibratory resonance heard with your stethoscope
aneurysm
a ballooned and weakened area in an artery
which of the following regarding pulse checks is true
carotids should be assessed one at a time
lymphatic system
lymph fluid from tissues back to blood stream
regulate fluids in body
filter pathogens in body
lymph
pertaining to lymphatics
anatomy of the lymphatic system
groups along blood vessels
filtration before venous system
cervical lymph nodes
drain head and neck
axillary lymph nodes
drain breast and upper arms
epitrochlear lymph nodes
drain hand and lower arms
inguinal lymph nodes
drain lower extremities, genitalia, anterior abdominal wall
physiology of lymphatic system
retrieves excess fluid and plasma proteins from the tissue spaces and returns them to the bloodstream
defends the body from disease- immune system!!
helps fight infection
lymphadenopathy
swollen lymph nodes usually caused by infection from bacteria or viruses
lymphedema
tissue swelling caused by accumulation of protein rich fluid
which of the following is a function of the lymphatic system
Defend the body against diseases
Return excess fluid and plasma protein to venous system
Helps the body fight infection
Nodes act as a filtration system for lymph fluid
review of systems for CV
present health status
medications
disease processes
HTN, hyperlipidemia, heart disease
past health history
surgeries and hospitalizations
open heart surgery- what kind
congenital heart defects
testing done
EKG, stress testing, ultrasounds
family history
personal and psychosocial history
exercise, stress, hobies
diet, alcohol intake
DASH diet helps
caffeine
tachycardia
drugs
tobacco use
vasoconstriction
any interest in quitting
problem based history
reported sympoms related to heart
chest pain, SOB, cough, nocturia, fatigue, syncope, edema of extremities, pain in legs or cramping, changes in skin, enlarged lymph nodes
inspection of CV
hand hygiene
name and DOB
provide comfort and privacy
general appearance, skin color, breathing effort
inspect anterior chest wall for contour, symmetry, and retractions
look with pen light from the side
look for landmarks
palpation technique
pulsation: finger pads
thrills: padding at the base of fingers
heaves/lifts: palm of hand
palpation of CV
may have to turn patient slightly onto left side
apical pulse
light pulsation
location and amplitude
thrills
paplable vibration
valve murmur
heaves or lifts
heaves: precordial impulse- cardiac or respiratory disease
pain
stethoscope use
diaphragm
S1 and S2
high frequencies
bell
murmurs and bruits
low frequencies
S3 and S4
auscultation CV
rate and rhythm
regular vs irregular
S1 (lub) and S2 (dub)
S1: begining of systole, when tricuspid and mitral valves close
S2: end of systole/beginning of diastole, when aortic and pulmonic valves close
extra heart sounds
murmus
tips for hearing heart sounds
patient positioning
upright and slightly forward
quiet room
patient breath holding
concentration
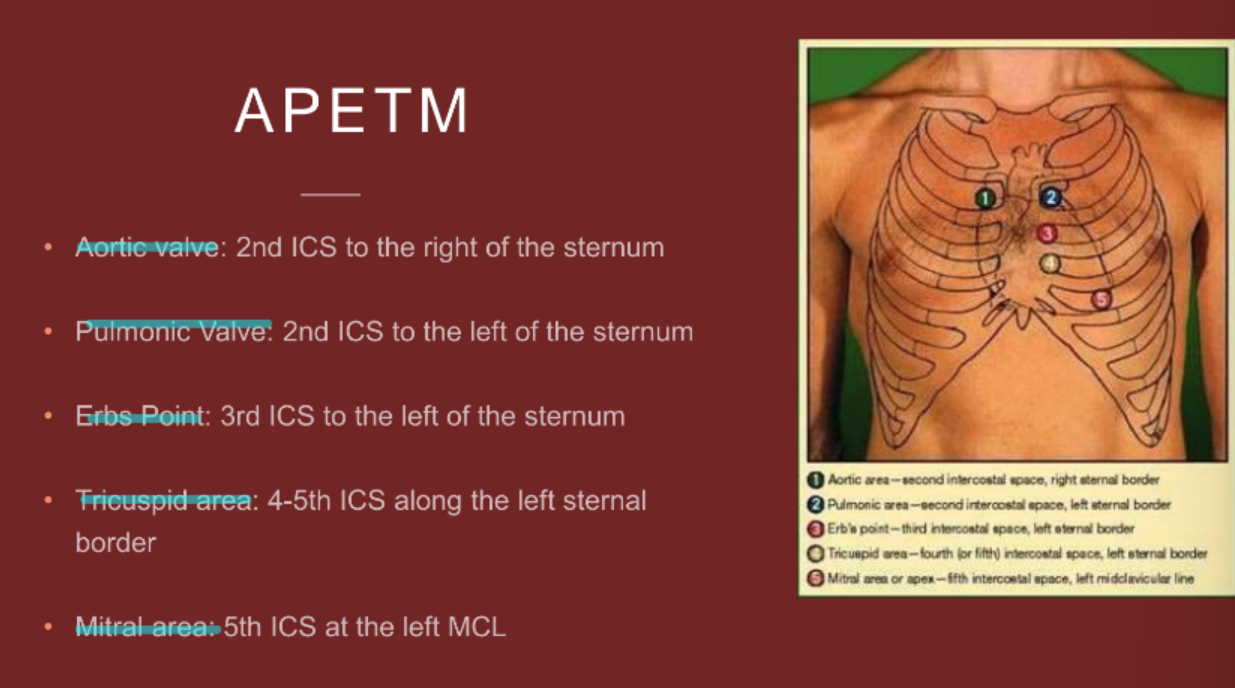
APETM
or
APE To Man
aortic valve
pulmonic valve
erbs point
tricuspid valve
mitral valve
extra and abnormal heart sounds
split S1 and S2
valves do not close at same time
S3:
found best with bell at apex
early ventricular gallop due to rapid ventricular filling
children and young adults
S4
cardiac apex with heart of bell
late diastolic sound- atrial gallop
decreased stretching of the ventricle/ diastolic dysfunction
children and young adults
murmurs
swooshing sound dur to turbulent blood flow
pericardiac friction rub
low pitched course rub or grating sound
age considerations CV
infants: fetal shunts (usually close within 10-15 hours). HR best auscultated
children and young adults: heart rate will slow as child grows and arrythmias are common
aging adults: orthostatic hypotension
pregnancy with CV
blood volume increase by 30-50%, increase stroke volume, cardiac output, and pulse rate
S3 sound can be heard as a normal variation- resolves usually once baby is delivered
monitor for increased BP
risk factors for hypertension and CAD
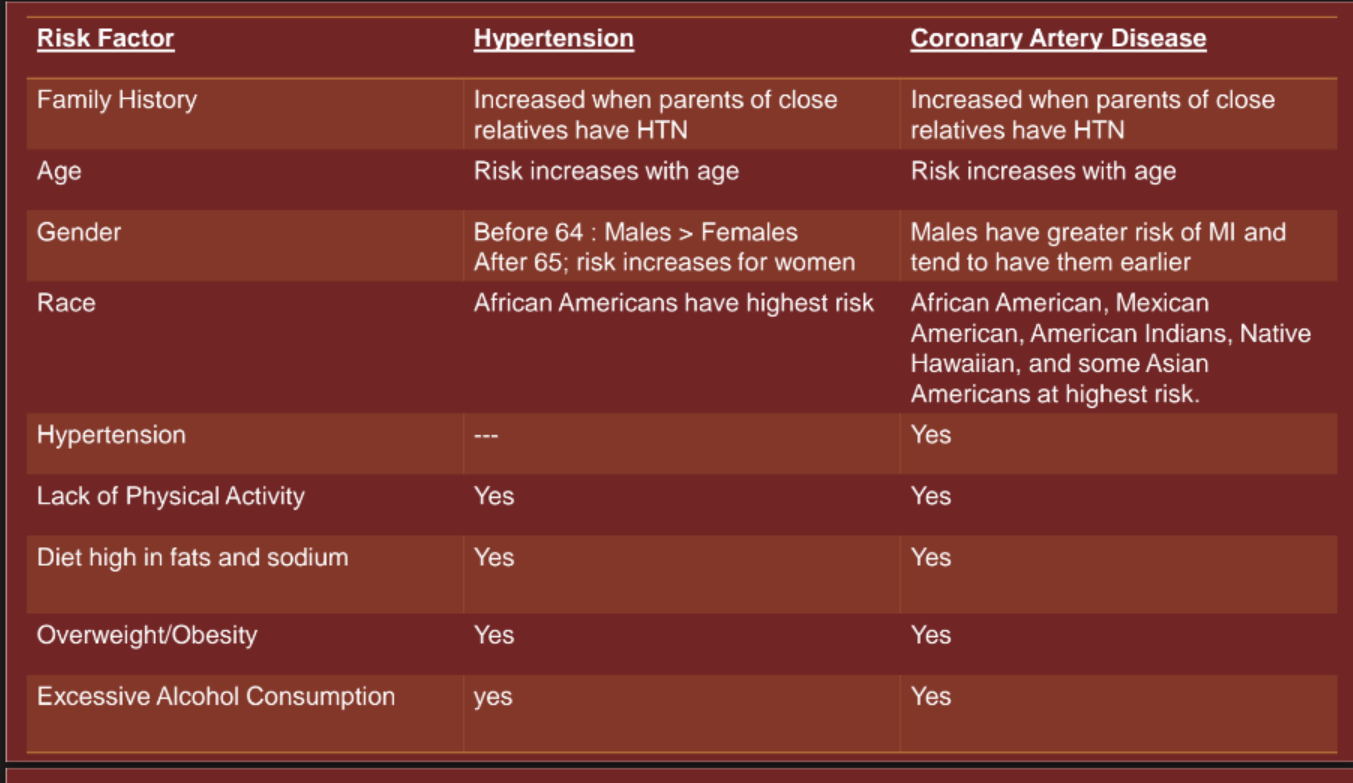
normal vs abnormal CV

red flags CV
top 5= s/s for MI
chest pain or discomfort in men
left arm pain, radiates into left jaw
elephant sitting on my chest
fatigue and SOB in women lasting more than 20 min
indigestion, nausea and diaphoresis
SOB at rest
new murmur
emergent heart conditions
cardiogenic shock: Inability of the heart to pump enough blood out of the rest of the body although there is plenty of blood present the heart is not able to squeeze or provide enough cardiac output to perfuse the rest of the body
s/s: Tachypnea, shortness of breath, sudden tachycardia, change in level of consciousness, weak pulses, low blood pressure, diaphoresis, and pale skin
causes: Systolic dysfunction, diastolic dysfunction, dysrhythmias, structural defects; most often seen myocardial infarctions
hypertensive emergency/urgency: When very high blood pressure is capable of impairing one or more of the organ systems such as brain eyes heart aorta kidneys etc
MAP is most indicative sign
conditions and common medical diagnoses
Hypertension (increased BP)
hyperlipidemia (increased lipids, high cholesterol)
valvular heart disease (Heart valve that does not close or open completely causing murmurs or abnormal heart sounds)
myocardial infarction (Decreased sensation of blood flow into a portion of the myocardium causing coronary artery blockage)
pericarditis (Inflammation of the pericardium causing a cardiac friction rub)
heart failure (Heart muscle can't pump as much blood as it should causing blood to blow back up)
heart failure
left sided
Left ventricle cannot pump sufficient blood forward causing blood to back up into the left atrium and eventually into the pulmonary capillaries causing pulmonary edema
Dyspnea, shortness of breath, decreased oxygen, tachypnea, cough, crackles, cyanosis
Right sided
Failure of the right ventricle to pump blood into the pulmonary arteries causing back flow of blood into the inferior and superior vena cava
risk factors: HTN, CAD, DM
Blood pulls in the body, deepened edema, ascites, enlarged liver and spleen, JVD, and increased weight
both
all symptoms
common nursing diagnoses CV
decreased cardiac output
risk for decreased cardiac tissue perfusion
excess fluid volume
documentation CV

During auscultation where is the best area for the nurse to listen for S3 and S4 heart sounds
5th ICS at the left MCL
review of systems PV
pain
edema
where
lumps
changes to the skin
color, wounds
erectile dysfunction in males
personal history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia
family cardiac and PV history
inspection PV
appearance of extremities
skin integrity, color
nail bed
color and angle
note asymmetry
jugulat vein distention (JVD)
Reflects right atrial pressure
Lie in supine position with head 30 to 45 degrees
auscultation PV
Carotid bruits: bell of stethoscope to listen for turbulent blood flow. Have them take a small breath in and hold it while you listen
hear a bruit = abnormal
palpation PV
temporal
carotid
one at a time
brachial
radial
popliteal
femoral
dorsalis pedis
posterior tibial
carotids assessment sequence
inspect
auscultate
palpate
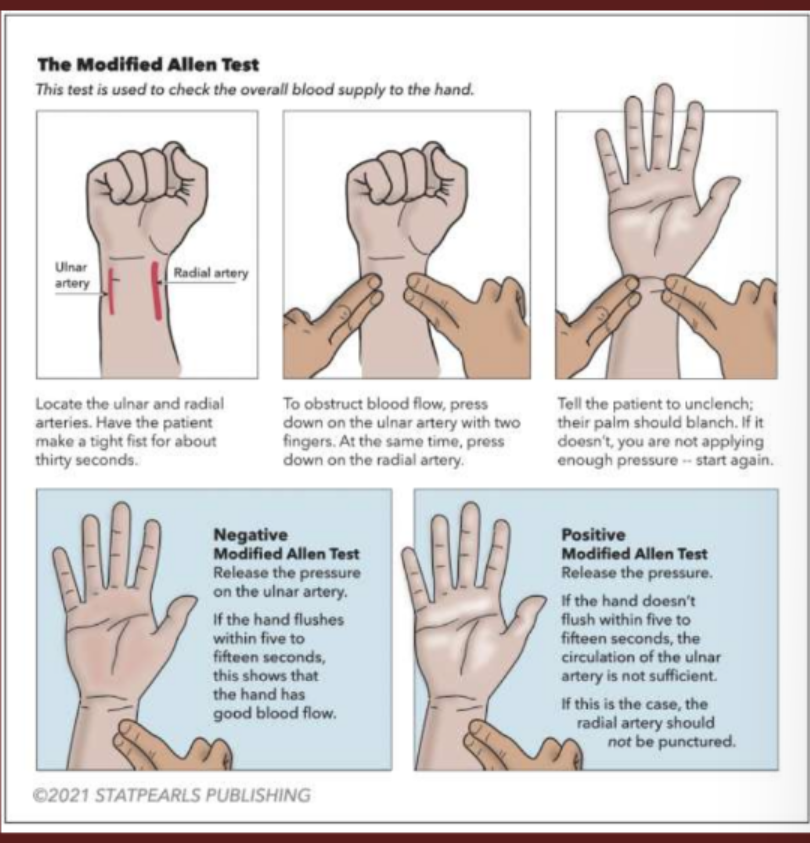
modified allen test
Used to measure how well blood flows into a patient's hand
normal vs abnormal PV

red flags PV
pain with or without walking (resolved with the other)
asymmetry
color changes
muscle atrophy
changes in pulse force and rhythm
absent pulse
confirm with doppler
conditions and common medical diagnoses
peripheral arterial disease
peripheral venous disease
raynaud’s syndrome
due to vasospasm
deep vein thrombosis
peripheral artery vs peripheral vascular diease
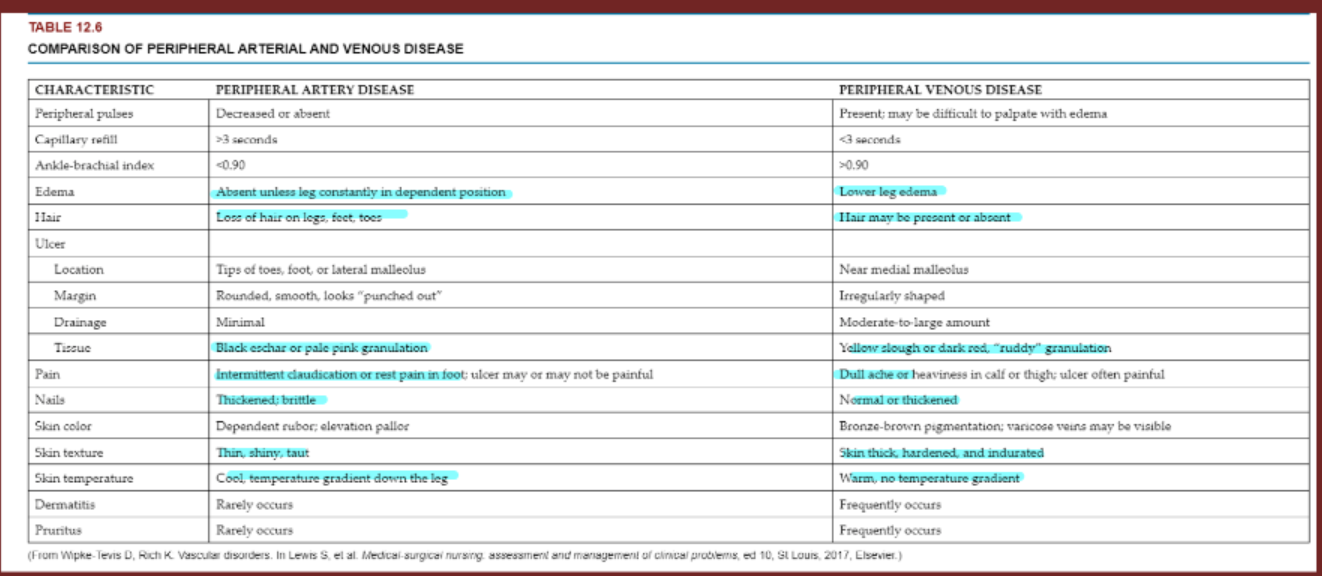
common nursing diagnoses PV
ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
risk for peripheral neurovascular dysfunction
activity intolerance
documentation PV

When assessing for JVD what is the best position to place the patient in
Supine position elevate head to around 30 to 45 degrees slightly tilt chin and look away from the side you are assessing
review of systems lymphatic
edema
new or all of the time
enlarged lymph nodes
OLD CARTS
inspections and palpation lymphatic
inspect skin
color, edema, skin integrity
one limb or both
epitrochlear lymph node- elbow
size
consistency
mobility
tenderness
warmth
measure lymphatics
leg circumfrence
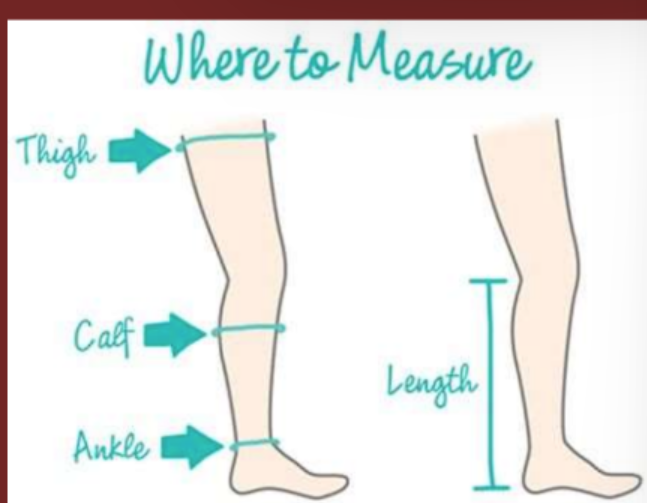
normal vs abnormal lymphatics

red flags lymphatics
asymmetry
common medical diagnoses lymphatics
lymphedema
lymphadenopathy
lymphedema vs lymphadenopathy
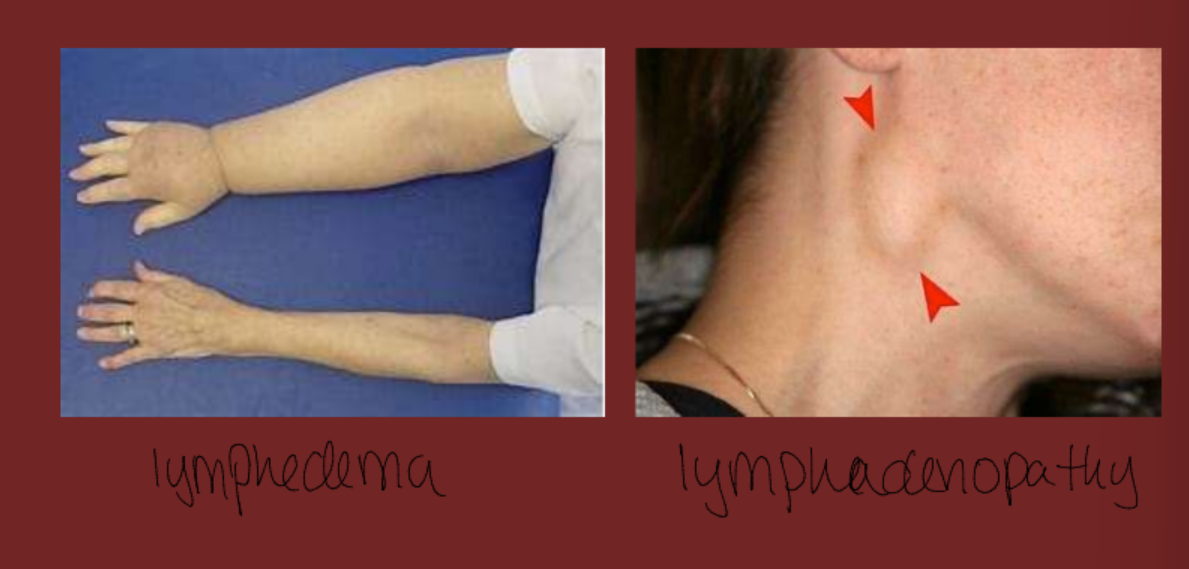
common nursing diagnoses lymphatics
acute pain
risk for peripheral neurovascular dysfunction
activity intolerance
impaired skin integrity
documentation lymphatics

Inspection of a person's right hand shows a red swollen area. to further assess for infection, you would palpate the
epitrochlear node
Esophag/o
esophagus
gastr/o
stomach
pylor/o
pylorus
duoden/o
small intestine
enter/o
intestine
jejun/o
jejunum
ile/o
ileum
append/o
appendix
appendic/o
appendix