3- Active transport
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What is active transport?
Movement of molecules/ ions into or out of a cell, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
As its movement is against the concentration gradient, carrier proteins and ATP are used
E.g. root hair cells accumulate more of an ion that they could via diffusion/ facilitated diffusion
Carrier proteins and active transport
Specific regions or sites which bind reversibly to a complementary shaped molecule
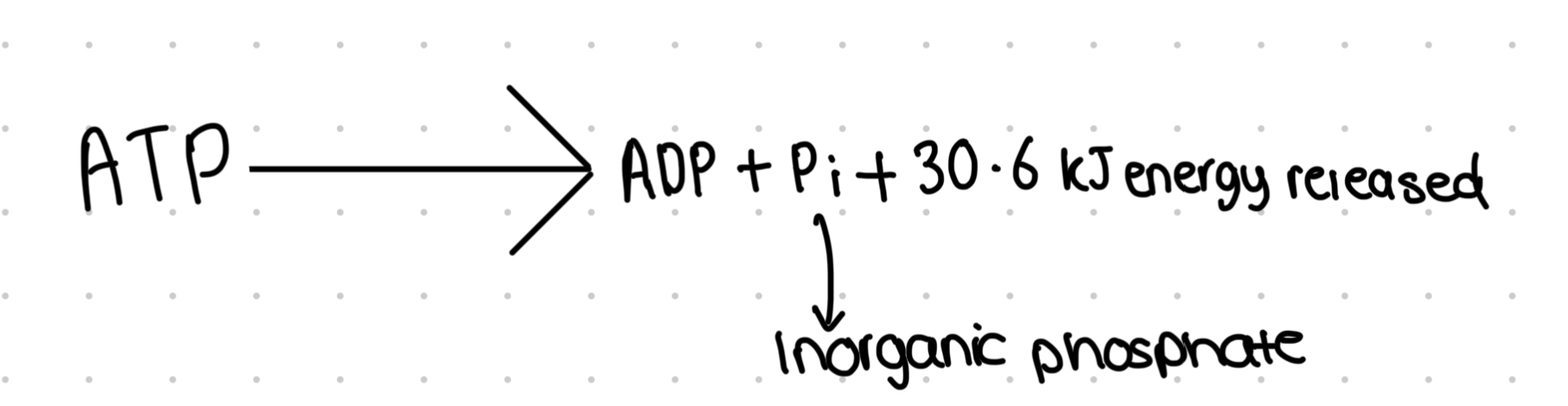
This then allows the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP which releases energy
The energy released changes there conformation of the carrier protein
In doing this, it moves the molecule form one side of the membrane to the other
Active transport process
Molecule binds to carrier protein
ATP binds to carrier protein on the opposite side of protein and hydrolysed to ADP
Free phosphate binding to the protein causes it to change shape
Molecule is released to the inside of the cell
Phosphate molecules are released from carrier protein and reforms ATP
Carrier protein returns to original shape
Molecule has been moved from a low to high concentration
Example: guard cells and potassium:
Guard cells use ATP provided by mitochondria
Actively transport potassium ions into the cells
Lowers water potential in the guard cell
Water moves in
Cell swells and stomata open
Bulk transport
Large molecules such as enzymes or hormones
Whole bacteria
Moved into and out of the cells Lowers water by bulk transport
Uses ATP for the movement of vesicles
Cytoskeleton moves the vesicles
Vesicle fuses with the CSM
Endocytosis
Movement of materials into cells
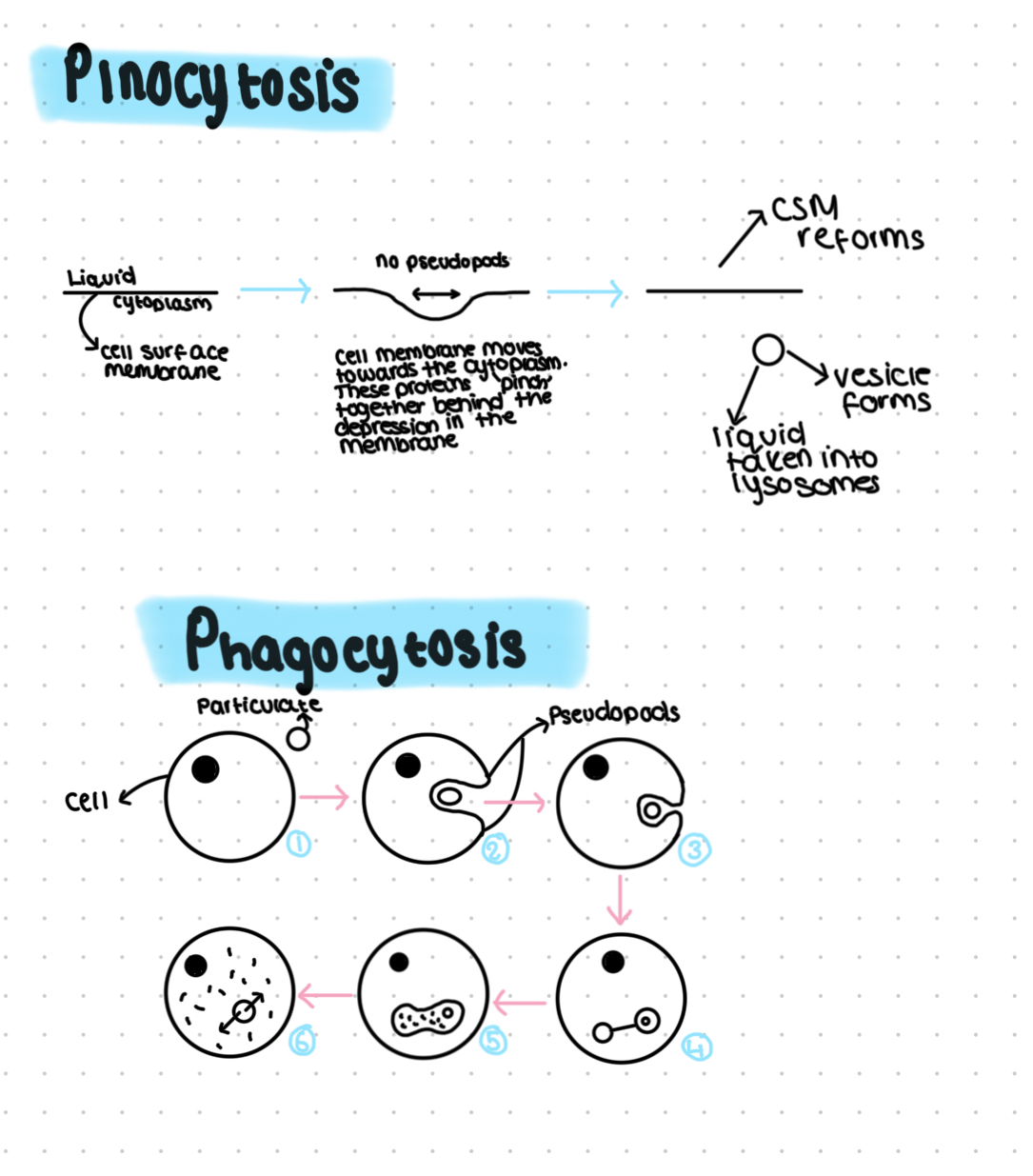
Phagocytosis- uptake of solids
Pinocytosis- uptake if liquids
Phagocytosis steps:
1)Encounter/ detection
2)Pseudopods form and move around substance/ cell
3)Pseudopods mobile to enclose the substance being phagocytosed, ‘engulfing’
4)Particulate is now internalised in a vesicle, cell surface membrane reforms
5)Cytoslelton moves vesicle to a lysosome where they fuse together, the hydrolytic enzymes breakdown/ hydrolyse what was in the vesicle
6)The broken down products of this are either absorbed by the cytoplasm or excreted by the cell if it is a waste product
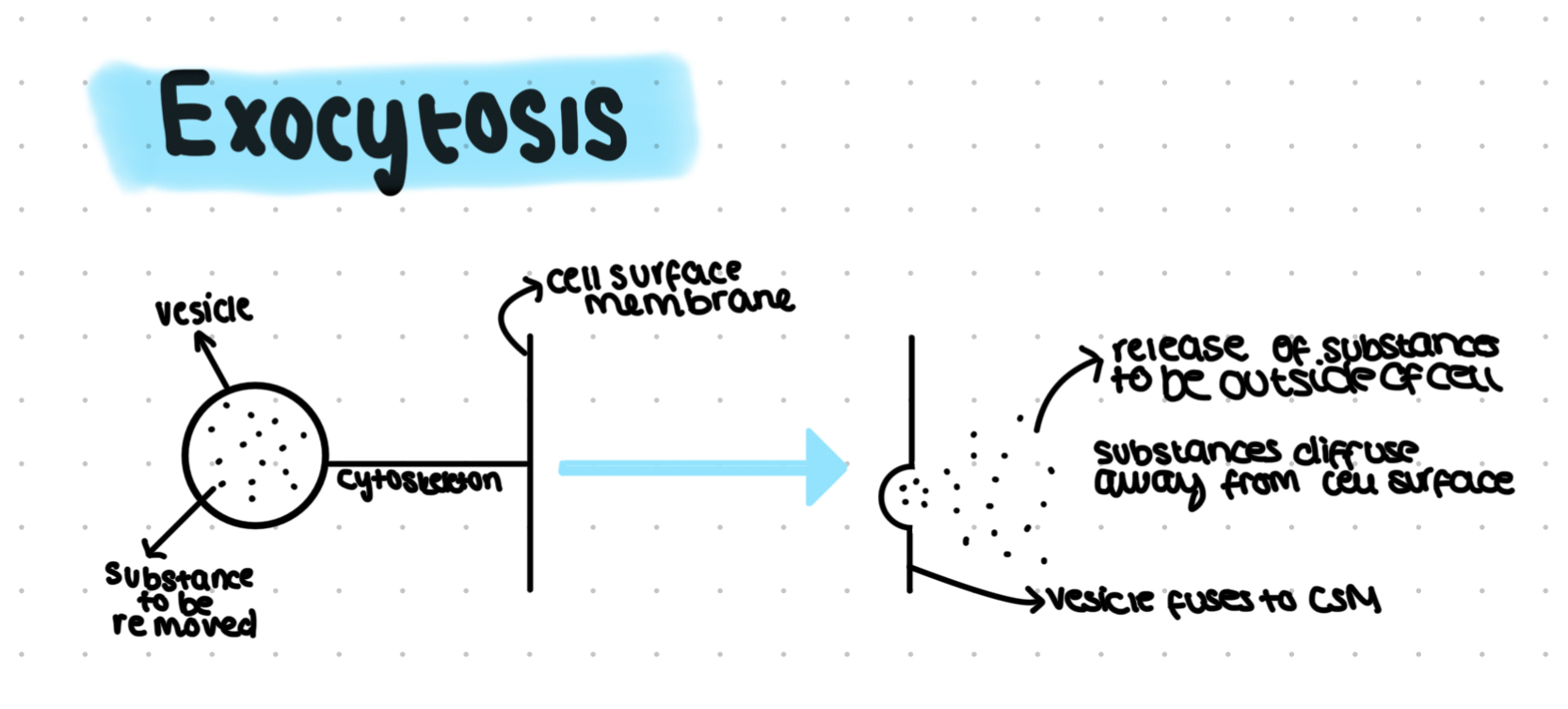
Exocytosis
Removal of substances from cells
Vesicles formed by Golgi move towards CSM
Vesicle fuses with CSM
Contents of vesicle released to outside of cell
Active process