oral radiology: xray production
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Wilhelm Rontgen revolutionized
diganostic resources in the medical and dental fields
Wilhelm Rontgen did research with
cathode rays and special screens that glowed when exposed
Wilhelm Rontgen experimented with vacuum tubes, where he noticed
greenish fluorescence on plates that were away from the tube
when Wilhelm Rontgen replaced the plates with photographic films, what was permanently recorded
shadows of the image
Wilhelm Rontgen first xray was of what
wife's hand bones
Dr. Otto Walkhoff was a pioneer of
dental radiology
Dr. Otto Walkhoff placed what in his mouth and exposed it for 25 mins
photographic glass plate
atom
smallest particle of an element having the chemical properties of the element
Bohr model of the atom
Model of the atom with a positive nucleus and electrons orbiting in energy levels
atomic nucleus composition
protons (+) and neutrons
orbital composition
electrons (-)
proton and neutron size
1 amu
electron size
0.0005 amu
atomic number
# of protons
atomic number determines what
what element it is
atomic number is fundamental for determining
element's chemical and physical properties
atomic mass
# of protons and neutrons
atomic mass determines
stability of element
# of electrons determines
charge of atom
ion
charged particle
ionization
creation of an ion
radiation
transmission of energy through space and matter in the form of waves and particles
ionizing radiation
high-energy radiation, capable of producing ions
radioactivity
spontaneous nuclear disintegration process of a molecule to acquire a more stable form
Particulate radiation
electrically charged (except for neutrons) tiny particles of matter that possess mass and travel in straight lines and at high speeds
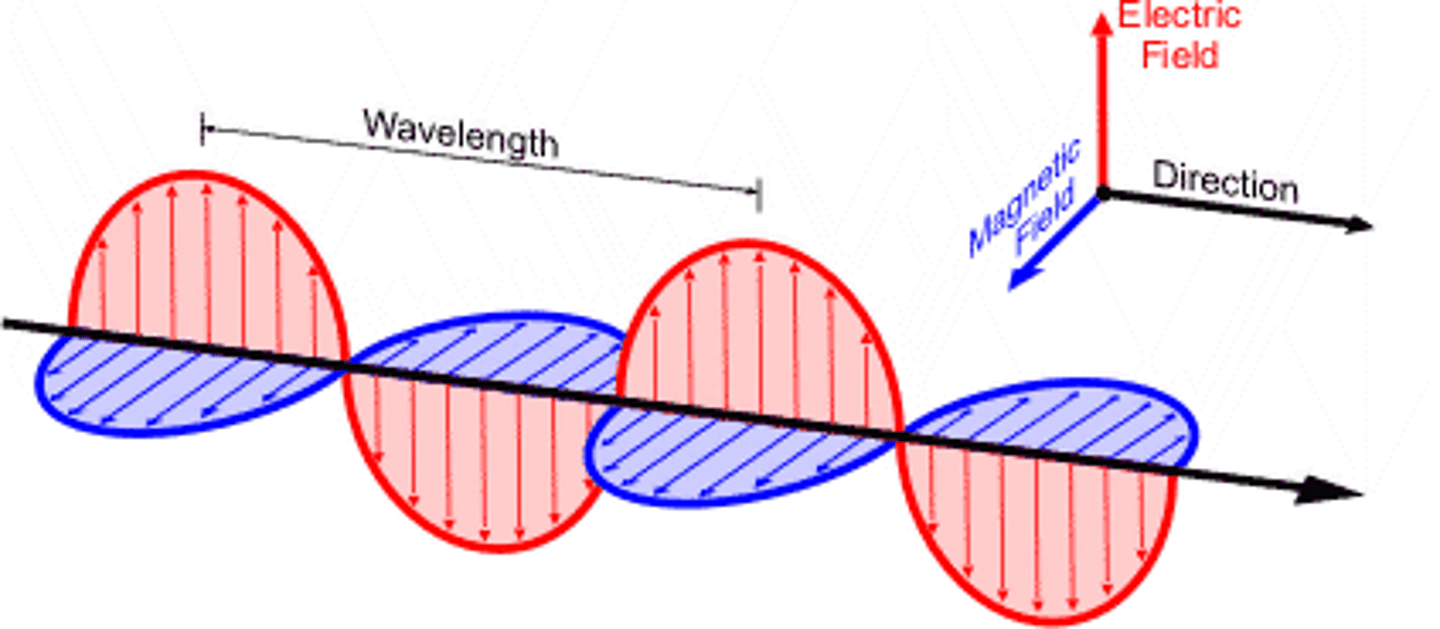
electromagnetic radiation
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space, with no mass
Electromagnetic radiation is generated when
the velocity of an electrically charged particle is altered
only higher energy particles can cause
ionization
two theories that can describe the properties of electromagnetic radiation
1. quantum theory
2. wave theory
quantum theory
small discrete bundles of energy (photons) that travels at the speed of light and contains a specfic amount of energy
wave theory
transverse waves of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, perpendicular to each other and the direction of travel, moving at the speed of light in a vacuum
xrays can
ionize matter
wavelength definition
distance between successive crests of a wave
frequency definition
number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given amount of time
wavelength unit
meters
frequency unit
hertz
the higher the frequency, the ____ the wavelength
shorter
non-ionizing radiation examples
1. radio waves
2. microwaves
3. infrared
4. visible
ionizing radiation examples
1. ultraviolet
2. xray
3. gamma ray
alpha particle
2 protons + 2 neutrons
beta particles (cathode rays)
electrons
Radioactivity is usually associated with
protons and neurons
higher the freqency, the ___ the energy
higher
the shorter the wavelengths, the ___ the energy
higher
xrays are a type of
electromagnetic radiation
xrays have no
mass and electrical charge
xrays are at the speed of
light
xrays have a ___ wavelength
short
xrays have an energy of
10^4 to 10^5 eV
xrays direction of propagation
straight line but can be deflected or scattered
do xrays travel parallel or diverge
diverge
xrays have effects on
imaging films and living beings
contents of xrays tube
1. cathode (-)
2. andoe (+)
3. evacuated glass envelope
cathode of xray tube is made of
1. tungsten filament
2. concave molydenium bowl
anode of xray tube is made of
1. tungsten
2. copper block
function of tungsten filament
source of electrons
function of concave molydenium bowl
focusing cup
function of tungsten
focal spot
function of copper block
thermal conductor
contents of evacuated glass envelope
lead glass with a window of non-lead glass
electricity definition
energy used to produce xrays
electric current definition
flow of electrons flowing through a conductor
circuits definition
path through which an electric current goes into the machine
transformers definition
responsible for increasing or decreasing the voltage electric current
steps of xrays production
1. electricity on the plug
2. current in the tungsten filament
3. heating the filament
4. fire button
5. high voltage circuit
6. upon reaching the tungsten target, kinetic energy is lost through xrays and heat
heating the filament creates
thermionic emission (release of electrons from a heated material's surface)
number of volts of current running in tungsten filament
3-10V
amperage/milliamperage (mA)
controls the electrical current/ number of electrons moving within the filament
kilovoltage (kv) / kilovolt peak (kVp)
maximum voltage that enables the movement of electrons from the cathode to the anode
higher the mA, the ___ electrons flowing within the filament
more
lower the mA, the ___ electrons flowing within the filament
less
the higher the kV, the ____ the velocity of the electrons
higher
the lower the kV, the ____ the velocity of the electrons
lower
2 types of xrays collisions
1. result in heat generation
2. result in xray production
when electrons get close to (stable) tungsten particles in outer shells they get deflected and lose energy in the form of ___
heat
when electrons hit (stable) tungsten particles in outer shells, ___ atoms get deflected and produce ___
both, heat
The closer the orbit is to the nucleus, the higher the
binding energy
The difference between heat production or xray production collisions
xray production collisions happen closer to the nucleus
Braking radiation (Bremsstrahlung) characteristics
1. 70% of X-rays produced
2. no collision with other electrons
3. broad spectrum of energy
4. keeps colliding with other atoms
another type of braking radiation characteristics
1. rare
2. electrons hits the nucleus of an atom
3. all kinetic energy is converted into high-energy x-ray photon
characteristic radiation characteristics
1. displacement of an electron of the inner shells
2. lesser amount of x-ray photons
3. requires energy greater than 70 kVp
4. electrons change of positions between orbitals
in characteristic radiation what is the result of electrons changing positions between orbitals
instability
when outer shell electrons move to inner shells in characteristic radiation what is lost
internal energy
primary radiation definition
xray beam produced in the anode, leaving the xray tube
secondary radiation definition
radiation produced by photons interacting with matter
scattering of radiation definition
deflected in all directions after interacting with the matter
types of xray interactions
1. no interaction
2. complete absorption/photoelectric absorption
3. compton scattering of the photons
4. coherent scattering of the photons
no interaction xray
xray photon passes through the patient unchanged and leaves atom unchanged
no interaction xray are responsible for producing ___
densities
absorption of energy/photoelectric effect xray interation definition
xray photon hits an electron of any orbital and photon is completely absorbed
in absorption of energy/photoelectric effect xray interation, there is atom ionization due to
ejected photoelectron - atom lost an electron
absorption of energy/photoelectric effect and compton scattering contribute to dangerous xrays due to what
ionization of the atom
compton scattering xray interaction definition
scattering with ionization where the photon loses some of its energy, is deflected, and continues with less energy
ejected electron is called
compton electron
coherent scattering xray interaction definition
photon interacts with a whole atom, the atom becomes momentarily excited and generates another photon with the same energy - no changes to the atom at the end