Transport across the cell membrane
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Passive
does not require energy, substances move with concentration gradient.
Active
does require energy, substances move against the concentration gradient
Osmosis
The diffusion of a solvent (water) through a differentially (semi) permeable membrane, the solvent can move through the membrane, but the solute is not able to fit through, the only way to reach equilibrium is for the solvent to move
Tonicity definition
The concentration of a solution as compare to another solution
What defines an isotonic solution
extracellular and intracellular ion concentration equal
What defines a hypotonic solution
extracellular concentration ion is less than intracellular
What defines a hypertonic solution
extracellular ion concentration is more than intracellular
What happens when a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution?
A cell placed in a hypotonic solution would result in movement of solvent (water) into the cell.
This is because the ion concentration is higher in the cell so water moves to move in the reach equilibrium, as solutes are not able to move through the semi permeable membrane.
This will lead to the cell swelling and possibly bursting.
simple Diffusion
the spreading out of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration to areas of low concentration resulting is even distribution of particles
Collision mechanism diffusion
This ‘spreading out’ of particles is brought about due to more collisions happening between particles at high concentrations.
This forces them to move away from each other into areas of low concentration where they experience less collisions.
Diffusion – Gradient and Rate
The difference in concentration that brings about diffusion is known as a concentration gradient (diffusion gradient).
The greater the difference between the two concentrations, the faster the rate of diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion – Core Definition
The spreading out of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration resulting in even distribution of particles.
Facilitated Diffusion – Selectivit
Occurs through integral proteins such as carrier and channel proteins, therefore it is selective.
Facilitated Diffusion – Polar Molecule
Generally used for water molecules and ions as they are polar molecules (polar molecules cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer)
Endocytosis – Core Definitio
The taking in of solids or liquids through vesicles.
Endocytosis – Membrane Action
Cell membrane folds around the substance (solid or liquid) until it is completely enclosed.
Vesicle then pinches off within the cytoplas
Term: Endocytosis – Types
Pinocytosis – taking in liquids (Cell drinking)
Phagocytosis – Taking in solid particles (Cell eating)
Which of the following groups correctly lists molecules which undergo facilitated diffusion?
) Water, oxygen and glucose
(b) Amino acids, glucose and sodium ions
(c) Glucose, fatty acids and oxygen
(d) Sodium ions, amino acids and carbon dioxide
b
Cell Membrane – Structure
or the cells of a body to function normally, they must remain in a stable environment.
Describe the structure of the cell membrane and explain how it allows the exchange of ions to occur (14 marks)
Made of phospholipid bilayer
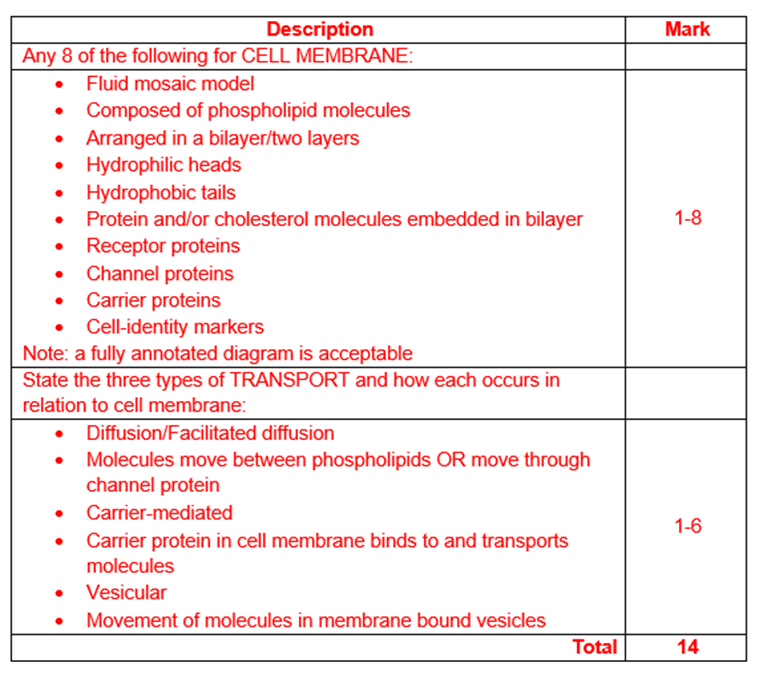
Arranged in a bilayer/double layers
Hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
Proteins embedded in membrane (channel and carrier proteins)
Cholesterol presentGlycoproteins and glycolipids present
Site of cell signalling, chemical reactions, recognition, attachment, and selective transport
Processes include diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis
Vesicles formed
Membrane is fluid
Term: Endocytosis
Definition:
Organelle E entered the cell via a process known as endocytosis.
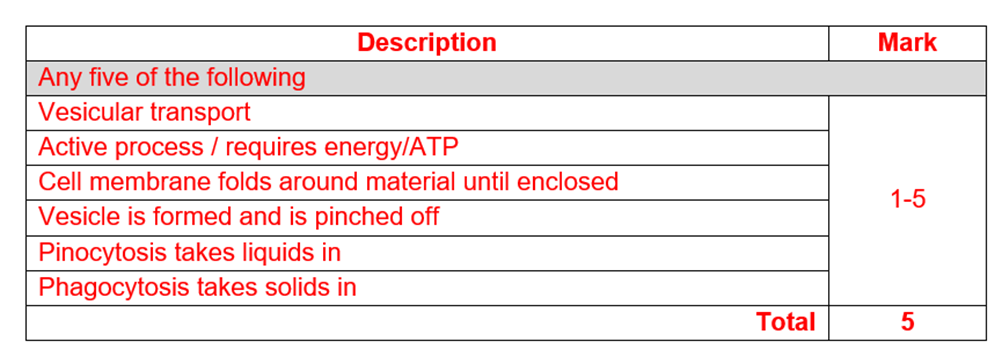
Describe this process 5marks
Vesicular transport
Active process / requires energy/ATP
Cell membrane folds around material until enclosed
Vesicle is formed and pinched off
Pinocytosis takes in liquids
Phagocytosis takes in solids
Exocytosis Describe how the structure of the cell membrane allows for transport of materials via exocytosis.
✅ Key Points:
Vesicles are made of the same phospholipid bilayer as the cell membrane, allowing for attachment
Membrane is fluid (contains cholesterol), so it can change shape
2 marks
Vesicles are made of the same phospholipid bilayer as the cell membrane, allowing for attachment
Membrane is fluid (contains cholesterol), so it can change shape
