Thyroid Gland section 2
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
quiz 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Thyroid Gland Properties
The Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland u
Ductless
Produces and secretes its products or hormones directly into the blood
Thyroxine - a hormone that stimulates the metabolic rate u Influences heart rate, body temperature, mood, alertness
Controlled by the pituitary gland u Not visible clinically
Can be palpated during H/N exam and should be movable during swallowing
Thyroid Gland Properties
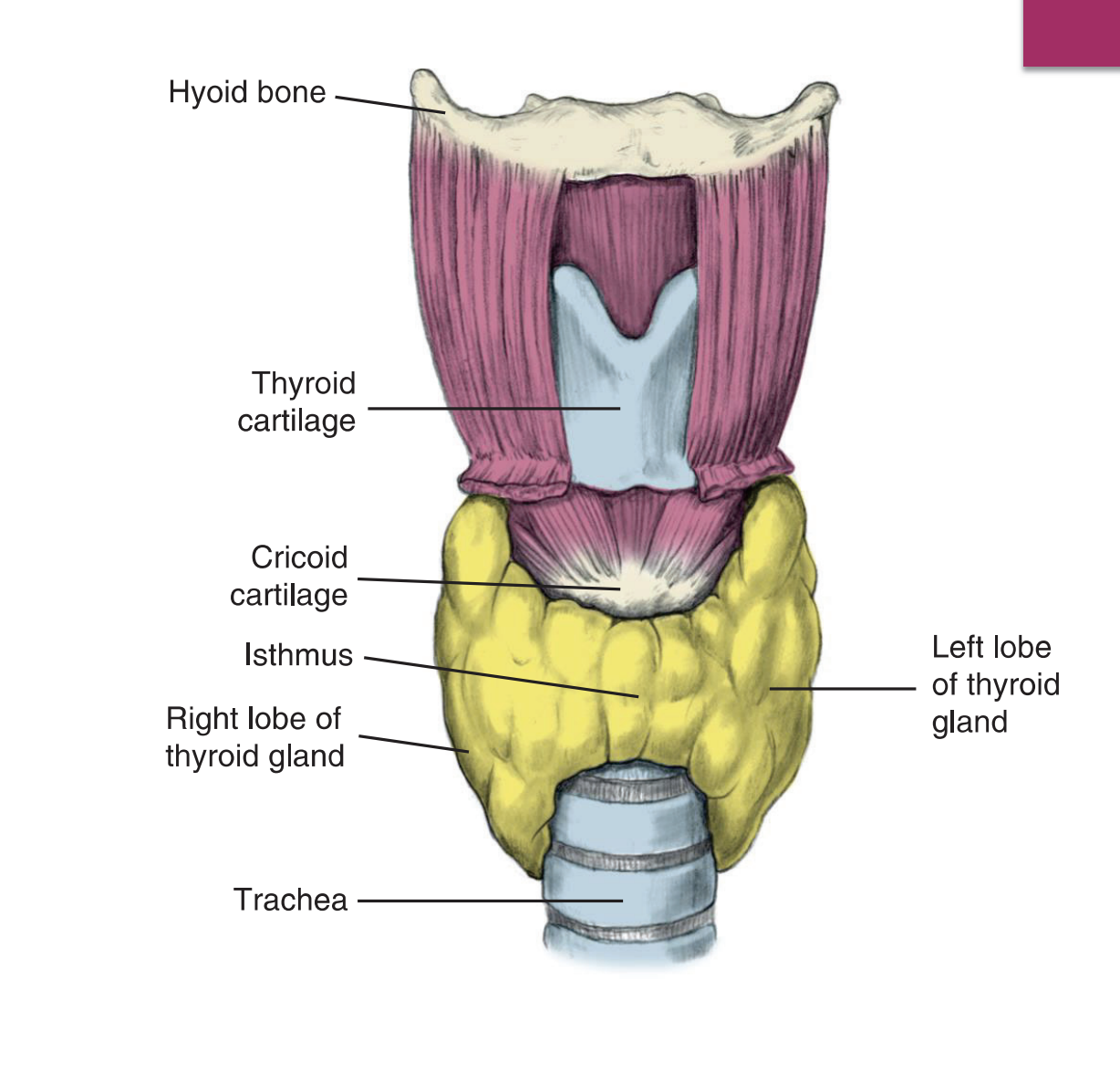
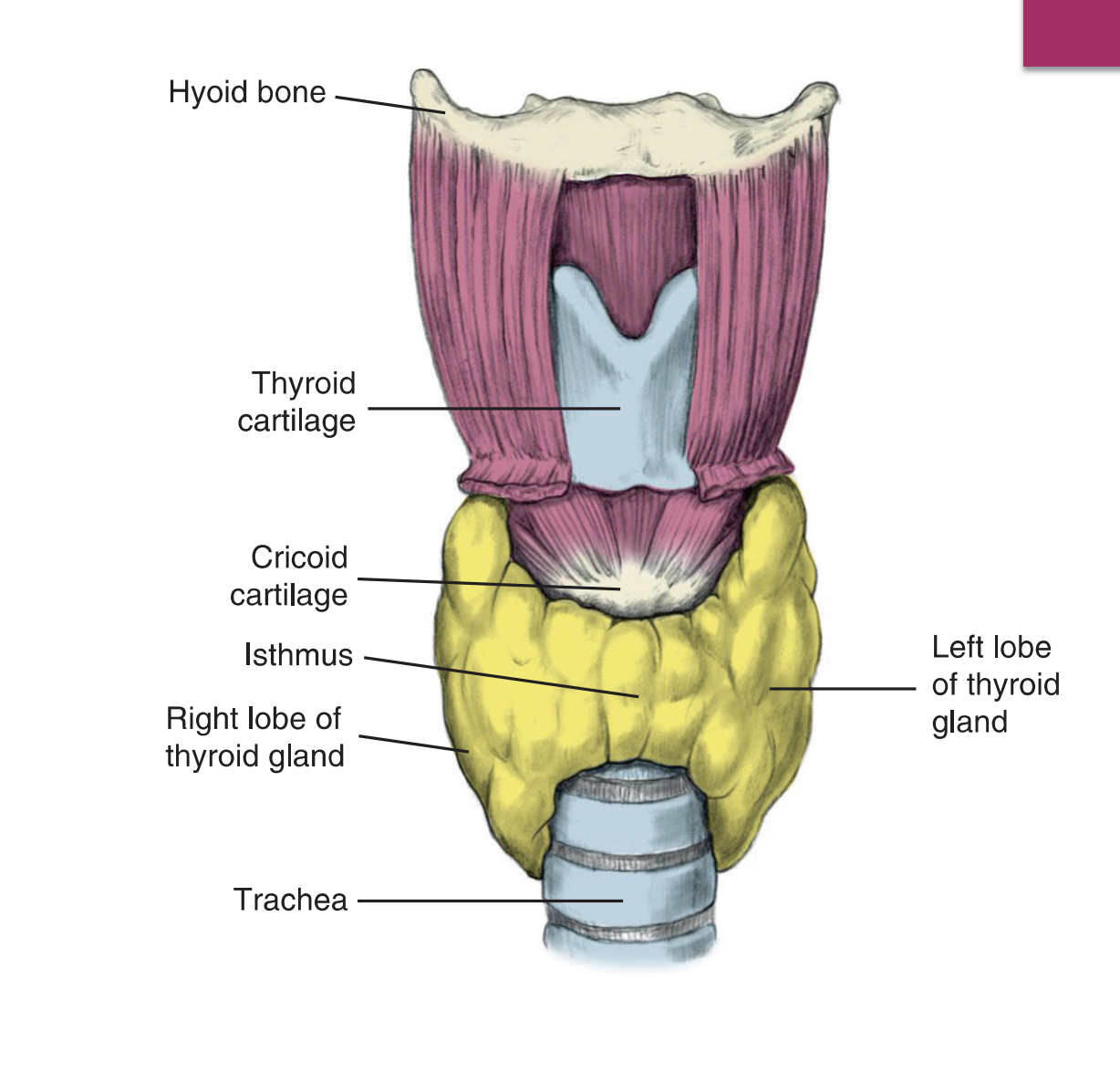
Located in the anterior and lateral regions of the neck
Inferior and lateral to the thyroid cartilage, at the junction between the larynx and the trachea
The gland consists of two lateral lobes connected anteriorly by the isthmu
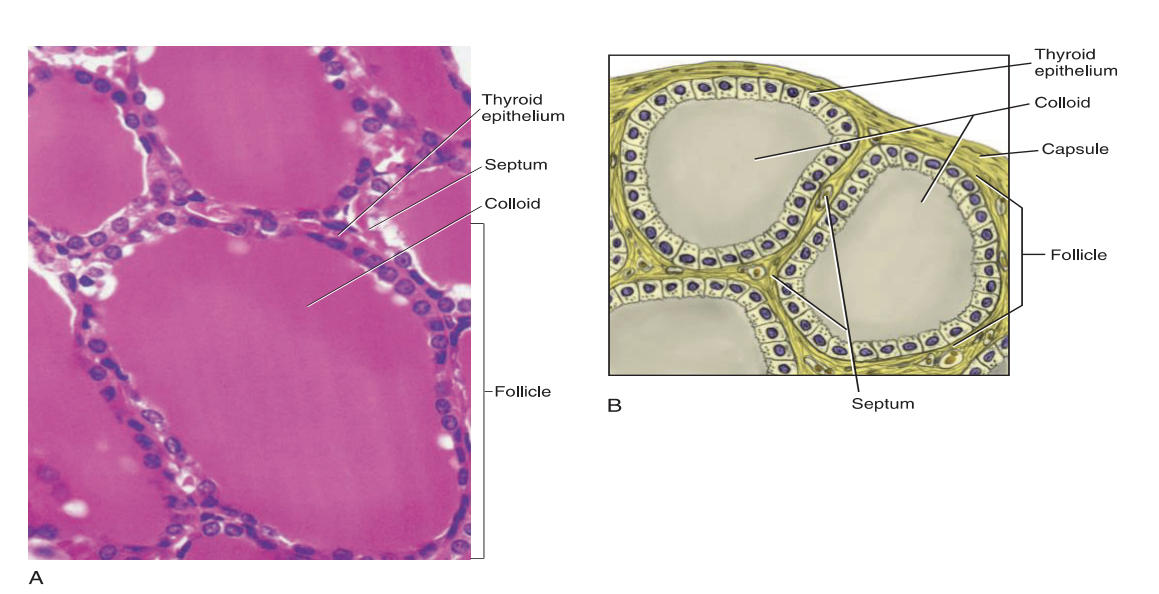
Thyroid Gland Histology
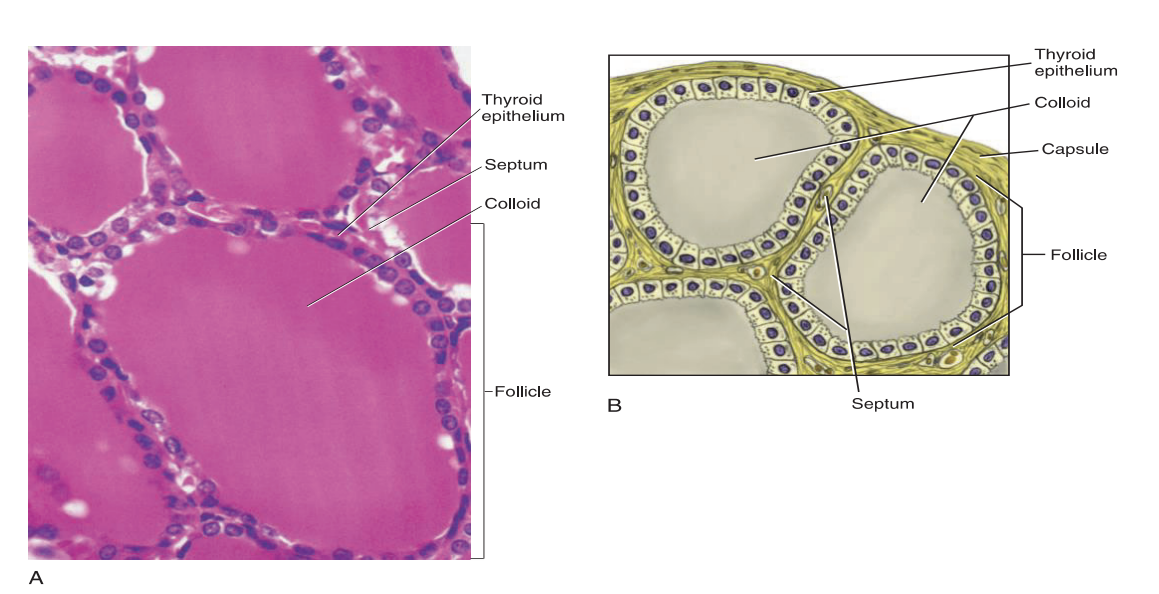
The thyroid gland is covered by a connective tissue capsule
The septa divide the gland into larger lobes and smaller lobules
Each follicle consists of a layer of simple cuboidal epithelium enclosing a cavity that is usually filled with colloid - produces thyroxine
Parathyroid Glands
Typically consist of four to eight small endocrine glands, two on each side, close to the thyroid gland
Not visible or palpable during an extraoral examination of the patient
The parathyroid glands may alter the physiology of the thyroid gland because of their involvement in a disease proces
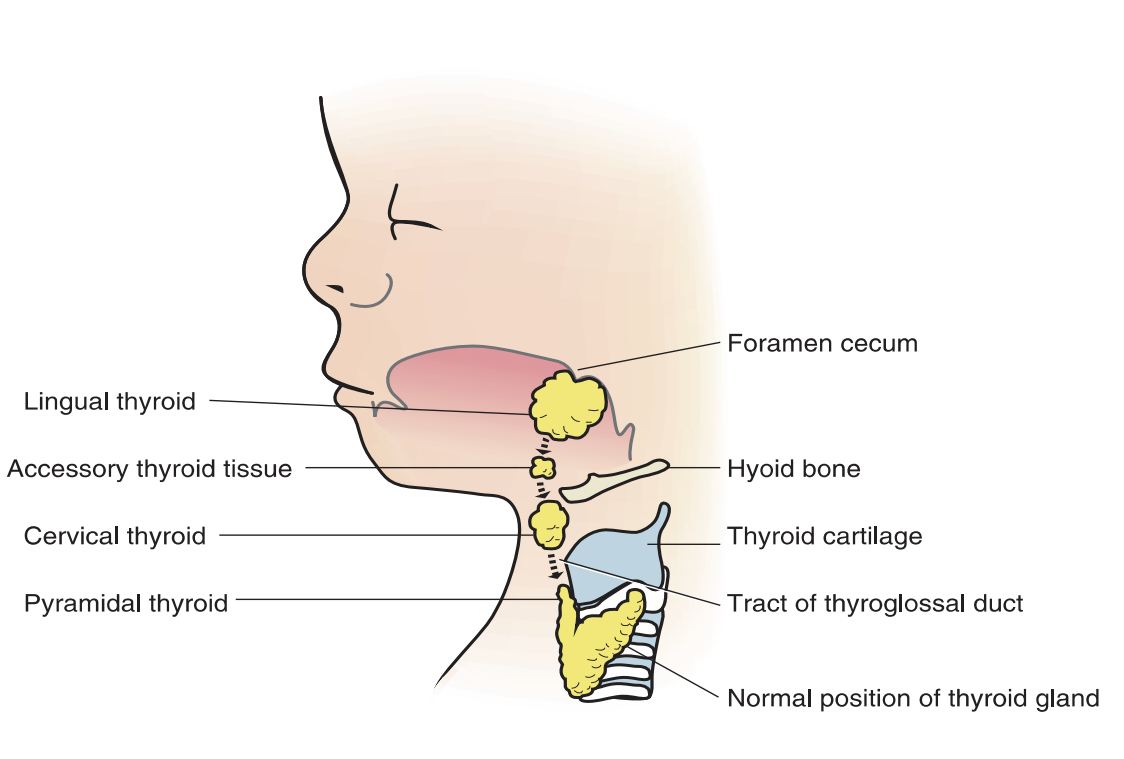
Thyroid Gland Development
The thyroid gland is the first endocrine gland to appear in embryonic development and develops from endoderm invaded by mesenchyme
Develops approx. 24th day of prenatal development
Forms from a median downgrowth at the base of the tongue, connected by a thyroglossal duct
Opening of the thyroglossal duct is the foramen cecum
Choice of imaging is ultrasound not radiographs
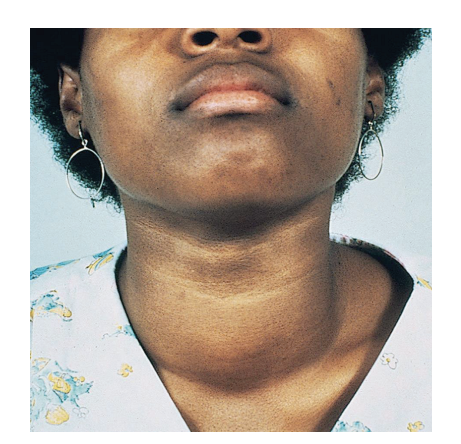
Clinical applications: Goiter
Gland may become enlarged and visible during extraoral exam
Enlarged thyroid is called a goiter
May be firm and tender when palpated
May contain hard masses
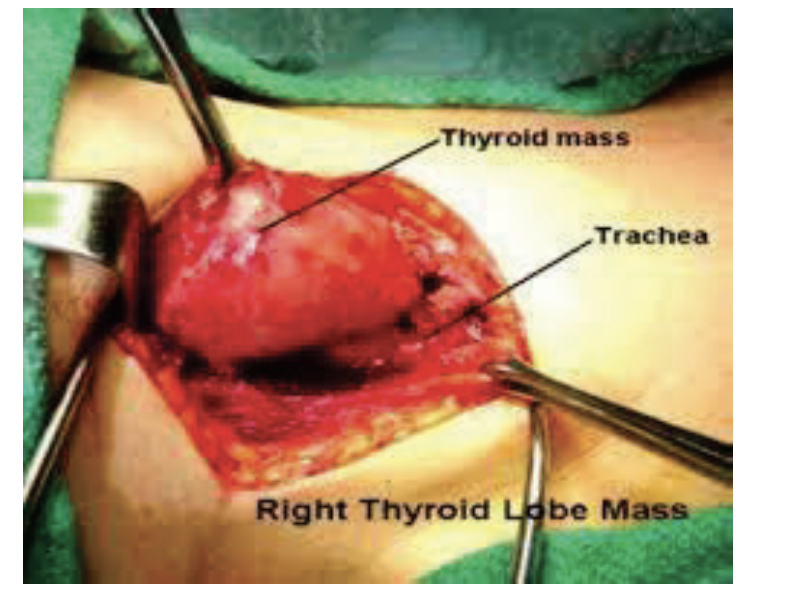
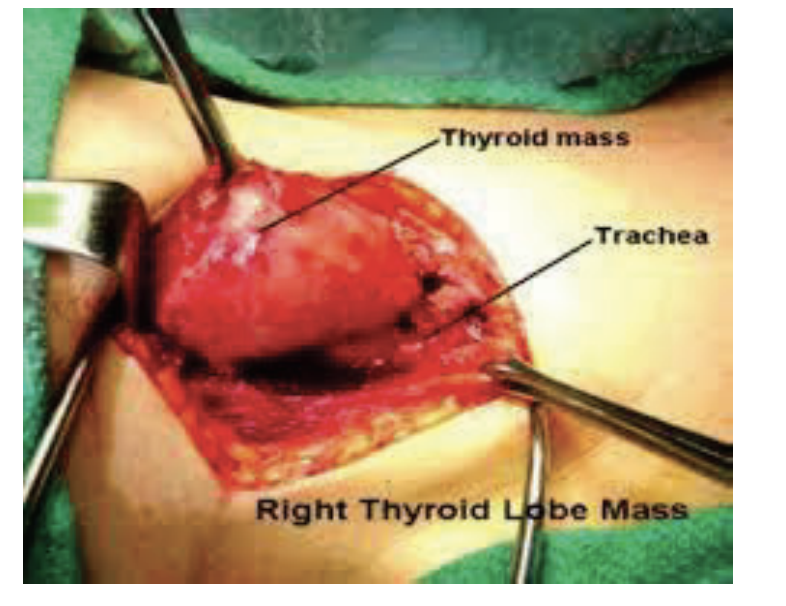
Clinical Consideration: Tumorous Thyroid Growth
Diseased gland may lose its mobility and not move up when the patient swallows; indicative of a tumorous growth
Only 4-5% of thyroid nodules are cancerous