structure of cell surface membrane
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
plasma membrane
controls how substances move in and out of the cell
composed of two layers of phospholipids with proteins and carbohydrates within
what is the fluid mosaic model
fluid- phospholipid molecules can move, membrane flexible so can change shape
mosaic- proteins embedded in bilayer vary in shape, size and patterns
Describe how a lipid soluble substance will move into a cell differently to a water soluble substance
lipid soluble moves through phospholipid bilayer by diffusion
water soluble - intrinsic proteins act as channels allowing it to pass into and out of cell, by facilitated diffusion which is limited
what does cholesterol do
provides strength and maintains membranes fluidity
describe why a phospholipid forms a bilayer
The hydrophilic phosphate head can hold at the surface of membranes to form phospholipid bilayer + tail
what can a phospholipid form
bilayer
liposome
micelle
what are the functions of the phospholipid in the membrane?
allow lipid soluble substances to enter and leave the cell
prevent water soluble substances from entering and leaving the cell
make the membrane flexible
give examples of membrane surrounded organelles
Mitochondria and chloroplast
what are intrinsic proteins
Occur at the surface of the bilayer and extend only halfway through it
provide mechanical support
allow water soluble substances to pass into and out of cell
What are extrinsic proteins
act throughout the whole bilayer
protein channels- water soluble ions to diffuse
carrier proteins- bind to molecules (glucose) and change shape to move molecules across the membrane
what are the functions of the protein in the membrane?
structural support
act as channels to transport water soluble ions across membrane
help cells adhere together
act as receptors for hormones
cell recognition
features of cholesterol
hydrophobic and prevent loss of water from the cell
they also pull together the fatty acids tails of the phospholipid molecules limiting their movement
functions of cholesterol in membrane
make membrane less fluid at high temperatures
prevents leakage of water from cell
reduce movement of other molecules
what is a glycolipid
are made up of a carbohydrate covalently bonded with a lipid
where does the gycolipid extend to?
The watery environment outside the cell where it acts as a receptor for specific chemicals
functions of glycolipid
Cell recognition
stability
cells attatch to one another and form tissues
where are carbohydrate chains attached to to form glycoprotein
extrinsic proteins on the outer surface of cell membrane
functions of glycoproteins
recognition sites for hormones
cells attach to one another and form tissues
allows cells to recognise eachother
why does the cell surface membrane do not allow all molecules to freely diffuse across it
not soluble in lipids and cannot pass through phospholipid bilayer
too large to pass through channels of membrane
same charge as charge on protein channels ( repelled)
electrically charged (polar) so difficulty passing through non polar hydrophobic tails
functions of membranes within cells
controls entry and exit of materials in cell
provide surfaces on which reactions can occur
fluid mosaic model diagram
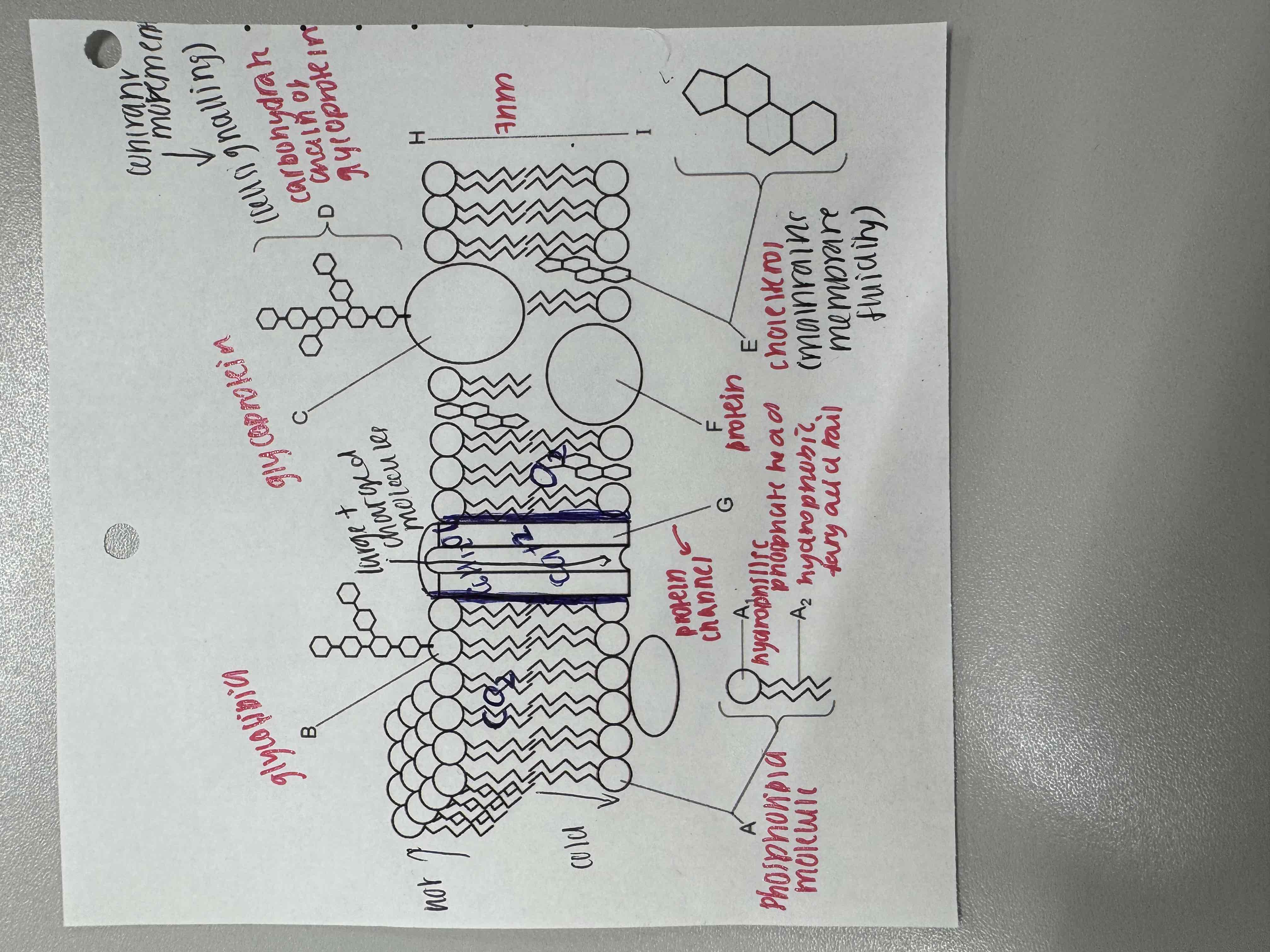
describe glycoprotein
branching carbohydrate chain from protein which acts as a recognition site for hormones
Describe glycolipid
acts as a recognition site