Neurons & synaptic transmission
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what is a neuron ?
the basic building blocks of the nervous system
neurons are nerves cells that process and transmit messages through electrical and chemical signals
what are sensory neurons
they carry out messages from the PNS to the CNS.
they have long dendrites and short axons
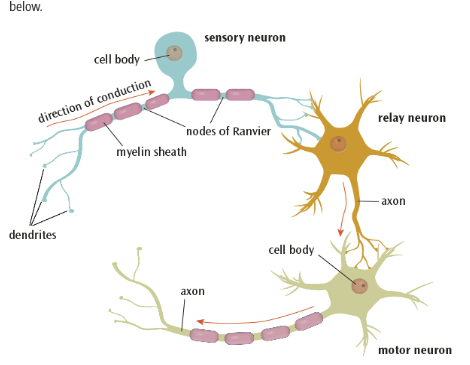
what are relay neurons ?
these connect the sensory neurons to the motor neurons or other relay neurons
they have short dendrites and long axons
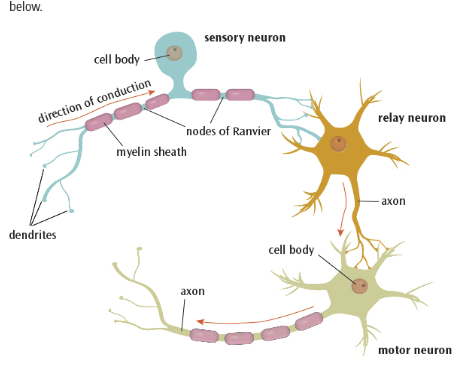
what are motor neurons
these connect the CNS to effectors such as muscle glands
They have short dendrites and long axons
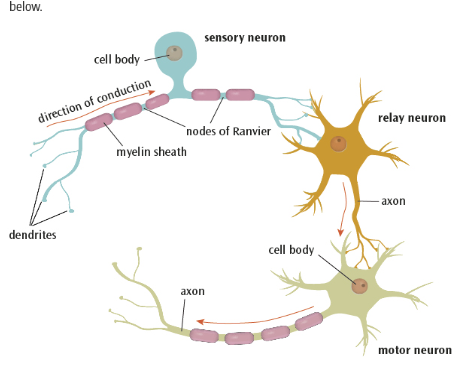
what are the main structures in neurons ?
cell body
nucleus
axon
dendrites
myelin sheath
nodes of ranvier
terminal button
what is the cell body ?
this contains the nucleus
what is the nucleus ?
this is where genetic material of the cell is
what are dendrites
these are branch like structures that protrude from the cell body.
they receive / carry nerve impulses from neighbouring neurons
axons
carries impulses away from the cell body down the length of the neuron
myelin sheath ?
this is a fatty layer that protects the axon and speed up electrical transmission of the impulse
nodes of ranvier
these are the gaps that segment the myelin sheath
these speed up the transmission of the impulse by forcing it to “jump” across the gaps along axon
terminal button
at the end of the axon
they communicate with the next neuron in the chain across a gap known as the synapse
where are sensory neurons located ?
located outside the CNS, in the PNS in clusters known as ganglia
where are relay neurons located ?
they make up 97% of all neurons and most are found within the brain and the visual system
where can motor neurons be found ?
the cell bodies of motor neurons may be located in the central nervus system but they have long axons which form part of the peripheral nervous system
action potential
occurs when a neuron is activated by a stimulus, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged for a split second causing action potential
what is the charge of a neuron at resting state compared to the outside of the neuron
it is negatively charged compare to the outside
what does action potential cause
his creates an electrical impulse that travels down the axon towards the end of the neuron known as electrical transmission
synaptic transmission
the process by which neighbouring neurons communicate with each other by sending chemical messages across the gap (synapse) that separates
neurotransmitter
Brain chemicals released from synaptic vesicles that relay signals across the synapse from one neuron to another
neurotransmitters can be broadly divided from excitatory function + those that perform an inhibitory function