Topic 1.6 Nucleic Acids
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
Phosphate group
5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA)
Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, G in DNA; A, U, C, G in RNA)
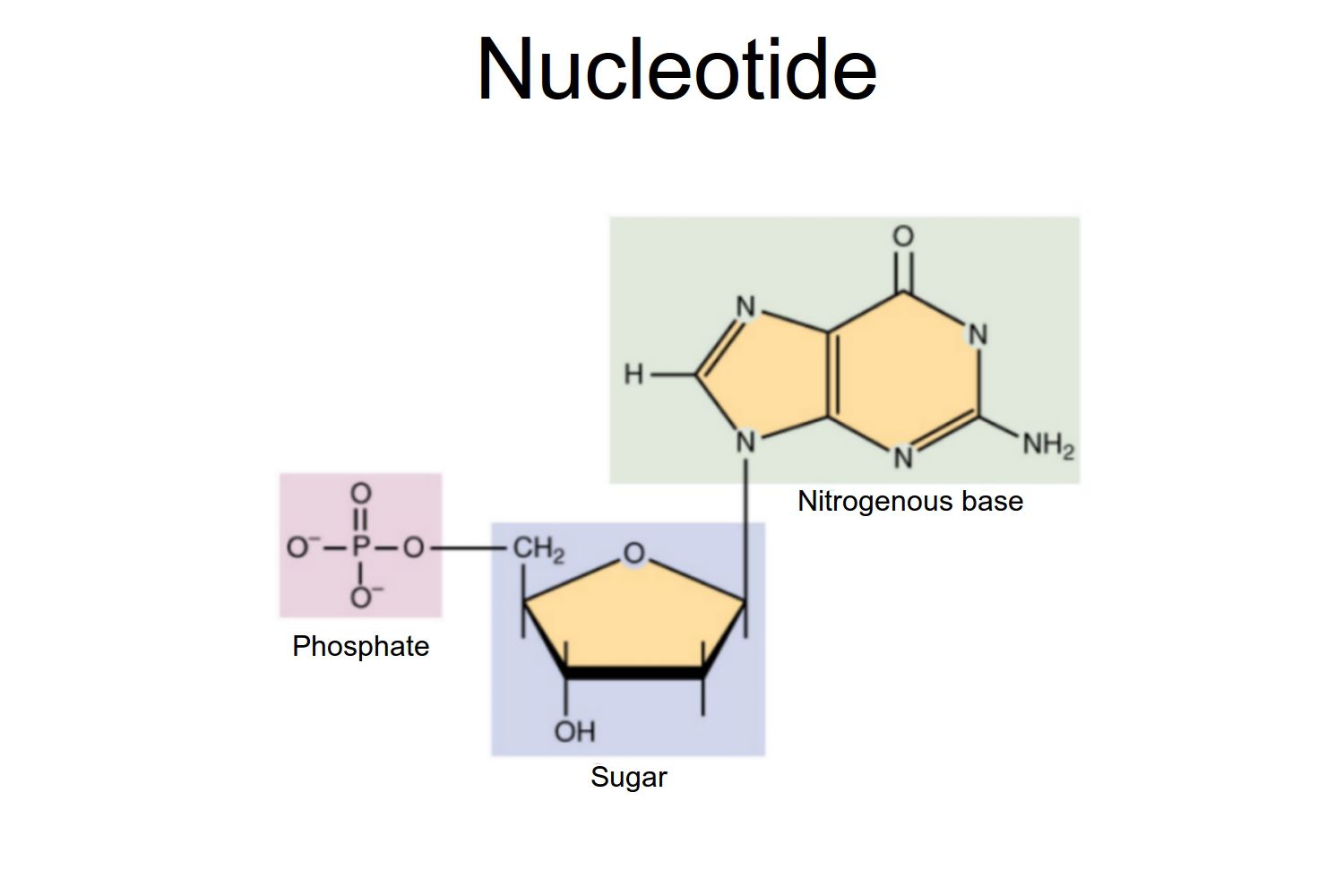
Diagram the monomer of a nucleic acid and label the structural components.
Nitrogenous base: A, T, C, G (DNA) or A, U, C, G (RNA)
5-carbon sugar: deoxyribose (DNA) or ribose (RNA)
Phosphate group: links nucleotides together via phosphodiester bonds
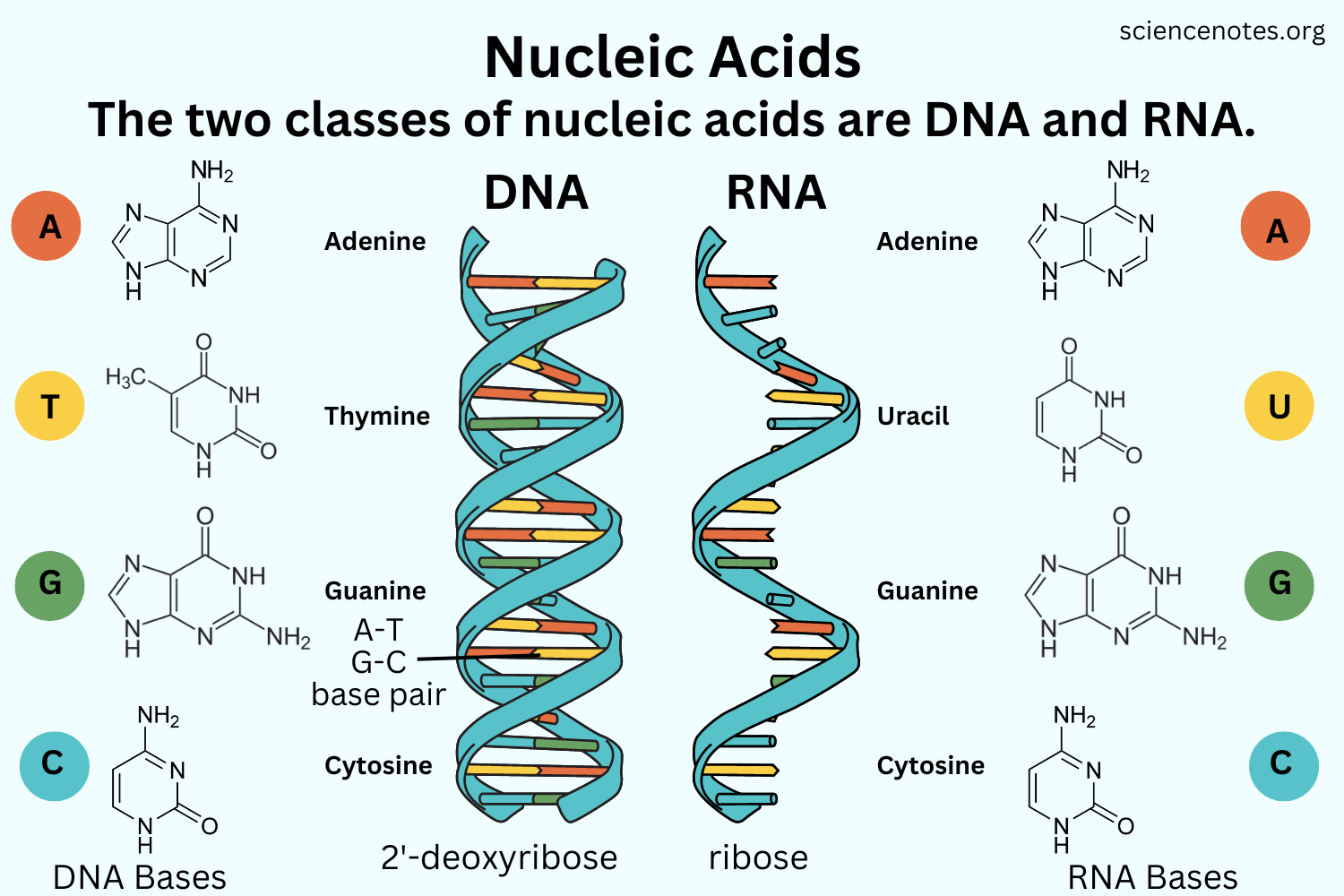
Identify the FIVE nitrogenous bases.
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T) – DNA only
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Uracil (U) – RNA only
Describe the difference between a purine and pyrimidine.
Purines:
Double-ring structure
Examples: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines:
Single-ring structure
Examples: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U)
Similarity: Both are nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids.
Identify which nitrogenous bases are purines.
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Hint: Purines have two rings in their structure.
Identify which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines.
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T) – DNA only
Uracil (U) – RNA only
Hint: Pyrimidines have a single-ring structure.
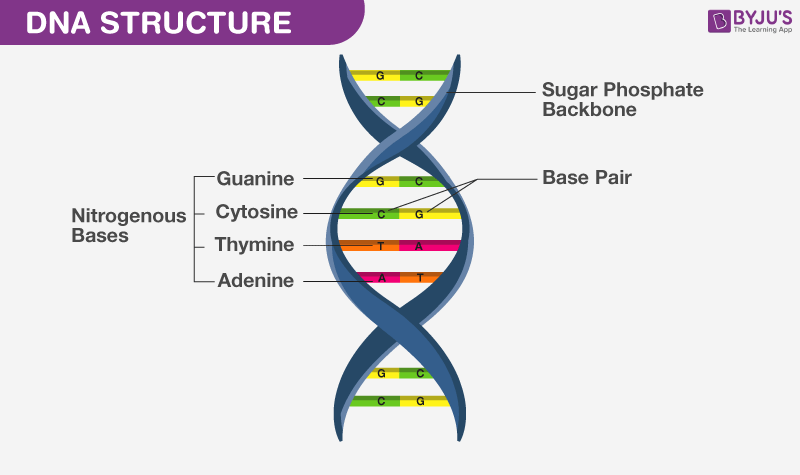
Describe the structure of the nucleic acid polymer.
Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) are polymers of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds.
Backbone: Alternating sugar and phosphate groups
Nitrogenous bases: Extend from the sugar, pair with complementary bases via hydrogen bonds (A–T or A–U, C–G)
DNA is double-stranded (double helix); RNA is single-stranded
What are the ends of a nucleic acid polymer called and what functional group is found at each end?
5′ end: Has a phosphate group (–PO₄³⁻) attached to the 5′ carbon of the sugar
3′ end: Has a hydroxyl group (–OH) attached to the 3′ carbon of the sugar
Directionality: Nucleic acids are synthesized and read from 5′ → 3′
Describe the directionality of a nucleic acid.
Nucleic acids have a 5′ end (with a phosphate group) and a 3′ end (with a hydroxyl group).
Directionality: DNA and RNA are synthesized and read from 5′ → 3′.
This orientation is important for replication and transcription.
Which end is the location of the growing nucleic acid strand?
Nucleic acids grow at the 3′ end, where a new nucleotide is added to the hydroxyl (–OH) group of the sugar.
Synthesis occurs in the 5′ → 3′ direction.
Describe the structure of DNA.
DNA is a double-stranded nucleic acid forming a double helix
Backbone: Alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups
Nitrogenous bases: Extend inward and pair via hydrogen bonds (A–T, C–G)
Strands are antiparallel: one runs 5′ → 3′, the other 3′ → 5′
Twist of helix: About 10 base pairs per turn
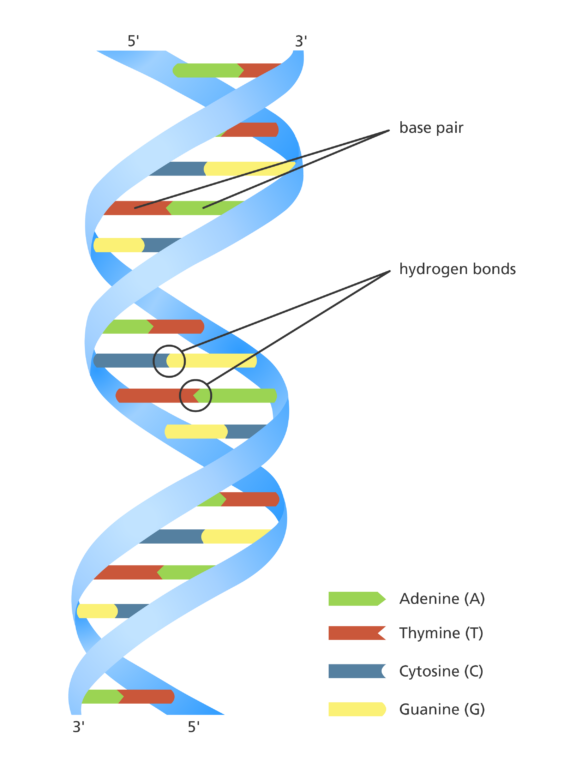
What are the complementary base pairings found in DNA?
Adenine (A) → Thymine (T) (2 hydrogen bonds)
Cytosine (C) → Guanine (G) (3 hydrogen bonds)
Complementary base pairing ensures accurate DNA replication and stable double helix structure
What are the complementary base pairings found in RNA?
Adenine (A) → Uracil (U)
Cytosine (C) → Guanine (G)
RNA is usually single-stranded, but can form short complementary regions via hydrogen bonding for structure and function.
What type of bond occurs between complementary base pairings in DNA or RNA?
Hydrogen bonds hold complementary bases together
A–T (or A–U in RNA): 2 hydrogen bonds
C–G: 3 hydrogen bonds
These bonds stabilize the nucleic acid structure but are weak enough to allow separation during replication or transcription.
Describe or diagram where the hydrogen bond is located in DNA or RNA.
Hydrogen bonds form between complementary nitrogenous bases (A–T or A–U, C–G)
They hold the two strands of DNA together or stabilize RNA secondary structures
Located inside the double helix, between the bases, not in the sugar-phosphate backbone
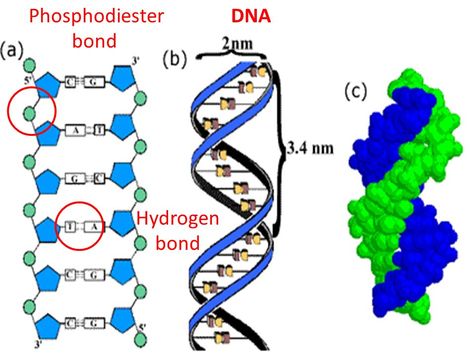
What are the three components of a DNA or RNA monomer?
Phosphate group – links nucleotides together via phosphodiester bonds
5-carbon sugar – deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA
Nitrogenous base – A, T, C, G (DNA) or A, U, C, G (RNA)
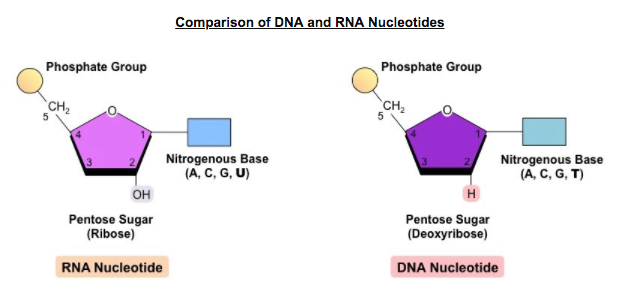
Identify differences between DNA and RNA using these four categories: Pentose sugar, nitrogenous base difference, strandedness (traditionally), and directionality.
Pentose sugar: DNA = deoxyribose, RNA = ribose
Nitrogenous bases: DNA = A, T, C, G; RNA = A, U, C, G
Strandedness: DNA = double-stranded; RNA = single-stranded
Directionality: Both = 5′ → 3′