Sci Q2 Chapter 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/45
Last updated 11:53 AM on 1/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Atoms
smallest unit of matter; building block of the universe
2
New cards
atomic structure
the atom consists of three component parts: Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons
3
New cards
Who discovered the electron?
JJ Thomson in 1897
4
New cards
Who discovered the proton?
Eugen Goldstein in 1886 (Rutherford 1917)
5
New cards
Who discovered the neutron?
James Chadwick in 1932
6
New cards
Who discovered the nucleus?
Ernest Rutherford in 1911
7
New cards
Democritus (400 BC)
greek philosopher that said all matter is made of tiny particles called "atomos" or atoms
8
New cards
John Dalton's Atomic Model
(billboard) all matter is composed of atoms; atoms cannot be divided
9
New cards
John Dalton developed his atomic structure
because of his nitric oxide experiment
10
New cards
JJ Thomson developed his atomic structure
by using the cathode ray tube
11
New cards
J.J. Thomson's Atomic Model
(plum pudding) atoms is made up of electrons floating in protons
12
New cards
Ernest Rutherford's Atomic Model
(nuclear) atoms have nucleus surrounded by electrons; he discovered nucleus
13
New cards
Ernest Rutherford developed his atomic structure
through gold foil experiment
14
New cards
Neil Bohr's Atomic Model
(planetary) electrons move in fixed orbit (s
15
New cards
Neil Bohr developed his atomic structure
through atomic spectra
16
New cards
Erwin Schrodinger's Atomic Model
(quantum model) this doesn't accurately tell us where an electron is
17
New cards
Werner Heisenberg and the uncertainty principle
posited the "uncertainty principle" no human could ever determine the path of an electron because observing the electron with light affected the location: we couldn't accurately predict anything physical.
18
New cards
principal quantum number
indicated the size of an electron
19
New cards
azimuthal quantum number
tells us the shapes of the electron orbitals (sphere
20
New cards
magnetic quantum number
indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus (up or down)
21
New cards
spin quantum number
indicate the two fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital (clockwise/counterclockwise)
22
New cards
quantum numbers
it gives us the idea how electrons behave; used to completely describe all the attributes of a given electron belonging to an atom
23
New cards
electron configuration
representation of the arrangement of the electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells
24
New cards
s, p, d, f orbitals
s shell: can hold 2 electrons per energy level \n \n p shell: can hold 6 electrons per energy level \n \n d shell: can hold 10 electrons per energy level \n \n f shell: can hold 14 electrons
25
New cards
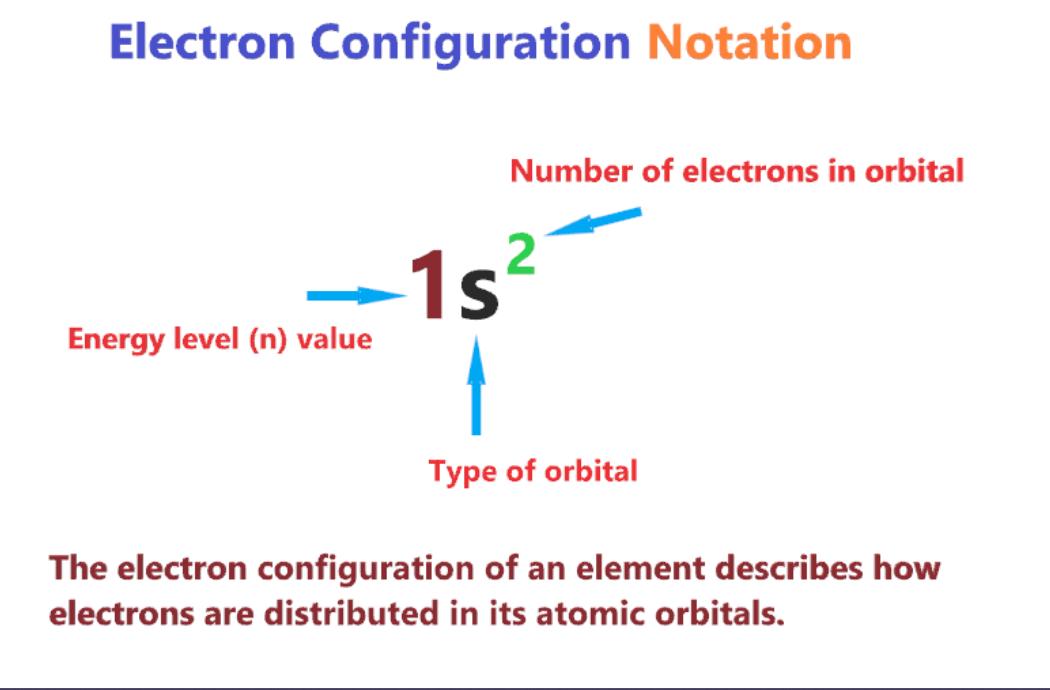
electron configuration notation
numbers of electrons are represented by adding a superscript to the sublevel designation
\
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p
\
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p
26
New cards
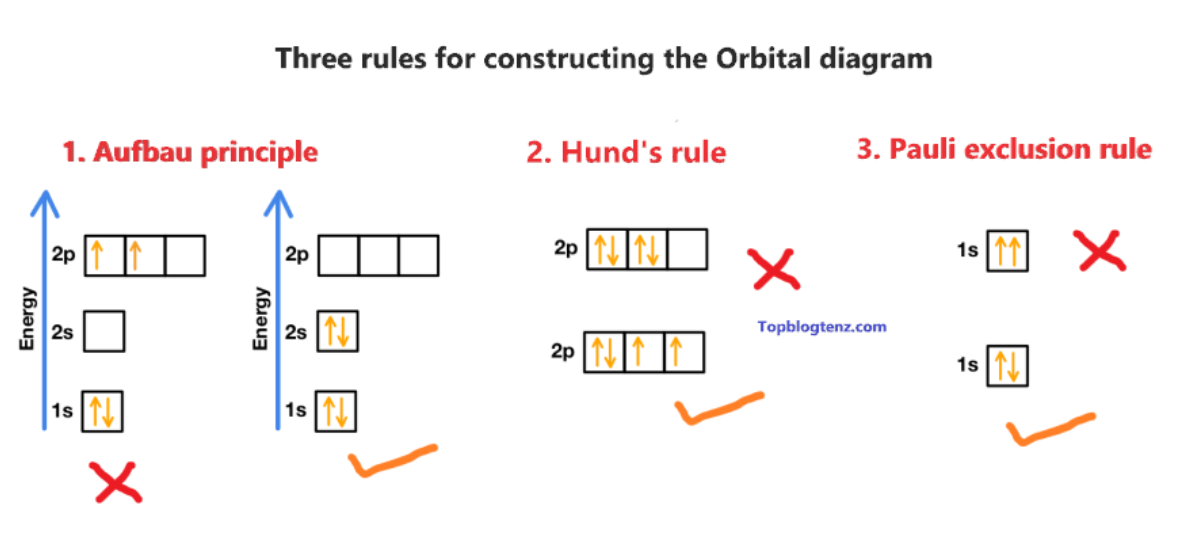
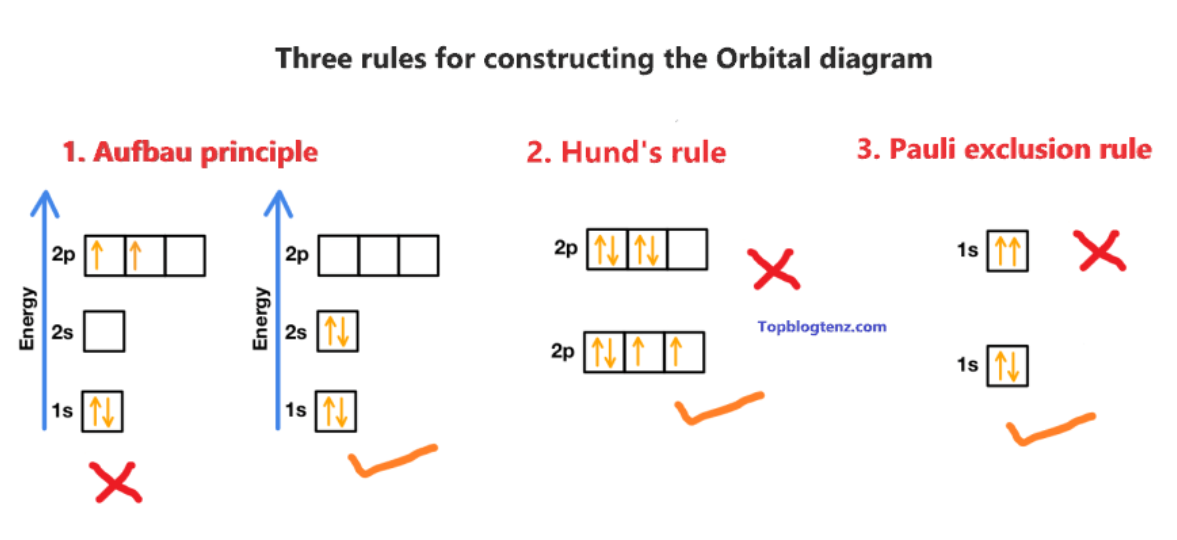
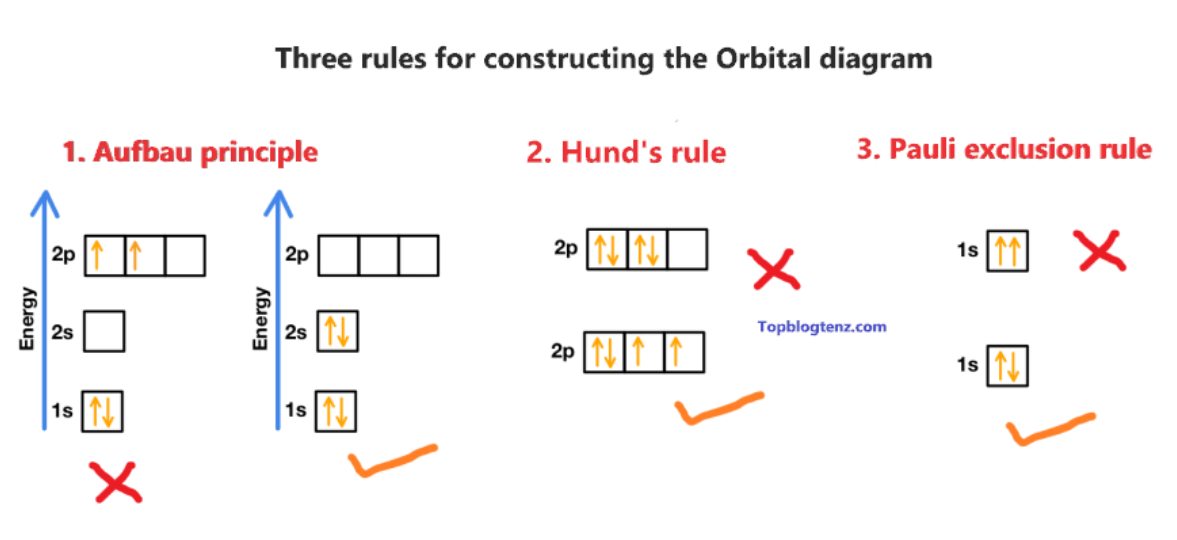
3 principles of electron configuration
Aufbau Principle; Pauli Exclusion; Hunds rule
27
New cards
Anfbau principle
electrons fill lower-energy atomic orbitals before filling higher-energy ones. (aufbau - means building up)
28
New cards
Pauli Exclusion Principle
states that a maximum of two electrons can occupy a single atomic orbital but only if the electrons have opposite spins
29
New cards
Hund's Rule
every orbital in a sublevel is singly occupied before any orbital is doubly occupied
30
New cards
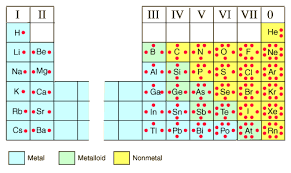
Periodic Table
tabular display of the chemical elements; it is arranged in increasing atomic number
31
New cards
Ion
a charged atom
32
New cards
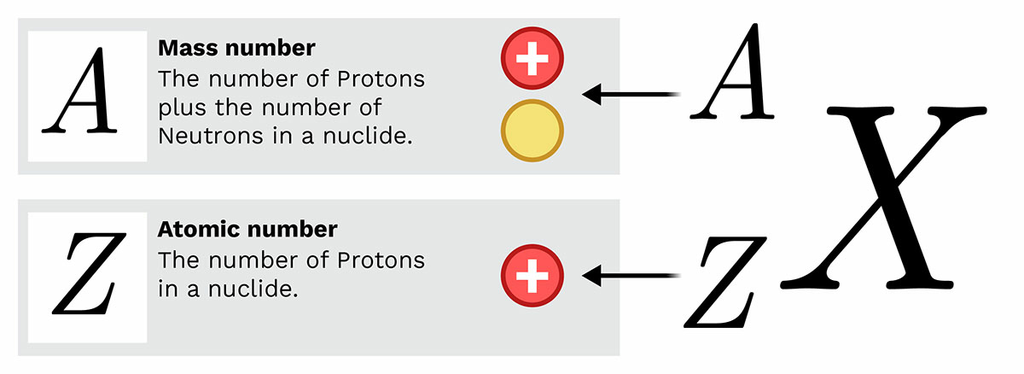
atomic number and mass
atomic number - protons; atomic mass - protons and electrons
33
New cards
series/periods
horizontal arrangement; rows (1-7)
34
New cards
family/group
vertical arrangement; column (1-18)
35
New cards
1A - 8A
representative elements (s and p elements)
36
New cards
1B - 8B
transition elements (d elements)
37
New cards
inner transition elements
latanites (57 - 71) and actinites (89 - 103)
38
New cards
alkali metals
group 1A
39
New cards
alkali earth metals
group 2A
40
New cards
halogens
group 7A
41
New cards
noble gases
group 8A
42
New cards
valence electrons
electrons on the outermost shell
43
New cards
electronegativity
tendency of an atom to attract electrons; non-metals have higher electronegativity
44
New cards
ionization energy
the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom; non-metals have higher ionization energy
45
New cards
octet rule
atoms tends to prefer to have 8 electrons to be stable; non-metals have higher tendency (we do not consider the f and d electrons)
46
New cards
lewis dot symbol
element surrounded by dots that represent its valence electrons. the number of dots in the Lewis dot symbol is the same as the number of valence electrons, which is the same as the last digit of the element's group number in the periodic table.