Cell Bio Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
ETC complex IV more info
- complex IV pumps 4 H+ per O2 reduced but requires 2 electron carriers (4 total e-s)
- per NADH, 2 H+ are pumped via complex IV
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- largest continuous membrane network in the cell
- continuous with the nuclear envelope
- central hub for protein and lipid biosynthesis
- architecture adapts to cellular demand
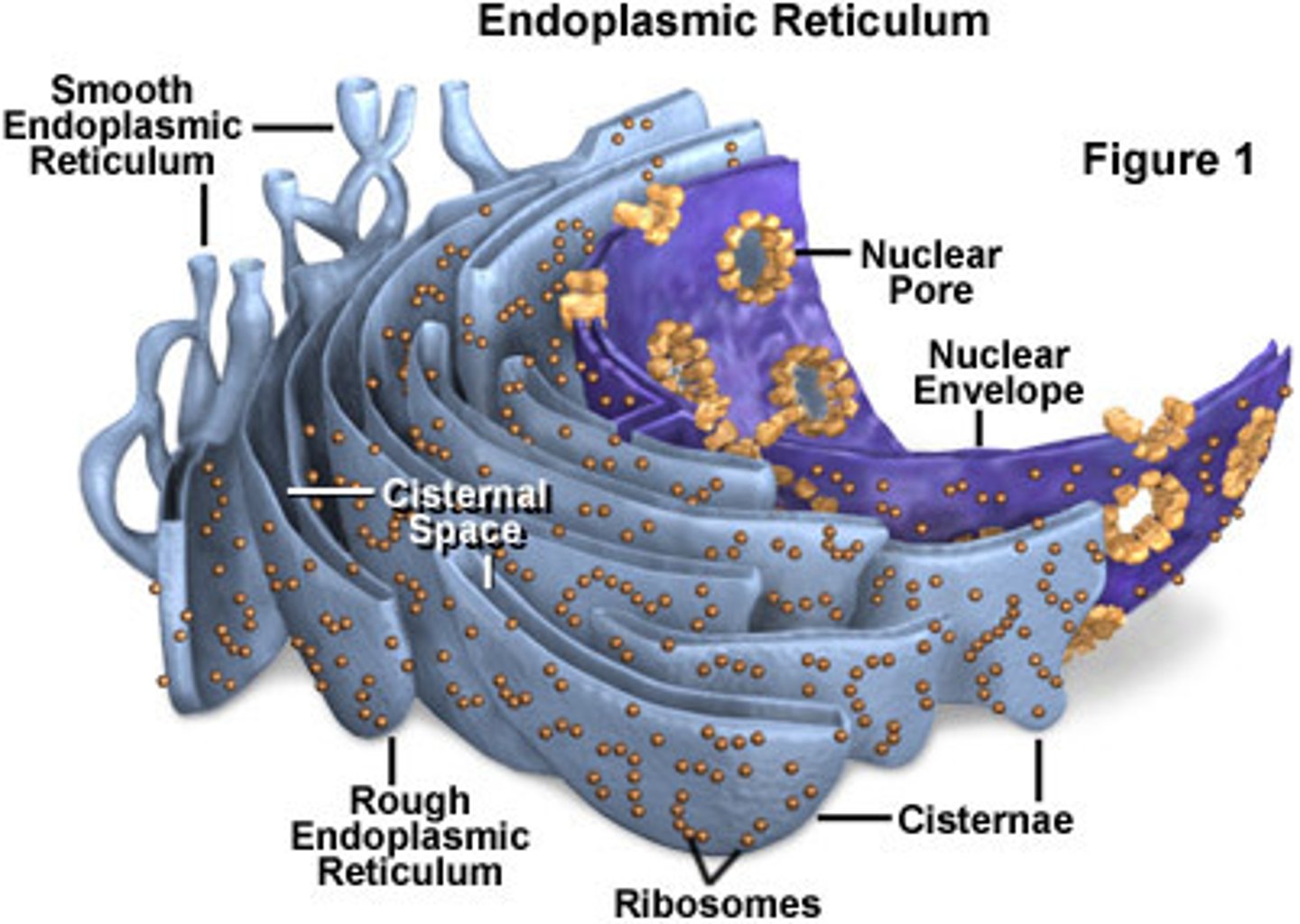
ER structure
- cisternae
- tubules
- form reflects function; balance shifts with cell needs
- continuous internal lumen throughout the network
cisternae
- flattened sacs
- site of protein synthesis near the nucleus
tubules
- branching network
- flexible for lipid metabolism and transport
rough ER (RER)
- ribosome studded
- entry for secretory/membrane proteins
- sheet like
smooth ER (SER)
- ribosome free
- major site for lipid related processes
- smooth tubular membranes
rough and smooth ER
- regions are continuous and interconvertible
- division of labor enhances efficiency
transmission electron microscopy of RER and SER
- TEM reveals structural differences
- arrangement reflects functional specialization
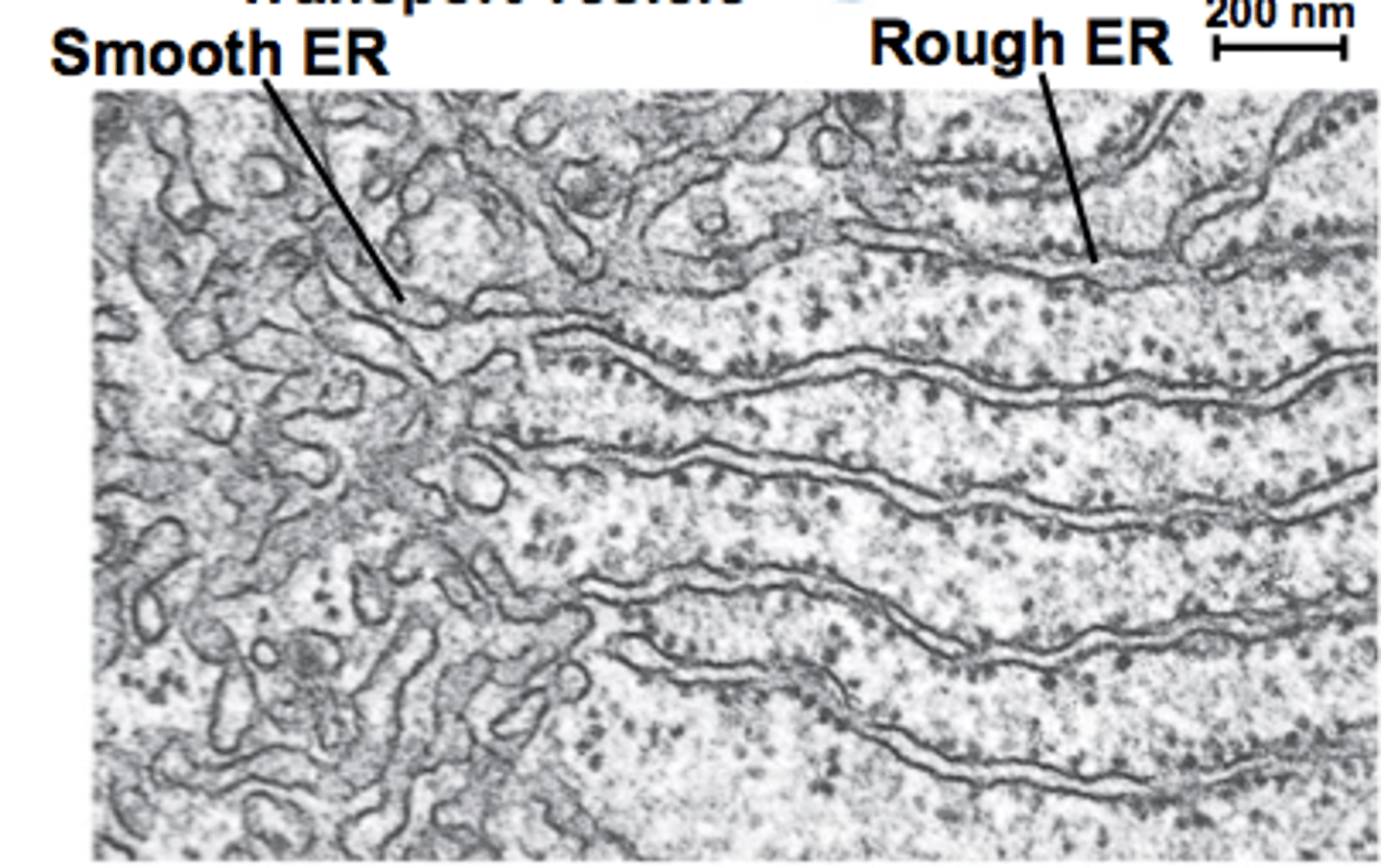
distribution of ER in different subtypes
- ER abundance/ratio varies by tissue demand
- ER plasticity supports specialization
secretory cells ER
expanded RER (eg exocrine pancreas)
membrane/lipid-active cells ER
expanded SER (eg liver, steroidogenic tissues)
functions of RER
- co-translational import of proteins
- folding and quality control
- initial N-linked glycosylation
- gateway to secretory pathway
co-translational import overview
- signal peptide directs ribosome to ER
- signal recognition particle (SRP) binds sequence
- SRP-ribosome complex docks at ER membrane (Translocon)
- translocon enables entry into ER lumen during polypeptide synthesis
signal peptide
short N-terminal motif that marks ER entry
tripartite features of signal peptide recognition
- positively charged N-region
- hydrophobic core
- cleavage region
signal peptide recognition
- tripartite features
- recognition occurs as the peptide emerges from the ribosome
- necessary and sufficient: swapping in a signal peptide re-routes proteins to ER
signal recognition particle (SRP)
- SRP = ribonucleoprotein complex
-> Alu domain and S domain
- binds hydrophobic signal peptide during translation
- temporarily pauses elongation
- directs ribosome-nascent chain to ER membrane
SRP receptor and translocon mechanism
- SRP-ribosome complex binds SRP receptor (ER membrane)
- ribosome aligns with Sec61 translocon
- GTP hydrolysis triggers SRP release
- translation resumes; chain threaded into ER
ribosome docking and translocation
- ribosome sits tightly over Sec61 translocon channel
- translation resumes into ER lumen seamlessly
- signal peptide usually cleaved by signal peptidase
- chaperones assist folding as chain enters lumen
BiP
ER-resistant Hsp70 chaperone
chaperones (BiP) in folding
- binds nascent chains entering lumen
- prevents misfolding and aggregation
- uses ATP hydrolysis to stabilize folding intermediates
disulfide bond formation (disulfide isomerase)
- favored in oxidizing ER lumen
- stabilizes tertiary and quaternary structures
- bonds can be rearranged to correct mispairing (isomerization)
- catalyzed by protein disulfide isomerase (PDI)
N-glycosylation initiation in ER
- addition of oligosaccharides to asparagine residues
- occurs co-translationally in the ER lumen
- catalyzed by oligosaccharyl transferase (OST)
- essential for folding, stability, and quality control
quality control: misfolded proteins retained
- only properly folded proteins exit the ER
- misfolded proteins retained by chaperones
- calnexin/calreticulin cycle monitors glycoprotein folding
- persistent misfolding -> ER-associated degradation (ERAD)
ER-associated degradation (ERAD)
- misfolded proteins retrotranslocated to cytosol
- tagged with ubiquitin for proteasomal degradation
- prevents accumulation of defective proteins in ER
- protects cell from proteotoxic stress
unfolded protein response (UPR)
- triggered by ER stress: accumulation of misfolded proteins
- activates three main sensors (IRE1, PERK, ATF6)
- expands folding capacity, reduces translation
- prolonged stress -> apoptosis
cystic fibrosis and misfolded CFTR
- cystic fibrosis caused by mutations in CFTR chloride channel
- leads to defective chloride transport in epithelia
- ΔF508 mutation -> misfolding in ER
- misfolded CFTR retained and degraded via ERAD
functions of the SER
- lipid and steroid biosynthesis
- detoxification of drugs/toxins
- calcium storage and release
- specialized roles in different tissues
lipid biosynthesis
- cytosolic leaflet of smooth ER
- phospholipids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones produced
- asymmetry: lipids added mainly to cytosolic leaflet
- scramblases and flippases redistribute lipids
cytosolic leaflet of smooth ER
primary site of lipid synthesis
cholesterol and steroid hormone production
- SER synthesizes cholesterol; cells also import it (LDL)
- StAR moves cholesterol into mitochondria on demand
- cholesterol first committed step to pregnenolone in mitochondria (CYP11A1)
- steroidogenesis proceeds in adrenal cortex and gonads (tissue-specific enzymes)
SER synthesizes cholesterol; cells also import it (LDL)
Acetyl-CoA -> mevalonate -> isoprenoids -> squalene -> cholesterol
detoxification (cytochrome P450 in SER)
- SER-localized CYP450s oxidize drugs/xenobiotics
- require heme + NADPH-CYP450 reductase (+/- cytochrome b5)
- induction/inhibition and polymorphisms alter drug levels
detoxification (cytochrome P450 in SER): reaction
RH + O2 + NADPH -> ROH + H2O
calcium storage/release (sarcoplasmic reticulum)
- SERCA pumps load Ca2+
- calsequestrin buffers luminal Ca2+
- RyR channels release Ca2+ on excitation
- rapid reuptake (SERCA) ends contraction
- phospholamban modulates cardiac SERCA
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
specialized smooth ER wrapped around myofibrils (actin, myosin)
liver (hepatocyte) cell specific adaptations
- expanded SER for xenobiotic metabolism
- RER for secreted proteins (eg albumin)
adrenal cortex cell specific adaptations
abundant SER + mitochondria for steroidogenesis (cholesterol -> hormones)
cell specific adaptations
- distinct enzyme complements and organelle architecture reflect tissue demands
- dynamic remodeling
retrotranslocon
opposite of translocons, go opposite direction (out)
dynamic remodeling
hormones/drugs can upregulate pathways and expand ER
golgi structure
polar stack of flattened cisternae: cis -> medial -> trans
cis cisternae in golgi
- entry
- adjacent to ER
- receives COPII vesicles
medial cisternae in golgi
intermediate processing compartment
trans/TGN cisternae in golgi
- exit
- late processing + staging for outbound traffic
cisternal maturation model
- cisternae themselves mature: cis -> medial -> trans
- cargo stays within the same cisterna as it matures
- golgi enzymes move backward (retrograde) to re-establish compartment identity
- explains transport of large cargo (e.g. procollagen)
vesicular transport model
- cisternae are static
- cargo moves forward in vesicles
- COPII
- COPI
- small/medium cargo packaged into forward carriers
- retrograde COPI retrieves ER residents and golgi enzymes
COPII in vesicular transport model
ER -> cis-golgi
COPI in vesicular transport model
- anterograde here
- cis -> medial -> trans
evidence for cisternal maturation model
- large cargo (procollagen) stays within a maturing cisterna
- cis/medial/trans markers exchange over time
evidence for vesicular transport model
- abundant COPI/COPII buds
- cargo receptors enrich small/medium cargo
- rapid pulse-chase transfer between cisternae
evidence for hybrid model (cisternal maturation and vesicular transport)
cells likely use both depending on cargo size/class and demand
glycosylation modifications in golgi
- N-linked processing
- O-linked initiation
- proteoglycans
- compartmentalization
glycosylation modifications in golgi: compartmentalization
enzyme sets are zoned (cis -> medial -> trans) to produce ordered, stepwise modifications
glycosylation modifications in golgi: N-linked processing
- ER core
- golgi (cis->medial)
glycosylation modifications in golgi: N-linked processing: ER core
- Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 -> trimmed
- quality check completed in ER
glycosylation modifications in golgi: N-linked processing: golgi (cis -> medial)
- mannose trimming
- (medial -> trans): add GlcNAc, Gal, Fuc, Sia
glycosylation modifications in golgi: N-linked processing: end types
- high-mannose
- hybrid
- complex
glycosylation modifications in golgi: N-linked processing: functions
- stability
- trafficking signals
- cell-cell interactions
glycosylation modifications in golgi: O-linked initiation
- initiates golgi on Ser/Thr
- GalNAc-T adds first GalNAc -> chains extend (Gal, GlcNAc)
- prominent in mucins
- affects viscosity, protection, signaling
glycosylation modifications in golgi: proteoglycans
- linker on Ser
- GAG types
- roles
glycosylation modifications in golgi: proteoglycans: linker on Ser
Xyl-Gal-Gal-GlcA -> tehn glycosaminooglycan (GAG) chain polymerized
glycosylation modifications in golgi: proteoglycans: GAG types
- chondroitin/dermatan
- keratan (tissue specific)
glycosylation modifications in golgi: proteoglycans: roles
- ECM structure
- growth factor binding
- filtration
- signaling
mannose trimming/complex sugar addition
- cis/medial golgi
- medial/trans golgi
- branching increases
- glycan remodeling tunes stability, recognition, and half life
mannose trimming/complex sugar addition: cis/medial golgi
mannosidases trim ER core (Man9 -> Man5)
mannose trimming/complex sugar addition: medial/trans golgi
- add GlcNAc -> Gal -> Sia (+/- Fuc)
- build hybrid/complex N-glycans
mannose trimming/complex sugar addition: branching increases
(bi-, tri-, tetra-, antennary) with sequential GlcNAc transferases
congenital disorders of glycosylation
- inborn errors of protein glycosylation -> multisystem disease
- Type I vs Type 2
common features of congenital disorders of glycosylation
- neurologic
- liver/coagulation
- GI/endocrine
congenital disorders of glycosylation: Type 1
- assembly/transfer
- ER
congenital disorders of glycosylation: Type 2
- processing
- golgi
sorting pathways
- trans-golgi network (TGN)
- secretion
- plasma membrane
- lysosomes
trans-golgi network (TGN)
sorting hub: cargo tagged/packaged for destinations
secretion
constitutive vs regulated
constitutive secretion
- default export
- continuous export from TGN -> surface/ECM
- ex: albumin, membrane lipids
regulated secretion
- stored
- stimulus triggered exocytosis
- cargo condenses into granules
- ex: insulin, neurotransmitters, digestive enzymes
plasma membrane
delivery of integral proteins/lipids to specific domains
lysosomes
M6P-tagged hydrolases sorted to degradative pathway
sorting at TGN
bulk flow vs signal/receptor-medicated packaging
endomembrane system: ER-golgi trafficking
- ER -> golgi via COPII carriers from ER exit sites
- cis-medial-trans golgi processing -> TGN sorting hub
- retrograde COPI returns ER/golgi residents and receptors
- net flow
endomembrane system: ER-golgi trafficking: net flow
- synthesize in ER
- refine in golgi
- route at TGN
protein flow
ER -> golgi -> final destination
ER step of protein flow
synthesis and folding/QA -> COPII export from ER exit sites
golgi step of protein flow
(cis -> medial -> trans)
- sequential trimming/adding of sugars -> TGN hub
TGN sorting step of protein flow
- to constitutive secretion
- regulated granules
- plasma membrane
- lysosomes (M6P)
retrieval signals
KDEL
KDEL
- KDEL C-terminal motif marks ER-resident soluble proteins
- KDEL receptor in cis-golgi binds escaped proteins (pH dependent)
- COPI vesicles return them to ER; release in ER conditions
- maintains ER protein composition despite bulk flow