MACRO T3 Economic Growth
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
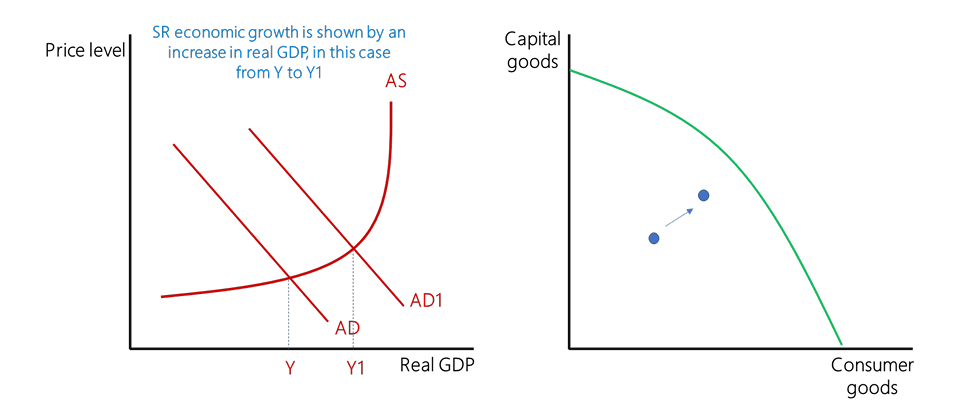
What is Short-Run Economic Growth?
An increase in real GDP, an increase in actual output.
At least one-factor input is fixed
Shift in AD
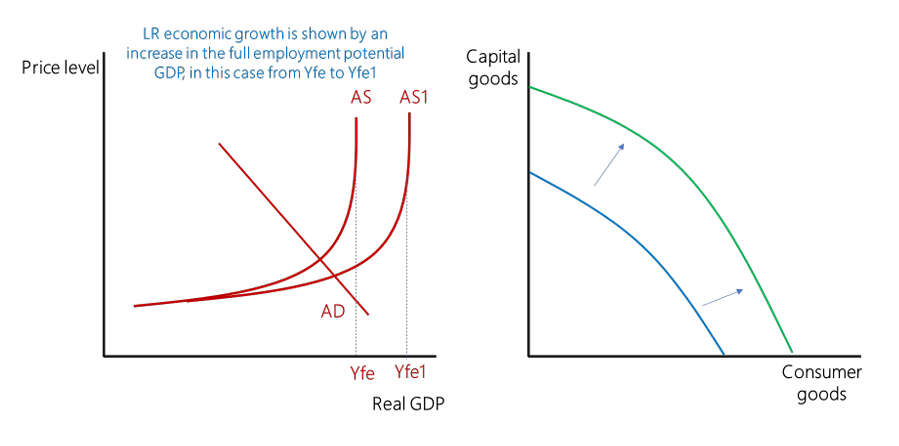
What is Long Run Economic Growth?
A sustained rise in a country’s productive potential.
The main drivers of long-run economic growth are higher productivity and gains from innovation and rising real incomes for households.
All factors inputs are variable
Shift in LRAS
What are factors that could cause Short-Run Economic Growth?
Changes in interest rates
Fiscal policy changes
Commodity prices such as oil, gas and food
Currency changes affect export and import demand
Trading conditions in other countries
Confidence of businesses and households
What are factors that could cause Long-Run Economic Growth?
Investment
Productivity
Labour Supply
Research and Development
Innovation
Enterprise
Define export-led growth.
Where a significant part of the expansion of real GDP, jobs and per capita incomes flows from the successful exporting of goods and services from one country to another.
In recent years a number of countries like Hong Kong, China, Vietnam, Ethiopia have experienced rapid growth across a number of export industries which has helped to fuel their long-run expansion.
What are the advantages of export led growth?
(X-M) IS an injection into the CFofY leading to a rise in AD and an expansion of output. This helps to raise per capita incomes and reduce extreme poverty especially in emerging economies.
Growing export sales provide revenues and profits for businesses which can then feed through to an increase in capital investment spending through the accelerator effect. Higher investment increases a country’s productive capacity which then increases exports’ potential. Many industries help facilitate trade such as trade insurance, logistics and port facilities.
An example is the importance of trade to countries such as the Netherlands, including the port of Rotterdam
What are the potential risks or drawbacks of export led growth?
Focusing heavily on exports can lead to vulnerability to external economic and political shocks due to over-reliance on trade partner countries' economic cycles.
Allocating production capacity primarily for exports can hinder meeting domestic needs, potentially lowering living standards unless imports are balanced with export revenue.
Rapid export-led growth may trigger demand-pull inflation and higher interest rates, undermining competitiveness in both domestic and international markets.
Export-driven growth could become unsustainable by depleting natural resources beyond long-term balanced growth requirements, leading to environmental degradation like deforestation and over-fishing.
What is the output gap?
The difference between the actual level of GDP and its estimated potential level.
Usually expressed as a percentage of the level of potential output.
What are positive and negative output gaps?
Positive is where actual GDP is above potential GDP – A sign of possible excess AD
Negative is where the economy has large margin of spare capacity of factor resources
What is underlying trend growth?
Long term average of the change of output
What is an economic boom?
Actual Output is above the trend
What is an economic recession?
Two successive quarters of negative economic growth
The economic cycle shows that
the economy will always move from boom to bust so maybe the government shouldn’t try to intervene.
Weakening the exchange rate will lead to
more expensive imports which will cause cost-push inflationary pressure.
Explain how environmental considerations and income equality impact the sustainability of increased economic growth in an economy.
Environmental Considerations: Economic growth often places stress on natural resources and ecosystems. Unsustainable resource extraction, deforestation, and pollution can lead to environmental degradation. Policies that fail to address environmental externalities and promote sustainable practices can undermine the long-term viability of economic growth.
Income Inequality: High levels of income inequality can lead to social and political instability, hindering long-term growth.
Inequitable access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities may limit the potential contributions of a significant portion of the population to overall economic productivity.
Explain how human capital development, technological innovation and progression impact the sustainability of increased economic growth in an economy.
Sustainable growth is closely tied to investments in human capital, including education, skills training, and healthcare. A skilled and healthy workforce is essential for innovation and productivity improvements. Inadequate investments in education and healthcare can hinder the long-term growth potential of an economy, creating barriers to economic advancement.
Sustainable growth requires continuous technological progress and innovation. Economies that fail to invest in RnD may face diminishing returns to capital and a slowdown in productivity improvements. Policies that promote a culture of innovation, protect intellectual property, and encourage RnD contribute to the sustainability of economic growth.
Explain how debt and fiscal policies impact the sustainability of increased economic growth in an economy.
Debt and Fiscal Policies: Excessive debt levels pose a threat to the sustainability of economic growth. It may lead to financial instability, reduced investment, and limited fiscal flexibility during economic downturns. Prudent fiscal policies that balance the need for public investments with long-term fiscal sustainability are crucial for maintaining economic growth.
What are some triggers of a fall in AD causing possible recession?
External events - A recession in a trading partner e.g. the European Union or the USA or a sharp rise in global commodity prices e.g. rising oil and gas prices
Tightening of macro policy - Higher interest rates leading to more expensive loans or contractionary fiscal policy. 15% in 1989.
Fall in asset prices or supply of credit - Steep decline in the level of share or house prices or a collapse in the supply of credit (2008)
Drop in business and consumer confidence - Lower business confidence cuts investment and may lead to job losses. Declining consumer confidence leads to less spending and more saving
How is recession cause by an shift left of SRAS?
Recession can also be caused by a supply shock
For example, higher import prices can lead to a rise in the general price level which leads to lower real incomes for consumers and falling profits for businesses.
A supply shock might lead to a period of stagflation – i.e. slower economic growth, higher inflation and higher unemployment. (1970s)
Sharp rises in world oil prices helped fuel UK inflation as well as industrial unrest seeing large wage increases for workers. The result was a large shift left of SRAS.
What are some short term effects of recession?
Falling demand can cause more businesses to fail and profits. Planned investment declines – hitting industries that make the capital goods
A steep decline in AD causes a fall in the demand for labour. This causes a contraction in employment and a rise in cyclical unemployment
Recession causes a decline in tax revenues and more welfare spending. The result is usually an increase in the budget deficit and a rising national debt
Many business offer price discounts to off-load excess unsold stocks. A deep recession risks causing a period of sustained deflation
What are some long term effects of recession?
Rising structural long-term unemployment and regional decline. Low rates of investment can reduce the size of the capital stock. Persistent budget (fiscal) deficits and a rising national debt leads to austerity (cut in public services)
Falling real wages hits average living standards and reduces demand. Widening inequality of income and wealth leading to rising poverty. Social costs such as loss of social cohesion and threats to democracy
What are two competing views about the effects of a recession?
Hysteresis - When an economy is in recession there is a big risk of a permanent loss of national output. Loss of productive capacity due to low capital investment + many business closures. High rates of structural unemployment may cause a shrinking labour force perhaps through outward migration
Creative Destruction - Recessions can cast a dark shadow, but capitalist market economies usually bounce back eventually. They see the emergence of new business models and an increase in start-ups. New technologies can act as a catalyst for renewed economic growth and investment
How best to sustain economic growth in the long run?
Building Trust / Social Capital
Growing a Dynamic Innovative Private Sector
Economies of scale & better competitiveness lower prices
Growing Intra-Regional Trade
Improving Institutions and Protecting Property Rights
Sound Macro Policies to control Inflationary Pressures
Focusing on addressing Equity / Fairness Issues
What is capital investment’s contribution to economic growth?
Provides an injection of demand for capital goods industries
Economies of scale & better competitiveness lower prices
Bigger capital stock can lift productivity / incomes e.g. in farming
Investment helps to sustain export led growth adding to GDP growth
What are some policies to attract FDI?
Attractive rates of corporation tax
Soft loans and tax reliefs / other subsidies
Special Economic Zones
Trade and investment agreements
Flexible labour markets
High-quality infrastructure
Open capital markets to allow remitted profits
Availability of low cost labour
What are the costs of economic growth?
Inflation and Purchasing Power: Unrestrained economic growth can lead to demand-pull inflation, potentially eroding the purchasing power gained from increased incomes.
Income Inequality: Economic growth may exacerbate income inequality, especially if benefits are concentrated in specific sectors or demographics, without adequate redistributive policies in place.
Environmental Degradation: Uncontrolled growth often leads to environmental destruction, including air and water pollution, deforestation, soil erosion, and resource depletion, resulting in welfare loss and potential negative impacts on living standards.
(X-M): Rapid economic growth can lead to increased imports, widening the current account deficit, which poses a challenge to overall economic stability.
What are the benefits of economic growth?
Increased Disposable Income: Economic growth leads to higher profits for firms, potentially resulting in higher wages and salaries for workers. This results in increased household income, improving living standards and access to better quality of life, including material and non-material aspects like education and healthcare.
Higher Employment: Economic growth generates more demand for goods and services, necessitating the employment of more workers. This boosts income levels and enhances living standards for workers.
Higher Profits for Firms: Firms enjoy higher profits during periods of economic growth, enabling them to invest in capital and trigger further growth through the accelerator effect. Additionally, higher profits contribute to increased tax revenues for the government.
Fiscal Dividend for the Government: Economic growth results in increased tax revenues for the government, allowing for greater spending on education, infrastructure, welfare, and public services, thus benefiting the overall economy.