IB Physics SL Vocabulary
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
1- Fundamental Units
seven basic units of the SI measurement system: kilogram, second, mole, meter, ampere, Kelvin, candela
1- Derived Units
units that are combinations of fundamental units. These combinations may or may not have a separate name. (eg. 1 kg m/s2 = 1 N)
1- Accuracy
An indication of how close a measurement is to the accepted value (a measure of correctness)
1- Precision
An indication of the agreement among a number of measurements made in the same way (a measure of exactness)
1- Random Error
An uncertainty produced by unknown and unpredictable variations in the experimental situation, such as temperature fluctuations and estimations when reading instruments. (Affects the precision of results -Can be reduced by taking repeated trials but not eliminated - shows up as error bars on a graph)
1- Systematic Error
An error associated with a particular instrument or experimental technique that causes the measured value to be off by the same amount each time. (Affects the accuracy of results - Can be eliminated by fixing source of error - shows up as non-zero y-intercept on a graph)
1- Vector
a quantity with both a magnitude and a direction
1- Scalar
a quantity with magnitude only
2- Displacement (s) *
distance traveled in a particular direction (change in position)
2- Velocity (u,v) *
rate of change of displacement
2- Speed (u,v) *
rate of change of distance
2- Acceleration (a) *
rate of change of velocity
2- Newton's First Law of Motion *
An object at rest remains at rest and an object in
motion remains in motion at a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force
2- Newton's Second Law of Motion *
An unbalanced force will cause an object to
accelerate in the direction of the net force. The acceleration of the object is proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to its mass. (Fnet = ma or Fnet = Δ p/Δ t (net force = rate of change of momentum))
2- Newton's Third Law of Motion *
When two bodies A and B interact (push or pull), the force that A exerts on B is equal and opposite to the force that B exerts on A
2- Translational Equilibrium
net force acting on a body is zero
2- Linear Momentum (p) *
product of mass and velocity
2- Impulse (J) *
change in momentum
2- Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum *
The total momentum of an isolated system (no external forces) remains constant
2- Work (W) *
The product of a force on an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force.
2- Kinetic Energy (EK)
product of ½ times the mass of an object times the square of an object's speed
2- Change in Gravitational Potential Energy
product of an object's mass times the gravitational field strength times the change in height
2- Principle of Conservation of Energy *
The total energy of an isolated system (no
external forces) remains constant. (OR - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed but only transformed from one form to another or transferred from one object to another.)
2- Elastic Collision *
a collision in which kinetic energy is conserved
2- Inelastic Collision
a collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved
2- Power (P) *
The rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred
2- Efficiency (eff) *
The ratio of the useful energy (or power or work) output to the total energy (or power or work) input.
2- Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
The force of gravity between two objects is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and acts along a line joining their centers. (NOTE: The objects are point masses. If they are not point masses but are very far apart, that is, the distance between them is very much greater than their
radii, they can be treated like point masses.)
2- Gravitational Field Strength (g)
gravitational force per unit mass on a point mass (g = Fg / m)
2- Gravitational Potential Energy (EP) *
the work done in moving a mass from infinity to a point in space (NOTE: the work done is path independent)
2- Impulse (J) - change in momentum *
the work done per unit mass in moving a mass from infinity to a point in space
6- Weightlessness in free-fall
a sensation of weightlessness because a person is falling freely toward the Earth, hence there is no normal force (reaction force) acting on the person due to gravity
6- Weightlessness in orbital motion
a sensation of weightlessness due to the spacecraft and all objects in it being in constant free-fall together as they circle Earth
6- Weightlessness in deep space
a sensation of weightlessness due to the minimal pull of gravity very far from any massive object
6- Angular velocity (ω)
the rate at which the angle is changing in circular motion
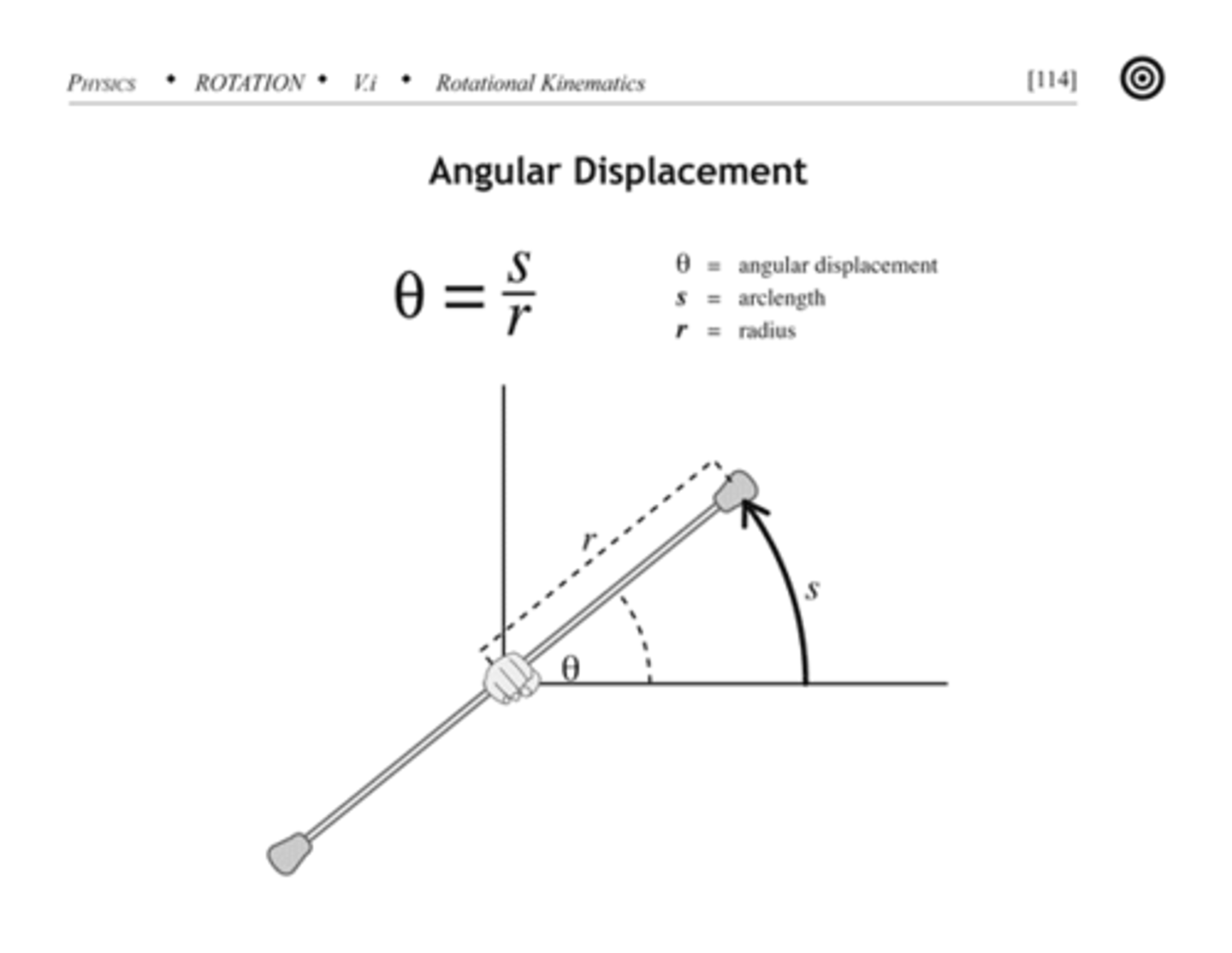
6- Angular displacement (θ)
The angle covered when a radius is moved over a distance
6- Centripetal force (F)
The force needed to cause circular motion to occur. This force is always directed towards the center of the circular motion.
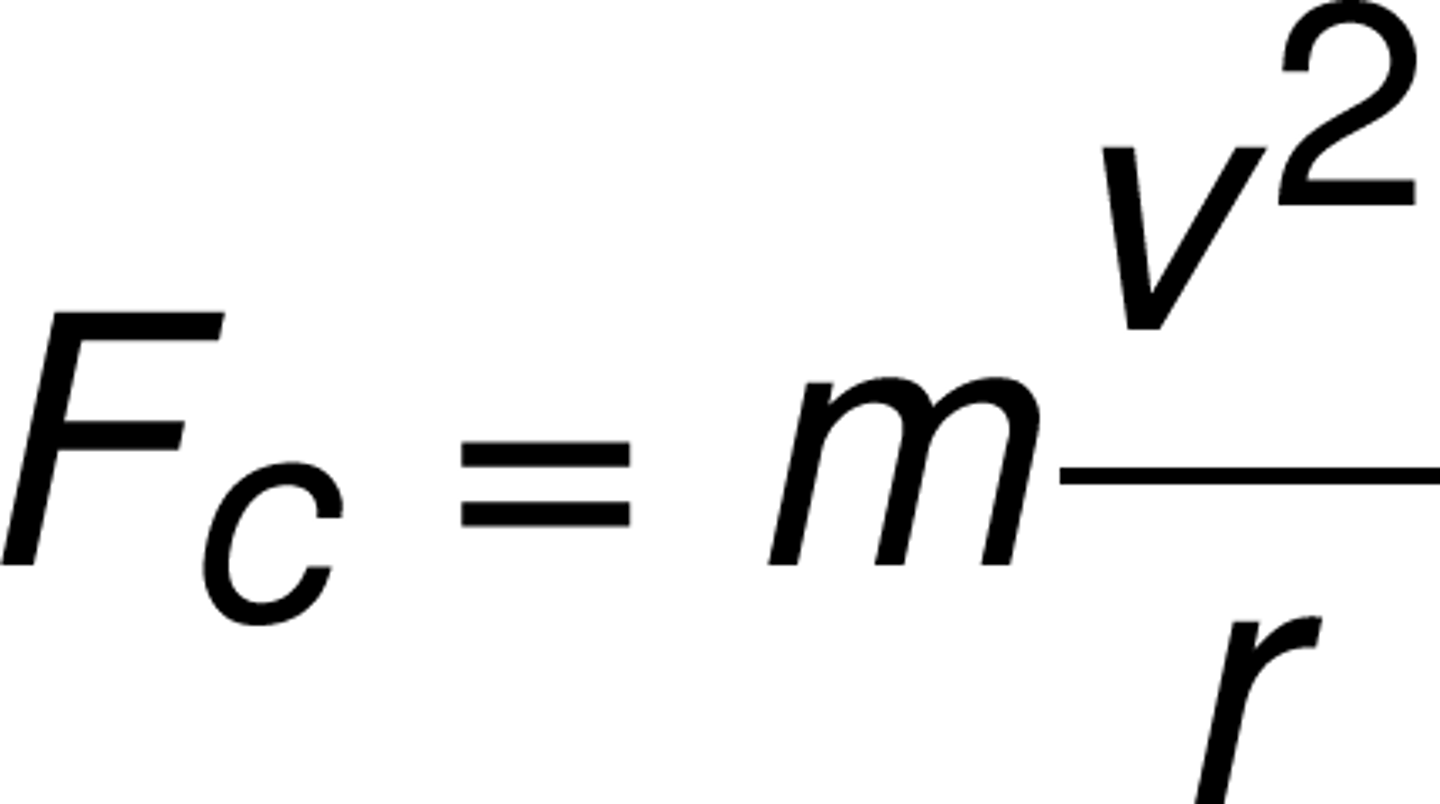
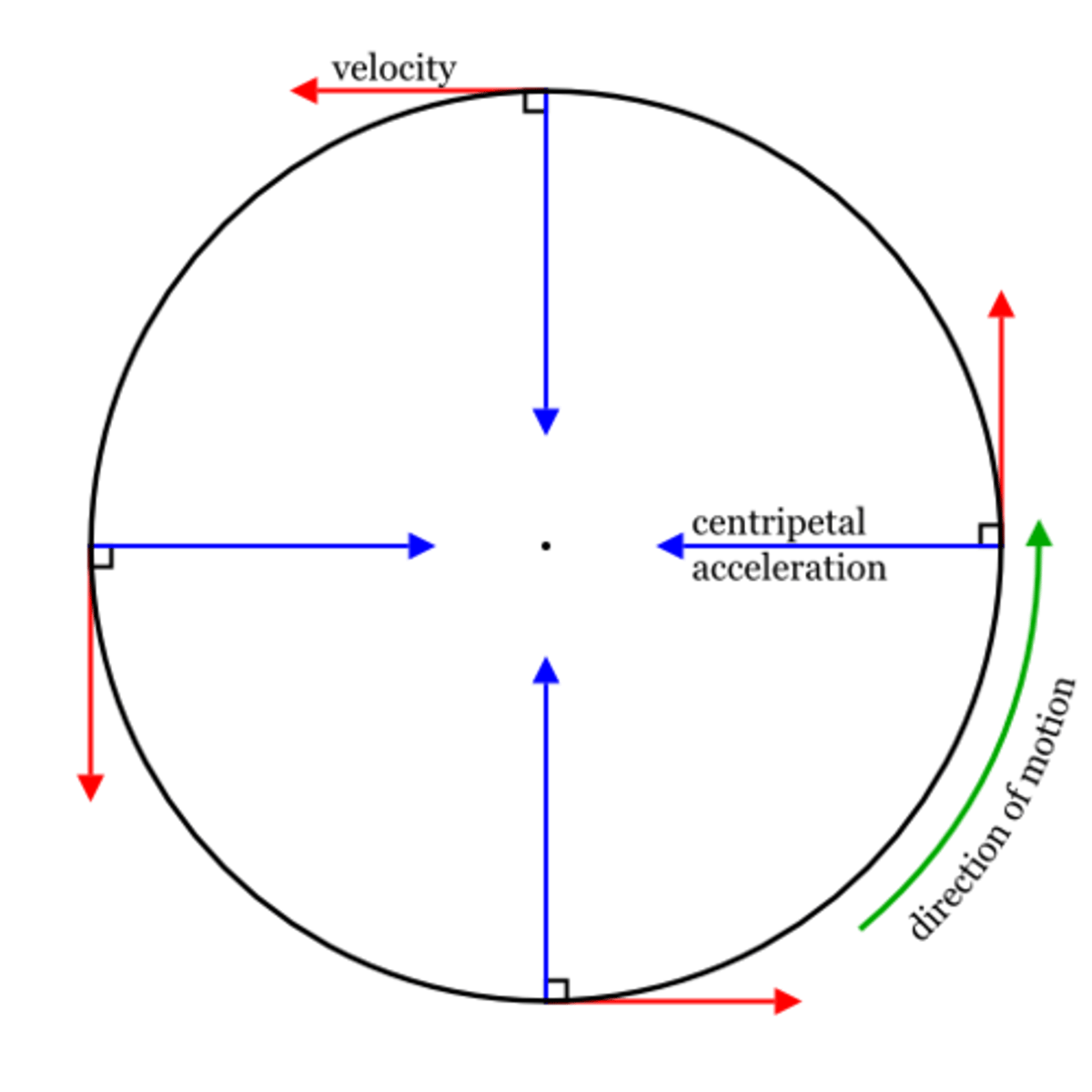
6- Centripetal acceleration (a)
The acceleration directed toward the center of motion. This acceleration is caused by a change in direction while maintaining a constant speed.
3- *Temperature (T)
a. The property that determines the direction of thermal energy transfer between
two objects.
b. A measure of the average random kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
3- Thermal Equilibrium
two objects are in thermal equilibrium when they are at the same temperature so that there is no transfer of thermal energy between them
3- *Internal Energy of a substance
The total potential energy and random kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance.
3- *Thermal Energy (Heat) (Q)
Energy transferred between two substances in thermal contact due a temperature difference
3- *Mole
An amount of a substance that contains the same number of atoms as 0.012 kg of 12 C.
3- *Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance.
3- *Avogadro constant (NA)
The number of atoms in 0.012 kg of 12 C ( = 6.02 x 10^23).
3- *Specific Heat Capacity (c)
energy required per unit mass to raise the temperature of a substance by 1K
3- Boiling
a phase change of a liquid into a gas that occurs at a fixed temperature
3- Evaporation
when faster moving molecules have enough energy to escape from the surface of a liquid that is at a temperature less than its boiling point, leaving slower
moving molecules behind which results in a cooling of the liquid
3- *Specific Latent Heat (L)
energy per unit mass absorbed or released during a phase change without a change in temperature.
3- *Pressure (P)
force per unit area acting on a surface
3- *Ideal Gas
a gas that follows the ideal gas equation of state (PV = nRT) for allvalues of P, V, and T (an ideal gas cannot be liquefied)
3- Real Gas
a gas that does not follow the ideal gas equation of state for all values of P, V, and T (a real gas can approximate an ideal gas in some circumstances)
3- Absolute Zero of Temperature
temperature at which a gas would exert no pressure. Molecular motion stops!
3- Kelvin scale of Temperature (AKA Absolute Temperature)
an absolute scale of temperature in which 0 K is the
absolute zero of temperature
3- Real Gas
a gas that does not follow the ideal gas equation of state for all values of P, V, and T (a real gas can approximate an ideal gas in some circumstances)
4- *Displacement (for waves)
distance a particle moves in a particular direction from
its mean (equilibrium) position
4- *Amplitude
maximum displacement from the mean position
4- *Frequency (f)
number of oscillations per unit time
4- *Period (T)
time taken for one complete oscillation (cycle) (OR: time taken for one cycle to pass a given point)
4- *Phase Difference
difference in phase between two points
4- *Simple Harmonic Motion
motion that takes place when the acceleration of an
object is proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position and is always directed toward its equilibrium position (NOTE: this motion is defined by the equation a = -ω^2x)
4- Damping
involves a force that is always in the opposite direction to the direction of motion of the oscillating particle (NOTE: this force is a dissipative force)
4- *Resonance
a transfer of energy in which a system is subject to an oscillating force that matches the natural frequency of the system resulting in a large amplitude of vibration
4- *Wave Pulse
single oscillation or disturbance in a medium
4- *Traveling Wave
series of periodic pulses (NOTE: involves a transfer of energy) (NOTE: each point on the wave has the same
amplitude)
4- *Transverse Wave
wave in which the direction of motion of the energy transfer (the wave) is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the particles of the medium. (NOTE: light waves are transverse) (NOTE: transverse waves cannot be propagated in gases)
4- *Longitudinal Wave
wave in which the direction of motion of the energy transfer (the wave) is parallel to the direction of motion of the particles of the medium. (NOTE: sound waves are longitudinal)
4- Wavefront
collection of neighboring points on a wave that are in phase
4- Ray
line drawn perpendicular to a wavefront indicating the direction of motion of the energy transfer
4- Crest
top of a transverse wave
4- Trough
bottom of a transverse wave
4- Compression
area of high pressure in a longitudinal wave
4- Rarefaction
area of low pressure (expansion) in a longitudinal wave
4- *Wavelength (λ)
shortest distance along the wave between two points in phase with one another (OR: distance traveled by the wave in one period)
4- *Wave Speed (v)
speed of transfer of the energy of the wave
4- *Intensity (I)
power received per unit area. (NOTE: for a wave, its intensity is proportional to the square of its amplitude)
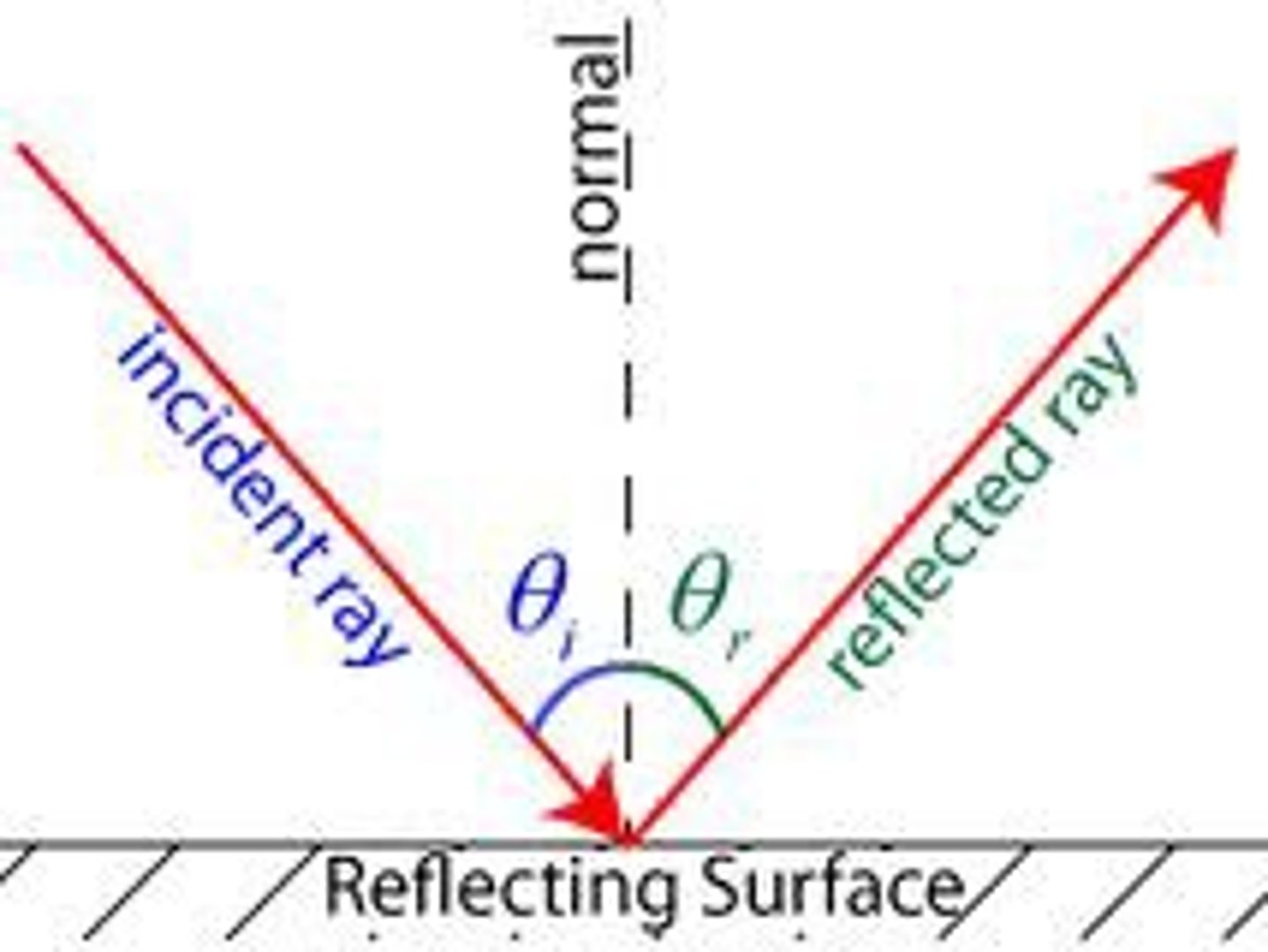
4- Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection when both angles are measured with respect to the normal line
4- *Snell's Law
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for a given frequency.
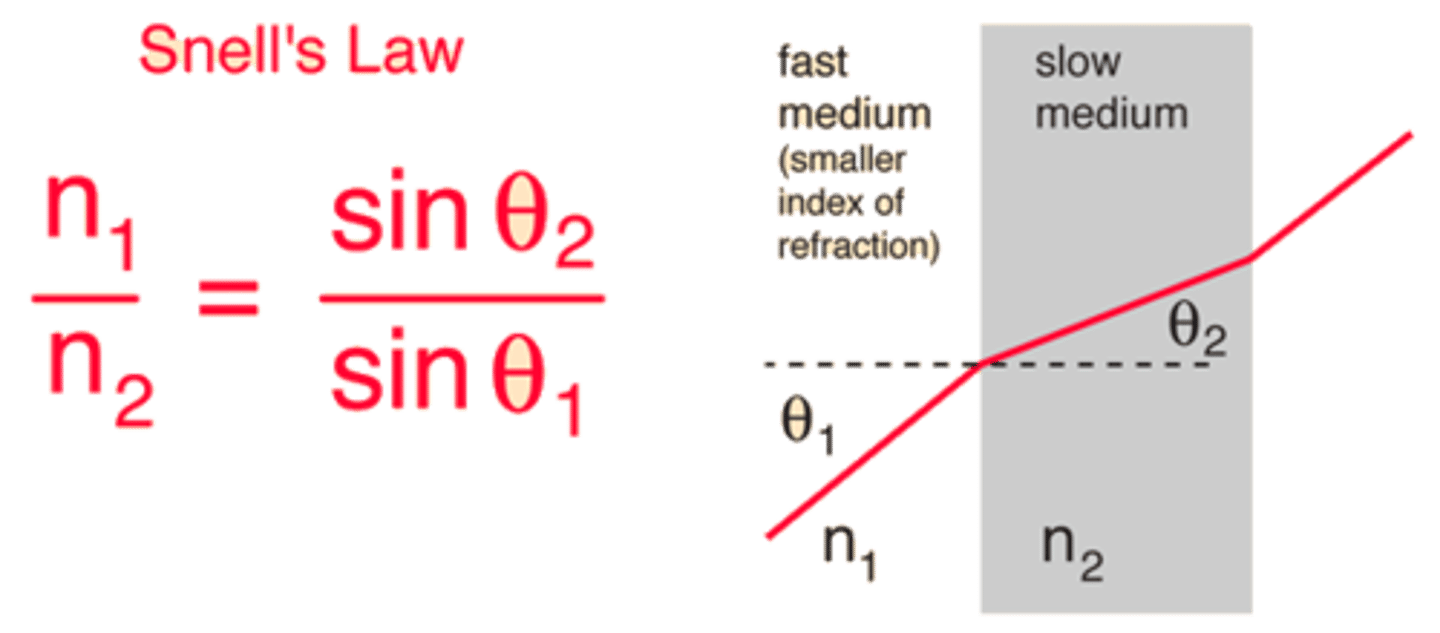
4- *Refractive Index (Index of Refraction) (n)
a. the ratio of the speed of the wave in the refracted medium to the speed of the wave in the incident medium
b. the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction
4- Diffraction
the bending of a wave around an obstacle or the spreading of a wave through an opening. (NOTE: diffraction is only noticeable when the size of the
opening is smaller than or on the same order of the size of the wavelength)
4- *Principle of Superposition
When two waves meet, the resultant displacement is
the vector sum of the displacements of the component waves.
4- Constructive Interference
superposition of two waves which are in phase with
each other
4- Destructive Interference
superposition of two waves which are out of phase with
each other
4- Path Difference
difference in the distances two waves must travel from their sources to a given point
4- Standing (stationary) wave
resultant wave formed when two waves of equal
amplitude and frequency traveling in opposite directions in the same medium interfere. (NOTE: does not involve a transfer of energy) (NOTE: points on the wave have varying amplitudes)
4- *Node
locations of constant complete destructive interference on a standing wave
4- *Antinode
locations of maximum constructive interference on a standing wave
4- Fundamental (First Harmonic)
lowest frequency mode of vibration of a standing wave
4- *Polarized Light
light in which the electric field vector vibrates in one plane only
4- *Polarizer
device that produces plane polarized light from an unpolarized beam
4- Malus' Law
the transmitted intensity of polarized light is equal to the productof the incident intensity times the square of the cosine of the angle between the direction of the analyzer and the direction of the electric field vibration of the polarized light (I = Io cos^2 θ )
5- *Law of Conservation of Charge
The total electric charge of an isolated system remains constant.
5- Conductor
material through with electric charge flows freely
5- Insulator
material through which electric charge does not flow freely
5- Direct Current
Current that flows in one direction with a constant amperage
5- *Coulomb's Law
The electric force between two point charges is directly
proportional to the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to square of the distance between them, and directed along the line joining the two charges. (F = kq1 q2 / r^2)
5- *Electric Field Strength (E)
Electric force per positive unit test charge (E = F/q)
5- Radial Field
field that extends radially (like the electric field around a point charge or the gravitational field around a planet)
5- *Electric Potential (V)
work done per unit charge moving a small positive test
charge in from infinity to a point in an electric field. (V = W/q) (V = kq/r) (NOTE: the work done is path independent)
5- *Electric Potential Energy (Ee)
energy that a charge has due to its position in an electric field