1.2.3, 1.2.4, and 1.2.5 bio-med
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:34 PM on 1/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
1
New cards
study of poisonous substances and their effects upon body parts
toxicology
2
New cards
A naturally-occurring poison produced by living organisms produced by living organisms such as bacteria, fungi, plants, insects, and algae.
toxins
3
New cards
Manufactured and extracted chemicals such as pesticides, cleaning agents, and industrial emissions
toxicants
4
New cards
A substance that the body needs to maintain life and health, such as proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals.
nutrient
5
New cards
A group of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
molecule
6
New cards
the mechanical breakdown of food
physical digestion
7
New cards
the breakdown of foods into molecules using enzymes and acid
chemical digestion
8
New cards
functions of the digestive system
ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination
9
New cards
where digestion begins. physical and chemical digestion takes place here.
function of the oral cavity (mouth)
10
New cards
kind of food digested in the mouth
carbs/starchers
11
New cards
enzyme that begins the chemical digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth
salivary amylase
12
New cards
blocks off your trachea (windpipe) when you swallow
epiglottis
13
New cards
bolus
term for the wad of food we swallow
14
New cards
where peristalsis begins. transports food from mouth to stomach
function of the esophagus
15
New cards
wave-like muscle contractions that moves food down the esophagus
peristalsis
16
New cards
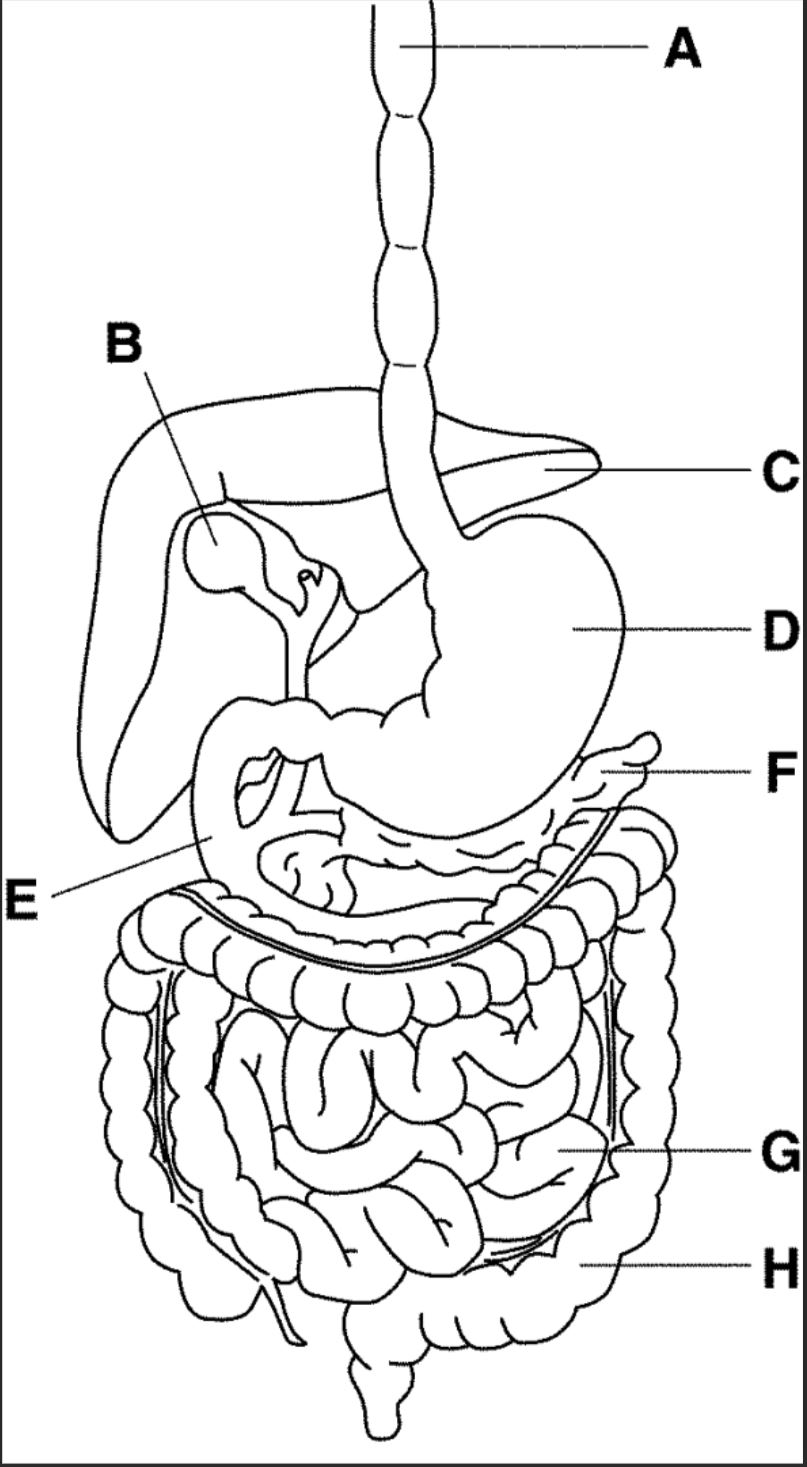
which letter points to the esophagus?
A
17
New cards
where protein digestion begins. produces hydrochloric acid and enzymes which break down food into nutrients
function of the stomach
18
New cards
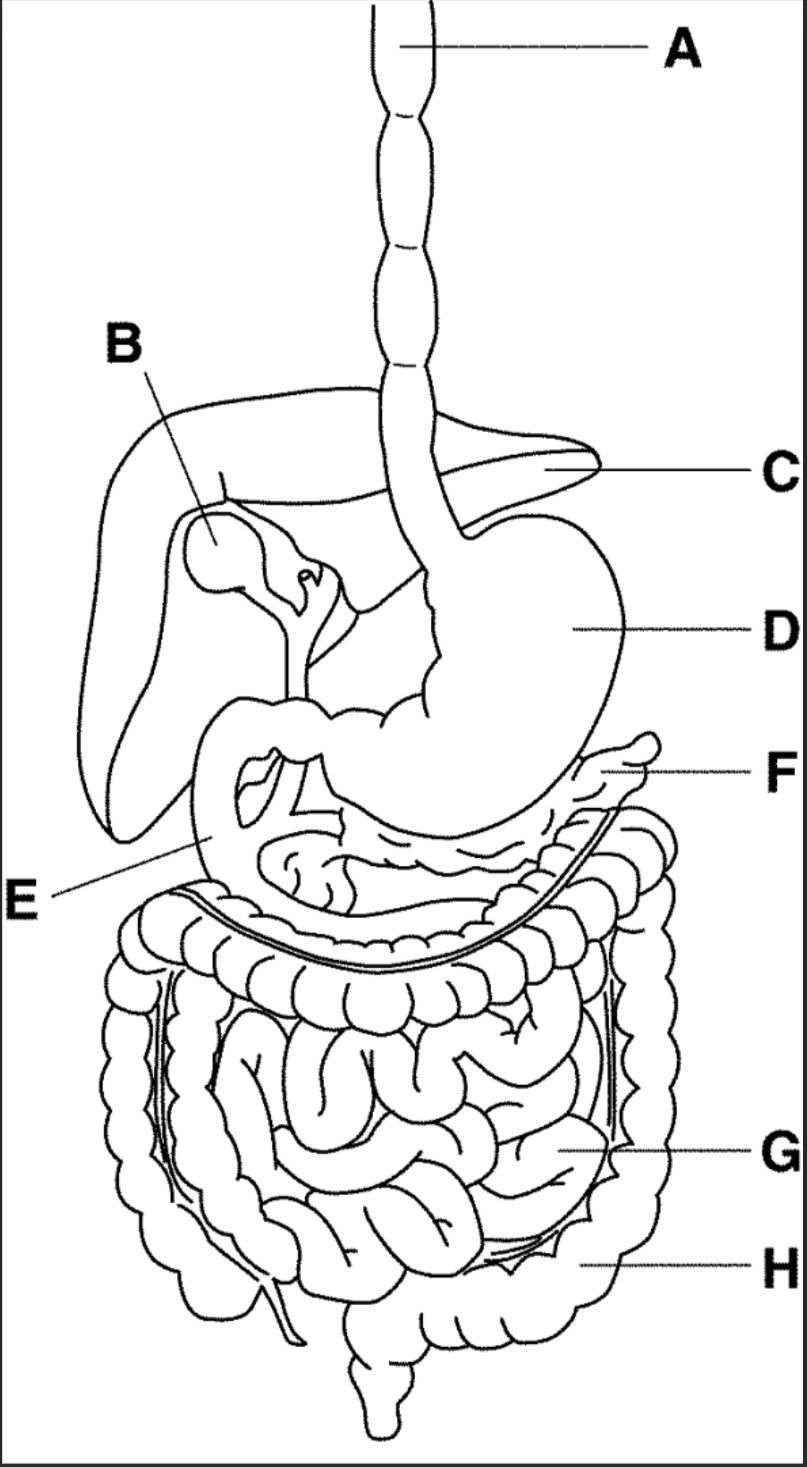
which letter points to the stomach?
D
19
New cards
where are two of the four sphincters in your digestive system found
both ends of the stomach
20
New cards
breaks down food/biomolecules and absorbs most nutrients.
Function of the small intestine
21
New cards
what gets broken down in the small intestine
proteins, carbs, lipids, nucleic acids
22
New cards
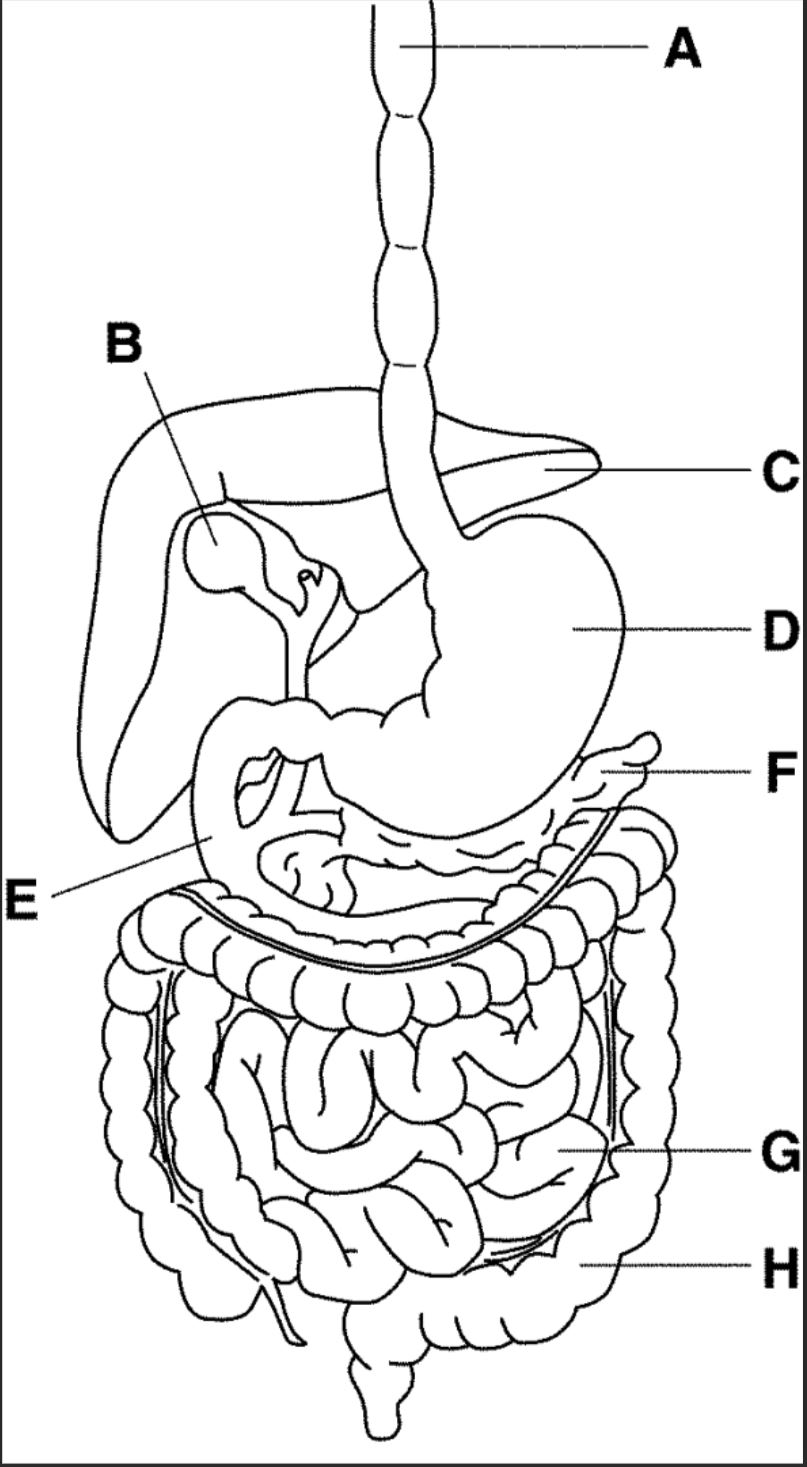
which letter points to the small intestine?
G
23
New cards
removes water from undigested waste (absorbs water)
function of the large intestine (colon)
24
New cards
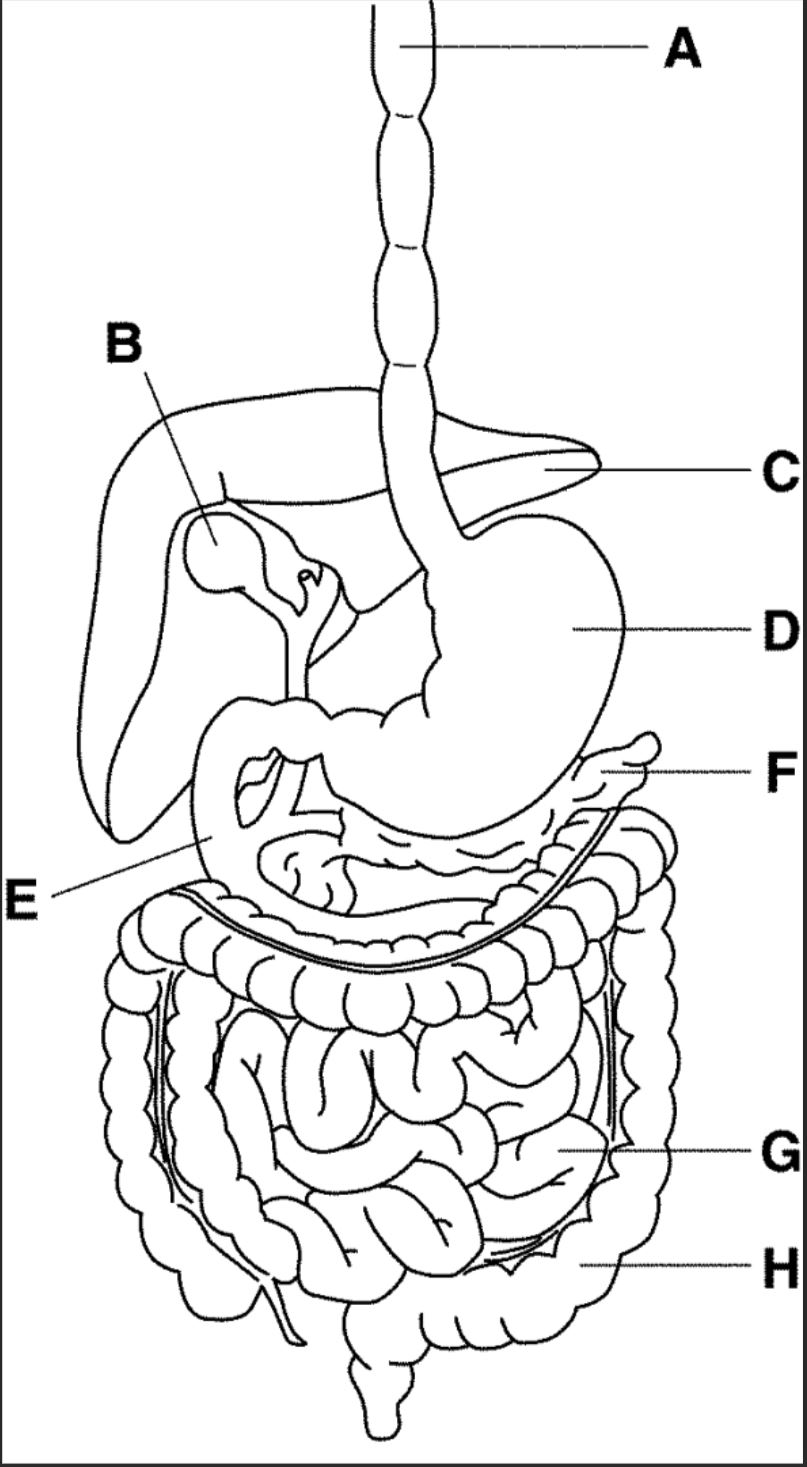
which letter points to the large intestine
H
25
New cards
accessory organs of the digestive system
liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
26
New cards
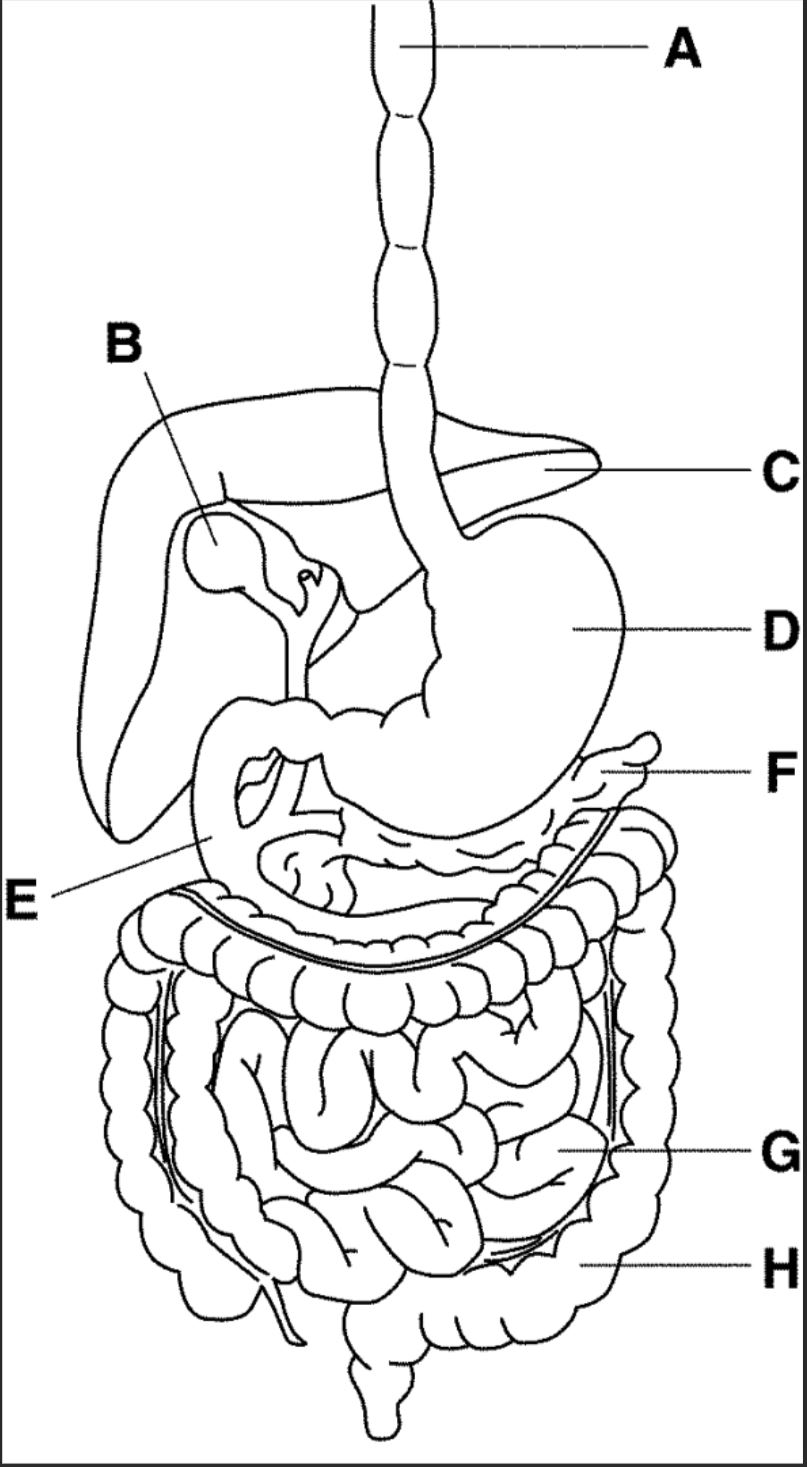
which letter points to the liver
C
27
New cards
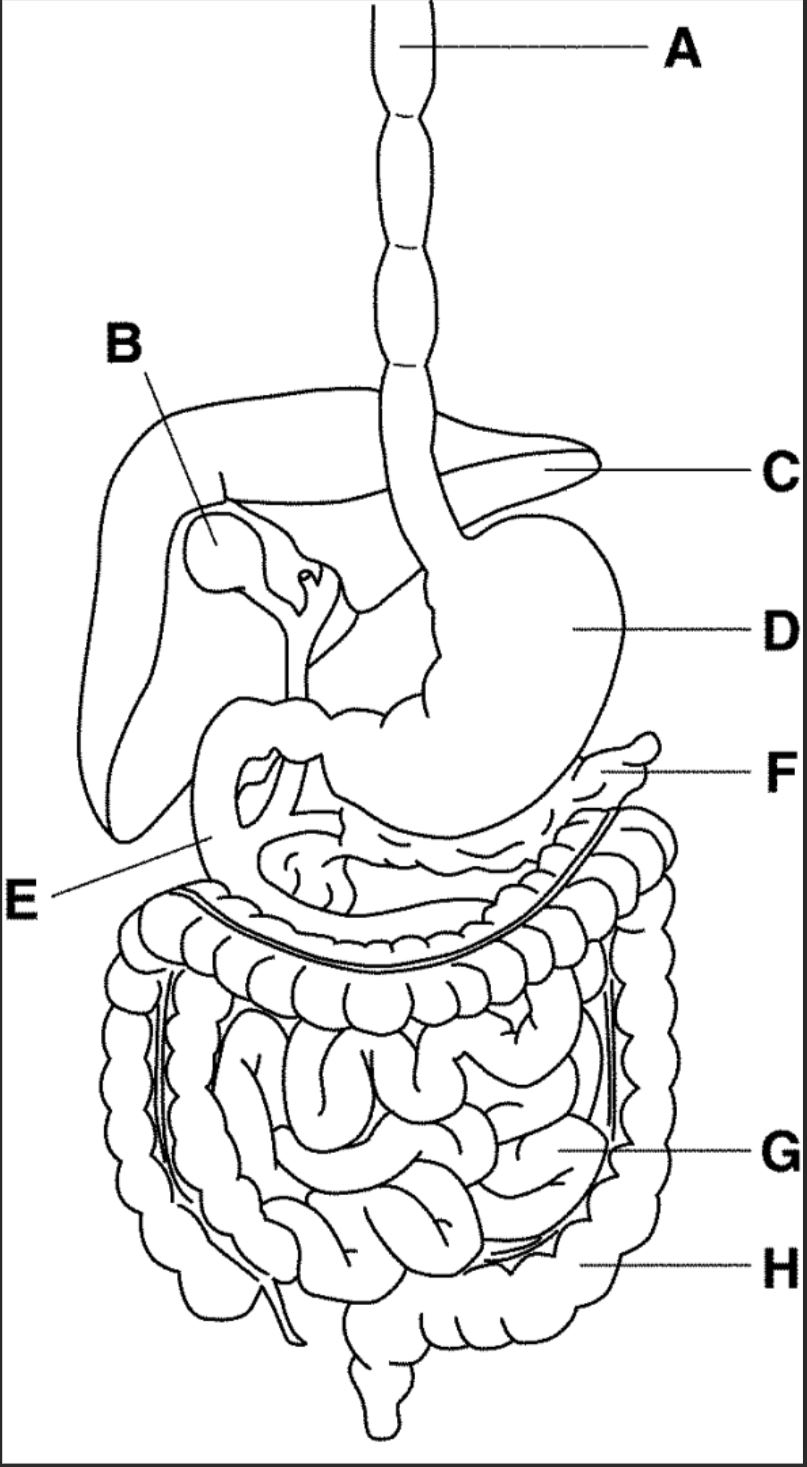
which letter points to the gallbladder
B
28
New cards
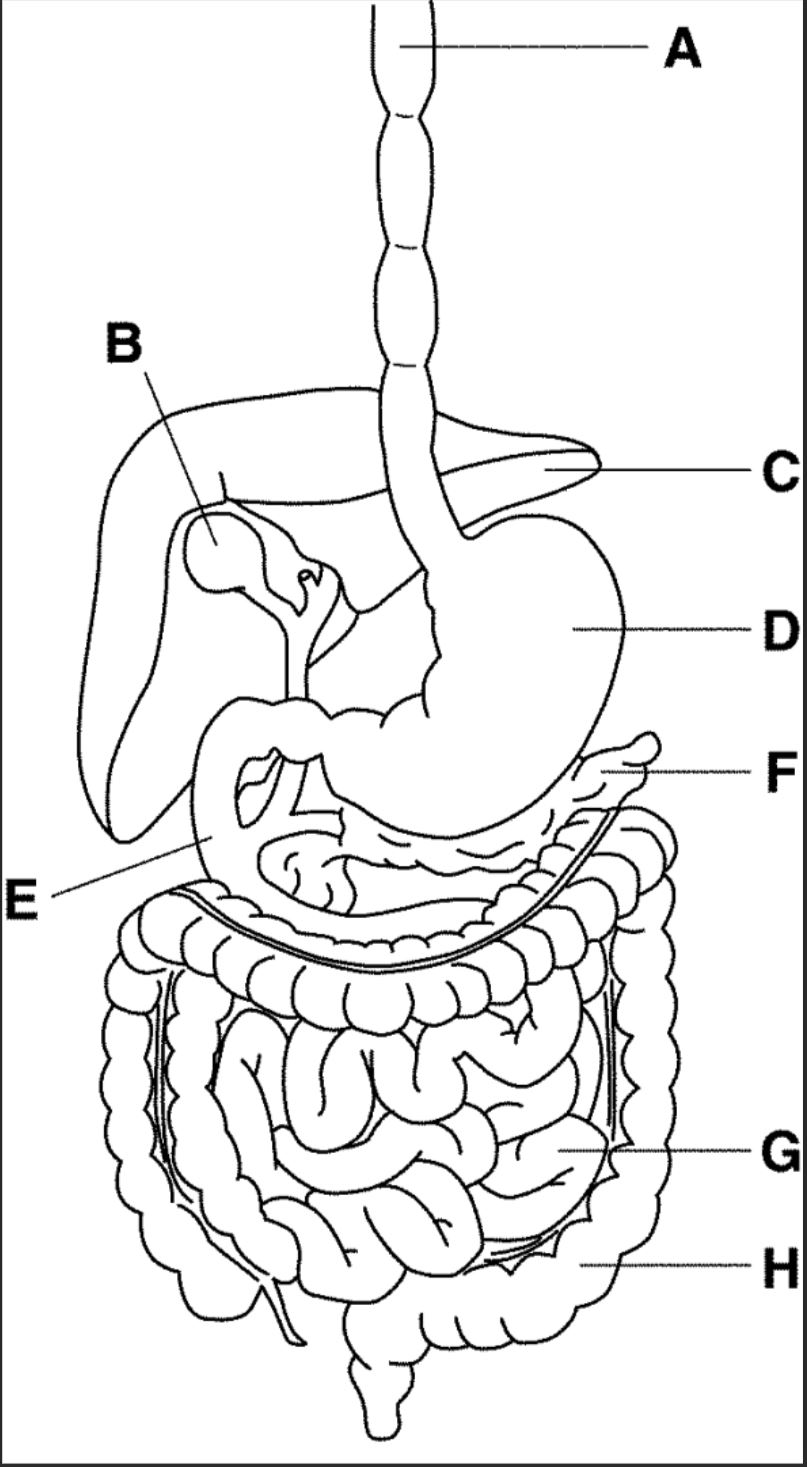
which letter points to the pancreas
F
29
New cards
the process of breaking down substances into molecules and then into energy for the body to use
metabolism
30
New cards
small molecules produced as byproducts during metabolism which can provide clues as to what substances were ingested by an individual and when.
metabolites
31
New cards
molecules necessary for every living thing to survive
biomolecules
32
New cards
what are the four biomolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acid
33
New cards
building block of a biomolecule
monomer
34
New cards
function of carbohydrates
fast source of energy
35
New cards
monomers of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
36
New cards
(elements) carbohydrates are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
37
New cards
example of carbohydrate
sugar\*, starches
38
New cards
function of lipids
provides insulation, long term energy (stores energy for long time)
39
New cards
monomers of lipids
glycerol, fatty acids
40
New cards
(elements) lipids are made of
2. carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
41
New cards
example of lipids
butter, oil, fats, cholesterol
42
New cards
what does the body use after it burns all your carbohydrates
it uses lipids (fat tissue)
43
New cards
function of proteins
acts as enzymes, muscle building, works in immune system
44
New cards
monomers of proteins
amino acids
45
New cards
(elements) proteins are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
46
New cards
examples of proteins
enzymes\*, hemoglobin, antibodies, meat, yogurt, nails and hair
47
New cards
function of nucleic acids
storage of genetic material
48
New cards
monomers of nucleic acids
nucleotides
49
New cards
(elements) nucleic acids are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
50
New cards
examples of nucleic acids
DNA, RNA
51
New cards
enzymes are…
proteins
52
New cards
active site
specifically shaped area on an enzyme of which substrates can bind to
53
New cards
function of enzymes
speed up reaction in the body
54
New cards
substrate
what binds to an enzyme’s active site
55
New cards
the end result items of the reaction between an enzyme and substrate are called the
products
56
New cards
enzymes often end in…
ASE
57
New cards
sugars often end in…
OSE
58
New cards
what do enzymes break down
carbohydrates (sugars), lipids, proteins for digestion
59
New cards
why are enzymes called catalysts
because they can speed up reaction without being altered. they can be used over and over
60
New cards
help bind substrates to enzymes, like vitamins
coenzymes and cofactors
61
New cards
enzymes have ideal…
pH and temperature ranges
62
New cards
when an enzyme’s shape becomes distorted due to changes in ideal pH and temperature
denaturization
63
New cards
Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose. What are the monomers of lact__**ase**__?
amino acids
64
New cards
Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose. What are the monomers of lact__**ose**__?
monosaccharides
65
New cards
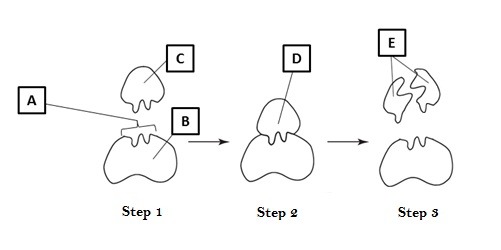
what letter points to the enzyme
B
66
New cards
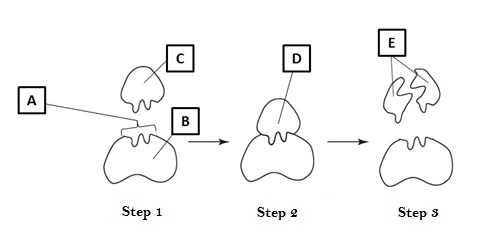
what letter points to the substrate
C
67
New cards
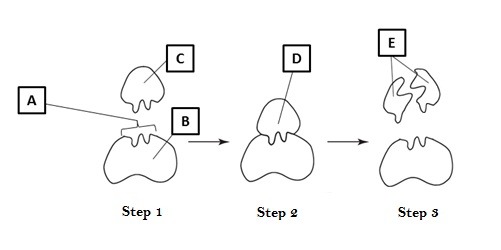
what letter points to the active site
A
68
New cards
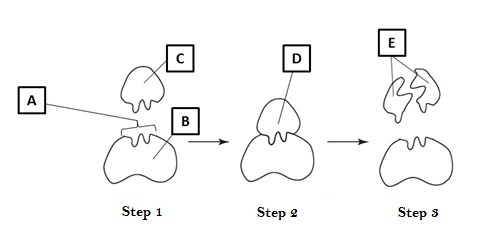
what letter points to the enzyme-substrate complex
D
69
New cards
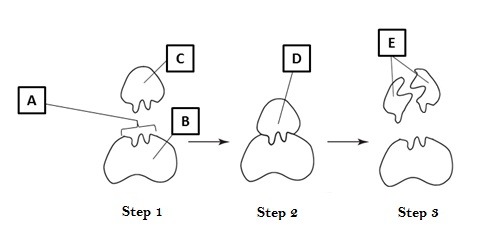
what letter points to the product
E
70
New cards
The study of the microscopic anatomy of tissues.
histology
71
New cards
assessment of tissue specimens by the unaided eye
gross examination
72
New cards
structures of the body from least complex to most complex
chemical, cellular, tissues, organs, organ systems, the body
73
New cards
groups of similar cells come together to perform a common function.
what are tissues
74
New cards
function of the nervous system
responsible for receiving, interpreting, and reacting to signals from inside and outside the body
75
New cards
what is the nervous system comprised of
brain, brain stem, spinal cord, and nerves
76
New cards
function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
brings information from the outside world and from within the body
77
New cards
parts of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
all nerves in the body
78
New cards
function of the central nervous system (CNS)
processes information, makes decisions, controls how we think, move, and learn
79
New cards
parts of the central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
80
New cards
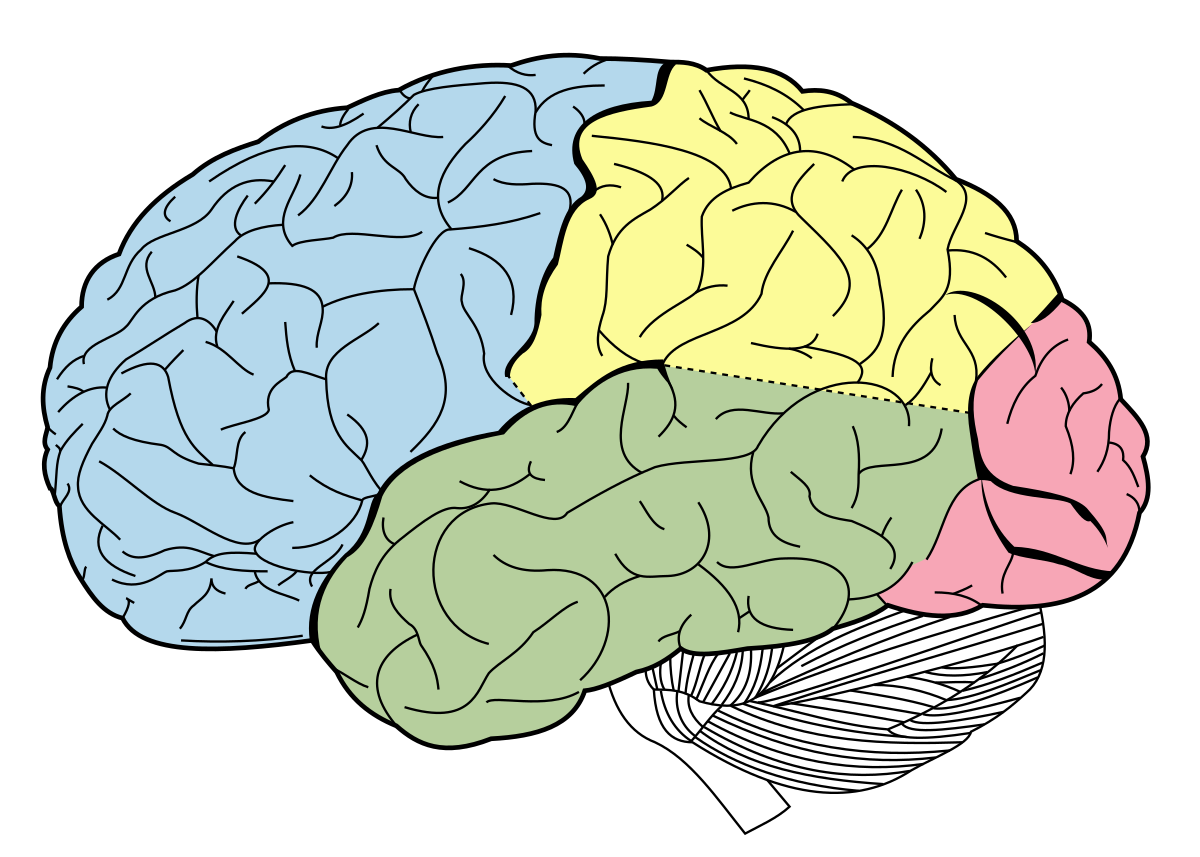
which color shows the frontal lobe
blue
81
New cards
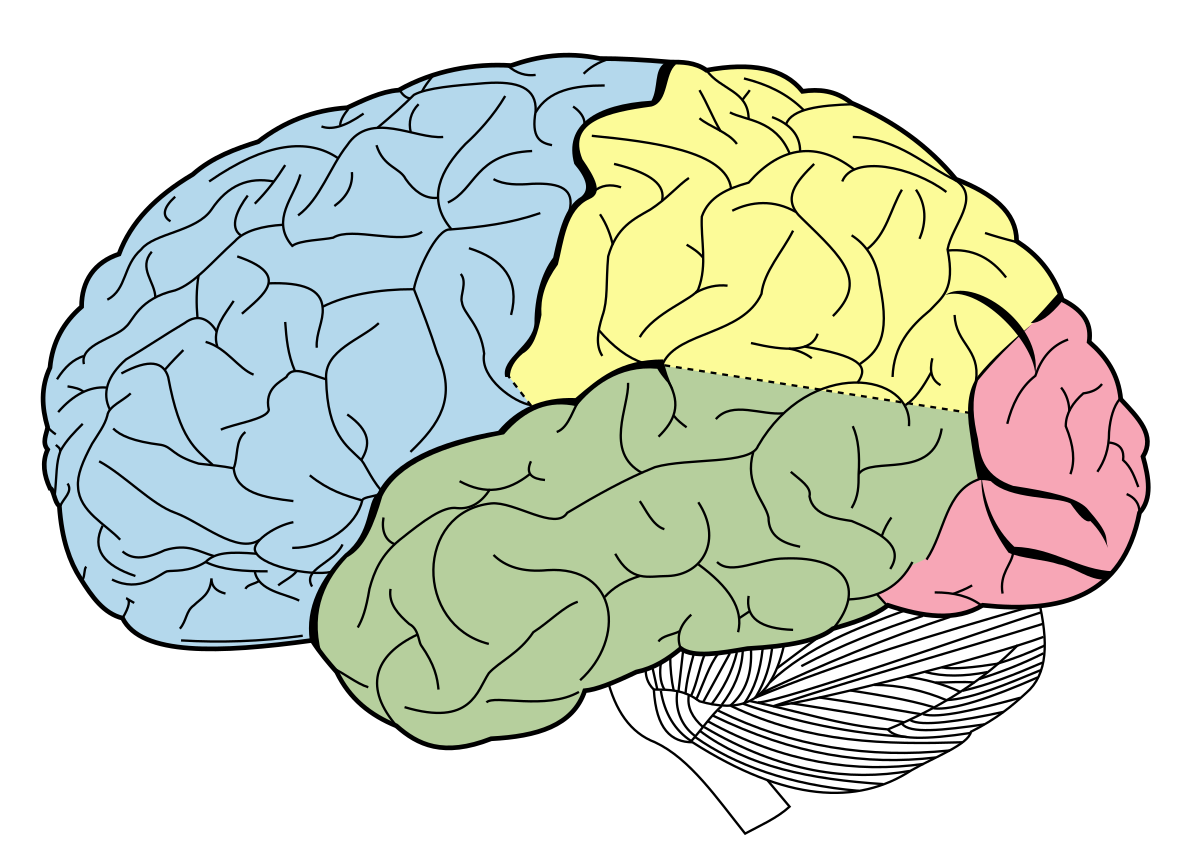
which color shows the parietal lobe
yellow
82
New cards
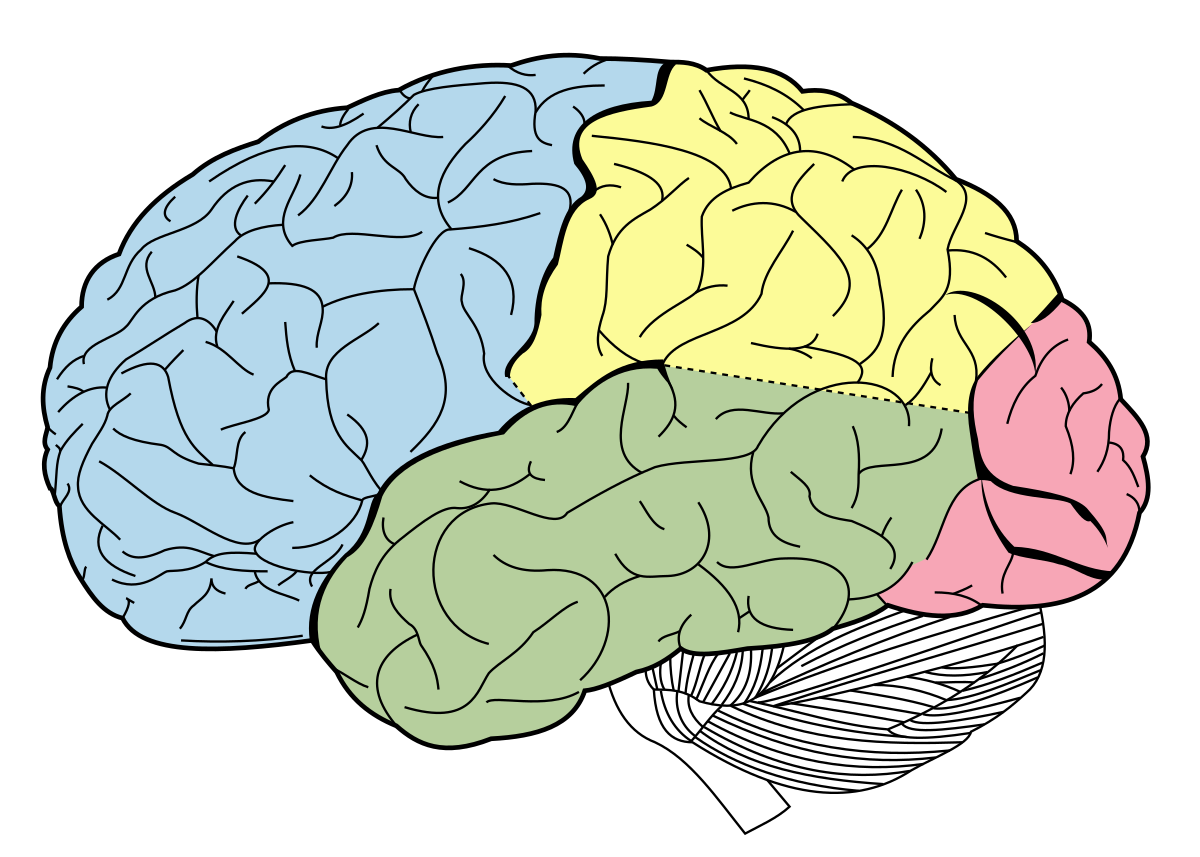
which color shows the temporal lobe
green
83
New cards
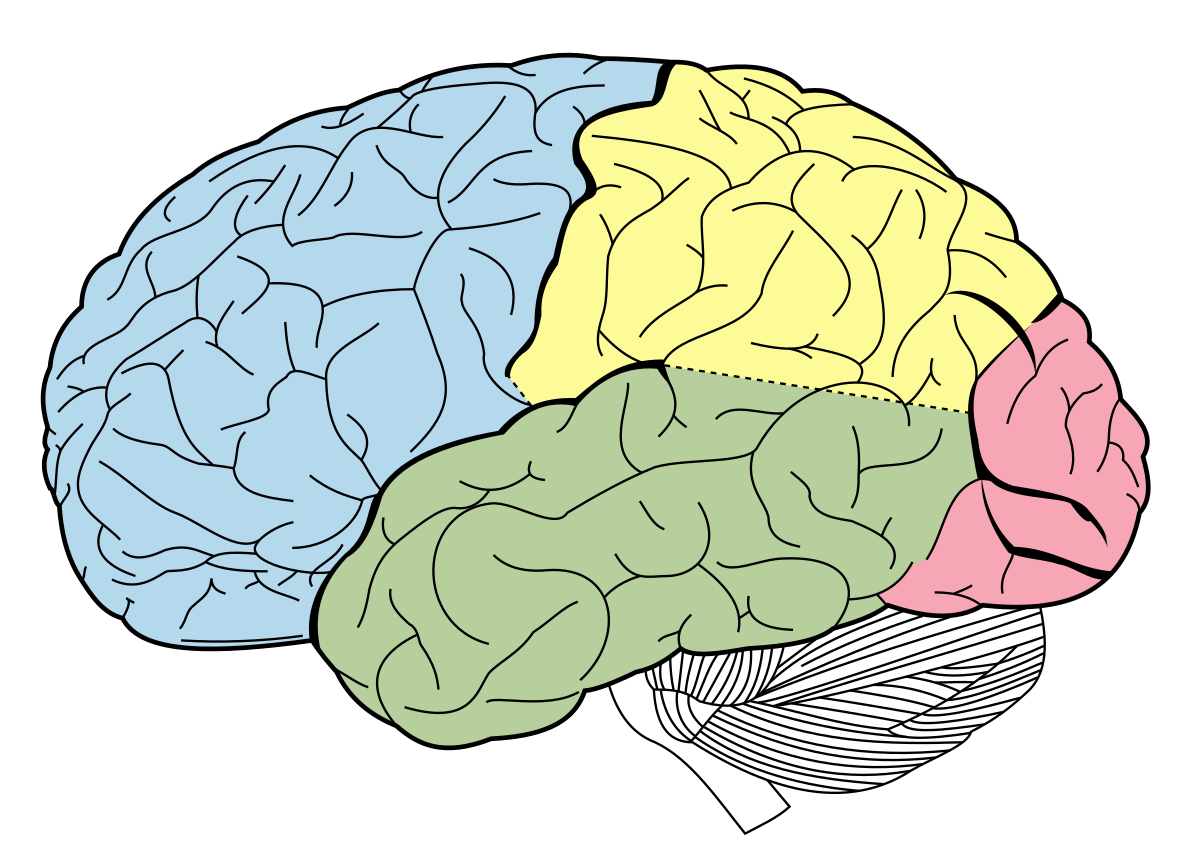
which color shows the occipital lobe
red
84
New cards
plans and organized incoming information; controls emotions and behavior
function of the frontal lobe
85
New cards
sensory perception and integration, including the management of taste, hearing, sight, touch, and smell
function of the parietal lobe
86
New cards
processes language and stores information in long-term memory
function of the temporal lobe
87
New cards
receives and processes sensory nerve impulses from the eyes
function of the occipital lobe
88
New cards
what is the last lobe of the brain to develop
frontal lobe
89
New cards
A brain dysfunction caused by an outside force to the head.
traumatic brain injury (TBI)
90
New cards
A progressive degeneration, and/or death, of nerve cells caused by repeated head injuries, such as repeated concussions.
chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
91
New cards
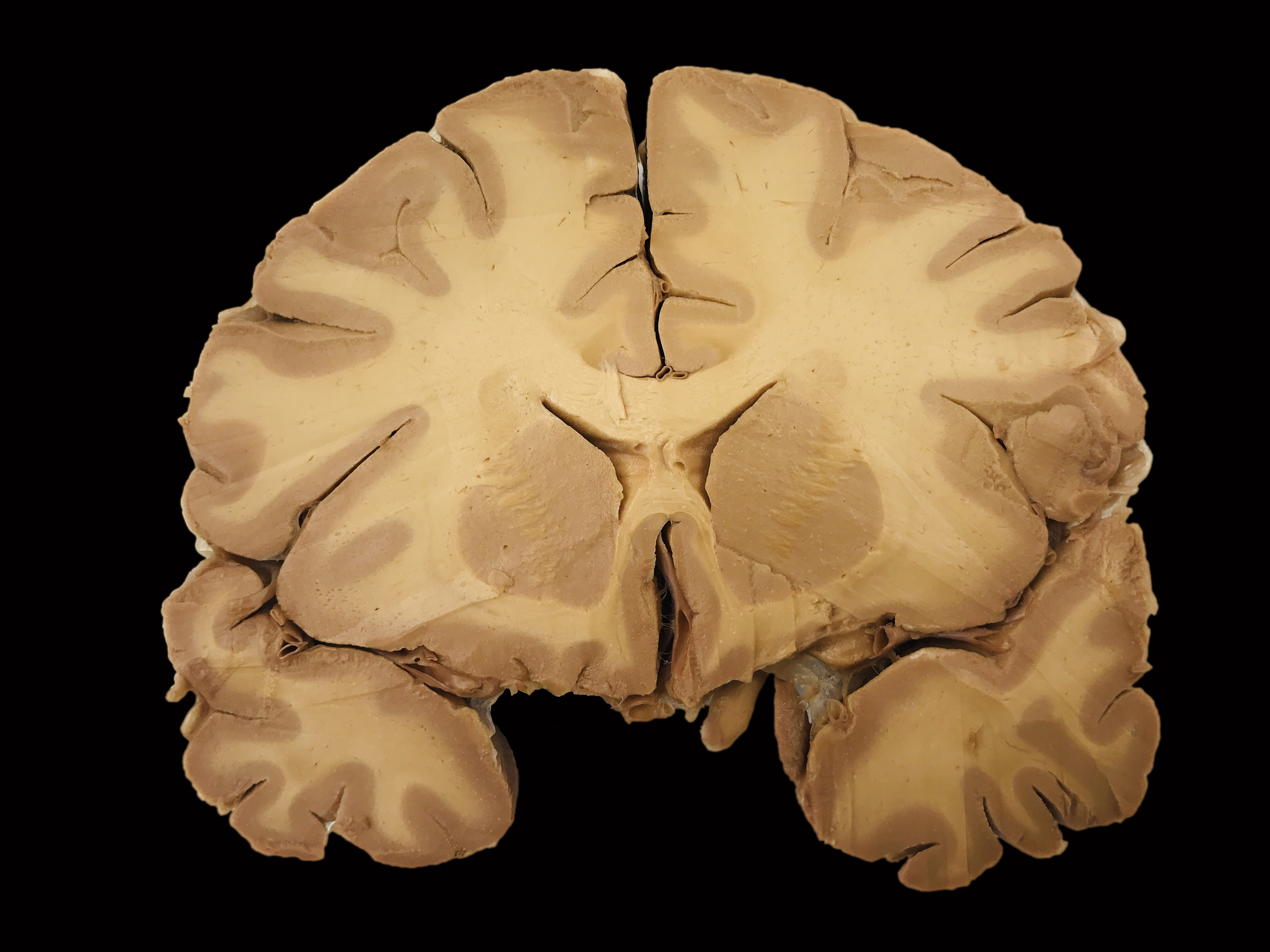
what type of brain does this MRI show
a normal brain
92
New cards
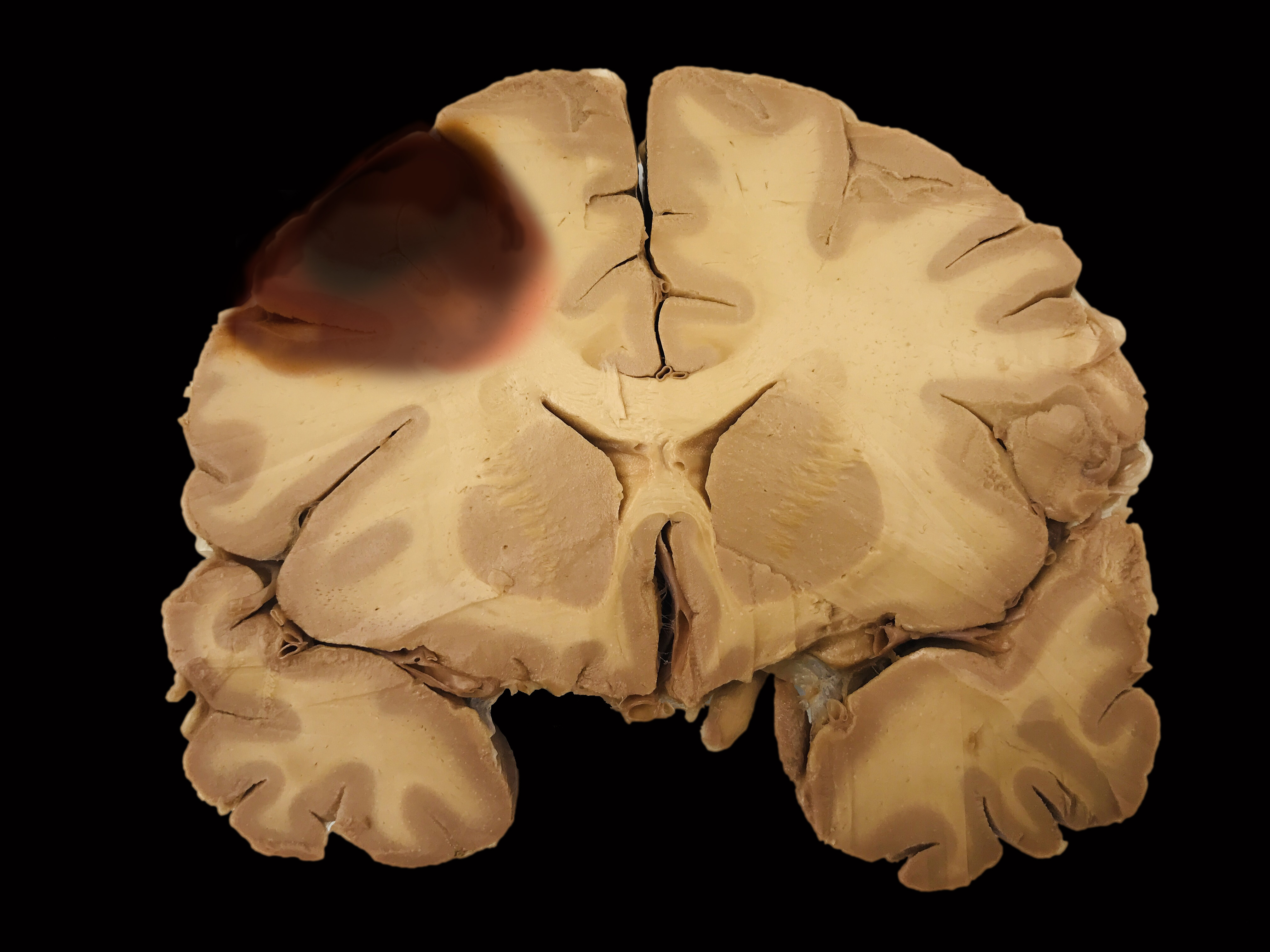
what type of brain does this MRI show
a brain with traumatic brain injury (TBI)
93
New cards
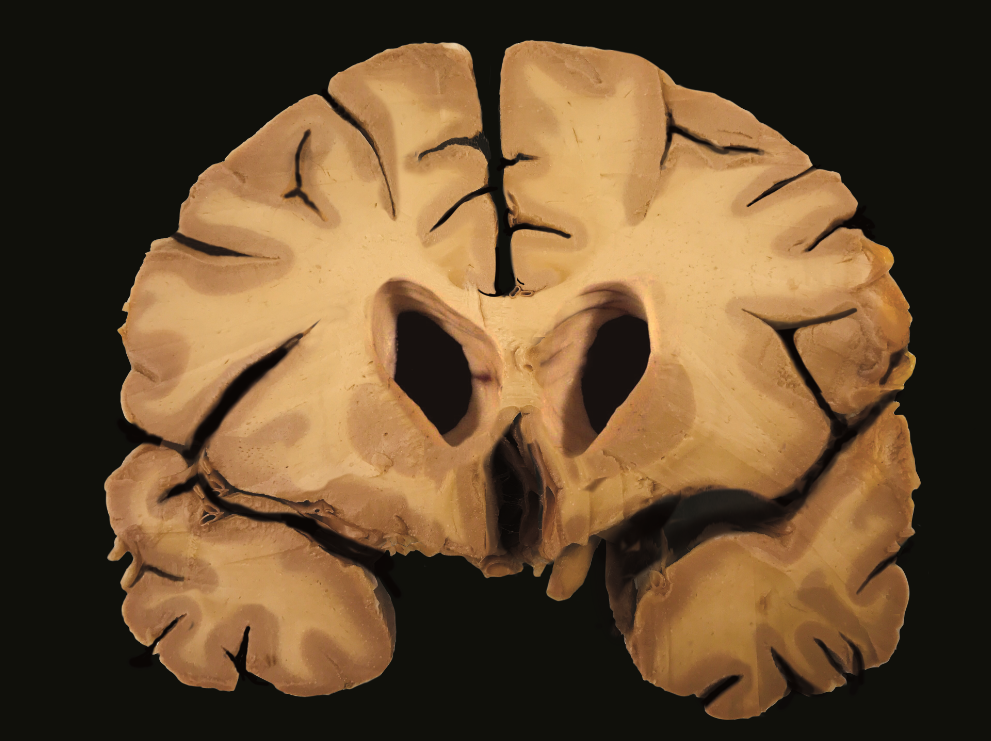
what type of brain does this MRI show
a brain with chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
94
New cards
the types of tissue in the human body
nervous tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue
95
New cards
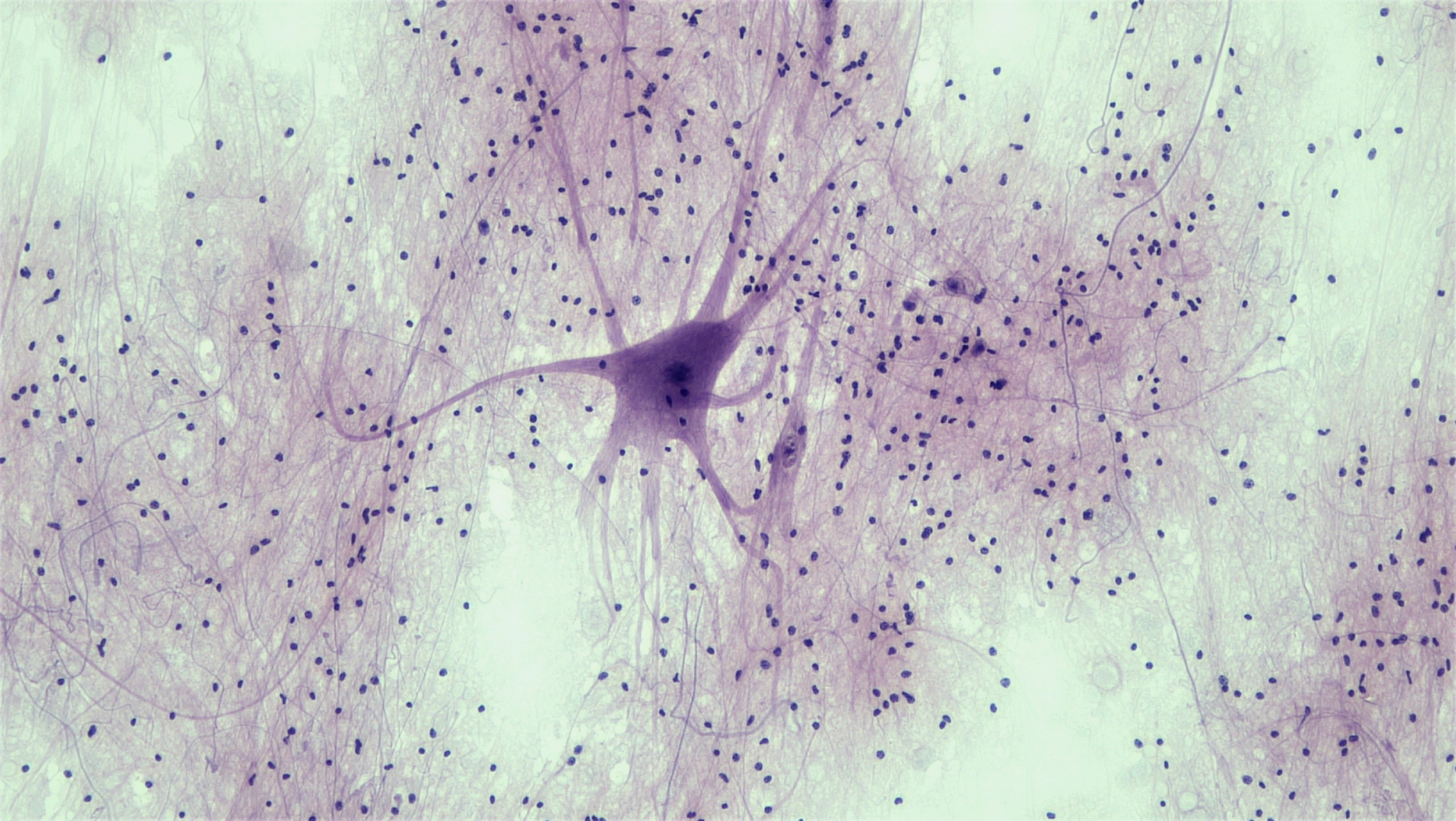
what type of tissue does this picture show
nervous tissue
96
New cards
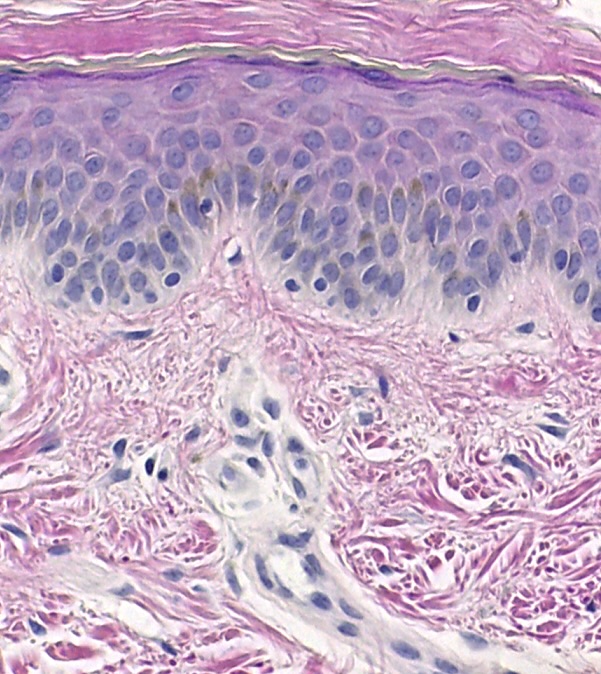
what type of tissue does this picture show
epithelial tissue
97
New cards
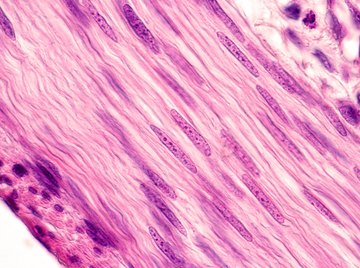
what type of tissue does this picture show
muscle tissue
98
New cards
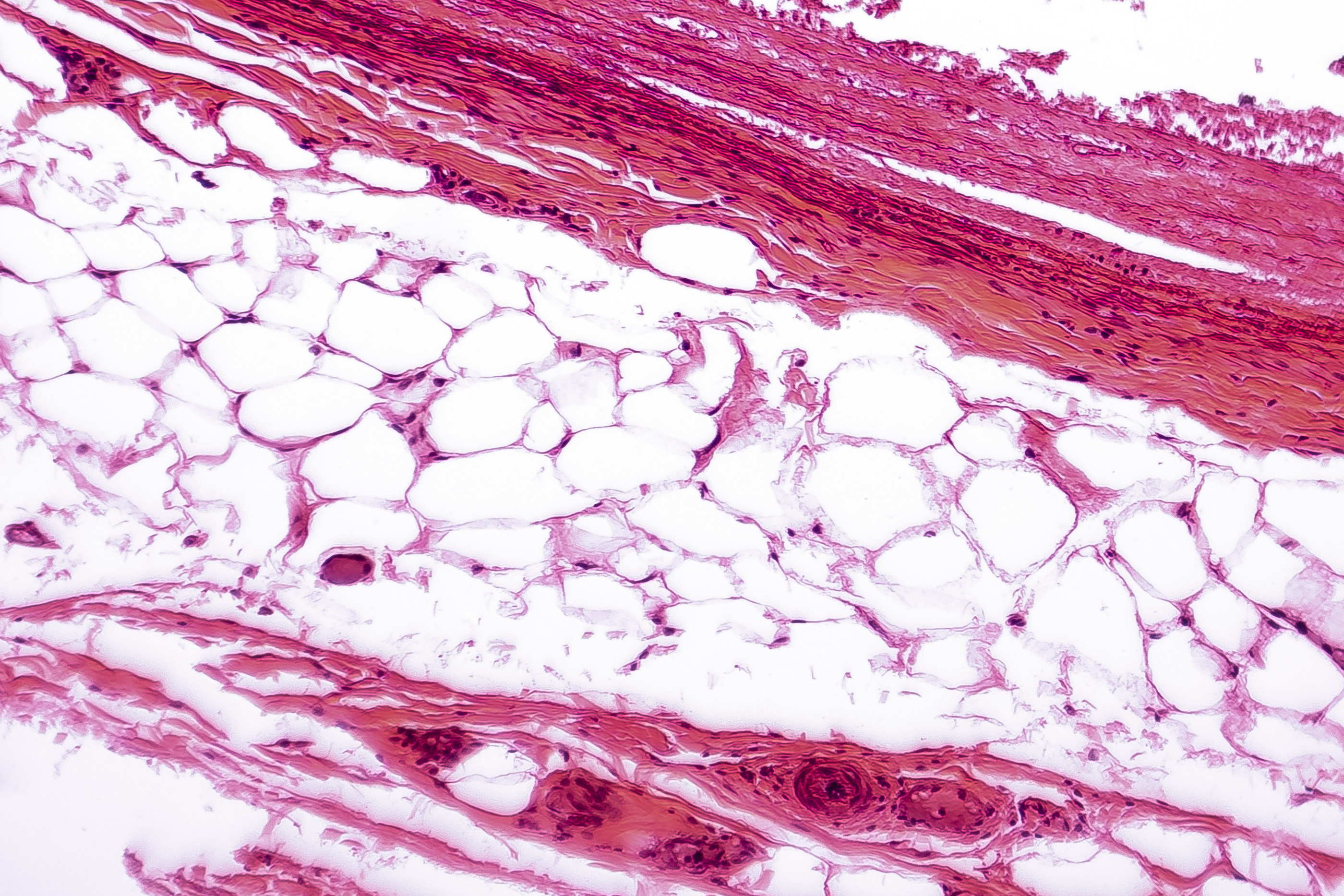
what type of tissue does this picture show
connective
99
New cards
receives, interprets, and responds to signals using specialized cells called neurons
function of nervous tissue
100
New cards
where is nervous tissue located
nerves, brain, spinal cord