Biopsychology
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
what is the endocrine system
network of glands that secrete hormones in the body
what are the 7 glands make up the endocrine system
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Pineal gland
Thyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Ovaries
testes
Hypothalamus function
stimulates and controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland
what hormone/function does the pituitary gland secrete
ACTH → stimulates the adrenal cortex and the release of cortisol during the stress response
Oxytocin → uterus contractions during childbirth
hormone and function of the pineal gland
Melatonin → Responsible for biological rhythms ( sleep wake cycle)
function and hormone of the Thyroid gland
Thyroxine → regulates metabolism
function and hormones of the adrenal gland
adrenaline / non adrenaline → key hormones in flight or fight
Cortisol → stimulates release of glucose providing body with energy / suppresses the immune system
hormone and function of the ovaries
Oestrogen → regulates the female reproductive system
hormone and function of the testes
testosterone → development of male sex characterises
steps of Flight or flight
A stressor is perceived → Activates the amygdala which sends stress signals to the hypothalamus → Hypothalamus activates the SAM pathway → SNS ( sympathetic) stimulates the adrenal medulla → Adrenal medulla secrete adrenaline and noradrenaline into the blood stream
Function of adrenaline in the Flight or fight response
Increases heart rate → increases amount of oxygenated blood to the working muscles ( work better )
increases breathing rate → increases oxygen intake
pupil dilate → enhances vision ( more light enters eyes)
increases sweating → regulate temperature
what are the ways of studying the brain?
fMRI
post-mortem examination
EEG
ERP ( event - related potentials )
benefits of studying the brain
tells us about our behaviour and mental processes
how do fMRI work ( AO1)
measure changes in blood flow in particular areas of the brain indicates increased neural activity
Researchers are able to produce maps showing which parts of the brain are involved in particular brain activity.
uses Radio waves and magnetic fields
How do EEG work ( AO1)
Electrode are put on the scalp and detect neural activity
Able to detect various types of brain disorders such as tumours and epilepsy
what are post-mortem examinations ( AO1)
Areas of damage within the brain are examined after death
used to establish the underlying neurobiology of a particular behaviour
how do ERPs work ( AO1)
Electrode are put on the scalp and detect neural activity of brain with a external stimulus
what are the four lobes of the brain
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
temporal lobe
Brain lobes ( Image)
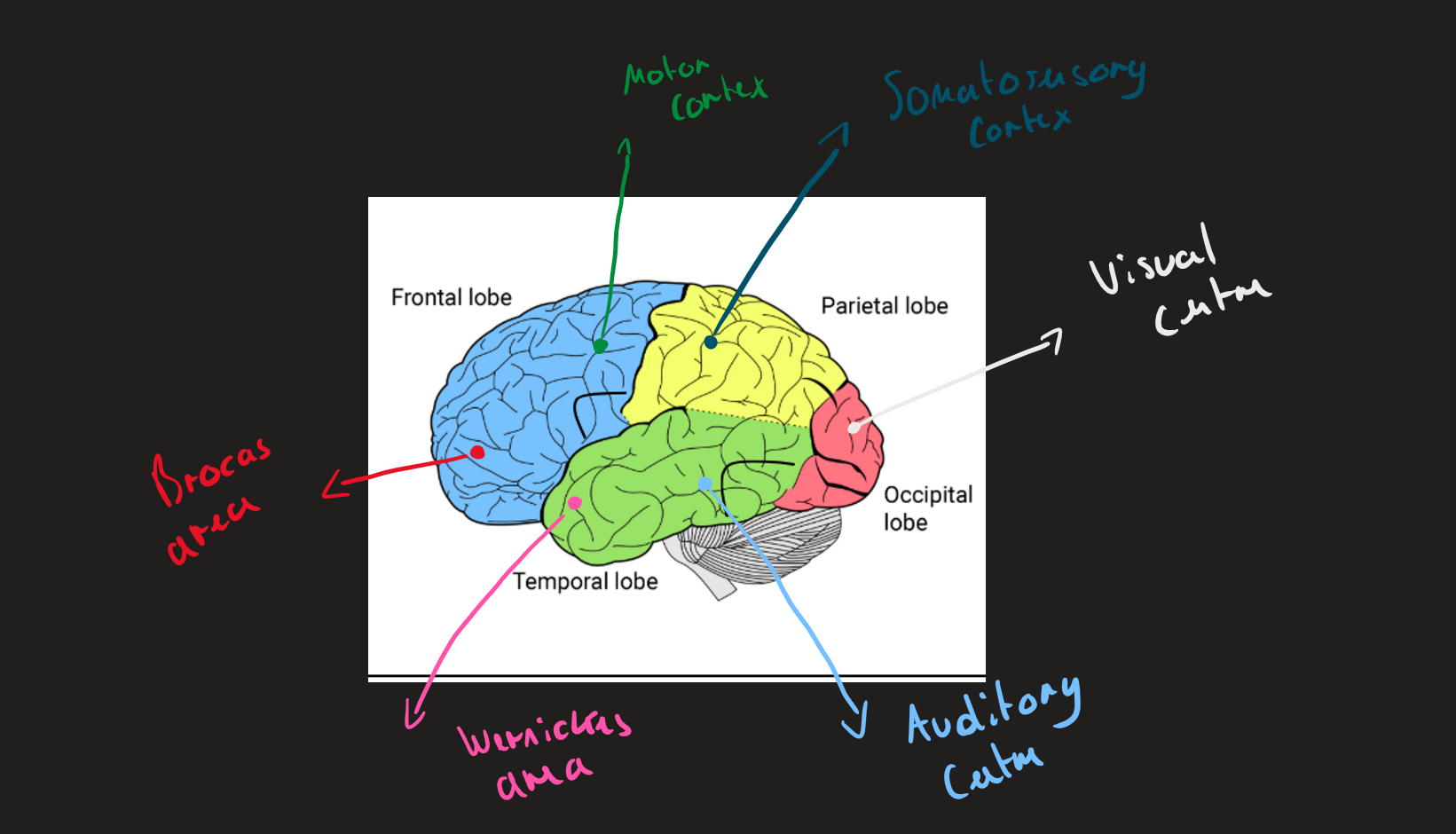
what is the localisation theory?
suggests that certain areas of the brain are responsible for certain processes/ behaviour
what are the 4 areas of the brain ( AO1)
Motor cortex
Somatosensory cortex
Visual centres
Auditory Centres
where is the motor cortex located
Frontal lobe ( left and right hemispheres)
where is the auditory centre located
Temporal lobe
where is the somatosensory Cortex located?
parietal lobe ( Right and Left hemispheres )
where is the Visual centre located
located in the Visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the brain
Function of the motor cortex
Responsible for the generation of voluntary motor movements
Function of the somatosensory cortex
Detects sensory information and produces sensations
what does contralateral control mean
Both hemispheres are responsible for movement on opposite sides of the body
which areas of the brain have contralateral control
Motor cortex
somatosensory
function of the visual centre
Processes visual information
Function of the Auditory Centre
processes auditory information
what are the 2 language centres in the brain
Broca’s area
Wernicke`s area
function and location of Broca’s area
back of frontal lobe in left hemisphere
Critical for speech production
Location and Function of Wernicke’s area
back of temporal lobe in the left hemisphere
critical for speech comprehension
effects of damage to Wernicke’s area
able to speak but able to understand language
effects of damage to Broca`s area
difficulty in producing speech
difference between human and other animal brains
human cortex is developed and it appears as grey matter
what is lateralisation
lateralisation is the fact that the two halves of the brain are functionally different and have there own specialisation
what joins the two hemispheres together
corpus callosum this allows communication between the two hemispheres
what is hemispheric lateralisation ?
The left Hemisphere specialises in language, problem solving and reasoning
The Right hemisphere specialises in Visual motor task.
Sperry (1968) findings
information presented to the left hemisphere could be spoken , couldn’t be spoken if delivered to right hemisphere
Right hemisphere could draw or select object using left hand
what theory does Sperry findings support ?
Lateralisation and localisation theory suggests that language centres are located on the left side of the brain
what were the 3 tasks involved in sperrys experiment
Tactile task
Drawing task
Describe what you see task ( visual task)
Sperry experiment image
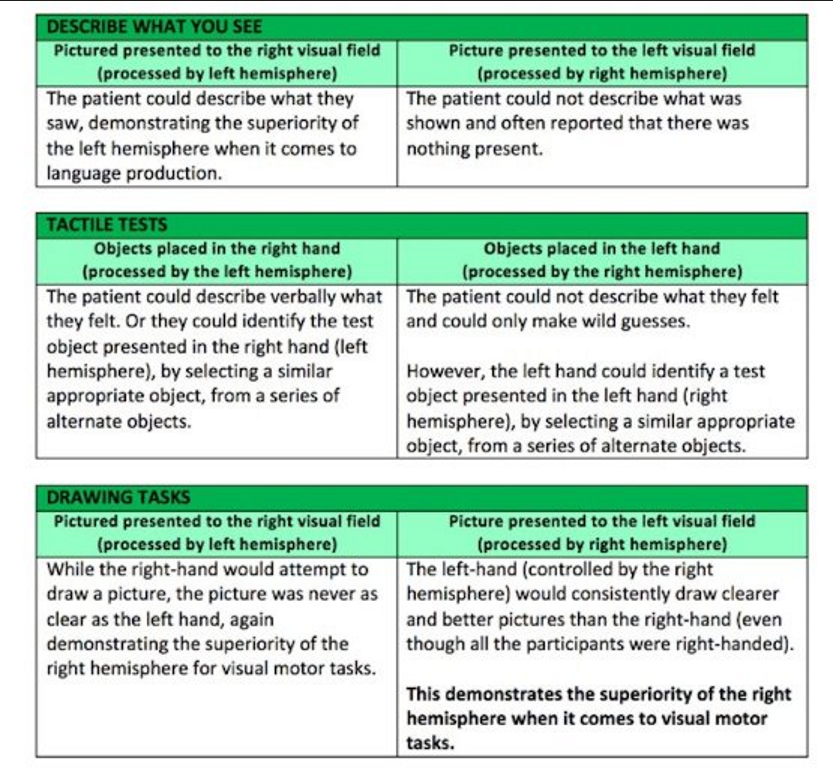
what is brain plasticity ?
The brain can adapt and change over time
why does brain plasticity occur?
As we gain new experiences, nerve pathways are used and develop stronger connections
neurons that are barely / never used die
how does age contribute to changes in the brain
as age increases , cognitive functioning naturally declines
what studys/ proccesses supports brain plasticity
Maguire et al ( taxi)
Kemperman et al ( rats)
fucntioning recovery of the brain after trauma
Maguire et al study and findings
studied brains of London taxi drivers using MRI
found larger volume of grey matter in posterior hippocampus than in control group
Positive correlation between size of posterior hippocampus and time as taxi driver
posterior hippocampus is associated with development of spatial and navigational skills
what are some structural changes that take place in the brain
Axonal sprouting
Reformation of blood vessels
Recruitment of homologous areas
Kemperman findings
Rats in the more complex environment showed a increased number of new neurons in brain ( especially hippocampus)
physical structure of brain changed
what is the functional recovery of the brain
After trauma unaffected brain areas can compensate and adapt for damaged areas
what happens to the brain during recovery
brain is able to rewire and reorganise itself to form new synaptic connections close to damaged area
secondary neural pathway are activated to continue functioning
results in the structural changes in the brain
what is Axonal sprouting
Growth of new nerve ending connects to undamaged nerve cells to form new neural pathways
what is Reformation of blood vessels
Activated areas of the brain experience higher deoxygenated blood level
what is the recruitment of homologous areas
homologous areas on opposite sides are used to perform specific tasks
danelli et al study and findings
E.B case study ( Removal of his LH)
RH can compensate for the language functions
Prefrontal activation likely reflects compensatory demands for complex tasks
what are the 3 types of biological rhythms
Circadian
Infradian
Ultradian
what are biological rhythms governed by
endogenous pacemakers
exogenous zeitgebers
what are endogenous pacemakers ?
body’s internal biological clock
what are exogenous zeitgebers
external changes in the environment
Duration of the Infradian rhythm
Longer then 24 hours
Example of Infradian rhythm
menstrual cycle
what controls the Infradian rhythm
the endogenous pacemakers are hormones
what are the endogenous pacemakers of the menstrual cycle
Oestrogen
when does ovulation occur
Occurs every 28 days
what is the duration for the Circadian rhythm
approximately every 24 hours
examples of Circadian rhythm
Sleep-wake cycle and body Temperature
what time is the Peak and lowest body temperature
Peak is 6pm
Lowest is 4am
why are Pacemakers constantly being reset
Synchronise our bodies rhythm with the outside world
what creates our circadian rhythm
Driven by out internal body clocks, found in every cell
synchronised by the Suprachiasmatic nuclei ( SCN) located in the hypothalamus
what external factors affect our Circadian rhythm
Lightness determine when we feel the need to sleep and wake up
What are the 2 systems of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
what is the CNS composed off
brain
spinal cord
what is the PNS composed off
neurones that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
structure of the nervous system ( image)
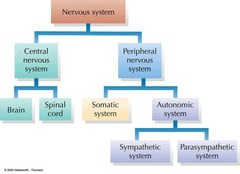
what are the two systems of the PNS
somatic nervous systems
autonomic nervous systems
function of somatic nervous system
consciously controls voluntary muscle movement
Function of the autonomic nervous system
unconsciously controls involuntary activities such as heartbeat and digestion
what systems can the autonomic nervous system be split into?
parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
what is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Activates your flight or fight response
what is the neurotransmitter involved in the sympathetic nervous system?
noradrenaline
adrenaline
what is the neurotransmitter involved in the parasympathetic nervous system?
Acetylcholine
what is the sympathetic system affect on activity levels
Increases
what is the parasympathetic system affect on activity levels
Decreases
what are the 5 structures of the brain
Cerebrum
cerebellum
Hypothalamus
Medulla oblongata
Pituitary gland
function of cerebrum
control Higher brain function ( decision making)
function of Hypothalamus
maintain homeostasis
maintains temperature, control Ψ of blood and hormone production
what is the pituitary gland controlled by
hypothalamus
function of the pituitary gland
produces hormones and stimulates other glands
function of cerebellum
Coordinate muscular movement and maintain balance
function of medulla oblongata
controls involuntary functions
heart rate, breathing rate and blood pressure
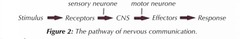
what are the three types of neurones?
Sensory,
relay
motor
what is the function of the Sensory neurones?
Transmit nerve impulses from receptors to the CNS
what is the function of the Motor neurones?
Transmit nerve impulse from the CNS to effectors
what is the function of the Relay neurones?
Transmit nerve impulse between sensory neurons and motor
Pathway of Nervous communication (image)
structure of neurons
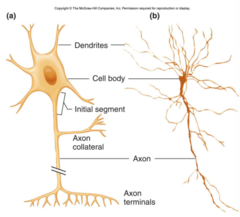
Do neurones have all the normal cell organelles ?
YES
Functions of dendrites and dendrons ?
carry nerve impulses towards the cell body