Early- American History review
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics from early American History: Colonial America to Civil War and Reconstruction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
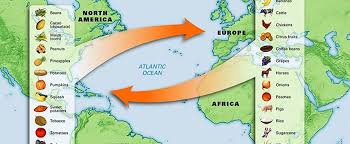
Colombian Exchange
The widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, and diseases between the Americas and the Old World following Christopher Columbus's voyages. It resulted in significant changes in agriculture, diets, and populations on both sides of the Atlantic.
Native Nations before European contact
Were diverse societies with complex cultures, economies, and political systems that thrived across North America long before Columbus's arrival.
European Colonization
Refers to the process by which European powers established settlements and imposed their control over various parts of the world, particularly in the Americas, beginning in the late 15th century.
Evolution of Jamestown
Established in 1607, evolved from a struggling outpost to a successful colony through adaptations in governance, relationship with Native Americans, and economic practices.
Transatlantic Slave Trade
The forced transportation of enslaved Africans to the Americas, initiated in the 16th century, creating a brutal network that contributed to the economy of plantation societies.
Triangular Trade
A trade system between Europe, Africa, and the Americas involving the exchange of goods, enslaved people, and raw materials that supported the transatlantic economy from the 16th to the 19th century.
Plimoth Massachusetts
Established in 1620 by Pilgrims seeking religious freedom, Plimoth became one of the first successful English colonies in North America, known for the Mayflower Compact and interactions with Native Americans.
Mayflower compact
A foundational document signed in 1620 by the Pilgrims aboard the Mayflower, establishing self-governance and legal order for their new colony of Plimoth.
Indentured Servitude
A labor system where individuals worked for a period of time, typically 4 to 7 years, in exchange for passage to America and eventual freedom.
Bacon’s Rebellion
A 1676 uprising led by Nathaniel Bacon against Virginia's colonial government, highlighting tensions between frontier settlers and the established elite.
King Philips War
A conflict in 1675-1676 between New England colonists and Native American tribes led by Metacom, also known as King Philip, resulting in significant casualties and the destruction of several towns.
William Penn’s Pennsylvania and Philadelphia
A colony founded by William Penn in 1681 as a place for religious freedom, which became known for its Quaker values, tolerance, and planned city layout in Philadelphia.
French and Indian War
A conflict from 1754 to 1763 between Britain and France in North America, part of the larger Seven Years' War, primarily over territorial disputes and control of the Ohio River Valley.
Albany Plan of Union ( Join or Die )
A proposal by Benjamin Franklin in 1754 aimed at uniting the thirteen American colonies for defense against French and Native American threats during the French and Indian War. The plan was ultimately rejected but laid the groundwork for future cooperation among the colonies.
Treaty of Paris
The 1763 agreement that ended the French and Indian War, granting Britain significant territorial gains in North America, including Canada and Florida.
British Tax/ Legislation
Policies imposed on American colonists to raise revenue, including the Stamp Act and Townshend Acts, leading to increased tensions and resistance.
Colonial Protests
Various actions taken by American colonists to resist British taxation and control, including protests, boycotts, and the formation of groups like the Sons of Liberty.
Boston Massacre
An incident on March 5, 1770, where British troops killed five colonists during a confrontation, escalating anti-British sentiments.
Boston Tea Party
A political protest on December 16, 1773, where American colonists dumped 342 chests of British tea into Boston Harbor to oppose the Tea Act, symbolizing resistance to British taxation.
Coercive/ Intolerable Acts
A series of punitive laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 in response to the Boston Tea Party, aimed at restricting colonial autonomy and enforcing obedience.
1st Continental Congress
A meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 American colonies that convened in Philadelphia in September 1774 to coordinate a response to British policies and assert colonial rights.
Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine in 1776 that argued for American independence from Britain. It was influential in persuading colonists to support the revolutionary cause.
Decoration of Independence
A document adopted on July 4, 1776, declaring the American colonies independent from British rule, authored primarily by Thomas Jefferson.
Franklin in France
Benjamin Franklin's diplomatic mission to France during the American Revolutionary War, where he secured French support for the American cause.
Valley Forge Winter Encampment Individual
The harsh winter quarters of the Continental Army during the winter of 1777-1778, where they faced severe cold, lack of supplies, and disease, but emerged stronger under the leadership of George Washington.
Contributes to the Revolution ( unsung heroes )
Battle of Yorktown
The last major battle of the American Revolutionary War, where American and French forces defeated the British, leading to their surrender.
Treaty of Paris
The agreement signed in 1783 that officially ended the American Revolutionary War and recognized American independence from Britain.
Articles of Confederation
The first constitution of the United States, ratified in 1781, which established a weak central government and was later replaced by the U.S. Constitution.
Shays Rebellion
An armed uprising in 1786-1787 by Massachusetts farmers protesting economic injustices and the lack of government response, highlighting the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation.
Constitutional Convention/ Compromises
The gathering in 1787 where delegates drafted the U.S. Constitution, addressing issues such as representation and federalism, ultimately leading to compromises like the Great Compromise and the Three-Fifths Compromise.
The Federal System
A system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units, allowing for shared governance and local autonomy.
Separation of Powers
A political doctrine where the powers of government are divided into distinct branches (executive, legislative, judicial) to prevent any one branch from exerting too much power.
Checks and Balances
A system that ensures that the different branches of government can limit each other's powers, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful.
Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the United States Constitution, which guarantee essential rights and civil liberties to individuals against government infringement.
Presidential Precedents
The customs and practices set by past presidents that serve as examples for future leaders, influencing the role and powers of the presidency.
Whiskey Rebellion
A 1794 uprising by farmers in western Pennsylvania against the federal excise tax on whiskey, highlighting tensions between rural citizens and the federal government.
Hamilton’s Economical Plain
A financial plan proposed by Alexander Hamilton aimed at stabilizing the American economy through federal control of state debts, the creation of a national bank, and the promotion of manufacturing.
XYZ Affair
A 1797 diplomatic incident between France and the United States that led to an undeclared naval conflict, spurred by French demands for bribes from American diplomats.
Bloodless Revolution of 1800
A political shift in the United States where Thomas Jefferson peacefully succeeded John Adams, marking the first transfer of power between political parties in American history.
Marbury v Madison
A landmark Supreme Court case from 1803 that established the principle of judicial review, allowing the Court to invalidate unconstitutional legislation.
Louisiana Purchase
The acquisition of the Louisiana Territory by the United States from France in 1803, which doubled the size of the nation and significantly expanded its resources and territory.
The Corps of Discovery
The expedition led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark from 1804 to 1806 to explore the newly acquired Louisiana Territory and find a route to the Pacific Ocean.
War of 1812
A military conflict between the United States and Great Britain from 1812 to 1815, driven by issues such as trade restrictions and the impressment of American sailors.
Era of Good Feelings