Sheep disection
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A&P Honors
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
temporal lobe
auditory lobe associated with processing sound and integrating sensory information.
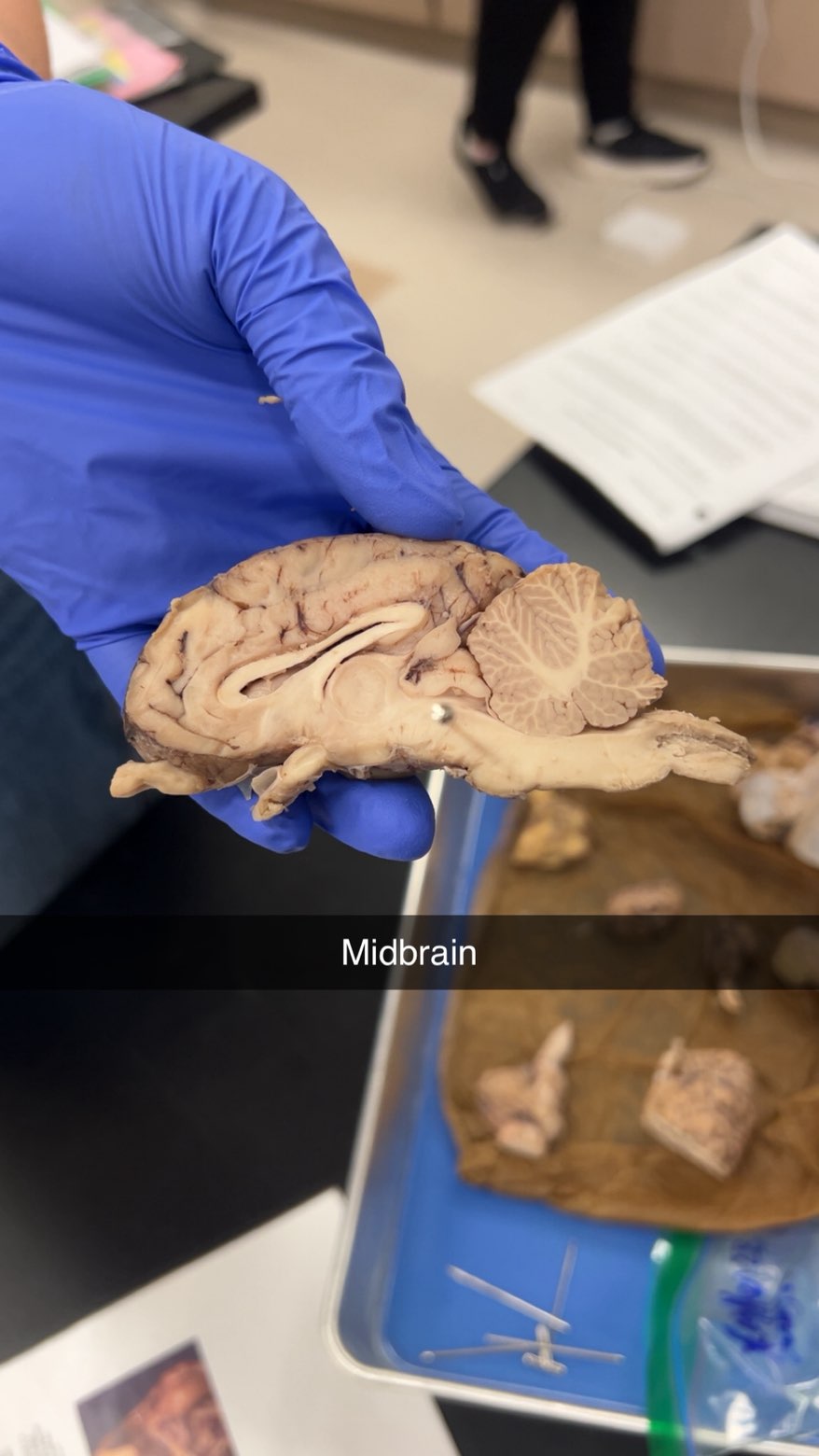
midbrain
reflex center in the spinal cord that processes and responds to sensory stimuli without direct involvement of the brain. vis & aud reflex
parietal lobe
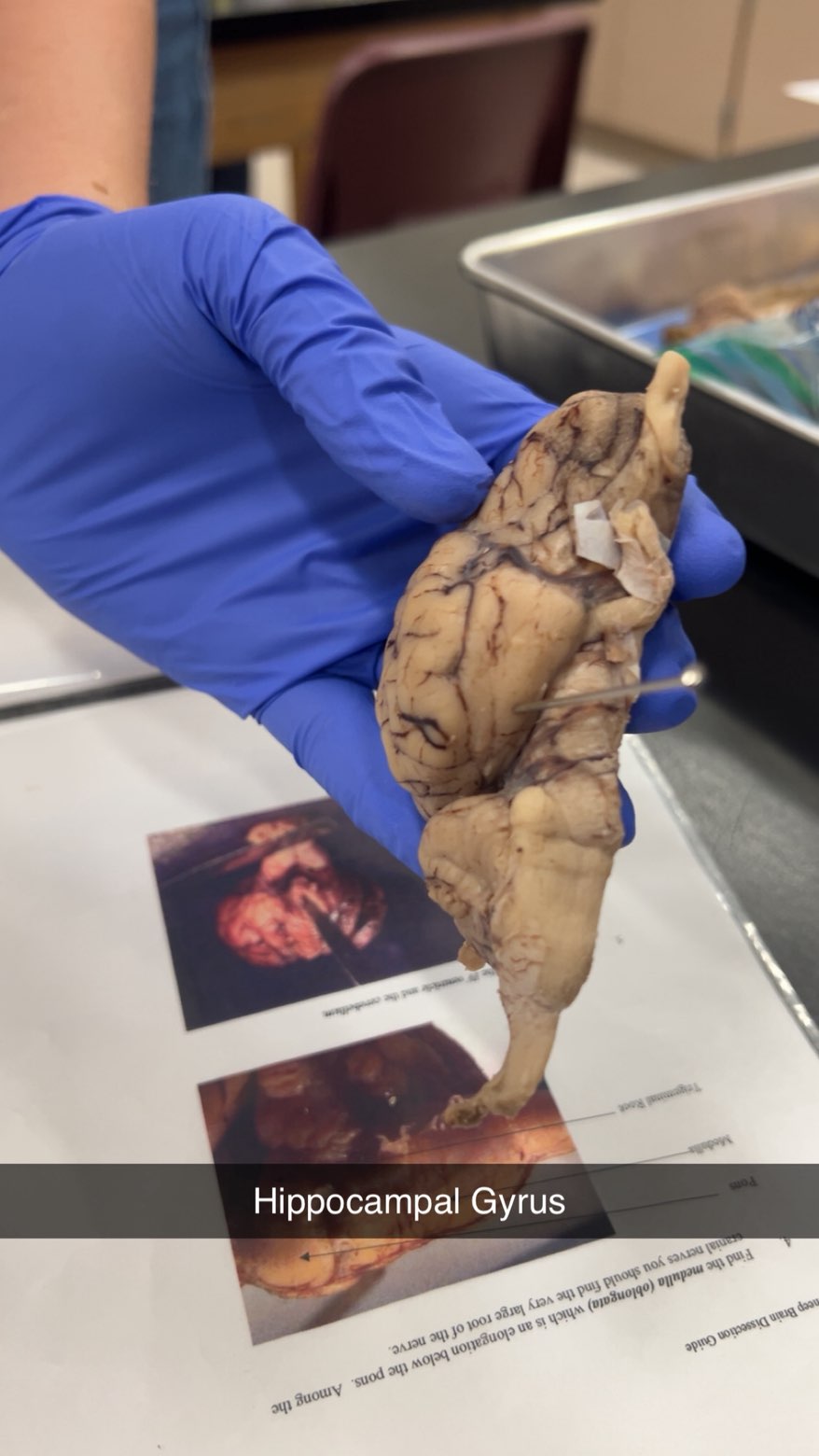
hippocampal gyrus
which is a gyrus in the temporal lobe that surrounds the hippocampus. It is a crucial part of the limbic system and plays a significant role in memory encoding and retrieval, including the recognition of places. The parahippocampal gyrus is also involved in processing emotions and is continuous with the lingual gyrus in the occipital lobe
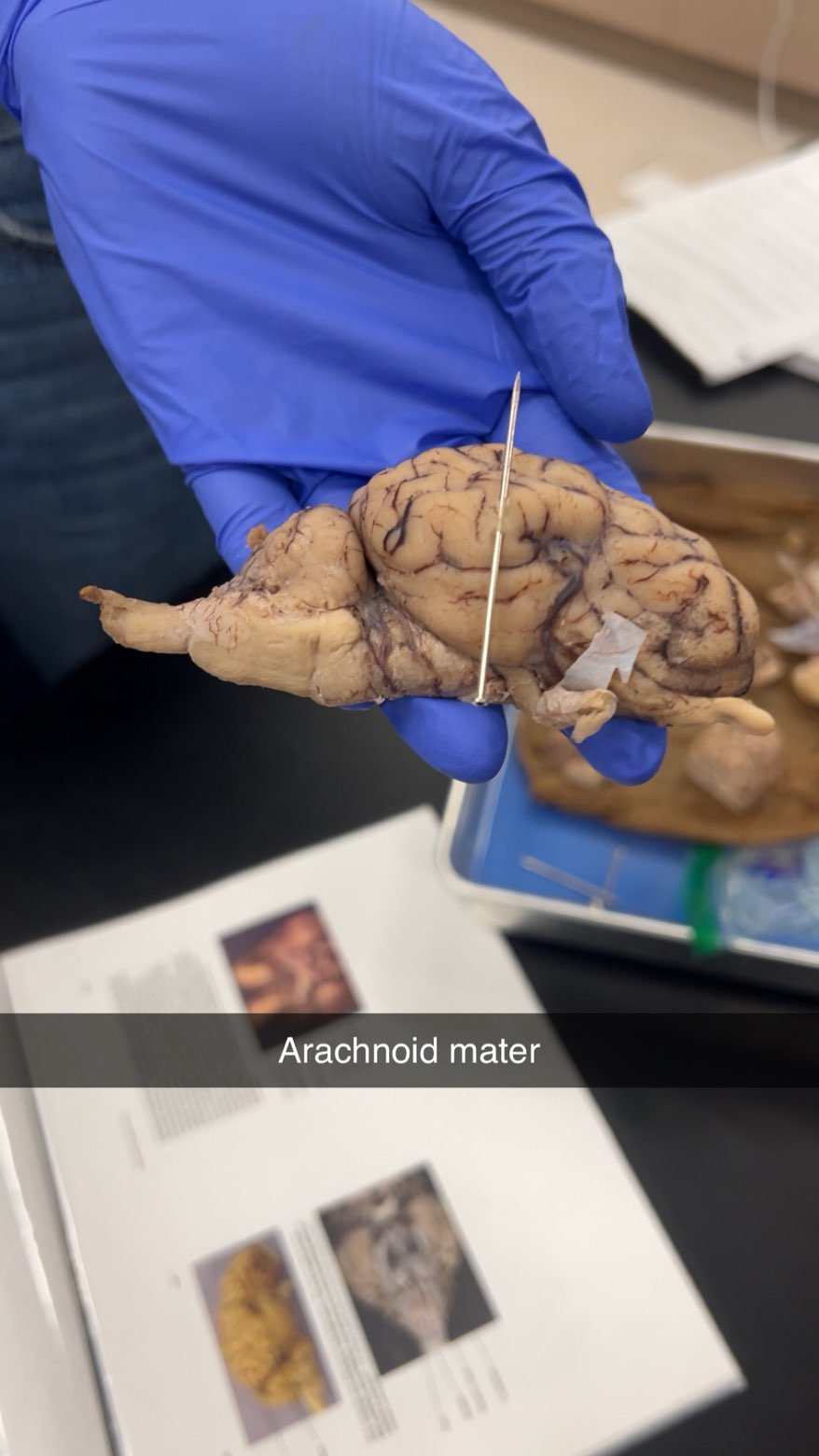
arachnoid mater
holds csf
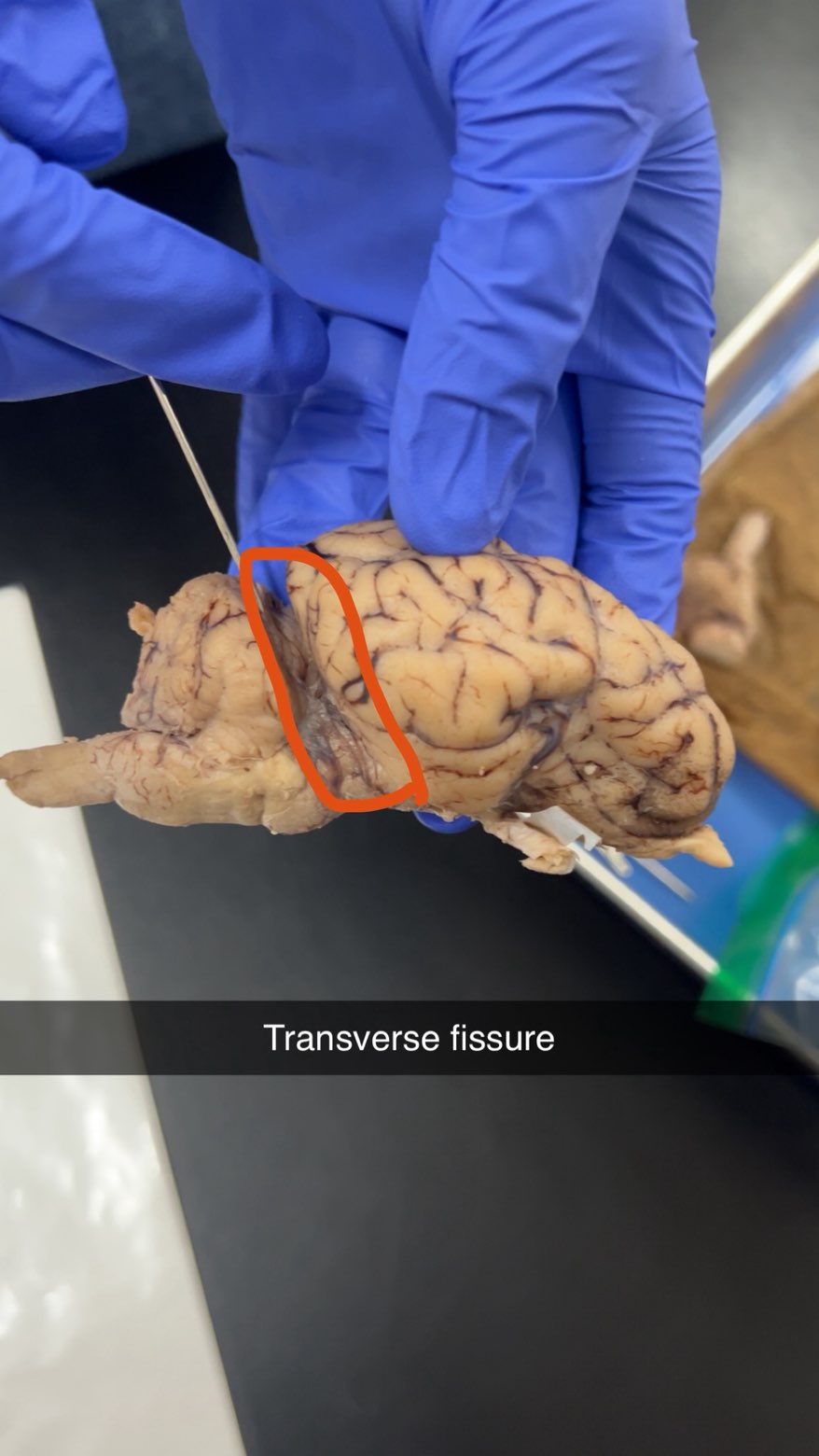
transverse fissure
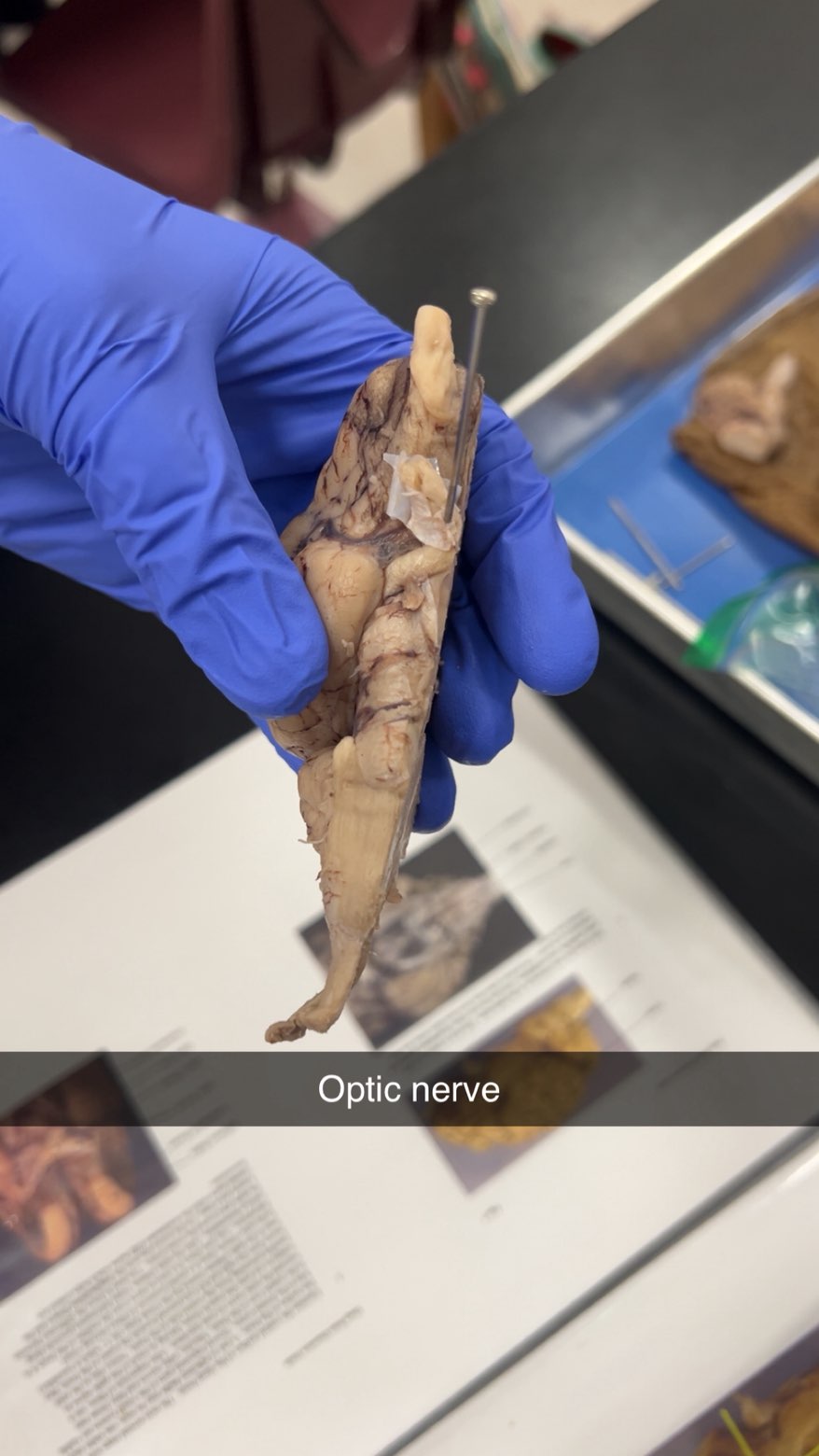
optic nerve
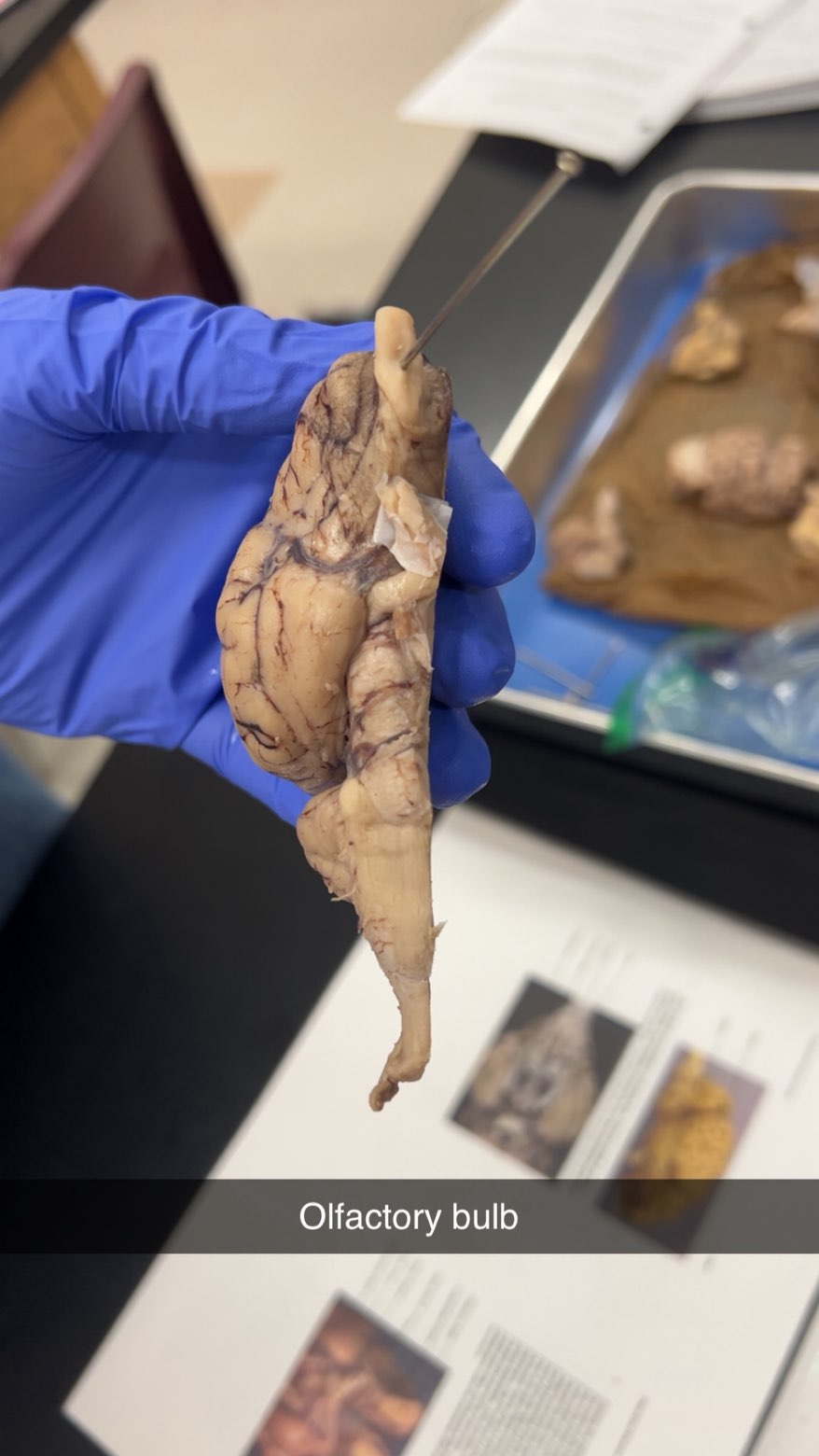
olfactory bulb
sense of smell
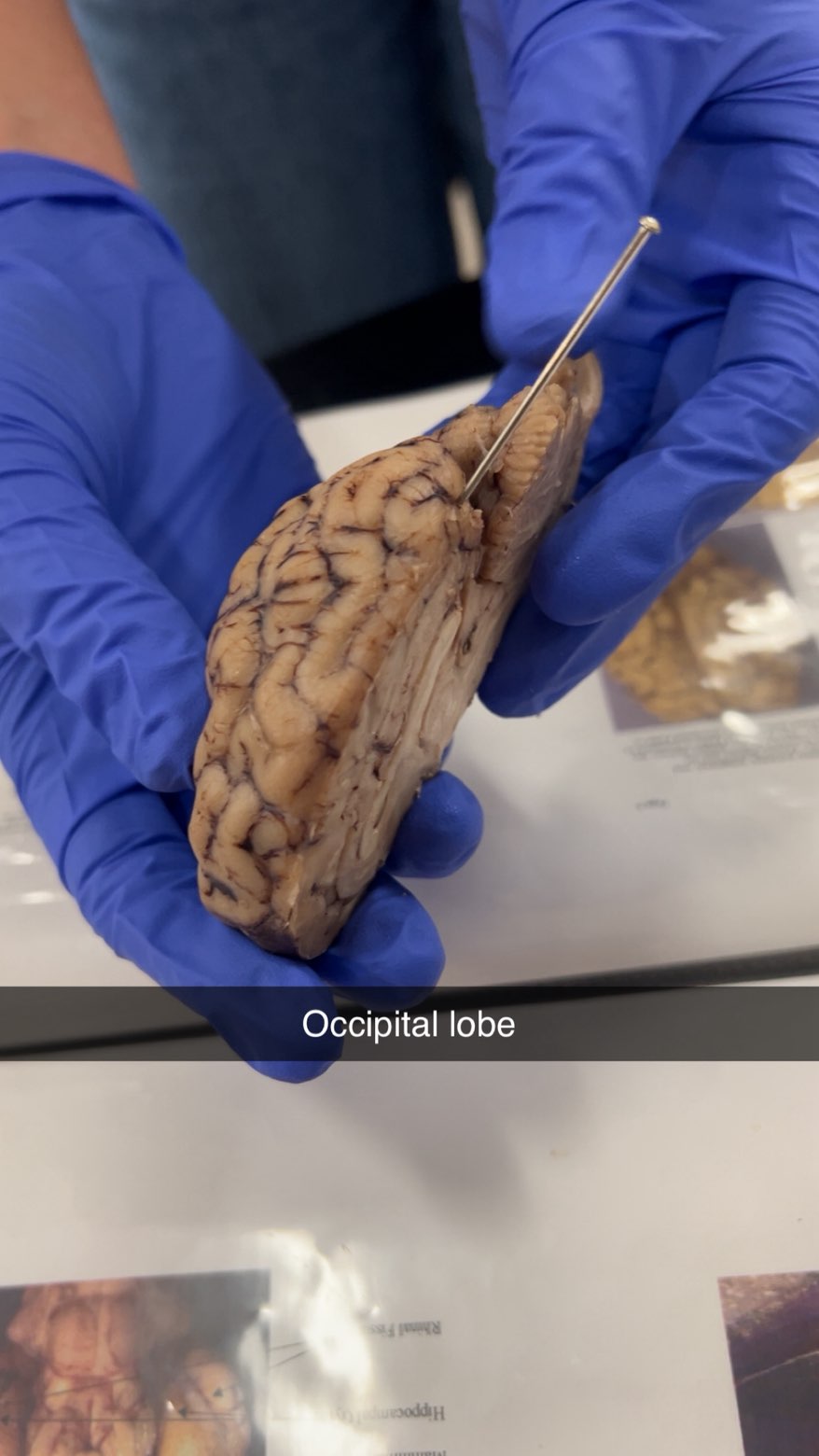
occipital lobe
the brain's visual processing center, located at the back of the skull. It's responsible for interpreting visual information, including sight, color, depth, and motion, and is home to the primary visual cortex, which receives signals from the eyes. Damage to this lobe can lead to a variety of visual impairments, such as vision loss in specific parts of the visual field or an inability to recognize objects
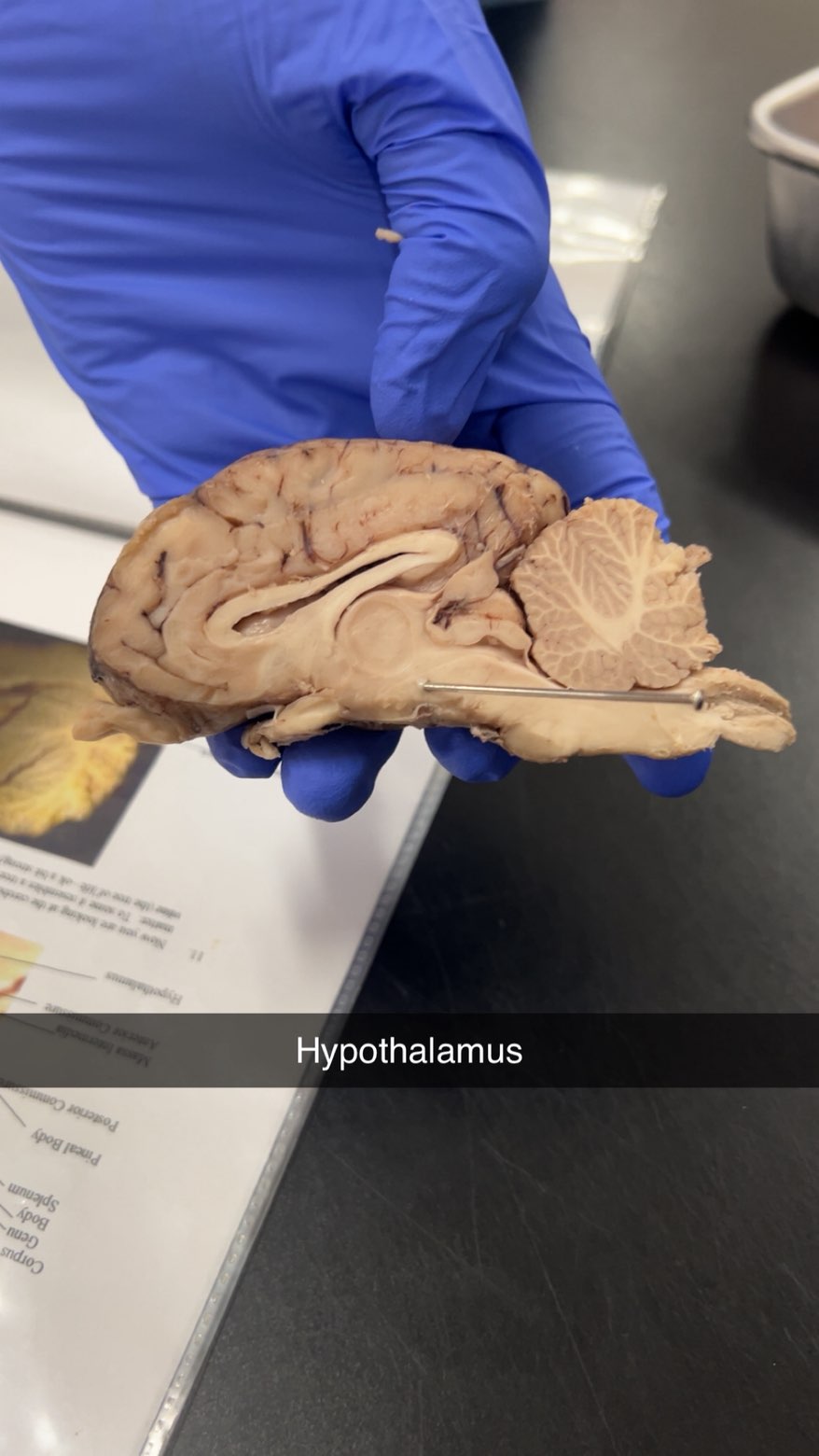
hypothalamus
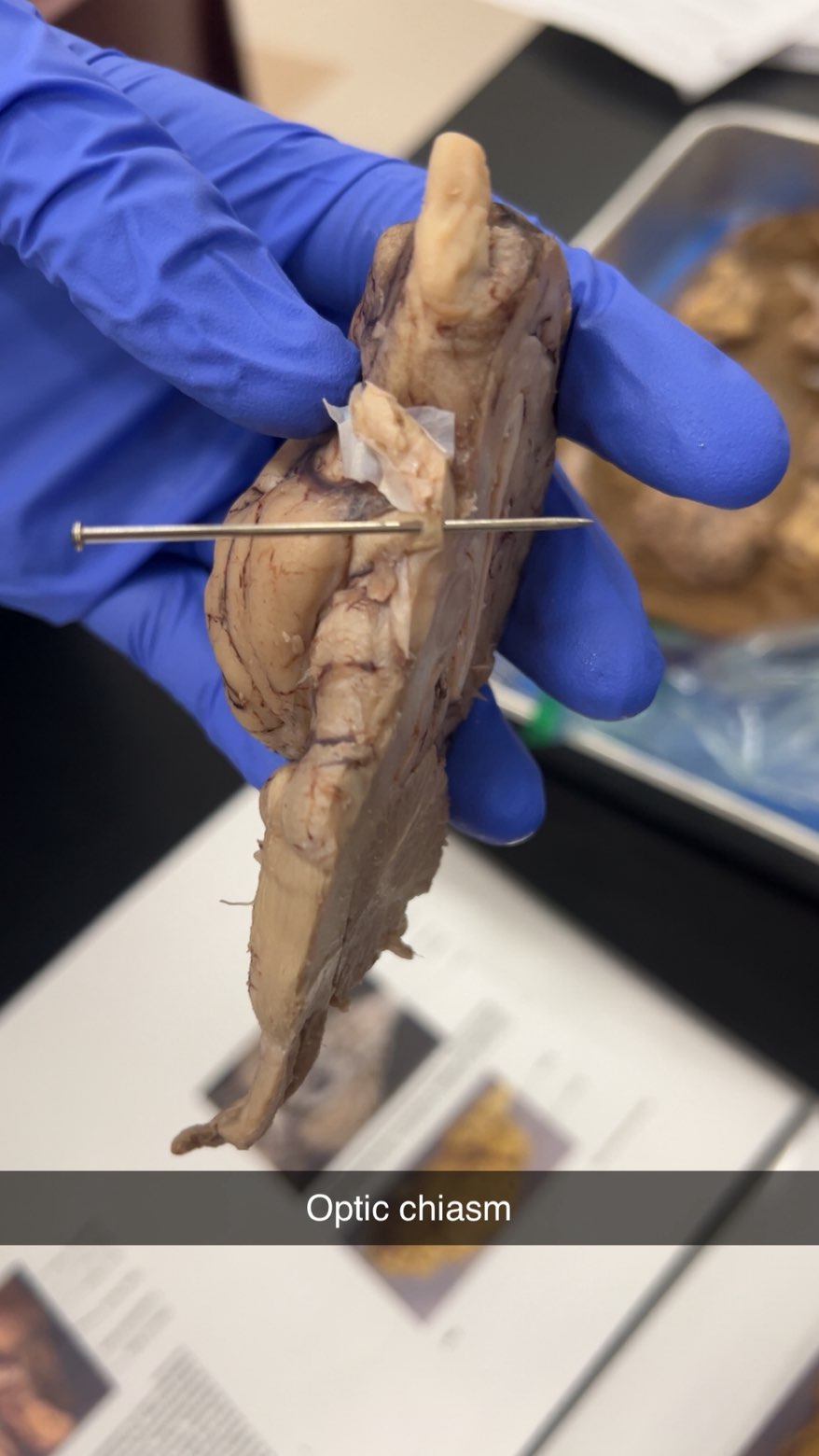
optic chiasm
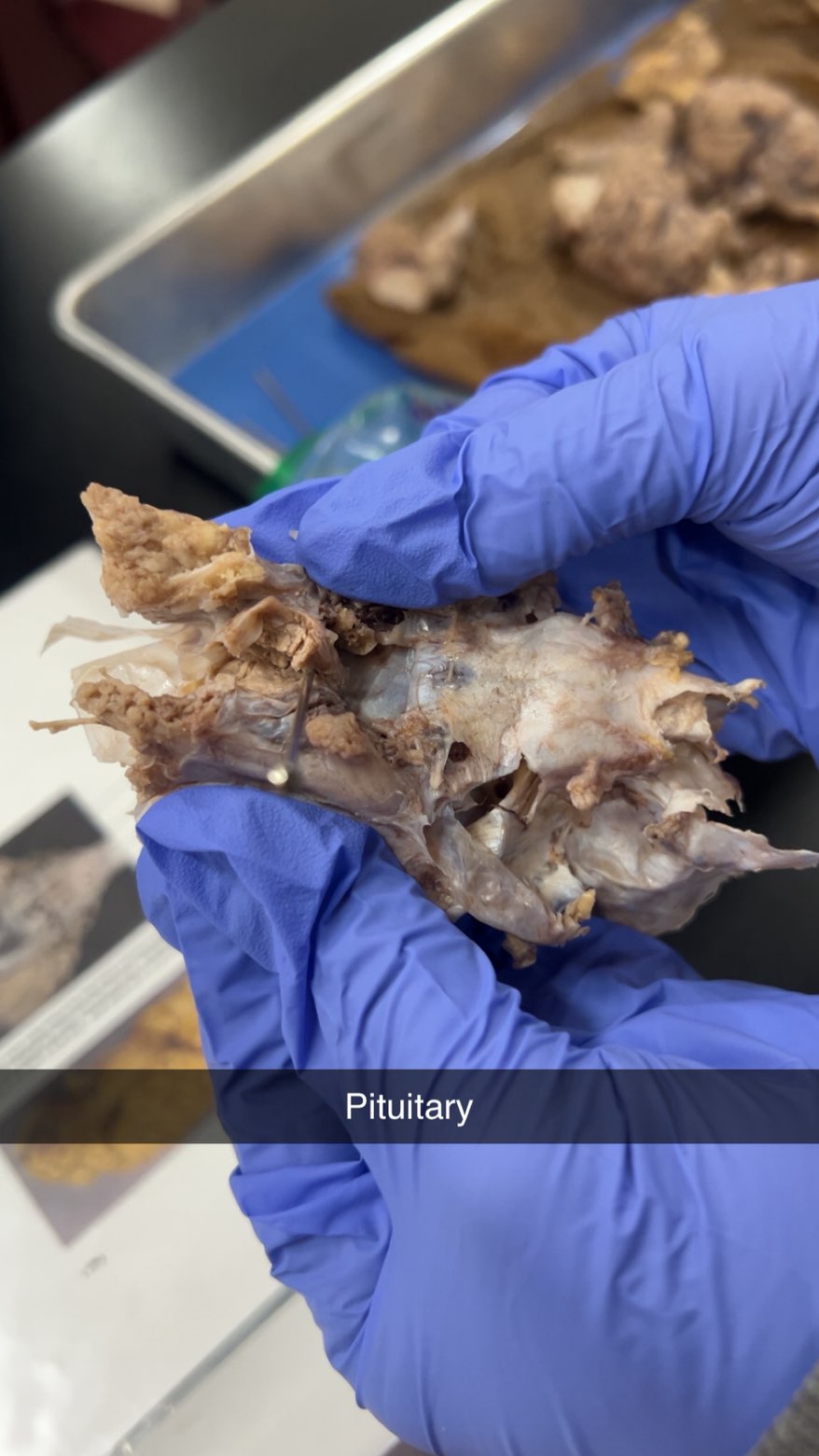
pituitary gland
pituitary is important in controlling growth and development and the functioning of the other endocrine glands.
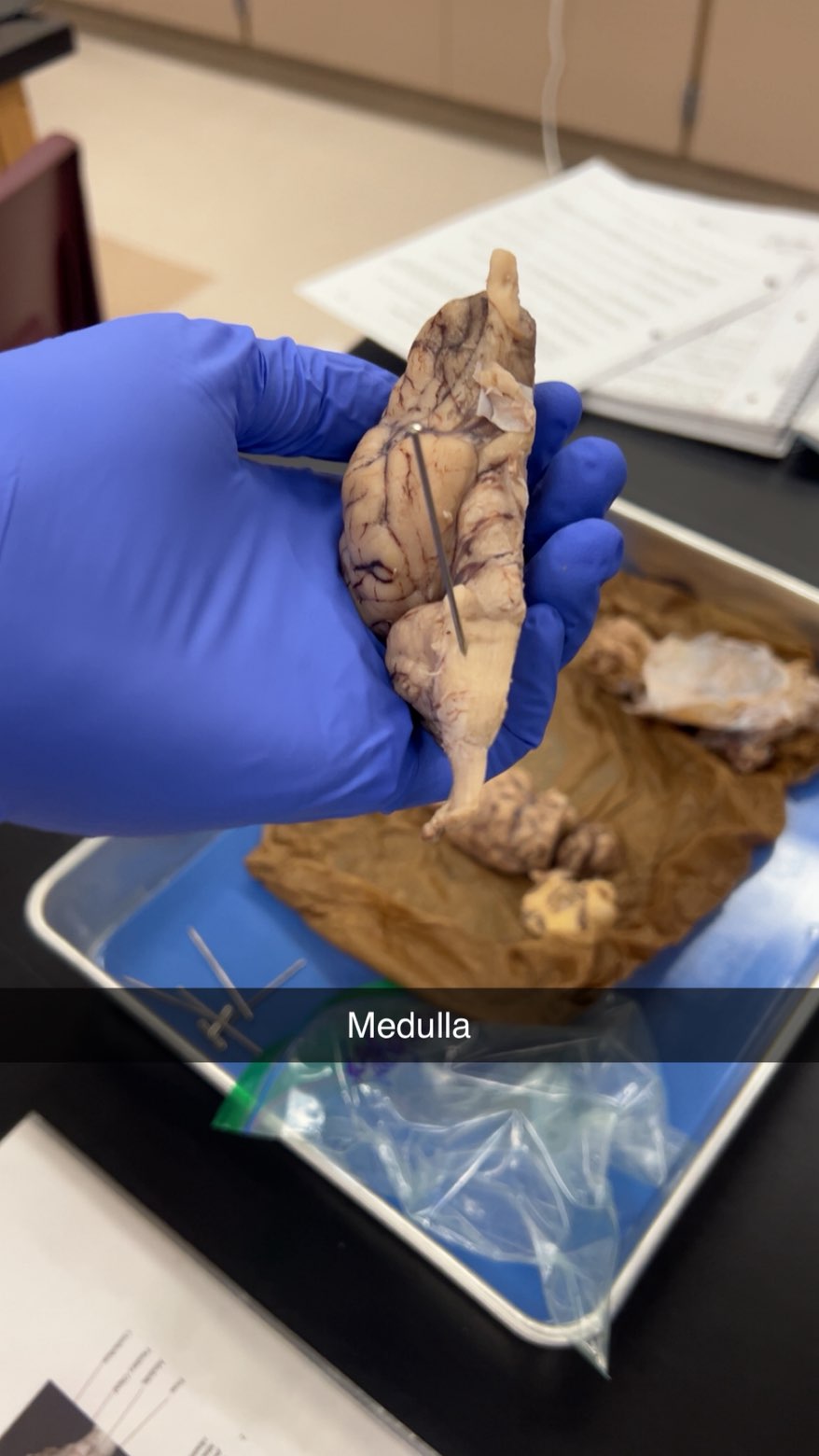
medulla
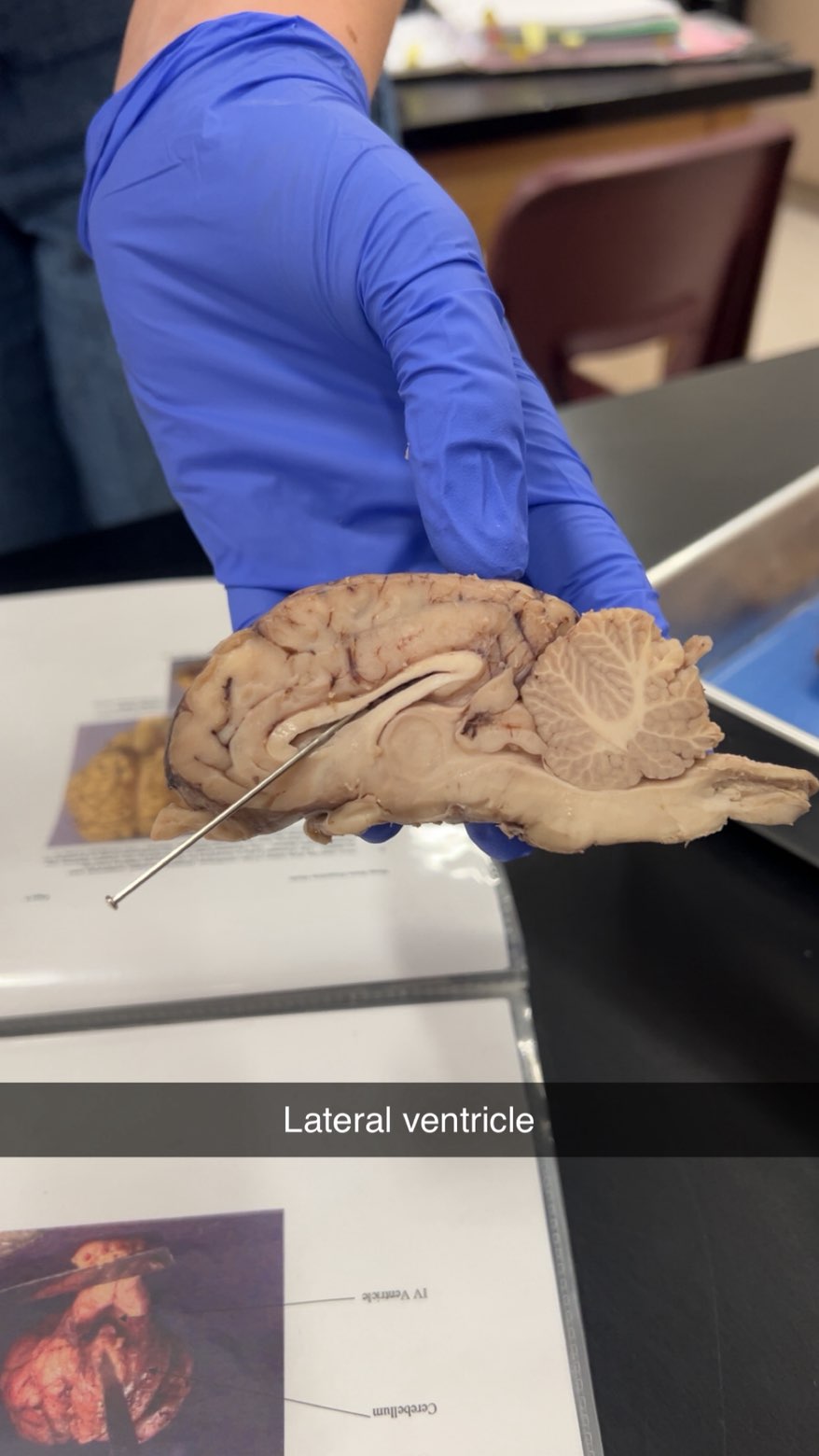
lateral ventricle
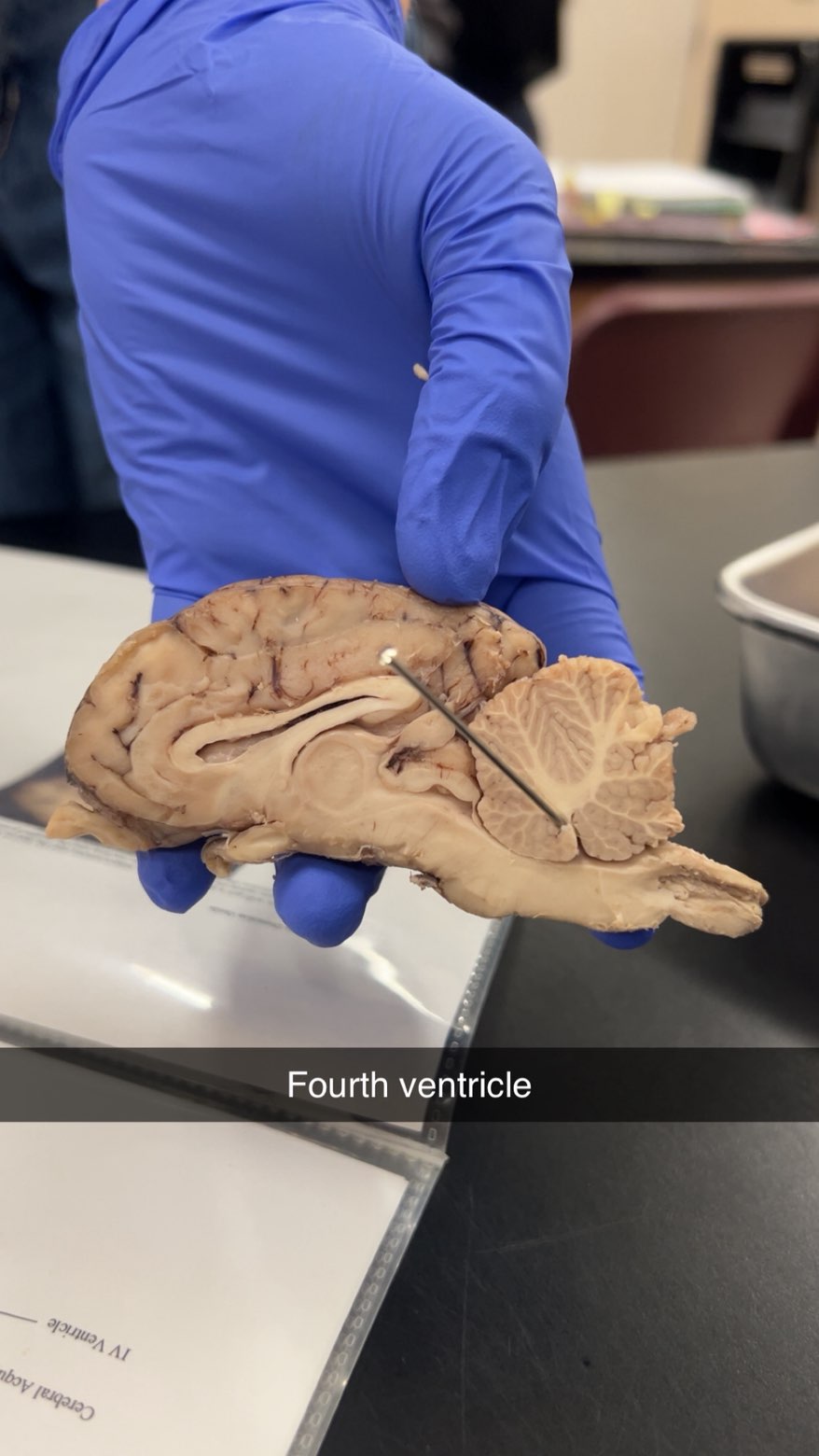
4th ventricle
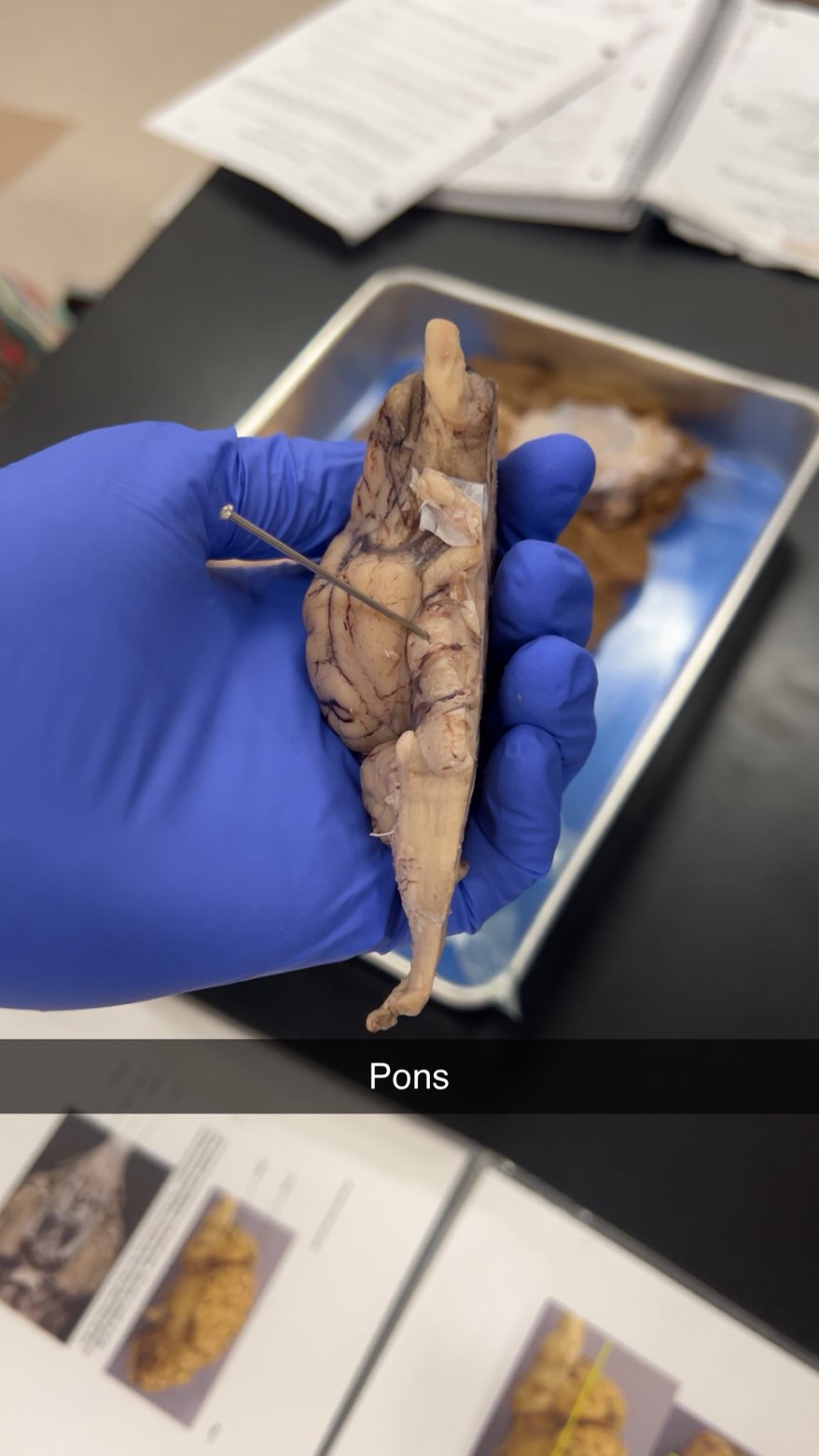
pons
bridge-like structure vital for functions including regulating breathing, relaying signals between the cerebrum and cerebellum, and processing sensory information like pain and touch
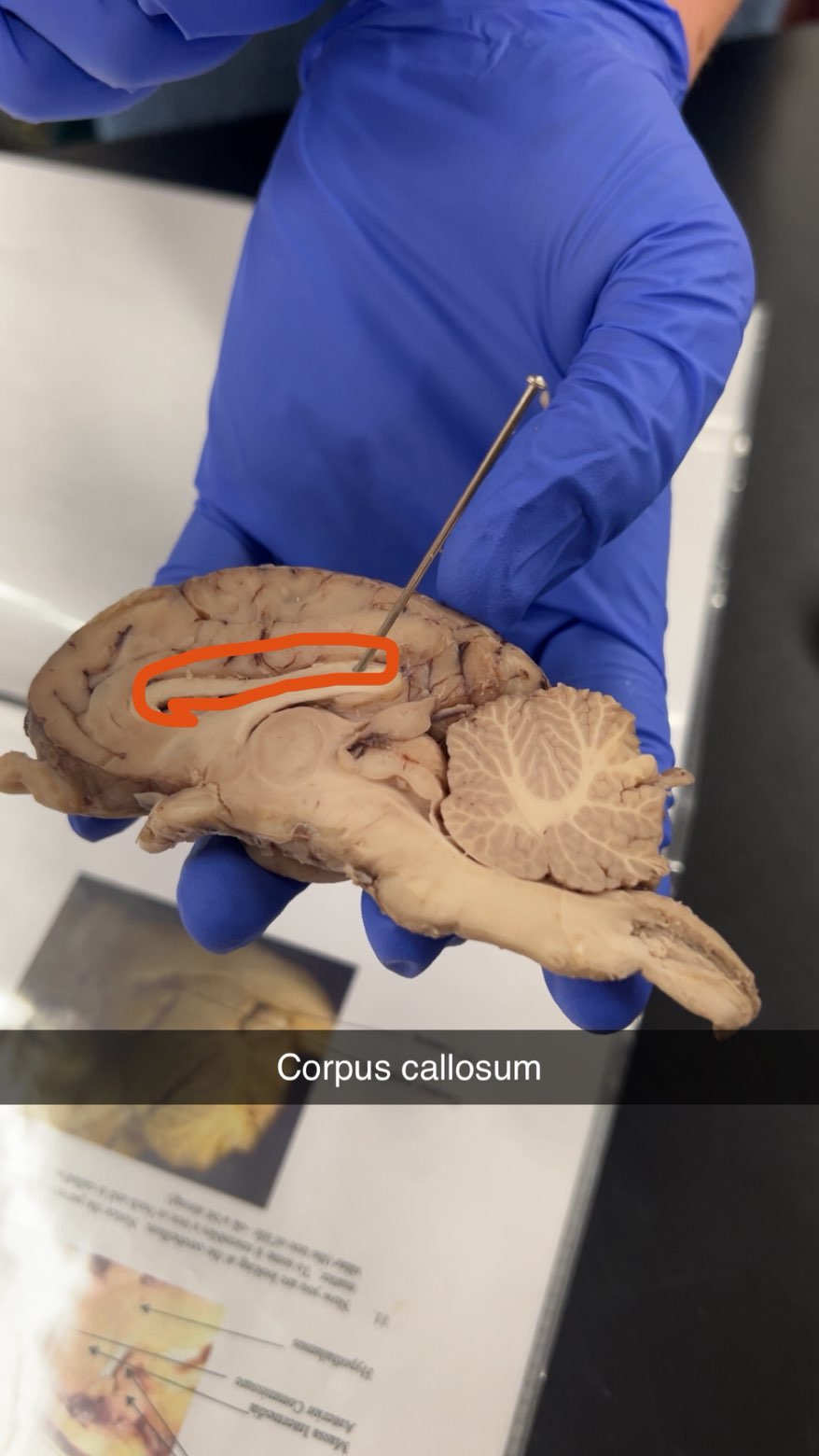
corpus callosum
connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, allowing them to communicate and coordinate functions
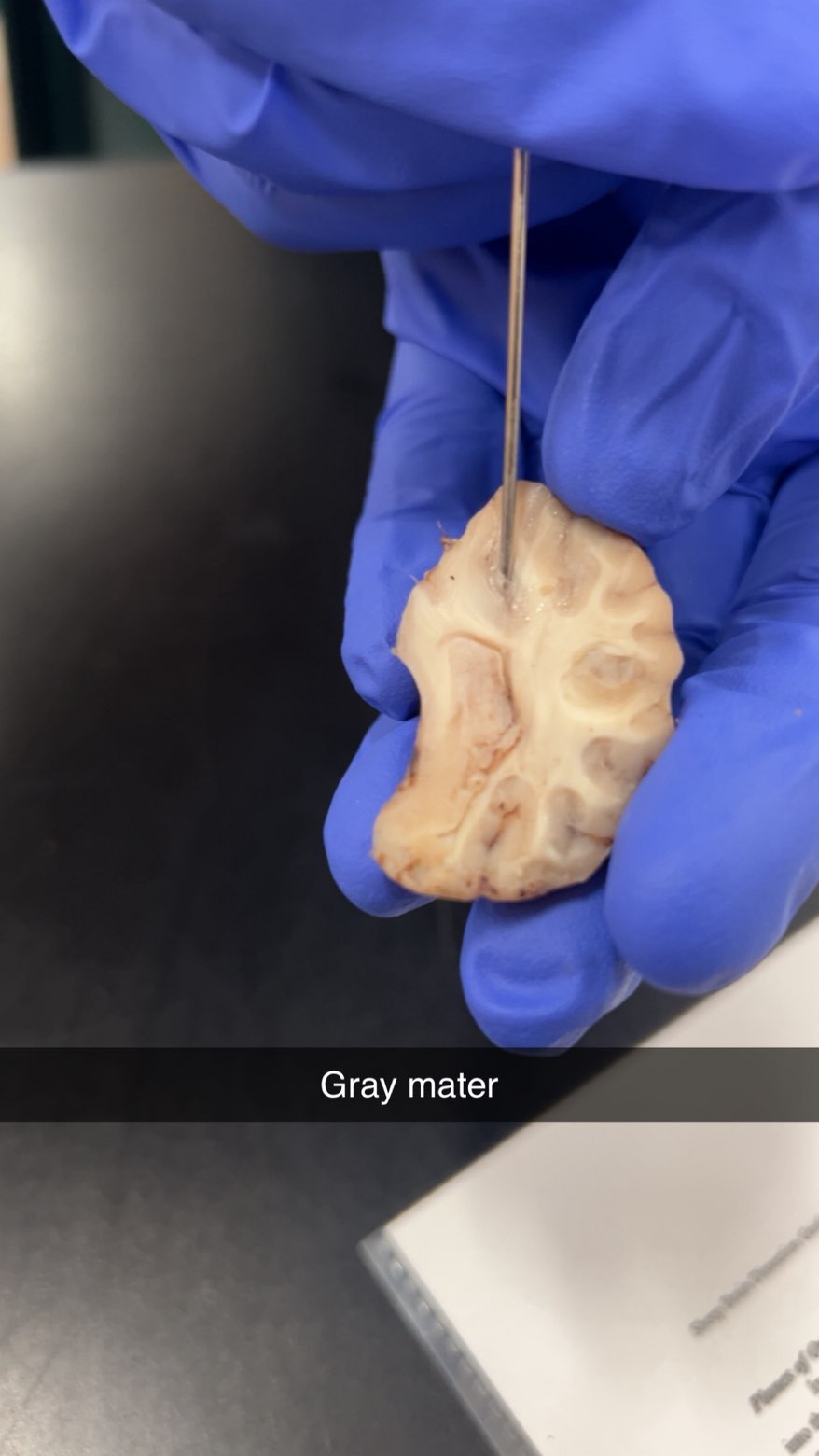
gray matter
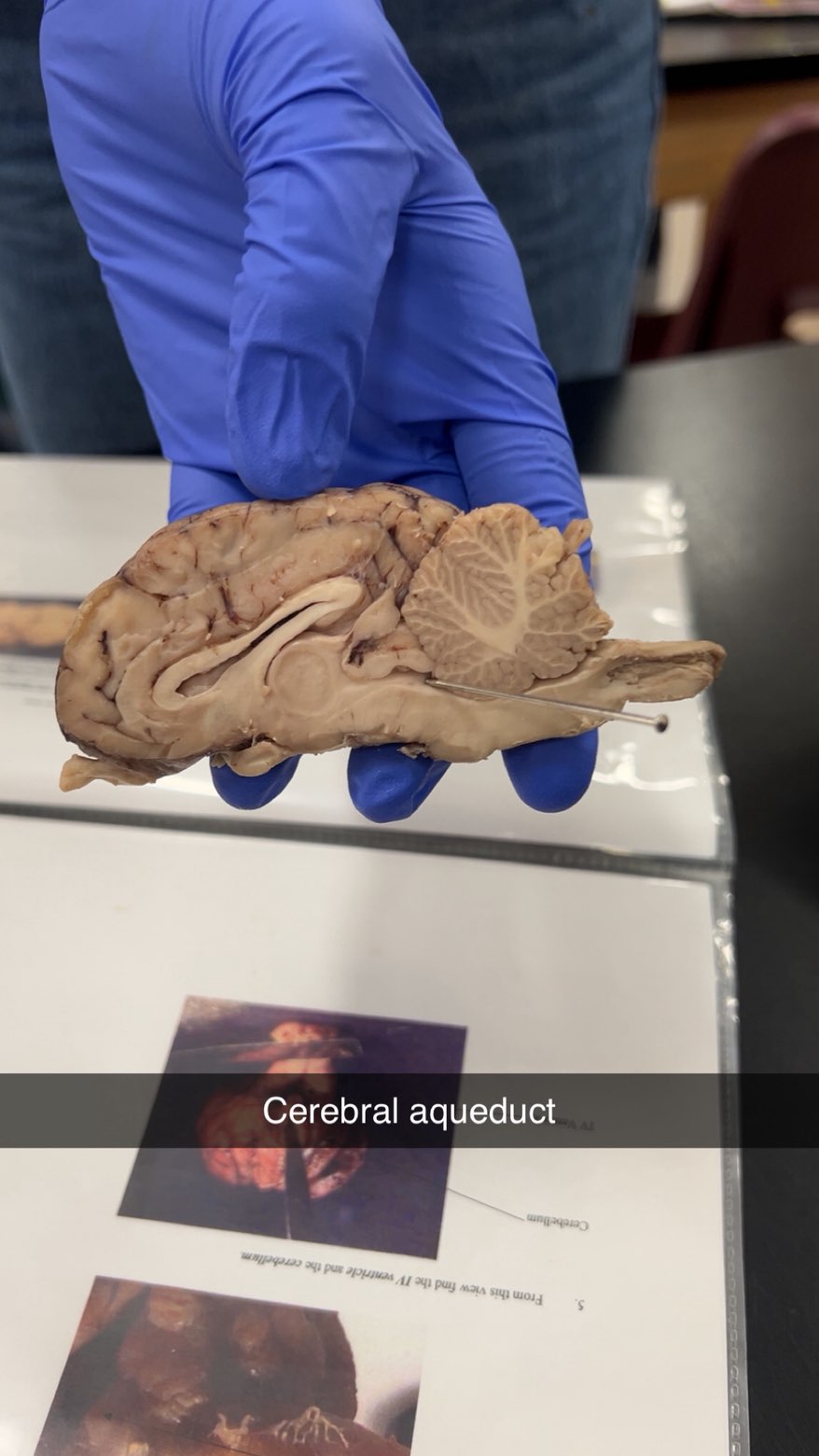
cerebral aqueduct
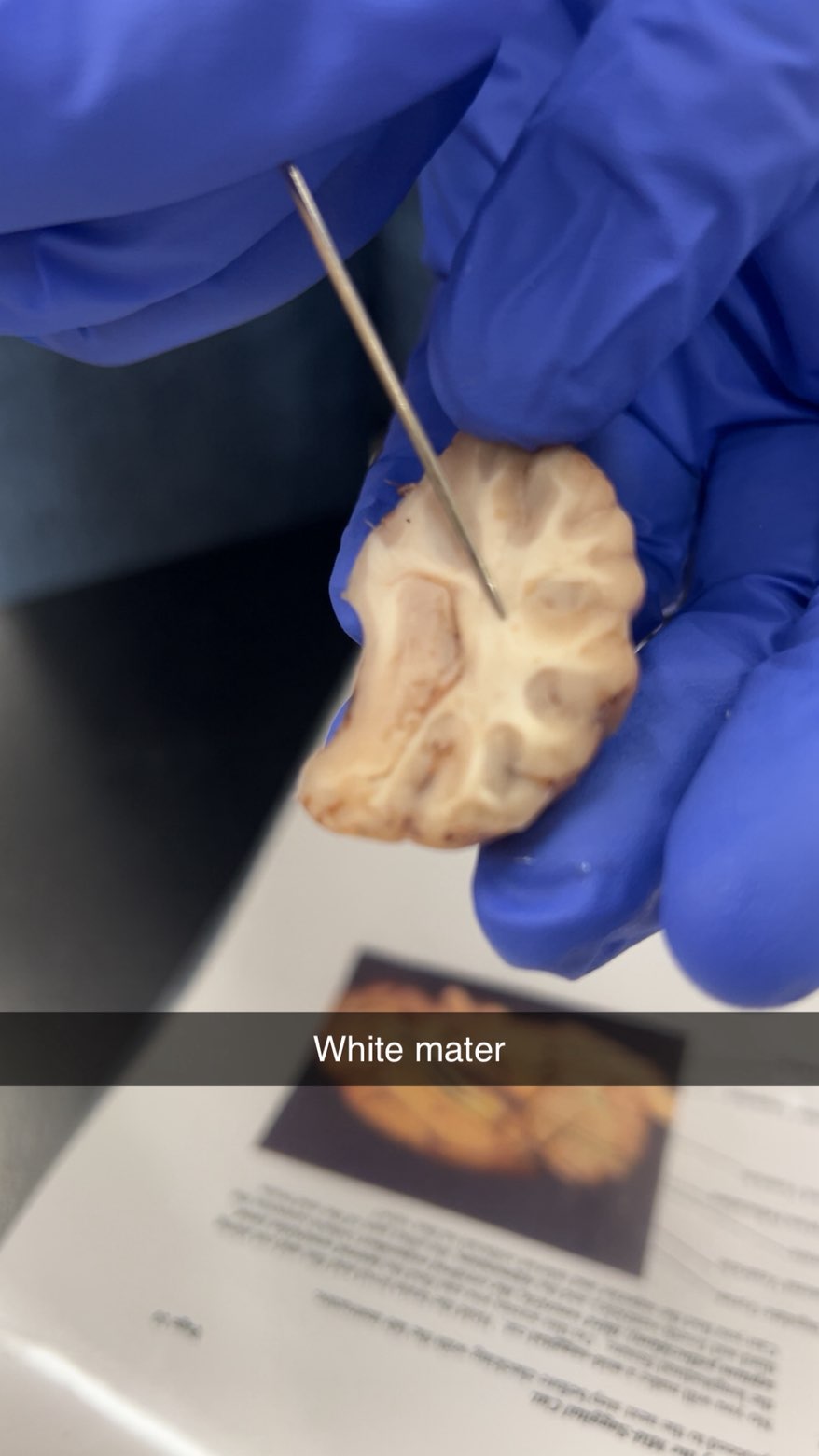
white matter
the nerve tissue in the brain and spinal cord that contains nerve fibers covered in a fatty substance called myelin, which gives it its white appearance and speeds up signal transmission
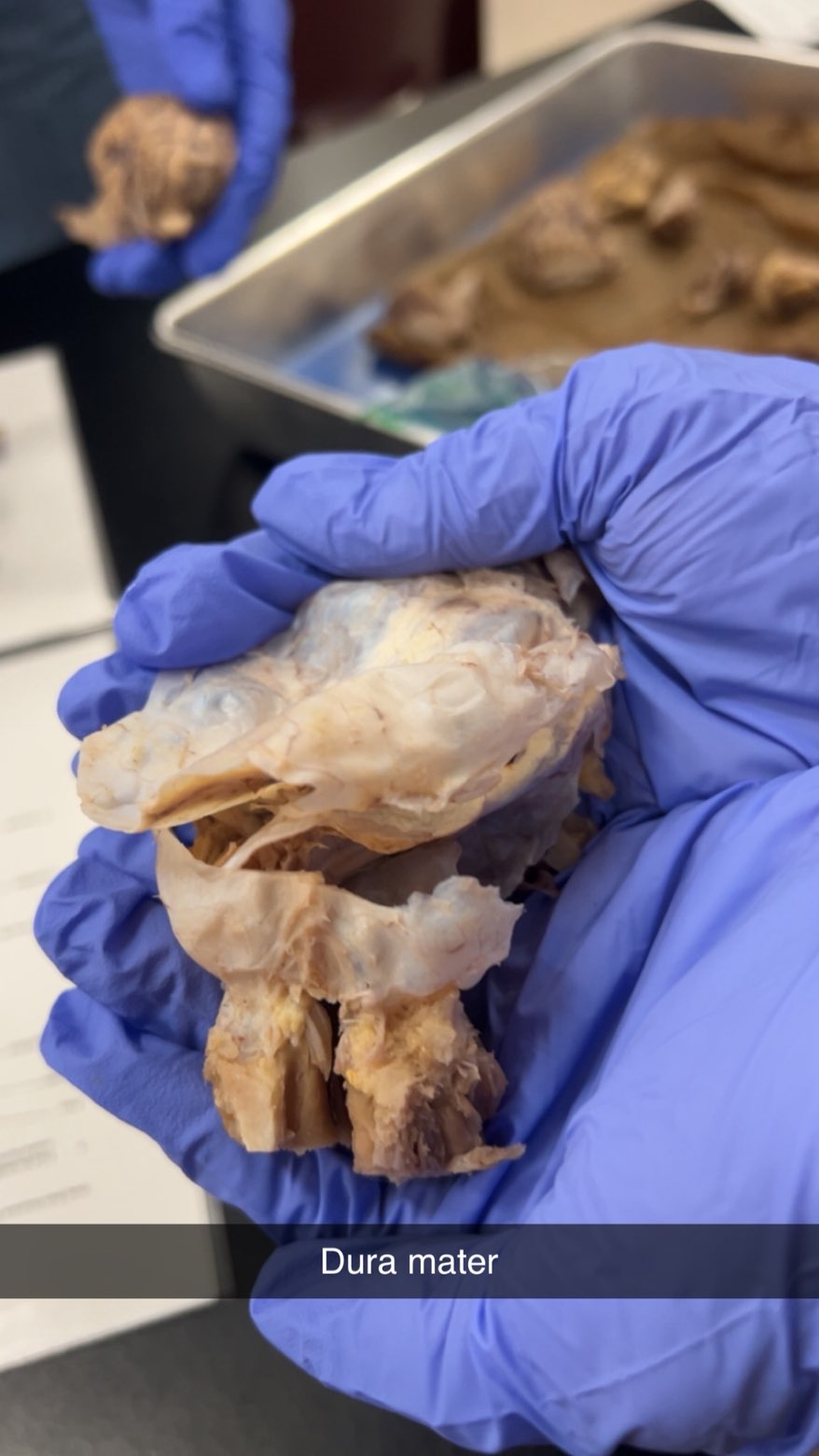
dura mater
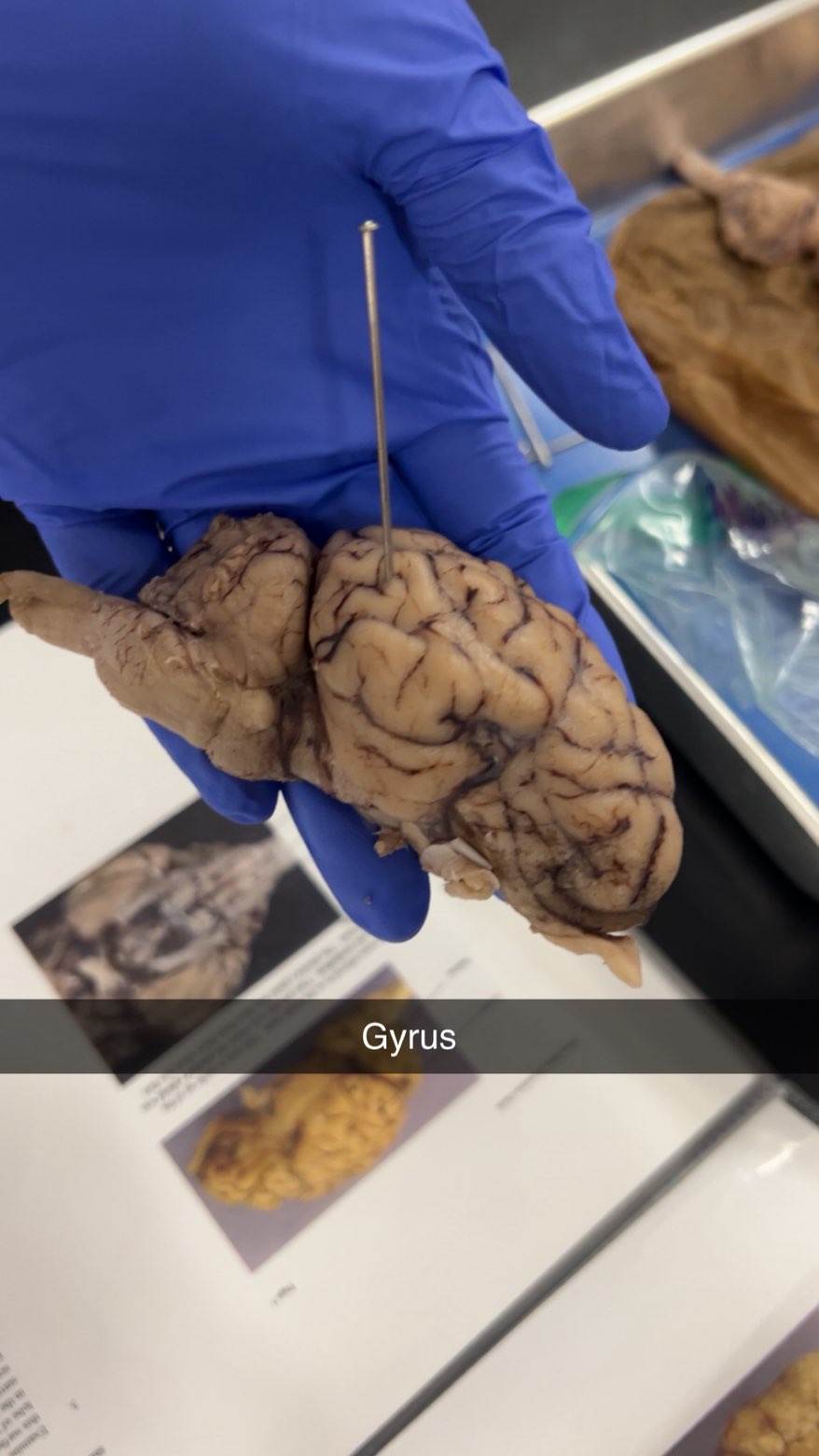
gyrus
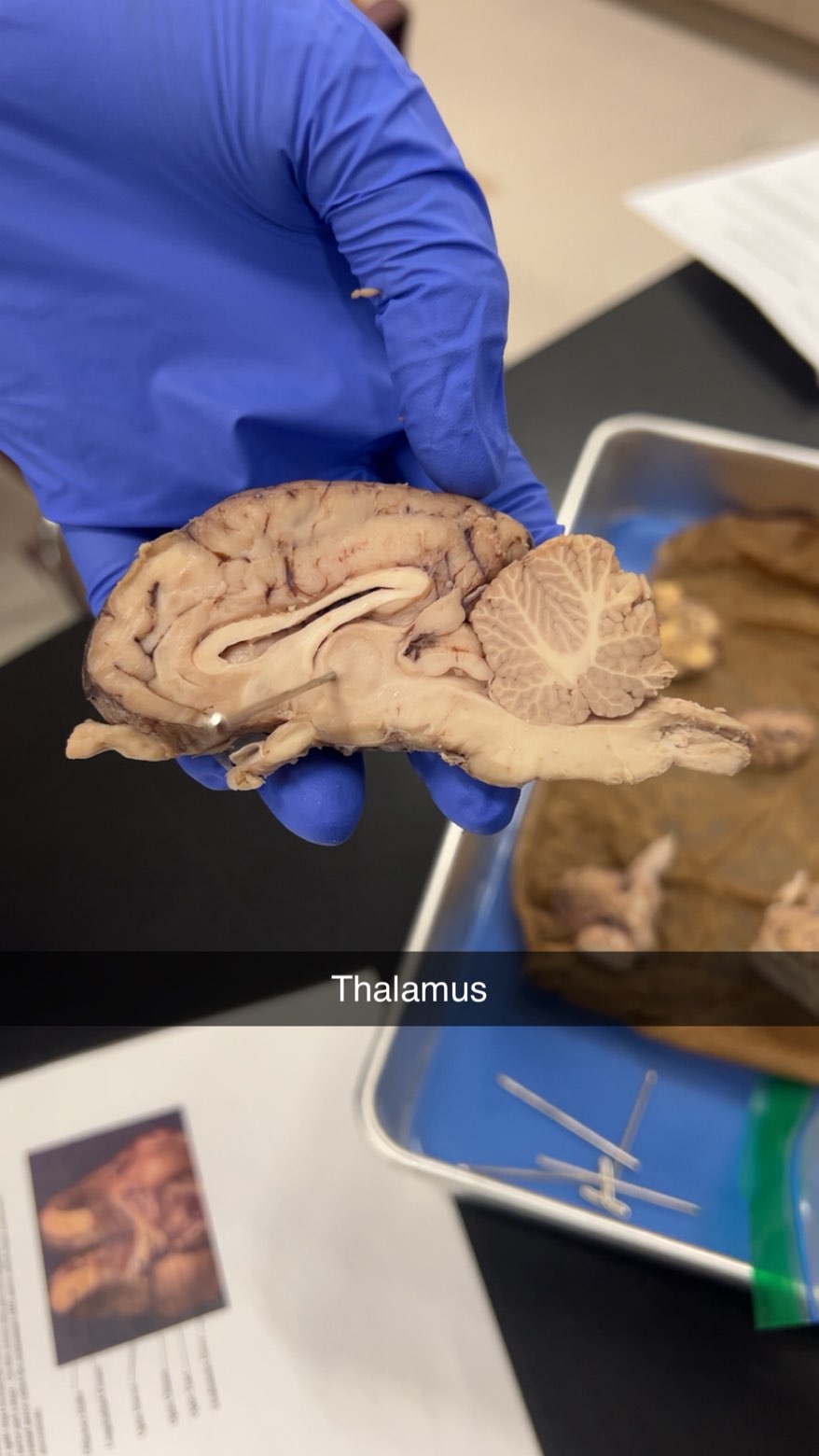
thalamus
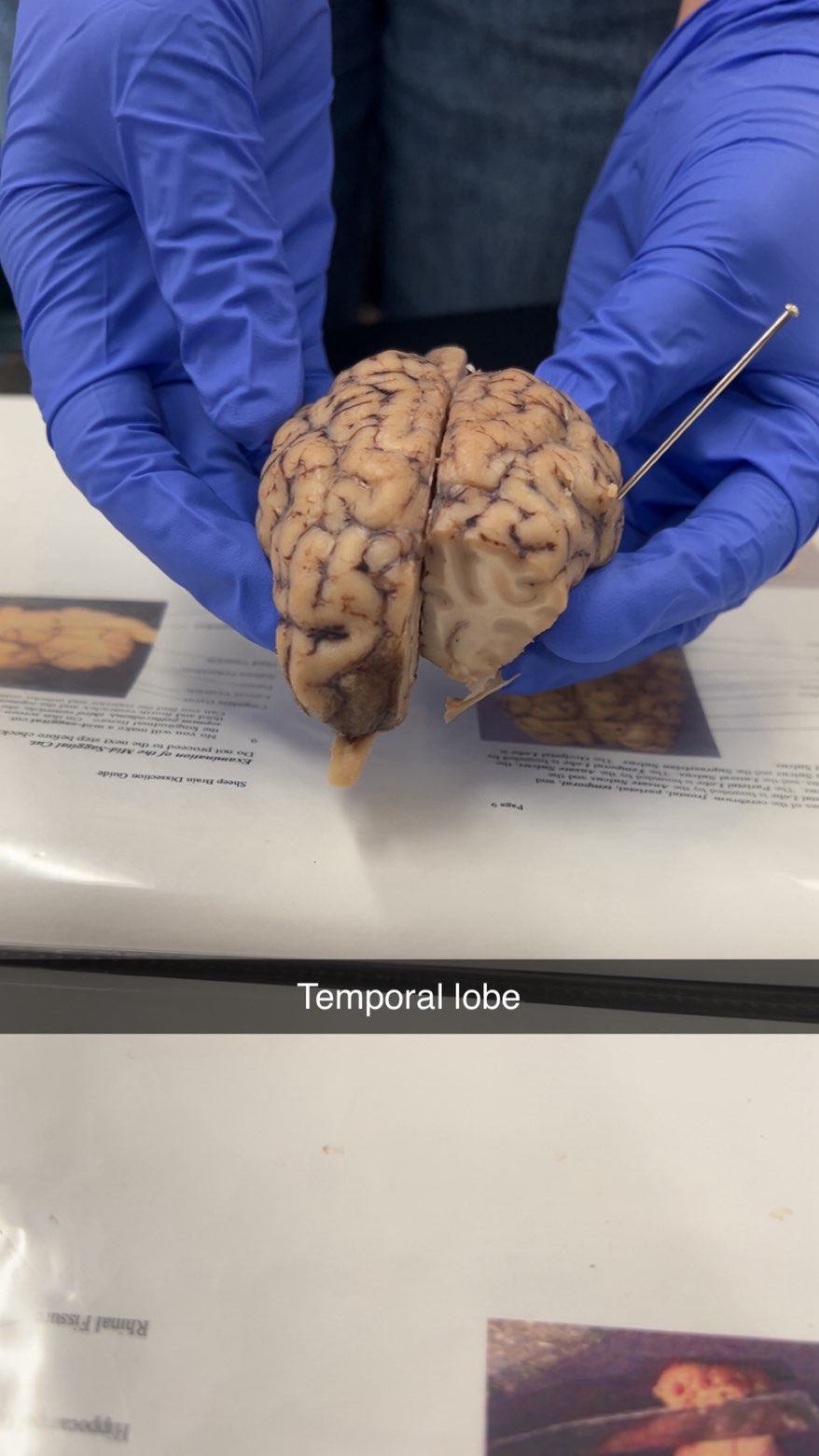
temporal lobe
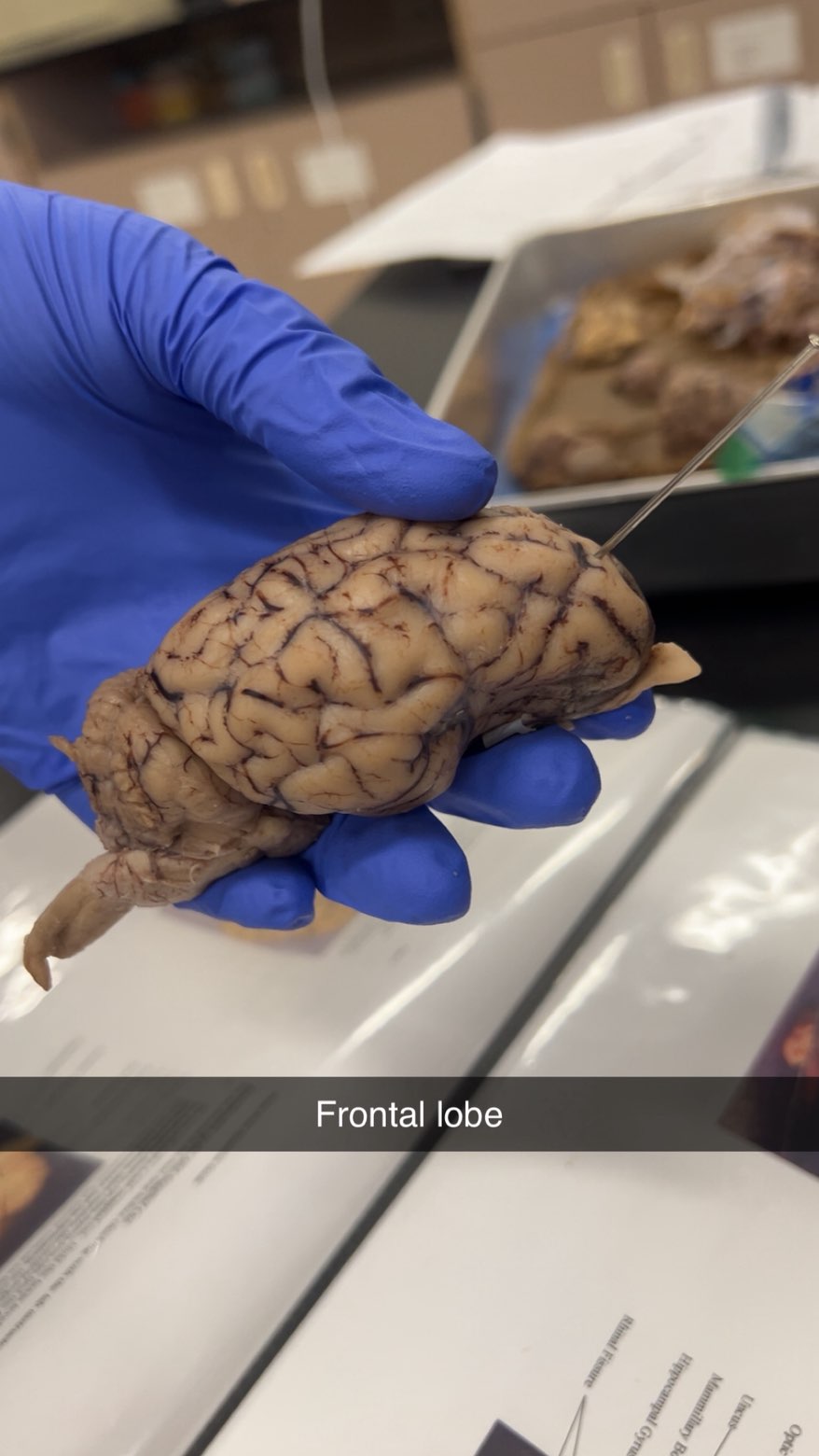
frontal lobe
responsible for higher cognitive functions, including reasoning, problem-solving, and planning.
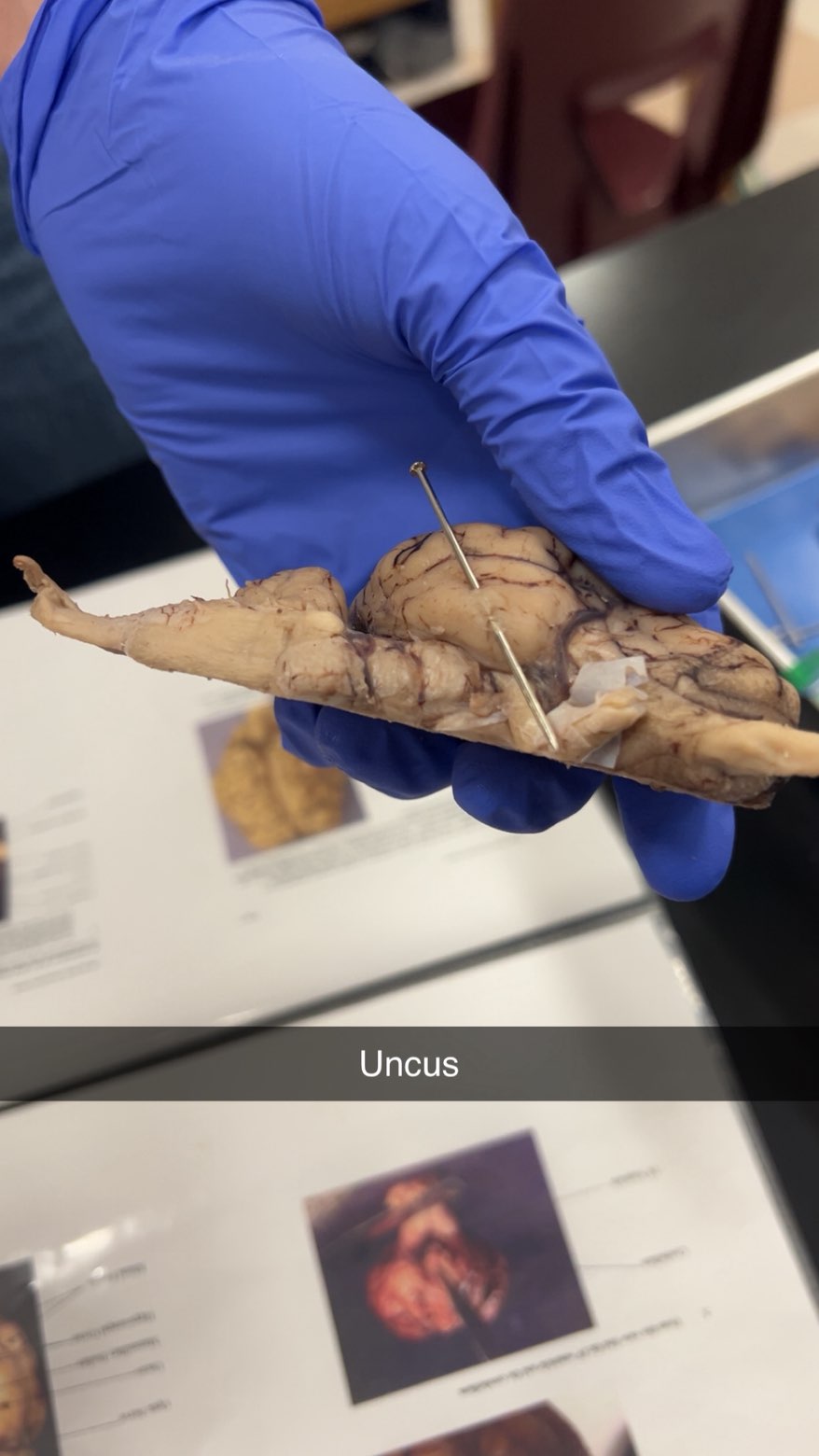
uncus
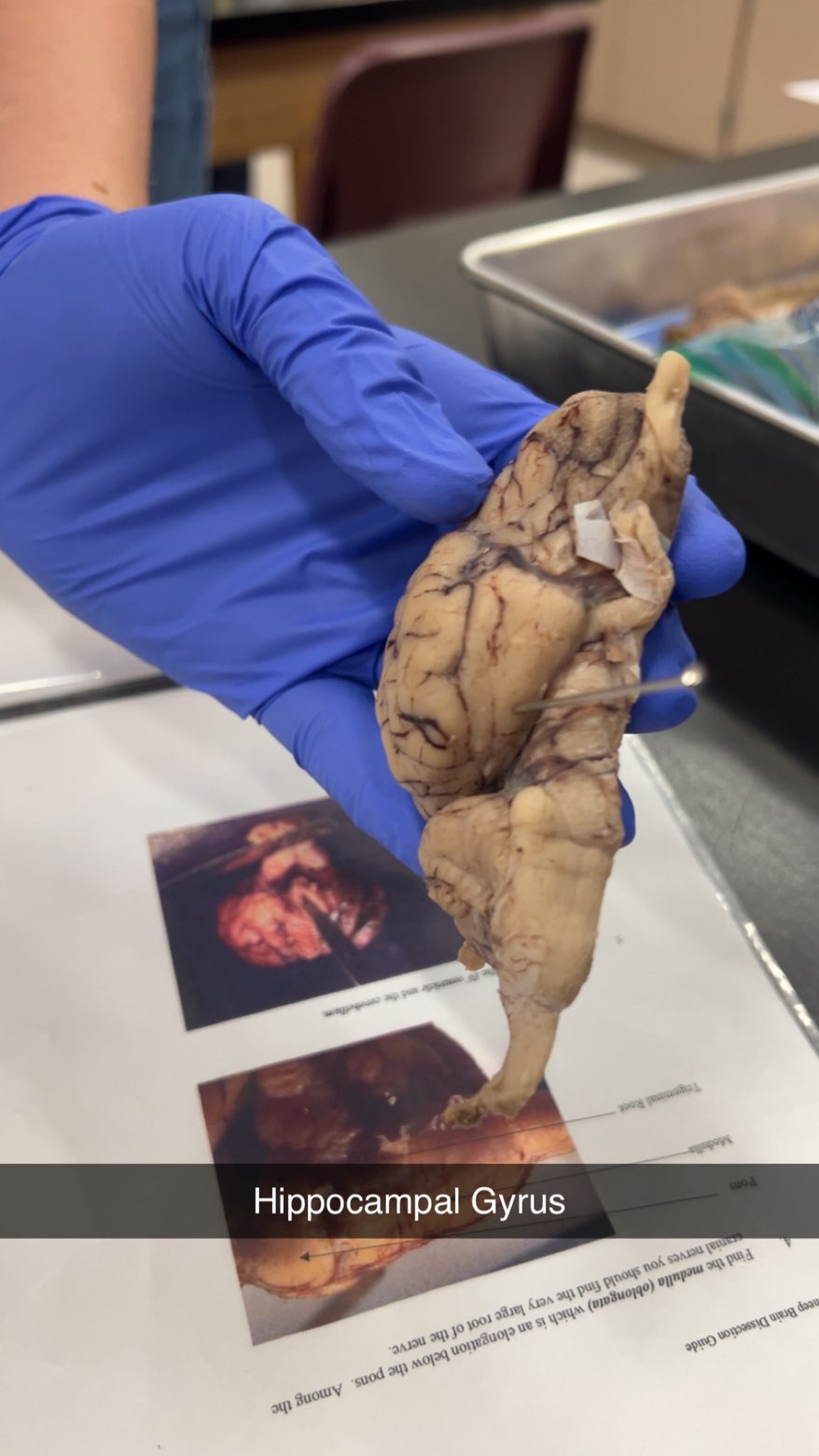
hippocampal gyrus
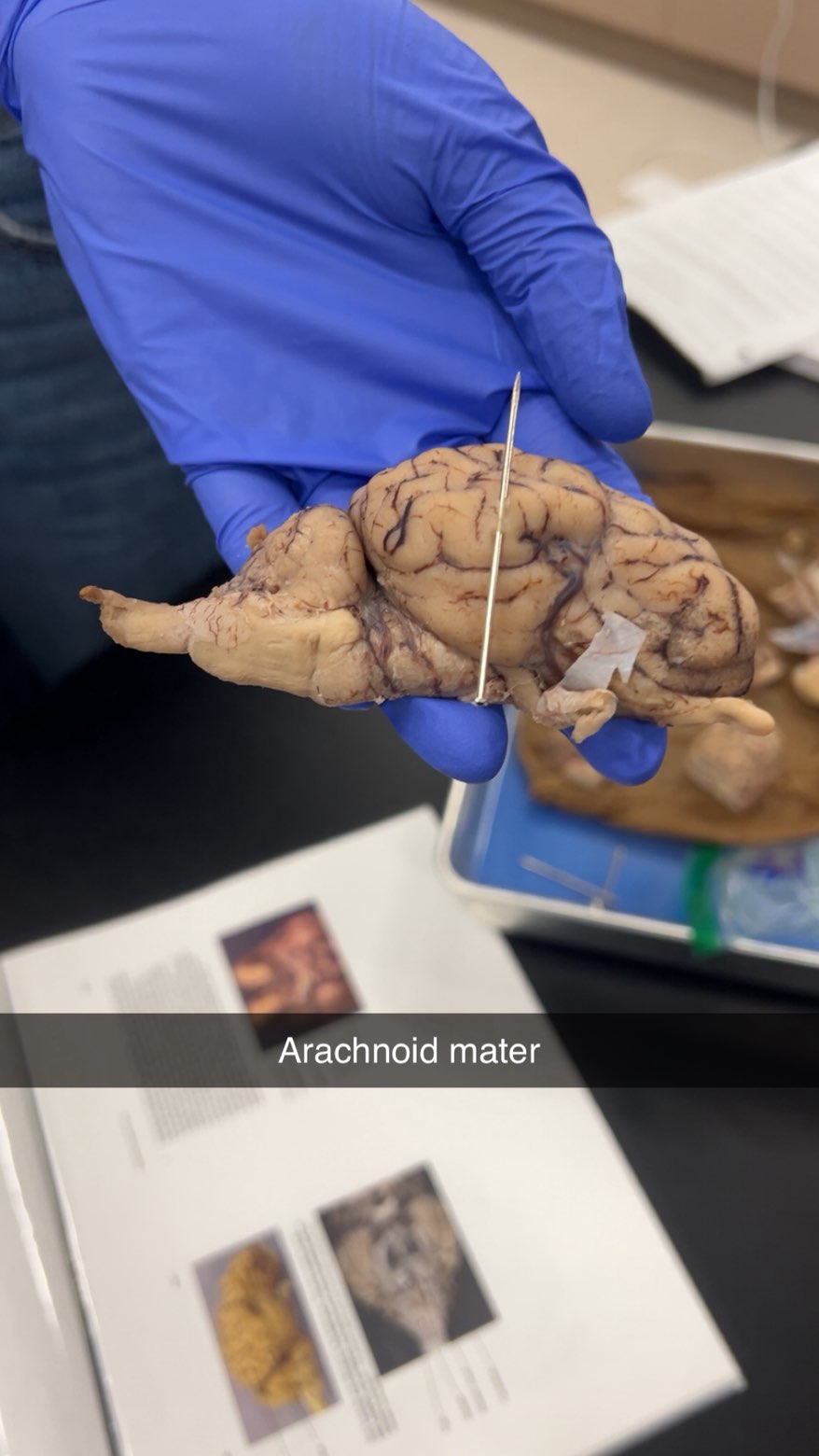
arachnoid mater
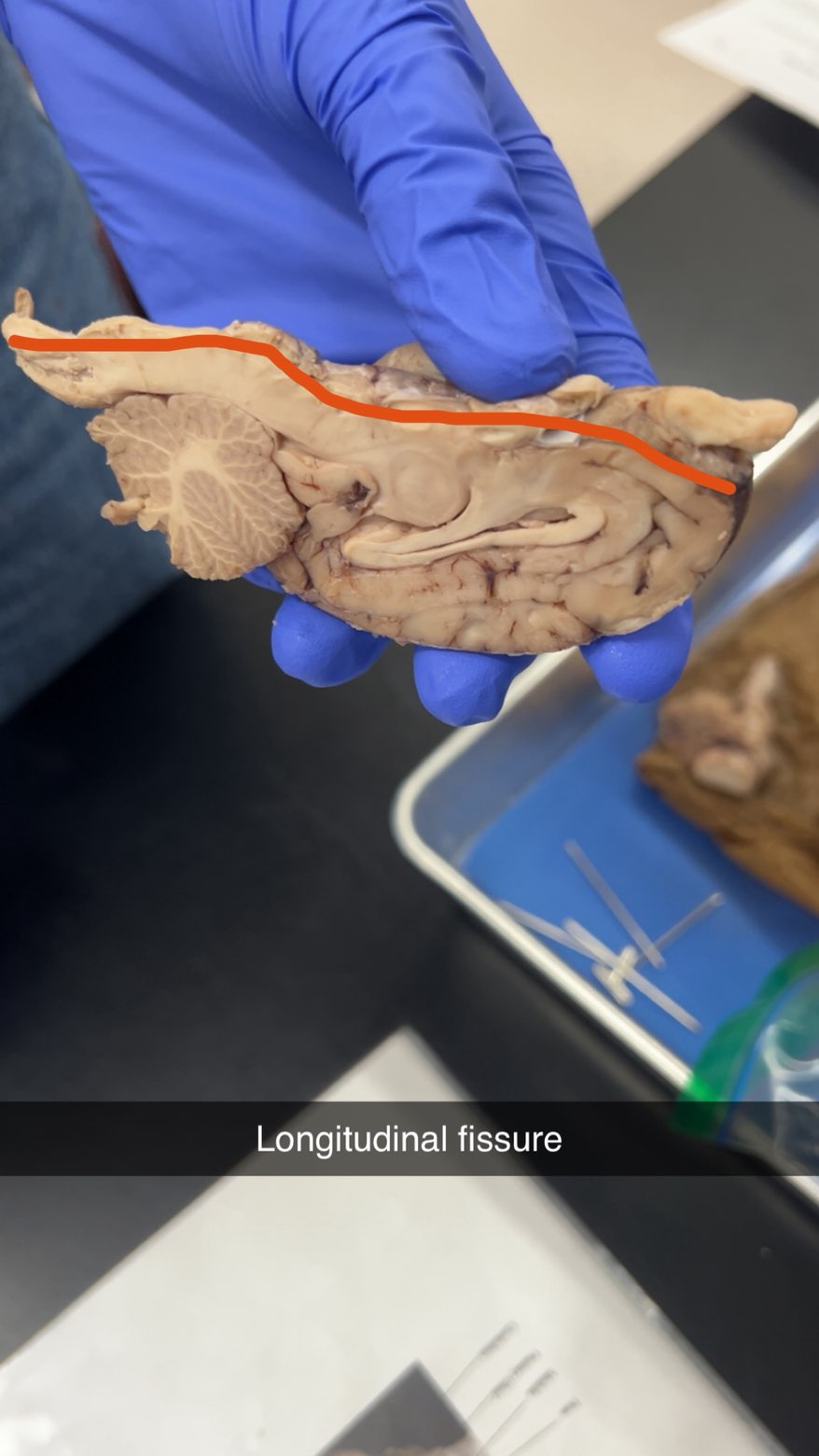
longitudinal fissure
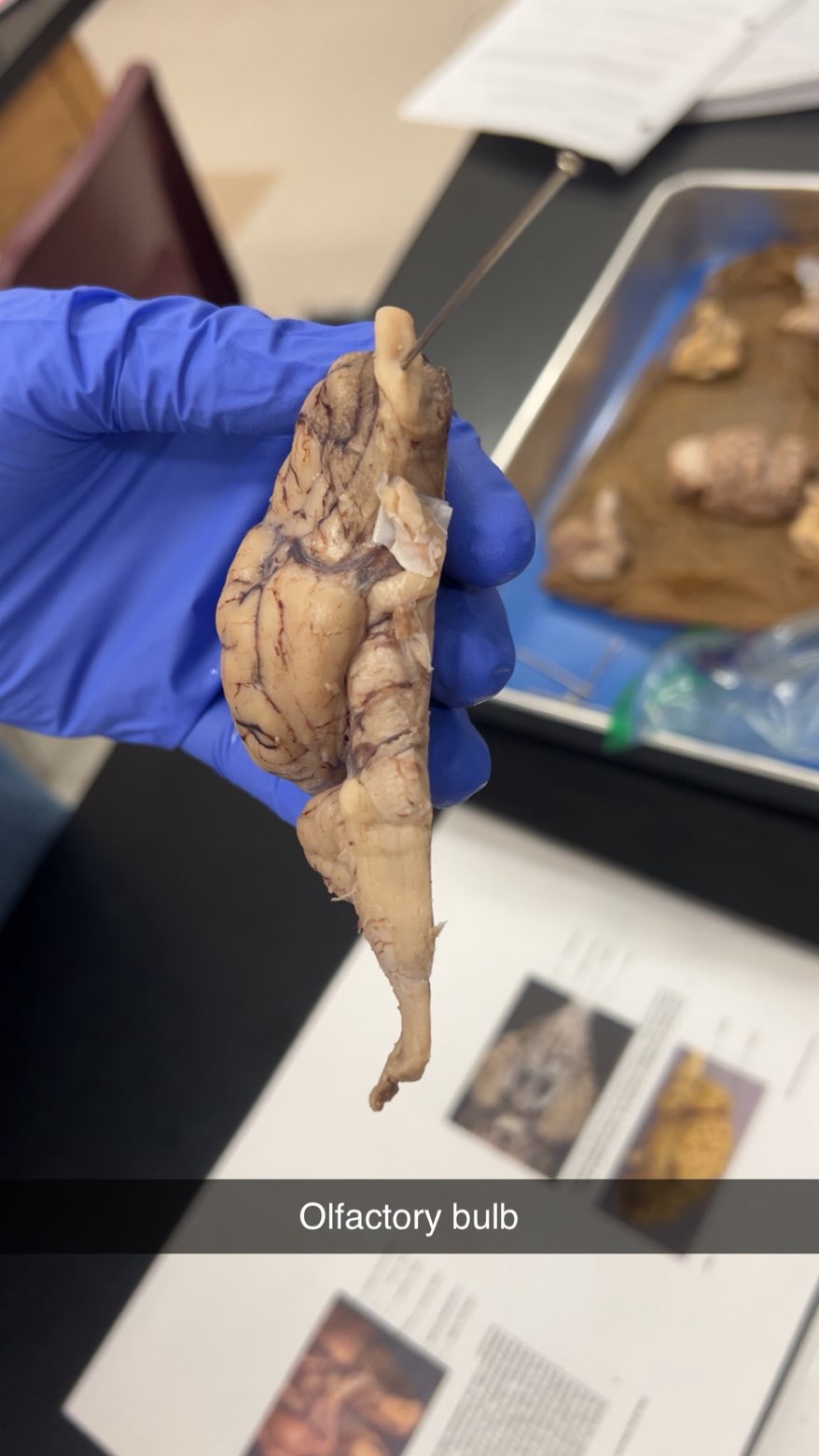
olfactory bulb
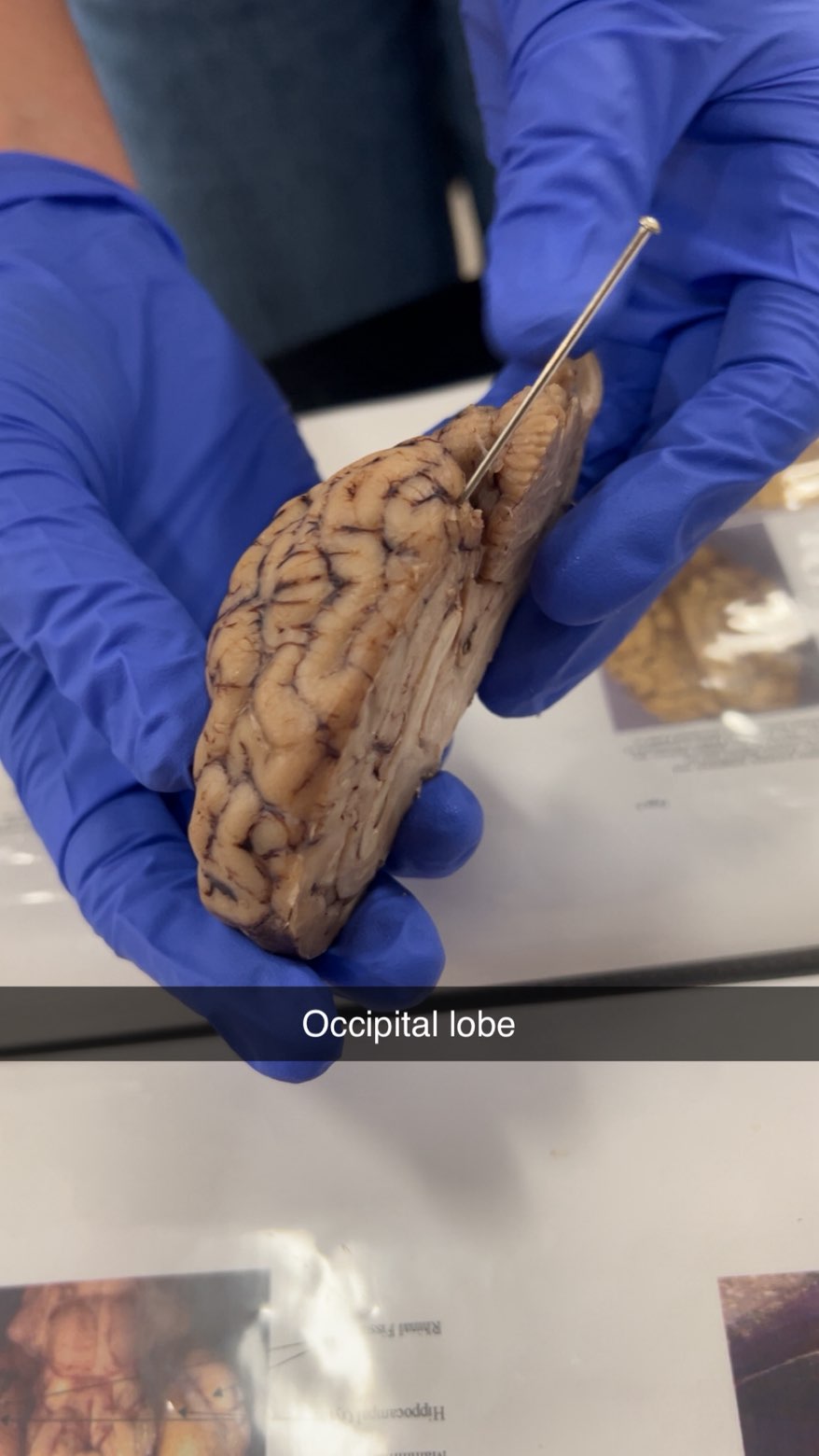
occipital lobe
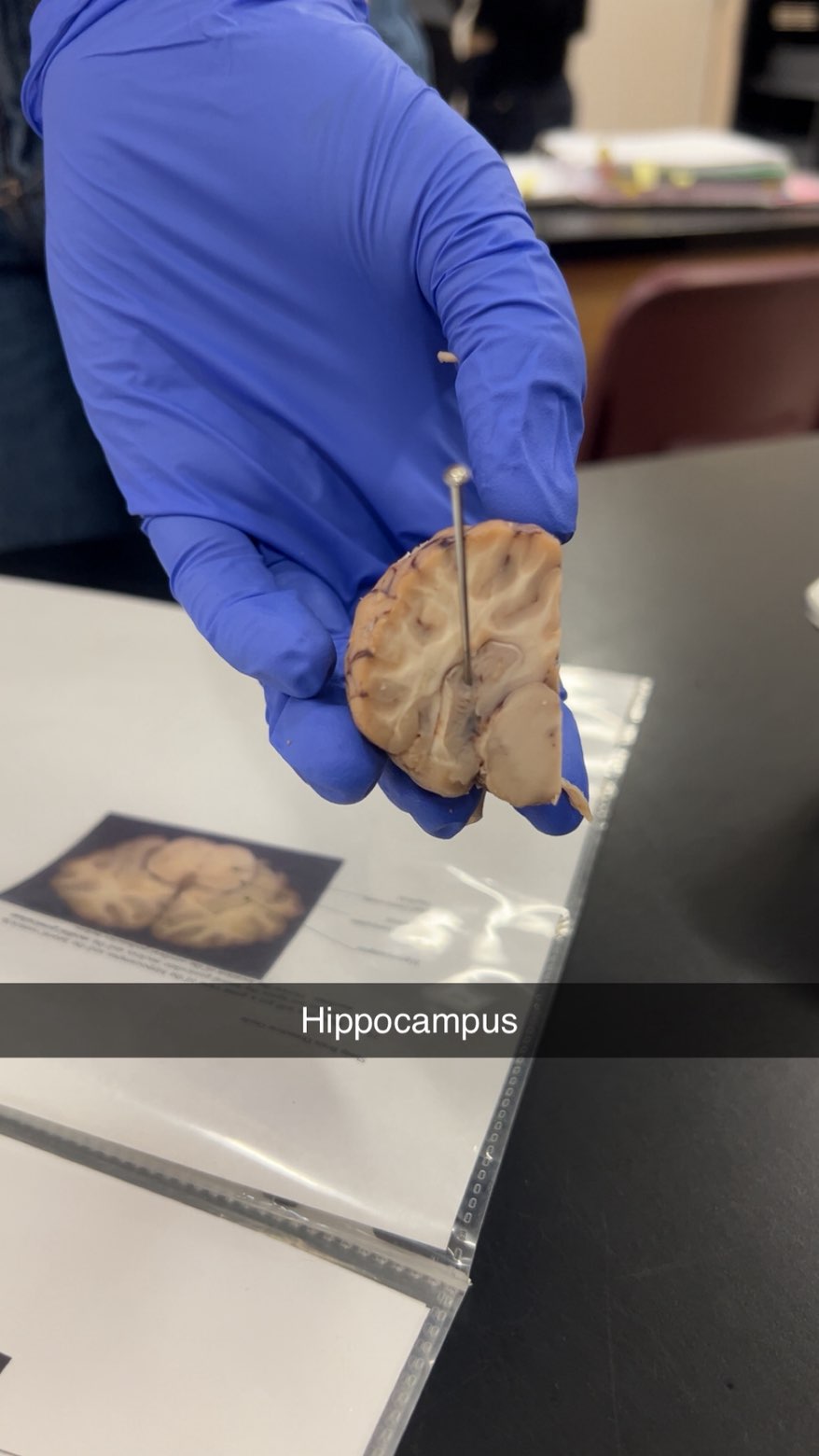
hippocampus
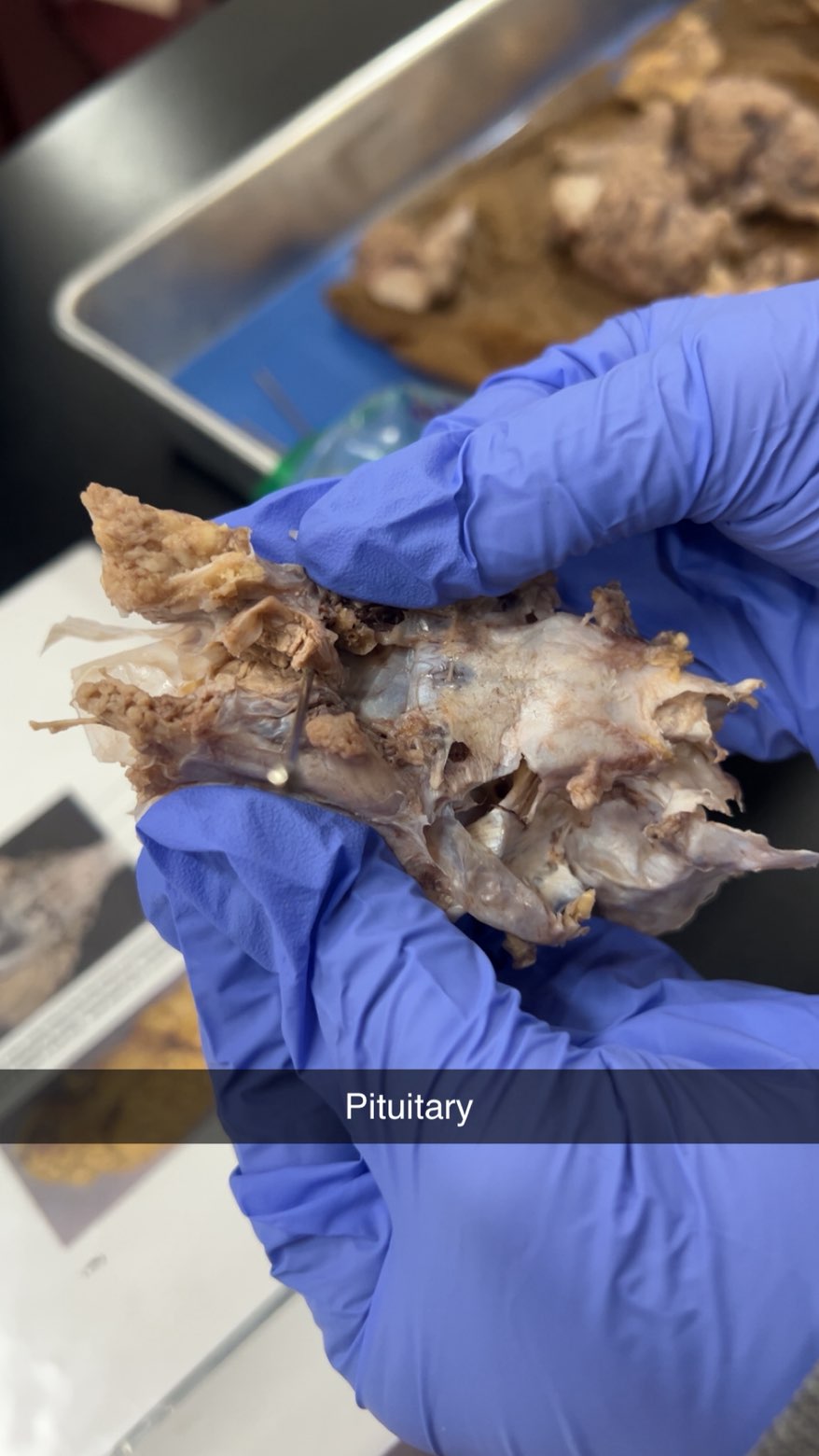
pituitary gland
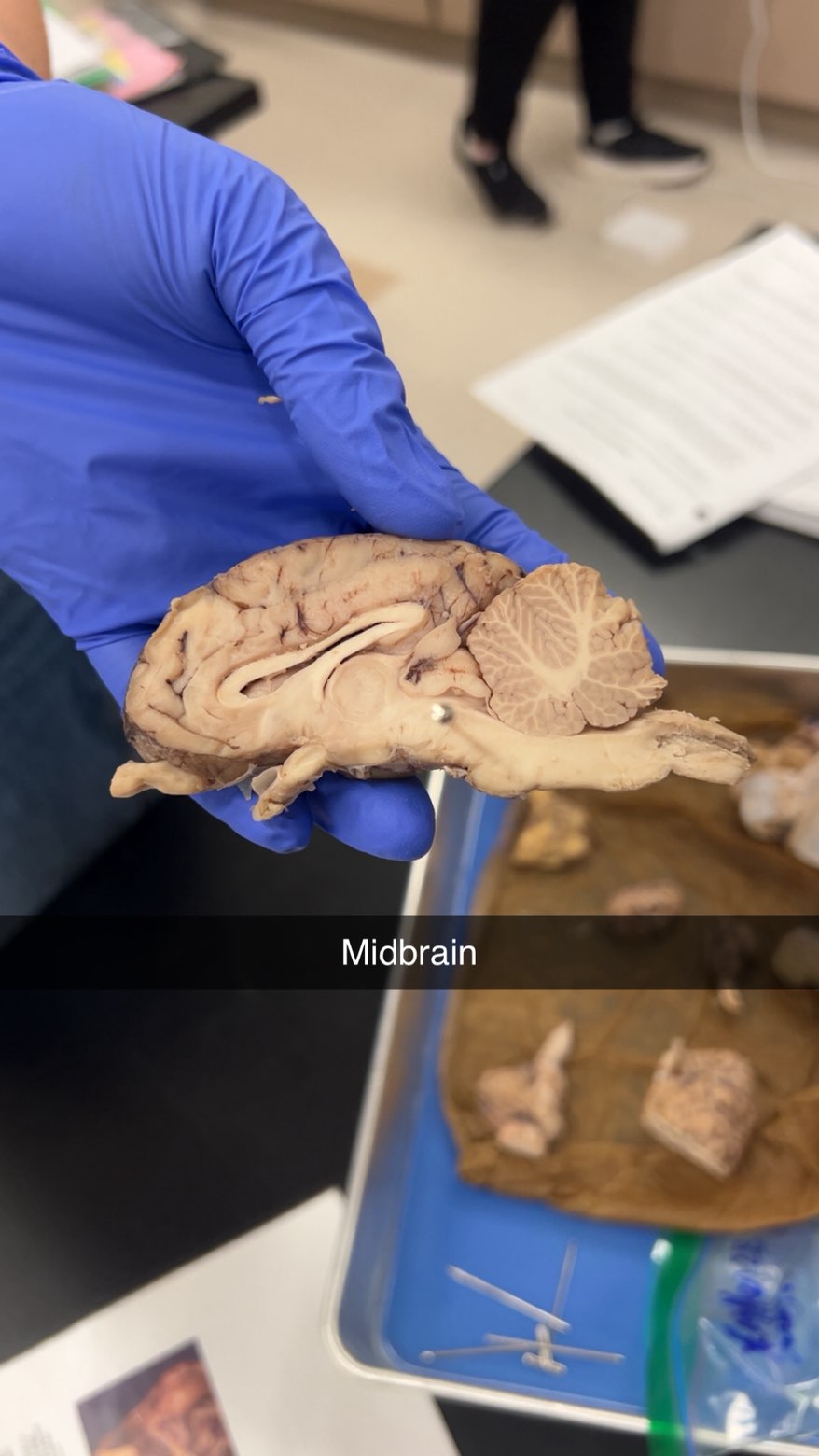
midbrain
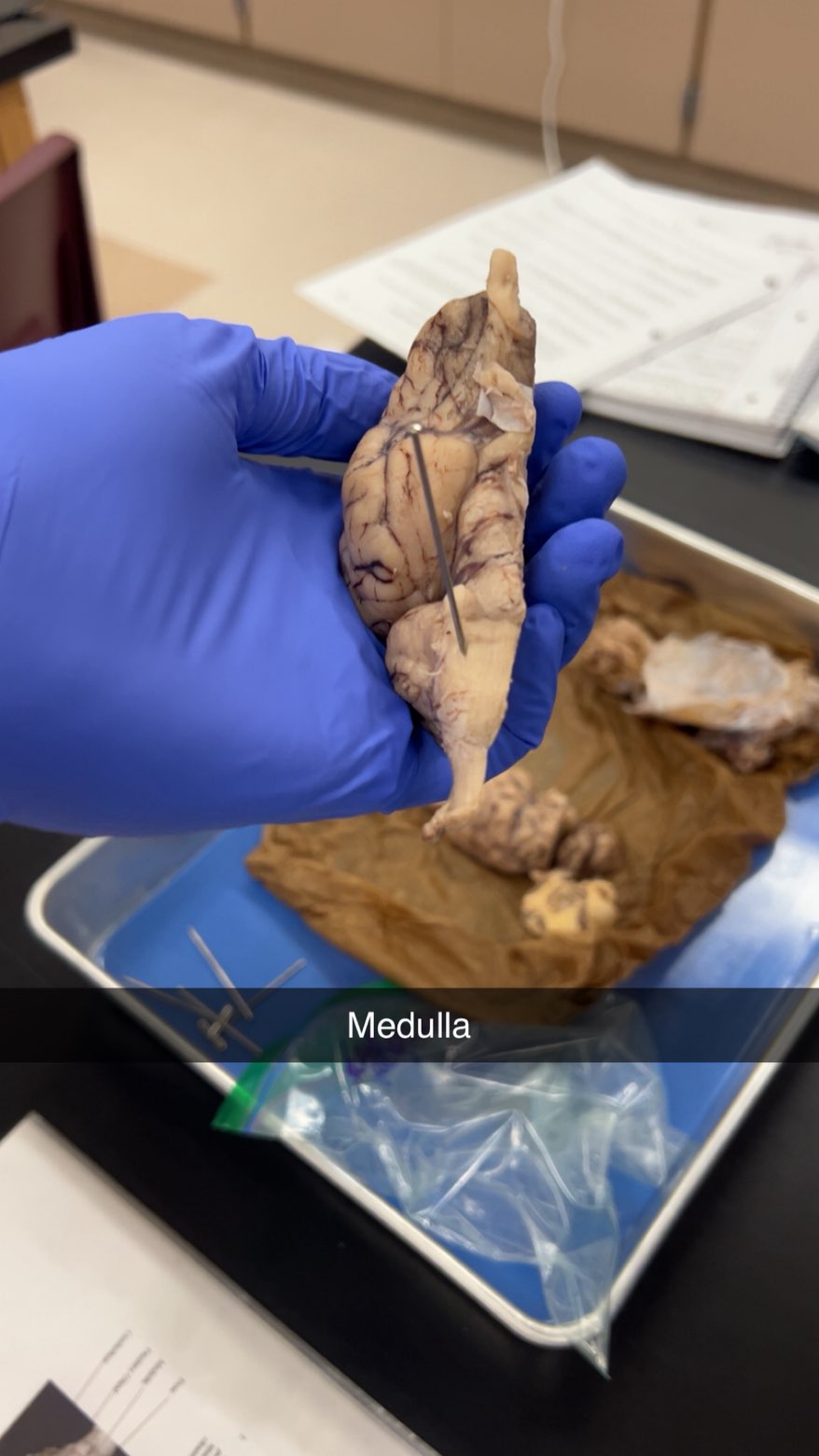
medulla
bottom section of the brainstem that controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate,
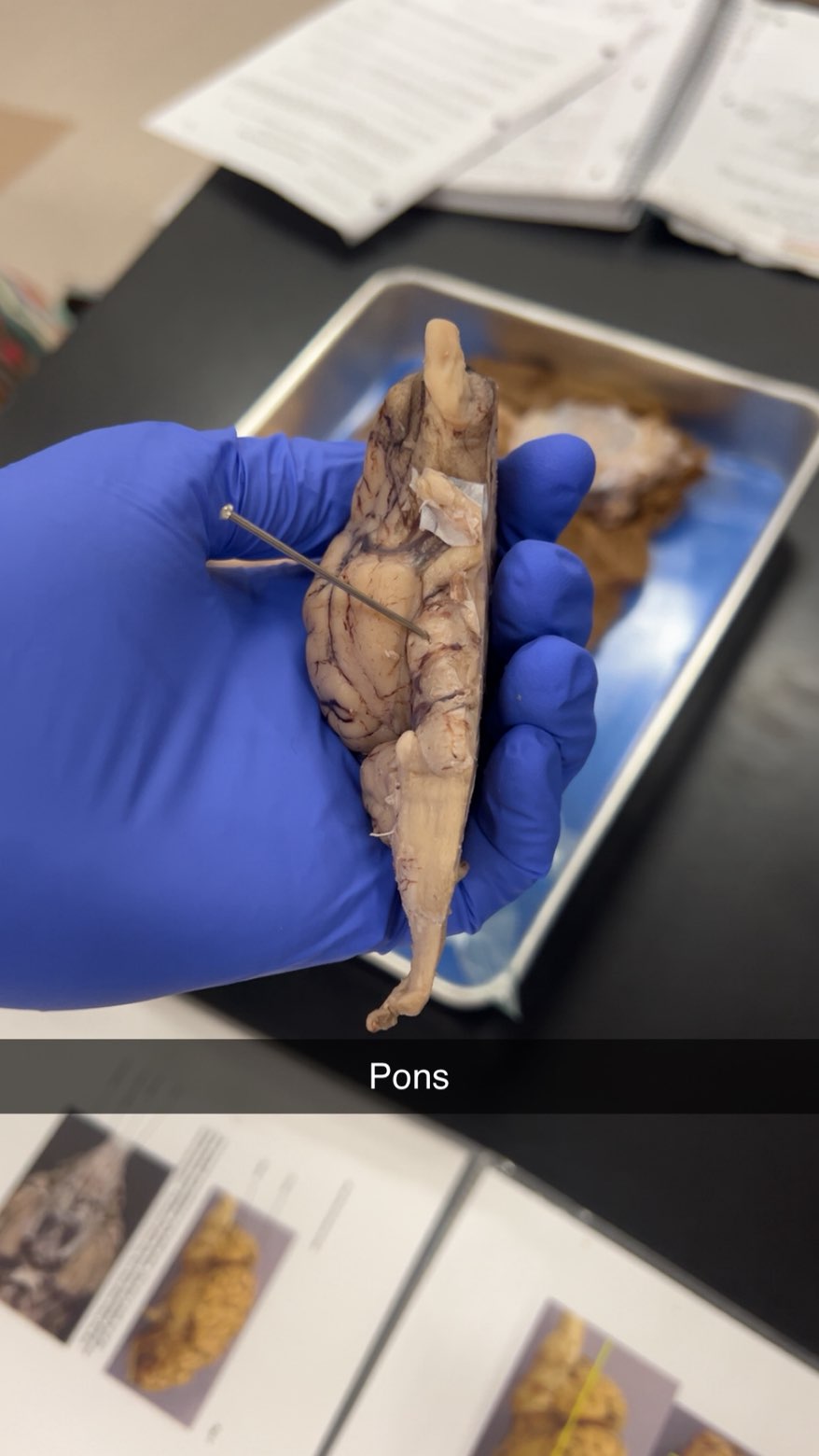
pons
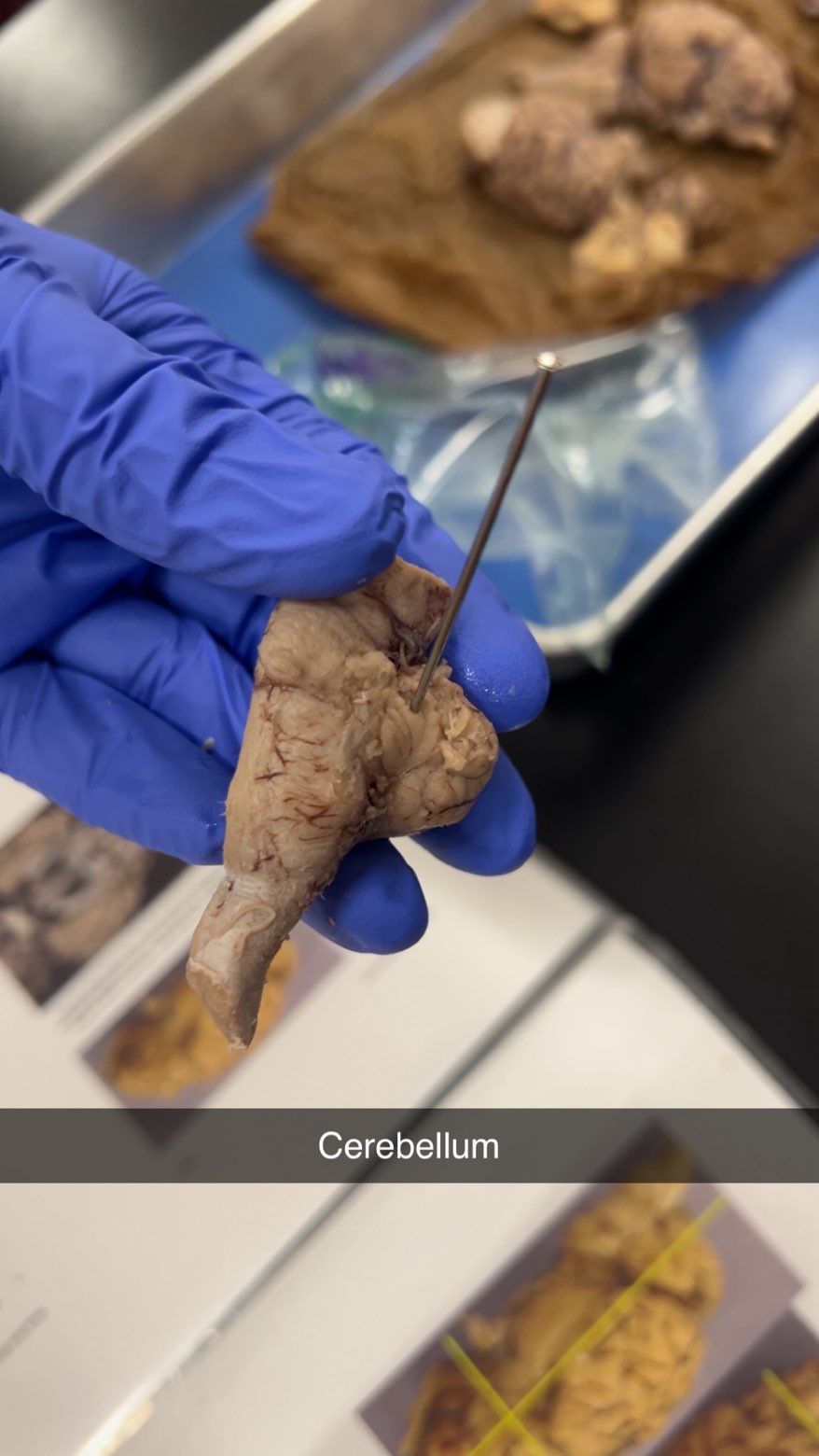
cerebellum
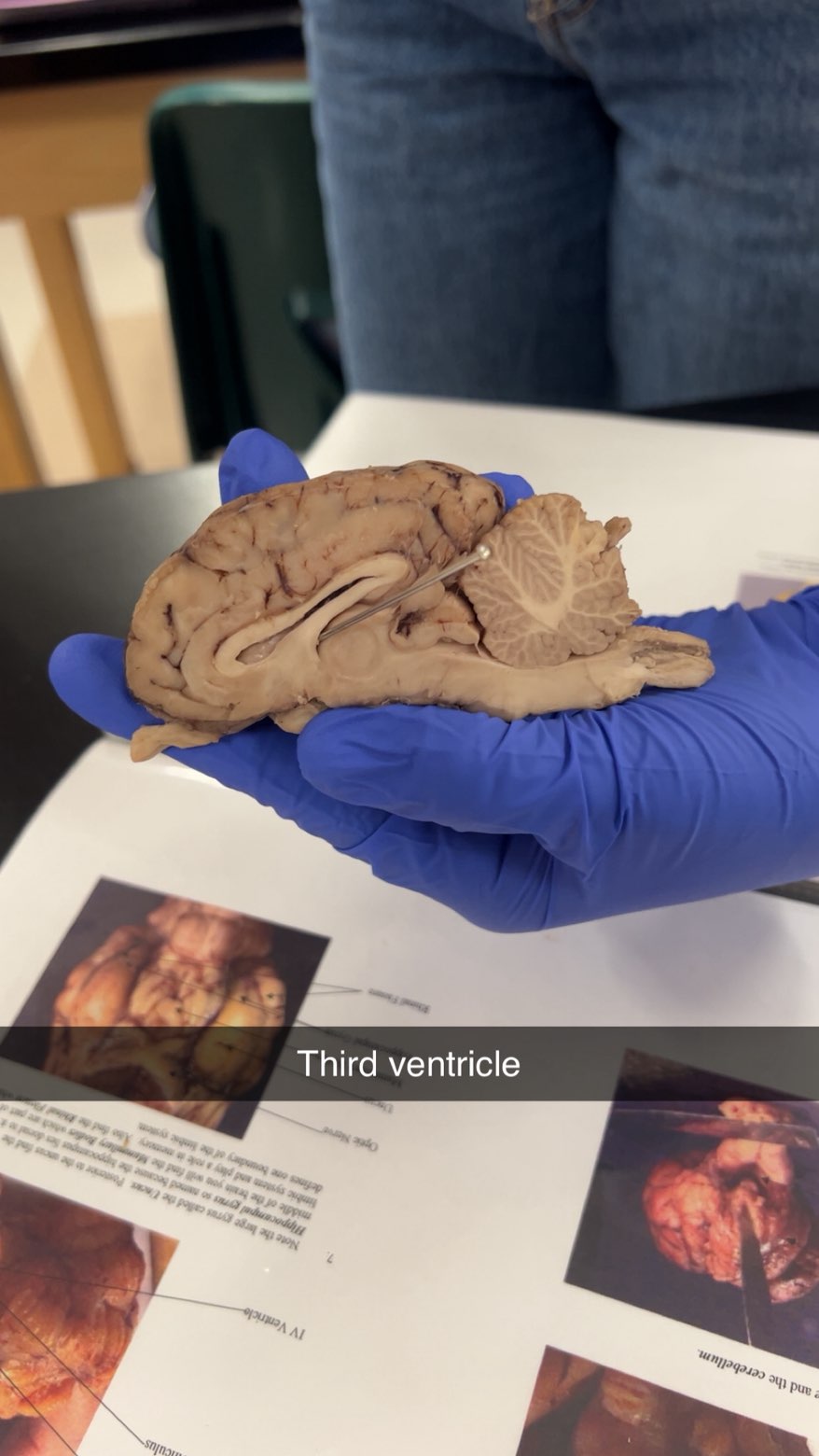
3rd ventricle
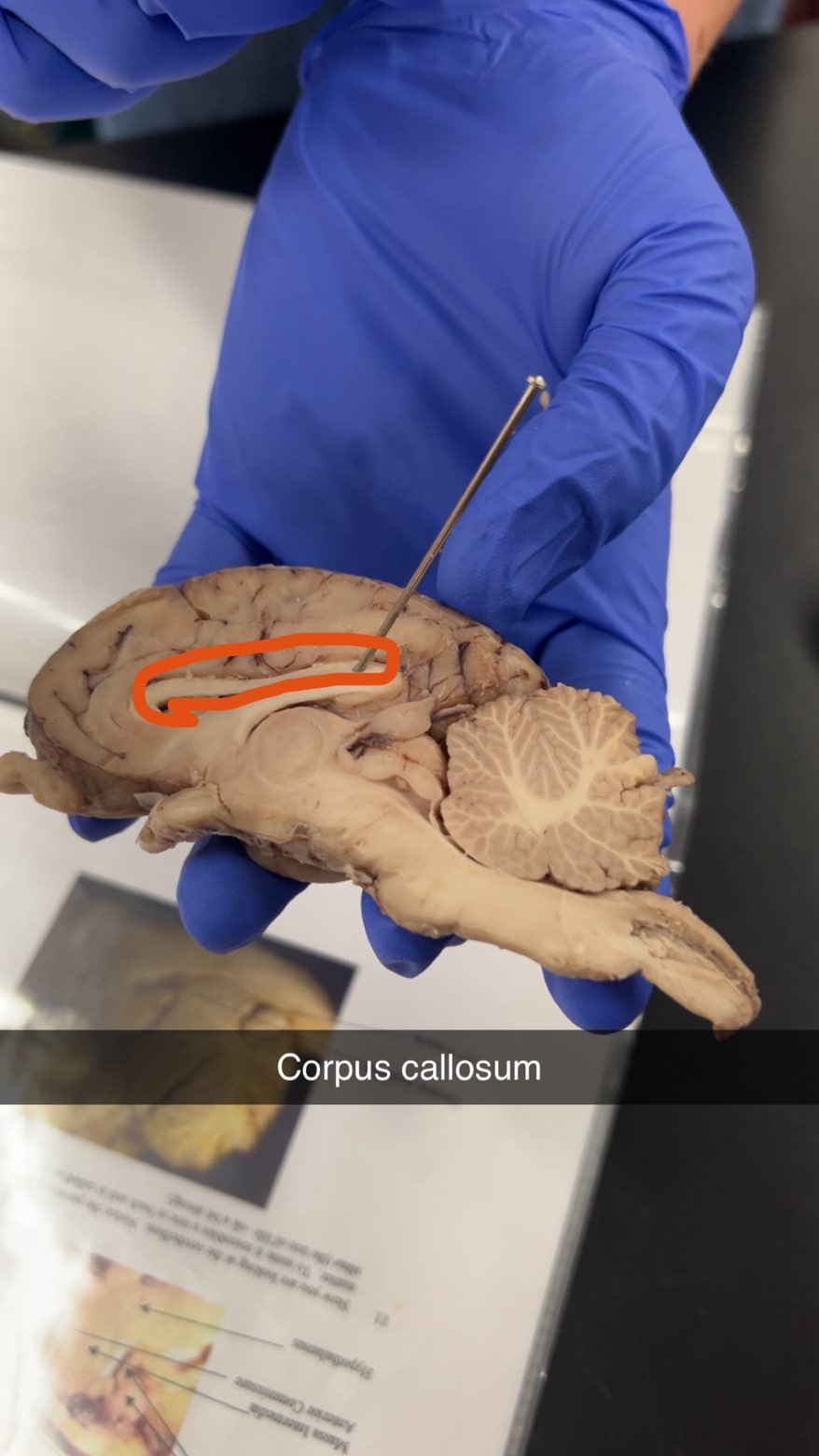
corpus callosom
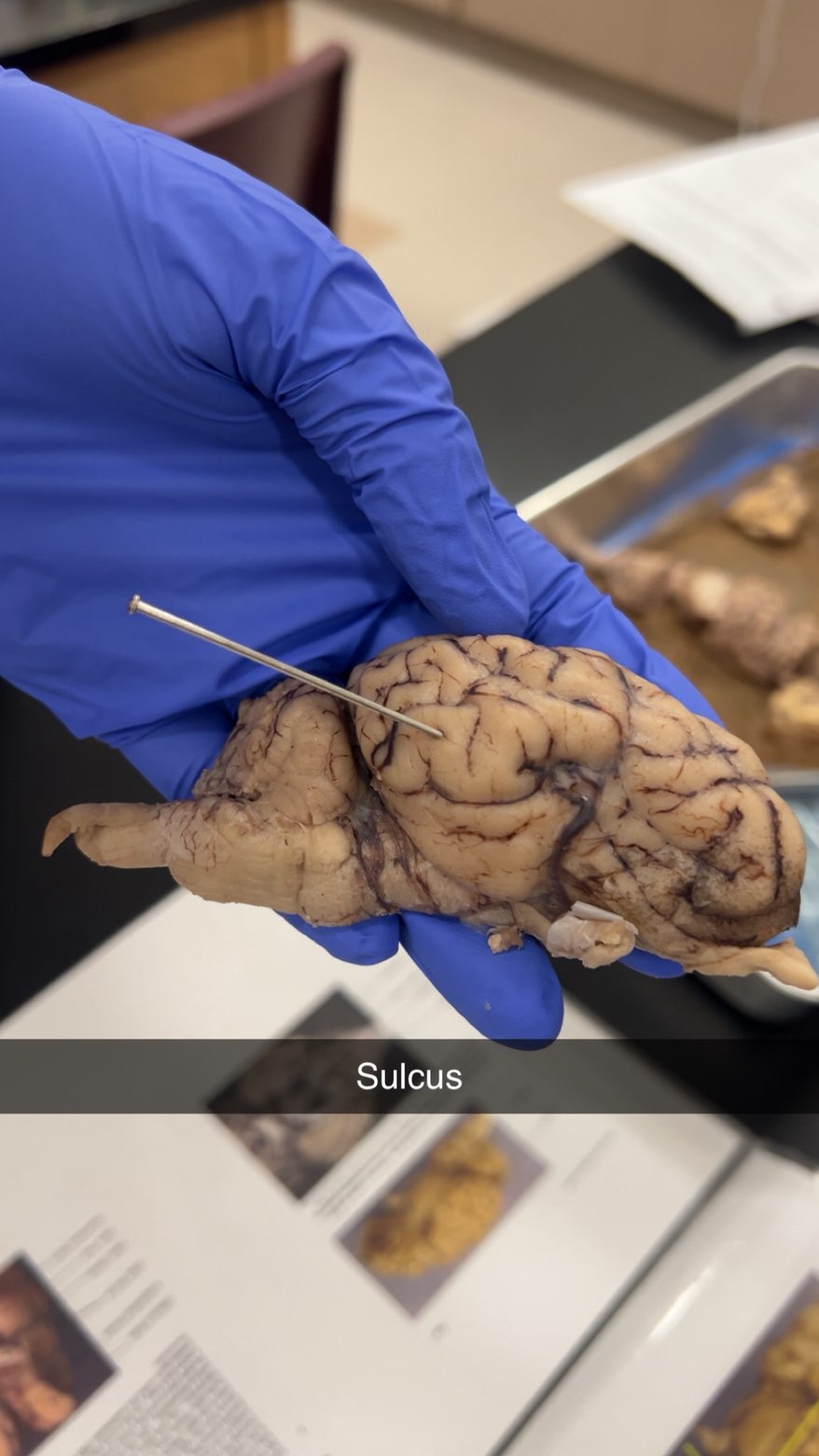
sulcus
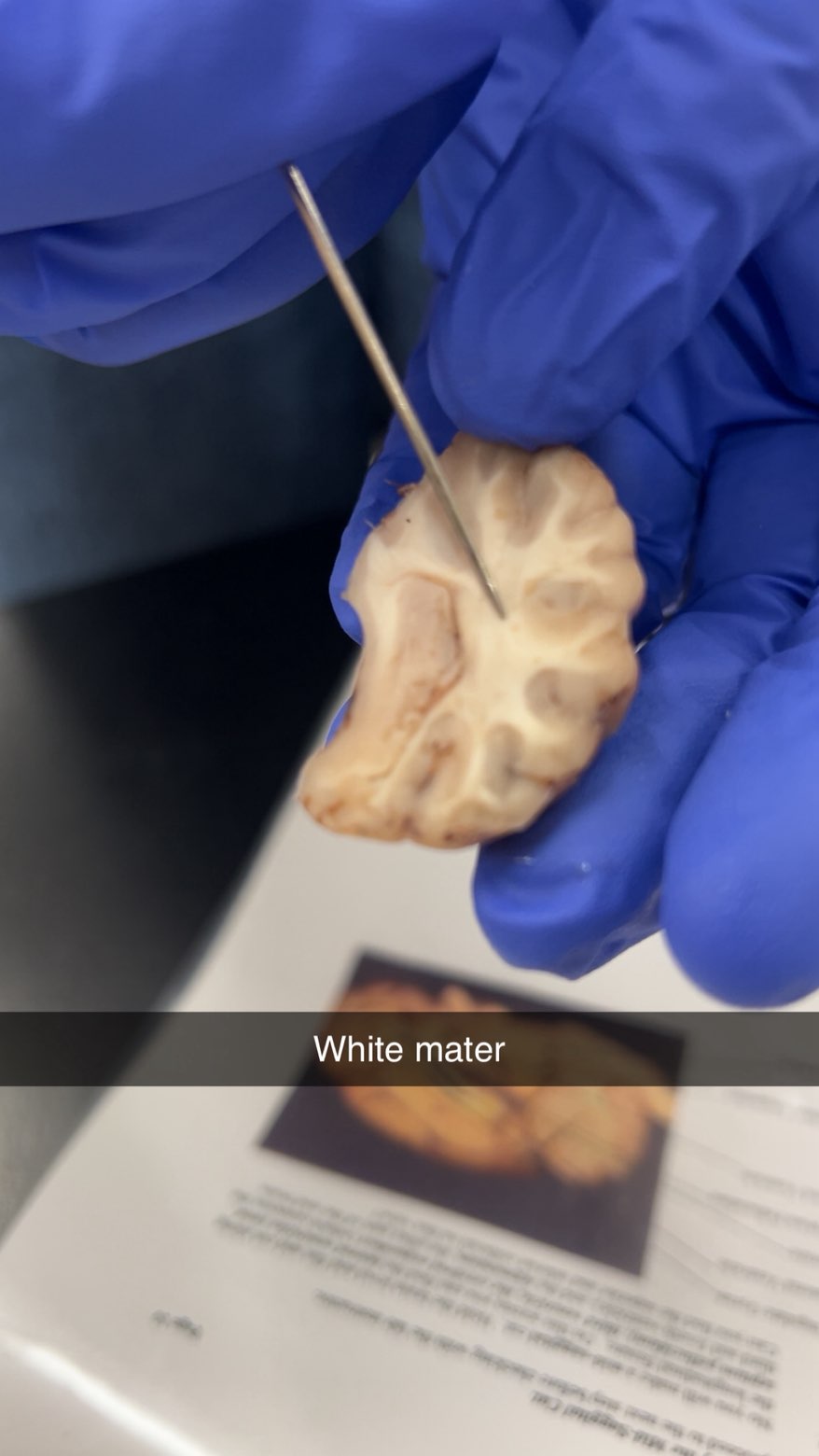
white matter
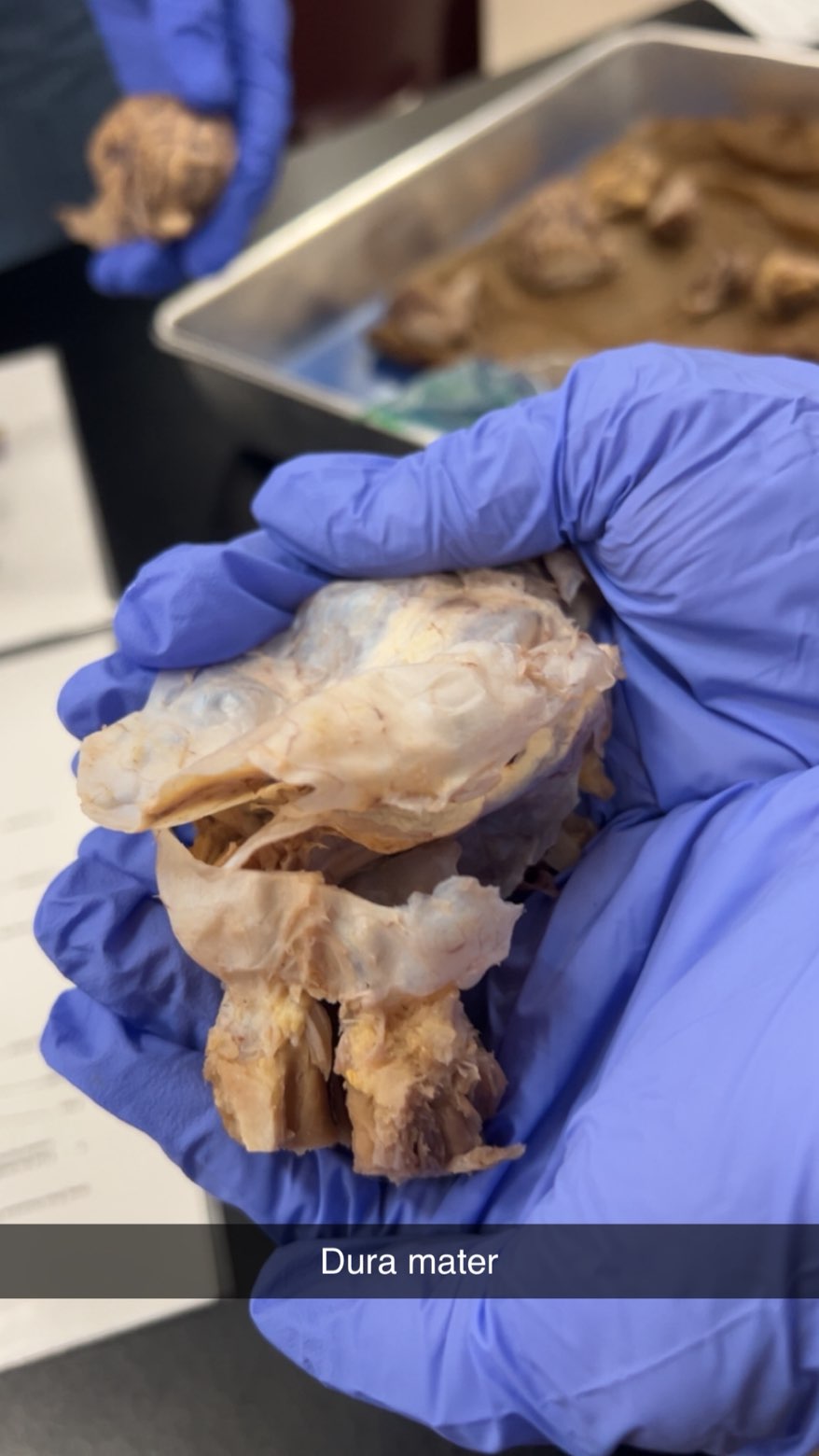
dura mater
responsible for higher cognitive functions, including reasoning, problem-solving, and planning.
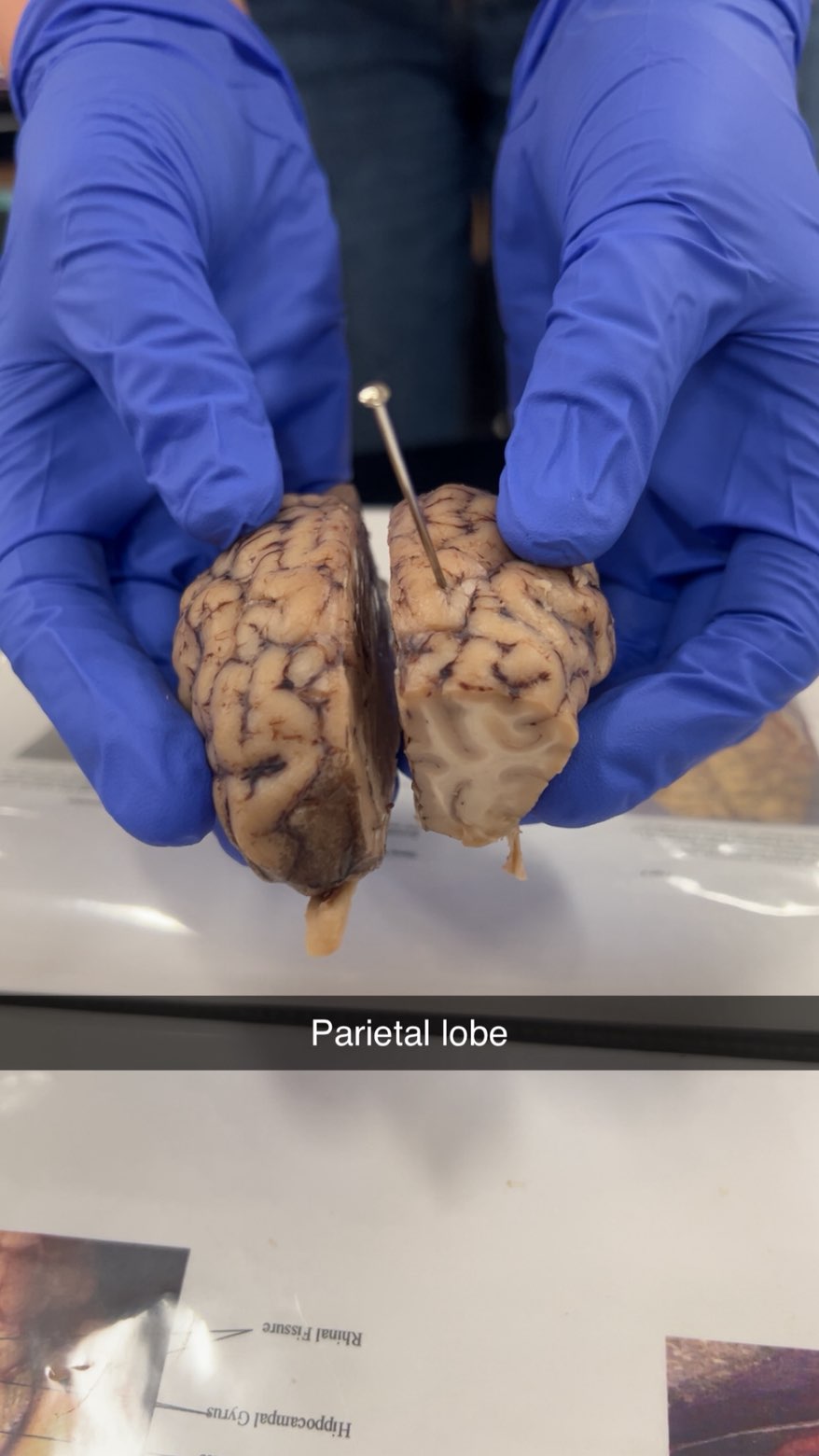
parietal lobe
the lobe responsible for processing sensory information related to touch, temperature, and pain.
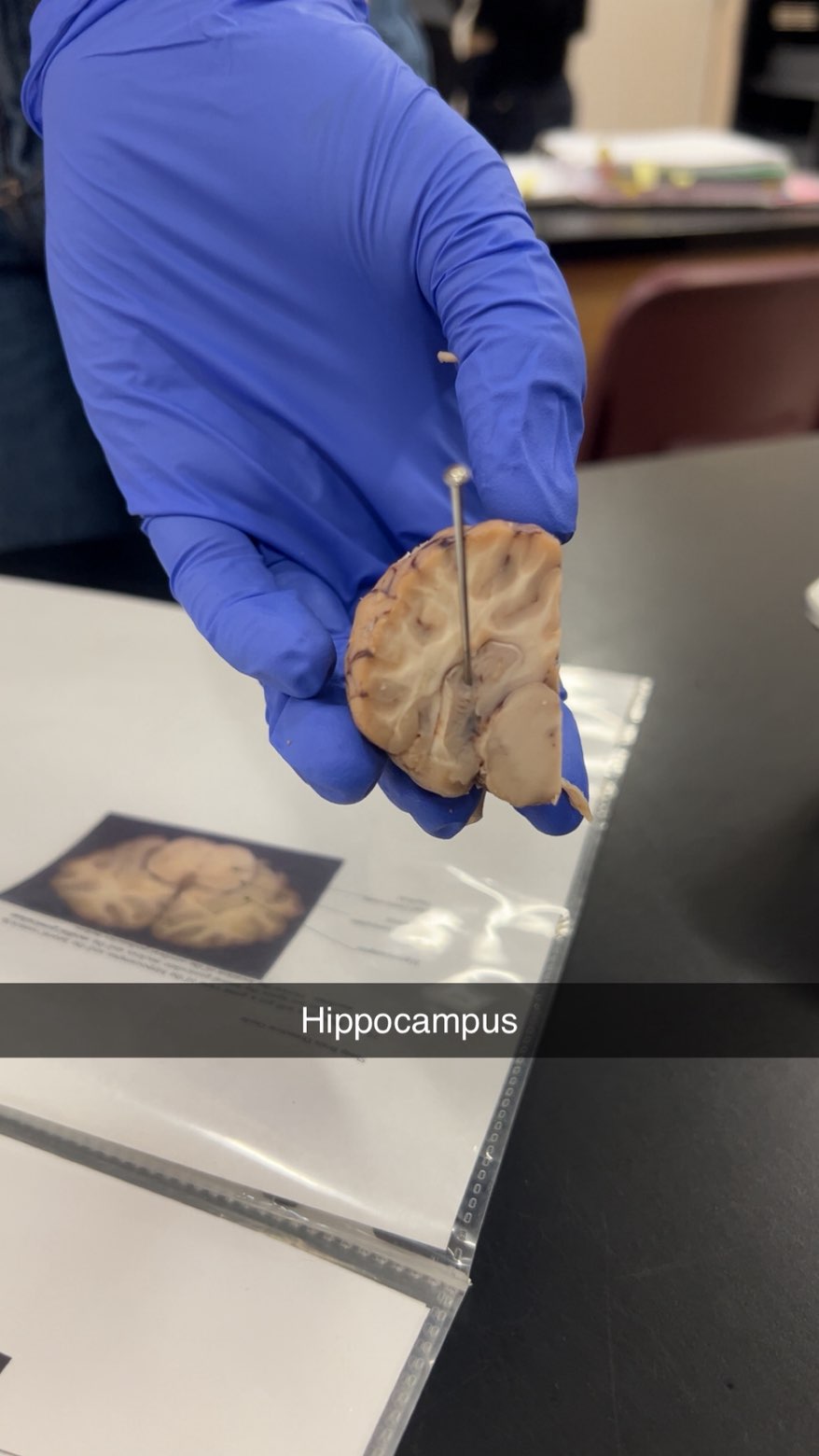
hippocampus
short to long term memory
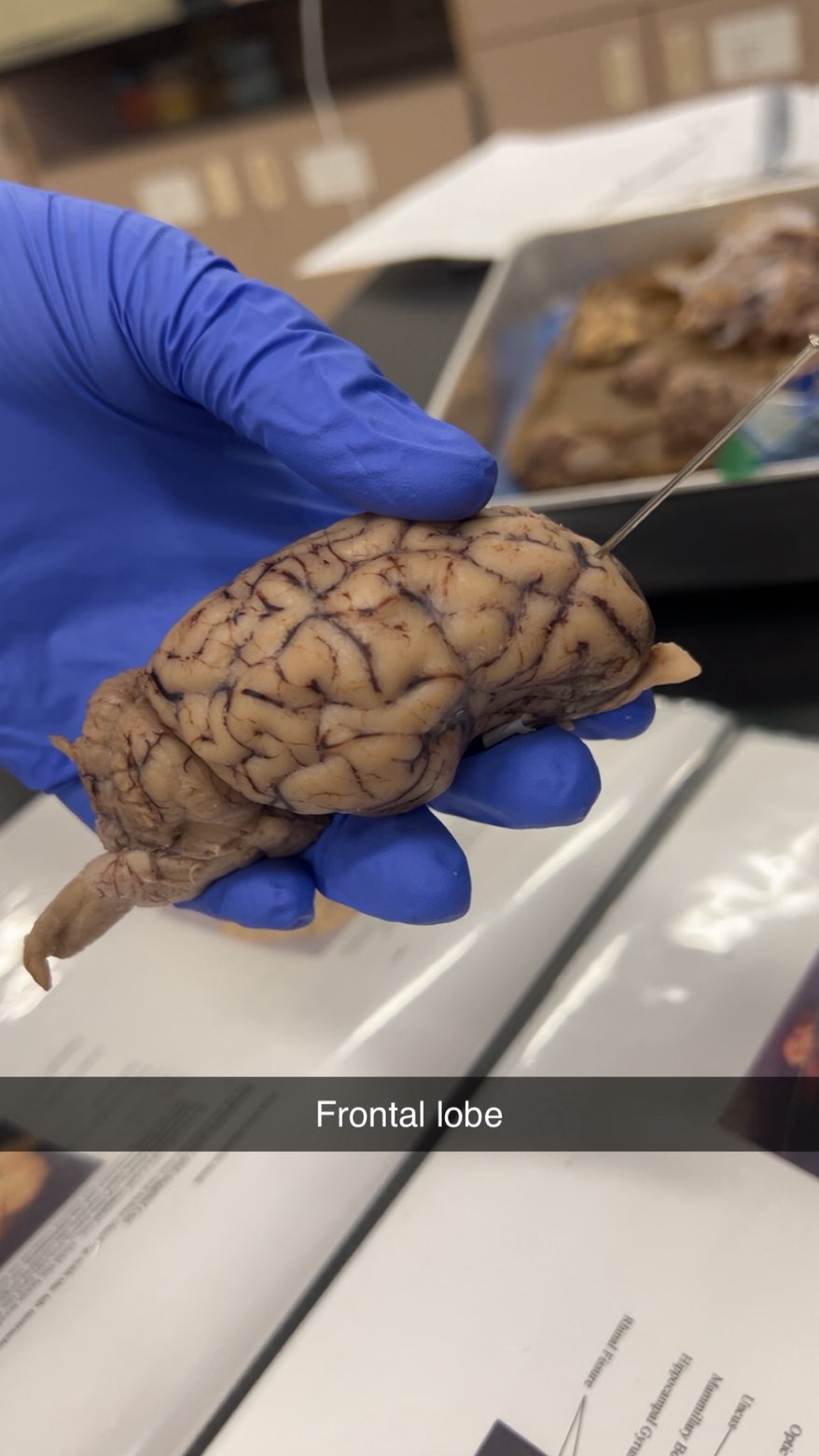
frontal lobe
gray matter
the "thinking" portion of the brain, responsible for processing information, controlling movement, and regulating emotions. It is composed of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons and is found in the outer layer of the brain (the cerebral cortex) and the central part of the spinal cord
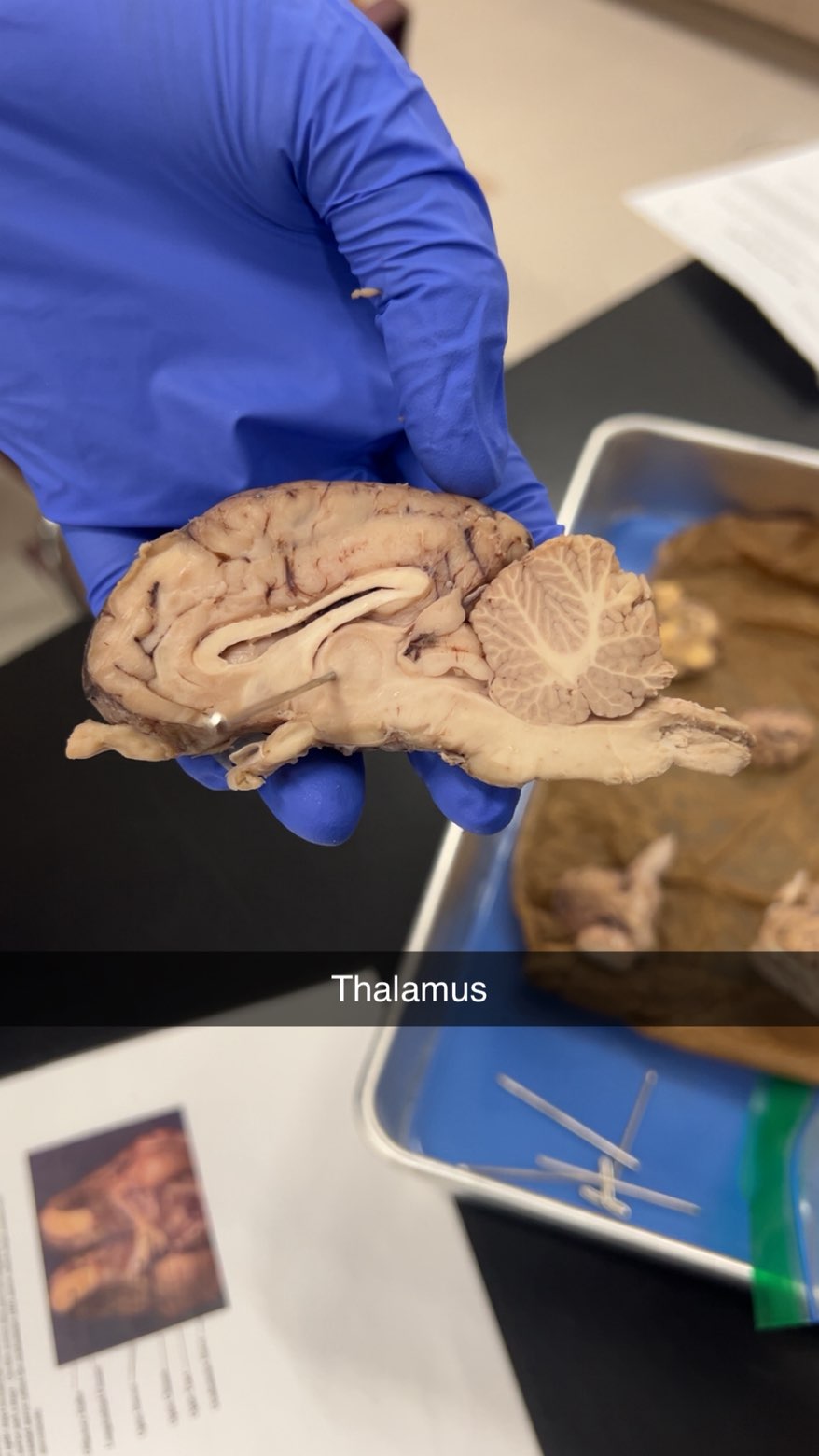
thalamus
a crucial relay center for sensory and motor information, processing and transmitting signals between the cerebral cortex and other parts of the brain. Its functions include relaying sensory data like touch, pain, temperature, and vision
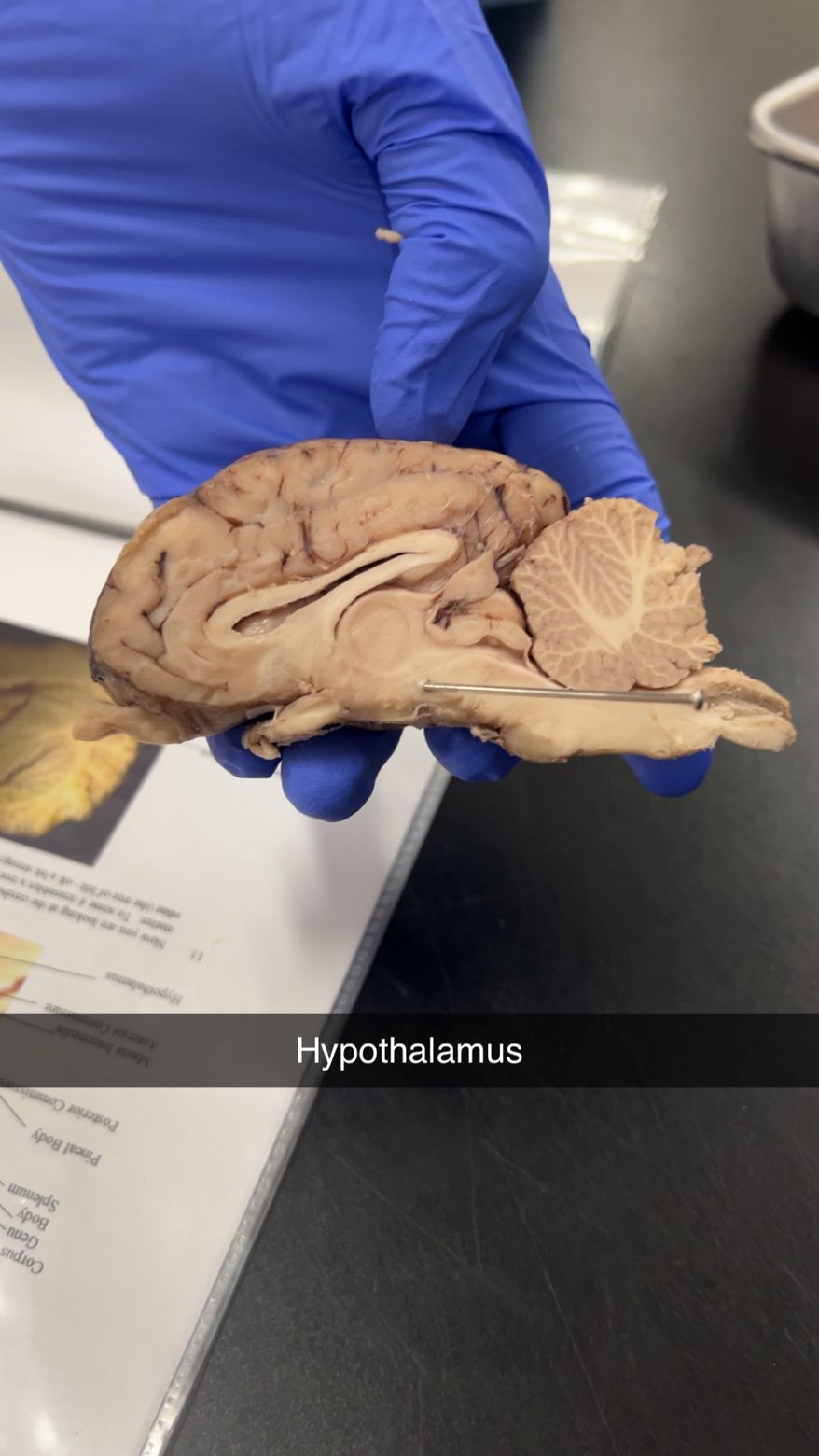
hypothalamus
regulates vital bodily functions, including body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep cycles, while also controlling the endocrine system by releasing hormones that manage the pituitary gland. It is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and is involved in regulating the autonomic nervous system and emotions
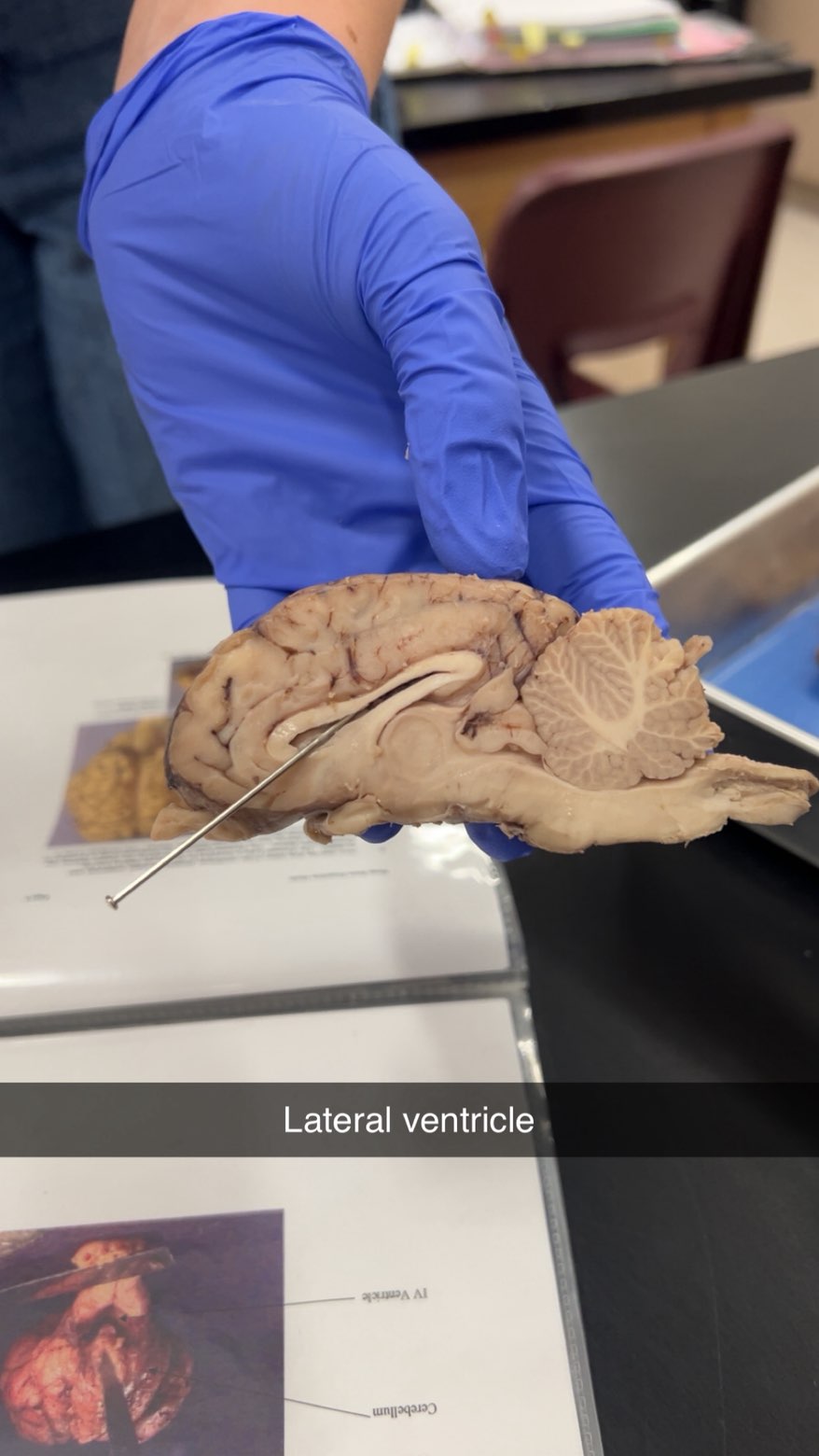
lateral ventricle
produce, circulate, and store cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
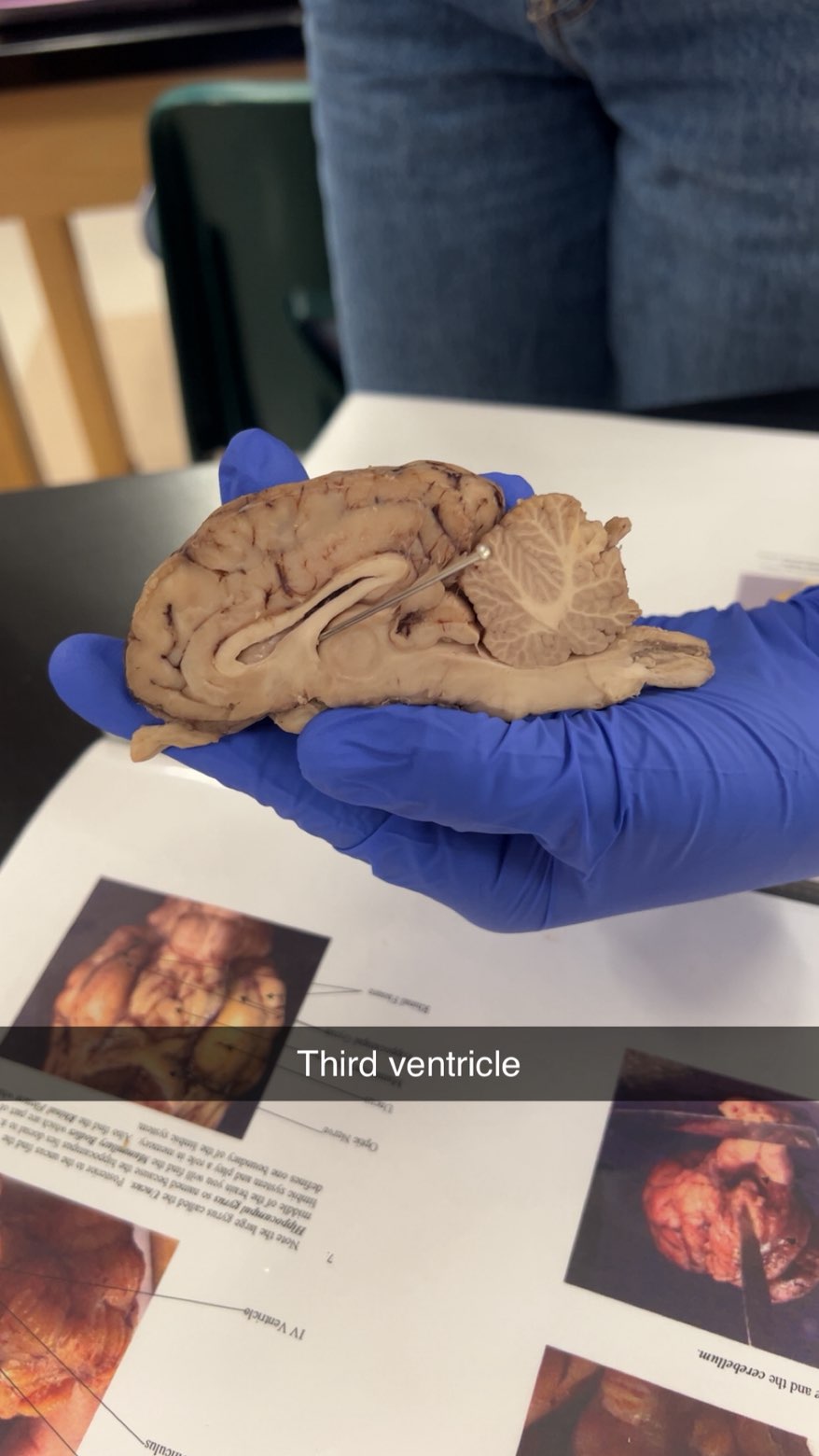
3rd ventricle
producing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which protects the brain, transports nutrients, and removes waste. pass to 4 ven
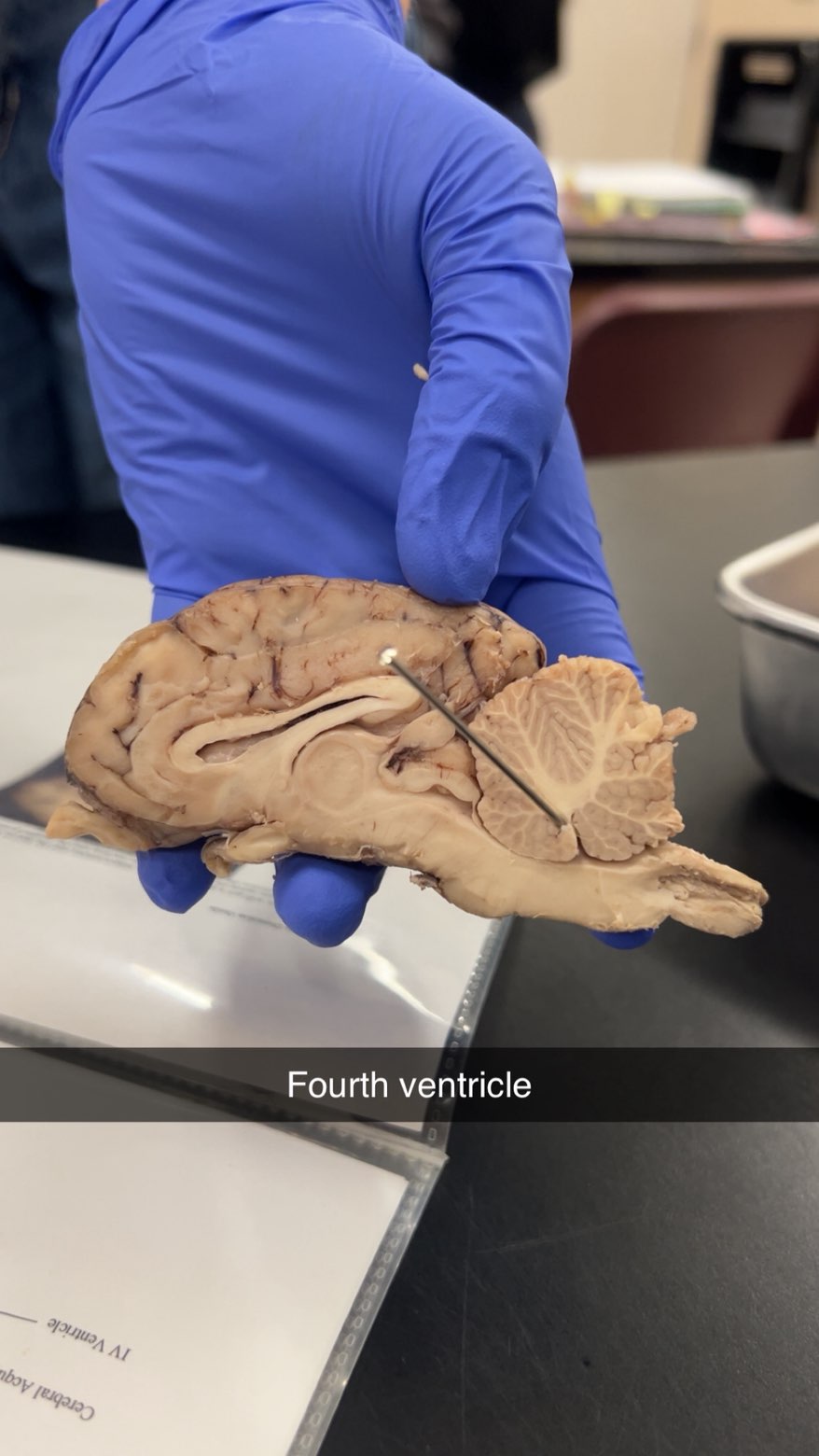
4th ventricle
produce, circulate, and drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It acts as a conduit, allowing CSF to flow from the brain's other ventricles to the central spinal canal and subarachnoid space, where it is absorbed
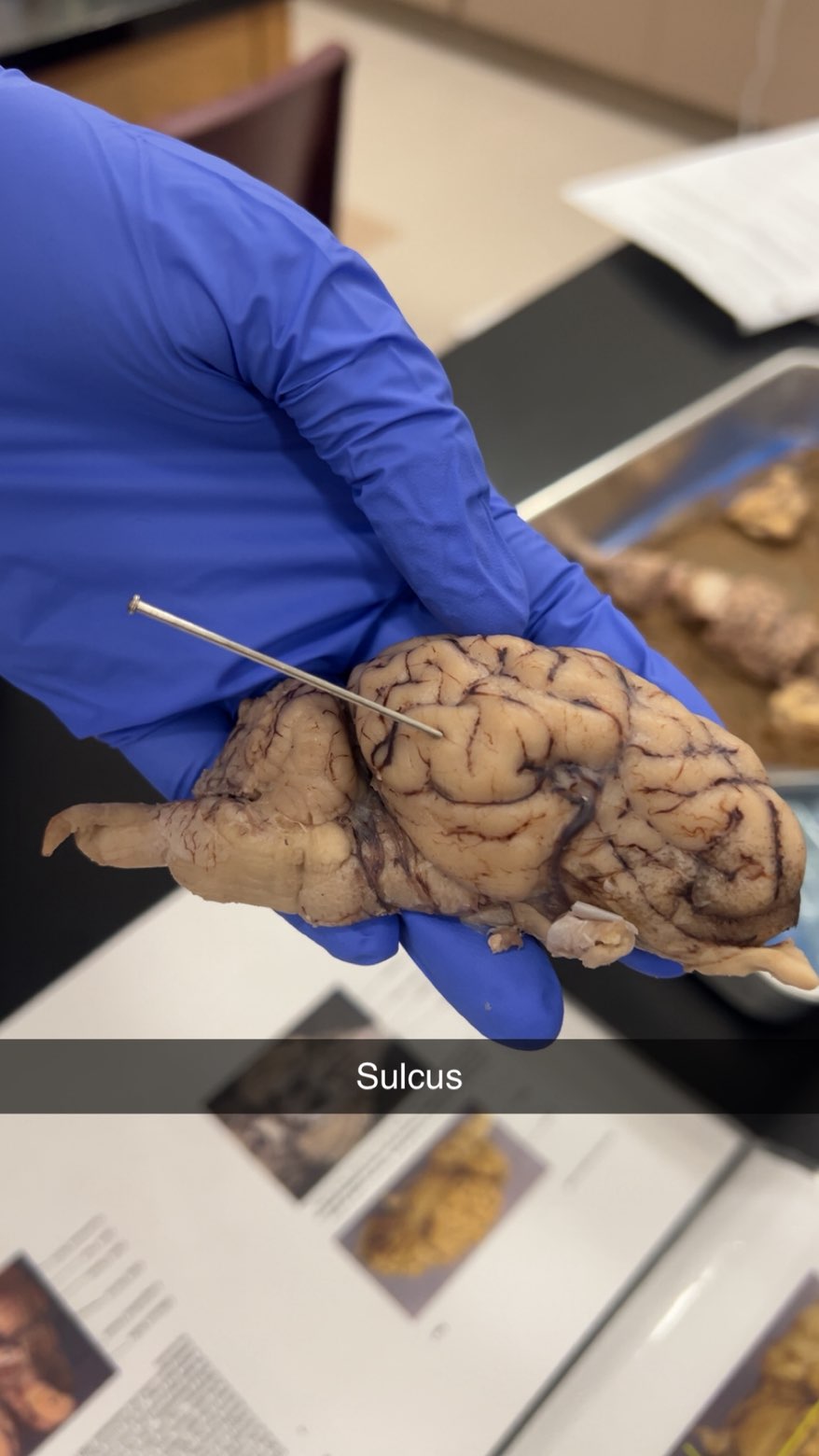
sulcus
vallies increases the cerebral cortex's surface area for more cognitive function and neural connections.
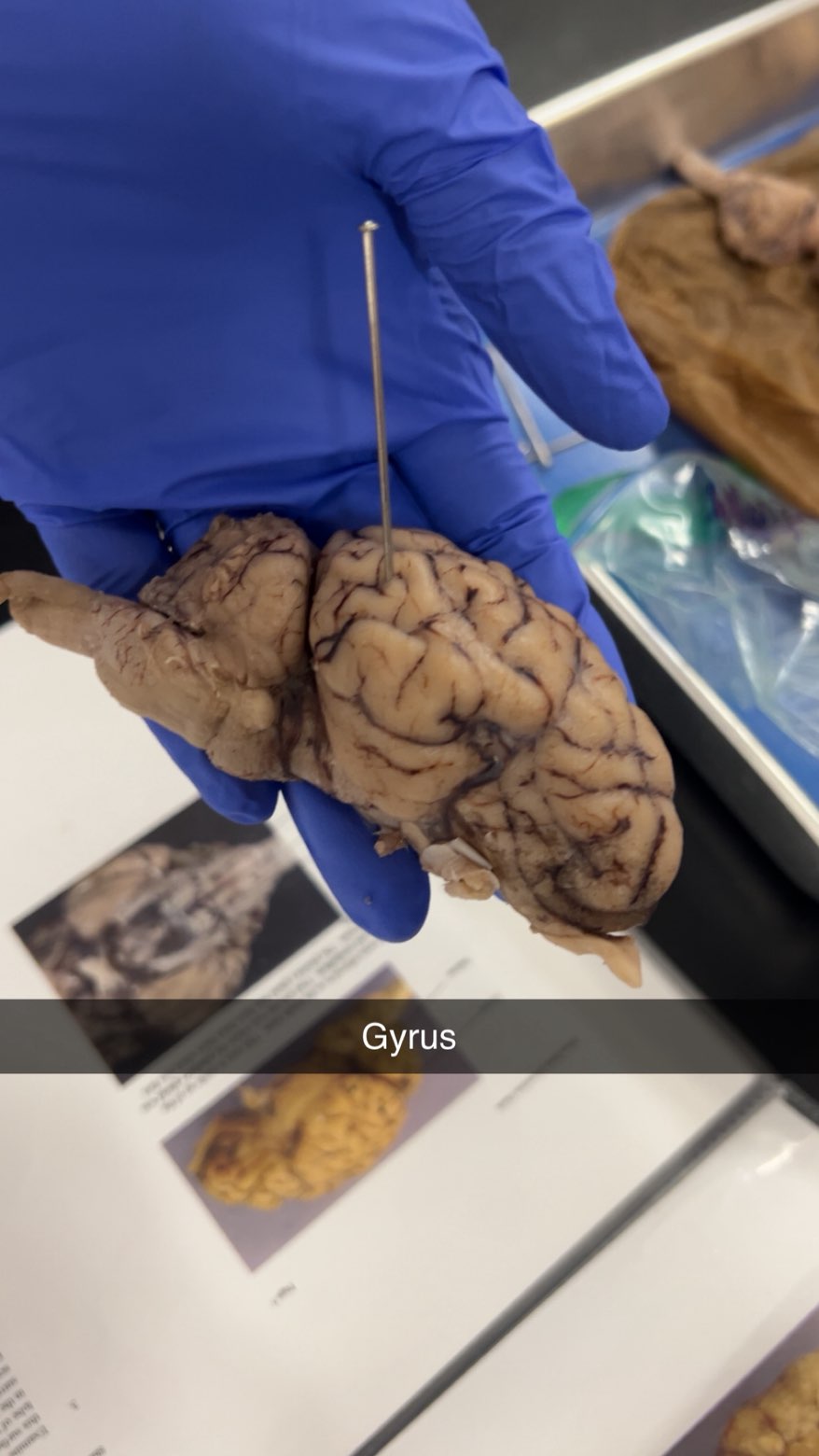
gyrus
Gyruses are the ridges on the surface of the brain that increase the surface area, allowing for greater cognitive function.
postcentral gyrus
sensory cortex
precentral gyrus
motor cortex
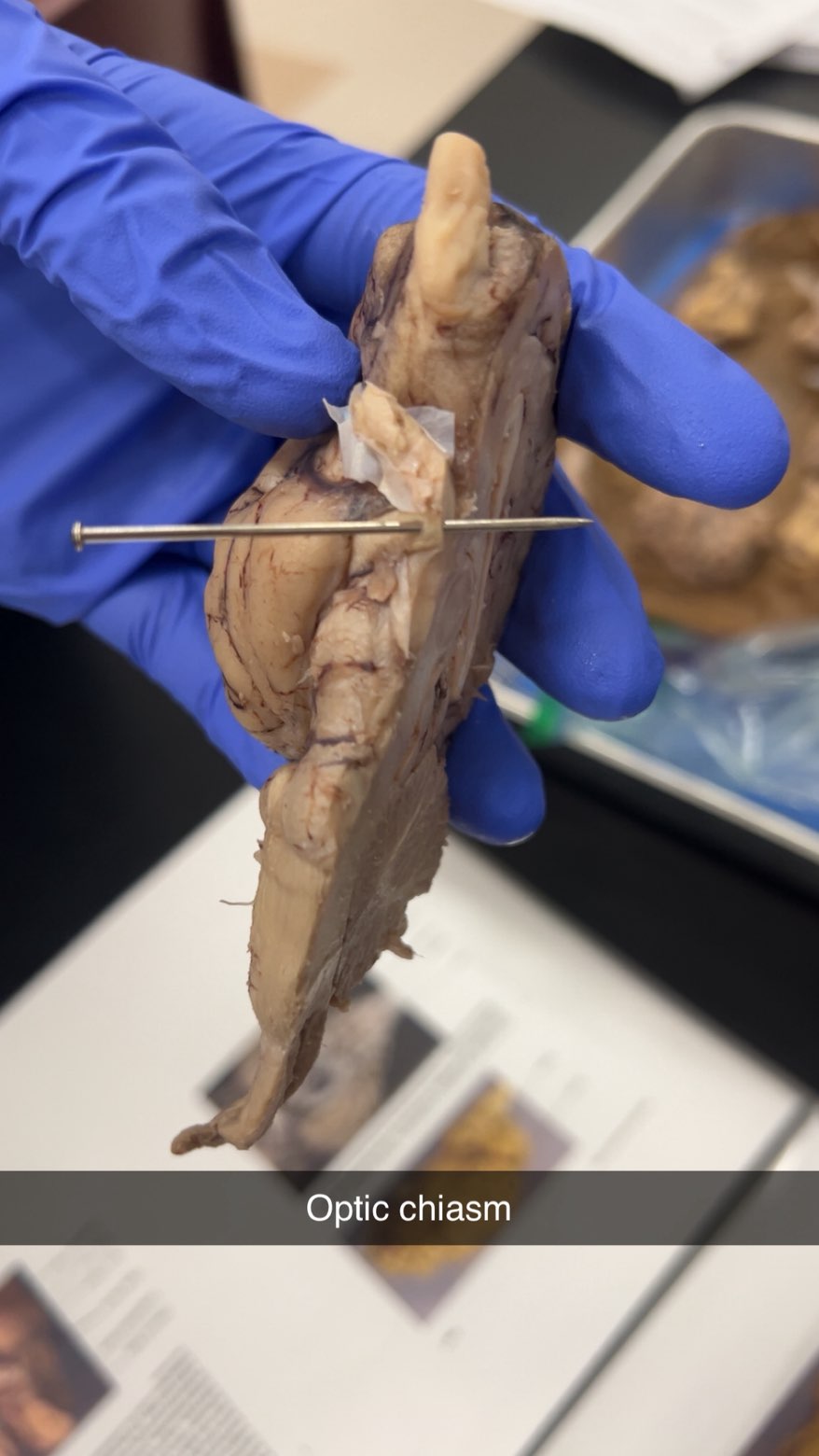
optic chiasm
where the optic nerves cross, allowing the brain to receive information from both eyes to create a unified visual field, near pituitary gland
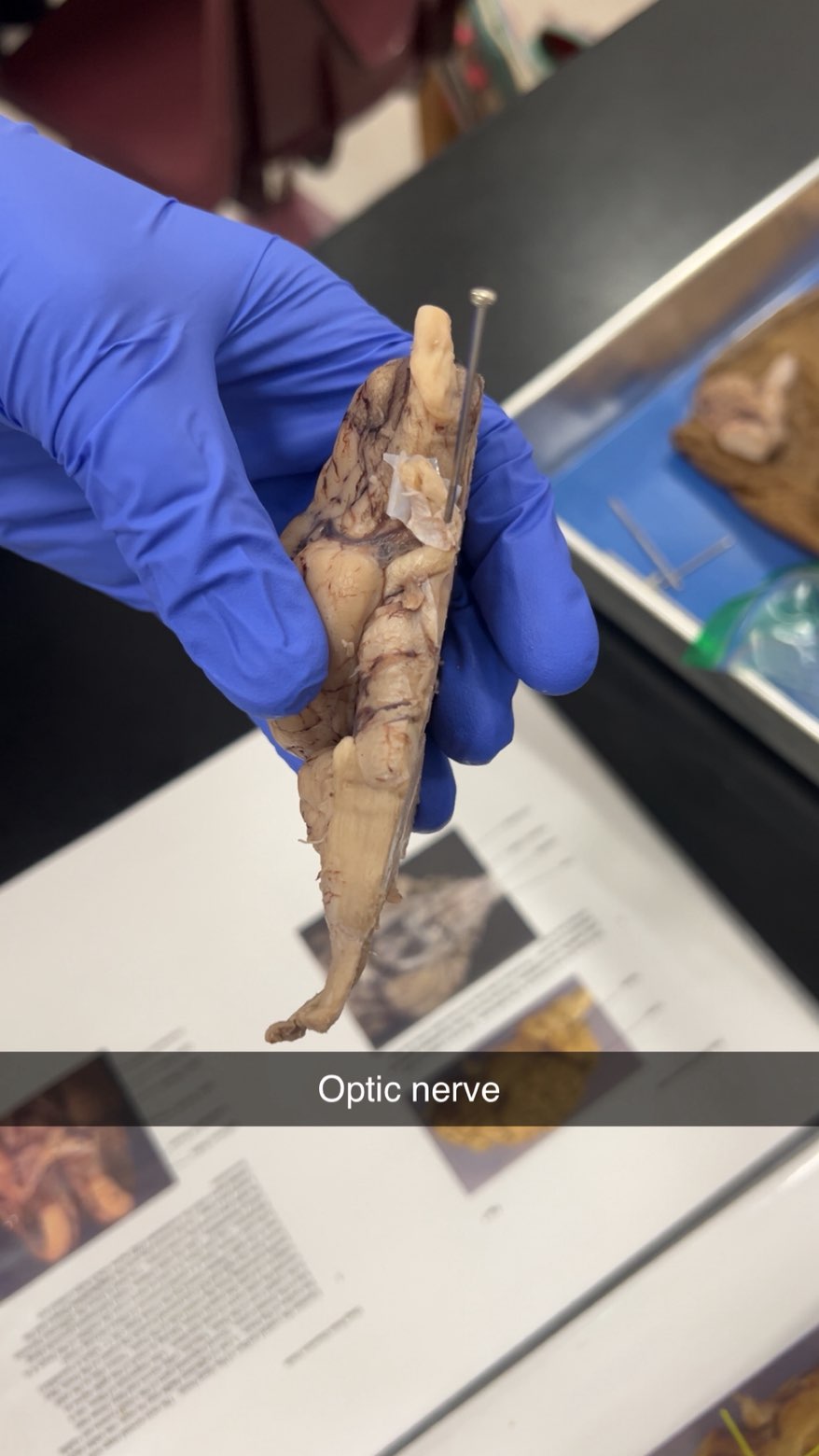
optic nerves
a pair of sensory nerves that transmit visual information from the retina to the brain, allowing us to see
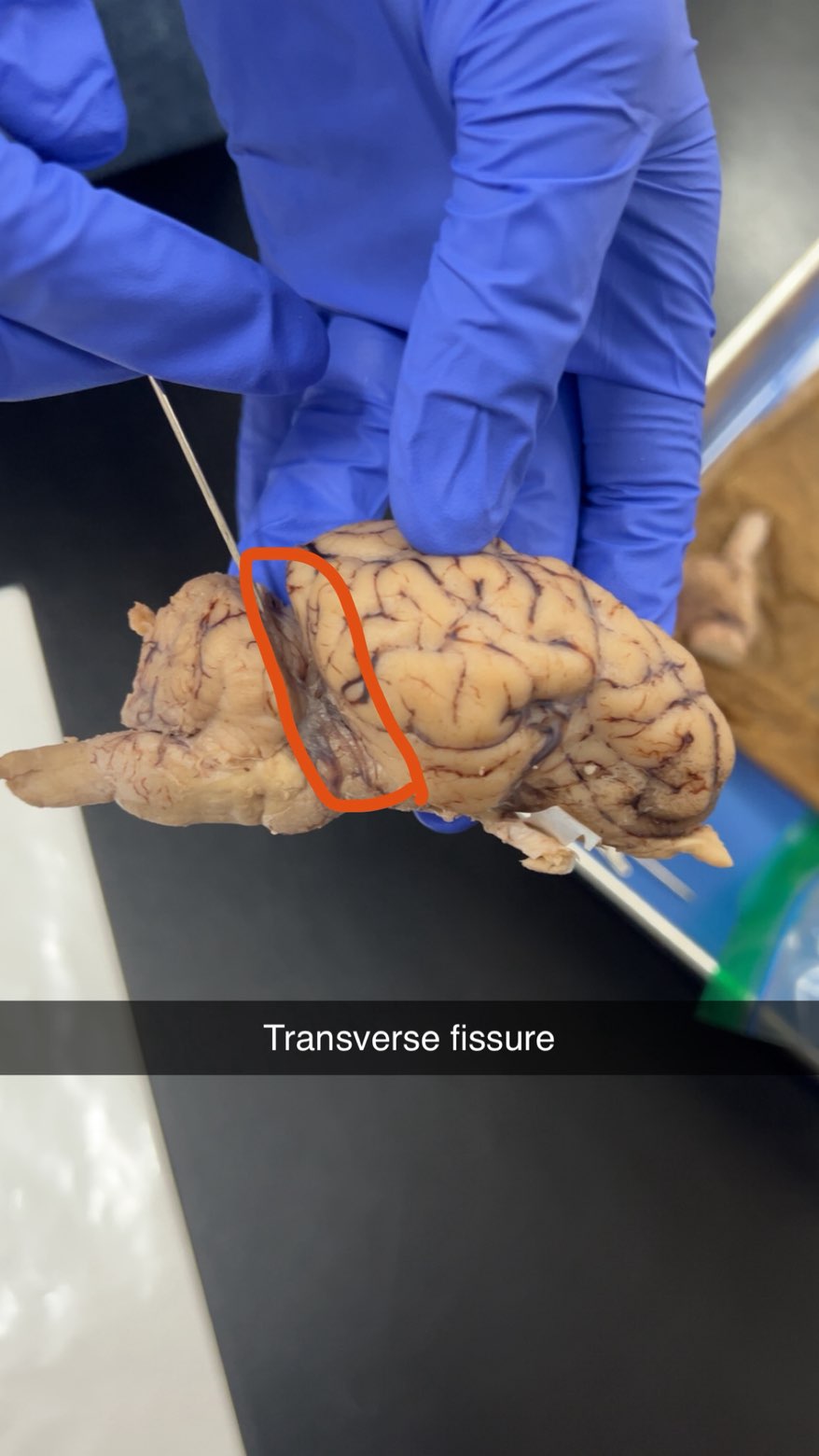
transverse fissure
deep groove separating the cerebrum from the cerebellum in the brain,
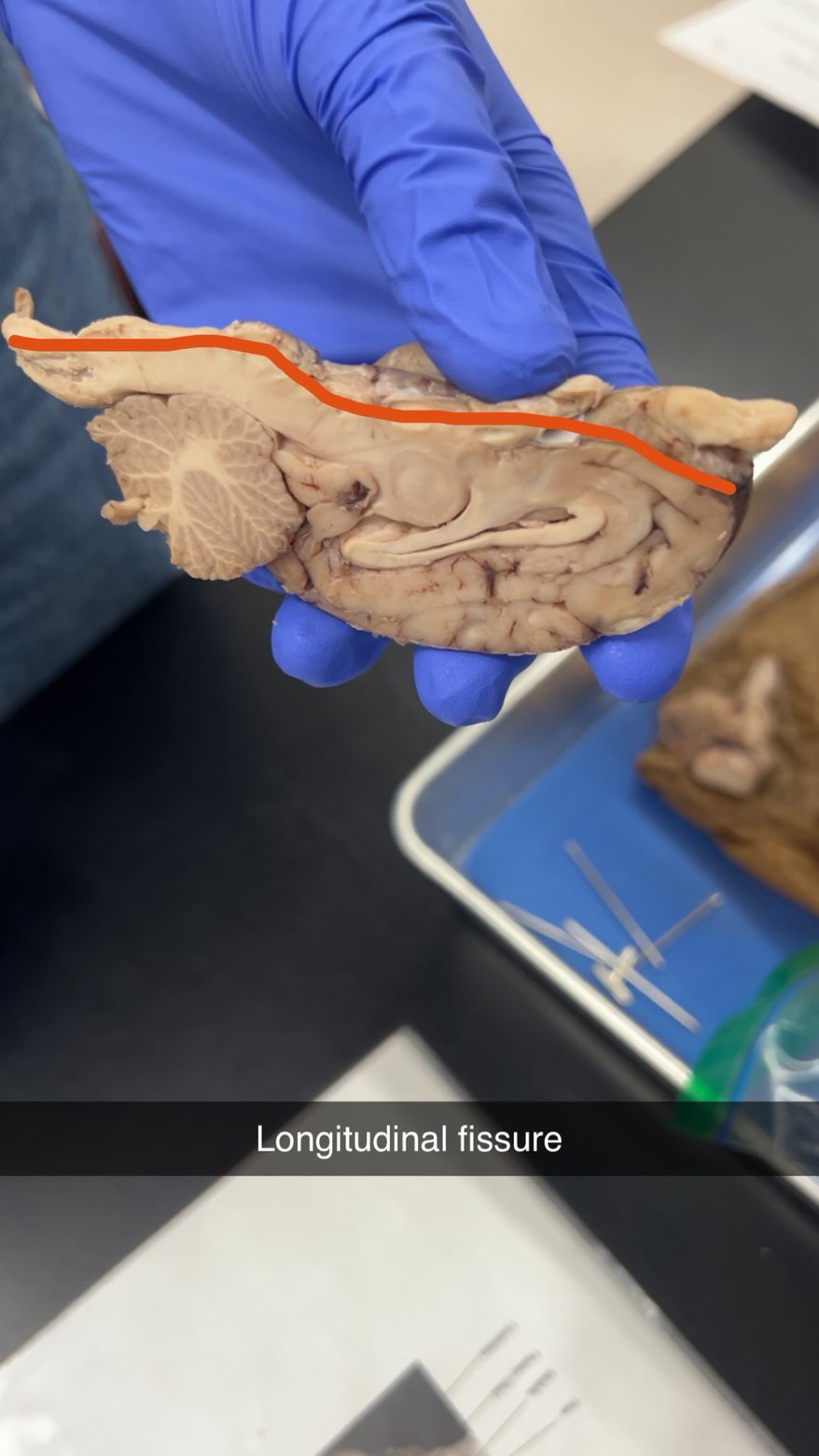
longitudinal fissure
separating the left and right cerebral hemispheres
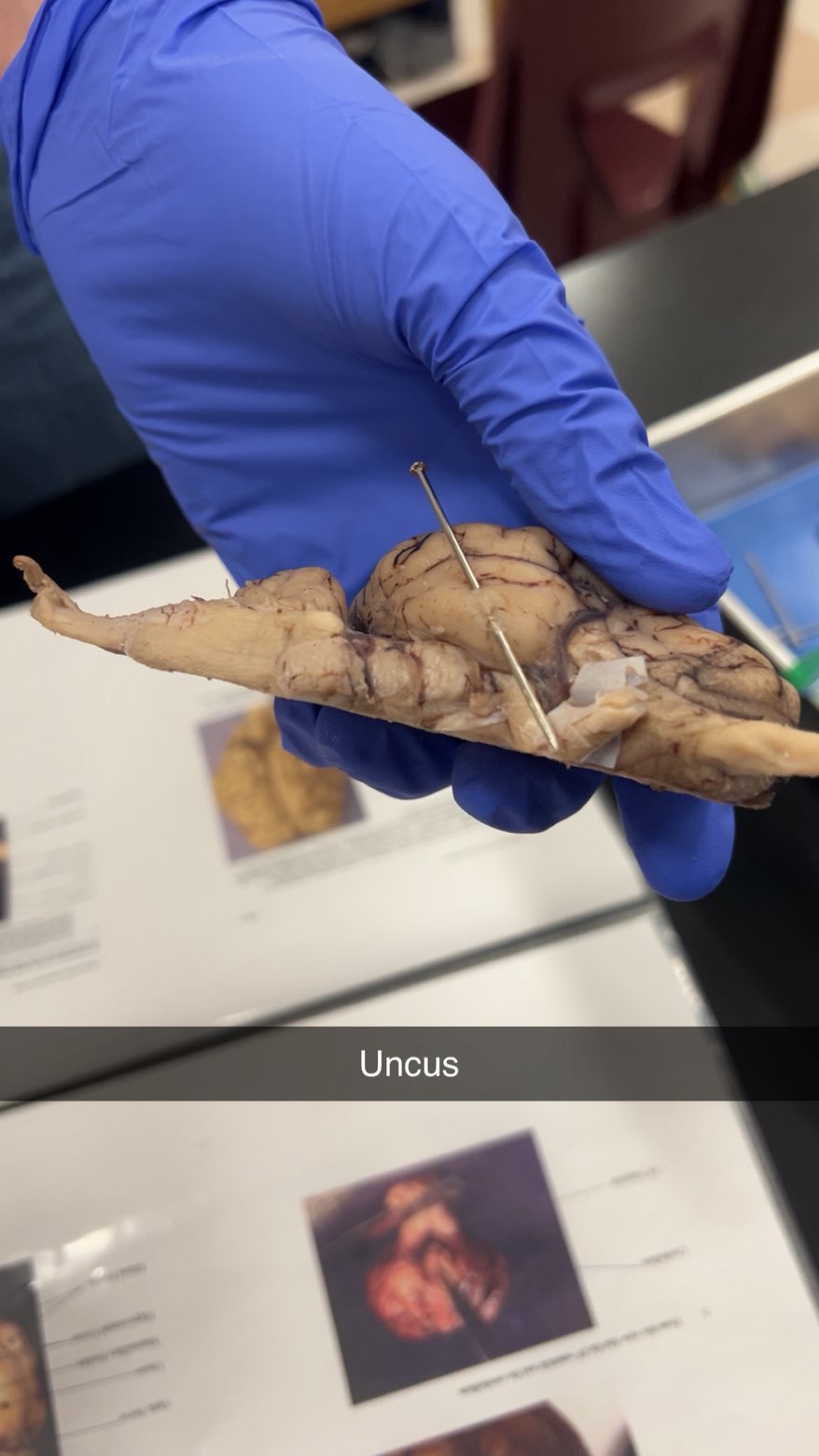
uncus
the curved, hooked part of the brain's temporal lobe or a hooked anatomical part in general. In the brain, it is a key component of the olfactory cortex and is involved in smell, memory, and emotion
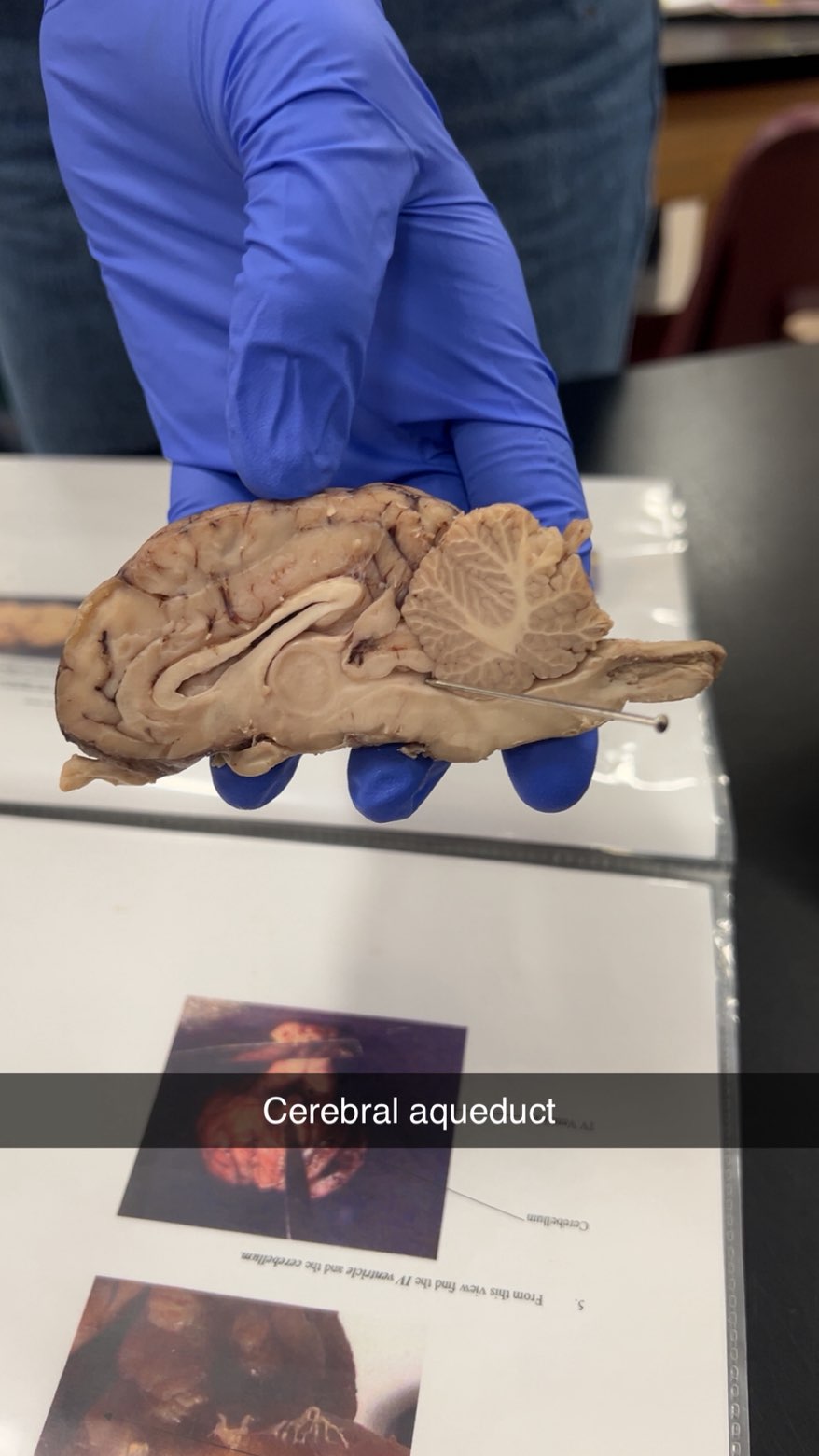
cerebral aqueduct
a fluid-filled canal that runs through the midbrain connecting the third and fourth ventricles.
temporal
responsible for processing auditory information, memory (especially short-term), language comprehension, and emotion
frontal
personality, decision-making, problem-solving, voluntary movement, planning, and language production
occipital
process sight
parietal
sensory process
cerebellum
coordinating voluntary movements, balance, posture, and motor learning
corpus callosum
connects hemispheres