Movement into and out of cells
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
concentration gradient
The difference in the concentration of a chemical across a membrane.
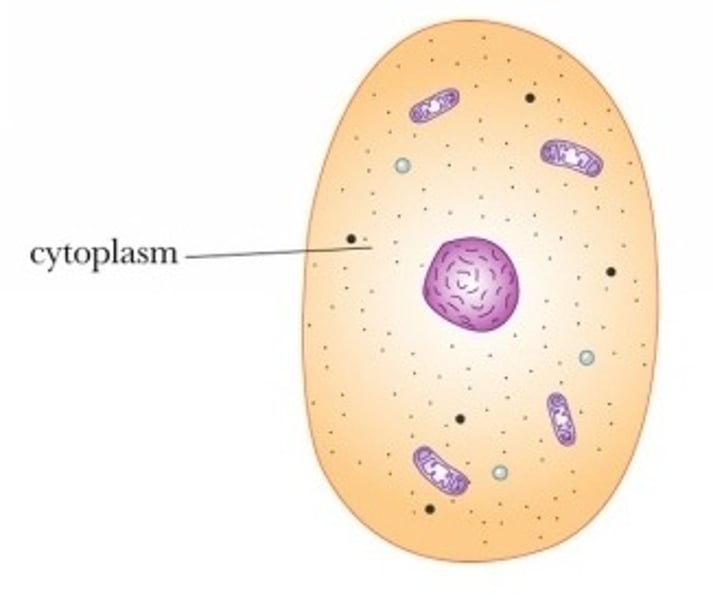
cytoplasm
The living substance inside a cell (not including the nucleus).
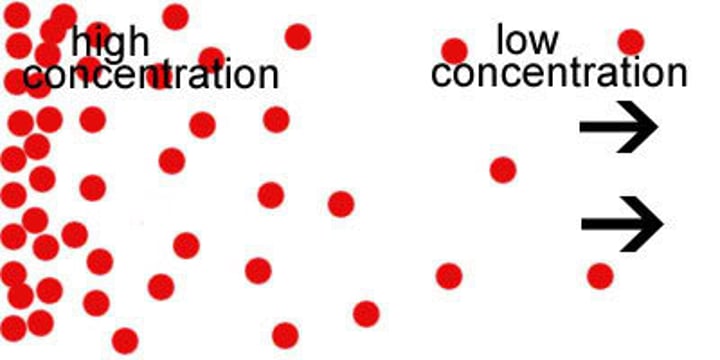
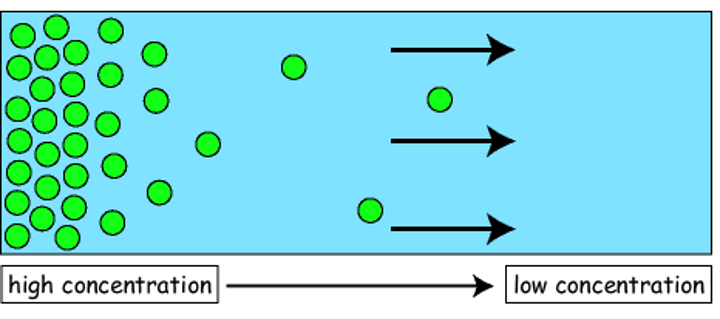
diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
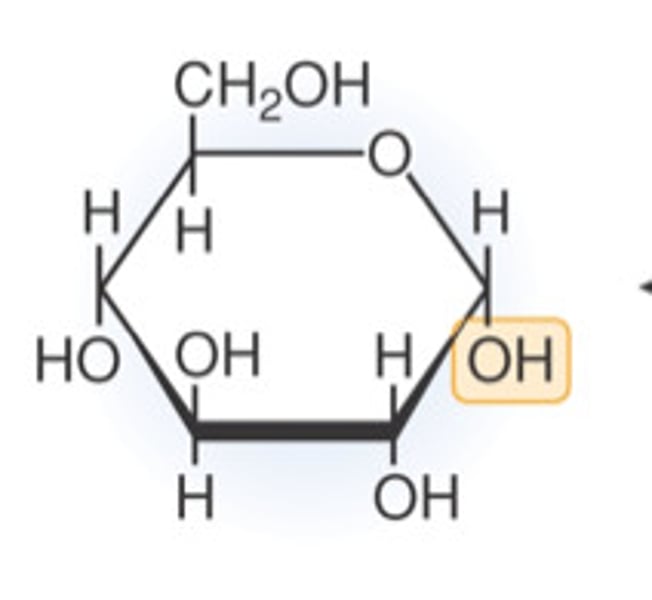
glucose
C6H12O6. A simple sugar used by cells for respiration.
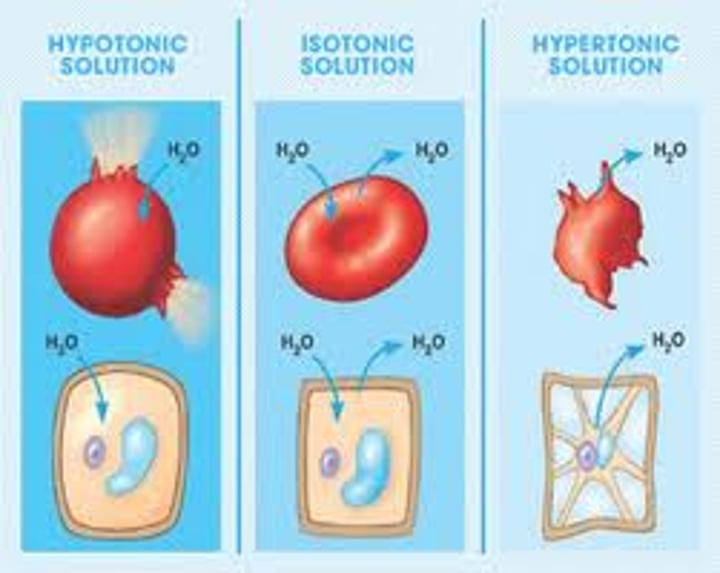
isotonic
Two solutions at the same concentration. An equal amount of water is entering and exiting the cell
mass
The amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g).
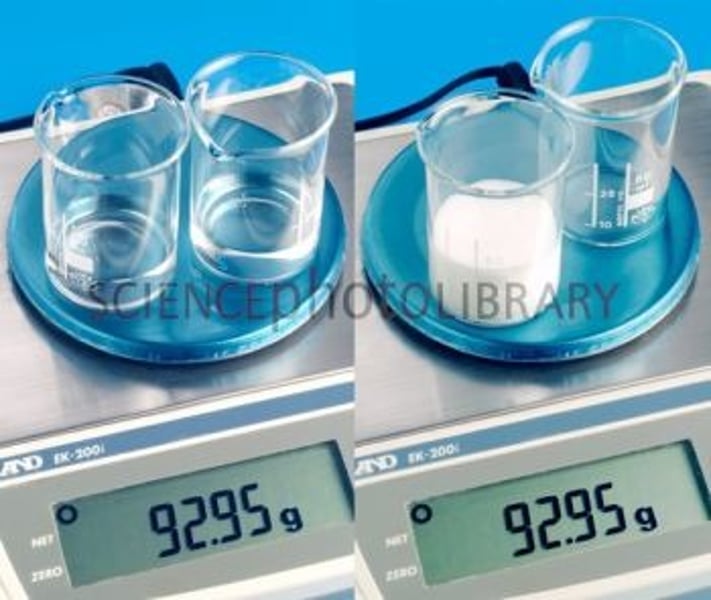

osmosis
The movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
partially permeable
Also called semi-permeable. A partially permeable membrane allows water and other small molecules to pass through, but not larger molecules such as starch.
respiration
The chemical change that takes place inside living cells, which uses glucose and oxygen to release the energy that organisms need to live. Carbon dioxide is a by-product.

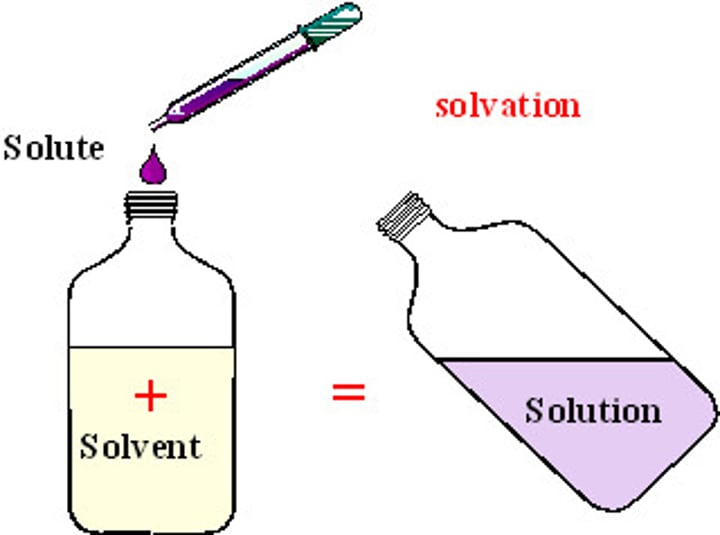
Solute
The dissolved substance in a solution.

solvent
The liquid in which the solute dissolves to form a solution.
sucrose
A disaccharide made from glucose and fructose. It is used as table sugar.

turgid
Enlarged and swollen with water. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis.

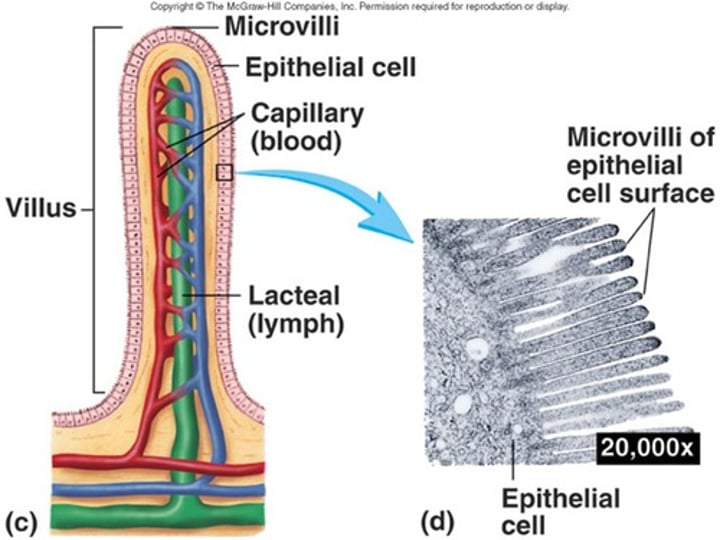
Villi
Finger-like projections in the small intestine that provide a large surface area for the absorption of food.
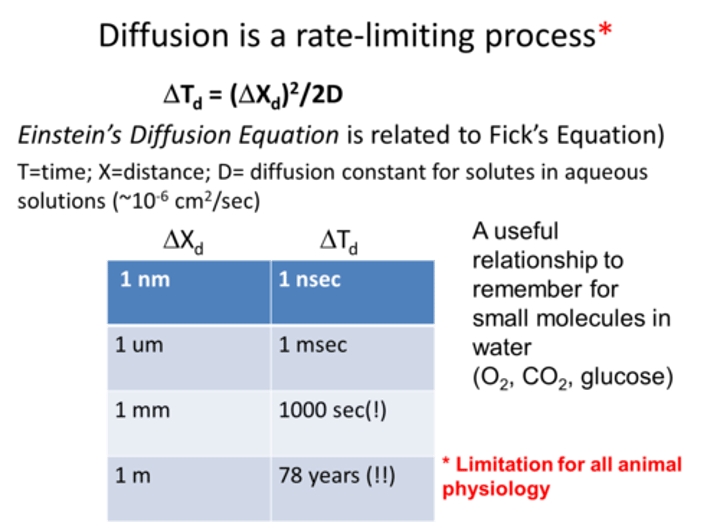
diffusion distance
the greater the distance over which diffusion must occur. The longer it takes, the lower the process.
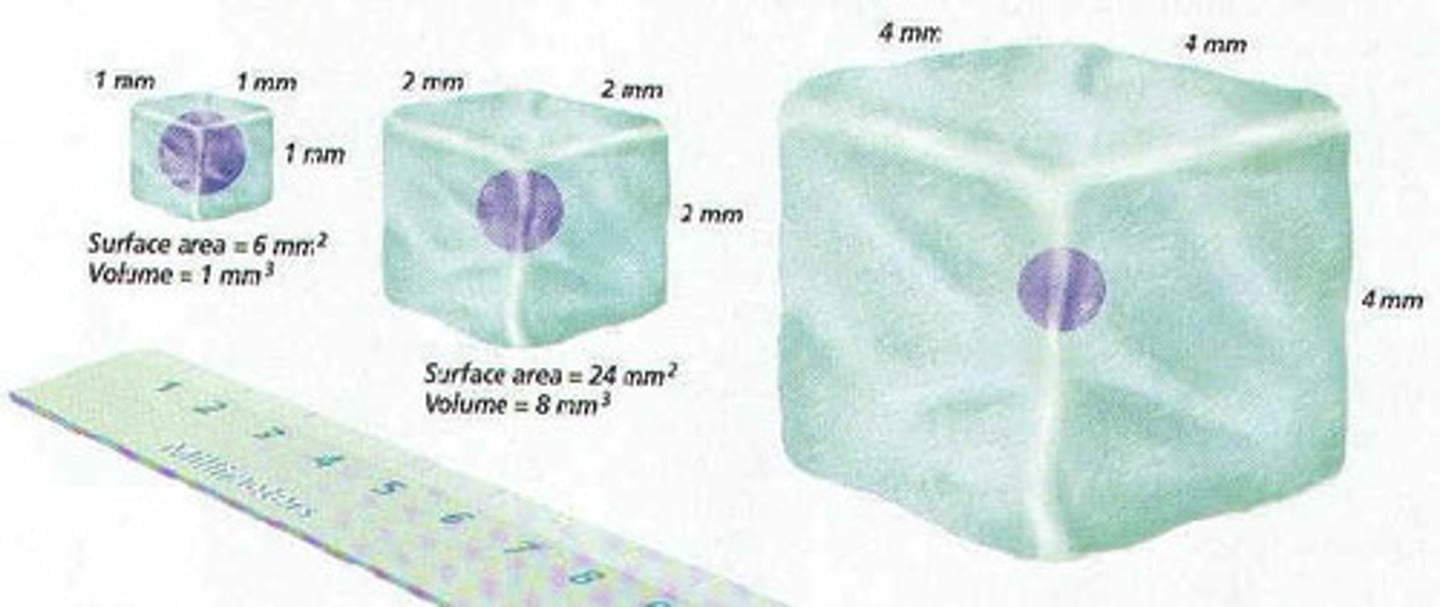
SA:Vol
surface area to volume ratio
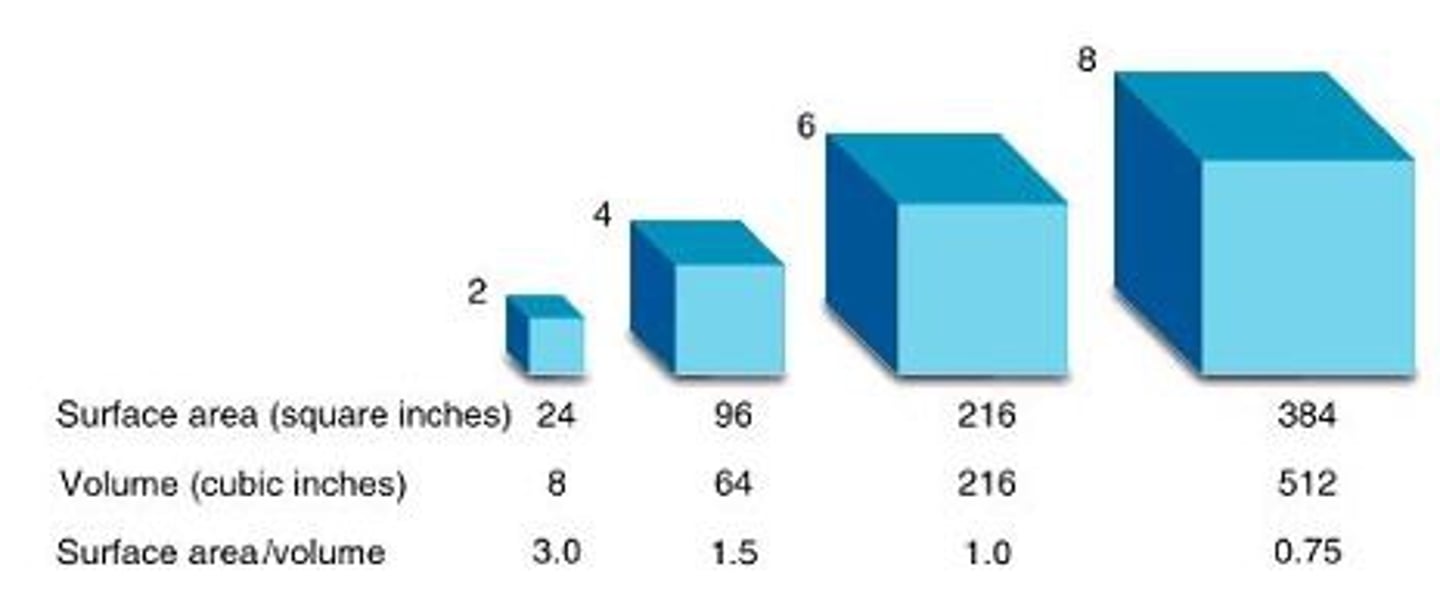
surface area to volume ratio
Ratio of a cell's outside area to its internal volume. A large number means the cell can quickly absorb.
kinetic energy
energy due to motion

active transport
the movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration against the concentration gradient.
Energy
ATP
Flaccid
Lacking firmness. Soft and drooping because of lack of water.
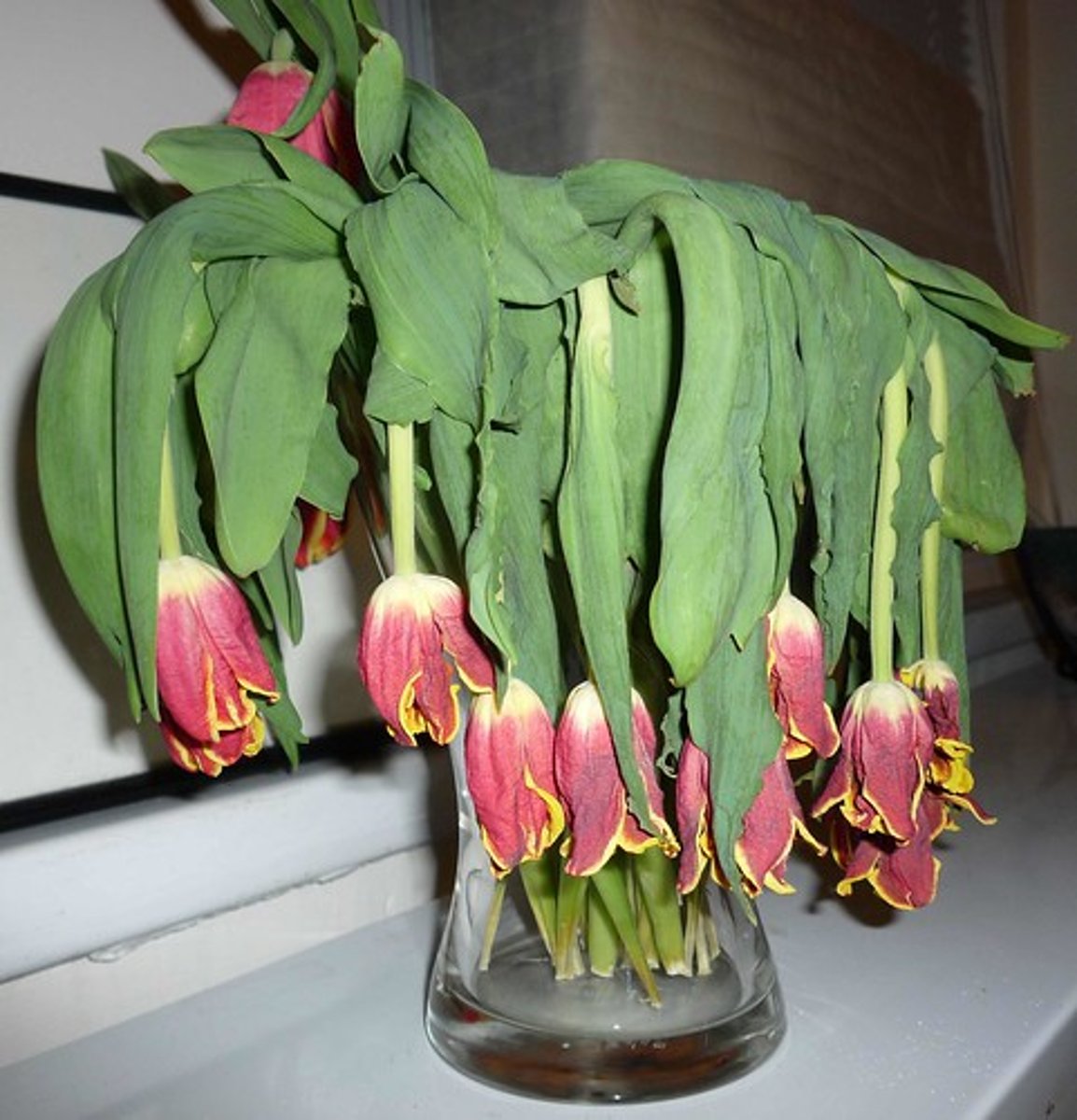

Plasmolysis
This happens when a cell shrinks inside its cell wall while the cell wall remains intact.
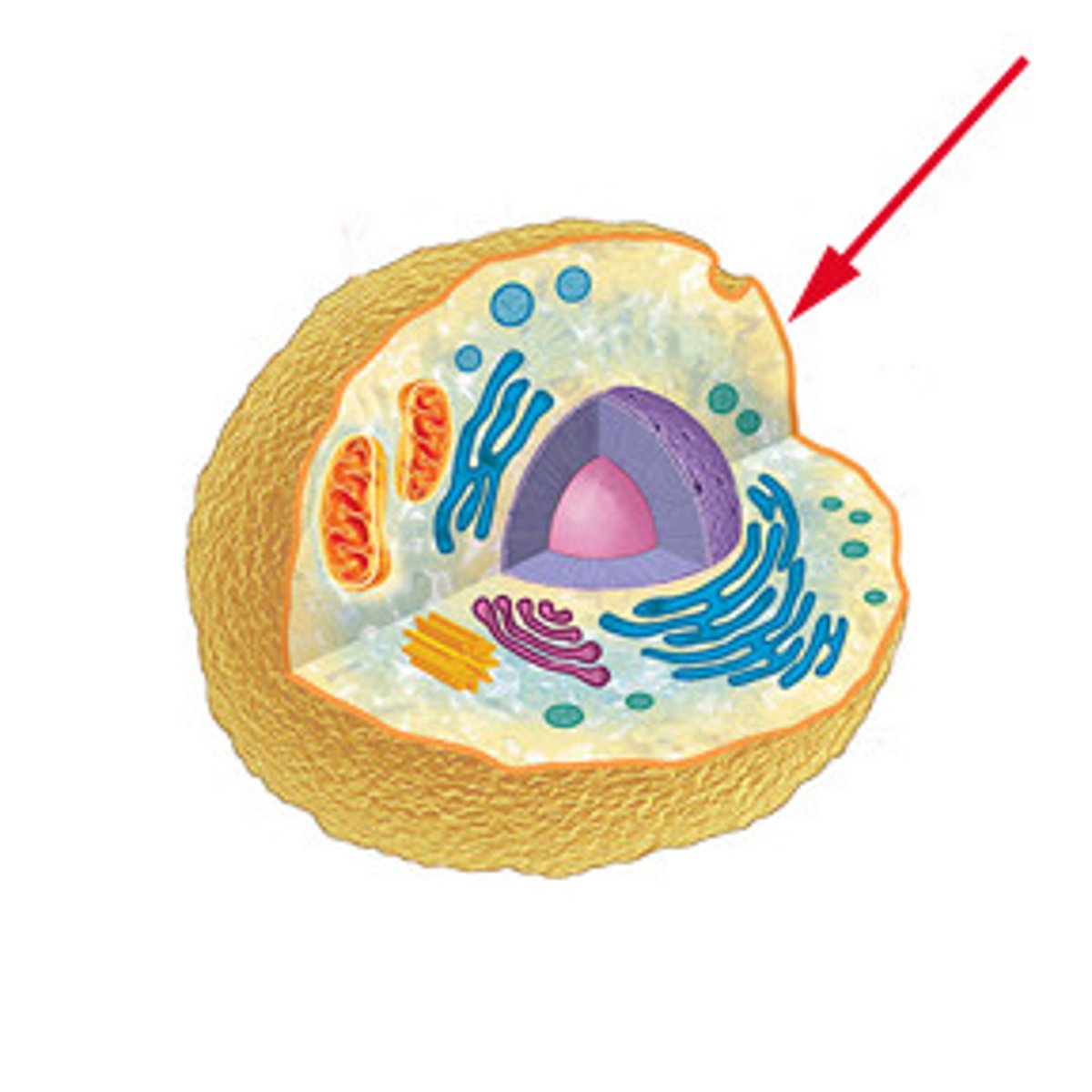
cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
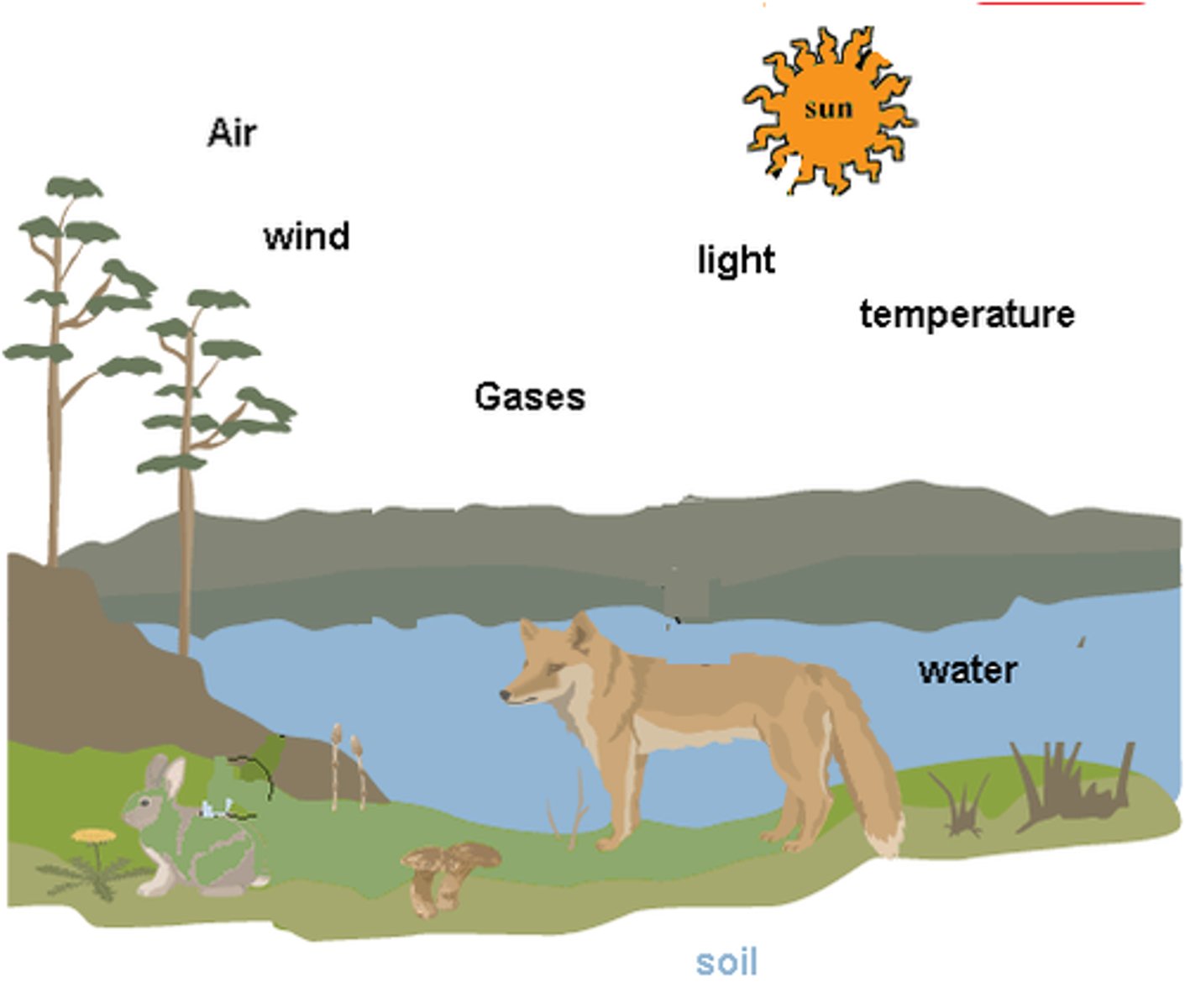
abiotic factors
Nonliving components of environment. Temperature, nutrients, pH.
John wanted to investigate the effect of the size of potato tissue on the rate of osmosis. He cut three different sized cubes of potato, one 0.5 × 0.5 x 0.5 cm, one 1 × 1 × 1 cm
and one 2 × 2 × 2 cm.
He weighed the potato cubes and recorded their masses.
He then placed each cube into a beaker of distilled water and left them for 1 hour. He weighed them again and recorded their new masses.
In each case the mass of the potato cubes increased.
Use your knowledge of osmosis to explain why the mass of each cube increased
water enters / water in / eq;
dilute to more concentrated solution / eq;
partially permeable membrane / eq;
Explain the effect of the different SA:Vol ratios on the rate of osmosis into the potato
more osmosis / faster (small cubes) / greater % increase / greater % change / eq;
larger SA:Vol ratio (of small cubes)
What is meant by the term diffusion
movement of molecules/particles/gases/named molecule;
high conc. to low conc. / down concentration gradient / eq;
Respiration takes place in the middle piece of the sperm cell. Explain why respiration is important to a sperm cell
energy / ATP;
swim / move / move tail / travel
What is meant by the term osmosis
1. water;
2. dilute solution to concentrated solution /
high conc. (of water) to low conc. (of water) / eq;
3. selectively permeable membrane / eq;
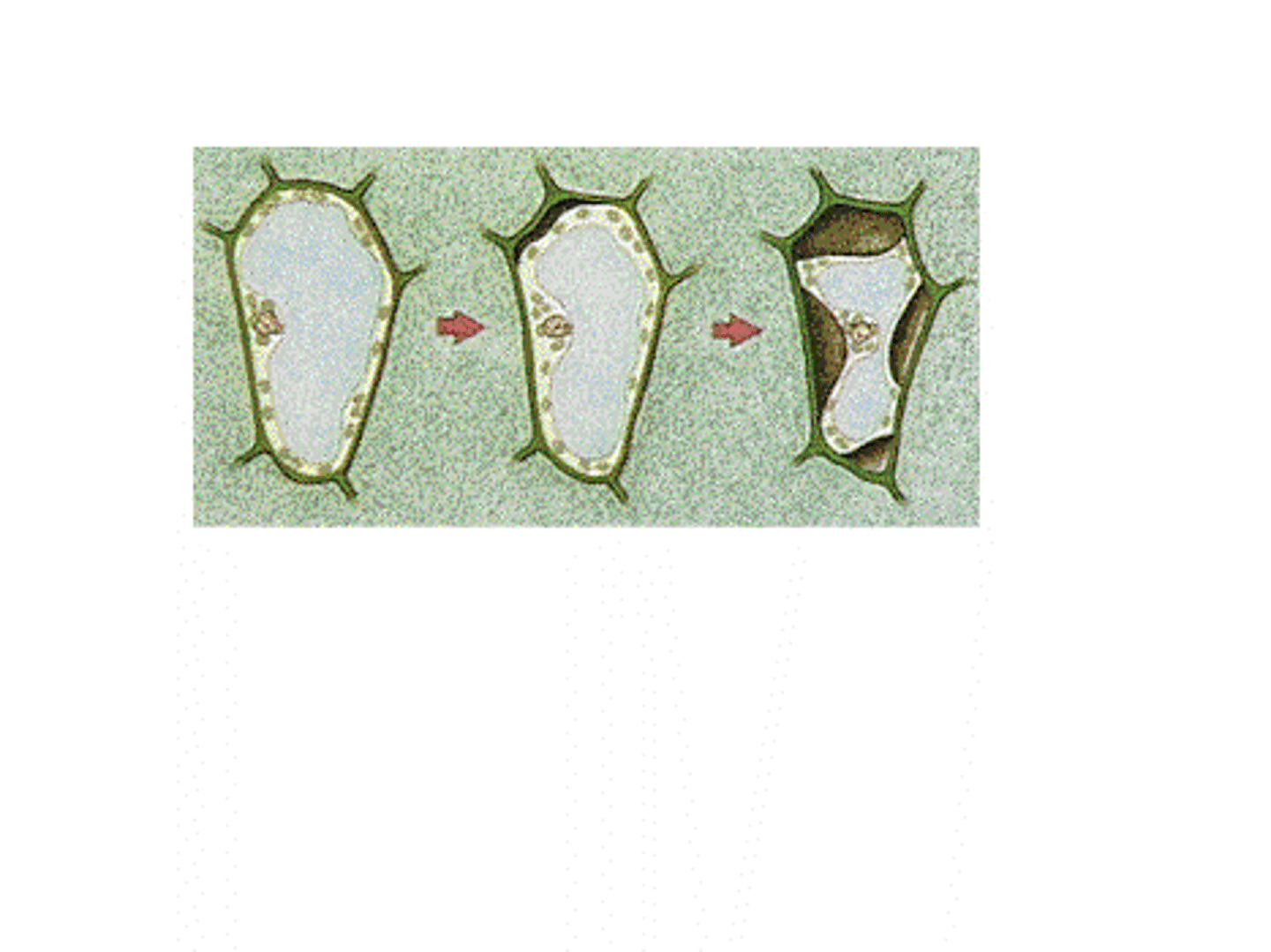
Explain why the cells in distilled water look different when compared to the cells in salt solution.
(in distilled water)
1. water into cells;
2. outside solution/distilled water more dilute
/ down concentration gradient / eq; 3. cell membrane against cell wall / eq; 4. turgid;
(allow converse in salt solution for each point)
1. water leaves cell;
2. outside solution/distilled water less
concentrated / eq;
3. cell membrane shrinks away from cell wall
/eq
4. plasmolysed / flaccid;
If red blood cells are placed in distilled water and examined under a microscope no cells are seen.
Explain why no red blood cells would be seen.
1. water into red blood cell / eq;
2. cells burst / haemolysis / eq;
3. no cell wall;
What is meant by the term anaerobic?
No oxygen
Write the word equation for the anaerobic respiration of yeast
Glucose = carbon dioxide + ethanol