mastering biology chapter 3
4.2(5)
Card Sorting
1/104
Last updated 3:02 AM on 12/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
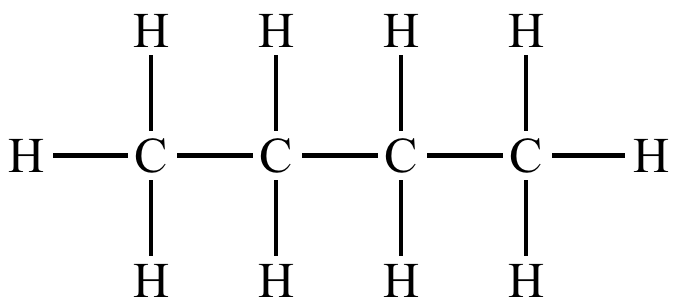
hydrocarbon
an organic compound containing only C and H
2
New cards
isomer
compounds with the same molecular formula but different 3D structures
3
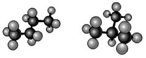
New cards
structural isomer
differs in covalent bonds between atoms
4
New cards
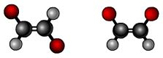
geometric isomer
differs in the arrangement of atoms around a double bond
5
New cards
enantiomer (stereoisomer)
molecules that are mirror images of each other
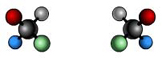
6
New cards
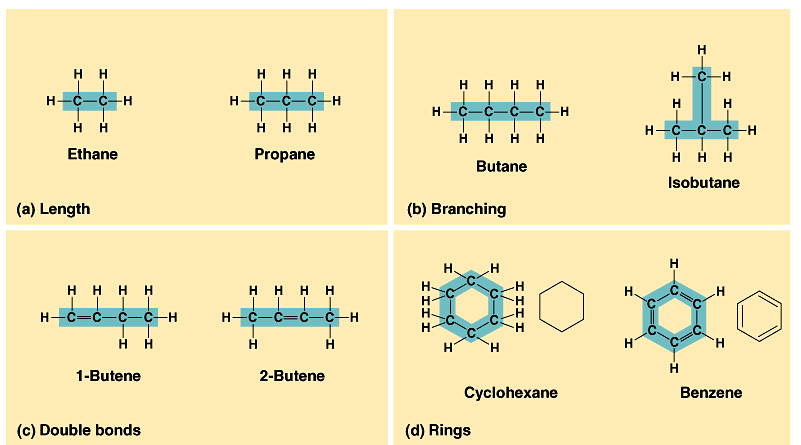
carbon chain (skeleton)
-varies in length
-varies in number & location of double bonds
-can be branched/unbranched
-can be arranged in rings
-varies in number & location of double bonds
-can be branched/unbranched
-can be arranged in rings
7
New cards
functional group
-atoms attached to a carbon skeleton involved in chemical reactions
-determines the characteristics of a molecule
-compounds that contain them are usually hydrophilic
-determines the characteristics of a molecule
-compounds that contain them are usually hydrophilic
8
New cards
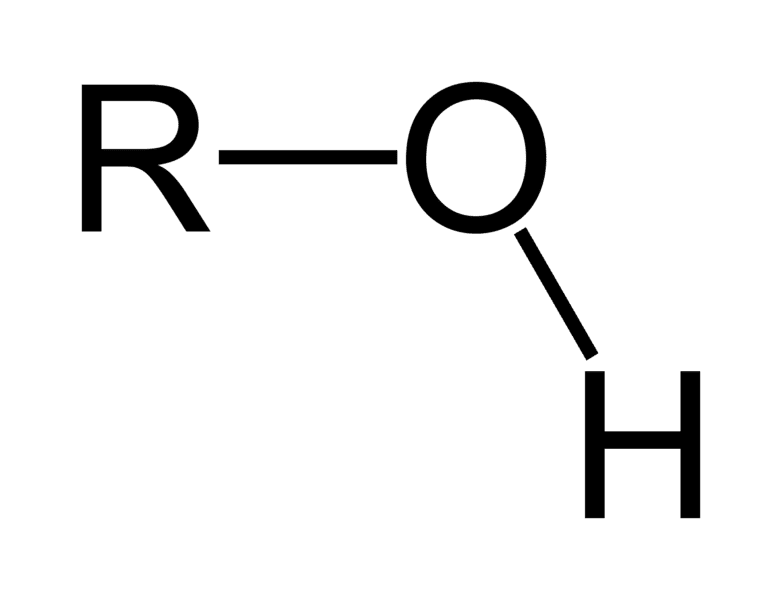
hydroxyl group
-O bonded to H
-needs to be bonded w/ a carbon skeleton
-needs to be bonded w/ a carbon skeleton
9
New cards
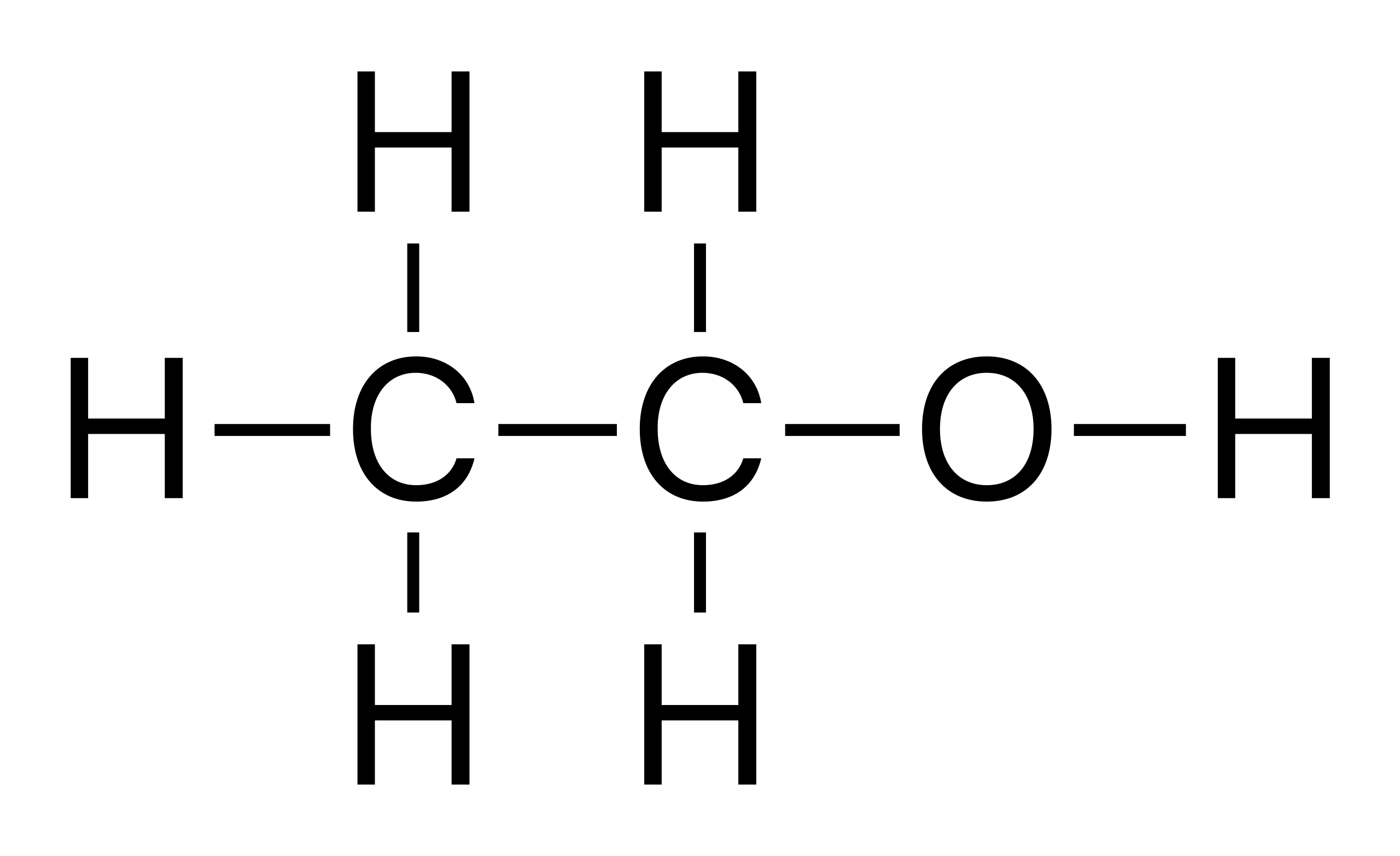
alcohol
organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (i.e. ethanol)
10
New cards
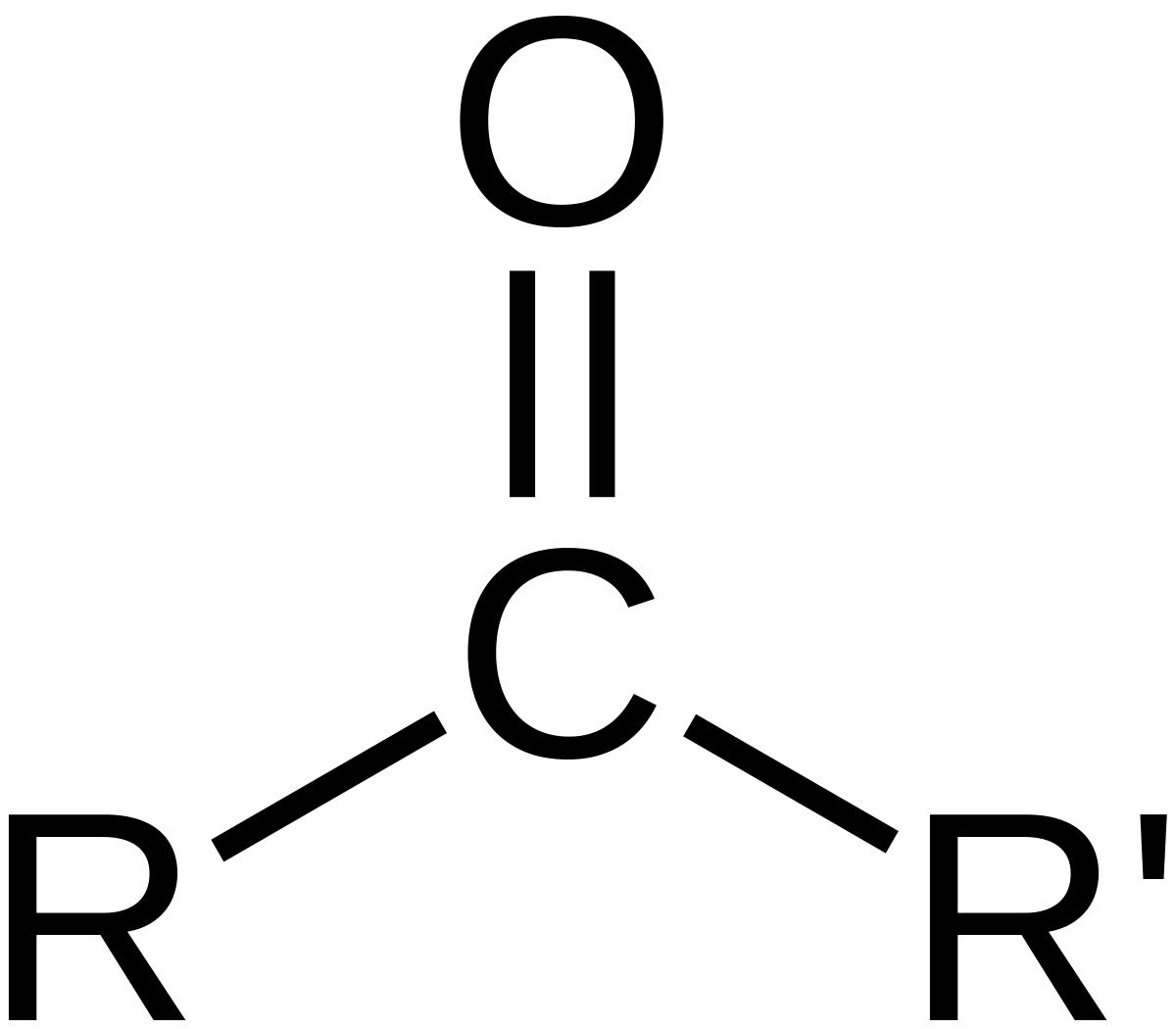
carbonyl group
-C double bonded to O
-can be located within or at the end of a carbon skeleton
-works w/ carboxyl groups to make sugars
-can be located within or at the end of a carbon skeleton
-works w/ carboxyl groups to make sugars
11
New cards
aldehyde
organic compound in which the carbonyl group is attached at the end of a carbon chain
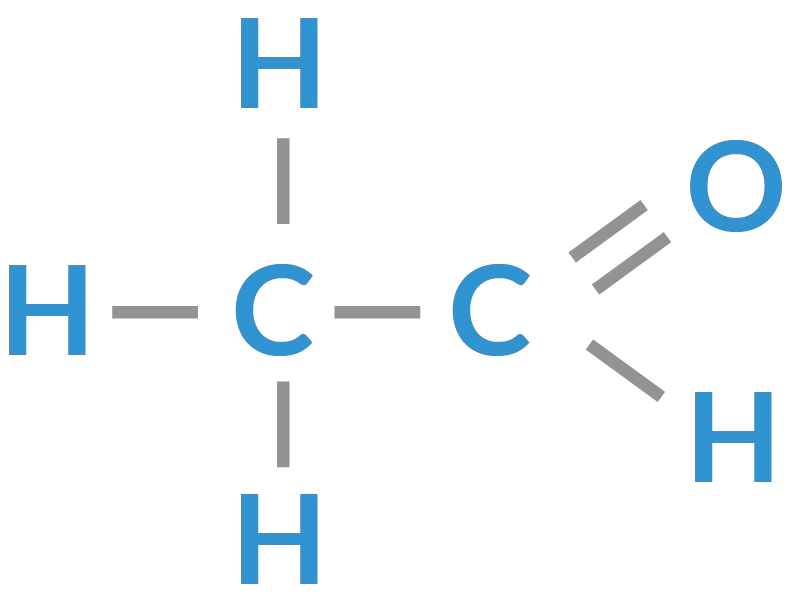
12
New cards
ketone
organic compound in which the carbonyl group is attached to a carbon atom within the carbon chain
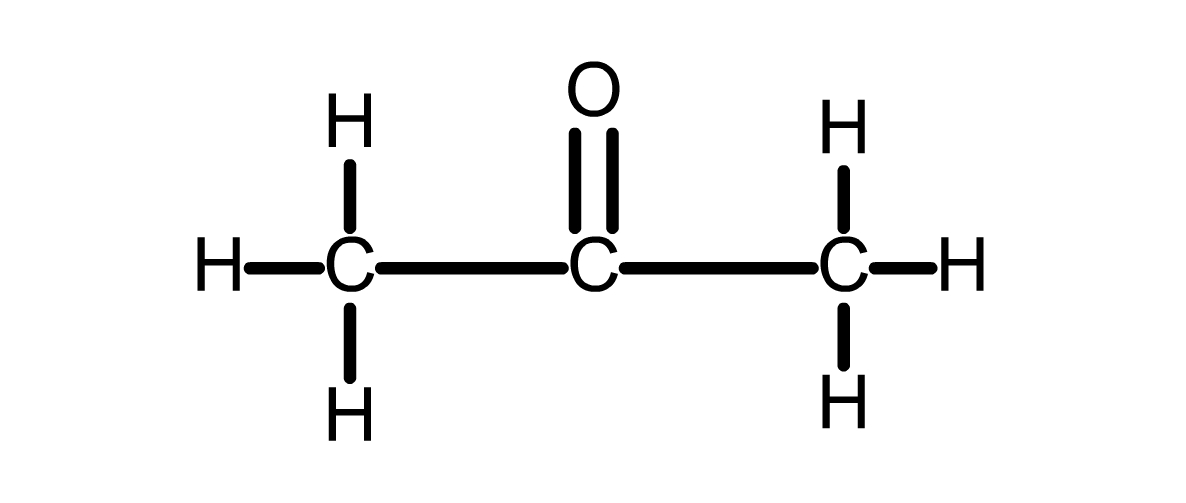
13
New cards
carboxyl group
-C double bonded to O and single bonded to a hydroxyl
-acts as an acid by donating H+
-found in all proteins
-acts as an acid by donating H+
-found in all proteins
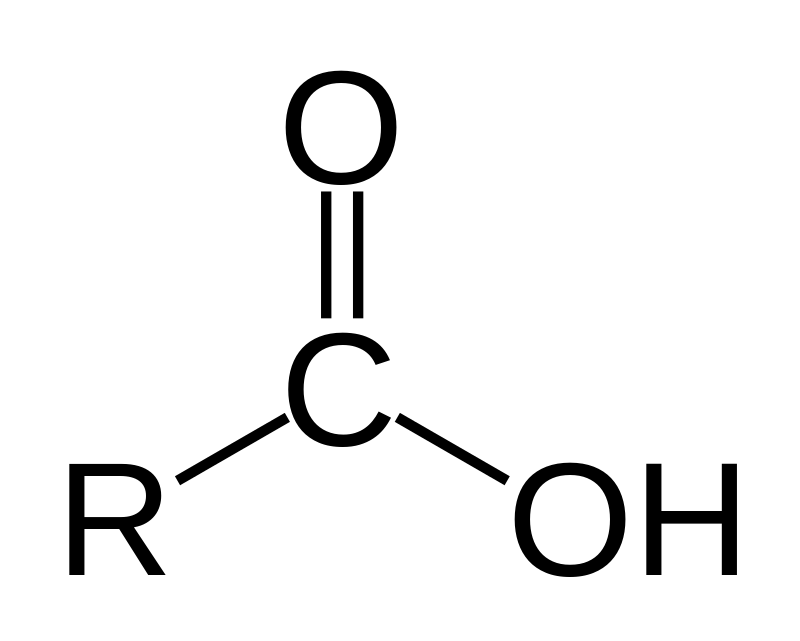
14
New cards
carboxylic acid
organic compound that contains a carboxyl group
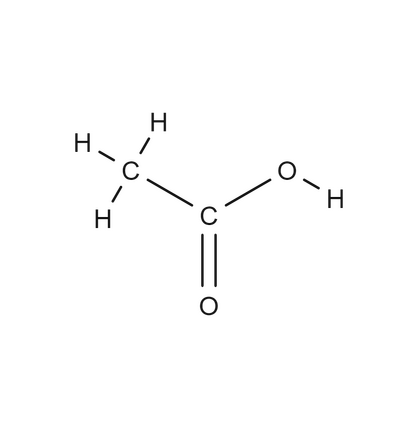
15
New cards
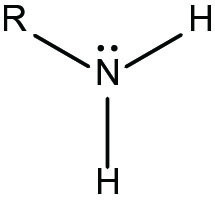
amino group
-N bonded to two H atoms
-acts as a base by picking up H+ from a solution to become ionized (NH3+)
-found in all proteins
-acts as a base by picking up H+ from a solution to become ionized (NH3+)
-found in all proteins
16
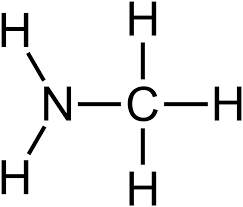
New cards
amine
compound containing an amino group
17
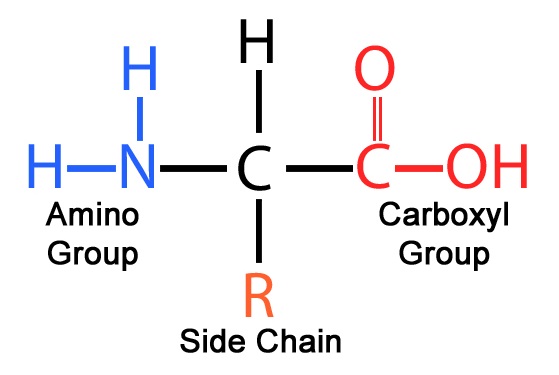
New cards
amino acid
-Organic compounds containing a central C bonded to an H atom, amino group, carboxyl group, and R group
-R-group that projects from the backbone makes each amino acid unique
-Building blocks of proteins
-R-group that projects from the backbone makes each amino acid unique
-Building blocks of proteins
18
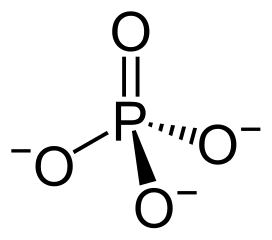
New cards
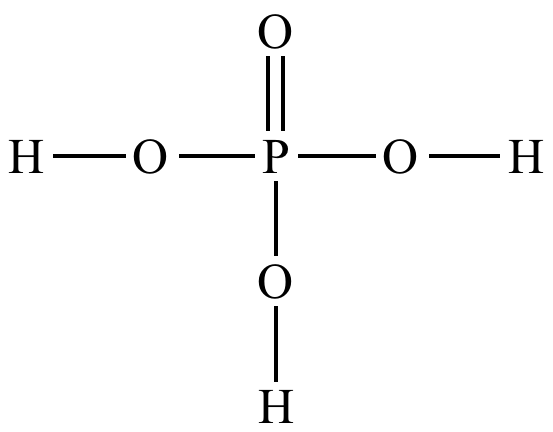
phosphate group
-P doubled bonded to O single bonded to 3 O atoms
-acts as an acid, losing H+
-acts as an acid, losing H+
19
New cards
phosphate
-organic compound containing phosphate groups
-involved in energy transfers (ATP)
-involved in energy transfers (ATP)
20
New cards
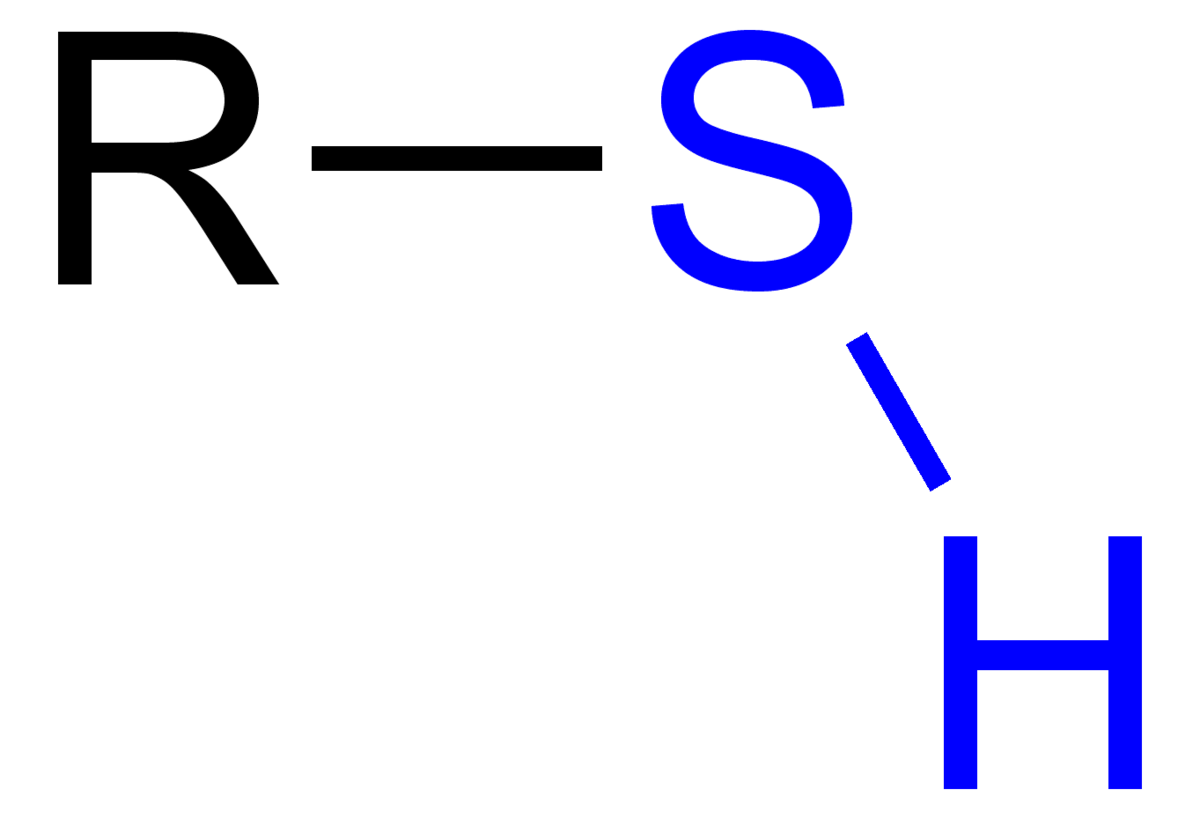
sulfhydryl group
-S bonded to H
-groups can react & form a crosslink that stabilizes the structure of many proteins
-groups can react & form a crosslink that stabilizes the structure of many proteins
21
New cards
thiol
organic compound that contains a sulfhydryl group
22
New cards
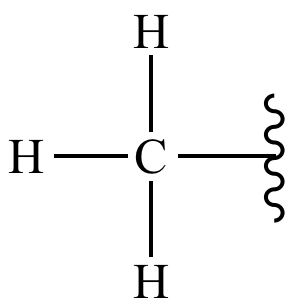
methyl group
-C bonded to 3 H atoms
-hydrophobic
-nonpolar
-hydrophobic
-nonpolar
23
New cards
methylated compounds
-organic compound that contains a methyl group
-component of DNA that affects gene expression
-component of DNA that affects gene expression
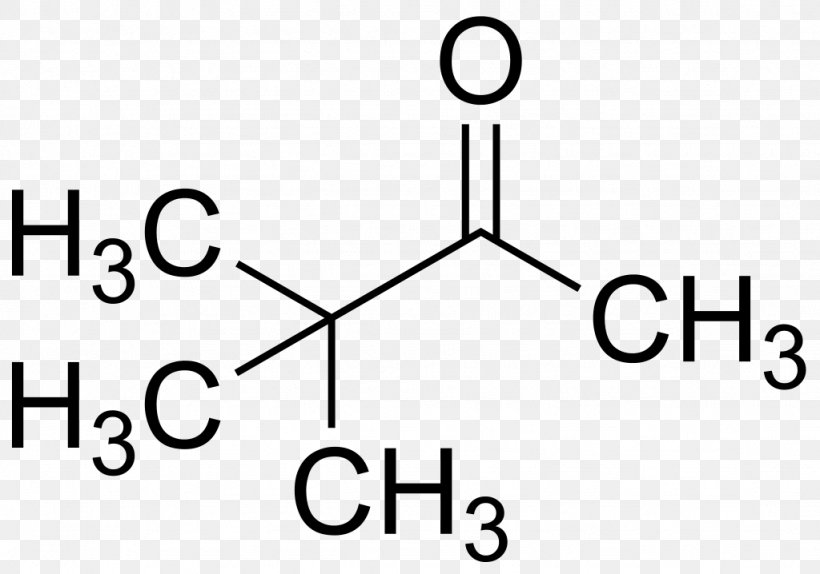
24
New cards
monomer
subunit that serves as a building block of polymers
25
New cards
polymer
-many monomers linked together by covalent bonds
-caused by dehydration
-caused by dehydration
26
New cards
dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction/polymerization)
-covalently bonding monomers to form a polymer through the removal of H2O (H and OH)
-energy can be stored when the bonds are formed
-energy can be stored when the bonds are formed
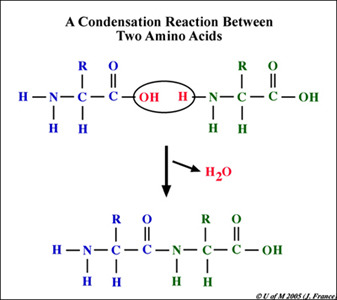
27
New cards
hydrolysis
-chemical reaction in which bonds between molecules in a polymer are broken down by the addition of H2O to form monomers (H and OH)
-energy is released when the bonds are broken
-energy is released when the bonds are broken
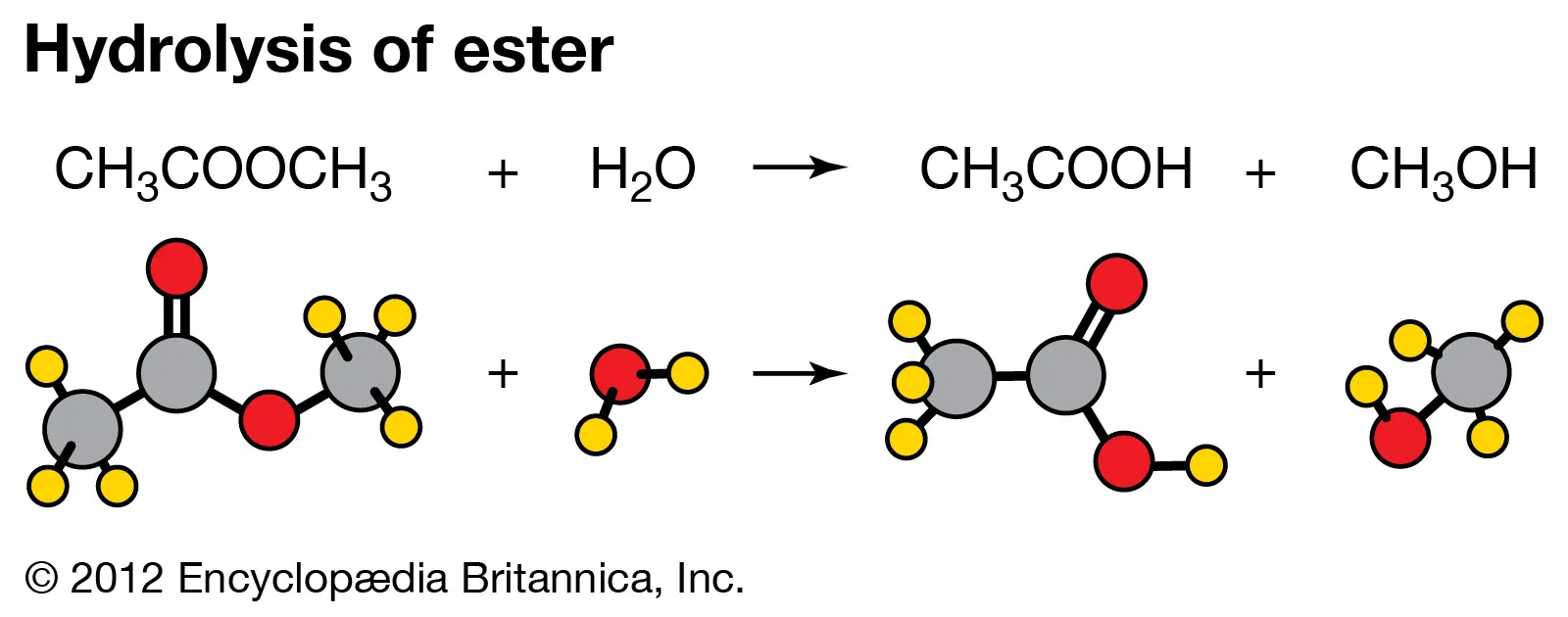
28
New cards
macromolecule (organic compound)
-giant molecule (polymer) formed by the joining of smaller molecules (monomers) through dehydration
-contains carbon
-contains carbon
29
New cards
nucleic acids
-contains C, H, O, N, P
-polymer made of nucleotide monomers
-sequence of nucleotides carries information
-polymer made of nucleotide monomers
-sequence of nucleotides carries information
30
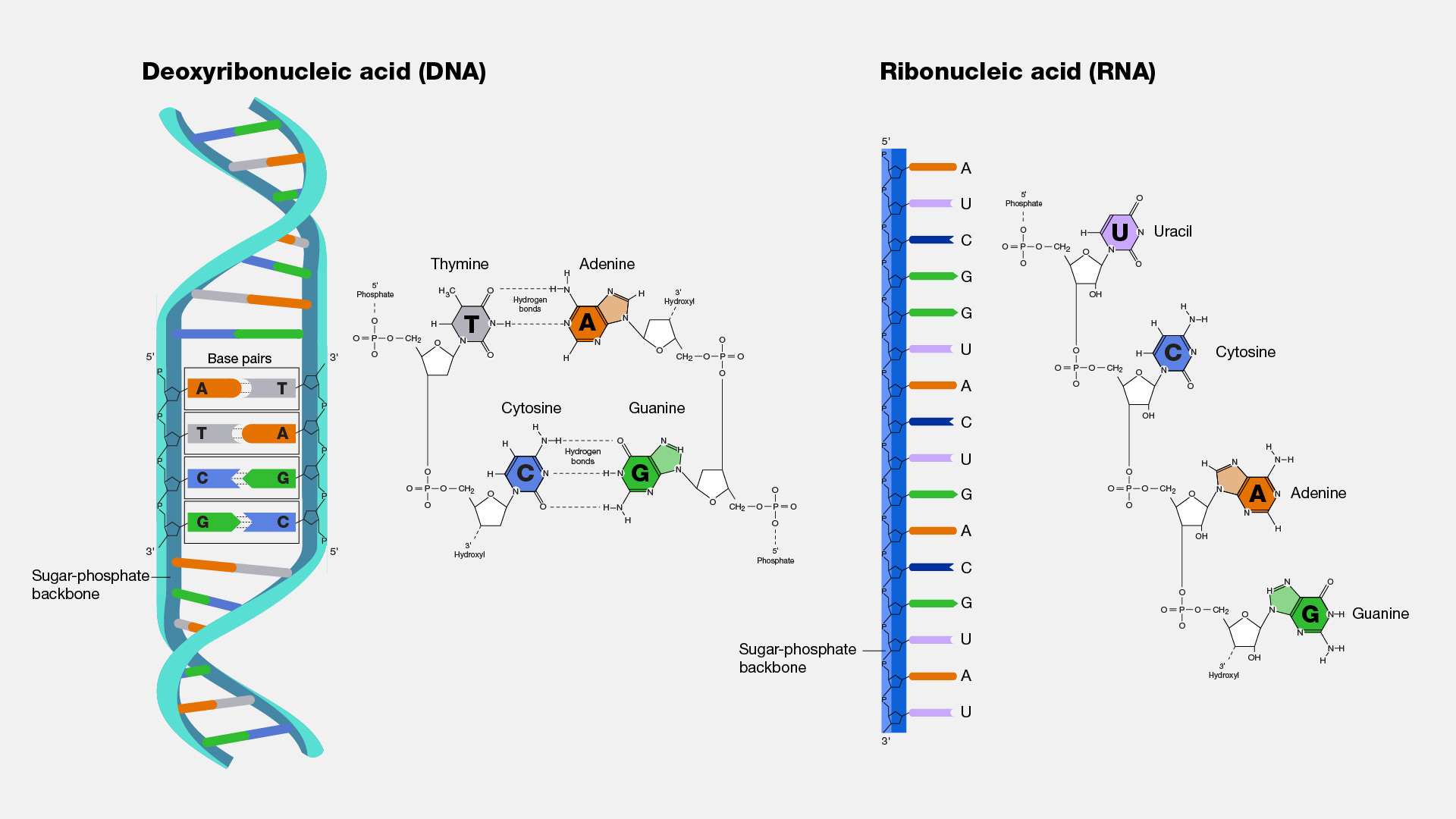
New cards
DNA
-Polymer that stores hereditary information
-Single molecule contains 2 polynucleotides
-Double helix formed by the twisting of 2 complimentary strands of nucleotides
-Backbone consists of alternating sugars and phosphates
-Strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases
-Single molecule contains 2 polynucleotides
-Double helix formed by the twisting of 2 complimentary strands of nucleotides
-Backbone consists of alternating sugars and phosphates
-Strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases
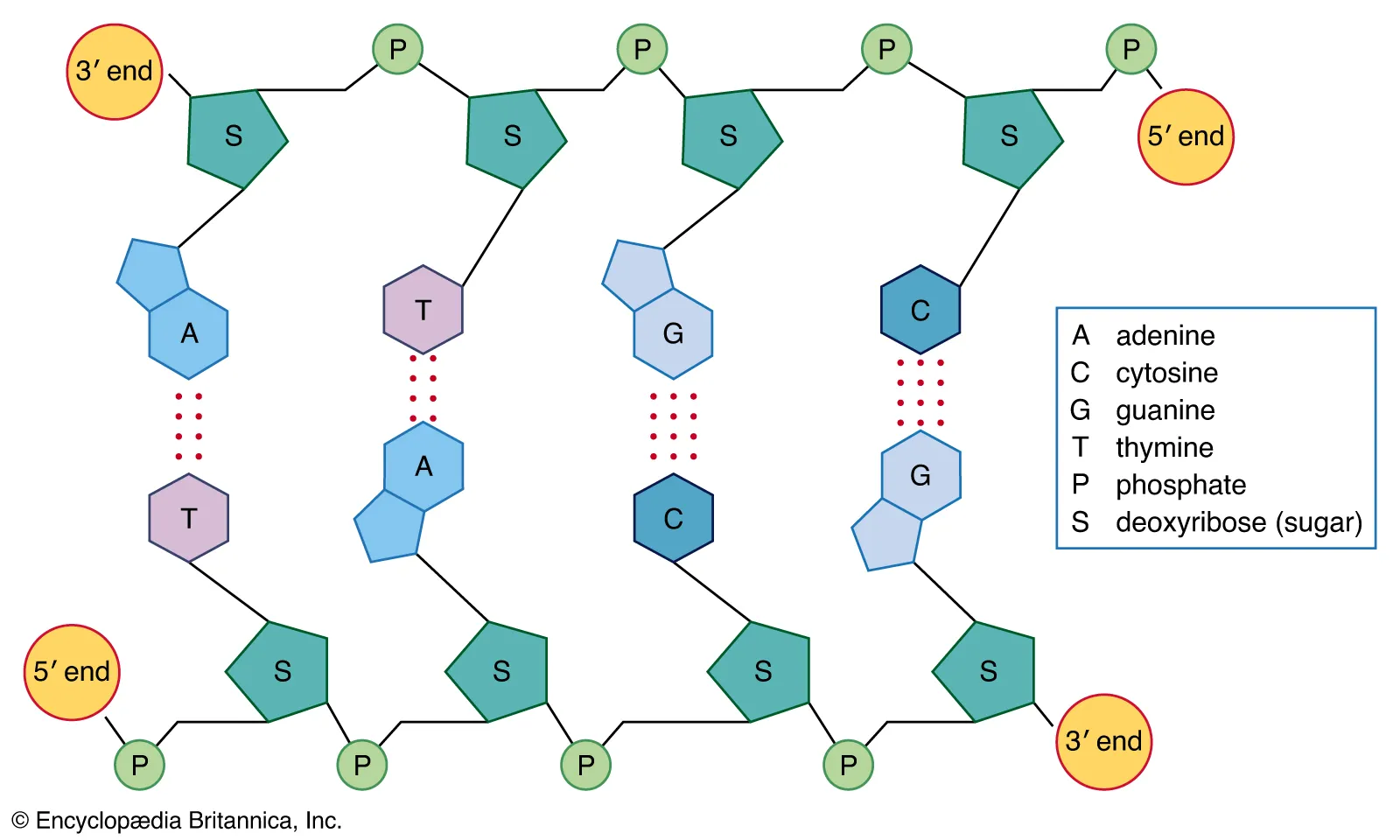
31
New cards
nitrogenous base pairs
-adenine w/ thymine (uracil in RNA)
-cytosine w/ guanine
-cytosine w/ guanine
32
New cards
RNA
-Polymer that synthesizes proteins
-Consists of a single-stranded polypeptide
-Contains ribose
-Uracil instead of thymine
-Copied from a DNA molecule
-Shorter than DNA
-Consists of a single-stranded polypeptide
-Contains ribose
-Uracil instead of thymine
-Copied from a DNA molecule
-Shorter than DNA
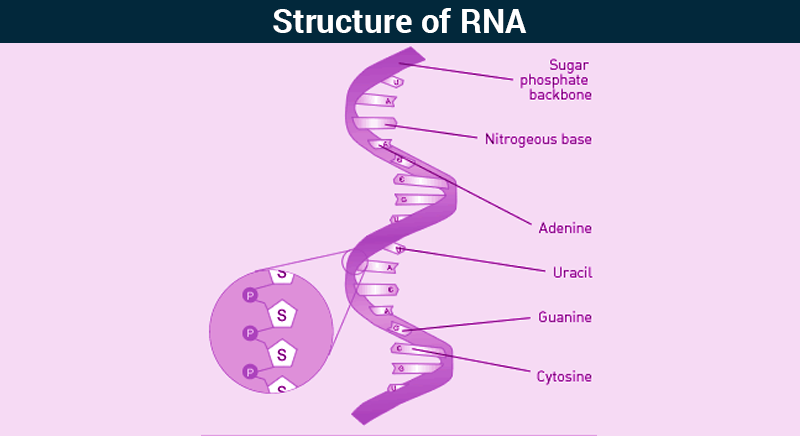
33
New cards
nucleotide
-building block of DNA/RNA
-consists of a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose/ribose), nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group
-consists of a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose/ribose), nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group
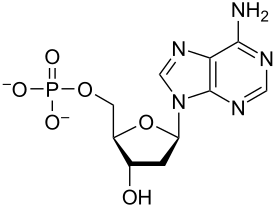
34
New cards
polynucleotide
-polymer of nucleotide monomers
-backbone consists of alternating sugars and phosphates
-bases are attached to the sugars
-backbone consists of alternating sugars and phosphates
-bases are attached to the sugars
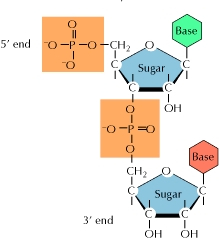
35
New cards
gene
-String of nucleotides
-Sequence of nucleotides determine the primary sequence of amino acids of the produced protein
-Contains the information necessary to build protein/molecule of RNA
-Carries information that is then translated into the amino acid sequence of proteins
-Sequence of nucleotides determine the primary sequence of amino acids of the produced protein
-Contains the information necessary to build protein/molecule of RNA
-Carries information that is then translated into the amino acid sequence of proteins
36
New cards
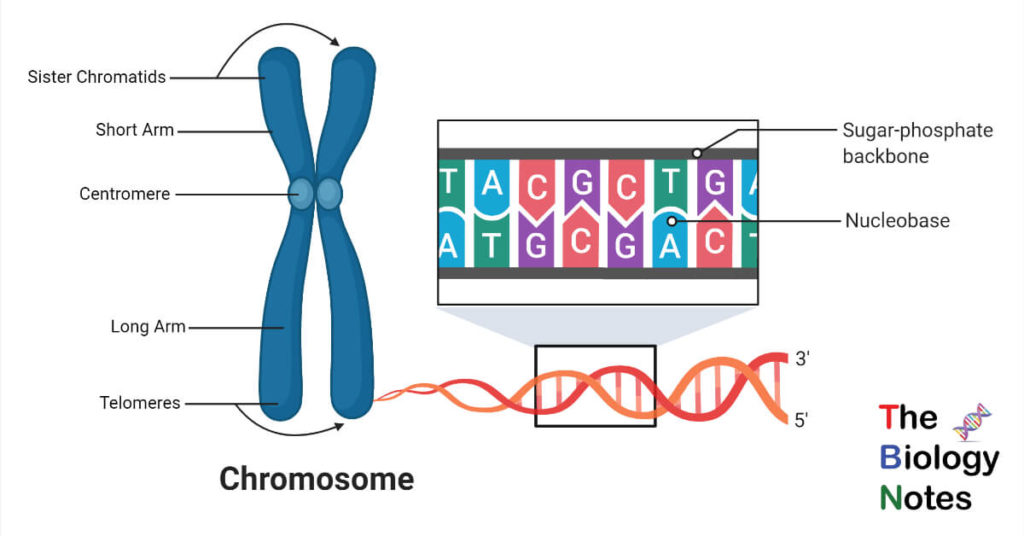
chromosome
-long DNA molecule with part of or all of the genes
-genes are separated by junk DNA
-genes are separated by junk DNA
37
New cards
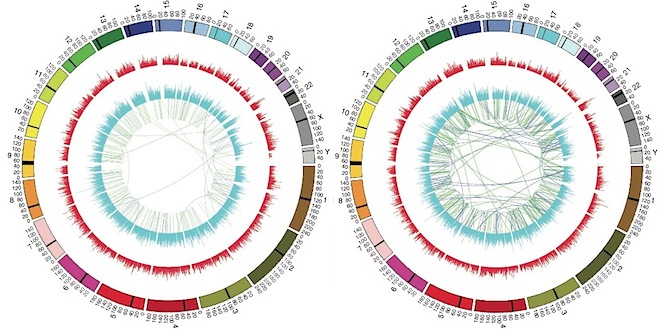
genome
complete collection of an organism's chromosomes and the genes within them
38
New cards
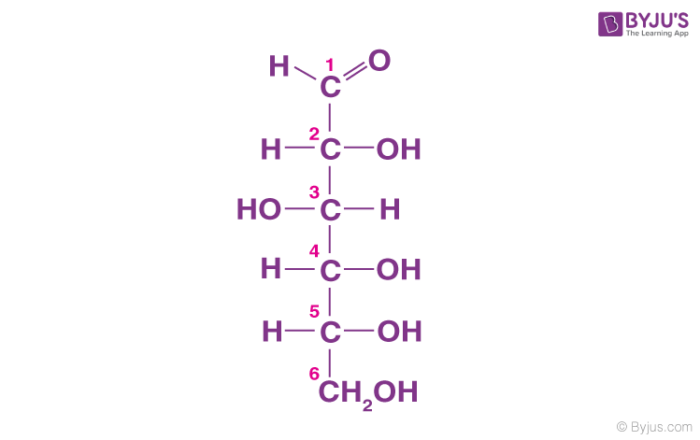
carbohydrates
-contains C, H, and O in a 1:2:1 ratio
-used as fuel for cellular work (form of immediate energy)
-form of glucose
-hydrophilic
-used as fuel for cellular work (form of immediate energy)
-form of glucose
-hydrophilic
39
New cards
membrane carbohydrates
-Marks the cell's identity
-Controls the cell's activities
-Protein made by other cells can bind to them
-Controls the cell's activities
-Protein made by other cells can bind to them
40
New cards
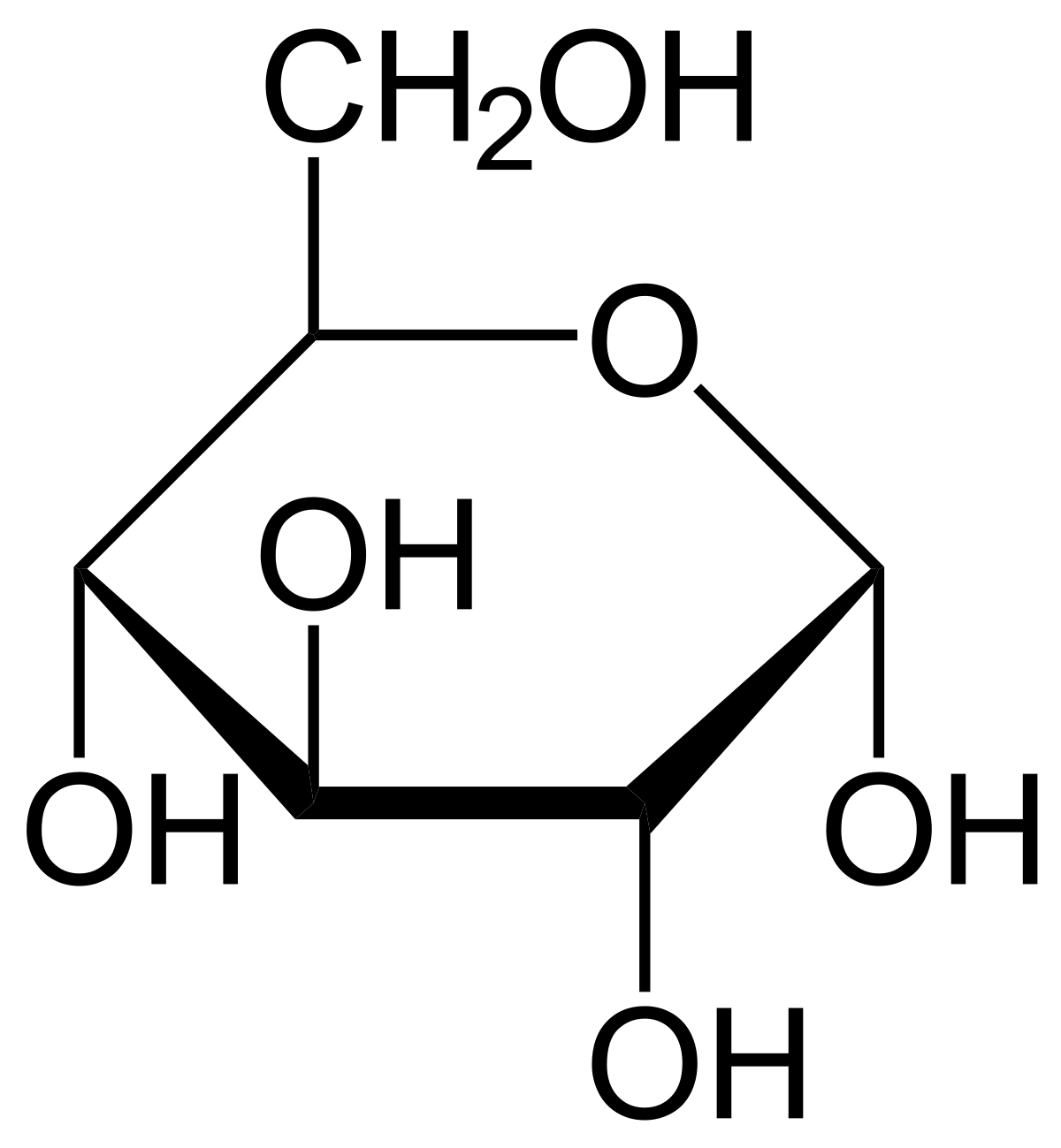
glucose
-Monosaccharide that serves as a building block for many polysaccharides
-Oxidation in cellular respiration is a source of ATP
-Carbon skeleton can be used to build many organic molecules
-Oxidation in cellular respiration is a source of ATP
-Carbon skeleton can be used to build many organic molecules
41
New cards
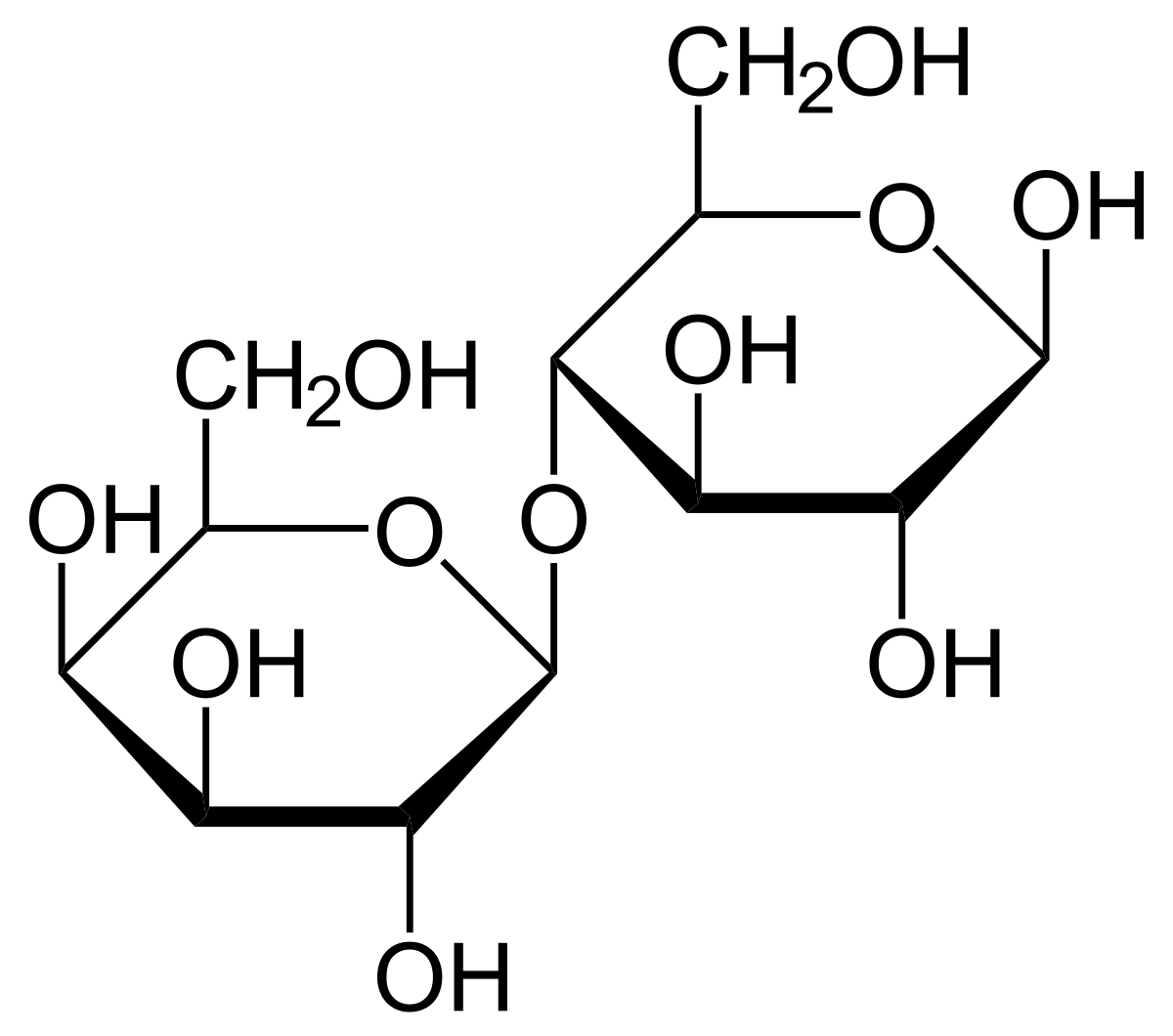
glycosidic bond
covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate w/ another group
42
New cards
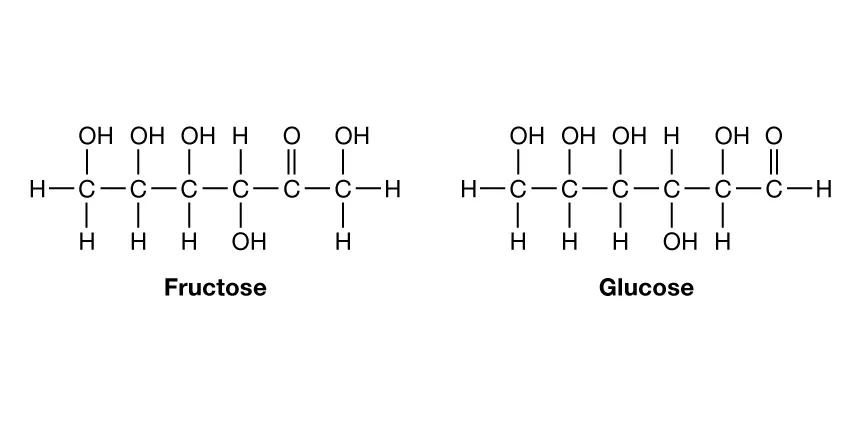
monosaccharide
-monomer of carbohydrates
-simple sugar
-similar 1:2:1 ratio
-contain numerous hydroxyl groups and a carbonyl group
-carbon skeletons range from 3 to 7 C's
-simple sugar
-similar 1:2:1 ratio
-contain numerous hydroxyl groups and a carbonyl group
-carbon skeletons range from 3 to 7 C's
43
New cards
polysaccharide
-long chains of sugars
-monosaccharides joined together via dehydration
-act as identification tags on cell membranes
-monosaccharides joined together via dehydration
-act as identification tags on cell membranes
44
New cards
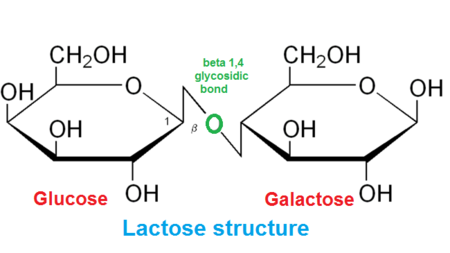
lactose
-disaccharide (sugar) consisting of glucose and galactose
45
New cards
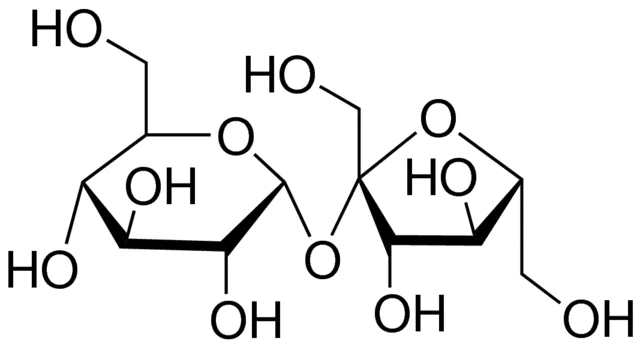
sucrose
-disaccharide consisting of glucose and fructose
-circulates in plant sap
-obtained from sugar cane and sugar beets to form table sugar
-circulates in plant sap
-obtained from sugar cane and sugar beets to form table sugar
46
New cards
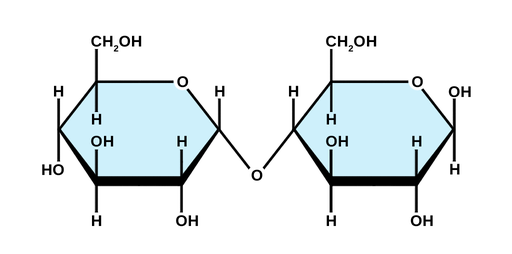
maltose
-disaccharide consisting of 2 glucose
-produced by the digestion of starch in a sprouting seed/intestine of an animal
-produced by the digestion of starch in a sprouting seed/intestine of an animal
47
New cards
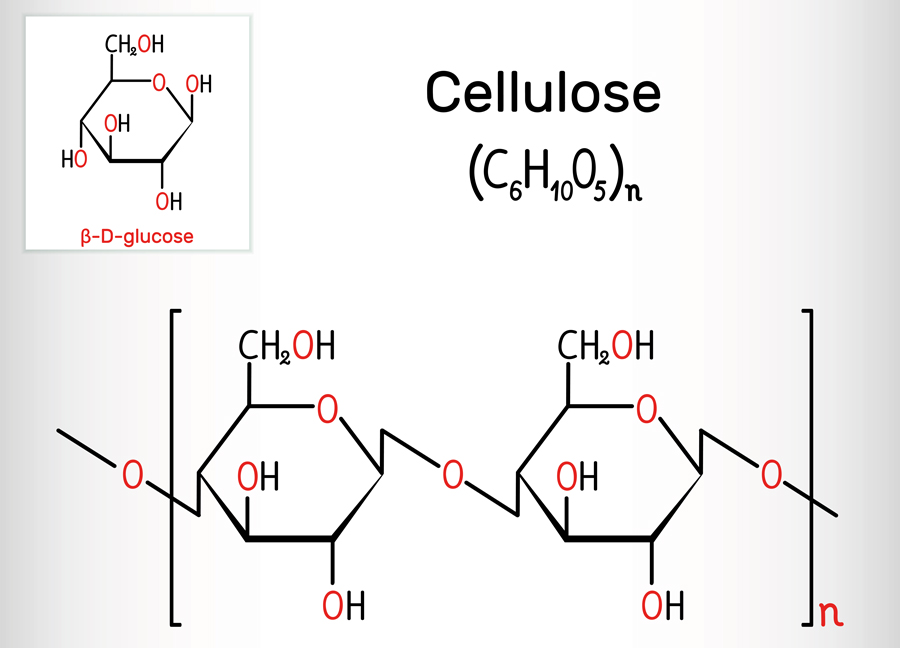
cellulose (fiber)
-polysaccharide that composes plant cell walls
-provides structural support
-most abundant organic compound
-indigestible without the help of bacteria
-provides structural support
-most abundant organic compound
-indigestible without the help of bacteria
48
New cards
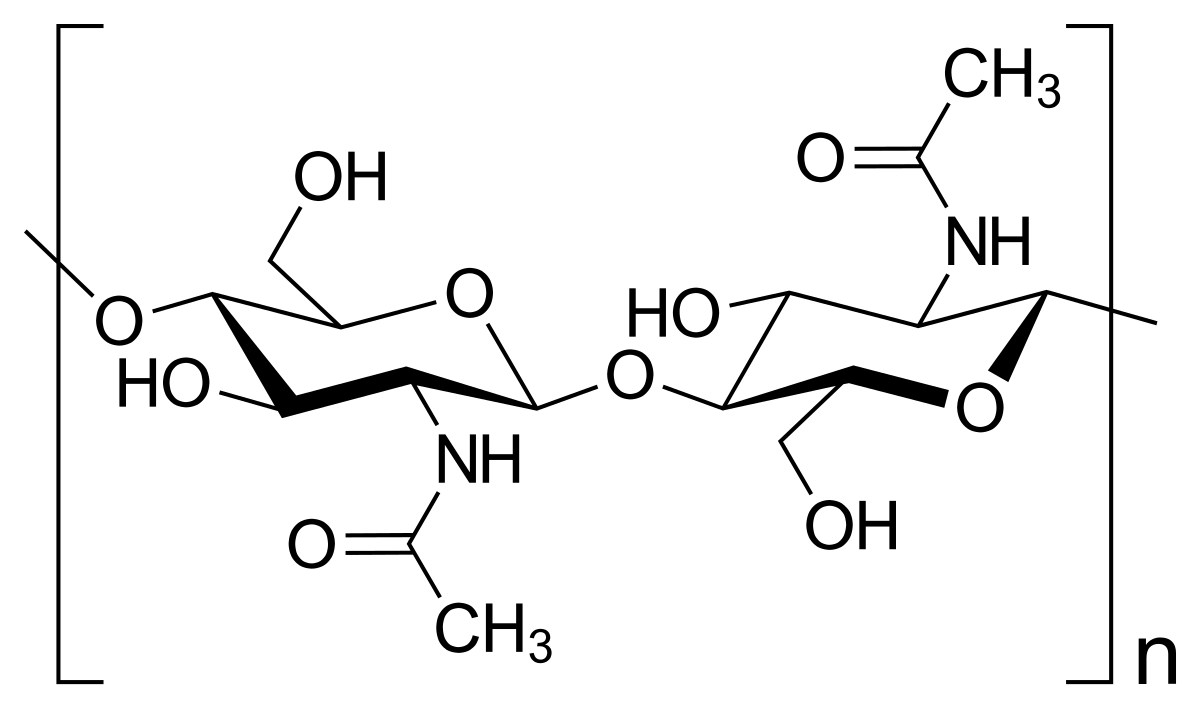
chitin
polysaccharide that provides structural support in animal cells
49
New cards
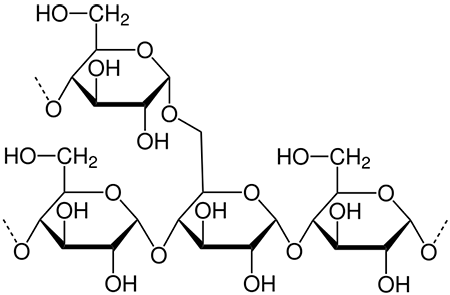
starch
-polysaccharide found in the chloroplast
-stores energy
-made of glucose
-stores energy
-made of glucose
50
New cards
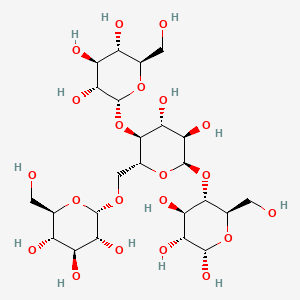
glycogen
-polysaccharide that stores energy in animal cells by linking sugar molecules with insoluble grains
-found in muscles & liver
-found in muscles & liver
51
New cards
lipids
-contains C, H, and O
-3 fatty acids joined to 1 glycerol
-stores energy between C and H bonds
-hydrophobic
-3 fatty acids joined to 1 glycerol
-stores energy between C and H bonds
-hydrophobic
52
New cards
plaque
lipid-containing deposit in a blood vessel
53
New cards
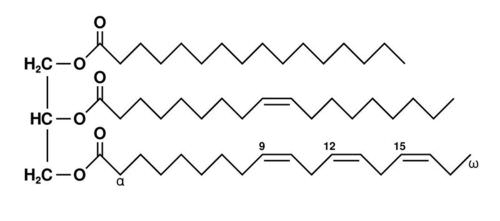
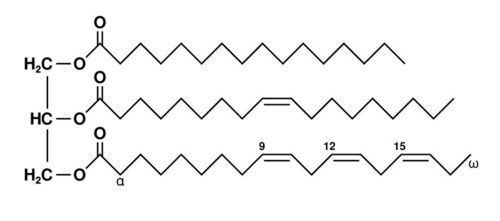
triglyceride (fat molecule)
-Glycerol bound w/ 3 fatty aids
-Varies in the length of hydrocarbon tails (4 to 26 C's)
-Varies in the number and location of double bonds (0 to 4)
-Stores energy in spherical droplets
-Contains more energy per gram than any other biological fuel
-Varies in the length of hydrocarbon tails (4 to 26 C's)
-Varies in the number and location of double bonds (0 to 4)
-Stores energy in spherical droplets
-Contains more energy per gram than any other biological fuel
54
New cards
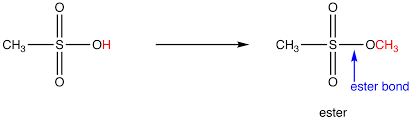
ester bond (ester linkage)
joins fatty acid tails to a glycerol backbone
55
New cards
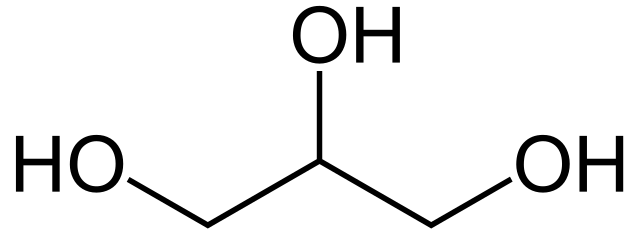
glycerol
-consists of three carbons
-each carbon is bonded to a hydroxyl and H
-each carbon is bonded to a hydroxyl and H
56
New cards
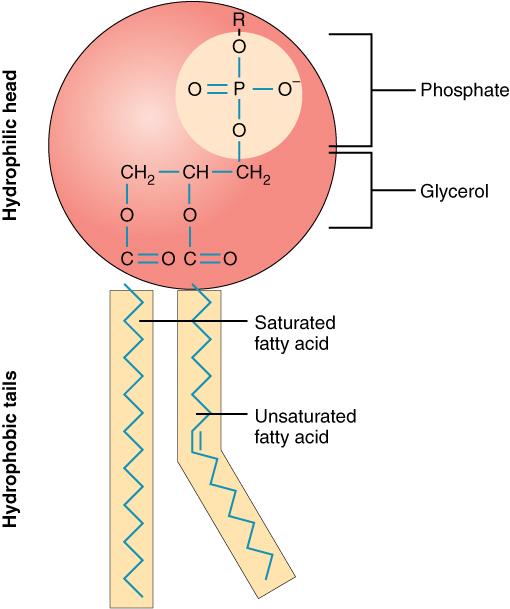
phospholipid
-glycerol bound to 2 fatty acid tails and phosphate group
-forms cell membrane
-hydrophobic fatty acid tails face inward, mingling together
-hydrophilic heads face outward, exposed to aqueous solutions on both sides of the membrane
-forms cell membrane
-hydrophobic fatty acid tails face inward, mingling together
-hydrophilic heads face outward, exposed to aqueous solutions on both sides of the membrane
57
New cards
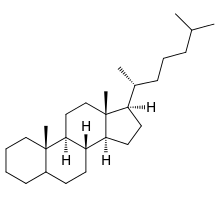
steroid
-lipid consisting of 4 fused rings
-differ in what is attached to the rings
-act as chemical messengers
-differ in what is attached to the rings
-act as chemical messengers
58
New cards
anabolic steroid
-steroids used to stimulate muscle growth
-can prevent bone growth
-synthetic variants of testosterone
-can prevent bone growth
-synthetic variants of testosterone
59
New cards
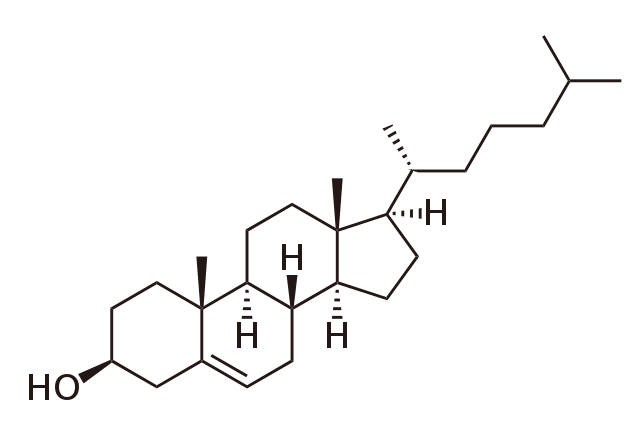
cholesterol
-Steroid that is an important component of animal cell membranes
-Acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other steroids
-Ratio to other membrane lipids impacts the ability of the cell & substances that are allowed to cross the membrane
-Acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other steroids
-Ratio to other membrane lipids impacts the ability of the cell & substances that are allowed to cross the membrane
60
New cards
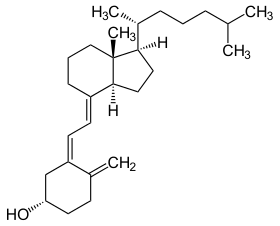
vitamin D
steroid that aids in calcium & phosphate metabolism
61
New cards
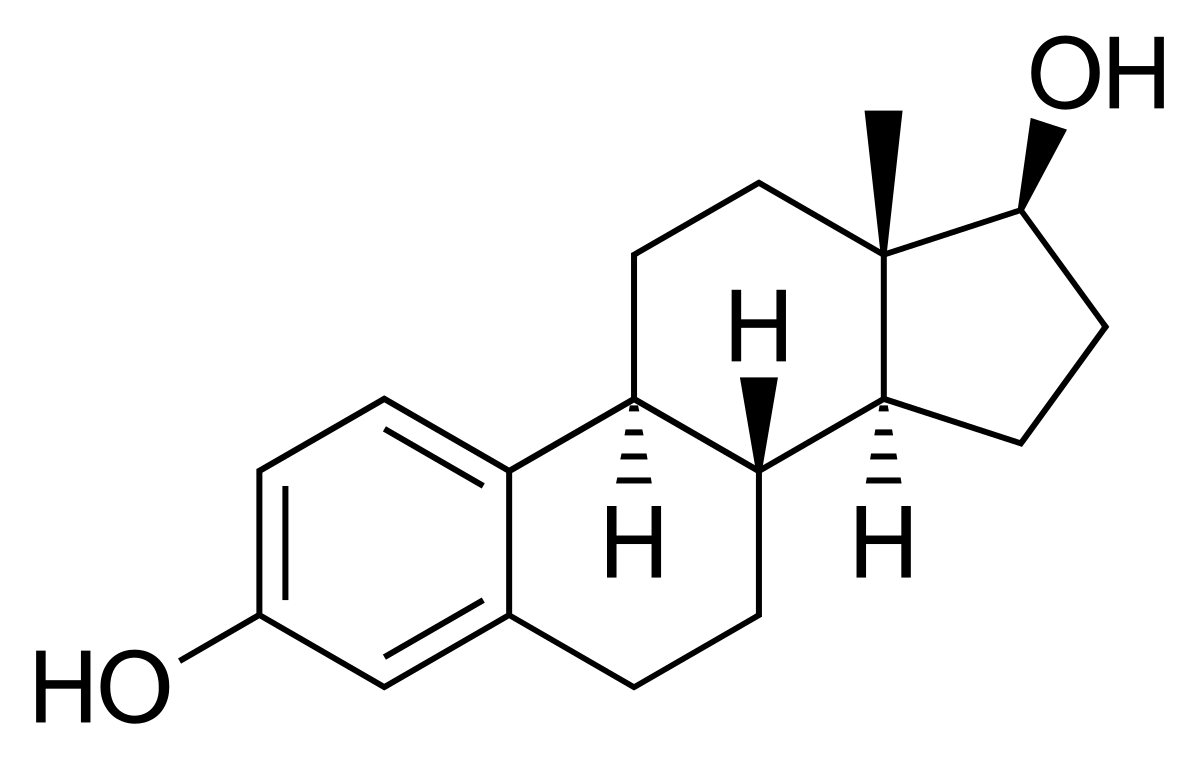
estradiol
steroid female sex hormone produced by the ovaries
62
New cards
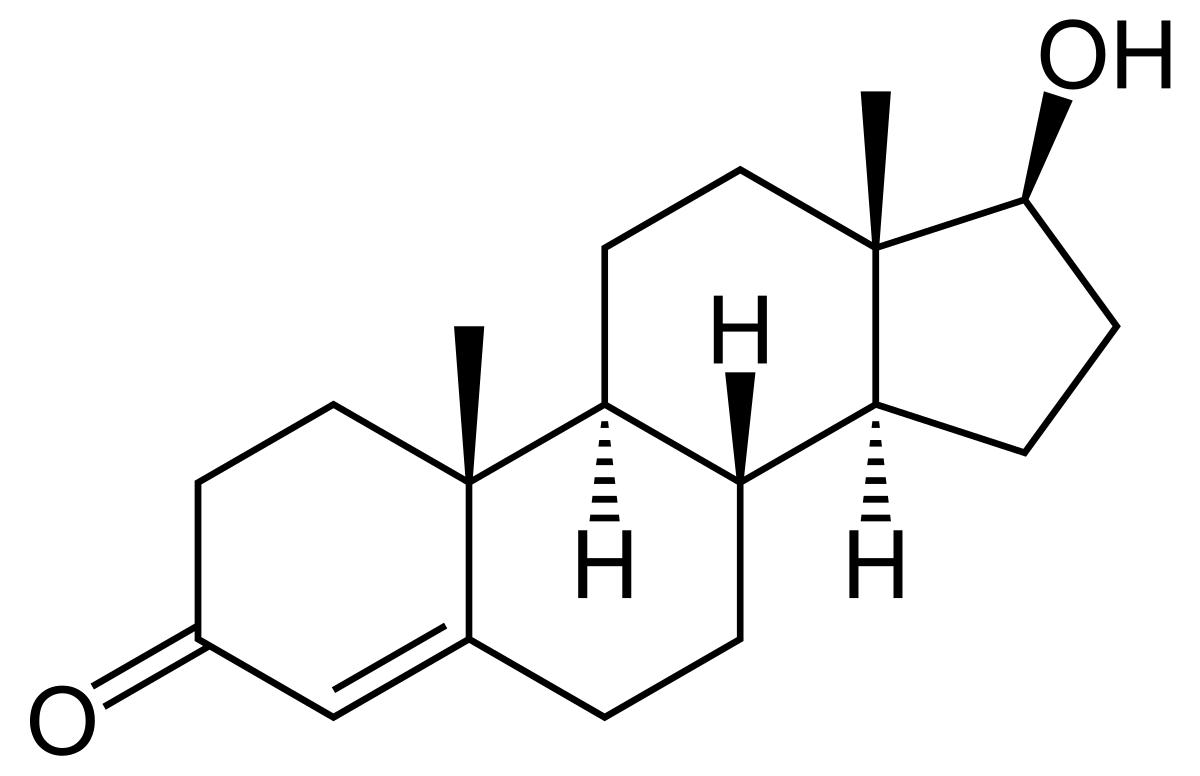
testosterone
steroid male sex hormone produced by the testes
63
New cards
wax
-dense, waterproof lipids
-saves water in plants and animals by coating their surfaces
-saves water in plants and animals by coating their surfaces
64
New cards
cuticle
waxy outercoating of plants
65
New cards
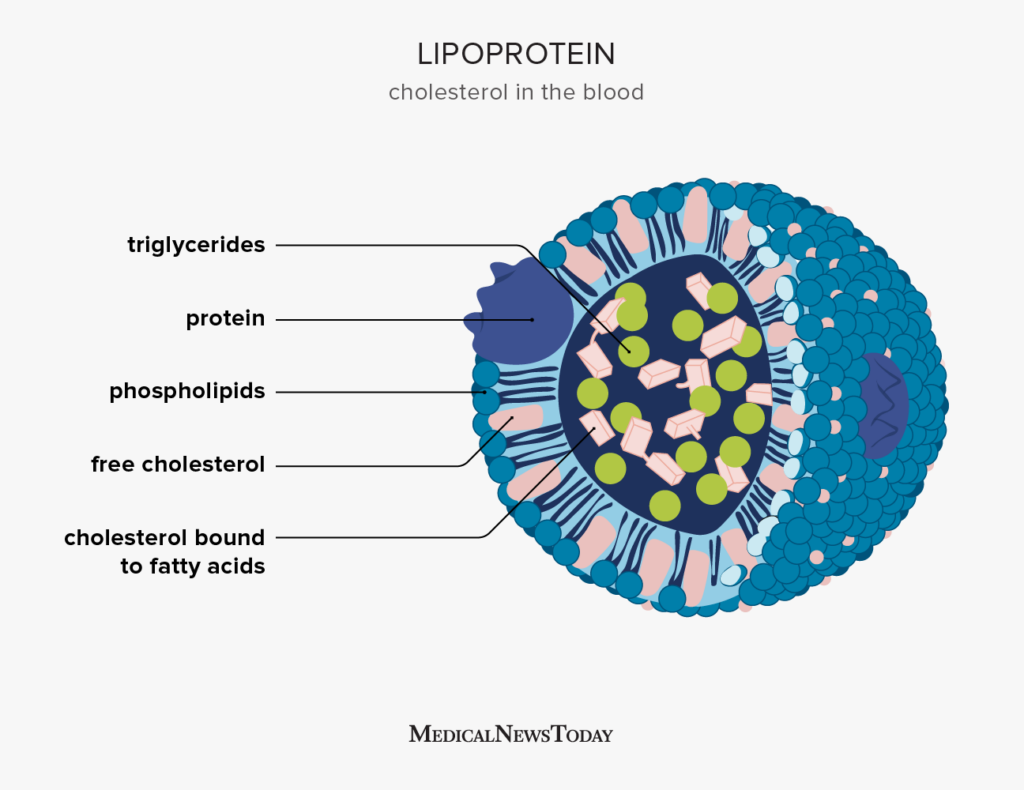
lipoprotein
-Lipid bound to proteins/phospholipids
-Phospholipids & proteins line the surface (they have parts that are compatible with water)
-Fats and steroids occupy the interior
-Helps lipids move through the body
-Phospholipids & proteins line the surface (they have parts that are compatible with water)
-Fats and steroids occupy the interior
-Helps lipids move through the body
66
New cards
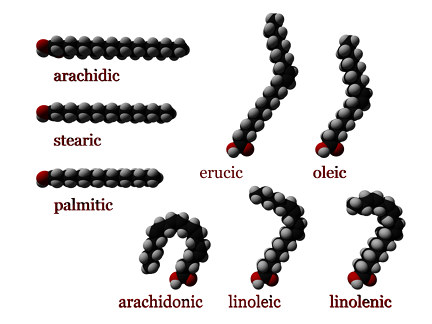
fatty acid
-Consists of a carboxyl group and long hydrocarbon chain
-Tails contain only nonpolar (C-H) bonds
-Hydrophobic
-Tails contain only nonpolar (C-H) bonds
-Hydrophobic
67
New cards
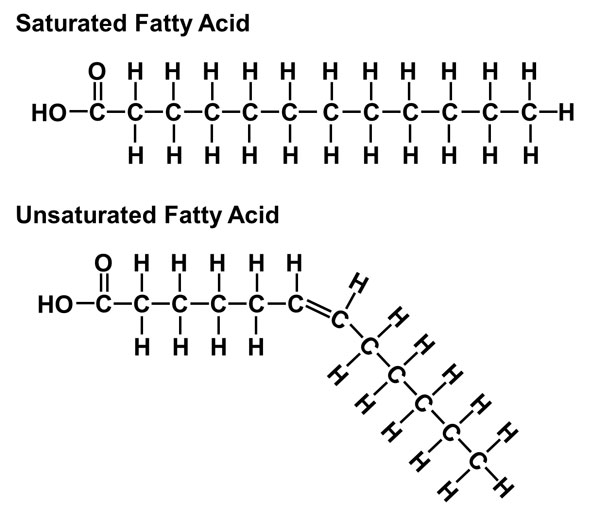
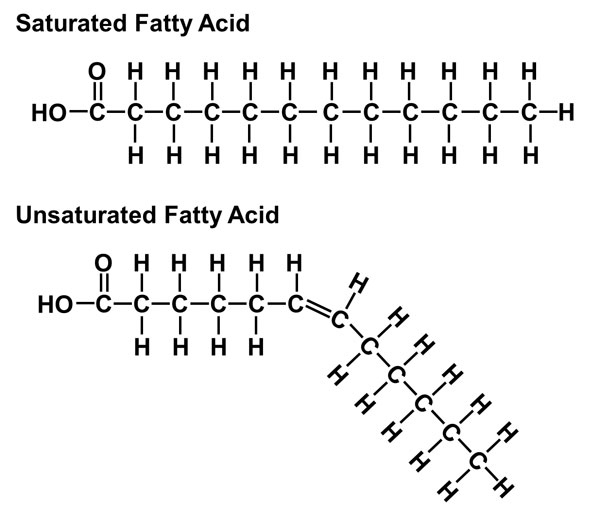
unsaturated fatty acid
-Contains at least one double bond (kink) in their hydrocarbon chain
-Reduced number of H's
-Usually found in vegetable oils
-Liquid at room temperature
-Stimulates the breakdown and secretion of cholesterol.
-Reduced number of H's
-Usually found in vegetable oils
-Liquid at room temperature
-Stimulates the breakdown and secretion of cholesterol.
68
New cards
saturated fatty acid
-Contain only single bonds in their hydrocarbon chains
-2 to 3 H's on each C
-Found in animal fats
-Solid at room temperature
-Impede the excretion of cholesterol
-Stimulate cholesterol synthesis in the liver
-2 to 3 H's on each C
-Found in animal fats
-Solid at room temperature
-Impede the excretion of cholesterol
-Stimulate cholesterol synthesis in the liver
69
New cards
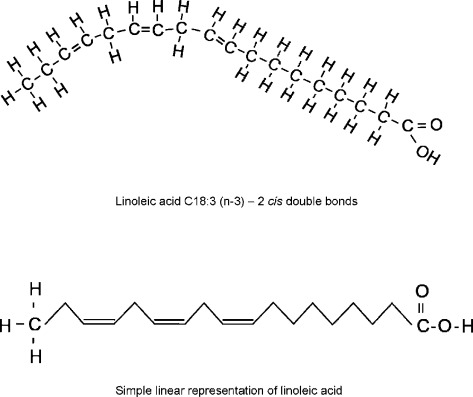
kink
-Formed by double bonds
-Prevents fatty acids from packing tightly
-Keeps them liquid at room temperature
-Prevents fatty acids from packing tightly
-Keeps them liquid at room temperature
70
New cards
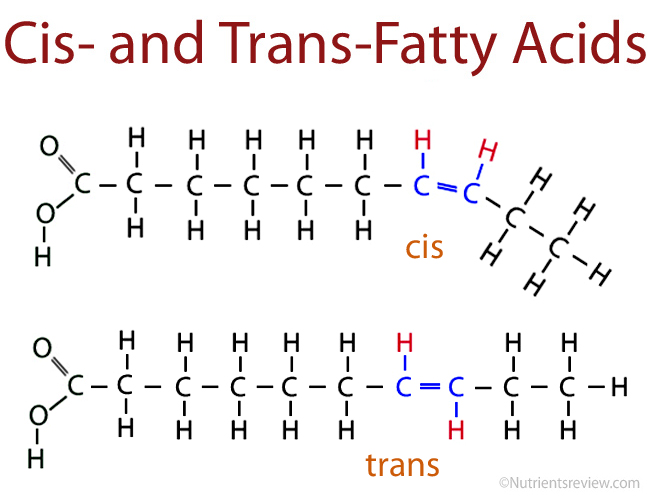
trans fat
-unsaturated fat formed during hydrogenation of saturated fat
-contain fewer double bonds
-linked to health risks (i.e. heart attacks)
-contain fewer double bonds
-linked to health risks (i.e. heart attacks)
71
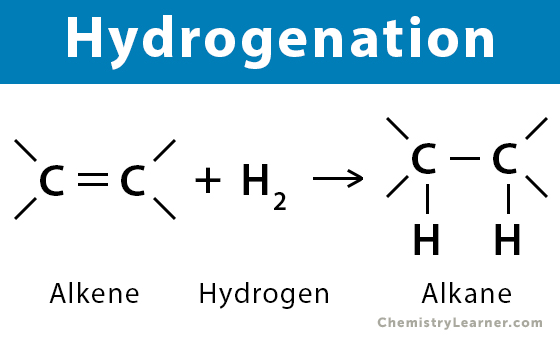
New cards
hydrogenation
process of adding hydrogen to double bonds
72
New cards
proteins
-contains C, H, O, N, sometimes S
-polymer of amino acids
-made from varying combinations of 20 amino acids
-consists of one or more polypeptides folded into a specific structure
-polymer of amino acids
-made from varying combinations of 20 amino acids
-consists of one or more polypeptides folded into a specific structure
73
New cards
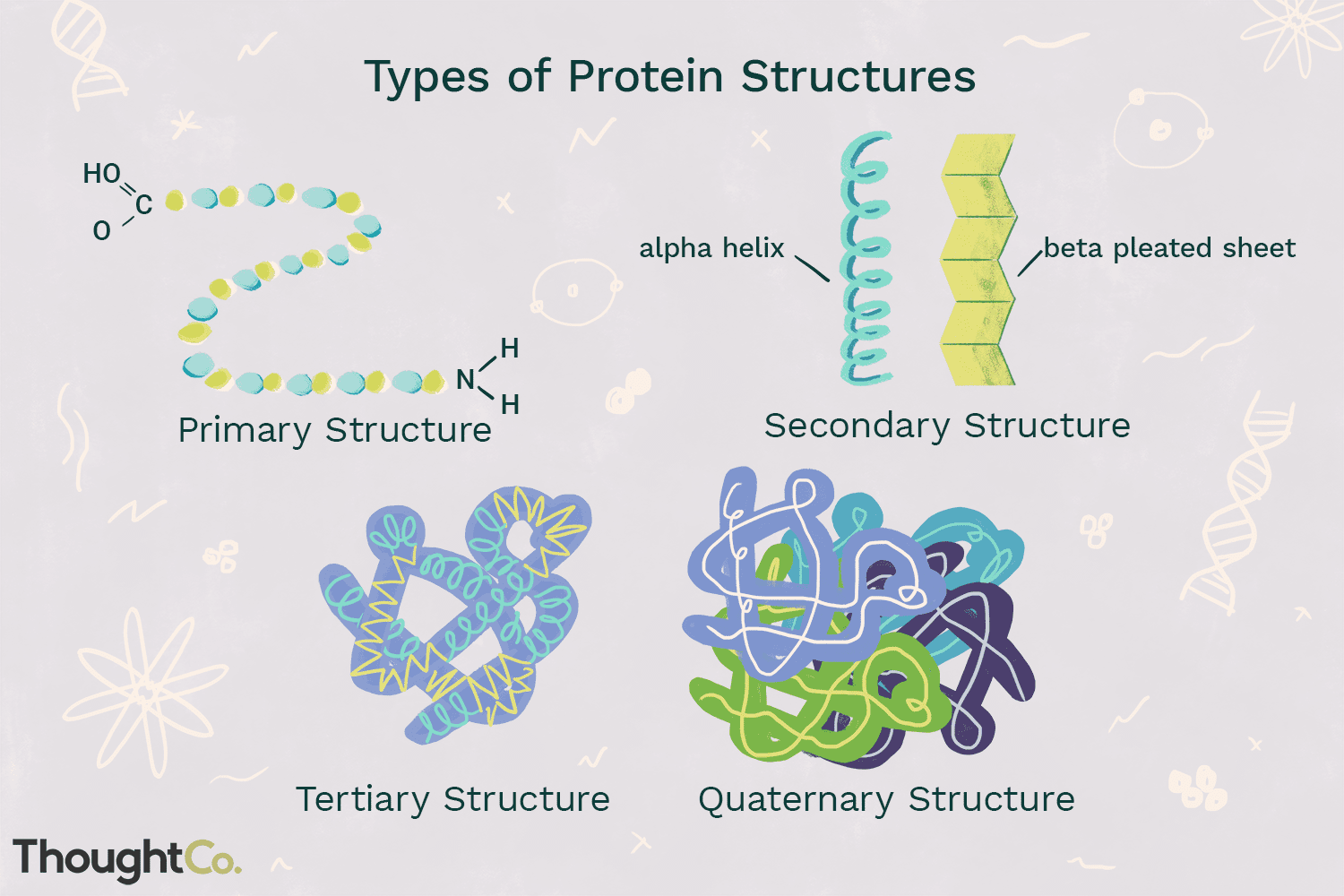
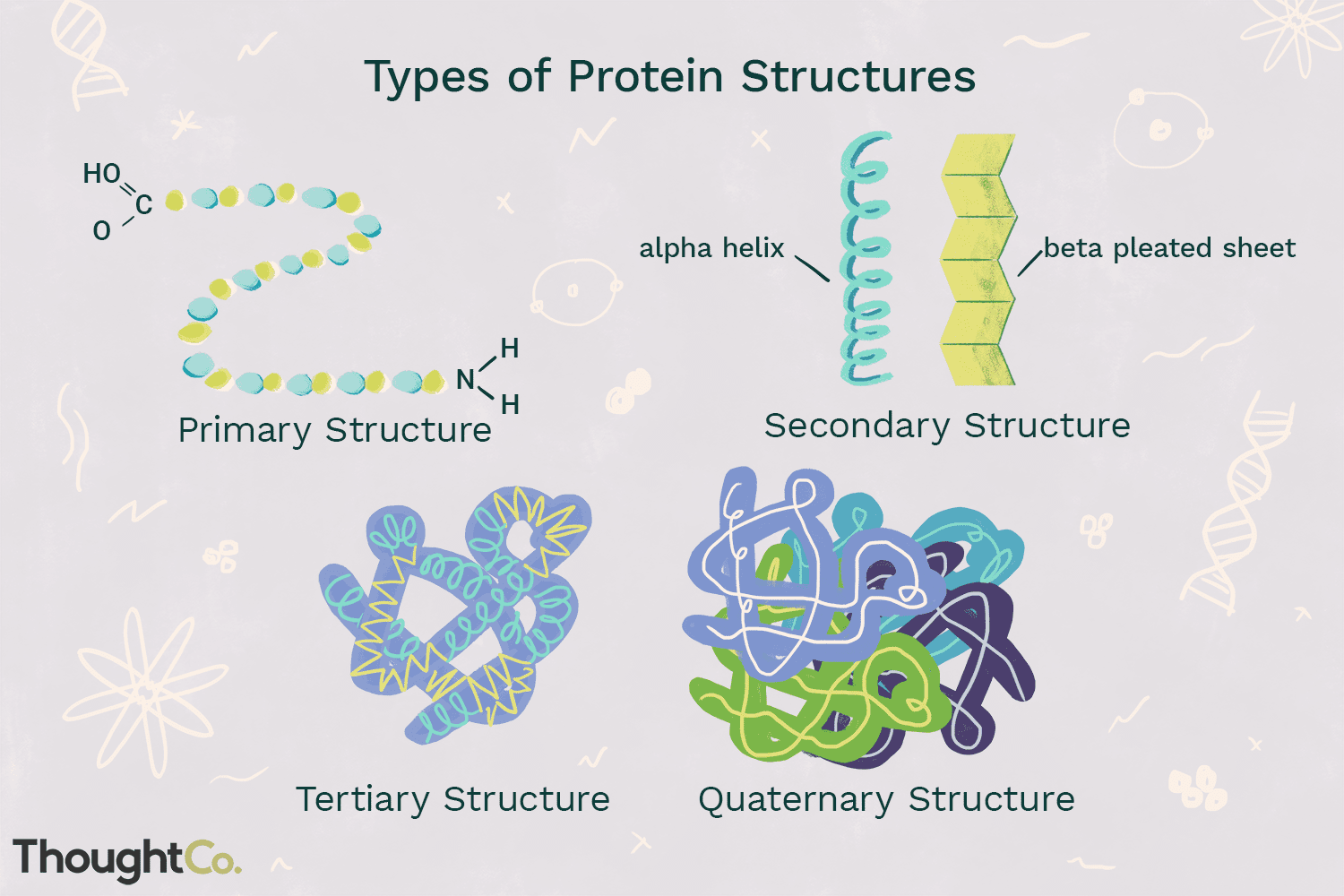
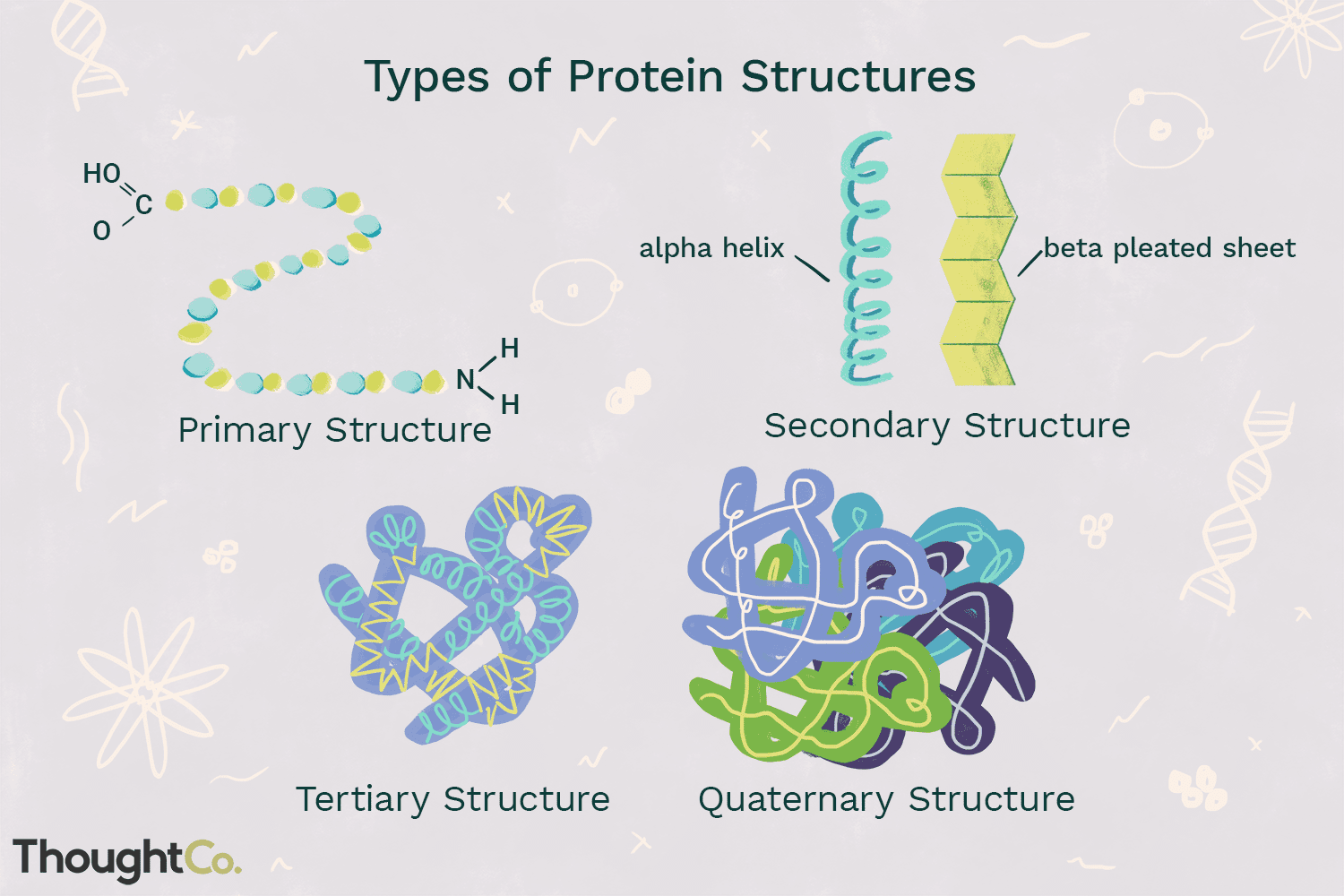
primary structure
-Linear string of amino acids that forms the backbone of the polypeptide chain
-Determined by genetic info
-Determined by genetic info
74
New cards
secondary structure
-Local patterns or folds of a polypeptide chain between amino & carboxyl groups
-Caused by interactions between R-groups
-Caused by interactions between R-groups
75
New cards
alpha helix
coiling of polypeptides
76
New cards
beta-pleated sheet
folding of polypeptides
77
New cards
tertiary structure
-Overall globular (3D) shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain
-Hydrophobic R-groups cluster in the center
-Positively/negatively charged R-groups can form ionic bonds
-Polar R-groups can form hydrogen bonds
-Sulfur-containing R-groups can form covalent bonds
-Hydrophobic R-groups cluster in the center
-Positively/negatively charged R-groups can form ionic bonds
-Polar R-groups can form hydrogen bonds
-Sulfur-containing R-groups can form covalent bonds
78
New cards
quaternary structure
-2 or more individual polypeptide subunits
-not present in all proteins
-not present in all proteins
79
New cards
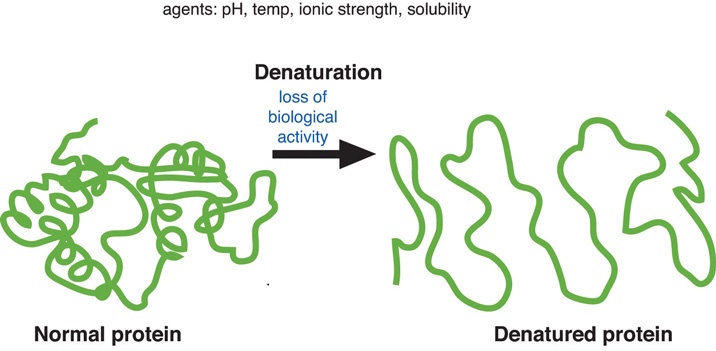
denaturation
-the unraveling of a protein, losing its structure and function
-the separation of 2 strands of DNA
-caused by changes in pH, salt concentration, or temperature
-the separation of 2 strands of DNA
-caused by changes in pH, salt concentration, or temperature
80
New cards
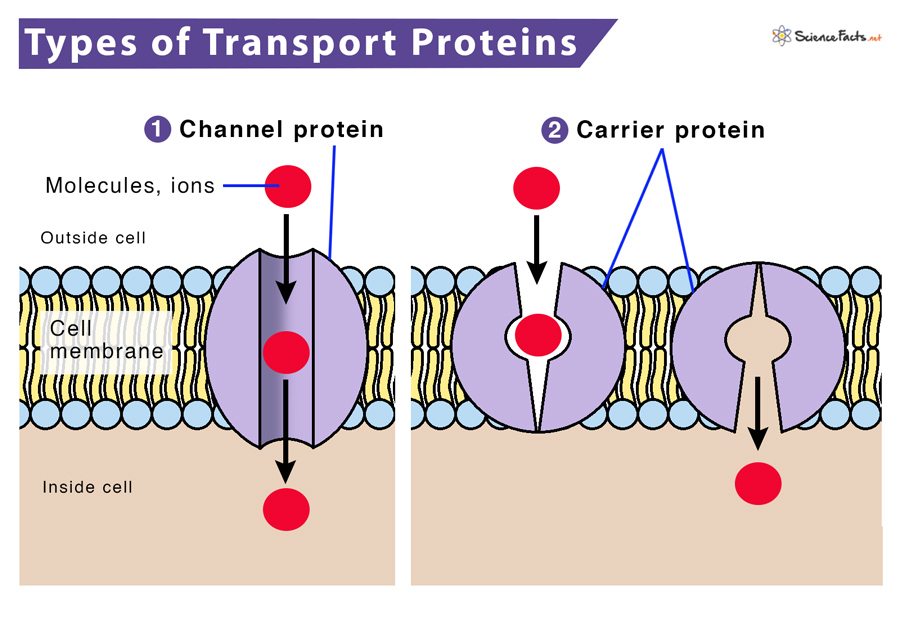
transport proteins
-embedded in cell membranes
-moves sugar molecules & other nutrients to cells
-carries molecules from place to place
-moves sugar molecules & other nutrients to cells
-carries molecules from place to place
81
New cards
structural proteins
-Shape cells
-Anchor cell parts
-Bind cells together, making organized units
-Anchor cell parts
-Bind cells together, making organized units
82
New cards
signal proteins
-Hormonal proteins that coordinate an organism’s activities by acting as signals between cells
-Bind to receptor proteins that can then relay messages in a cell
-Bind to receptor proteins that can then relay messages in a cell
83
New cards
sensory proteins
-proteins that detect environmental changes (i.e. light)
-respond by emitting or producing signals that call for a response
-respond by emitting or producing signals that call for a response
84
New cards
storage protein
-proteins that stockpile building components in cells that can be used to make other proteins
-storage proteins in seeds provide raw materials used by the developing plant
-storage proteins in seeds provide raw materials used by the developing plant
85
New cards
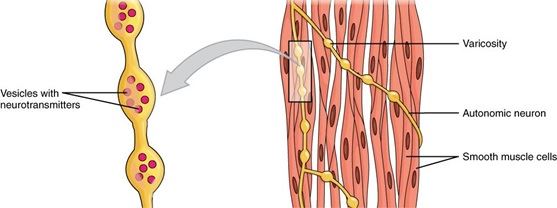
contractile protein (motor proteins)
-Protein that move parts of the cell
-Works together in muscle cells to move a whole animal
-Works together in muscle cells to move a whole animal
86
New cards
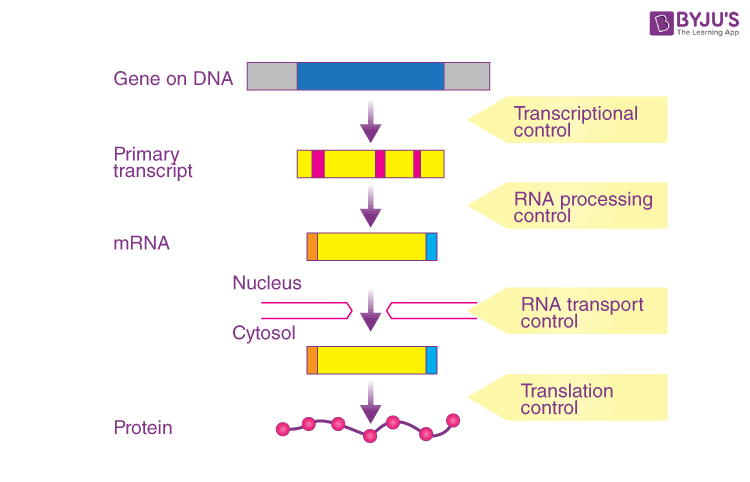
gene regulatory protein
-Protein that bind to DNA in specific locations
-Control whether or not genes will be read
-Allows cells to become specialized for different functions & respond to changes in their surroundings
-Control whether or not genes will be read
-Allows cells to become specialized for different functions & respond to changes in their surroundings
87
New cards
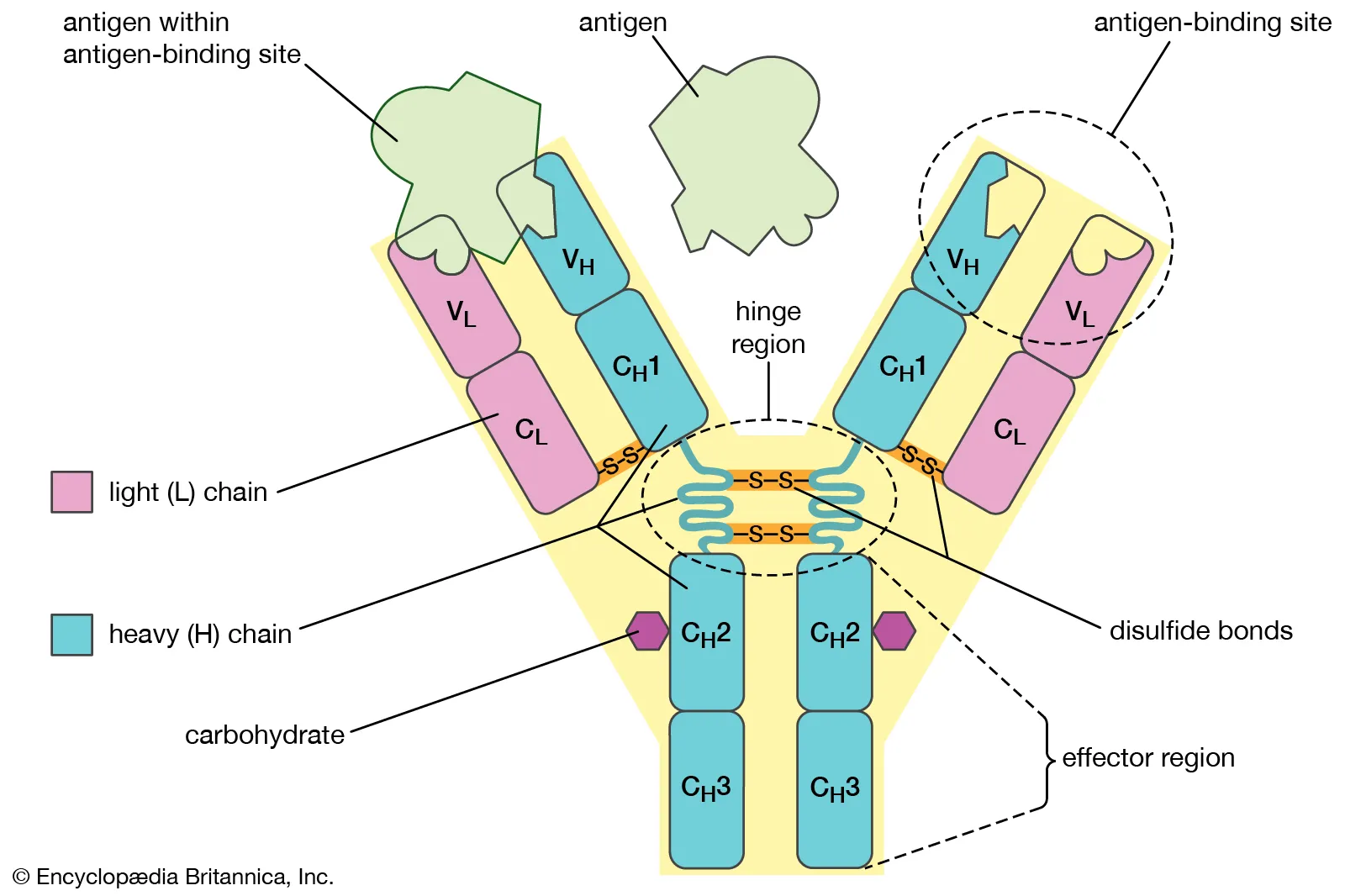
antibody
defensive proteins of the immune system that bind to pathogenic invaders, marking the foreign objects for destruction
88
New cards
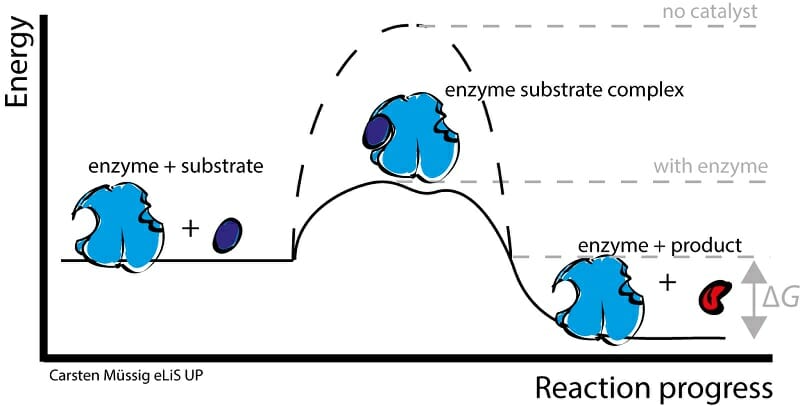
enzyme
-Organic protein that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it
-Catalyze and regulate chemical reactions
-Only work on specific substrates
-Lower activation energy
-Reusable
-Catalyze and regulate chemical reactions
-Only work on specific substrates
-Lower activation energy
-Reusable
89
New cards
active site
binding site between an enzyme and its substrate
90
New cards
lock and key hypothesis
the active site of an enzyme is specifically shaped to fit only 1 specific substrate.
91
New cards
lactase
enzyme that only works on the substrate lactose
92
New cards
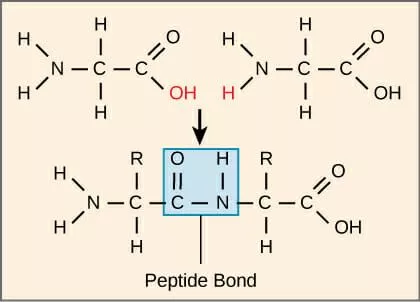
peptide bond
-covalent bond between an amino group of one subunit w/ a carboxyl group of another subunit
-formed by dehydration
-formed by dehydration
93
New cards
disulfide bridge (bond)
-covalent bond between S atoms of 2 cysteine amino acids
-stabilizes structure of proteins
-stabilizes structure of proteins
94
New cards
covalent bond
formed by the equal sharing of outer-shell electrons
95
New cards
ionic bond
-formed by the transfer of electrons
-1 atom loses an electron to form a positive ion & the other atom gains an electron to form a negative ion
-held together by charge differences
-1 atom loses an electron to form a positive ion & the other atom gains an electron to form a negative ion
-held together by charge differences
96
New cards
hydrogen bond
-formed by the attraction between H+ of one water molecule & O- atom of another water molecule
-holds water molecules together
-form, break, and reform with great frequency because they are weak
-holds water molecules together
-form, break, and reform with great frequency because they are weak
97
New cards
polar bond
-formed by the unequal sharing of electrons
-one atom is positively charged and the other is negatively charged
-one atom is positively charged and the other is negatively charged
98
New cards
nonpolar bond
-formed by the equal sharing of electrons
-no charge separation
-no charge separation
99
New cards
cohesion
-sticking together of 2 like molecules (H2O)
-caused by the attraction of opposite charges (polarity)
-caused by the attraction of opposite charges (polarity)
100
New cards
adhesion
-sticking together of 2 unlike molecules (H2O & another substance)
-caused by the attraction of opposite charges (polarity)
-caused by the attraction of opposite charges (polarity)