Sign and Magnitude
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Sign and Magnitude
Method to represent negative numbers in binary.
Two's Complement
Alternative method to represent negative binary numbers.

Binary Addition
Process of adding binary values using logic circuits.
Overflow Error
Occurs when addition exceeds bit capacity.
Logic Gates
Electronic components performing binary operations.
Arithmetic Operators
Operators for addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
Comparison Operators
Operators for comparing binary values.
Carry Bit
Bit carried over in binary addition.
Fixed Point Binary
Represents fractions using a fixed number of bits.
Binary Values
Values expressed in base-2 numeral system.
Most Significant Bit (MSB)
First bit indicating sign in binary representation.
Binary Representation
Encoding numbers using binary digits (0s and 1s).
Denary
Decimal number system, base-10.
Bit Capacity
Maximum number of bits a computer can handle.
Range of Values
Determined by number of bits in binary.
Negative Representation
Methods to express negative integers in binary.
Binary Addition Rules
Rules governing addition of binary digits.
Binary Fraction
Fraction represented in binary format.
Bit
Basic unit of information in computing, 0 or 1.
Byte
Group of 8 bits used for data storage.
Exponentiation
Mathematical operation of raising a number to a power.
DIV Operator
Integer division operator in binary arithmetic.
MOD Operator
Remainder operator in binary arithmetic.
Two's Complement
Method to represent negative binary values.
Byte
Storage unit consisting of 8 bits.
Maximum Value (1 Byte)
Largest number is 255 in one byte.
Integer Storage
Commonly uses 2 or 4 bytes.
Floating-Point Representation
Used to represent fractions in computing.
Negative Number Representation
Achieved using two's complement method.
Sign and Magnitude
Method representing both sign and magnitude.
MSB (Most Significant Bit)
Indicates sign in two's complement representation.
Binary Arithmetic
Mathematical operations performed on binary numbers.
Flipping Bits
Changing 0s to 1s and vice versa.
Adding One
Final step in calculating two's complement.
Denary to Binary
Converting decimal numbers to binary format.
Binary to Denary
Converting binary numbers back to decimal.
Negative Denary Conversion
Process to convert negative decimal to binary.
Example of -3
Binary representation is 11111101.
Example of -96
Binary representation is 10100000.
Example of -5
Binary representation is 11111011.
Example of -10
Binary representation is 11110110.
Example of -20
Binary representation is 11101100.
Bit Flipping Rule
Change digits until the first '1' is reached.
Signed Binary Representation
Method to represent both positive and negative numbers.
Binary Addition Rule
In binary, 1 + 1 = 0 with carry.
Two's Complement
Method for representing negative binary numbers.
Binary Subtraction
Using addition of two's complement for subtraction.
Overflow
Result exceeds maximum representable value in bits.
Fixed-Point Binary
Binary representation with a fixed binary point location.
Fractional Values
Negative powers of 2 representing decimal fractions.
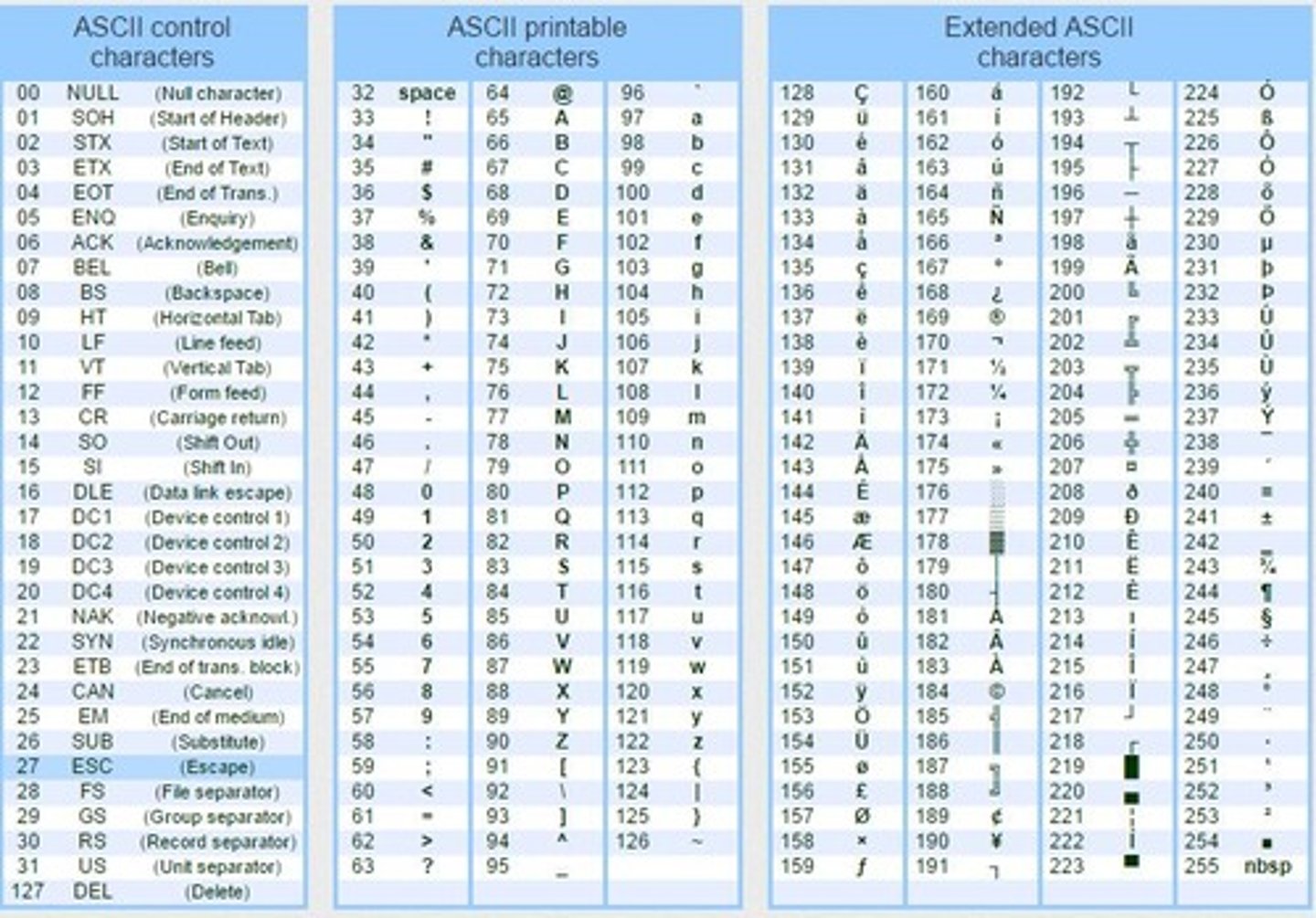
ASCII
Character encoding standard for text representation.
Unicode
16-bit character encoding for global language support.
Binary Fractions
Bits right of binary point represent fractional values.
Decimal Equivalent
Value conversion from binary to decimal format.
Character Set Size
Determines number of characters a system can use.
ATM Character Set
Limited character set for cash machine interfaces.
Binary Point
Fixed position in fixed-point binary representation.
Negative Powers of 2
Values like 2^-1, 2^-2 represent fractions.
8-Bit Representation
Uses 8 bits to represent values, max 255.
Character Value
Unique numeric value assigned to each character.
Localisation of Software
Adapting software for different cultural interfaces.
Two's Complement Calculation
Example: 6510 + -4310 equals 2210.
Binary Addition
Combining binary numbers to produce a sum.
Bit Allocation
Number of bits assigned for data representation.
Standard Binary Addition
Regular addition method for binary numbers.
Document Handling
Using Unicode for multilingual document support.
Bit Representation
Binary format used to represent data values.
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
7-bit ASCII
Represents 128 characters using 7 bits.
8-bit ASCII
Extends 7-bit ASCII with 128 additional characters.
ASCII value of '5'
Binary 0110101, decimal 53.
ASCII value of '8'
Binary 0111000, decimal 56.
Character encoding scheme
Method to represent characters in computers.
EOL command
Indicates end of line in text.
CR
Carriage return, moves cursor to start.
Fixed point binary
Represents binary fractions in a fixed format.
ASCII for 'Z'
Decimal 90, binary 01011010.
ASCII for 'X'
Decimal 88, binary 01011000.
ASCII for 'D'
Binary 1000100, decimal 68.
ASCII for 'G'
Binary 1000111, decimal 71.
ASCII for 's'
Binary 1110011, decimal 115.
ASCII for 'm'
Binary 1101101, decimal 109.
Benefit of ASCII
Uses 8 bits per character, saving memory.
Benefit of Unicode
Supports a wider range of characters.
Total characters in 7-bit ASCII
2^7 = 128 different characters.
Unicode
Character encoding supporting multiple languages.
ASCII for 'Ç'
Binary representation for extended ASCII character.
ASCII for 'Ð'
Binary representation for extended ASCII character.
ASCII for 'Ö'
Binary representation for extended ASCII character.
ASCII for 'ŵ'
Binary representation for extended ASCII character.
ASCII for 'φ'
Binary representation for extended ASCII character.
ASCII for 'έ'
Binary representation for extended ASCII character.