AP Psychology Unit 3 PART B: Development and Learning (Modules 3.5, 3.7a-3.9)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
language
our agreed-upon systems of spoken, written, or signed words, and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning.
phoneme
in a language, the smallest distinctive sound unit. (ex. cat = k/a/t)
morpheme
in a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or a part of a word (such as a prefix). (ex; un-break-able)
semantics
the study of meaning in language, focuses on how words and phrases acquire their meaning
how we understand the meaning of complex expressions based on their individual parts
syntax
set of rules and principles that govern how words are arranged to form sentences in a language
grammar
in a language, a system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others. Semantics is the language’s set of rules for deriving meaning from sounds, and syntax is its set of rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences.
universal grammar (UG)
humans’ innate predisposition to understand the principles and rules that govern grammar in all languages.
cooing stage
an early stage of infant language where babies produce soft, vowel like sounds, often resembling “coo” or “goo” typically occurring between 2-3 months old
babbling stage
the stage in speech development, beginning around 4 months, during which an infant spontaneously utters various sounds that are not all related to the household language.
one-word stage
the stage in speech development, from about age 1 to 2, during which a child speaks mostly in single words.
two-word stage
the stage in speech development, beginning about age 2, during which a child speaks mostly in two-word sentences.
telegraphic speech
the early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram —“go car”— using mostly nouns and verbs.
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impairing understanding).
Broca’s area
a frontal lobe brain area, usually in the left hemisphere, that helps control language expression by directing the muscle movements involved in speech.
Wernicke’s area
a brain area, usually in the left temporal lobe, involved in language comprehension and expression.
linguistic determinism
Whorf’s hypothesis that language determines the way we think.
linguistic relativism
the idea that language influences the way we think.
associative learning
learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequence (as in operant conditioning).
stimulus
any event or situation that evokes a response.
respondent behavior
behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus.
operant behavior
behavior that operates on the environment, producing a consequence.
cognitive learning
the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language.
behavioral perspective
a psychological approach that focuses solely on observable behaviors, explaining human actions as learned responses to environmental stimuli through conditioning (classical or operant)
argues that behavior is a result of past experiences and interactions, not internal mental processes
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which we link two or more stimuli; as a result, to illustrate with Pavlov’s classic experiment, the first stimulus (a tone) comes to elicit behavior (drooling) in anticipation of the second stimulus (food).
behaviorism
the view that psychology
(1) should be an objective science that
(2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes.
Most research psychologists today agree with (1) but not with (2).
acquisition
in classical conditioning, the initial stage — when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. (In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.)
neutral stimulus (NS)
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning.
unconditioned response (UCR)
in classical conditioning, an unlearned, naturally occurring response (such as salivation) to an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) (such as food in the mouth).
unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally — naturally and automatically — triggers an unconditioned response (UCR).
conditioned response (CR)
in classical conditioning, a learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus (CS).
conditioned stimulus (CS)
in classical conditioning, an originally neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS), comes to trigger a conditioned response (CR).
extinction
in classical conditioning, the diminishing of a conditioned response when an unconditioned stimulus does not follow a conditioned stimulus. (In operant conditioning, when a response is no longer reinforced.)
higher-order conditioning
second order conditioning; a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus.
Ex: an animal learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone
classical conditioning of emotions
a learning process that creates associations between stimuli, which can lead to conditioned emotional responses
ex; you associate a certain song with a breakup you had in highschool. every time you hear that song, you think of the breakup
one trial conditioning (taste aversions)
a learning phenomenon where a single pairing of a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus is enough to create a conditioned response
biological preparedness (taste aversions)
a biological predisposition to learn associations, such as between taste and nausea, that have survival value.
habituation
the process where an organism's response to a stimulus decreases after repeated exposure to that stimulus
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of a weakened conditioned response.
stimulus generalization
in classical conditioning, the tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to the conditioned stimulus to elicit similar responses.
In operant conditioning, when responses learned in one situation occur in other, similar situations.
stimulus discrimination
in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and other stimuli that have not been associated with a conditioned stimulus.
In operant conditioning, the ability to distinguish responses that are reinforced from similar responses that are not reinforced.
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which a behavior becomes more likely to recur if followed by a reinforcer or less likely to recur if followed by a punisher.
law of effect
Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable (or reinforcing) consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable (or punishing) consequences become less likely.
operant chamber
in operant conditioning research, a chamber (also known as a Skinner box) containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; attached devices record the animal’s rate of bar pressing or key pecking.
reinforcement vs punishment
in operant conditioning, any event that strengthens the behavior it follows.
VS.
a negative consequence that is intended to reduce the likelihood of an undesirable behavior happening again
shaping
an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior.
superstitious behaviors
the behavior that results from accidental reinforcement of an action so that the organism continues to repeat it
learned helplessness
a psychological condition where an individual feels powerless to change their situation due to repeated failures or negative outcomes in the past.
discriminative stimulus
in operant conditioning, a stimulus that elicits a response after association with reinforcement (in contrast to related stimuli not associated with reinforcement).
positive reinforcement
increasing behaviors by presenting a pleasurable stimulus. A positive reinforcer is any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response.
negative reinforcement
increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing an aversive stimulus. A _______ reinforcer is any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response. (Note: ________ reinforcement is not punishment.)
primary reinforcer
an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need.
secondary reinforcer
a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. (Also known as a conditioned reinforcer.)
reinforcement discrimination
the ability of an organism to distinguish between different stimuli and respond only to the specific stimulus that has been consistently paired with reinforcement
reinforcement generalization
the tendency for a learned behavior, reinforced in one specific situation, to be exhibited in similar situations or when encountering similar stimuli
reinforcement schedule
a pattern that defines how often a desired response will be reinforced.
continuous reinforcement schedule
VS.
partial (intermittent) reinforcement schedule
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs.
VS.
reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction than does continuous reinforcement.
fixed-ratio (schedules of reinforcement)
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses.
variable-ratio schedule
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses.
fixed-interval (schedules of reinforcement)
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed.
variable-interval schedule
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals.
punishment
an event that tends to decrease the behavior that it follows.
instinctive drift
the tendency of learned behavior to gradually revert to biologically predisposed patterns.
cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one’s environment.
ex; after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a _________ ___ of it.
latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it.
insight learning
solving problems through sudden insight; contrasts with strategy-based solutions.
observational learning
learning by observing others. (Also called social learning.)
vicarious conditioning
the process of learning a behavior or response by observing another individual's reaction to a stimulus
modeling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior.
mirror neurons
neurons that some scientists believe fire when we perform certain actions or observe another doing so. The brain’s mirroring of another’s action may enable imitation and empathy.
prosocial behavior
positive, constructive, helpful behavior. The opposite of antisocial behavior.
antisocial behavior
negative, destructive, harmful behavior. The opposite of prosocial behavior.
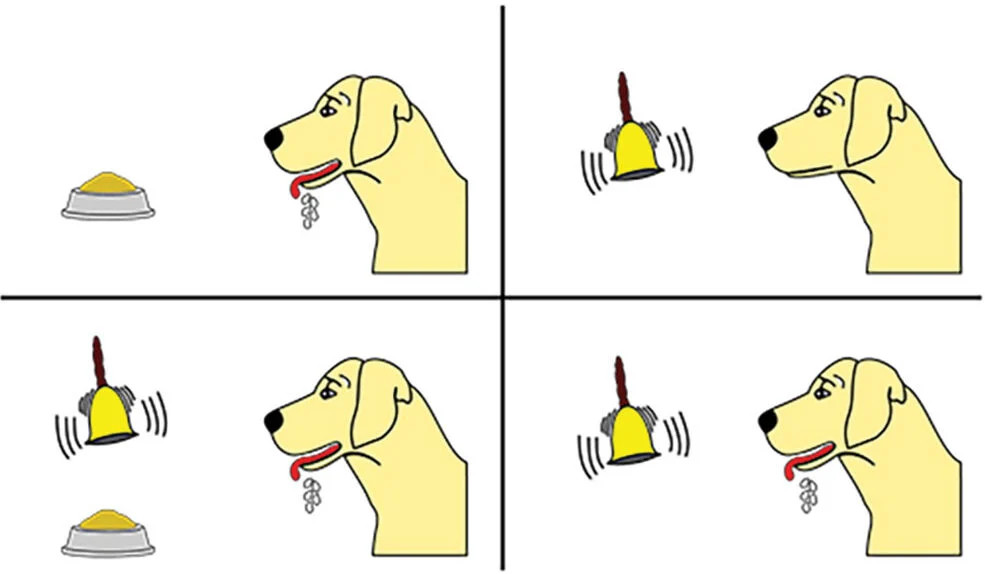
Ivan Pavlov
discovery of classical conditioning; dog experiment with the bell, food and saliva. whenever dog heard bell, knew it would get food and start salivating
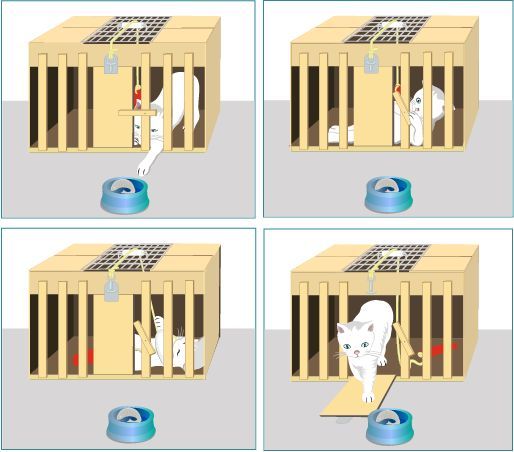
Edward Thorndike
theory he called the law of effect, which emerged from his research on how cats learn to escape from puzzle boxes;
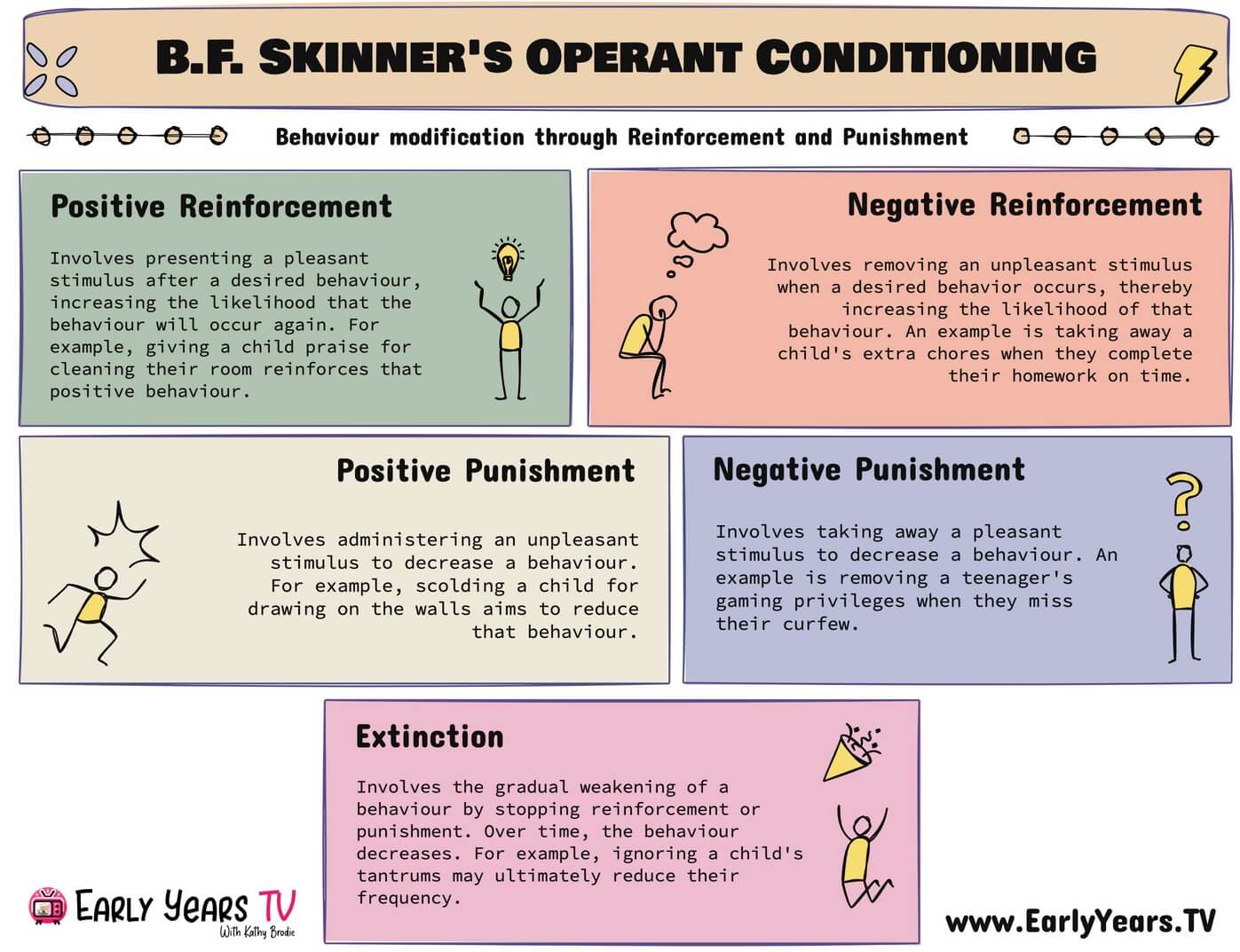
BF Skinner
behaviorism, specifically operant conditioning and schedules of reinforcement; a person is first exposed to a stimulus, which elicits a response, and the response is then reinforced (stimulus, response, reinforcement
Lev Vygotsky
children learn through: 1. interaction with others 2. scaffolding (breaking info down into more manageable pieces) 3. zone of proximal development (zone of learning where we can’t perform the task or skill yet on your own but can with the help of a expert ex; tying shoes)
postive reinforcement
giving a pleasant consequence that increases the behavior in the future
negative reinforcement
removal of something unpleasant after a behavior which increases the behavior in the future
positive punishment
giving an unpleasant consequence that decreases a behavior in the future
negative punishment
removal of a pleasant consequence that will decrease behavior in the future