Epi - Lecture 5 - Critical appraisal 2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
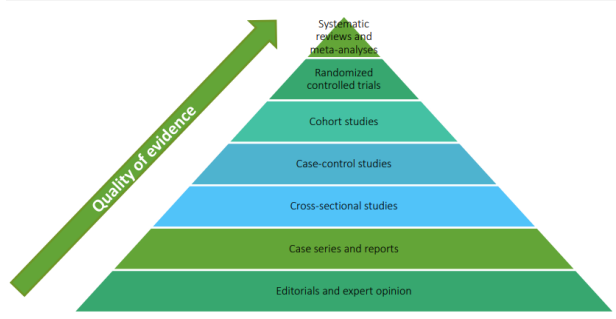
evidence hierarchy
system used to rank different types of research based on their reliability, validity, and strength
internal validity
refers to the extent to which the results of a study accurately reflect the relationship between the exposure and the outcome
external validity
refers to the extent to which the study's findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or times
two forms of external validity
population validity → the participant characteristics have to represent the larger population you want to generalise
ecological validity → how similar the setting is to the real world and how the world changes over time
shortcomings evidence hierarchy
does not take into account that the quality of research is also affected by how the research is performed,
qualitative (anthropological) studies are not included → shortcoming because these studies are crucial to understand cultural factors (important for health interventions in certain communities).
different conflicts of interest
financial → source of funding
non-financial → strong personal, political or religious beliefs on a topic
why is a critical appraisal important
helps to narrow down quantities of literature to relevance and high quality
helps to assess validity and applicability
helps to identify bias in studies
is essential to a literature review
is important for treatment and intervention planning
what are the 2 critical appraisal tools
CAT (critical appraisal tool) → assesses whether a study is internally and externally valid.
standard reporting guidelines → focuses on guiding researchers on what to report or what elements to include in an article.
CAT, critical appraisal tool
to evaluate/assess whether a study is internally and externally valid
focuses on evaluating methods and results of a study, but does not always thoroughly investigate the whole stud
standard reporting guidelines
provides guidelines for researchers on what to report or what elements to include in an article
focuses more on guiding researchers on what to report while drafting a research article
more thorough → looks at all elements of the study, from intro to discussion
things to specifically check when assessing a case control study
selection of the control
recall and social desirability bias
how well do controls fit with the cases
things to specifically check when assessing a cohort study
participant characteristics (what does the cohort look like, is it representative)
the follow up (relevant for the outcome)
confounders (what has been controlled for)