Psych - General
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is psychology?
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behaviour
What is the mind?
The mind is defined as the part of us that reasons, thinks, feels, perceives, and judges
What is behaviour?
The response of living organisms to stimulus, both internal and external
Nature vs. Nurture
Nature is the natural/genetic behaviours of a person, while Nurture is the environmental factors of how a person was rasied
Why is Psychology still not considered a science in some places?
Due to methodological challenges, historical baggage, and misconceptions
Cognitive process
explains how the mind works. These include memory, perception, attention, deicision-making, and thinking/reasoning
What makes a good theory? (TEACUP)
T - Testiable (Flaseafilable)
E - Experiment
A - Application (Can be applied to real world situations)
C - Concepts
U - Unbiased
P - Perdictable
What psychological factors can affect our behaviour and cognition?
Neurotransmitters/Brain structure
Hormones
Genes
Interactionist approach
Lots of things are responsible for psychological effects
Reductionist approach
One thing is responsible for psychological effects
What is the difference between MRI, FMRI, and PAT scans?
MRI - 3D picture of the brain structure
FMRI - Scan of brain activity
PAt - invasive brain scan
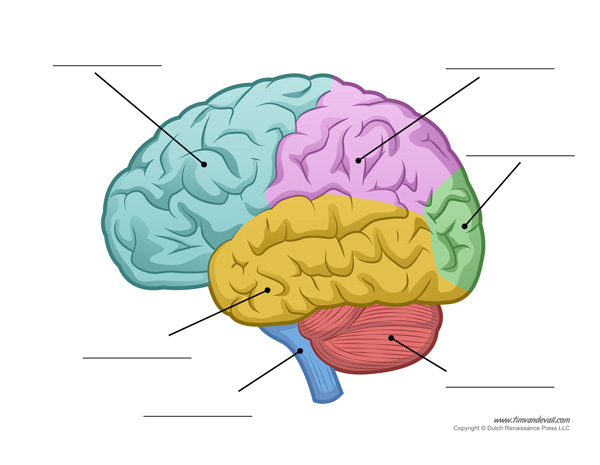
Label the brain
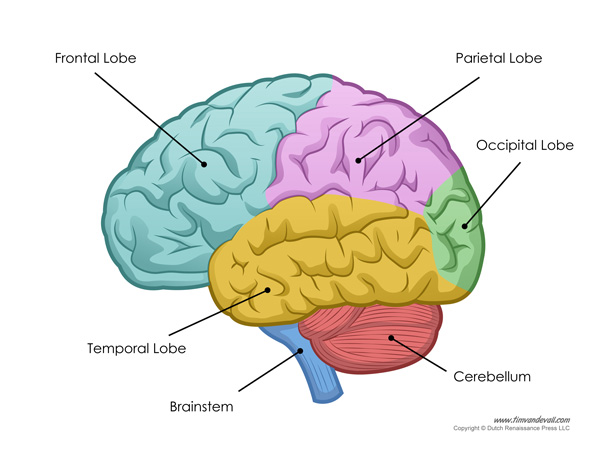
What is Neuroplasticity?
The brain’s ability to change it’s structure in response to stimuli
LTP
Long term potentiation - The process of strengthening the connection between neurons
Synaptic Pruning
The breaking of neural connections
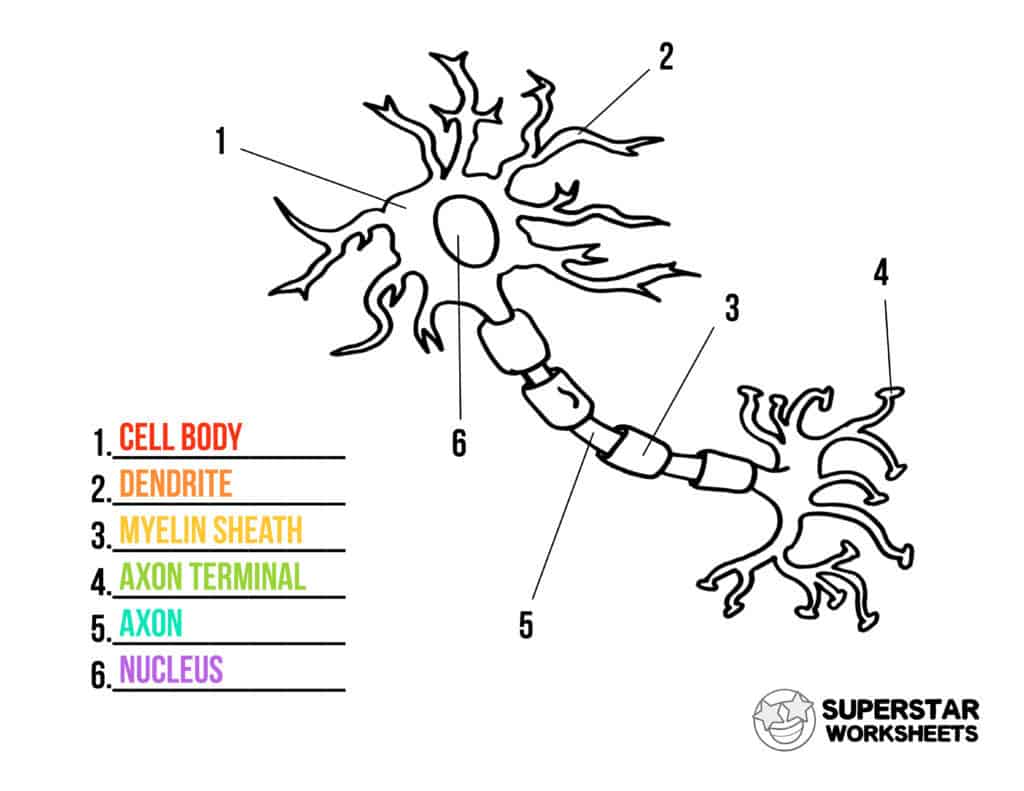
What is a synapse?
A signal sent to the detrite, passes through the body of the neuron, then through the axon terminal to another neuron
What are the two types of synapses?
Electrical - Less complex signals and allows ions to pass through
chemical - Slower than electrical signals but more complex
What are neurotransmitters?
electro-chemical signals
What happens if neurotransmitters aren’t taken by the post-synaptic neuron?
They are either diffused by enzymes or taken back by the pre-synaptic cell via a process called “re-uptake”
What are hormones?
Hormones are similar to neurotransmitters but are secreted by glands in the body and travels through the blood
What are beta-blockers and what are they used for?
blocks/stops development of emotional memories and are used to prevent PTSD
Excitatory
Higher likelihood of a neuron firing to another neuron by depolarizing the neuron
Inhibitory
Lowers likelihood of a neuron firing to another neuron by hyper-polarizing the neuron
Diathesis Stress Model
Behaviour is determined by both a person’s genetic vulnerability and environmental factors
Genetic predisposition
Your likelihood of developing a certain trait based on your genetics (inheritance)
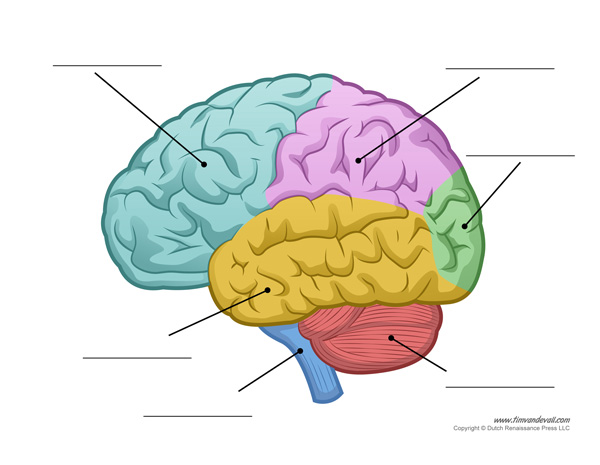
Label
.
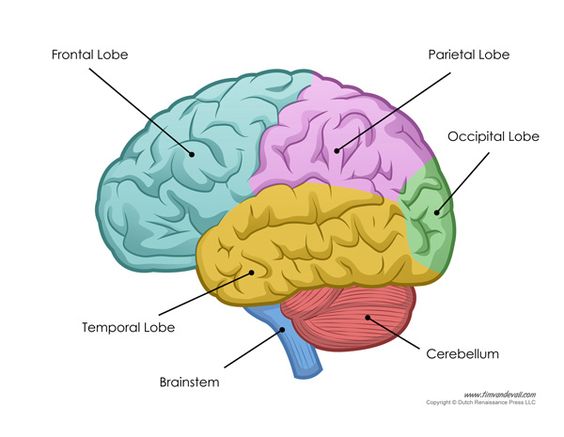
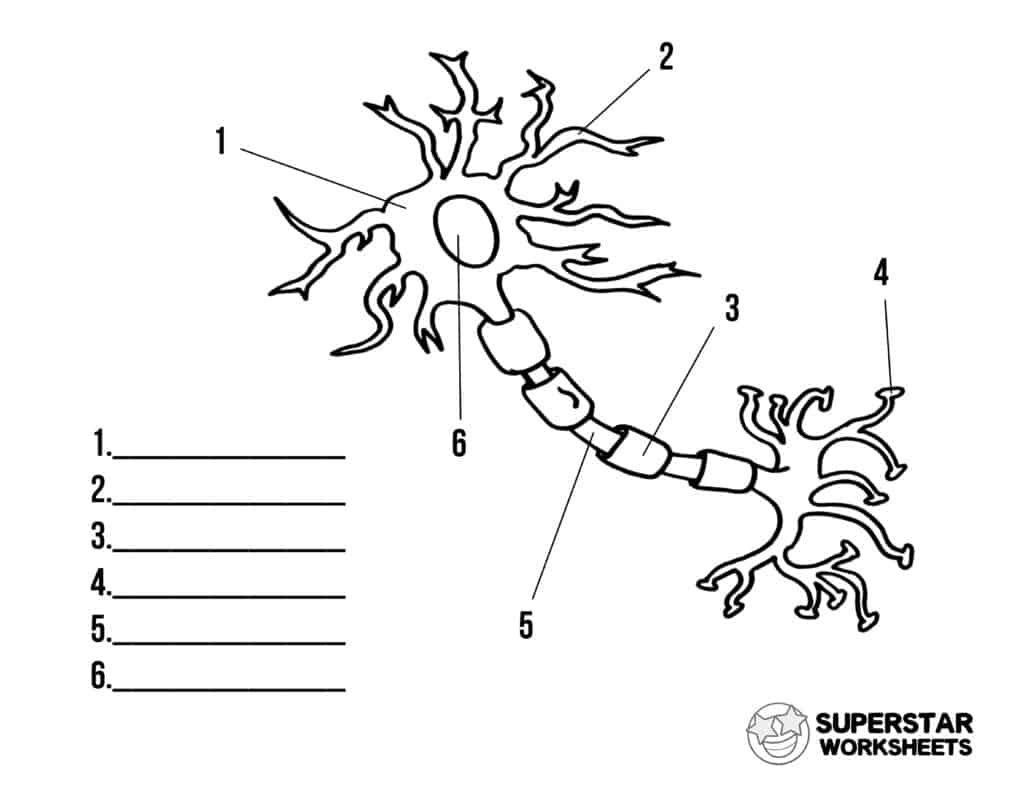
Label
.
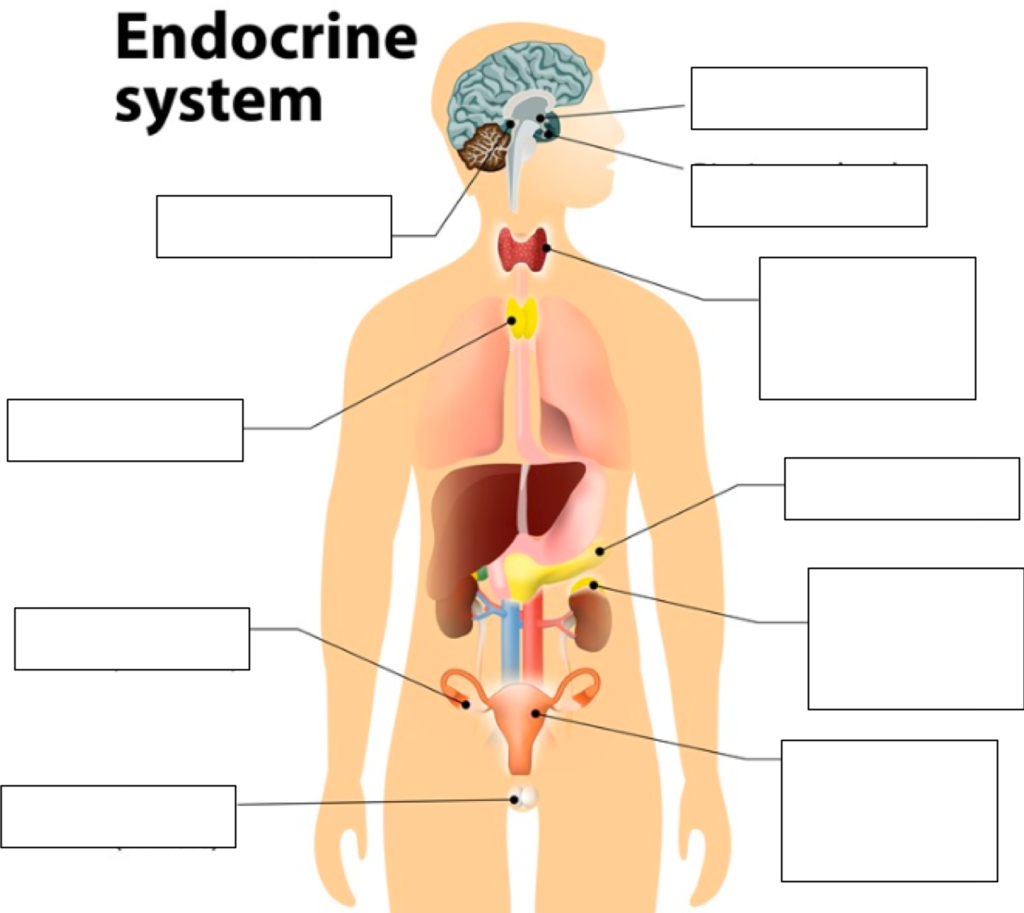
Label
.
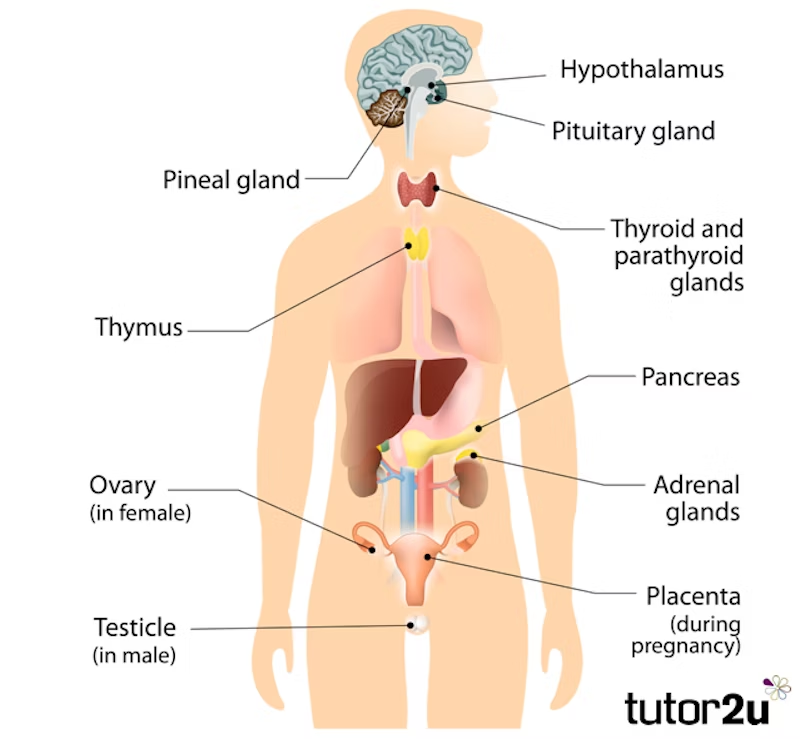
What is a memory model?
It is a hypothesised representation of memory it is more of an outline of different processes that shows how memory might work
Limitation of MSM (4)
Too simplified
Dosnt explain distortion or emotional memories
There are several times that we rehearse stuff but it doesn't go to long term.
backed up by both psychological and biological research
Strengths of MSM (3)
Supports the theory of separate memory stores
It gave psychologists a way to talk about memory.
Has historical importance
Central executive
Drives the whole system (e.g., the boss of working memory) and allocates data to the subsystems: the phonological loop and the visuospatial sketchpad.
Episodic buffer
A limited capacity storage system responsible for integrating information from several sources to create a unified memory
Visuospatial sketchpad
Being able to visualize stuff that you have seen before (example being able to imagine your house and how many windows it has)
Inner voice
Your internal monologue is the result of certain brain mechanisms that cause you to “hear” yourself talk in your head without actually speaking and forming sounds.
Inner ear
A sound that you process by your hearing
What is reconstructive memory?
Memories that add details not part of the actual event or omit details that were. An individual's life experiences can shape and change memory and alter its content.
What is flashbulb memory?
A flashbulb memory is a memory you can’t forget due to emotional prevalence (the memory can be both positive and negative)
What is the most common accepted model of the flash bulb memory?
the importance driven model
Who introduces the concept of flashbulb memory?
Brown and kulik
What are the two parts of the brain responsible for creating the flash bulb memory?
The hippocampus (helps with formation of the memory)
the amygdala (responsible for the formation of emotional memories)
Explain a CASE STUDY that allowed researchers to determine the role of biological factors on flashbulb memories
Sharot et al
Aim:
To determine the role of biological factors on flashbulb memories
Procedure:
The study was conducted three years after the 9/11 terrorist attacks in Manhattan. Participants were put in an fMRI machine and whilst in the scanner they were presented with word cues on the screen alongside the word summer or September to get the participant to link the words to either the summer holidays or the 9/11 attack. Participant’s brains were scanned and recorded while they were recalling events. The memories of personal events from the summer were used as a baseline of brain activity for evaluating the nature of the 9/11 attacks. Afterwards, participants were asked to rate their memories for vividness, detail, confidence in accuracy and arousal. They were also asked to write down their memories.
Results:
Sharot and her team found that the activation of the amygdala for the participants who were downtown was higher when they recalled memories of the terrorist attack than when they recalled events from the preceding summer, whereas those participants who were further away from the event had equal levels of response in the amygdala when recalling both events. The strength of amygdala activation at retrieval was shown to correlate with flashbulb memories. These results suggest that close personal experience may be critical in engaging the neural mechanisms that produce the vivid memories characteristic of flashbulb memory.
Conclusion:
The study is correlational and does not establish a cause-and-effect relationship. The experiment is highly artificial - and thus low in ecological validity. The sample size is small and culturally biased. Research indicates that individualistic cultures are more likely to have flashbulb memories than collectivistic cultures. This makes the findings difficult to generalise to the world population as a whole. The results were partly self-reported, which allows for errors in the results. However, the use of more than one method of data collection is triangulation which increases the validity of the results.
Explain the Loftus and Palmer CASE STUDY
Aim:
To investigate whether the usage of leading questions would affect eyewitness estimation of speed.
Procedure:
45 people were divided into 5 Groups and all watched the same video. They saw 2 cars crashing into each other. They were asked to state what they saw and they were asked a leading question. They were asked to gage how fast the car was going, but the catch is that the verb was changed in each sentence with some words being more extreme:
How fast did the cars contact each other?
How fast did the cars hit each other?
How fast did the cars bump into each other?
How fast did the cars collide with each other?
How fast did the cars contact each other?
Results:
The ones with the more intense words claimed that the speeds were higher than the ones with the less intense words.
Conclusions:
This implies that people can reconstruct or fabricate false memories based on perception.
Explain the Warrington and shallice CASE STUDY
Aim:
The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between short-term memory and long-term memory when short-term memory has been impaired.
Procedure:
Participant: Patient KF had experienced brain damage after a motorcycle accident. His LTM was intact but his STM showed impairment.
Researchers directly observed his behavior and administered memory recall tests during which they asked him to recall lists of words and numbers as well as learning tasks.
Results:
It was found that KF quickly forgot numbers and words when they were presented to him orally, but was able to remember them when they were presented to him visually. His impairment was mainly for verbal information and not for visual information
Conclusions:
This implies that there are two separate memory stores for verbal/oral information and visual information, which supports the WMM.
Explain the Multistore Memory Model (MSM)
Proposes that memory consists of three stores; the sensory register, the short-term memory (STM) and the long-term memory (LTM).
Explain Working Memory Model (WMM)
The Working Memory Model is a cognitive theory that explains how our short-term memory works.
Explain Schema
schema describes patterns of thinking and behavior that people use to interpret the world
Biological Evidence of the MSM
HM Milner studies in the biological approach, It’s another evidence that STM and LTM are located in different stores in the brain. HM had anterograde amnesia (couldn’t transfer new information to long-term memory).
Explain Tversky and Kahneman (1974) CASE STUDY
Tversky and Kahneman (1974)
In this study, high school students were used as participants. Participants in the "ascending condition" were asked to quickly estimate the value of 1X2X3X4X5X6X7X8 in five seconds.
Those in the "descending condition were asked to quickly estimate the value of 8X7X6X5X4X3X2X1.
Since we read from left to right, the researchers assumed that group 1 would use "1" as an anchor and predict a lower value than the group that started with "8" as the anchor. The expectation was that the first number seen would bias the estimate of the value by the participant The researchers found that the median for the ascending group was 512: and the median for the descending group was 2250. The actual value is 40320
Anchoring bias
Tendency to rely on the 1st piece of information given to you when making a decision
Eg.
If someone sets a price at 500$, you wouldn’t bargain down to 100$ because you would gravitate close to the 500$
The reliability of one of our cognitive processes (memory/decision-making)
Flashbulb memory & Sharot et al
Contrast and compare two memory models

Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) CASE STUDY
Aim:
To investigate recency effect in free recall (i.e. in any order).
Procedure:
Glanzer and Cunitz presented two groups of participants with the same list of words. One group recalled the words immediately after presentation, while the other group recalled the words after waiting 30 seconds. These participants had to count backwards in threes (the Brown-Peterson technique), which prevented rehearsal and caused the recency effect to disappear. Both groups could free recall the words in any order.
Results:
Participants recalled words from the beginning of the list (primacy effect) and the end of the list (the recency effect) best. The results showed a U-shaped curve.
1. The words at the end of the list are only remembered if recalled first and tested immediately. Delaying recall by 30 seconds prevented the recency effect.
2. If participants were given a filler task just after hearing the last words, the primacy effect disappeared but the recency effect remained.
3. The recency effect could be due to the words still being active in STM (working memory).
4. Rehearsal could be a factor in transfer of information into LTM.
Conclusion:
1. The study supports the idea of multiple stores (STM and LTM).
2. This is a controlled laboratory study with highly controlled variables, but there is no random allocation of participants to experimental conditions so it is not a true experiment.
3. There may be problems with ecological validity.