Microevolution Quiz
4.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/22
Last updated 1:42 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
gene flow
moving alleles through populations
2
New cards
speciation
breeding between populations stops when there is enough genetic drift between them
3
New cards
genetic drift
random changes in allele frequencies, not due to fitness, small populations are more susceptible
4
New cards
bottle neck effect
genetic diversity is greatly decreased due to a random event killing a portion of the population (greater risk of genetic disorder, traits can be lost)
5
New cards
founder effect
a new population is started that only has a couple organisms form a previous population
6
New cards
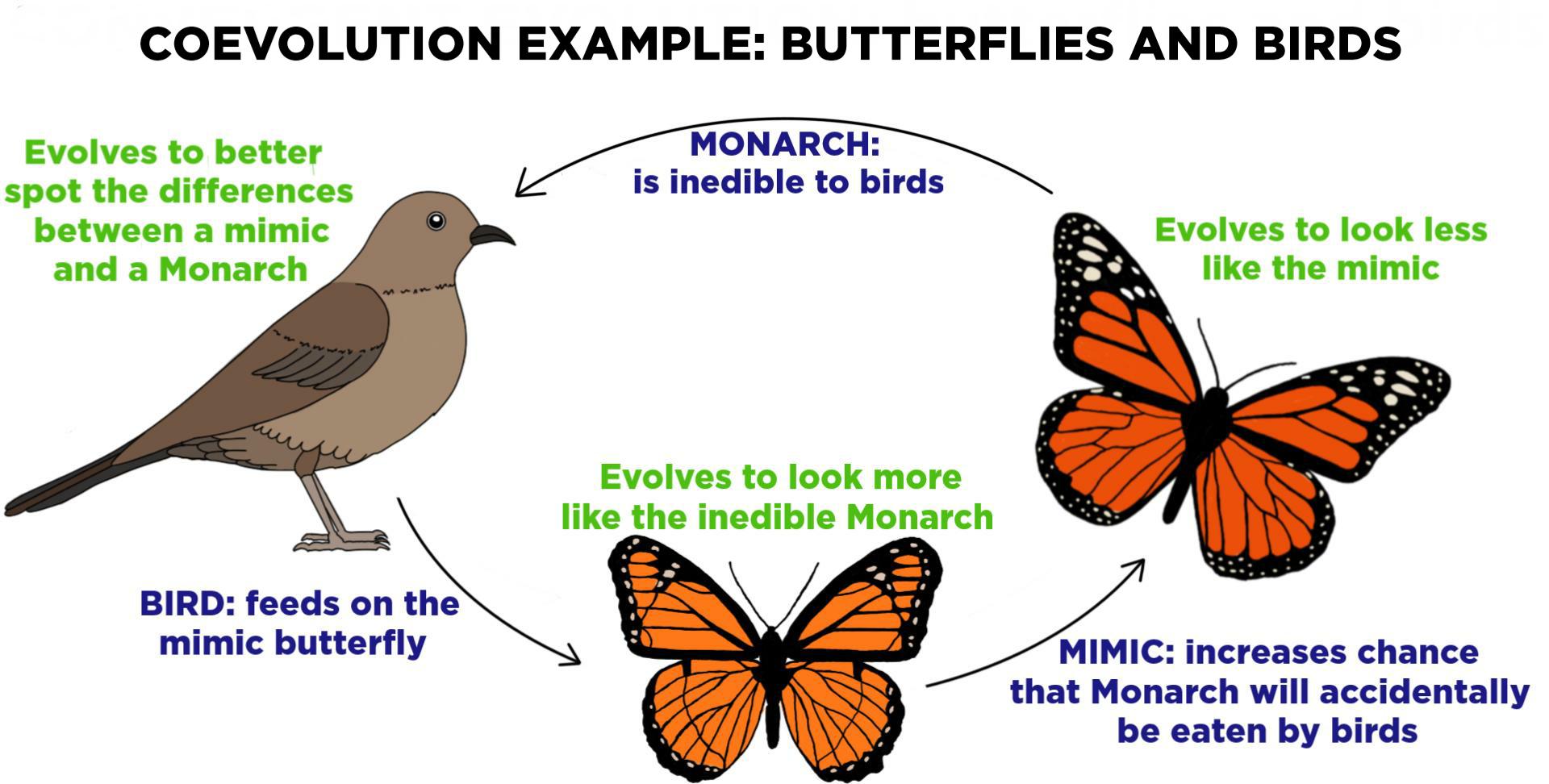
coevolution
when species become interconnected and cause each other to evolve
7
New cards
evolutionary pressure
something that increases or restrics evolutionary success
8
New cards
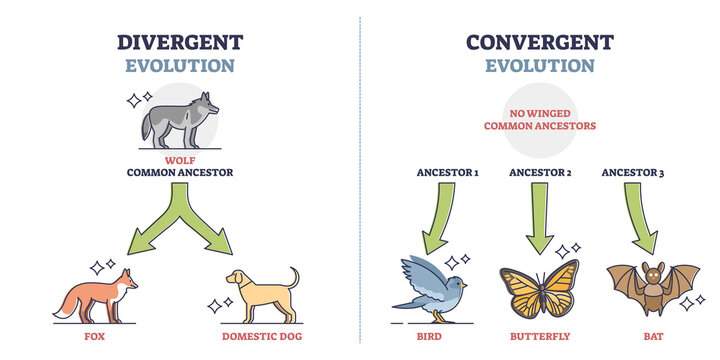
convergent evolution
2 species that are not closely related but develop similar traits because they have similar environmental pressures
9
New cards
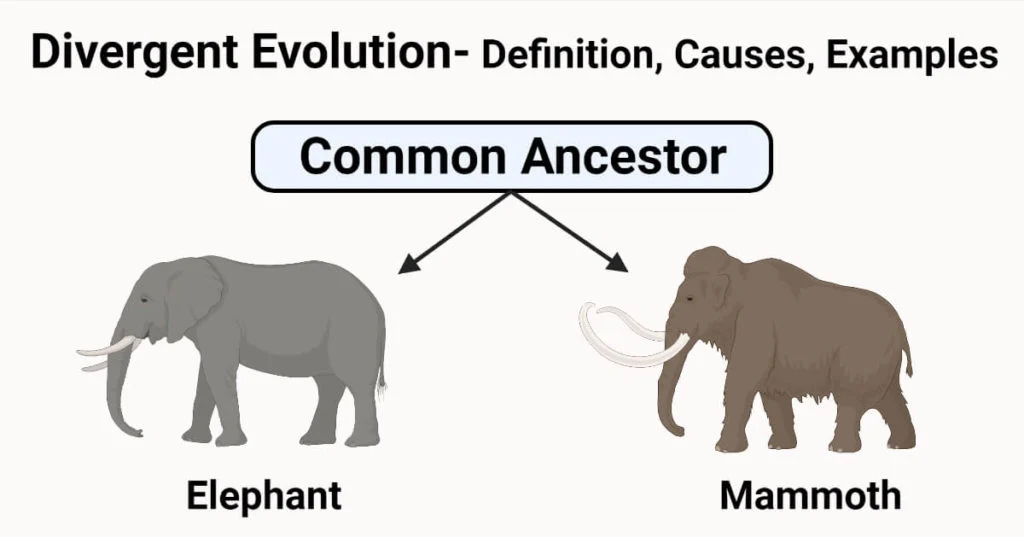
divergent evolution
2 species have similar ancestors but build differences that lead to evolution of 2 different species
10
New cards
adaptive radiation
many common ancestors, branch of divergent evolution
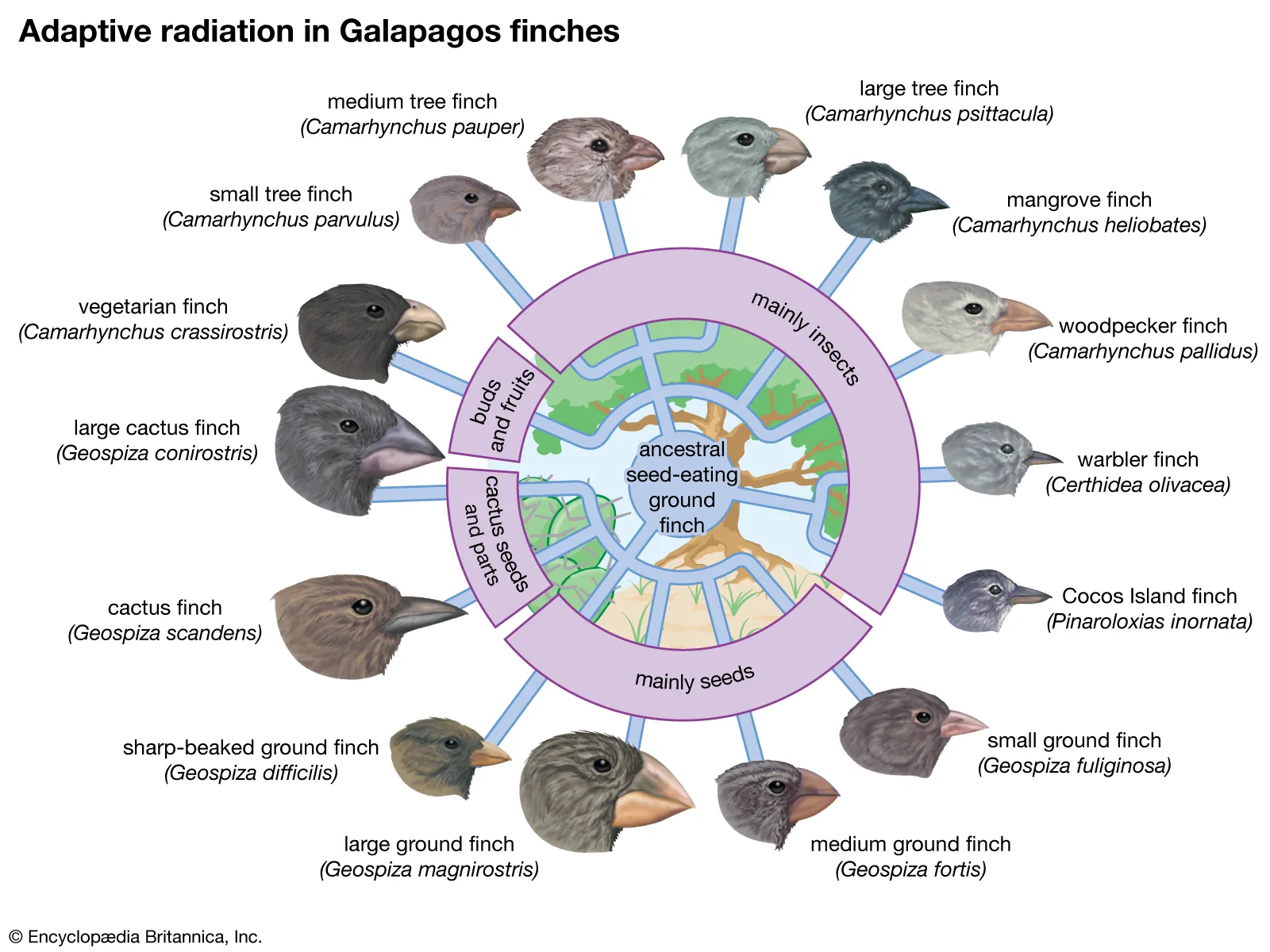
11
New cards
allopatric speciation
populations are separated by a physical barrier, the two populations can’t mate because of the barrier (random mutations and selective pressures make speciation)
12
New cards
sympatric speciation
reproductive isolation in a subpopulation not due to a physical barrier (unable to breed because of a pre-zygotic or post-zygotic barrier)
13
New cards
habitat isolation
two species live in the same geographic area but occupy different habitats and rarely encounter each other
14
New cards
temporal isolation
mates at different times, during night or day, summer or winter
15
New cards
behavior isolation
mating behavior (swims, flies, dances)
16
New cards
mechanical isolation
physically can not breed (bird and horse)
17
New cards
gametic isolation
the sperm can’t fertilize the egg
18
New cards
reduced hybrid vitality
the animal doesn’t live long enough to reproduce
19
New cards
reduced hybrid fertility
the offspring can’t have kids
20
New cards
hybrid breakdown
the first generation can have offspring, the second generation can, but the third generation can’t
21
New cards
stabilizing selection
any selective force or forces which push a population toward the average, or median trait
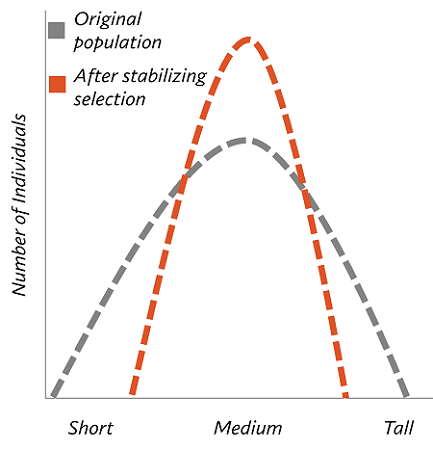
22
New cards
directional selection
individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or reproduce more than those on the other
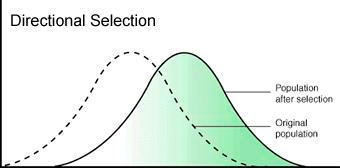
23
New cards
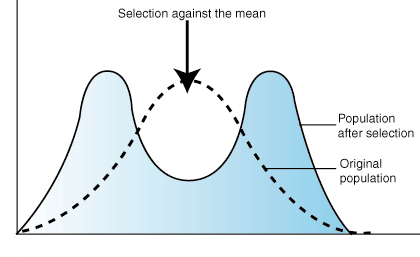
disruptive selection
when more extreme phenotypes (or genotypes) within a population have a fitness advantage over intermediate individuals