Thyroid Gland
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
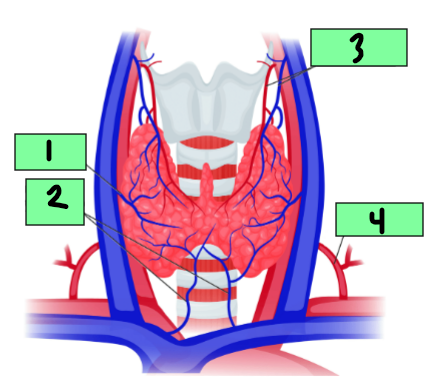
Right lobe
1
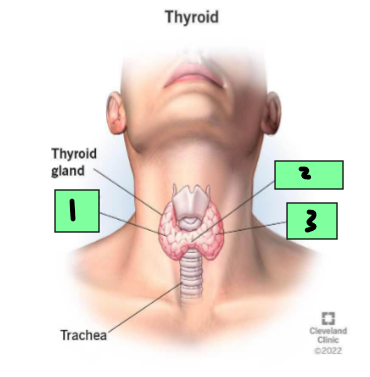
Isthmus
2
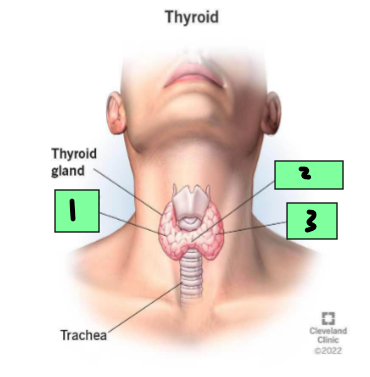
Left Lobe
3
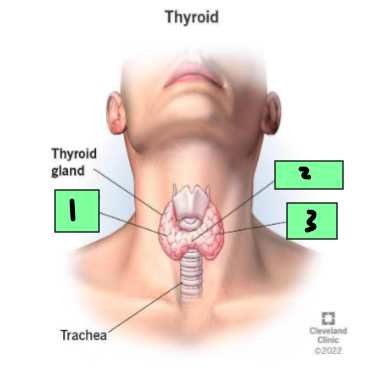
Middle thyroid vein
1
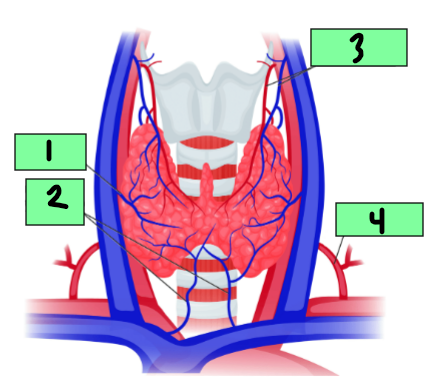
Inferior thyroid vein
2
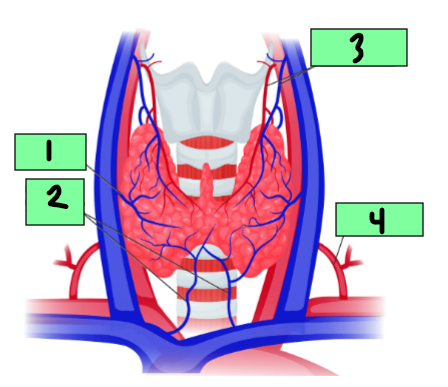
Superior thyroid arthery and vein
3
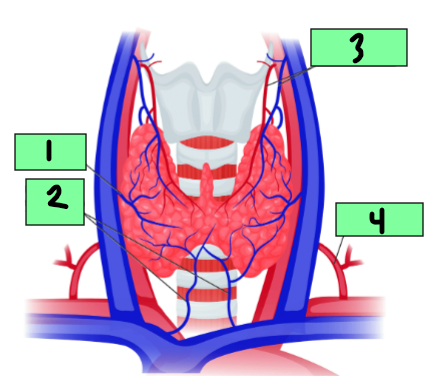
Inferior thyroid artery
4
Follicular cells
Synthesize and secrete thyroid hormones
blood, follicular, acetylcholine, thyroid
Histology → Follicular Cells
Autonomic Nervous System neurons terminate in ______ vessels of thyroid and on ____________ cells
Signals from ____________, catecholamines, and other peptides travel through this and will prompt follicular cells to secrete ________ hormone
Colloid
Stores thyroid hormone
iodine, thyroid, calcitonin, ghrelin
Histology
Colloid
Concentrates ________ that is imported through blood supply, which is necessary for process of producing ________ hormone
Parafollicular cells (AKA C cells)
Secrete regulatory peptides → __________, small amounts of neuropeptides ________, serotonin, and somatostatin
iodine, thyroglobulin, T3, T4, storage
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
It uses ________ (from food) and a protein called ______________ to make two main hormones
__ (triiodothyronine) - active form
__ (thyroxine) - _________ form that becomes T3 in the body
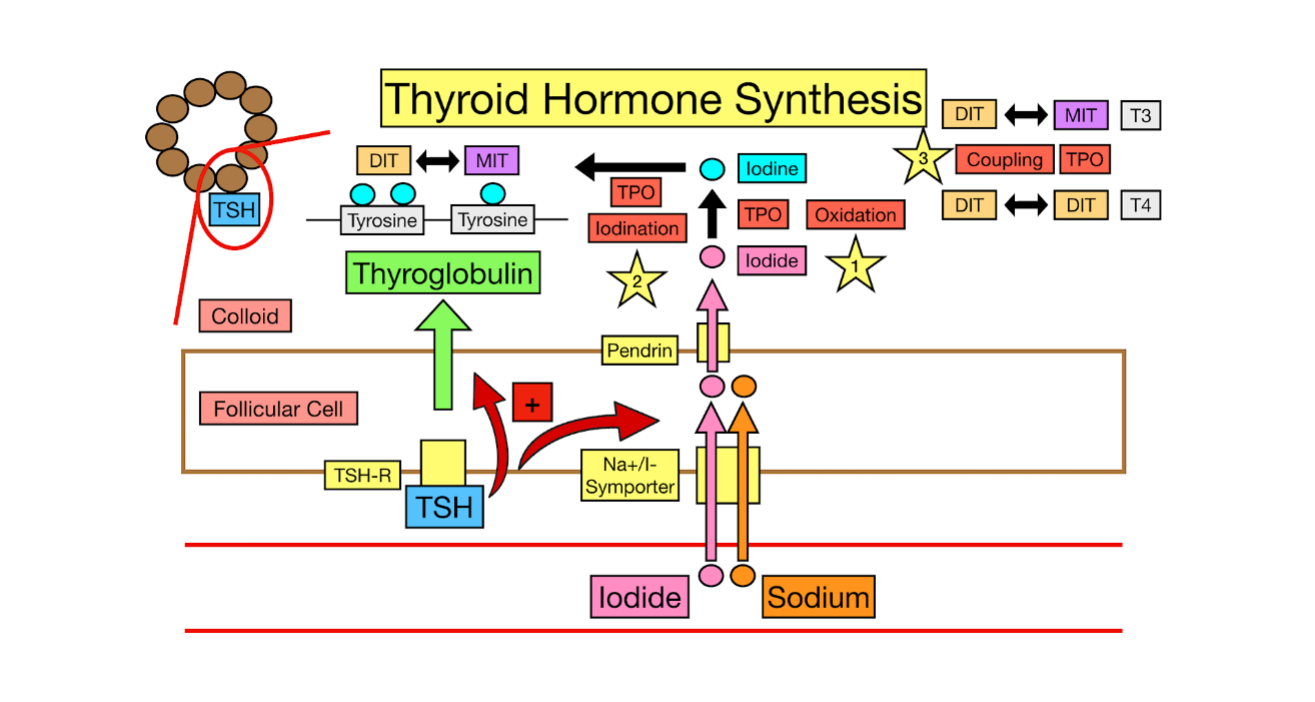
iodide, sodium, activated, thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin, follicular, tyrosine
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
_________ enters the thyroid
From your died (iodized salt, seafood)
Transported into the thyroid cells by a special “pump” called the __________-iodide symporter (NIS)
Iodine is _________
Iodide is converted into a reactive form (iodine) by the enzyme ______ __________ (TPO) (Job #1)
___________ is made
This is a large protein made by thyroid ___________ cells, rich in __________ (an amino acid)
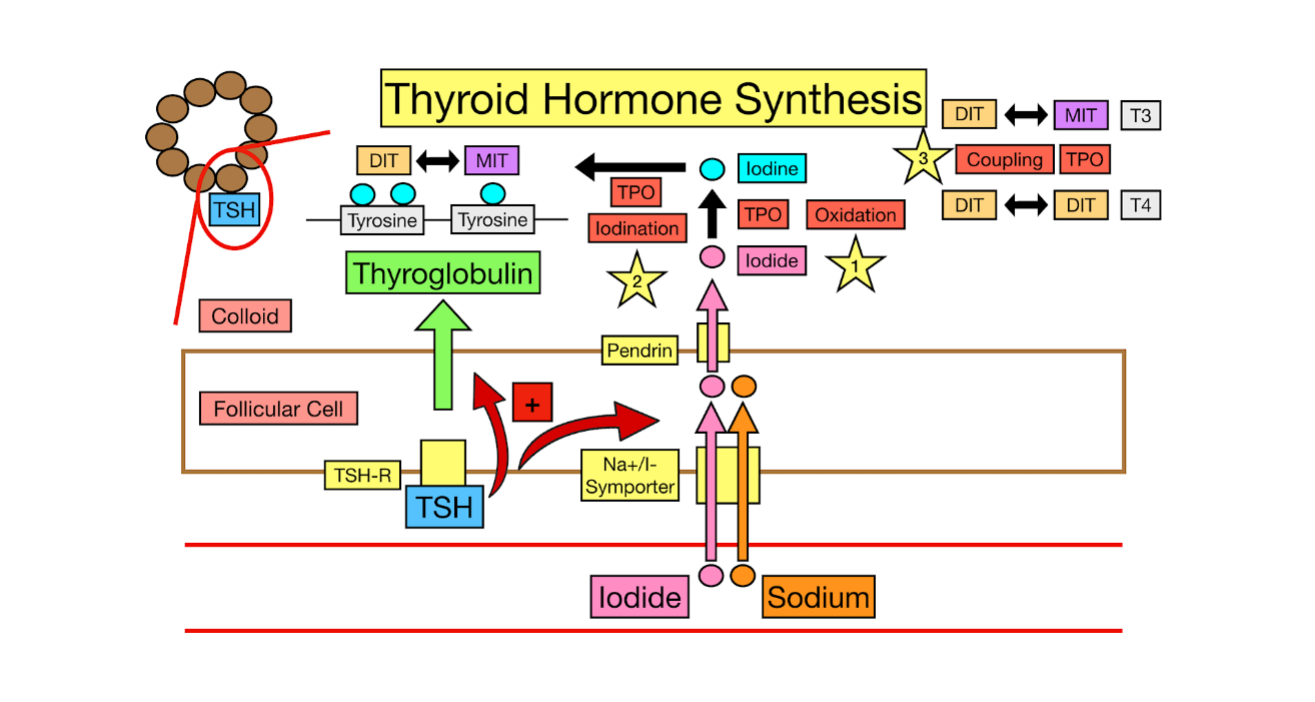
tyrosine, TPO, MIT, DIT, TPO, T3, T4
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
Iodine + ___________ = MIT and DIT
Iodine is added to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin (facilitated by ___ → Job 2)
One iodine = ___
Two iodine = ___
Coupling Reaction
Facilitated by ___ (job 3)
MIT + DIT = __ (active form)
DIT + DIT = __ (storage form)
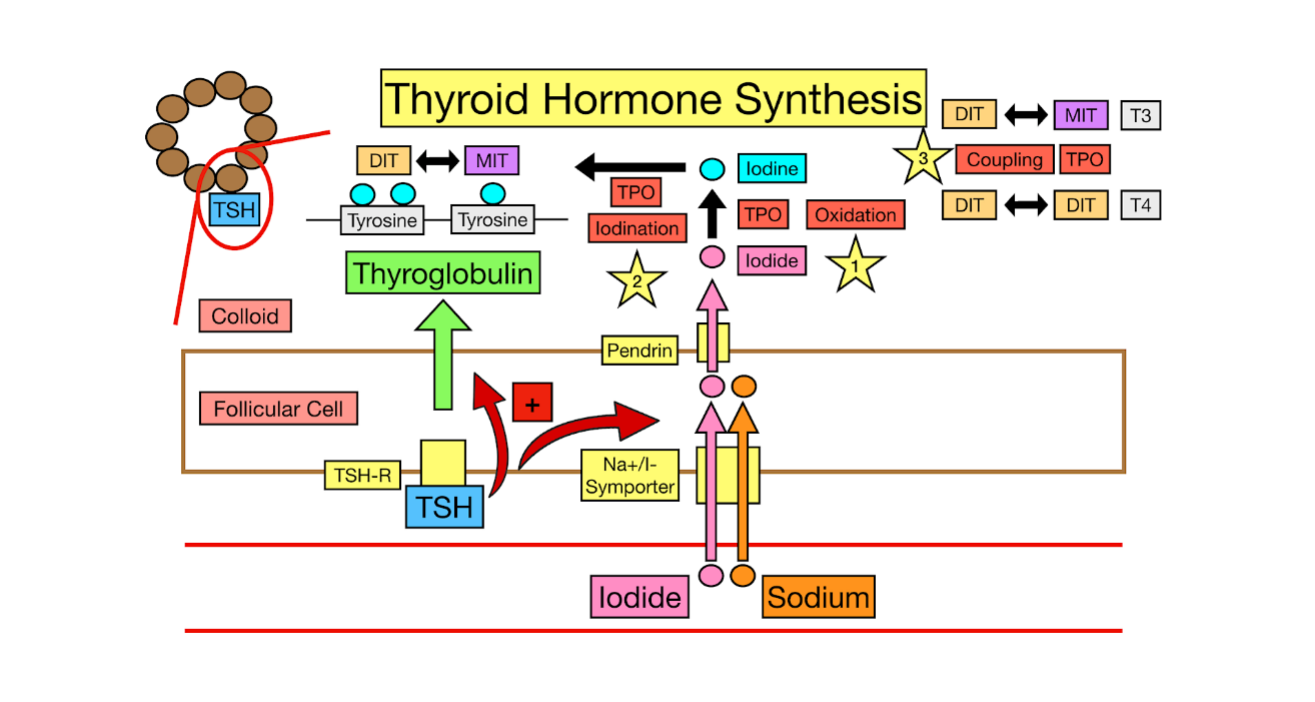
thyroglobulin, colloid, blood, TSH, pituitary
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
Storage in colloid
These T3 and T4 hormones stay attached to _____________ in a gel-like substance called the ________, inside thyroid follicles
Release into the ______
When the body needs thyroid hormone (signaled by ___ from teh __________ gland)
The thyroid takes in the thyroglobulin
T3 and T4 are cut free and released into the bloodstream
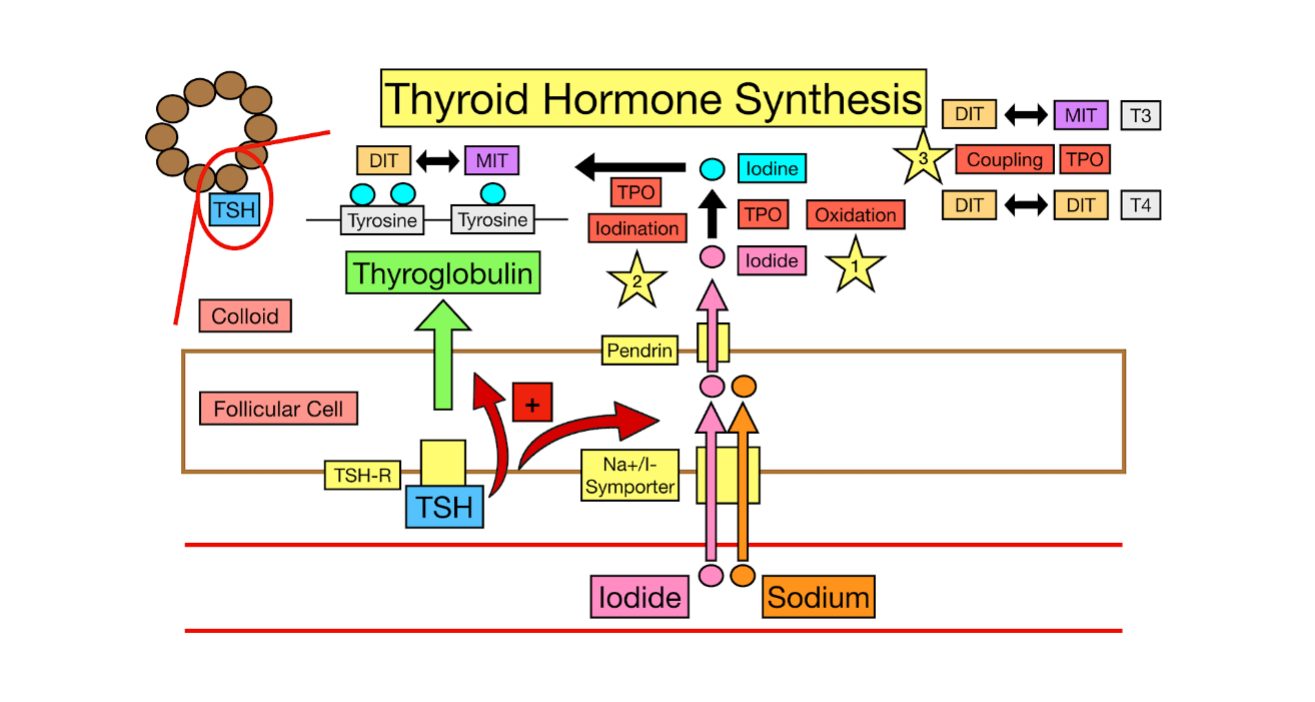
active, directly, 1, 1, beta, storage, T3, liver
Thyroid Hormones
Triiodothyronine (T3)
10% produced from thyroid gland
_______ form
__________ acts on target cells
Binds to thyroid receptors alpha-_, beta-_, _____-2
Thyroxine (T4)
90% of what thyroid gland produces
________ form
Converted to __ within body tissues, mostly ______
These bound forms serve as thyroid hormone storage within circulation, active form of hormone is when unbound
Thyroxine-binding globulin, albumin, lipoproteins
What are the three carrier proteins that are used to primarily transport thyroid hormones?
large, unbound, nuclear, unbound, free, increased, decreased
Unbound Thyroid Hormone
AKA Free Hormone
Able to enter into cells, bound hormone is too ______ to cross cell membrane
Only _________ T3 and T4 can enter the cells and bind to _________ receptors
Labs
________ = ____ hormone, free hormones are what is measured when checking true thyroid function (more accurate than total thyroid hormone)
Impact on feedback system
Hypothalamus and pituitary monitor free T3 and T4, not total hormone levels
Low free T3/T4 → increased TRH by hypothalamus and increased TSH by pituitary → __________ thyroid hormone production
High free T3/T4 → decreased TRH by hypothalamus and decreased TSH by pituitary → __________ thyroid hormone production
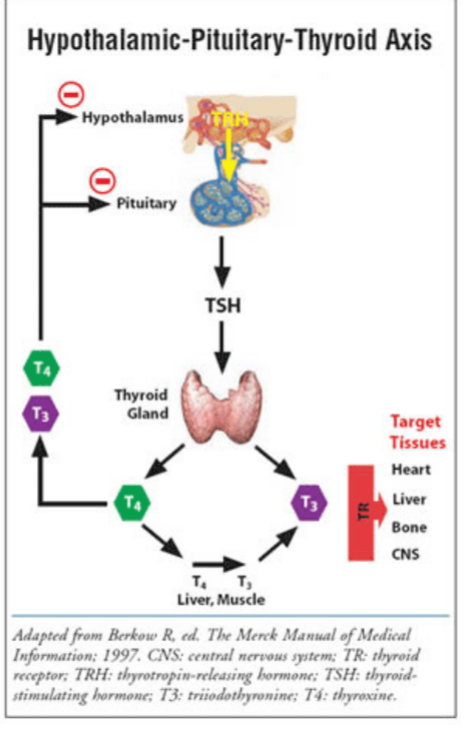
T4, T3, liver, feedback
Deiodinase Enzymes
Special enzymes to remove one iodine atom from __ → active form, __
Occurs mostly in ______, but in various body tissues when stimulated by ________ system
catabolism, all, temperature, growth, CNS, cardiac, RBC, insulin
Thyroid Hormone Effects
Metabolism → protein, fat, carb ____________
Metabolic rate of ___ cells
Body _____________
_______ hormone secretion → skeletal health
Muscle tone
___ development
__________ rate, how body uses oxygen
GI regulation
___ production
Cholesterol turnover
_________ antagonist