Sediment transportation, LSD and landforms
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is traction?
sediment rolls along the sea floor, pushed by waves and currents
The sound of it can be heard from the beach
Pebbles, cobbles and boulders are moved
What is saltation?
sediment bounces along
Caused by wind or the force of water
On dry windy days bouncing sediment can be seen on shore
Small, sand sized particles
What is suspension?
sediment is carried in the water column
Soft rock coasts (holderness) the sea is often brown due to suspended silt and clay
What is solution?
dissolved material is carried in the water as a solution
Of limited importance
Limestone is carried as chemical compounds
What is a swash aligned coast?
Waves meet parallel to the coast
Limited longshore movement of sediment
What is a drift aligned coast?
wave crests break at an angle to the coast so sediment is carried and deposited at an angle
This causes consistent LSD and elongated depositional features
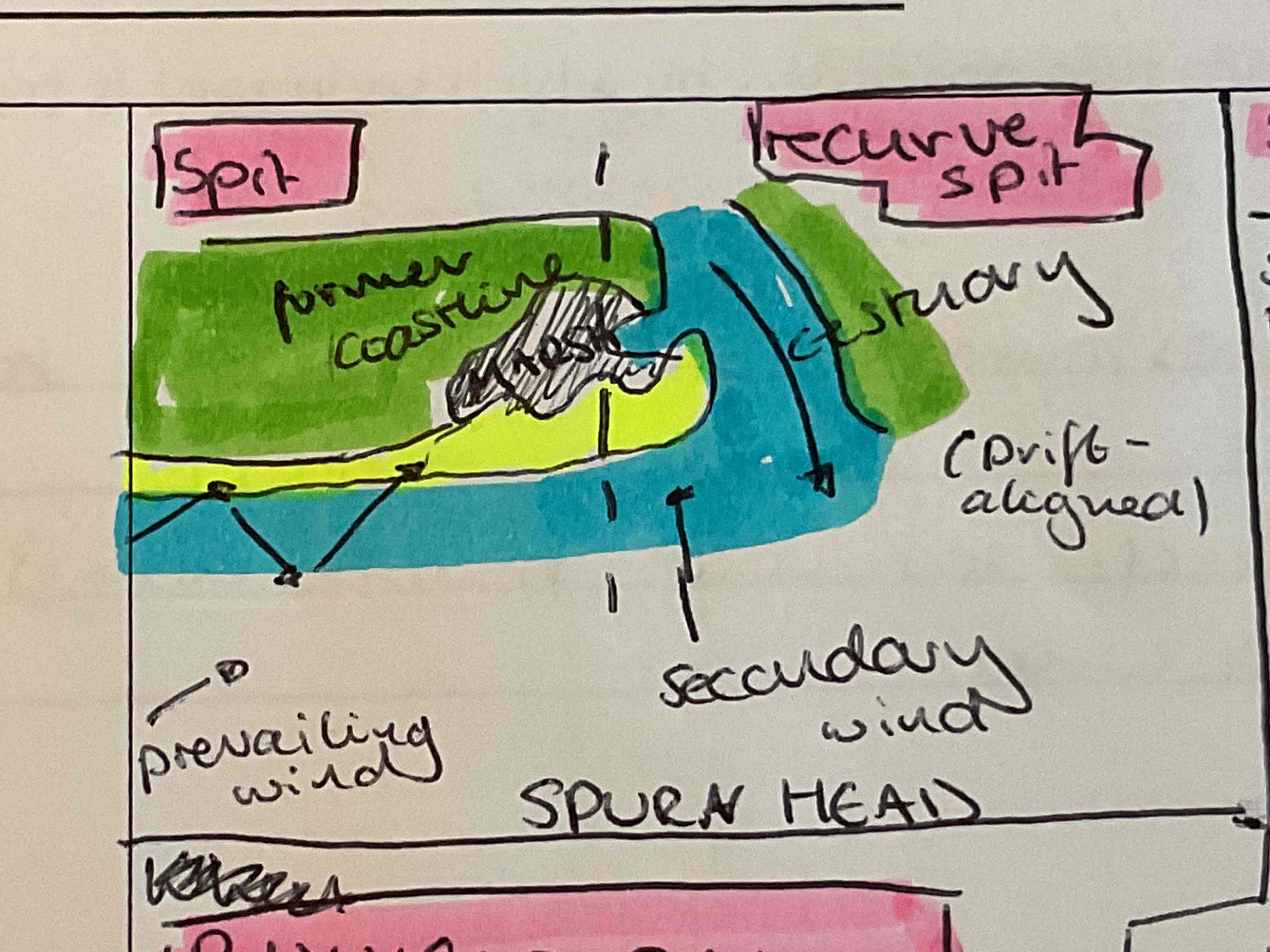
What is the formation of (recurve) spits? - Spurn Head (spit) -Hurst Castle (recurve)
Spit
LSD continuously deposits sediment beyond a turn in the coastline
Length is dependent on amount of sediment transported or the flow of a river carrying sediment away
Recurve
when the end of a spit curves landwards into shallower water due to secondary wind
Bayhead beach - lulworth cove, Dorset
swash aligned coast deposits sediment to form a beach
Due to wave refraction and erosion is concentrated on headlands beaches eventually have more deposition
Bar/ barrier beach - Chesil beach
drift aligned
A sand or shingle beach connecting two areas of land with a shallow water lagoon behind
This is caused when a spit grows so long it extends across a whole bay, closing it off
Tombolo - St Ninions, Shetland
drift aligned
A sand/shingle bar that connects to an offshore island
Forms due to wave refraction around an island that creates an area of still water when it collides
Deposition increases
Opposing LSD currents can also cause still water also
Cuspate Foreland - Dungeness Kent
drift aligned
A triangular shapes feature extending out from a shoreline
Thought to form from the growth of two spits from opposing LSD directions
What is gravity setting?
energy transporting water becomes too low to carry sediment
Large sediment us deposited first
Why are depositional features vulnerable?
Made from unconsolidated material
Vulnerable to change
Dynamic
Storms can cause change
Storms at spring tide can cause more extreme change
Leads to redeposition elsewhere