8 Science Term 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Last updated 11:22 AM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process carried out by plants in order to produce food.
2
New cards
The chemical equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon Dioxide (6xCO2) + Water (6xH2O) → Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen (6xO2)
3
New cards
The place where photosynthesis occurs
Photosynthesis occurs on the leaves of a plant
4
New cards
the two other things necessary for photosynthesis
Sunlight and Chlorophyll.
5
New cards
purpose of roots?
Roots anchor the plant and also help the plant to obtain water and minerals.
6
New cards
structure of the roots
A main root, lateral roots, root hairs
7
New cards
purpose of root hairs
to maximise surface area to collect more water and minerals.
8
New cards
structure of the stem
The conducting tissue
9
New cards
Conducting tissue
Xylem and Phloem.
10
New cards
Xylem
Transports water and minerals, only goes upwards
11
New cards
Phloem
The Phloem transports nutrients like Glucose (translocation) in any direction
12
New cards
Purpose of the stem
Hold up the plant and transport nutrients around the plant
13
New cards
purpose of leaves
Collecting water, producing food, transpiration
14
New cards
structure of leaves
Guard cells, stomata, an epidermis, a cuticle, conducting tissue, and the Mesopyll; including the spongy mesopyll and palacade mesophyll.
15
New cards
Stomata and guard cell
Openings at the bottom of the plant allow for the release of water and the exchange of gases.
16
New cards
Epidermis
Absorbs sunlight with chlorophyll
17
New cards
Mesophyll layer
The Palacade mesophyll and the spongy mesophyll. The Palacade Mesophyll is where photosynthesis occurs, while the Spongy Mesophyll has gaps to allow for the movement of gases around the leaf.
18
New cards
Cuticle
A waxy, thin layer at the top of the leaf that prevents foreign substances from entering the leaf.
19
New cards
Biotic factors
Things that are living or once living
20
New cards
Abiotic factors
Things that are non-living
21
New cards
Producers
Organisms that create food with photosynthesis.
22
New cards
Consumers
Organisms that rely on other organisms for its food.
23
New cards
Predators
An animal that hunts for its food.
24
New cards
Prey
An animal hunted by other animals for food.
25
New cards
Detritivores/Scavengers
Organisms that feed on dead material.
26
New cards
Decomposers
Organisms that break down organic material
27
New cards
Herbivores
Animals that only eat plants.
28
New cards
Carnivores
Animals that only eat meat (other animals)
29
New cards
Omnivores
Animals that eat both plants and animals
30
New cards
5 trophic levels.
Producers, Primary consumers, Secondary Consumers, Tertiary Consumers, Apex predators
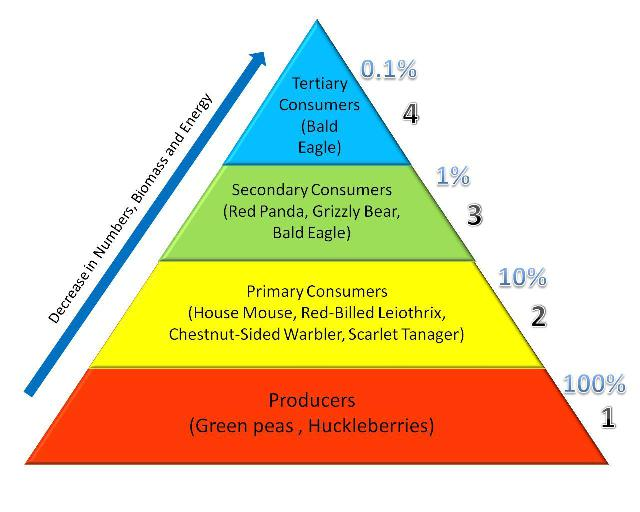
31
New cards
Food Chains
Show the direction of energy flow in an ecosystem.
32
New cards
Food webs
Multiple food chains that represent an ecosystem
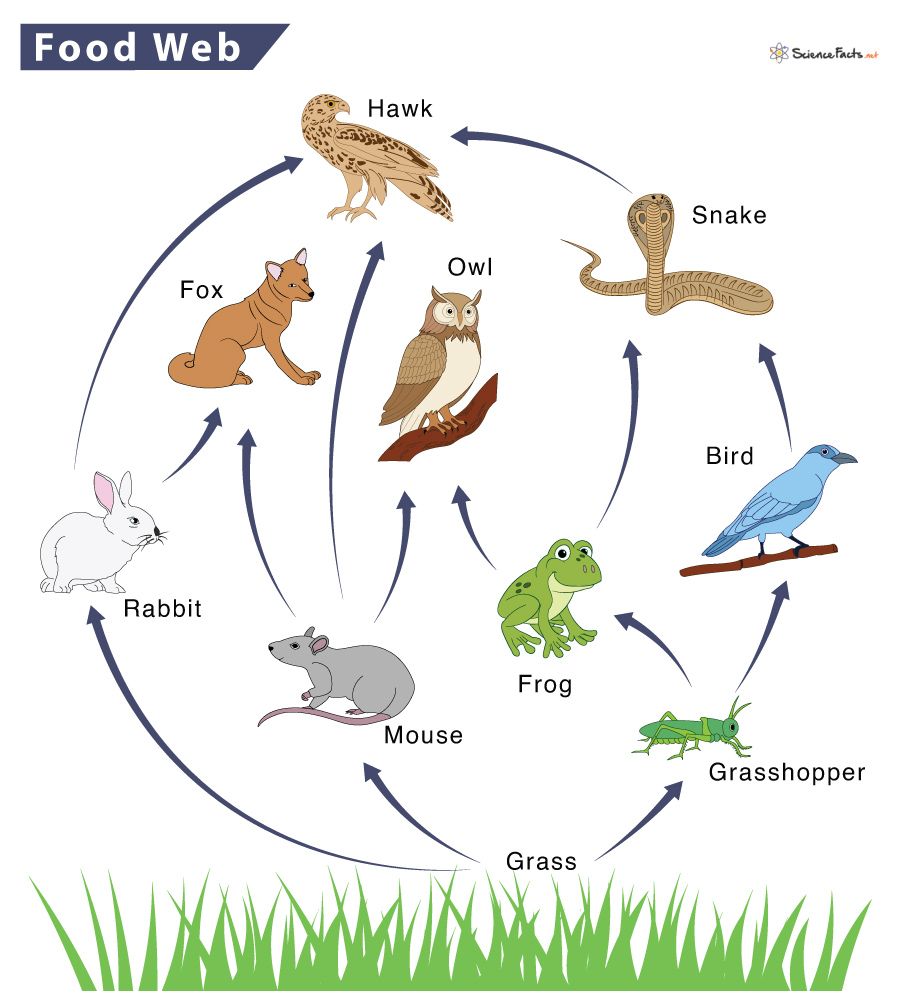
33
New cards
Biomass
Biomass is the dry mass of the organisms at a trophic level. More biomass is required at the bottom level to support the top level.
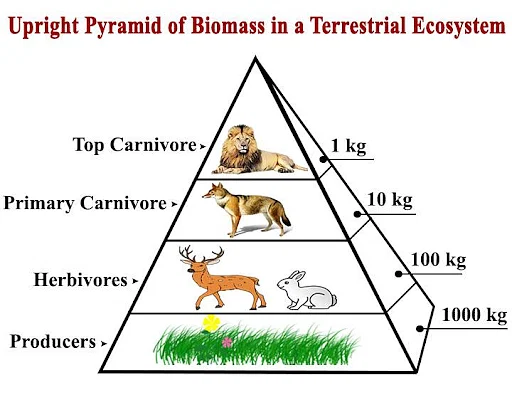
34
New cards
The ways the periodic table is seperated.
Groups, periods and families.
35
New cards
Order of the Periodic table
Increasing atomic number
36
New cards
An element from the periodic table has…
A name, a chemical symbol, an atomic number, and an atomic weight.
37
New cards
Elements
A sample of matter containing only one type of atom.
38
New cards
Metals
Elements that conduct heat and electricity. They are generally solid, Malleable, Shiny, and Ductile, and have a high melting point.
39
New cards
Non-Metals
Elements that don’t conduct heat or electricity. They can easily melt and can easily turn into liquids. They are brittle, often coloured, and look dull and glassy.
40
New cards
Metalloids
Share properties with both metals and non-metals.
41
New cards
Atoms
Made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons, Mostly space
42
New cards
Compounds
Compounds contain two or more __types__ of atoms that are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio.
43
New cards
Molecules
Molecules contain two or more atoms that are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio.
44
New cards
The three types of particles in an atom
Protons, electrons, and neutrons.
45
New cards
Protons and Neutrons
They are the same size and are both found in the nucleus.
46
New cards
Electrons
2000 times smaller than protons and neutrons, spinning around in constantly changing paths called orbits
47
New cards
Name the electric charges of subatomic particles
Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have a neutral charge, and electrons have a negative charge.
48
New cards
The reason why the electron orbits the nucleus
They have an electrical attraction
49
New cards
Do neutral atoms have the same amount of protons and electrons
Yes, so there is no electrical charge