AP Macroeconomics Unit 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Economics
the study of how people try to satisfy seemingly unlimited wants with limited resources; the study of how society allocates scarce resources
factors of production
inputs or resources that go into the production function to produce goods and services: land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
Inputs
Resources such as people, raw materials, energy, information, or finance that are put into a system (such as an economy, manufacturing plant, computer system) to obtain a desired output. Inputs are classified under costs in accounting.
Capital
resources (buildings, machinery, and equipment) used to produce goods and services; also called investment goods.
Microeconomics
portion of economics concerned with the individual elements that make up the economy; households, firms, government, and resource input prices
macroeconomics
the portion of economics concerned with the overall performance of the economy; focused on aggregate demand-aggregate supply relationship, and the resultant output, income, employment, and price levels
positive economics
(as opposed to normative economics) is the branch of economics that concerns the description and explanation of economic phenomena. It focuses on facts and cause-and-effect behavioral relationships and includes the development and testing of economics theories.
normative economics
(as opposed to positive economics) is a part of economics that expresses value or normative judgments about economic fairness or what the outcome of the economy or goals of public policy ought to be.
ceteris paribus
with other conditions remaining the same.
Scarcity
the imbalance between limited productive resources and unlimited human wants
opportunity cost
the value of the sacrifice made to pursue a course of action
model
a representation of an object or situation that is simplified while including enough of the key features to help us understand the object or situation; economists use the term model instead of theory; models are used to test theories; an applied or empirical representation
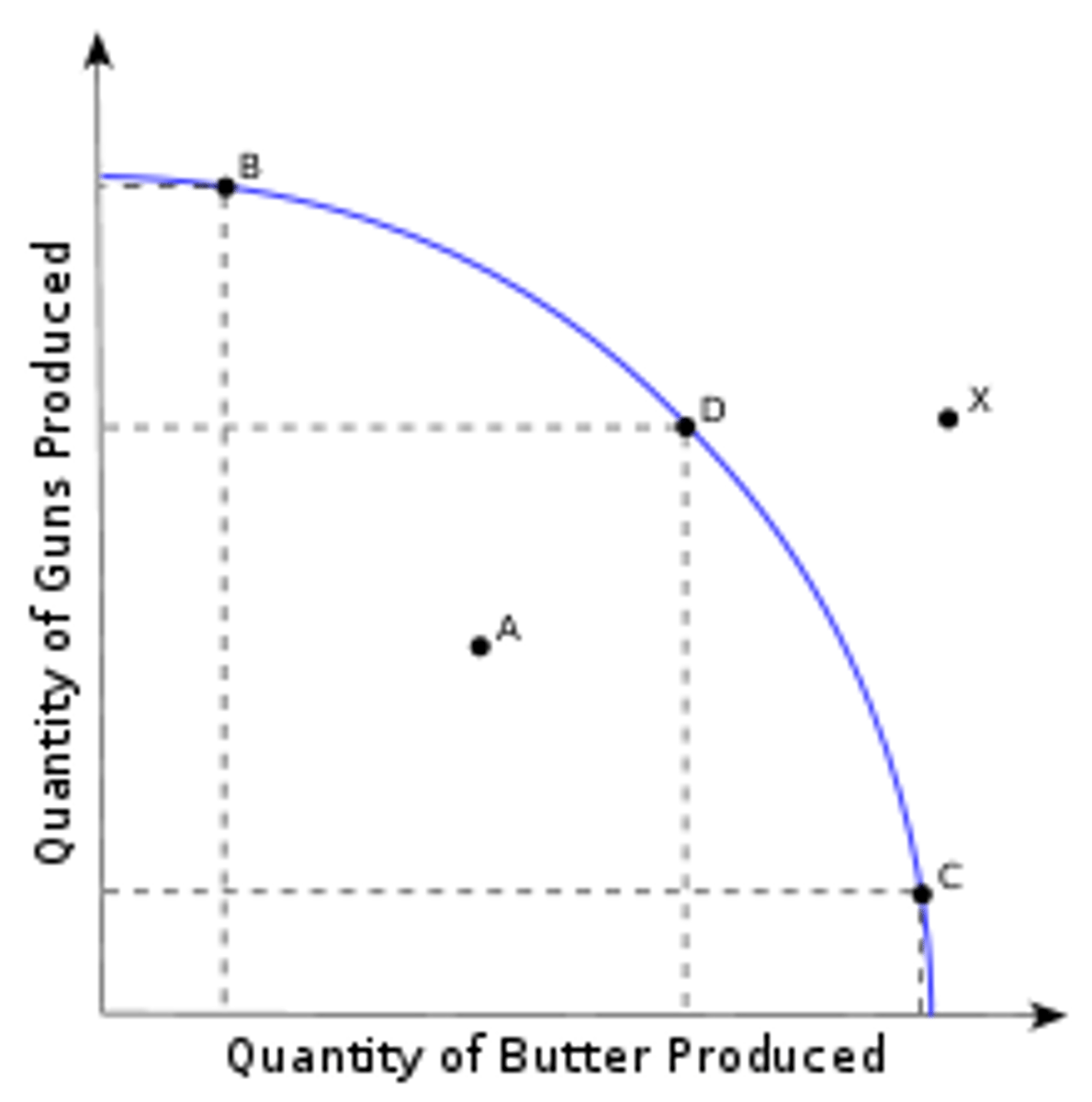
Production possibilities
the different quantities of goods that an economy can produce with a given amount of scarce resources
constant costs
An industry in which the ratio comparing units produced to production cost per unit remains the same regardless of industry volume or demand growth. This supply-curve equilibrium occurs when input costs do not increase in response to increased demand.
law of increasing opportunity cost
the principle that as the production of a good increases, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit rises.
absolute advantage
the ability to produce more of a good than all other producers
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at lower opportunity cost than all other producers
Specialization
production of goods, or performance of tasks, based upon comparative advantage
terms of trade
the ratio at which a country can trade its exports for imports from other countries
Demand
the quantities of a good or service that buyers wish to buy at various prices
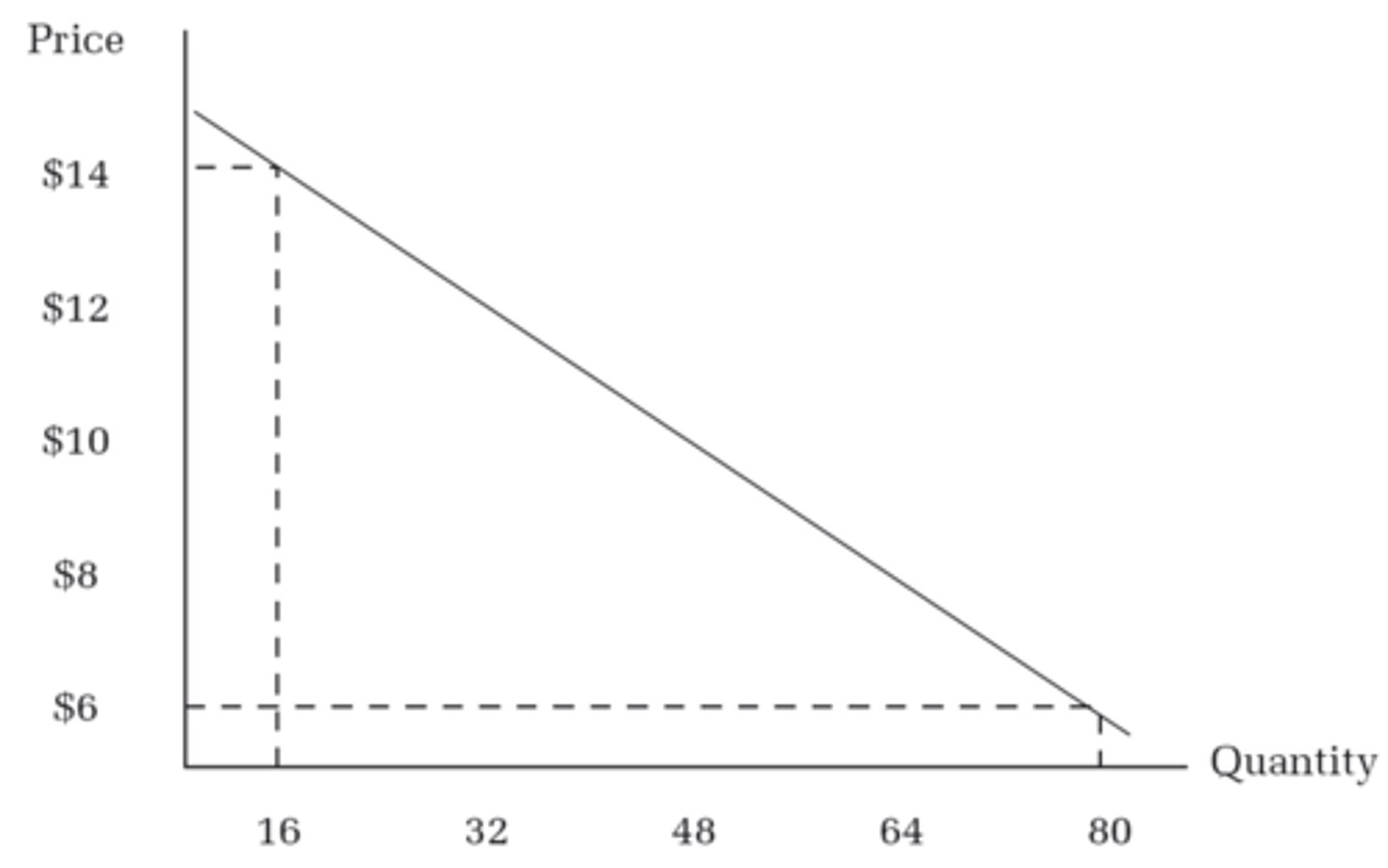
law of demand
all else equal, when the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded of that good falls
quantity demanded
various amounts along a consumer demand curve showing the quantity consumers will buy at various prices
market demand
Market demand is the sum of the individual demand for a product from buyers in the market.
Substitutes
two goods are consumer substitutes if they provide essentially the same utility to the consumer
Complements
two goods that provide more utility when consumed together than all other producers
normal goods
a good for which demand increases with an increase in consumer income
inferior goods
a good for which demand decreases with an increase in consumer income
supply
Supply is a fundamental economic concept that describes the total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers. Supply can relate to the amount available at a specific price or the amount available across a range of prices if displayed on a graph.
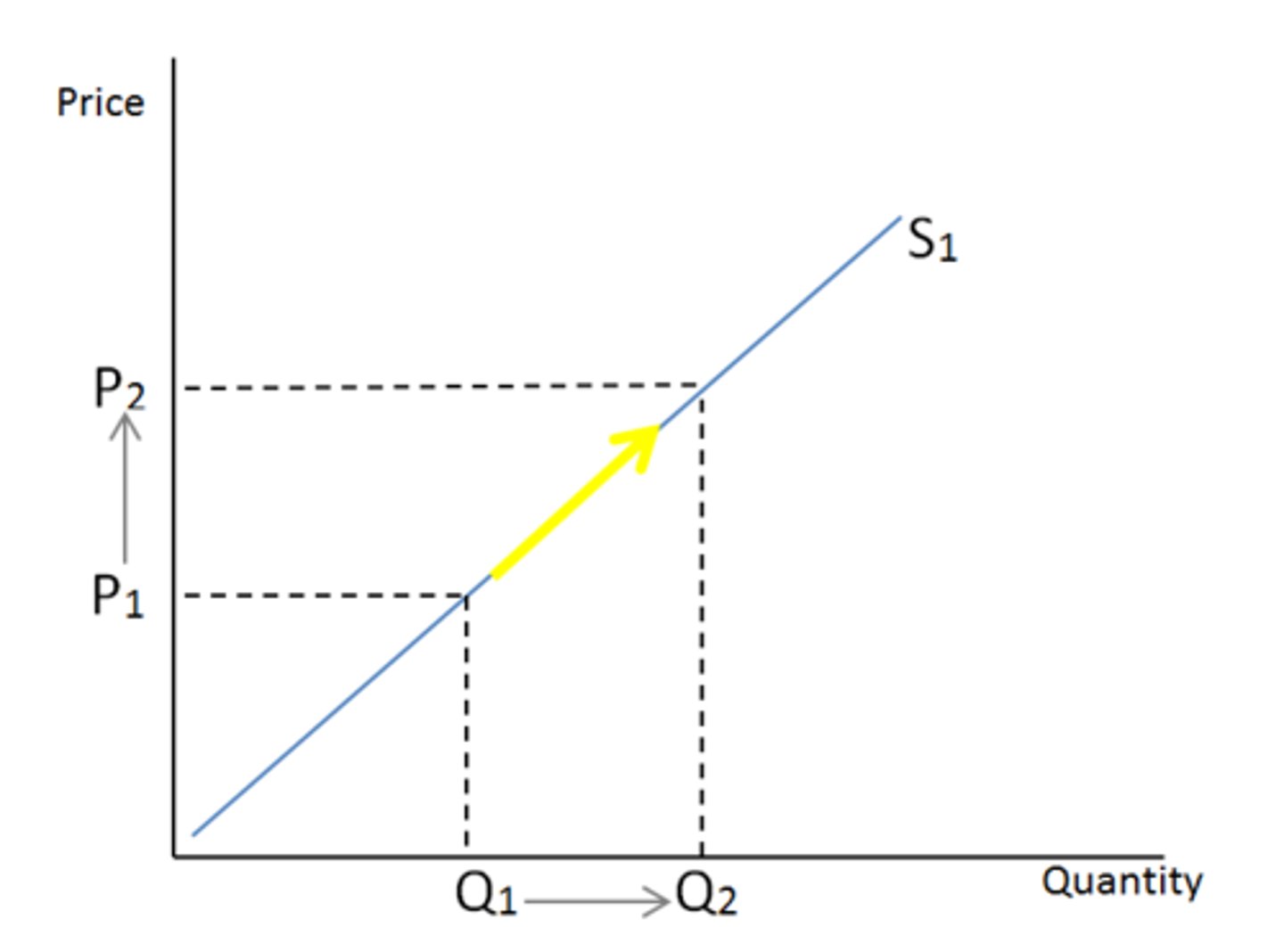
law of supply
all else equal, when the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied of that good rises
quantity supplied
various amounts along a producer supply curve showing the quantity producers will sell at various prices
market equilibrium
exists at the only price where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. Or, it is the only quantity where the price consumers are willing to pay is exactly the price producers are willing to accept.
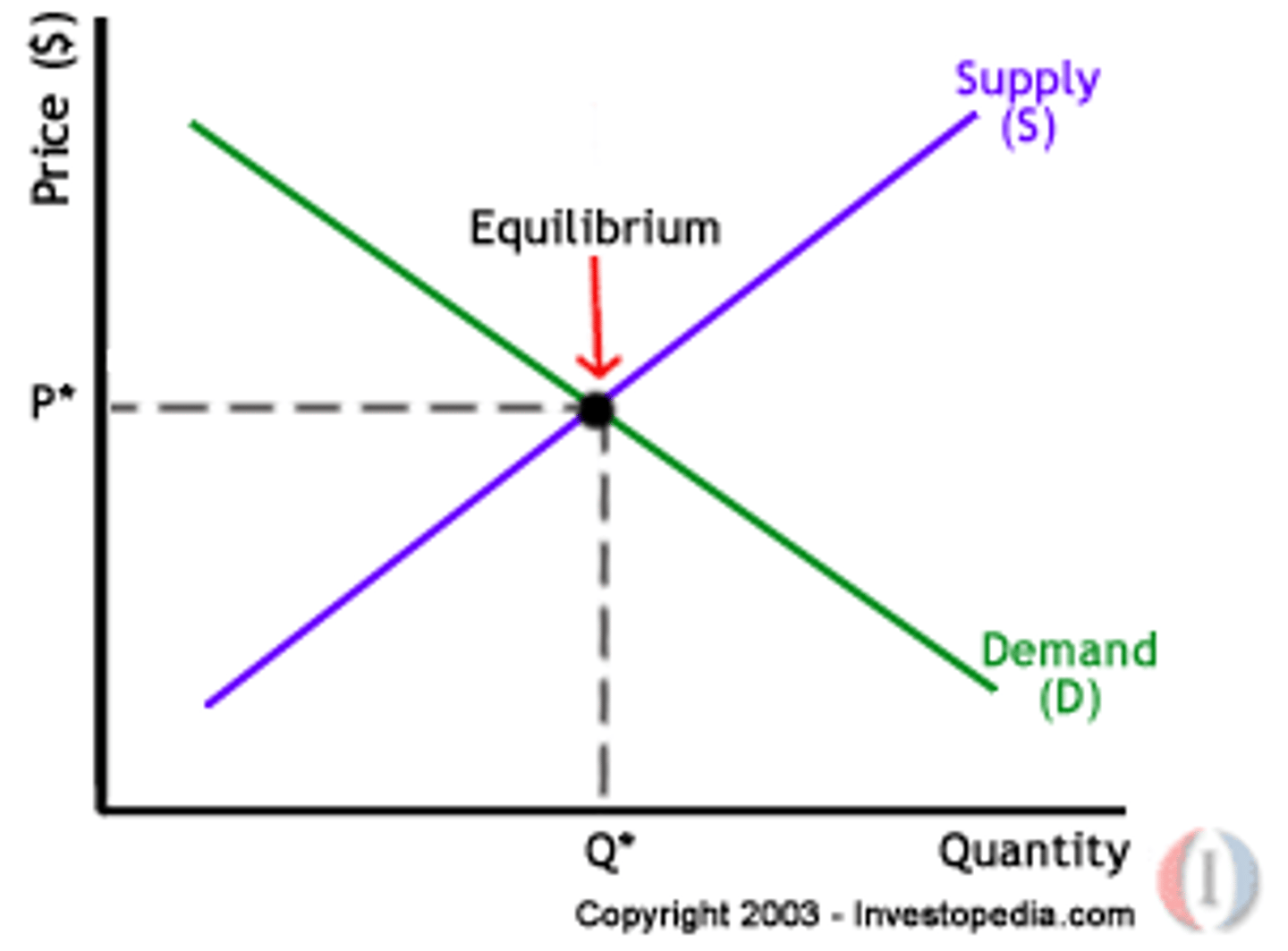
equilibrium price
price at which the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied are equal (intersect), shelves clear, and price stability occurs
equilibrium quantity
quantity demanded and supplied at the equilibrium price
supply shock
An unexpected event that causes the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift
marginal
additional
Utility
Ability or capacity of a good or service to be useful and give satisfaction to someone.
aggregate
Gathered into a whole; total
3 Shifters of the PPC
1. change in resource quantity or quality
2. change in technology
3. change in trade
price
monetary value of a product as established by supply and demand
cost
the expenses incurred in producing a product
command economy
An economic system in which the government controls a country's economy.
mixed economy
An economy in which private enterprise exists in combination with a considerable amount of government regulation and promotion.
free market economy
an economic system in which decisions on the three key economic questions are based on voluntary exchange in markets
Price Controls
legal restrictions on how high or low a market price may go
Shifters of Demand
1. Tastes and Preferences
2. Number of Consumers
3. Price of Related Goods
4. Income
5. Future Expectations
Shifters of Supply
Price of inputs used in production, technology, expectations, taxes and subsidies, number of consumers,
Terms of Trade (TOT)
the prices a country receives for its exports to the prices paid for its imports
LACES
Label:
AXES
CURVES
EQUILIBRIUM
SHIFTS
Productivity
(economics) the ratio of the quantity and quality of units produced to the labor per unit of time
Disequilibrium
describes any price or quantity not at equilibrium; when quantity supplied is not equal to quantity demanded in a market
surplus
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
shortage
A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
Price signals
The process by which changes in demand are communicated to firms by the price consumers are willing to pay.
Law of Supply
the claim that, other things equal, the quantity supplied of a good rises when the price of the good rises
subsidy
government payment to encourage or protect a certain economic activity