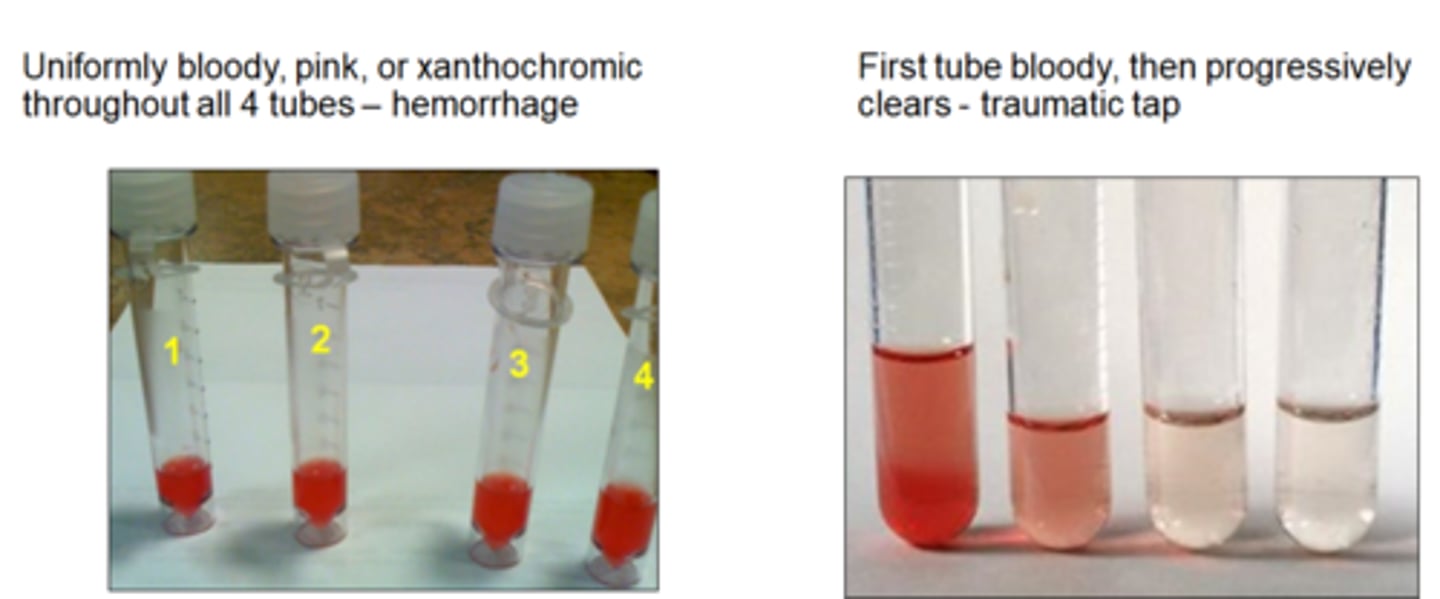
CSF
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the primary function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
To maintain constant volume and pressure, act as a shock absorber, and transport nutrients, hormones, and metabolites.
Where is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced?
By active secretion from the choroid plexus epithelial cells.
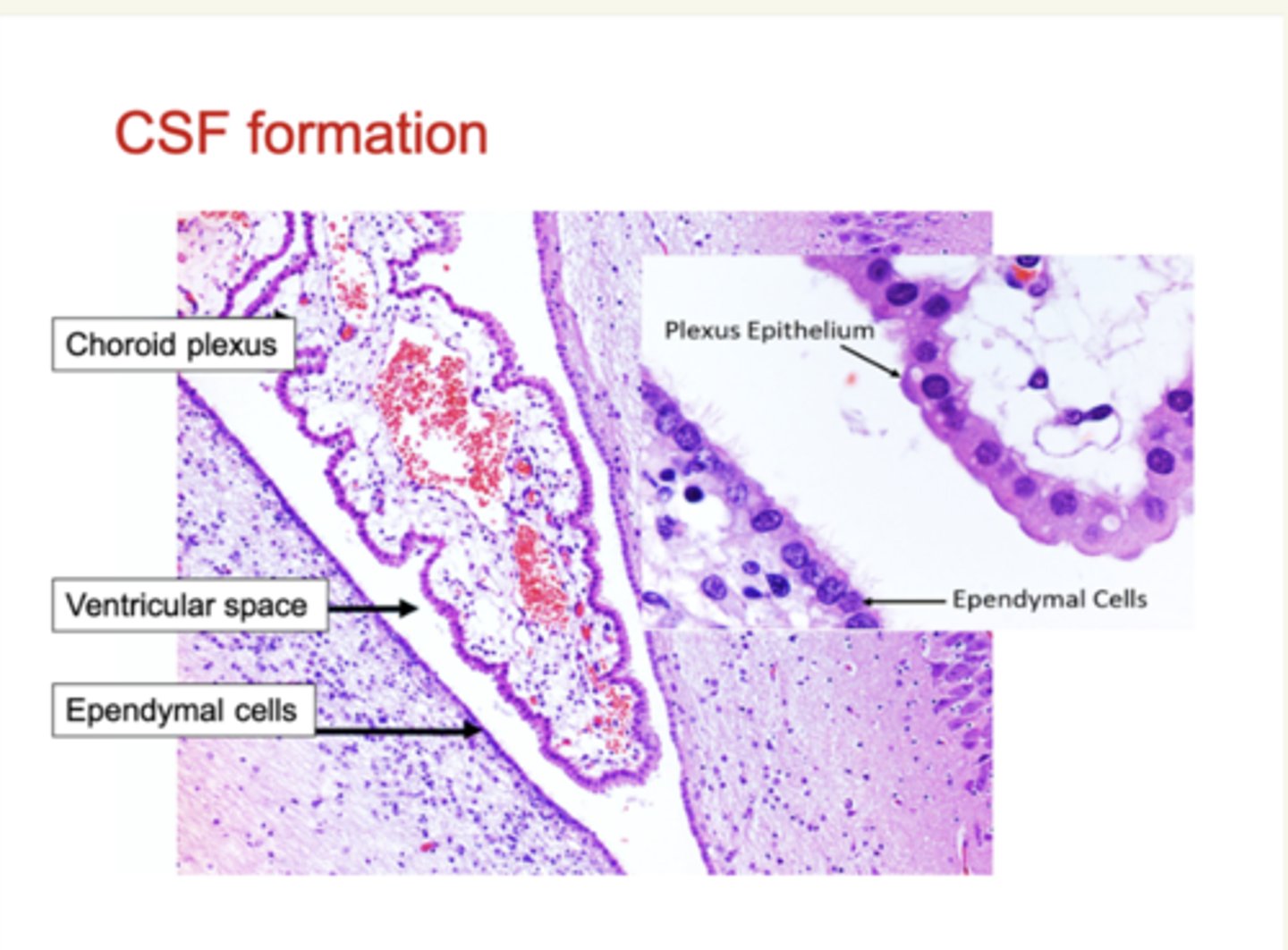
How is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) absorbed?
Through the arachnoid villi.
What does normal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) look like?
Clear.
It does not have RBC
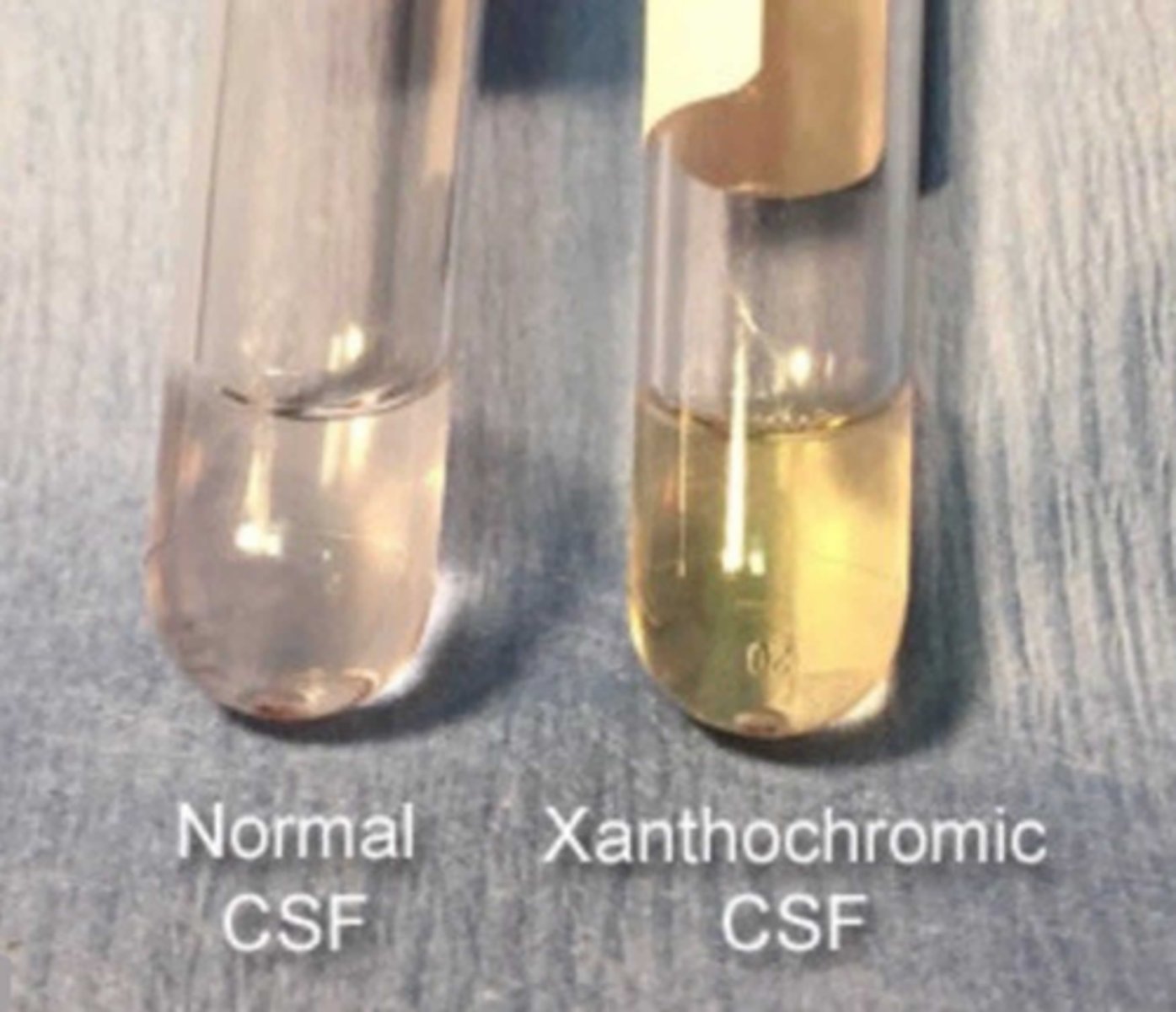
What does turbid cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) indicate?
An increase in cells or protein concentration.
What is the normal cellular composition of CSF in dogs?
80-90% mononuclear cells, primarily lymphocytes.
What is the normal protein concentration in CSF?
Low protein concentration
measured in mg/dL
with albumin being the most common protein from plasma.
What is albuminocytologic dissociation?
A condition where there is a high protein concentration in CSF with normal cellularity.
What are some causes of albuminocytologic dissociation?
Neurodegenerative diseases, vascular issues, neoplastic conditions, chronic compressive disease, traumatic tap, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, and inflammation.
What is a common finding in bacterial meningitis regarding CSF?
Neutrophilic pleocytosis with severe cell counts greater than 1000 cells/mL.
What is the CSF finding in Eastern equine viral encephalitis?
Neutrophilic pleocytosis.
What are the indications for CSF analysis?
abnormal neurologic exams
neck/limb pain
fever of unknown origin
diagnosis of infectious diseases.
What are some contraindications for CSF analysis?
Rabies suspicion, anesthesia risk, post-trauma, or increased intracranial pressure due to conditions like cerebral edema, hydrocephalus, or intracranial hemorrhage.
What is the proper technique for collecting CSF?
Use sterile technique with a spinal tap needle/stylet,
Collect in EDTA lavender top tubes for cytology or culture.

How soon should CSF be processed after collection?
Within 30 minutes or stored at 4°C for up to 24 hours.
What can affect cell morphology in CSF samples?
Low protein concentration and time before processing.
What is the normal RBC and WBC count in CSF for dogs?
Normal RBC count is 0.5 cells/mL, and WBC count is 6-8 cells/mL.
What is pleocytosis in the context of CSF?
An increase in the number of white blood cells in the CSF.
What is a common fungal organism found in CSF infections? (etiologic agent)
Cryptococcus neoformans.
What type of pleocytosis is associated with parelaphostrongylus infection in camelids?
Eosinophilic pleocytosis.
Most common complication in collecting CSF?
blood contamination
neck stiffness
infection
brain hemorrhage