Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the purpose of DNA fingerprinting?
To identify individuals based on differences in restriction enzyme cleavage patterns, which manifest as unique molecular genetic profiles.
What are some applications of DNA fingerprinting?
Forensic science, paternity and maternity cases, and identification of disaster victims.

What is the main principle behind gel electrophoresis?
Separation of molecules based on size/mass.
What type of gel is used in SDS-PAGE, and what does it separate?
Polyacrylamide gel, which separates proteins based on their molecular weight.
How does the percentage of polyacrylamide affect protein separation?
A higher percentage allows for the resolution of smaller proteins.
What is the charge of DNA, and how does it affect its movement in gel electrophoresis?
DNA is negatively charged, causing it to migrate towards the positive electrode during electrophoresis.
What types of gel electrophoresis are used for different sizes of DNA?
SDS-PAGE for small DNA (100-1000 bp), agarose gel for large DNA (1-25 Kbp), and pulse field gel electrophoresis for larger DNA (>25 Kbp).
What is the role of a DNA ladder/marker in gel electrophoresis?
To determine the size of DNA fragments by comparing them to known standards.
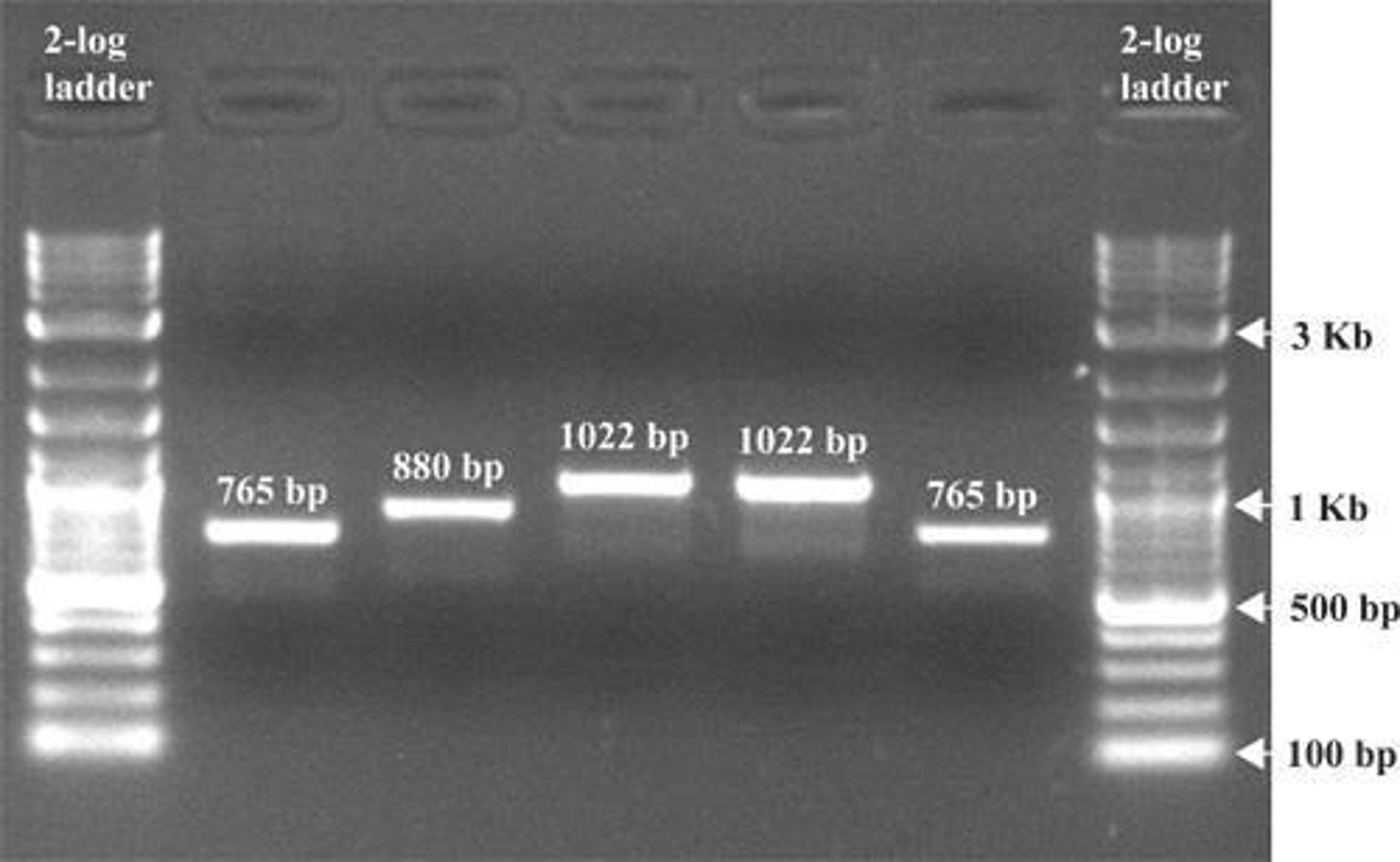
What are some staining methods used in agarose gel electrophoresis?
Ethidium Bromide (most sensitive but hazardous), SYBR gold and SYBR green (expensive), Crystal Violet, and Methyl Blue (least sensitive).
What happens to the pore size of agarose gel as the percentage of agarose increases?
The pore size decreases, allowing only smaller DNA fragments to be resolved.
What is the fractionation range for 0.6% agarose gel?
1-20 kbp for linear double-stranded DNA.
What is the expected result of the DNA fingerprinting experiment described?
Evidence 2 identifies Suspect 2 at the crime scene, Evidence 1 belonged to the victim, and no DNA for Suspect 1 was found.
What are the steps involved in preparing for the DNA electrophoresis experiment?
1. Gel preparation, 2. DNA fragmentation of samples, 3. Gel running with TAE buffer, 4. Gel observation under UV light.
What temperature is used for DNA fragmentation during the experiment?
37°C.
What voltage is typically used when running the gel in electrophoresis?
150 V.
What is the significance of the Rf value in molecular mass determination?
Rf (retention factor) can be plotted against Log Mr (molecular weight) to determine the molecular mass of DNA fragments.
What is the purpose of using UV light in gel observation?
To visualize the DNA bands stained with ethidium bromide or other dyes.
What is the molecular weight range for DNA that can be separated using 1.2% agarose gel?
0.4-6 kbp for linear double-stranded DNA.
What does the term 'post staining' refer to in gel electrophoresis?
Applying stain to the gel after electrophoresis to visualize DNA bands.
What is the expected outcome for the DNA samples from the victim and suspects?
The victim's DNA will match Evidence 1, and Suspect 2's DNA will match Evidence 2.
What is the significance of the experiment objectives?
To learn agarose gel electrophoresis techniques and apply DNA fingerprinting for identification.
What is the role of TAE buffer in gel electrophoresis?
To maintain the pH and provide ions necessary for the conduction of electricity during electrophoresis.