Software Defined Networking, 0 trust, IaC, IPv6
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
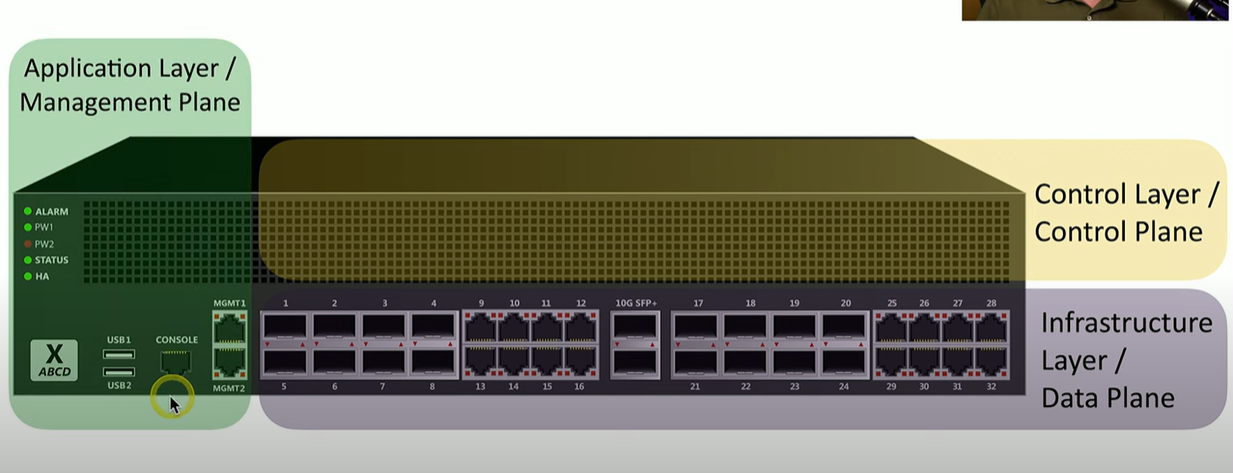
What are the different planes of operations for networking devices?
Data
Control
Management Planes
What is the infrastructure layer/ data plane in SDN?
Processes the network frames and packets, does the heavy lifting
forwarding, trunking, encrypting, NAT
What is the control layer/ control plane in SDN?
part of the network responsible for making decisions about how traffic should flow through the network
manages the actions of the data plane
routing tables, session tables
dynamic routing protocol updates
What is the application layer/management plane for SDN?
Where we configure and manage the device
When you SSH into a console, or control a device from a browser, you’re using this plane.
Using an example of a firewall, describe how we extend physical architecture
What does SD-WAN stand for?
Software Defined Networking in a Wide Area Network
What is a SD-WAN?
A WAN built for the cloud
What is DCI and what does it do?
Data Centre Interconnect
Connects multiple data centres together, seamlessly spanning across geographic distances
What are some issues when it comes to scaling across data centers?
when you have devices in different data centres, IP addressing may be very different across those different data centres
Data centers can be connected in different ways, MPLS, high speed optical, metro ethernet, etc
What is the solution to these underlying issues, and other infrastructure issues when it comes to scalling datacentres?
VXLAN
What does VXLAN stand for?
Virtual Extensible LAN
What does a VXLAN do?
Can support upto 16 million possible virtual networks, and it tunnels frames across a layer 3 network
How does VXLAN encapsulation work?
VXLAN encapsulation takes the original frame and wraps it with extra headers, including a VXLAN header, before sending it over the network.

What does Zero Trust mean in terms of security?
Zero Trust in security means never trusting anything by default, whether inside or outside a network. Every user, device, and application must continuously verify its identity and security status before accessing resources
What is policy-based authentication?
Adaptive Identity: Policy-based authentication enforces access control based on factors such as
user roles
device type
location
ip address
What is policy-driven access control?
combines the adaptive identity with a predefined set of rules, it evaluates each access decision based on policy and other information.
etc: may grant access at 1pm at headquarters, but not at 2am at a remote location…
What is least privilege access?
users and systems are given only the minimum permissions needed to perform their tasks, reducing security risks
Example: A customer service agent can view customer records but cannot modify billing details or access administrative settings
What does SASE stand for?
Secure Access Service Edge
What is SASE?
A next generation VPN that moves security technologies in the cloud, and are located close to existing cloud services.
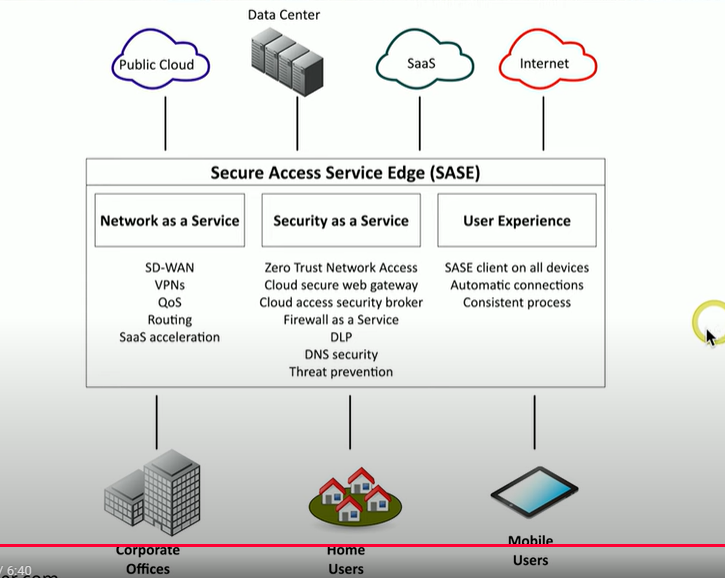
Where are SASE clients installed?
On all user’s devices
What is IaC?
Infrastructure as Code
practice that involves managing and provisioning computing infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files, rather than through manual processes
Why is IaC useful?
automates infrastructure management, reducing manual errors and improving consistency across environments. It also enables faster deployments, scalability, and version control, making it easier to manage infrastructure in a more efficient and repeatable way
What are playbooks?
Conditional steps to follow; a broad process that can be reused and automated
etc:
investigating a data breach
recover from ransomware
Playbooks are often integrated with a______ platform
SOAR
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response.
What are some use cases for automation with IaC?
ensuring same configurations for all systems
change a configuration with a single line of code
modify and update compliance and software
What is source control?
The practice of tracking and managing changes to software code over time. It allows multiple developers to collaborate on the same project, enables rollback to previous versions, and helps maintain a history of changes for better code management.
ex. GIT
What is conflict identification?
the process of detecting discrepancies or clashes between different versions of code or files, typically during collaborative work in version control systems. It occurs when changes made by multiple contributors interfere with each other,
What is branching, in source control?
Branching is the process of creating a separate line of development in a version control system, allowing developers to work on new features, bug fixes, or experiments independently without affecting the main codebase
Why was IPv6 introduced?
There are an estimated 20 billion devices, and IPv6 can only support 4.29 billion addresses
How long are IPv6 addresses?
128-bit addresses or 16 bytes

How can we abbreviate groups of zeros in IPv6?
roups of consecutive zeros can be abbreviated using double colons (::), which replace one or more contiguous blocks of 0000
BUT:
- This abbreviation can only be used once in an address to avoid ambiguity. For example, 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 can be shortened to 2001:db8::1.
Are leading zeros option?
Compress this IPv6 address.
2600:DDDD:0001:0000:0000:0000:0001
Yes, leading zero are optional’
Step 1:
remove leading zeros
2600:DDDD:1111:1:0:0:0:1
Step 2:
Abbreviate 2+ groups of zeros with DOUBLE colons
2600:DDDD:1111:1::1
Not all devices can talk to IPv6, for example?
Legacy devices
embedded devices
What is one way we can make ipv6 and ipv4 devices communicate?
Tunnelling: Encapsulate one protocol within another
What are 2 other ways we can bridge the gap between IPV6 and IPV4
Dual-Stack: Have the option to use both IPv4 and IPv6
Translate: Convert between IPv4 and IPv6
What is 6to4 addressing? What are some issues?
transition mechanism that allows IPv6 packets to be transmitted over an IPv4 network by encapsulating them inside IPv4 packets.
however:
No support for NAT
Requires relay routers
No longer used as an option in Windows
What is dual-stack routing?
Dual-stack routing is a network configuration that allows devices to run both IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously. It enables seamless communication across both protocols
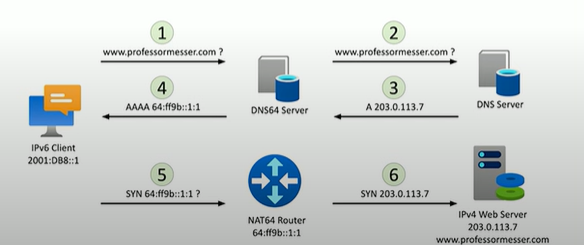
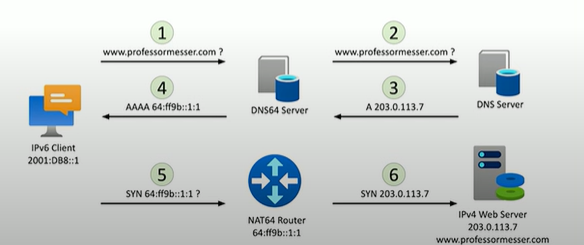
What is NAT64?
Translates between IPv4 and IPv6, and is seamless to the end user.
What is the caveat of NAT64?
Requires something in the middle. IPv6 is not backwards compatible with IPv4, so we need to use a NAT64-capable router
What is DNS64?
Works with a DNS64 server to translate the DNS requests
How does a routing table work?
First it identifies the destination through the IP packet, if the IP destination is on a locally connected subnet, it will forward it to the local device. If the destination IP is on a remote subnet, it will forward it to the next-hop router/gateway
What is static routing?
routing method where routes are manually configured and set by the network administrator. These routes remain fixed unless they are manually updated or changed
What are the advantages of static routing?
Easy to configure and manage on smaller networks
No overhead from routing protocols (CPU, memory, bandwidth)
Easy to configure on stub networks
more secure
What is a stub network?
A stub network is a network that has only one route for inbound and outbound traffic, meaning it is connected to only one other network or router.
What are the disadvantages of static routing?
Difficult to administer on larger networks
No automatic method to prevent routing loops
No automatic rerouting if an outage occurs
If there’s a network change, you have to manually update the routes
What is Dynamic Routing?
method where routers automatically discover and maintain routes to network destinations using routing protocols.
Unlike static routing, which requires manual configuration, dynamic routing allows routers to adapt to changes in the network and determine the best paths based on real-time conditions
What are the advantages of dynamic routing?
No manual route calculations or management
New routes are populated automatically
Very scalable
What are the disadvantages of Dynamic Routing?
Some overhead required (CPU, memory, bandwidth)
Requires some initial configuration to work properly
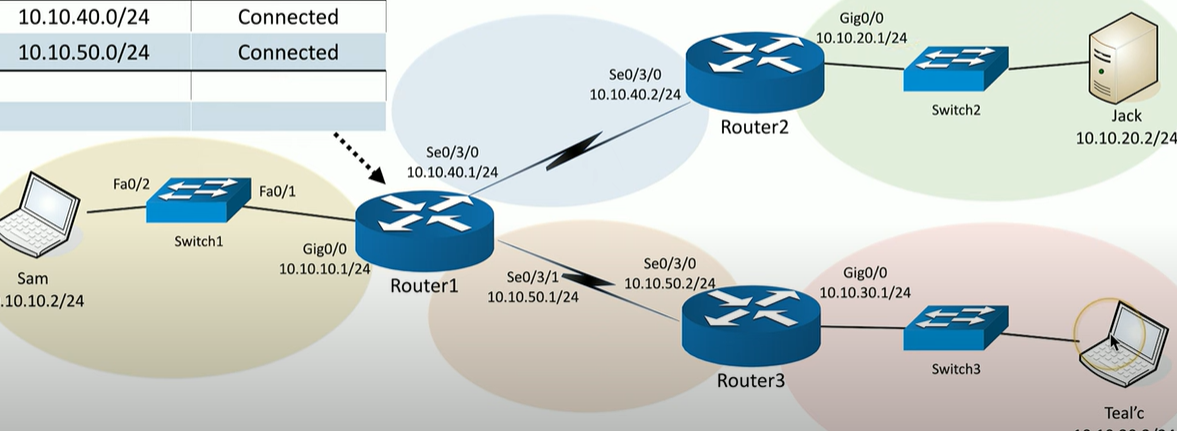
Router 1 is directly connected to 3 different subnets, but there are 2 subnets on the other side, than router 1 simply cannot see.
So we need some way to communicate this.
One way to do this is to get router 2 to send router 1 a __________ update. Router 1 receives this update, and updates its own _____ _____
EIGRP Update
Routing Table
What is the process/protocols for dynamic routing?
Router listens for subnet information from other routers
Once a router builds its routing table, it needs to inform other routers about what it knows. It will send its own updates to other routers.
Once the other routers receive this update, they need to interpret this information, and determine the best route
When network changes occur, update the available routers
How do we determine the routing protocols to use?
Is it based on the state of the link?
Is it based on how far away it is?
How does the protocol determine the best path?
Some formula is applied to the criteria to create a metric
Rank routes from the best to worst
What are some common standard protocols for routing?
OSPF and BGP
What does EIGRP stand for?
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
What is EIGRP?
a dynamic routing protocol developed by Cisco.
Partly proprietary to Cisco
Commonly used on internal Cisco-routed networks
Why is EIGRP so good?
Cleanly manages topology changes
Minimizes bandwidth use
Relatively easy to enable and use
What does OSPF stand for?
Open Shortest Path First
What is OSPF
Routing protocol that is well established and used within a single autonomous system
OSPF uses a Link-state protocol, what is Link-state?
Determines the best route based off uptime and availability of OSPF routers
What does BGP stand for
Border Gateway Control
What is BGP?
a routing protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks on the internet. It helps determine the best paths for data to travel across multiple autonomous systems
What is an autonomous system?
autonomous system (AS) is a network or group of networks controlled by one organization.
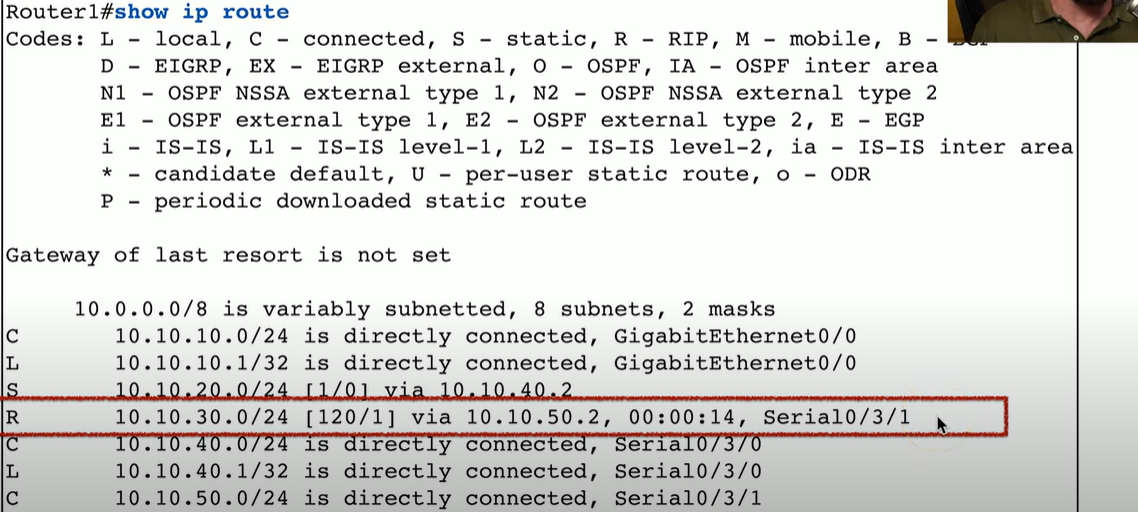
Would does the highlighted line represent?
R = the Route Code
10.10.30.0/24 = Destination Subnet (/24 prefix)
120 = Administrative Distance
1 = Metric
VIA
10.10.50.2 = Next Hop
00:00:14 = Route Timestamp (tells us how long the route has been active)
Serial0/3/1 = Outgoing Interface
How do we decide the best possible route?
Most specific route “wins”
A combination of the subnet ID and prefix length
How do we know what is more “specific”?
Routes are more specific as the prefix increases
Which is the best route for an address of 192.168.1.6?
192.168.0.0/16
192.168.1.0/24
192.168.1.6/32
All are valid, but 192.168.1.6/32 would be the most specific route.
What do we do if we have two routing protocols, and both know about the exact same specific route to a subnet?
We look at administrative distance
What are administrative Distances?
is a value that ranks the trustworthiness of a routing source. Lower AD values are preferred, with 0 for directly connected routes (local)
static routes are considered 1 since it “trusts” you
In some cases, the routing protocol itself may be in a position where there are duplicate routes to a particular location, and the routing protocol has to make the decision.
In that case, we look at the ______ _____
Routing Metrics
What are routing metrics?
Routing metrics are values used by routing protocols to determine the best path to a destination. They can include hop count, bandwidth, delay, and reliability.
Can the different metrics be compared across different protocols? etc, can you use a BGP metric with OSPF or EIGRP?
No, you cannot compare them, as they have different sets of metrics.
What is First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP)
Your computer is configured with a single default gateway.
FHRP ensures network uptime by using a virtual IP (VIP) as the default gateway. If the active router fails, a standby router takes over, keeping traffic flowing without interruption.
This ensures network availability by automatically switching to a standby router if the active one fails.
What are subinterfaces?
are virtual interfaces created on a single physical router interface. They allow the router to handle multiple VLANs or networks while keeping traffic separate.
4o
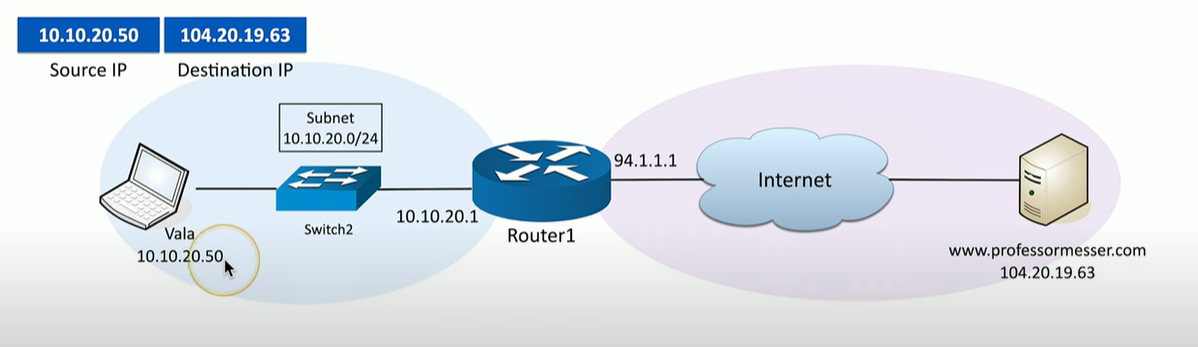
Explain how NAT works for this communication
Vala’s IP address of 10.10.20.50 is private, however it wants to communicate with the public IP of 104.20.19.63
First, this address will hit the router, that is configured with NAT. The router knows that 10.10.20.50 is private, so the router will translate it to something different (etc: 94.1.1.1).
Now we have a public IP address that can connect to the public IP of www.professormesser.com
when going back, the destination and source IP flip, and the router will translate the destination IP back to that private Vala IP.
What is NAT overload/PAT?
is a technique where multiple internal devices share a single public IP address. It uses unique port numbers to distinguish between connections, allowing many devices to access external networks through one IP address.
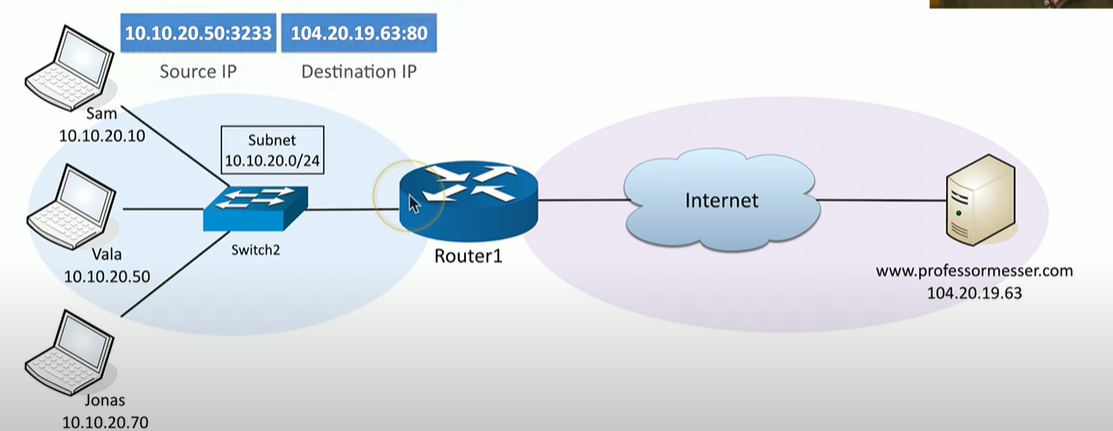
Explain how NAT overload/PAT works
Again, Vala wants to communicate to messer.com
Notice, in the source IP, we also have the source port number (3233)
When the packet is received by the router, it understands that the private address needs to be translated. Inside, is a NAT table, that shows both the private and public address it’s translated to.
After that translation, it is public and received by messer.com
Because we are using the IP and Port number, other devices on the network can use the same public IP address
A LAN or Local Area Network is:
A group of devices in the same broadcast domain
What are Virtual Local Area Networks?
re logical network segments that separate devices into different broadcast domains within the same physical switch
How are VLANs configured?
They are defined by numbers:
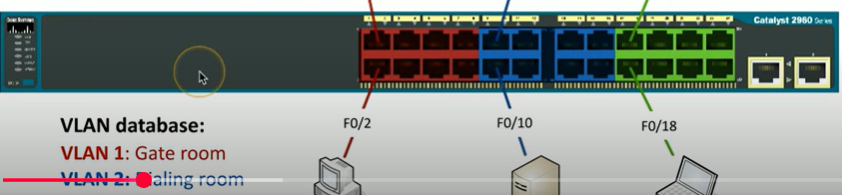
What happens if VLANs exist on different switches without a proper connection?
VLANs act like separate networks, meaning devices in the same VLAN but on different switches cannot send data to each other.
You can use an ethernet but it is not scalable/efficient
How do we connect multiple switches with different VLANs then?
802.1Q VLAN Trunking
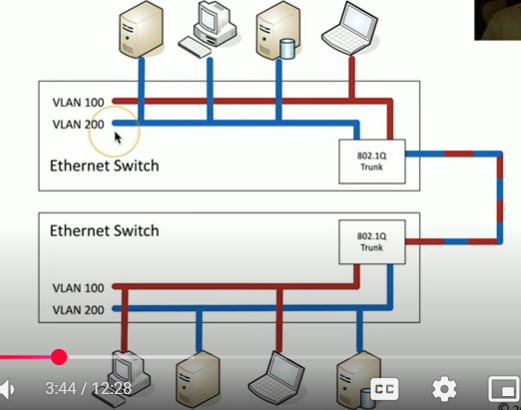
What is VLAN trunking?
Instead of multiple ethernet connections between the VLANs, we have a single ethernet connection between the 2 switches
How is the trunk able to keep track of what traffic is coming from VLAN 100 and 200?
First we take a normal Ethernet Frame
Then, we add a VLAN header in the Frame (between source mac and type)
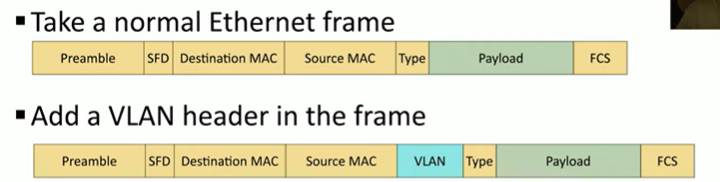
How long are VLAN ids?
12 bits long
What is the native VLAN?
When you first set up a switch, it uses VLAN 1 as the default for all ports. This means all devices connected to the switch are in the same VLAN (VLAN 1) by default.
but there is another type of VLAN configuration inside a switch called a Native VLAN
Can traverse a trunk, but a VLAN tag is not added to any of the traffic
Why does Native VLAN not add any tags?
Some devices wont talk to 802.1Q
What is a layer 3 switch?
A Layer 3 switch is a switch that can perform routing functions in addition to regular Layer 2 switching
its useful because its one device, and it saves space/power
Why is it called a layer 3 switch?
Switching still operates at OSI layer 2
Routing still operates at OSI layer 3
What are Switched Virtual Interfaces? (SVI)
virtual interface on a Layer 3 switch that allows the switch to route traffic between VLANs.
Why don’t layer 3 switches replace stand alone routers?
Layer 3 switches are faster for local routing, while routers handle more complex tasks and external connection
its fine at home for simple tasks, but its better to have stand alone for more complex tasks
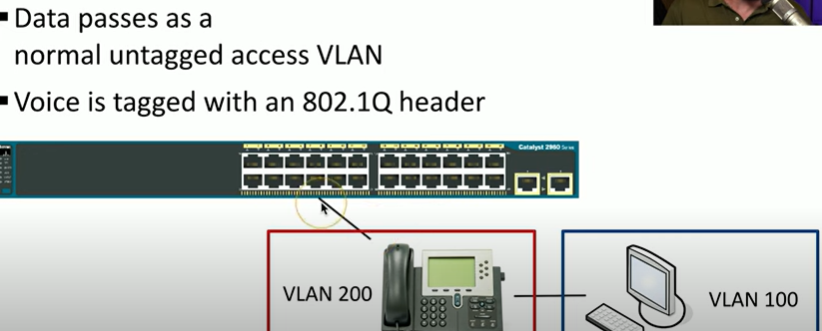
What is voice over IP or VoIP?
Back in the day, we connected a computer to a switch, and a phone to a PBE, Private Branch Exchange, which was 2 physical cables and 2 different techonologies.
But now we have VoIP, which connects all devices to the Ethernet switch and has one network cable for both.
What is one of the challenges of adding both voice and data to the same network?
Voice is very sensitive to congestion
Data loves to congest the network
So, we can put the computer on one VLAN, and the phone on another, and then use trunking (the switch we use needs to recognize that we are using voice a computer at the same time)
When setting up a basic interface configuration, what is speed?
How fast the connection is going to run
etc
10 mb connection / 100 mb / 1000mb / 10 gig
When setting up basic interface configuration, do both sides need to have the same speed configuration, or will they adjust automatically?
They both need the same speed considering we manually selected the speed.
But, if we use automatic configuration the switch will automatically adjust.
What do we need for the IP configuration for the interface?
they all need an IP address, subnetmask/CIDR block, default gateway, DNS (optional)
Values usually assigned by a network administrator.
What is link aggregation/port bonding?
Connecting multiple interfaces together on 2 devices. Normally, we would not like to do this because it would be creating a loop, but if you configure all those interfaces as LAG (Link aggregation) The switch will interpret them as one large connection
What is LACP?
Link Aggregation Control Protocol, automatically does the underlying link aggregation, and manages them
What are Jumbo frames?
Ethernet frames with more than 1500 bytes of payload, and we can increase the size of an ethernet frame upto 9216 bytes of an MTU
many devices use a maximum high end of 9000 for a jumbo frame.
useful and efficient, but all devices must support jumbo frames, and not all devices are compatible with each other!
What is IEEE standard 802.1D or also known as?
Spanning Tree Protocol