Unit 4.1 Regulation & Feedback Mechanisms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:36 PM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
1
New cards
Regulation & Feedback Mechanisms
1. Animal Form & Function at All Levels of Organization
- Evolution of Animal Size & Shape
- Exchange with the Environment
- Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
- Coordination & Control
2. Feedback Control
- Regulating and Conforming
- Homeostasis
3. Thermoregulation
- Endothermy and Ectothermy
- Variation in Body Temperature
- Balancing Heat Loss and Gain
- Acclimatization
- Physiological Thermostats
4. Energy Requirements
- Energy Allocation and Use
- Quantifying Energy Use
- Minimum Metabolic Rate &
- Thermoregulation
- Influences on Metabolic Rate
- Torpor and Energy Conservation
- Evolution of Animal Size & Shape
- Exchange with the Environment
- Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
- Coordination & Control
2. Feedback Control
- Regulating and Conforming
- Homeostasis
3. Thermoregulation
- Endothermy and Ectothermy
- Variation in Body Temperature
- Balancing Heat Loss and Gain
- Acclimatization
- Physiological Thermostats
4. Energy Requirements
- Energy Allocation and Use
- Quantifying Energy Use
- Minimum Metabolic Rate &
- Thermoregulation
- Influences on Metabolic Rate
- Torpor and Energy Conservation
2
New cards
natural, adaptation, relative
Animal Form & Function at All Levels of Organization
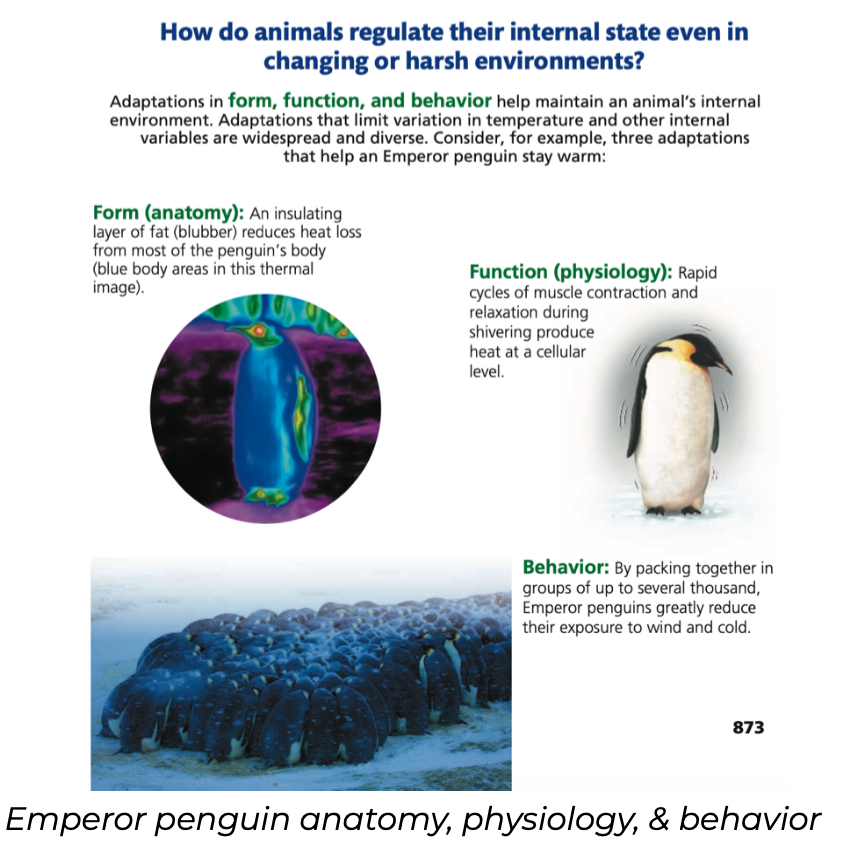
● Animal species obtain nutrients and oxygen, fight off infection, survive to produce offspring, and share other basic requirements
● Vary in anatomy due to ______ selection and _______
○ Natural selection favors those variations in a population that increase ______ fitness
○ Evolutionary adaptations that enable survival vary among environments and species but frequently result in a close match of form to function
● Animal species obtain nutrients and oxygen, fight off infection, survive to produce offspring, and share other basic requirements
● Vary in anatomy due to ______ selection and _______
○ Natural selection favors those variations in a population that increase ______ fitness
○ Evolutionary adaptations that enable survival vary among environments and species but frequently result in a close match of form to function
3
New cards
Anatomy
➔ Study of the biological structure
4
New cards
Physiology
➔ Study of the biological function
➔ Examining anatomy provides clues to this
➔ Examining anatomy provides clues to this
5
New cards
Evolution of Animal Size & Shape
Physical laws that govern strength, diffusion, movement, and heat exchange limit the range of animal form
6
New cards
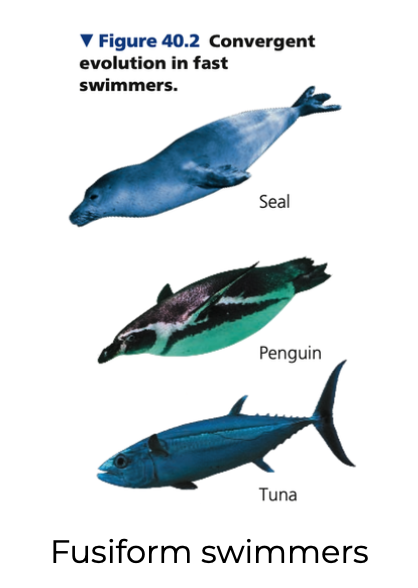
1000, ray
1. Water is _____x denser than air and is far more viscous
- Limits possible animal shapes for fast swimmers
○ Any bump on an animal body’s surface that causes drag would impede it more than a flier or runner
○ Tuna and other fast __-finned fishes can swim at speeds up to 80 km/hr
○ Sharks, seals, penguins, dolphins
- Limits possible animal shapes for fast swimmers
○ Any bump on an animal body’s surface that causes drag would impede it more than a flier or runner
○ Tuna and other fast __-finned fishes can swim at speeds up to 80 km/hr
○ Sharks, seals, penguins, dolphins

7
New cards
Fusiform
➔ Streamline shape that is tapered on both ends
➔ An example of convergent evolution in speedy vertebrate swimmers
➔ An example of convergent evolution in speedy vertebrate swimmers
8
New cards
size, Thicker, locomotion
2. Increase in body dimensions with regard to maximum ___
● _______ skeletons are required to maintain adequate support
○ Affects internal skeletons (vertebrates) and external skeletons (insects and arthropods)
● Muscles required for ________ represent a larger fraction of the total body mass
○ Mobility will become limited at some point
○ Tyrannosaurus rex: some say top running speed is that of an Olympic sprinter (30km.hr) while others say it was at best a fast walker
● _______ skeletons are required to maintain adequate support
○ Affects internal skeletons (vertebrates) and external skeletons (insects and arthropods)
● Muscles required for ________ represent a larger fraction of the total body mass
○ Mobility will become limited at some point
○ Tyrannosaurus rex: some say top running speed is that of an Olympic sprinter (30km.hr) while others say it was at best a fast walker
9
New cards
aqueous, plasma
Exchange with the Environment
● Animals must exchange nutrients, waste products, and gases with their environment
○ Imposes an additional limitation on body plans
● Exchange occurs as substances dissolved in an ________ solution move across the _______ membrane of each cell
1. Unicellular
2. Multicellular
● Animals must exchange nutrients, waste products, and gases with their environment
○ Imposes an additional limitation on body plans
● Exchange occurs as substances dissolved in an ________ solution move across the _______ membrane of each cell
1. Unicellular
2. Multicellular
10
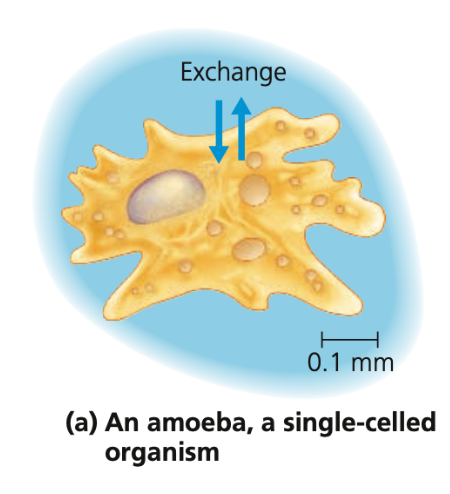
New cards
Amoeba
Unicellular
● _______ has a sufficient membrane surface area in contact with environment to facilitate exchange
● _______ has a sufficient membrane surface area in contact with environment to facilitate exchange
11
New cards
Rate, surface, Amount, volume
Multicellular
● Multicellular organization only works if every cell has access to suitable aqueous environment
■ ____ of exchange is proportional to membrane _______ area
■ ______ of material must be exchanged is proportional to total body _____
1. Simple animals (hydra, tapeworm)
2. Complex animals
● Multicellular organization only works if every cell has access to suitable aqueous environment
■ ____ of exchange is proportional to membrane _______ area
■ ______ of material must be exchanged is proportional to total body _____
1. Simple animals (hydra, tapeworm)
2. Complex animals
12
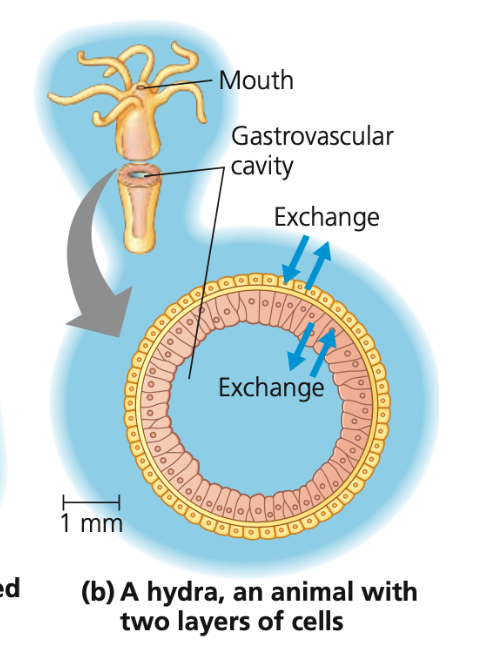
New cards
Hydra, sac, gastrovascular, intestinal
Simple animals
○ ____ has a ___like body plan and a body only 2 cell layers thick
■ Its _________ cavity opens to the external environment, both outer and inner layers are constantly bathed in pond water
○ Parasitic tapeworm’s thin and flat shape places most cells in direct contact with its particular environment (________ fluid)
○ ____ has a ___like body plan and a body only 2 cell layers thick
■ Its _________ cavity opens to the external environment, both outer and inner layers are constantly bathed in pond water
○ Parasitic tapeworm’s thin and flat shape places most cells in direct contact with its particular environment (________ fluid)
13
New cards
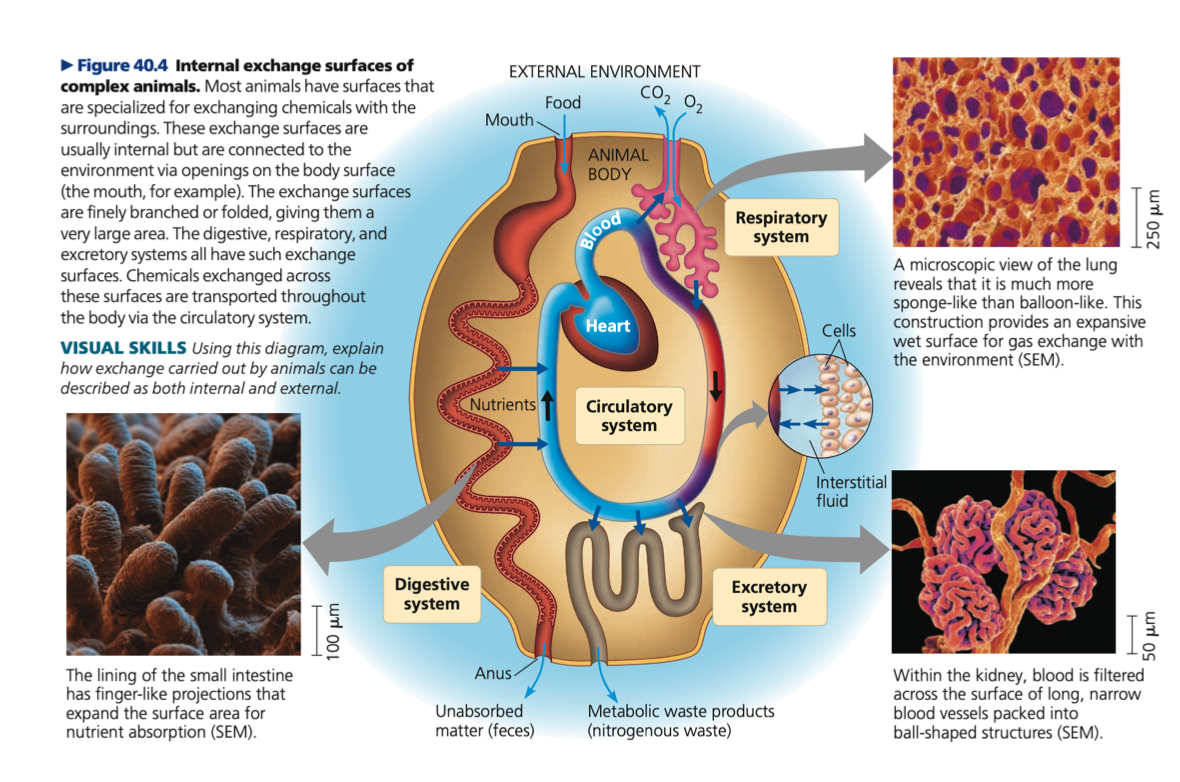
cells, decreases, branched, interstitial, circulatory
Complex animals
○ Increasing the number of ____ __________ the ratio of surface area to total volume
■ SA:TV of whale is hundreds of thousands of times smaller than of a water flea
○ Evolutionary adaptations enable sufficient exchange with the environment are often specialized surfaces that are _______ or folded
■ Branching and folding greatly increases SA
■ In humans, exchange surfaces for digestion, respiration, and circulation are 25X larger than skin
○ Contain ______ fluid and _______ fluid (blood)
1. Excretory
2. Digestive
3. Circulatory
4. Respiratory
○ Increasing the number of ____ __________ the ratio of surface area to total volume
■ SA:TV of whale is hundreds of thousands of times smaller than of a water flea
○ Evolutionary adaptations enable sufficient exchange with the environment are often specialized surfaces that are _______ or folded
■ Branching and folding greatly increases SA
■ In humans, exchange surfaces for digestion, respiration, and circulation are 25X larger than skin
○ Contain ______ fluid and _______ fluid (blood)
1. Excretory
2. Digestive
3. Circulatory
4. Respiratory
14
New cards
Interstitial fluid
➔ From Latin for “stand between”
➔ Fluid that fills the space between cells in animals
➔ Fluid that fills the space between cells in animals
15
New cards
External, sensory, digestive, filtration, land
Complex body advantages
○ Offers numerous benefits such as:
1. ______ skeleton protects against predators
2. ______ organs provide detailed information
on surroundings
3._______ organs can break down food
gradually, controlling release of stored energy
4. Specialized _______ systems can control
internal fluid that bathes cells
○ Complex body plan is advantageous
for _____ animals where external environment is highly variable
○ Offers numerous benefits such as:
1. ______ skeleton protects against predators
2. ______ organs provide detailed information
on surroundings
3._______ organs can break down food
gradually, controlling release of stored energy
4. Specialized _______ systems can control
internal fluid that bathes cells
○ Complex body plan is advantageous
for _____ animals where external environment is highly variable
16
New cards
emergent
Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
● Cells form a working body through their ________ properties, which arise from successive levels of structural and functional organization
1. Tissues
2. Organs
3. Organ systems
● Cells form a working body through their ________ properties, which arise from successive levels of structural and functional organization
1. Tissues
2. Organs
3. Organ systems
17
New cards
Tissues
➔ Groups of cells with similar appearance and common function
18
New cards
Organs
➔ Different types of tissues are further organized into these
◆ Simplest animals (e.g. sponges) lack true tissues and organs
◆ Simplest animals (e.g. sponges) lack true tissues and organs
19
New cards
Organ system
➔ Groups of organs that work together
◆ Skin is an organ of the integumentary system, which protects against infection and regulates body temperature
◆ Skin is an organ of the integumentary system, which protects against infection and regulates body temperature
20
New cards
Digestive system
● Main components:
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, anus
● Main functions:
Food processing (ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination)
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, anus
● Main functions:
Food processing (ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination)
21
New cards
Circulatory system
● Main components:
Heart, blood vessels, blood
● Main functions:
Internal distribution of materials
Heart, blood vessels, blood
● Main functions:
Internal distribution of materials
22
New cards
Respiratory system
● Main components:
Lungs, trachea, other breathing tubes
● Main functions:
Gas exchange (uptake of oxygen, disposal of carbon dioxide)
Lungs, trachea, other breathing tubes
● Main functions:
Gas exchange (uptake of oxygen, disposal of carbon dioxide)
23
New cards
Immune & Lymphatic system
● Main components:
Bone marrow, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, lymph vessels
● Main functions:
Body defense (fighting infections & virally induced cancers)
Bone marrow, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, lymph vessels
● Main functions:
Body defense (fighting infections & virally induced cancers)
24
New cards
Excretory system
● Main components:
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
● Main functions:
Disposal of metabolic wastes, regulation of osmotic balance of blood
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
● Main functions:
Disposal of metabolic wastes, regulation of osmotic balance of blood
25
New cards
Endocrine system
● Main components:
Pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, & other hormone- secreting glands
● Main functions:
Coordination of body activities (e.g., digestion & metabolism)
Pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, & other hormone- secreting glands
● Main functions:
Coordination of body activities (e.g., digestion & metabolism)
26
New cards
Reproductive system
● Main components:
Ovaries/testes & associated organs
● Main functions:
Gamete production, promotion of fertilization, & support of developing embryo
Ovaries/testes & associated organs
● Main functions:
Gamete production, promotion of fertilization, & support of developing embryo
27
New cards
Nervous system
● Main components:
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory organs
● Main functions:
Coordination of body activities, detection of stimuli, & formulation of responses to them
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory organs
● Main functions:
Coordination of body activities, detection of stimuli, & formulation of responses to them
28
New cards
Integumentary system
● Main components:
Skin and its derivatives (hair, claws, sweat glands)
● Main functions:
Protection against mechanical injury, infection, dehydration, and thermoregulation
Skin and its derivatives (hair, claws, sweat glands)
● Main functions:
Protection against mechanical injury, infection, dehydration, and thermoregulation
29
New cards
Skeletal system
● Main components:
Skeleton (bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage)
● Main functions:
Body support, protection of internal organs, movement
Skeleton (bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage)
● Main functions:
Body support, protection of internal organs, movement
30
New cards
Muscular system
● Main components:
Skeletal muscles
● Main functions:
Locomotion and other movement
Skeletal muscles
● Main functions:
Locomotion and other movement
31
New cards
more, enzymes, sugar, emergent, specialization
Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
● Many organs have ___ than one physiological role
○ Pancreas produce ______ for the digestive system and regulate ____ level in the blood for the endocrine system
● Viewing the body’s organization from bottom-up (cells to organ system) reveals ________ properties, top-down view of the hierarchy reveals multilayered basis of ___________
● Organ systems include specialized organs made of specialized tissues and cells
○ Top-down view of human digestive system:
● Many organs have ___ than one physiological role
○ Pancreas produce ______ for the digestive system and regulate ____ level in the blood for the endocrine system
● Viewing the body’s organization from bottom-up (cells to organ system) reveals ________ properties, top-down view of the hierarchy reveals multilayered basis of ___________
● Organ systems include specialized organs made of specialized tissues and cells
○ Top-down view of human digestive system:

32
New cards
tissue
Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
● Specialized and complex organ systems are built from a limited set of cell and ______ types
○ Lungs and blood vessels have different functions but are lined with the same basic type of cell and therefore share properties
● Specialized and complex organ systems are built from a limited set of cell and ______ types
○ Lungs and blood vessels have different functions but are lined with the same basic type of cell and therefore share properties
33
New cards
outside, cavities, junctions, barrier, interfaces
Epithelial tissue
● Epithelia (plural), epithelium (singular)
● Cover the _______ of the body and line organs
and _______ within the body
● Are closely packed (often with tight _______) and function as a ______ against mechanical injury, pathogens, and fluid loss
● Also form active ________ with the environment
○ Nasal passage epithelium is crucial for olfaction, the sense of smell
● Epithelia (plural), epithelium (singular)
● Cover the _______ of the body and line organs
and _______ within the body
● Are closely packed (often with tight _______) and function as a ______ against mechanical injury, pathogens, and fluid loss
● Also form active ________ with the environment
○ Nasal passage epithelium is crucial for olfaction, the sense of smell
34
New cards
Types of tissue
1. Epithelial tissue
- Squamous
- Cuboidal
- Columnar
2. Connective tissue
- Collagenous
a. Fibrous/Dense
b. Loose
- Specialized
a. Adipose
b. Bone
c. Blood
d. Cartilage
3. Muscle tissue
- Skeletal
- Smooth
- Cardiac
4. Nervous tissue
- Glia
- Neurons
- Squamous
- Cuboidal
- Columnar
2. Connective tissue
- Collagenous
a. Fibrous/Dense
b. Loose
- Specialized
a. Adipose
b. Bone
c. Blood
d. Cartilage
3. Muscle tissue
- Skeletal
- Smooth
- Cardiac
4. Nervous tissue
- Glia
- Neurons
35
New cards
Epithelial tissue
1. Squamous
- Simple squamous
- Stratified squamous
2. Cuboidal
- Simple cuboidal
- Stratified cuboidal
3. Columnar
- Simple columnar
- Stratified columnar
- Pseudostratified columnar
- Simple squamous
- Stratified squamous
2. Cuboidal
- Simple cuboidal
- Stratified cuboidal
3. Columnar
- Simple columnar
- Stratified columnar
- Pseudostratified columnar
36
New cards
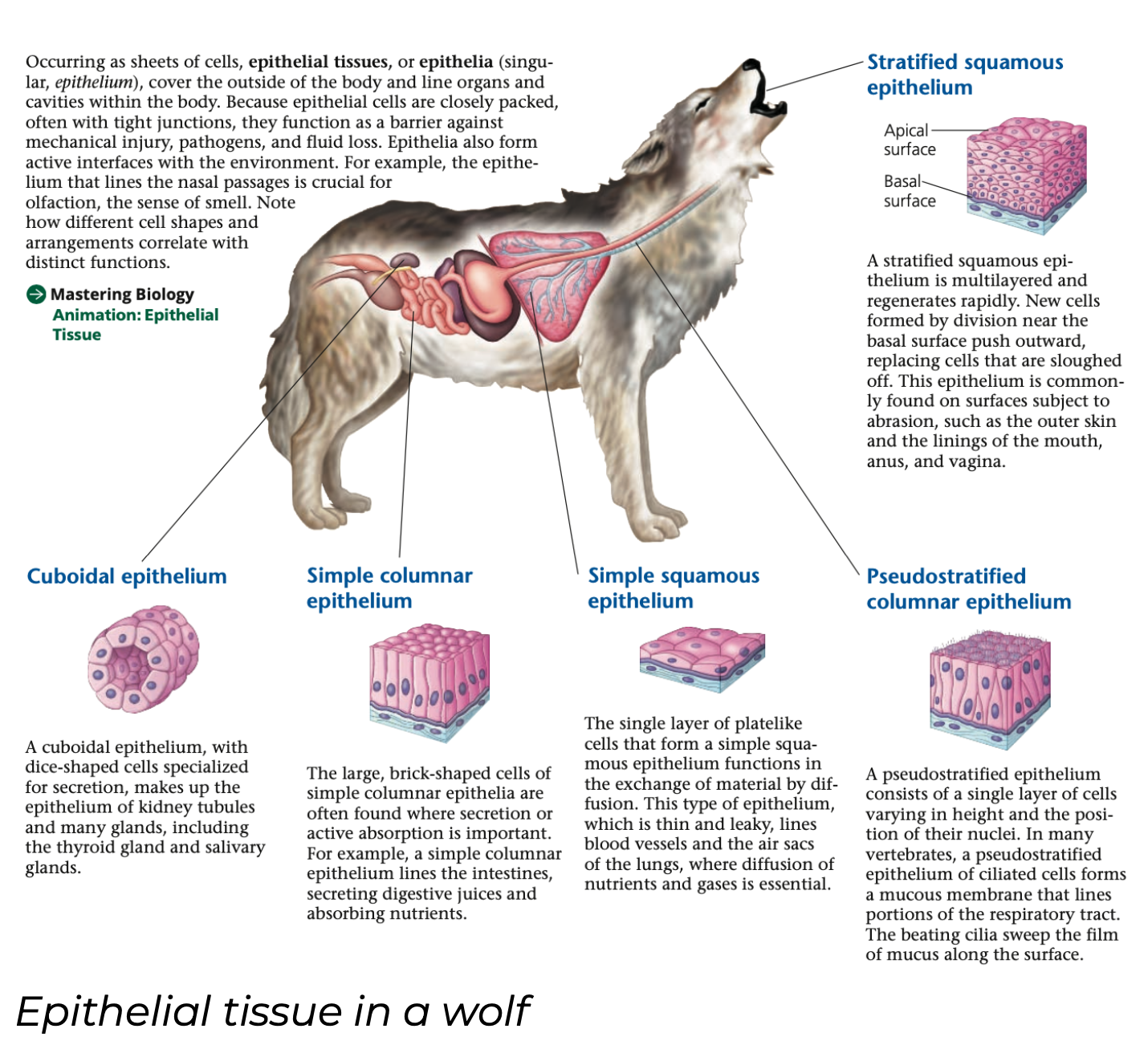
plate, diffusion, vessels, sacs
Simple squamous
➔ Single layer of ____like cells
➔ Function in exchange of material by _______ as it is thin and leaky
➔ Lines blood _____ and air ___ of lungs where diffusion of nutrients and gases is essential
➔ Single layer of ____like cells
➔ Function in exchange of material by _______ as it is thin and leaky
➔ Lines blood _____ and air ___ of lungs where diffusion of nutrients and gases is essential
37
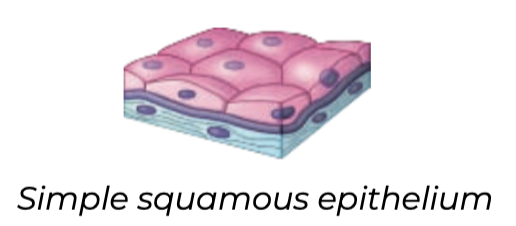
New cards
generates, basal, abrasion, skin, mouth, anus, vagina
Stratified squamous
➔ Multilayered and _______ rapidly
➔ New cells and formed by division near the ____ surface push outward, replacing cells that slough off
➔ Found on surfaces subject to _______ such as outer ___, linings of the _____, ____, and ______
➔ Multilayered and _______ rapidly
➔ New cells and formed by division near the ____ surface push outward, replacing cells that slough off
➔ Found on surfaces subject to _______ such as outer ___, linings of the _____, ____, and ______
38
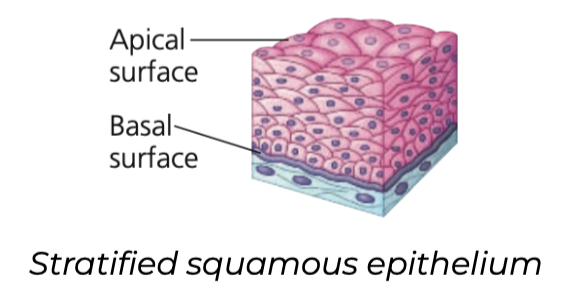
New cards
secretion, kidney, glands
Cuboidal
➔ Dice-shaped cells that specialize in _______
➔ Make up the epithelium of _____ tubules and many ______ (e.g., thyroid and salivary glands)
➔ Dice-shaped cells that specialize in _______
➔ Make up the epithelium of _____ tubules and many ______ (e.g., thyroid and salivary glands)
39
New cards
secretion, absorption, intestines
Simple columnar
➔ Large, brick-shaped cells are often found where _______ or active ______ is important
➔ Lines the ______, secreting digestive juices and absorbing nutrients
➔ Large, brick-shaped cells are often found where _______ or active ______ is important
➔ Lines the ______, secreting digestive juices and absorbing nutrients
40
New cards
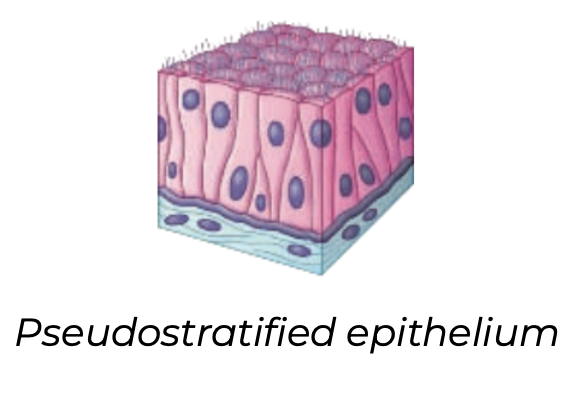
nuclei, ciliated, respiratory
Pseudostratified columnar
➔ Single layer of cells varying in height and the position of their _____
➔ In vertebrates, pseud. strat. epithelium of ______ cells forms mucous membrane that lines portions of the ________ tract
◆ Beating cilia sweep film of mucus along the surface
➔ Single layer of cells varying in height and the position of their _____
➔ In vertebrates, pseud. strat. epithelium of ______ cells forms mucous membrane that lines portions of the ________ tract
◆ Beating cilia sweep film of mucus along the surface
41
New cards
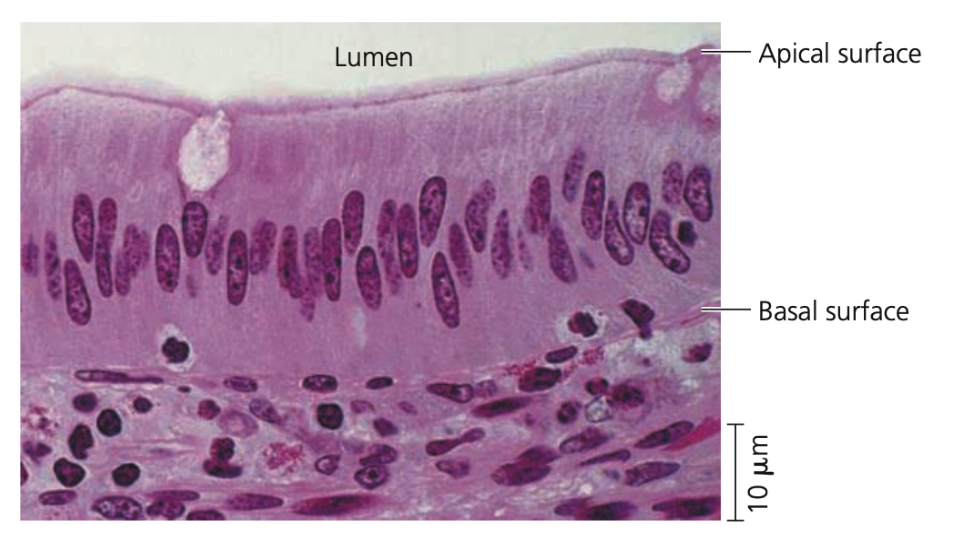
Polarity of epithelia
➔ All epithelia are polarized - have two different sizes
42
New cards
Apical surface
◆ Faces the lumen (cavity) or outside of the organ is exposed to fluid or air
◆ Specialized projections often cover this surface (microvilli in small intestine epithelium)
◆ Specialized projections often cover this surface (microvilli in small intestine epithelium)
43
New cards
Basal surface
◆ Opposite of the apical surface
44
New cards
sparse, extracellular matrix, fibroblasts, macrophages
Connective tissue
● Consisting of a ______ population of cells scattered throughout _________ ______
● Holds tissues and organs together in place
○ Matrix generally consists of a web of fibers embedded in a liquid, jellylike, or solid foundation
○ Contain ______ (secrete fiber proteins) and ________ (engulf foreing particles and cell debris through phagocytosis)
● Consisting of a ______ population of cells scattered throughout _________ ______
● Holds tissues and organs together in place
○ Matrix generally consists of a web of fibers embedded in a liquid, jellylike, or solid foundation
○ Contain ______ (secrete fiber proteins) and ________ (engulf foreing particles and cell debris through phagocytosis)
45
New cards
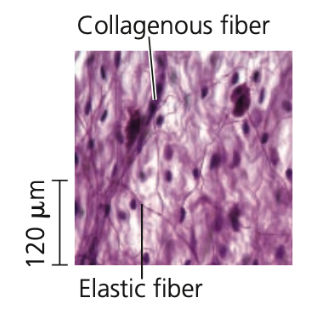
Connective tissue fibers
1. Collagenous
2. Reticular
3. Elastic
● Collagenous and reticular fibers prevent skin from being pulled far from the bone
● Elastic fibers restore the skin to its original shape
2. Reticular
3. Elastic
● Collagenous and reticular fibers prevent skin from being pulled far from the bone
● Elastic fibers restore the skin to its original shape
46
New cards
Collagenous fibers
➔ Provide strength and flexibility
47
New cards
Reticular fibers
➔ Join connective tissue to adjacent tissues
48
New cards
Elastic fibers
➔ Make tissues elastic
49
New cards
Connective tissue
1. Collagenous
a. Fibrous/Dense
b. Loose
2. Specialized
a. Adipose
b. Bone
c. Blood
d. Cartilage
a. Fibrous/Dense
b. Loose
2. Specialized
a. Adipose
b. Bone
c. Blood
d. Cartilage
50
New cards
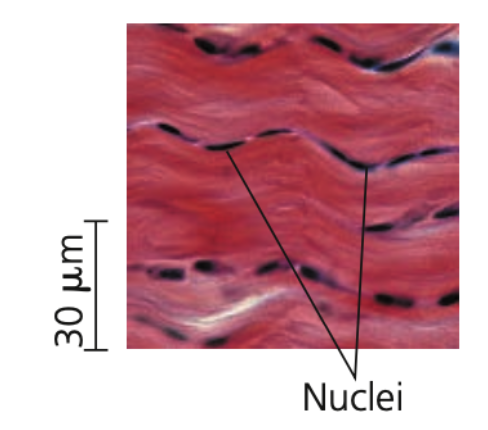
collagenous, tendons, ligaments
Fibrous connective tissue
➔ Dense with _______ fibers
➔ Is found in ______ (attaches muscle to bones) and _______ (connect bones at joints)
➔ May be further subdivided into:
◆ Dense regular
◆ Dense irregular
➔ Dense with _______ fibers
➔ Is found in ______ (attaches muscle to bones) and _______ (connect bones at joints)
➔ May be further subdivided into:
◆ Dense regular
◆ Dense irregular
51
New cards
widespread, epithelium
Loose connective tissue
➔ Most ________ connective tissue in vertebrates
➔ Bind _______ to underlying tissues and holds organs in place
➔ Named after loose weave of its fibers (includes the 3 types)
➔ Found in the skin and throughout the body
52
New cards
cells, insulates, fuel, droplet
Adipose tissue
➔ Specialized connective loose tissue that stores fat in adipose ____ distributed throughout its matrix
➔ Pads and ______ the body and stores ___ as fat molecules
➔ Each adipose cell contains a large fat ______ that swells when at is stored and shrinks when the body uses that fat as fuel
➔ Specialized connective loose tissue that stores fat in adipose ____ distributed throughout its matrix
➔ Pads and ______ the body and stores ___ as fat molecules
➔ Each adipose cell contains a large fat ______ that swells when at is stored and shrinks when the body uses that fat as fuel
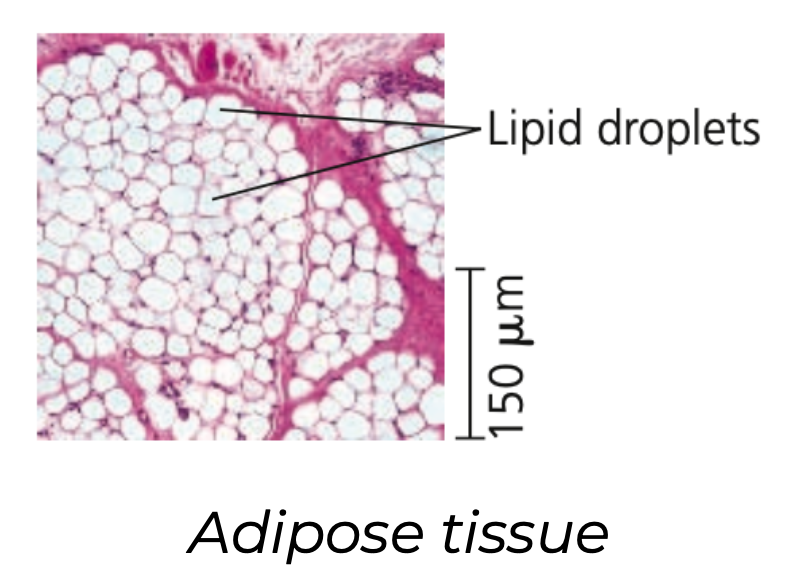
53
New cards
Mineralized, blasts, collagen, ns, canal
Bone
➔ ________ connective tissue
➔ Osteo____: deposit a matrix of ______. Calcium, magnesium, and phosphate ions combine into a hard mineral with the matrix.
➔ Osteo__: microscopic structure of hard mammalian bone consists of repeating units of these
◆ Each has concentric layers of the mineralized matrix, which are deposited around a central ____ containing blood vessels and nerve
➔ ________ connective tissue
➔ Osteo____: deposit a matrix of ______. Calcium, magnesium, and phosphate ions combine into a hard mineral with the matrix.
➔ Osteo__: microscopic structure of hard mammalian bone consists of repeating units of these
◆ Each has concentric layers of the mineralized matrix, which are deposited around a central ____ containing blood vessels and nerve
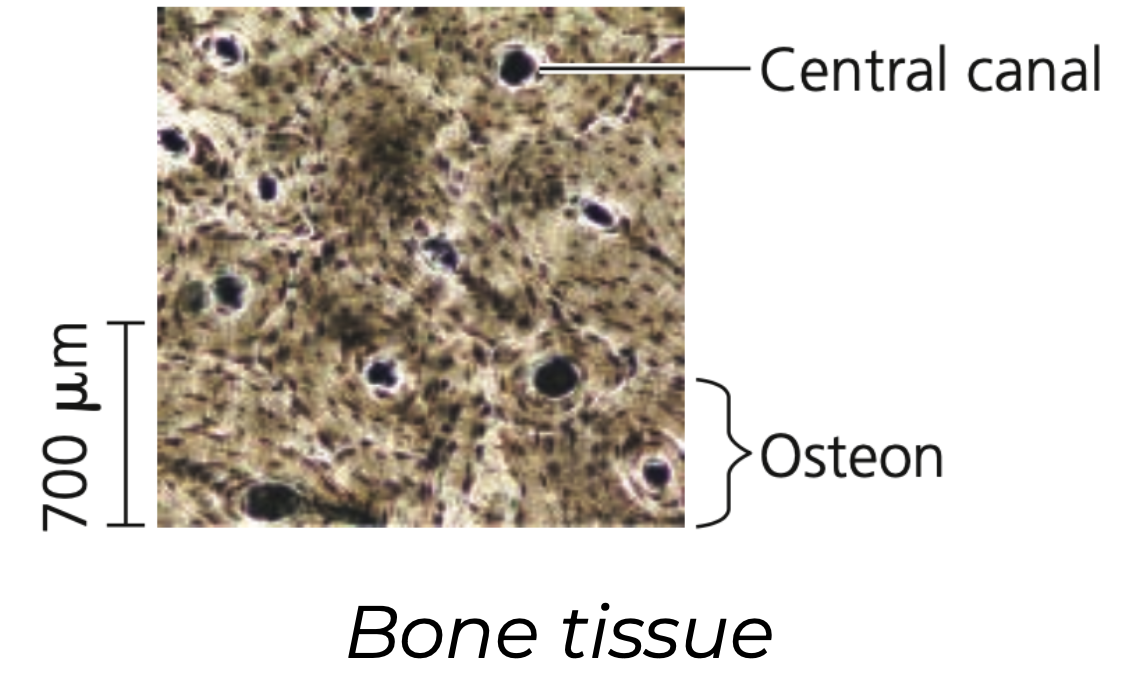
54
New cards
plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
Blood
➔ Has a liquid extracellular matrix called ______ (water, salts, & dissolved proteins)
➔ Suspended in plasma are
◆ _______ (RBCs) - carry oxygen
◆ ________ (WBCs) - defense
◆ cell fragments (_____) - in blood clotting
➔ Has a liquid extracellular matrix called ______ (water, salts, & dissolved proteins)
➔ Suspended in plasma are
◆ _______ (RBCs) - carry oxygen
◆ ________ (WBCs) - defense
◆ cell fragments (_____) - in blood clotting
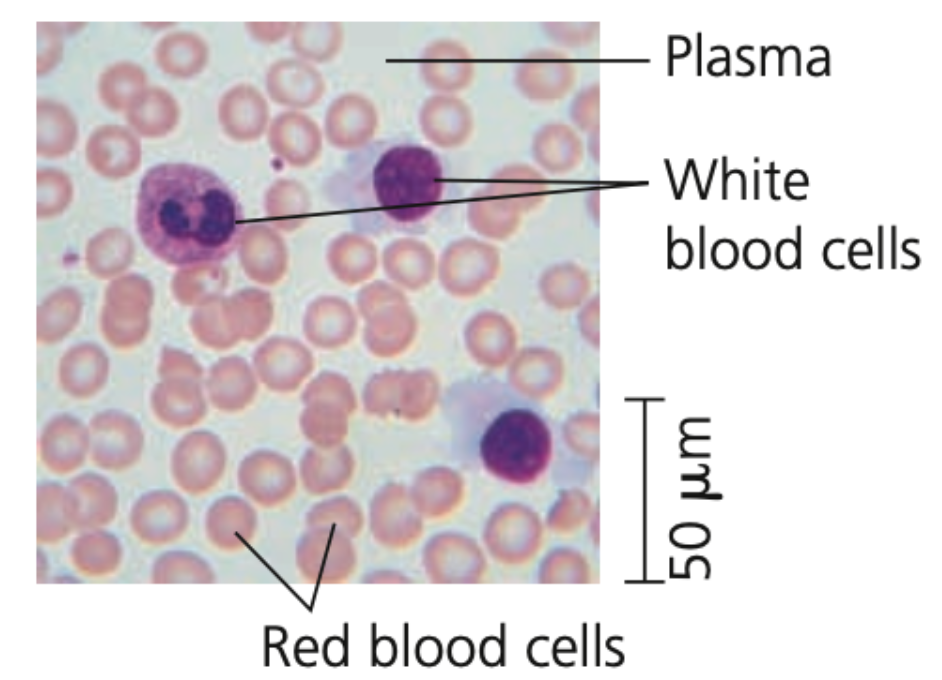
55
New cards
chondroitin, Chondrocytes, embryos, disks
Cartilage
➔ Contains collagenous fibers embedded in a rubbery protein-carbohydrate complex (_______ sulfate)
➔ _________ secrete the collagen and chondroitin sulfate, which make cartilage strong yet flexible support material
➔ Skeletons of many vertebrate ______ contain cartilage that is replaced by bone as it matures
◆ Cartilage remains in some locations, such as the ___ that act as cushions between vertebrate
➔ Contains collagenous fibers embedded in a rubbery protein-carbohydrate complex (_______ sulfate)
➔ _________ secrete the collagen and chondroitin sulfate, which make cartilage strong yet flexible support material
➔ Skeletons of many vertebrate ______ contain cartilage that is replaced by bone as it matures
◆ Cartilage remains in some locations, such as the ___ that act as cushions between vertebrate
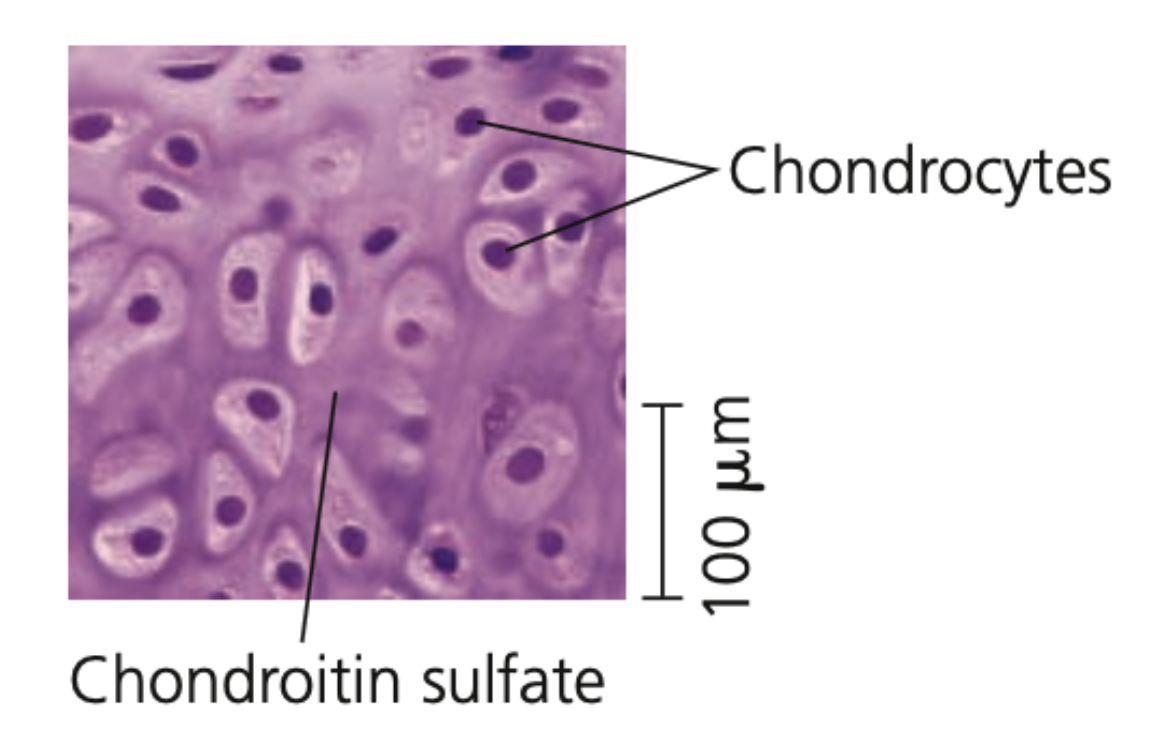
56
New cards
actin, myosin
Muscle tissue
● Responsible for nearly all types of body
movement
● Consist of filaments containing proteins ____ and ____, which together enable muscles to contact
● Responsible for nearly all types of body
movement
● Consist of filaments containing proteins ____ and ____, which together enable muscles to contact
57
New cards
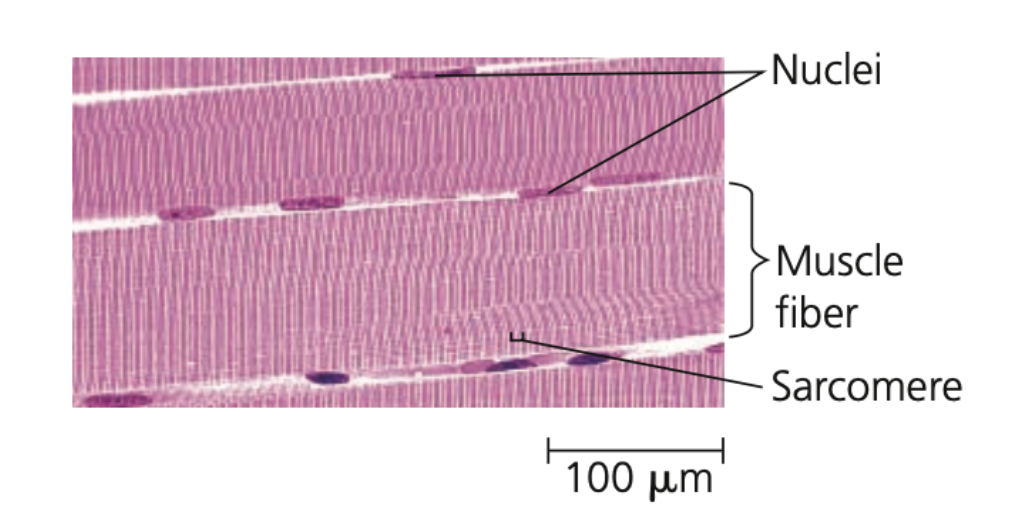
striated, voluntary, bundles, fusion, sarcomeres, size
Skeletal muscle
➔ Also known as ______ muscle
➔ Responsible for _______ movements
➔ Consists of ____ of long cells that
are muscle fibers
◆ Skeletal muscle fibers form by the _____ of many cells, resulting in multiple nuclei in each muscle fiber
◆ Arrangement of contractile units (______), along the fibers gives the cells a striated appearance
➔ In adult mammals, building muscle increases ___ but not number of muscle fibers
➔ Also known as ______ muscle
➔ Responsible for _______ movements
➔ Consists of ____ of long cells that
are muscle fibers
◆ Skeletal muscle fibers form by the _____ of many cells, resulting in multiple nuclei in each muscle fiber
◆ Arrangement of contractile units (______), along the fibers gives the cells a striated appearance
➔ In adult mammals, building muscle increases ___ but not number of muscle fibers
58
New cards
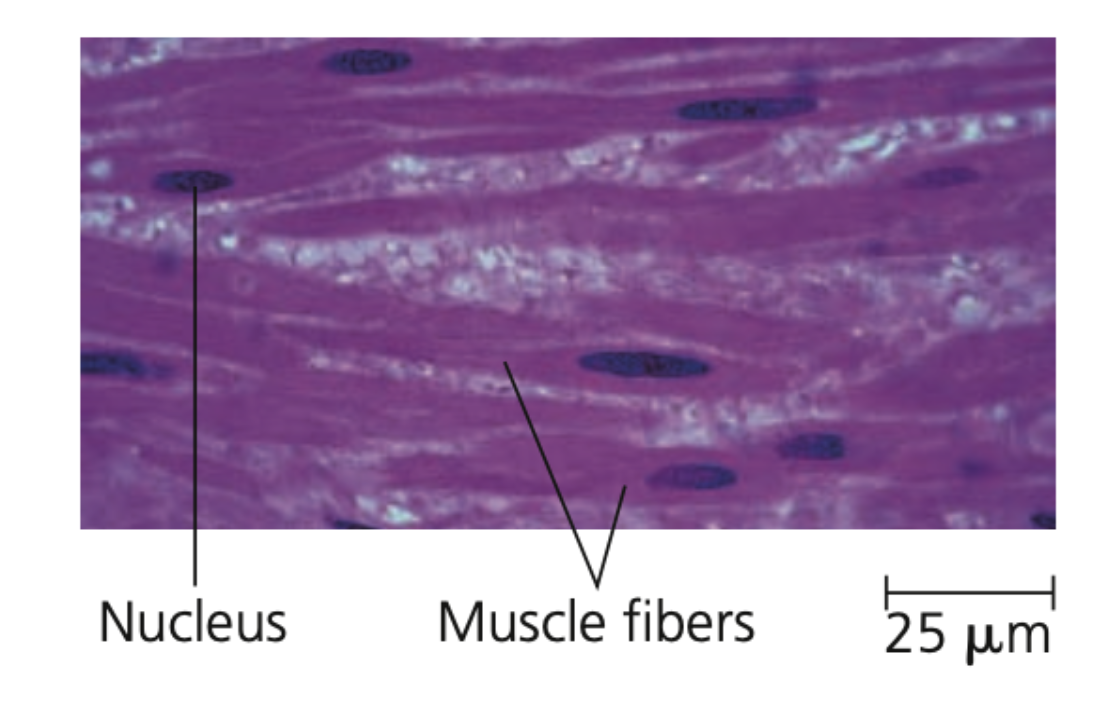
bladder, internal, spindle, involuntary
Smooth muscle
➔ Lacks striations, found in the walls of the digestive tract, urinary _____, arteries, and other internal organs
➔ Cells are ______-shaped
➔ _______ body activities, such as churning of stomach and construction of arteries
➔ Lacks striations, found in the walls of the digestive tract, urinary _____, arteries, and other internal organs
➔ Cells are ______-shaped
➔ _______ body activities, such as churning of stomach and construction of arteries
59
New cards
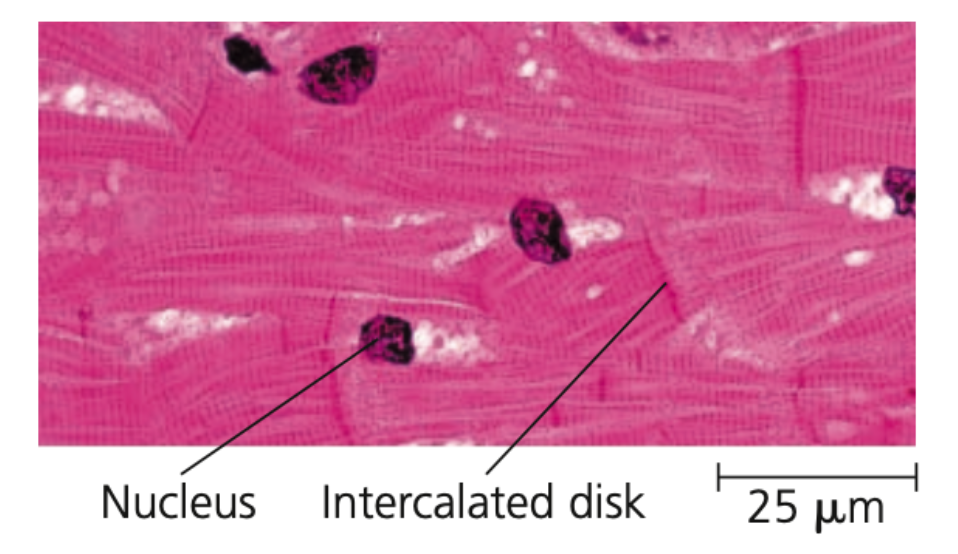
contractile, striated, branched, intercalated
Cardiac muscle
➔ Forms the ______ wall of the heart
➔ _____ and has similar contractile properties to skeletal muscle
➔ Unlike skeletal muscle, has ______ fibers that interconnect via _______ disks, which relay signals from cell to cell and help synchronize heart contraction
➔ Forms the ______ wall of the heart
➔ _____ and has similar contractile properties to skeletal muscle
➔ Unlike skeletal muscle, has ______ fibers that interconnect via _______ disks, which relay signals from cell to cell and help synchronize heart contraction
60
New cards
brain
Nervous tissue
● Receipt, processing, and transmission of information
● Contains
○ Neurons (nerve cells), which transmit nerve impulses
○ Glial cells support nerve cells
● A concentration of nervous tissue forms a ___, an information-processing center
● Receipt, processing, and transmission of information
● Contains
○ Neurons (nerve cells), which transmit nerve impulses
○ Glial cells support nerve cells
● A concentration of nervous tissue forms a ___, an information-processing center
61
New cards
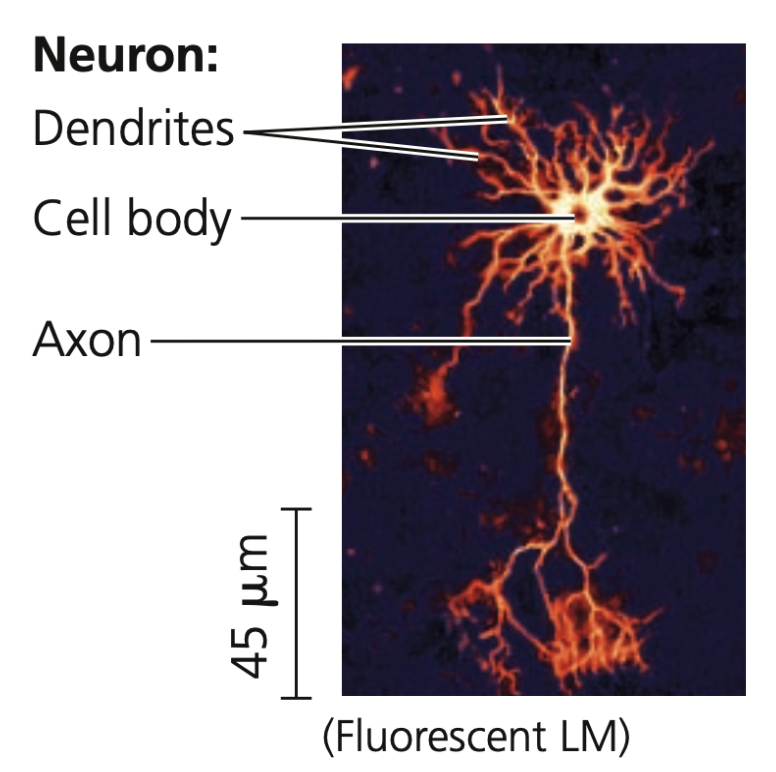
body, dendrites, axons
Neurons
➔ Basic units of the nervous system
➔ Receives nerve impulses from other neurons via its cell ___ and multiple extensions called ______
➔ Transmits impulses through ____
➔ Basic units of the nervous system
➔ Receives nerve impulses from other neurons via its cell ___ and multiple extensions called ______
➔ Transmits impulses through ____
62
New cards
modulate
Glia
➔ Various types of glia help nourish, insulate, and replenish neurons
➔ Can also ______ neuron function
➔ Various types of glia help nourish, insulate, and replenish neurons
➔ Can also ______ neuron function
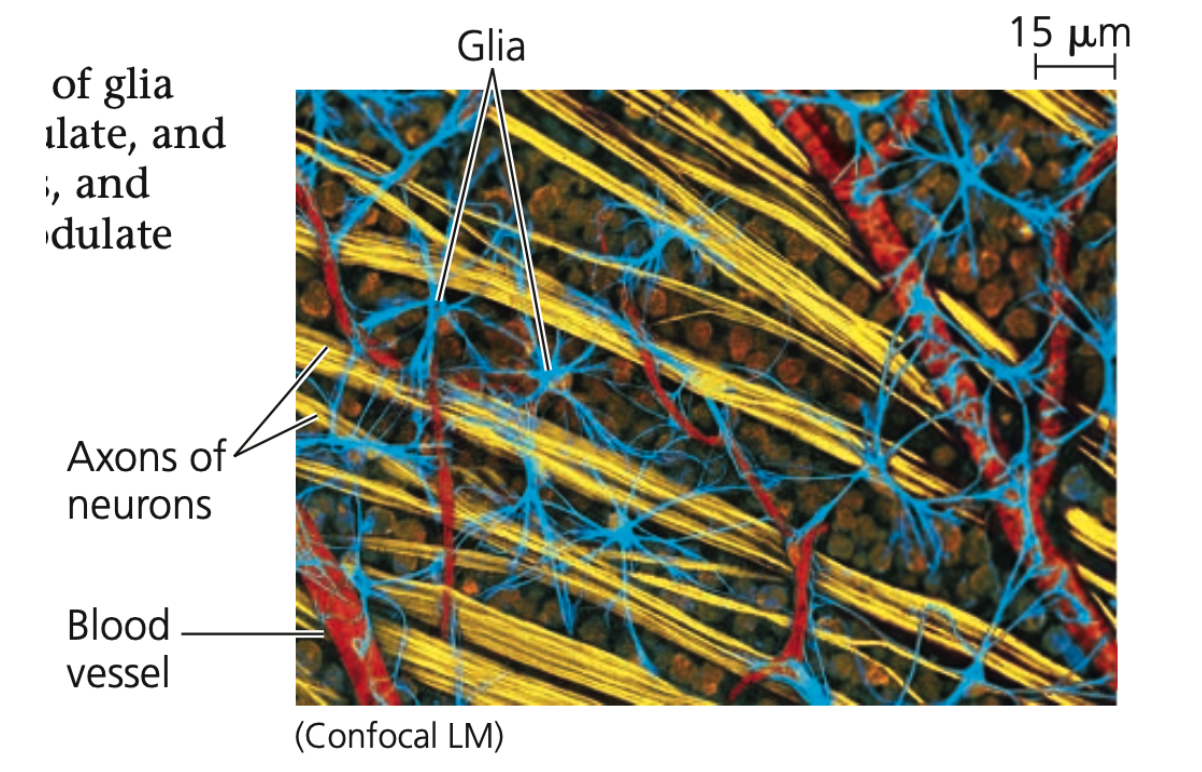
63
New cards
stimuli
Coordination & Control
● Animals have two major systems for coordinating and controlling responses to ______:
1. Endocrine
2. Nervous
● Animals have two major systems for coordinating and controlling responses to ______:
1. Endocrine
2. Nervous
64
New cards
bloodstream, all
Endocrine system
➔ Signaling molecules released into the ________ by endocrine cells to all locations in the body
➔ Signaling molecules released into the ________ by endocrine cells to all locations in the body
65
New cards
routes, specific
Nervous system
➔ Neurons transmit signals along dedicated ______ connecting ______ locations in the body
➔ Neurons transmit signals along dedicated ______ connecting ______ locations in the body
66
New cards
Signal, Trans, Speed, Duration
Coordination & Control
● Pathway in each system is the same regardless of whether the signal’s ultimate target is at the other end of the body or a few cell diameters away
● Differ in:
1\. ____ type
2\. ____mission
3\. ______
4\. ______
● Two systems work in close coordination and help maintain a stable internal environment
● Pathway in each system is the same regardless of whether the signal’s ultimate target is at the other end of the body or a few cell diameters away
● Differ in:
1\. ____ type
2\. ____mission
3\. ______
4\. ______
● Two systems work in close coordination and help maintain a stable internal environment
67
New cards
gradual, growth, repro, metabolic, digestion
Endocrine system
● Well adapted for coordinating ______ changes that affect the entire body (_____, development, ____duction, ______ processes, and _____)
● Well adapted for coordinating ______ changes that affect the entire body (_____, development, ____duction, ______ processes, and _____)
68
New cards
molecules, long, receptors
Hormones
➔ Signaling _______ that are broadcast throughout the body
➔ ___-lasting effects as they can remain in the bloodstream for minutes or even hours
➔ Depending on cell ______, hormone may have an effect in just a single location or in sites throughout the body
➔ Signaling _______ that are broadcast throughout the body
➔ ___-lasting effects as they can remain in the bloodstream for minutes or even hours
➔ Depending on cell ______, hormone may have an effect in just a single location or in sites throughout the body
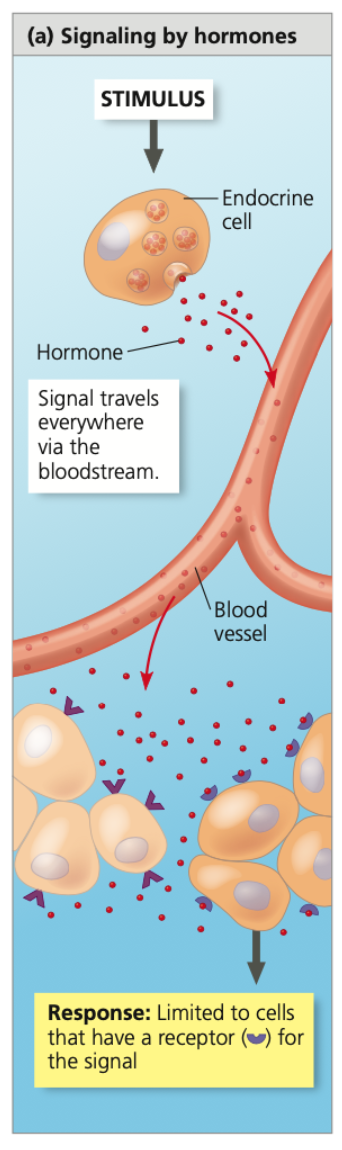
69
New cards
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
➔ acts solely on cells in the thyroid gland and in turn, release thyroid hormone which increases oxygen consumption and heat production
70
New cards
neurons, muscle, glands, pathway, type, immediate
Nervous system
● Nerve impulses can act on other _______, on _____ cells, and _____ that produce secretions
● Unlike endocrine, conveys information by the _____ the signal takes
○ A person can distinguish different musical notes because each note’s frequency activates neurons in the ear that connect to slightly different locations in the brain
● Usually involves more than 1 ___ of signal
○ Nerve impulses travel long distances along axons as changes in voltage
○ In contrast, passing info from one neuron to another often involve very short-range chemical signals
● Well suited for directing _______ and rapid responses to the environment, such as reflexes and other rapid movements
● Nerve impulses can act on other _______, on _____ cells, and _____ that produce secretions
● Unlike endocrine, conveys information by the _____ the signal takes
○ A person can distinguish different musical notes because each note’s frequency activates neurons in the ear that connect to slightly different locations in the brain
● Usually involves more than 1 ___ of signal
○ Nerve impulses travel long distances along axons as changes in voltage
○ In contrast, passing info from one neuron to another often involve very short-range chemical signals
● Well suited for directing _______ and rapid responses to the environment, such as reflexes and other rapid movements
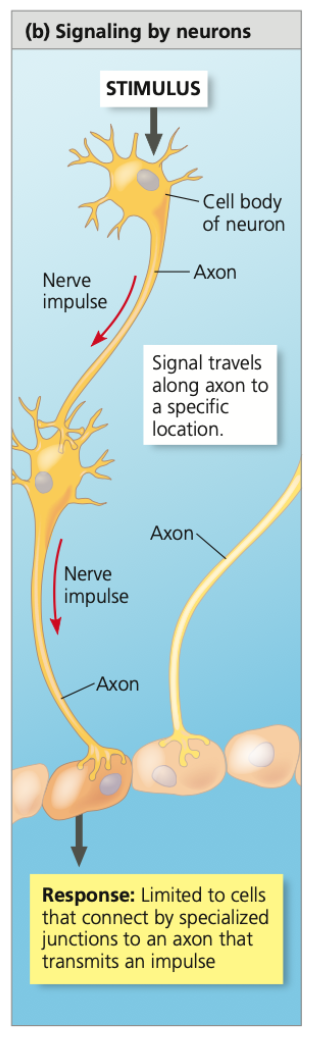
71
New cards
Feedback control
1. Regulating and Conforming
2. Homeostasis
- Mechanisms
- Feedback control
- Alterations
2. Homeostasis
- Mechanisms
- Feedback control
- Alterations
72
New cards
internal, Otter
Regulator
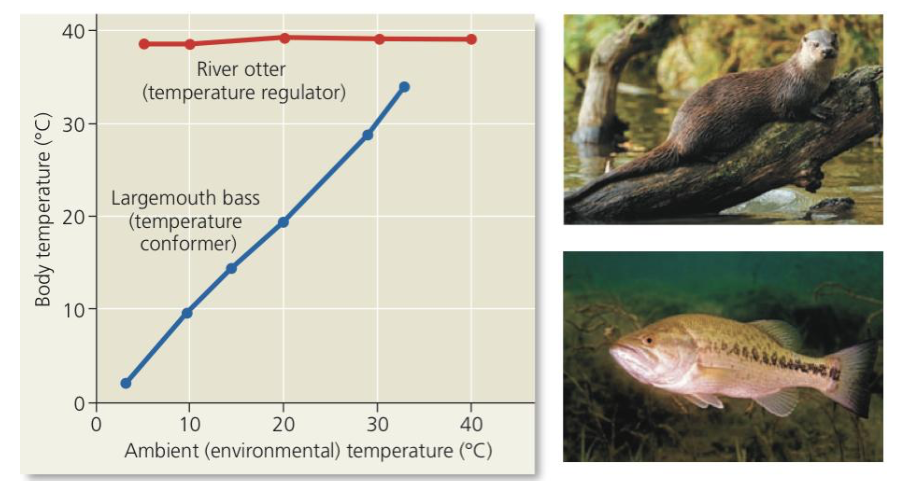
➔ Animal uses _____ mechanisms to control internal change in the face of external fluctuation
◆ Ex. River ___ - regulator for temperature, body temperature is largely dependent on surrounding water
➔ Animal uses _____ mechanisms to control internal change in the face of external fluctuation
◆ Ex. River ___ - regulator for temperature, body temperature is largely dependent on surrounding water
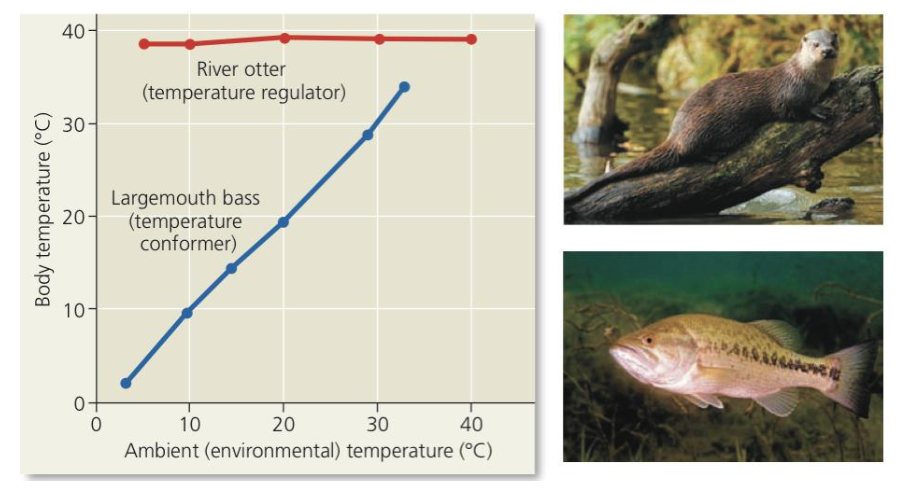
73
New cards
external, Bass, temperature, crabs, solute
Conformer
➔ Animal allows its internal condition to change in accordance with _____ changes in particular variables
◆ Ex. Largemouth ____ - conforms to the ________ of the lake it inhabits
➔ Does not need to involve changes in an internal variable
◆ Marine invertebrates (ex. Spider ____)
● Internal ____ concentration conforms to stable salinity of their environment
➔ Animal allows its internal condition to change in accordance with _____ changes in particular variables
◆ Ex. Largemouth ____ - conforms to the ________ of the lake it inhabits
➔ Does not need to involve changes in an internal variable
◆ Marine invertebrates (ex. Spider ____)
● Internal ____ concentration conforms to stable salinity of their environment
74
New cards
interstitial
Regulating and Conforming
● An animal may regulate some conditions and conform to the environment for other variables
○ Ex. Largemouth Bass
■ Conforms to the temperature of the water
■ Regulates the solute concentration in its blood and ______ fluid
● An animal may regulate some conditions and conform to the environment for other variables
○ Ex. Largemouth Bass
■ Conforms to the temperature of the water
■ Regulates the solute concentration in its blood and ______ fluid
75
New cards
steady, constant, temperature, pH, glucose
Homeostasis ● Maintenance of internal balance or a “_____ state” ○ ______ internal environment even when the external environment changes significantly ● Humans maintain a constant body _____, blood , __and blood _____ concentration
76
New cards
Mechanisms
1. Set point
2. Stimulus & sensor
3. Response
2. Stimulus & sensor
3. Response
77
New cards
set point
● Homeostatic control system in animals maintains a variable at or near a particular value known as the ____ ______
78
New cards
stimulus, sensor
● Fluctuations in the set point serves as the _____ and is detected by a _____
79
New cards
response
● Sensor signals a control center which triggers a ______
○ Physiological activity that helps return the variable to set point
○ Physiological activity that helps return the variable to set point
80
New cards
Feedback control
1. Negative feedback
2. Positive feedback
2. Positive feedback
81
New cards
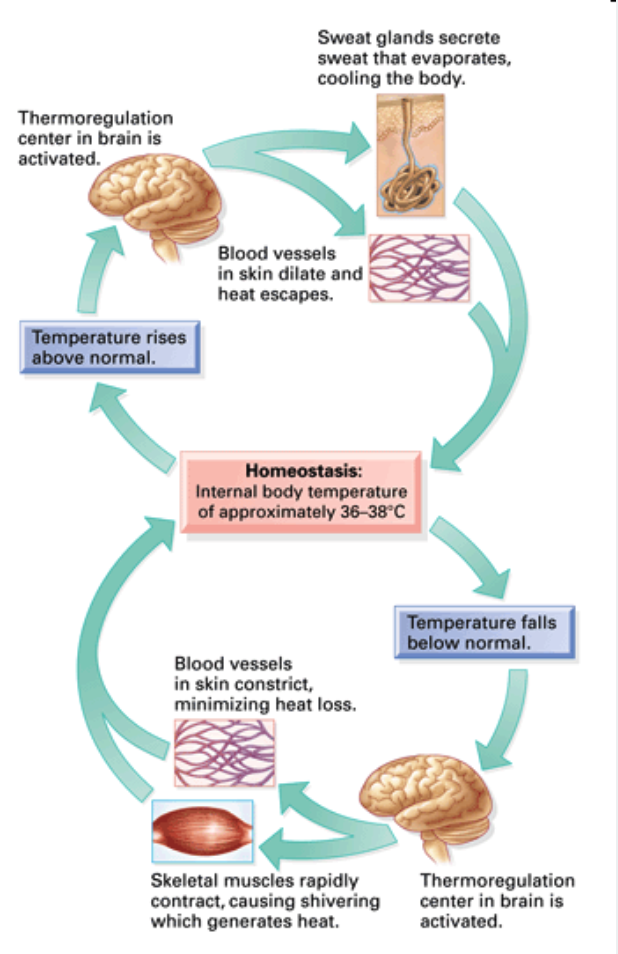
reduces, Nervous, sweating
Negative feedback
➔ Control mechanisms that _____ or “damps” stimulus
◆ Ex. Exercise increases body temperature
● _____ system triggers ______
● Evaporation of sweat cools the body
➔ Control mechanisms that _____ or “damps” stimulus
◆ Ex. Exercise increases body temperature
● _____ system triggers ______
● Evaporation of sweat cools the body
82
New cards
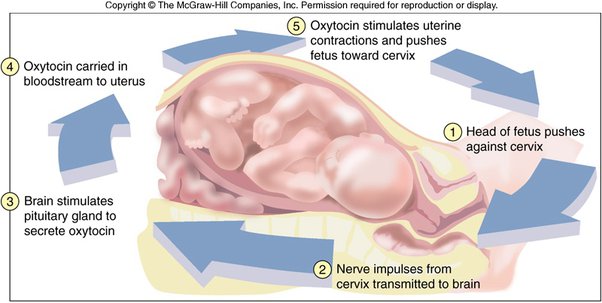
amplifies, pressure, contract,
Positive feedback
➔ Control mechanisms that ______ stimulus
◆ Ex. Childbirth
● ______ of baby’s head against receptors near uterus stimulates uterus to _______
● Contractions result in greater pressure until the baby is born
➔ Helps drive homeostatic processes into completion
◆ Do not play a major role in homeostasis
➔ Control mechanisms that ______ stimulus
◆ Ex. Childbirth
● ______ of baby’s head against receptors near uterus stimulates uterus to _______
● Contractions result in greater pressure until the baby is born
➔ Helps drive homeostatic processes into completion
◆ Do not play a major role in homeostasis
83
New cards
dynamic, oppose
Feedback control
● Homeostasis is a ______ equilibrium
○ Interplay between external factors that tend to change the internal environment
○ Internal control mechanisms _____ such changes
● Homeostasis is a ______ equilibrium
○ Interplay between external factors that tend to change the internal environment
○ Internal control mechanisms _____ such changes
84
New cards
moderates, range, adaptations
**Feedback control**
* Homeostasis _____ but doesn’t eliminate changes in the internal environment
* Fluctuations are greater if a variable has a normal ____ rather than a set point
* Refers to an upper and lower limit
* Homeostasis is enhanced by ______ that reduce fluctuations
* Homeostasis _____ but doesn’t eliminate changes in the internal environment
* Fluctuations are greater if a variable has a normal ____ rather than a set point
* Refers to an upper and lower limit
* Homeostasis is enhanced by ______ that reduce fluctuations
85
New cards
Alterations
1. Regulated changes
2. Circadian rhythm
2. Circadian rhythm
86
New cards
stages, puberty, cyclic, menstrual
● Regulated changes in the internal environment are essential to normal body functions
○ Set points and normal ranges for homeostasis can change under various circumstances
● Regulated changes can be in accordance with _____ of life
○ Ex. There is a radical shift in hormone balance that occurs during puberty
● Regulated changes can be ____
○ Ex. Variation in hormone levels responsible for a woman’s ______ cycle
○ Set points and normal ranges for homeostasis can change under various circumstances
● Regulated changes can be in accordance with _____ of life
○ Ex. There is a radical shift in hormone balance that occurs during puberty
● Regulated changes can be ____
○ Ex. Variation in hormone levels responsible for a woman’s ______ cycle
87
New cards
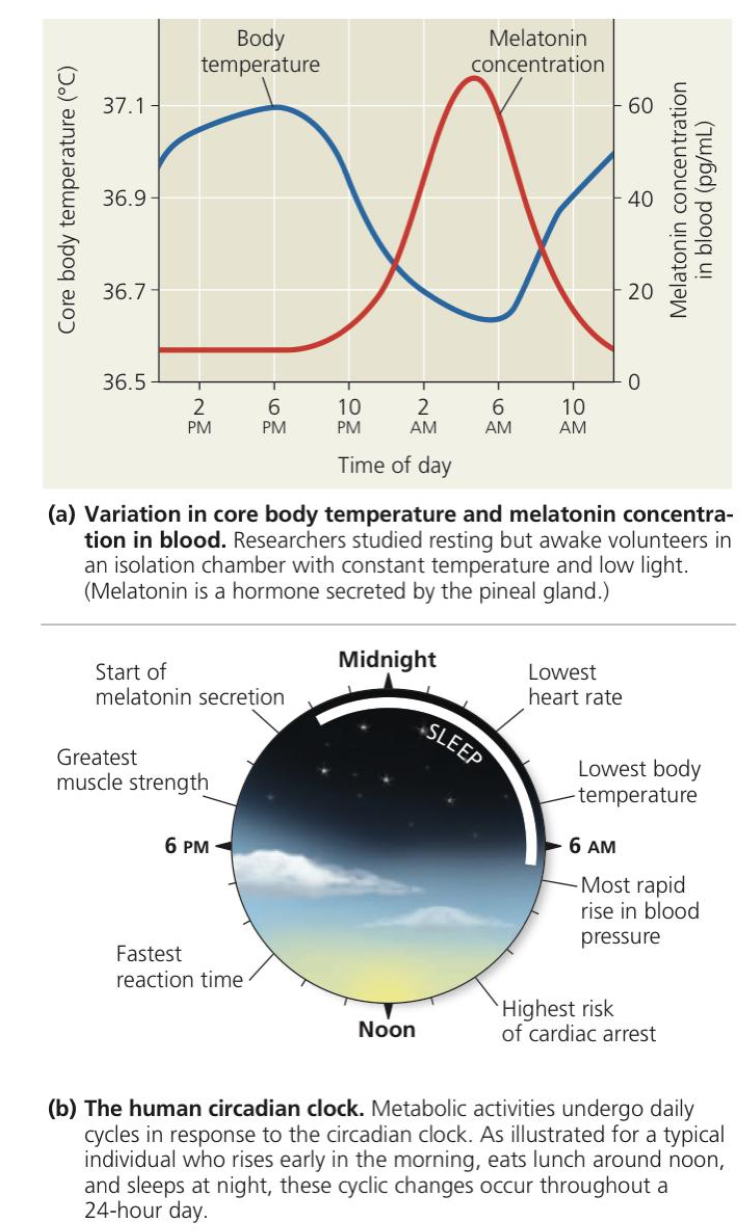
Circadian rhythm, 24, light, temperature, External, lag
● Cyclic alterations in all animals and plants reflect a _______ _____
○ Set of physiological changes that occur roughly every ___ hours
○ Intrinsic to the body
■ Normally coordinated with the cycle of ____ and
darkness in the environment
○ Observed in the cyclic rise and fall of human ________ in a 24-hour period
○ ______ stimuli can reset the biological clock, but the effect is not immediate
■ Ex. Flying across several time zones results in jet ___
● Mismatch between circadian rhythm and local environment
○ Set of physiological changes that occur roughly every ___ hours
○ Intrinsic to the body
■ Normally coordinated with the cycle of ____ and
darkness in the environment
○ Observed in the cyclic rise and fall of human ________ in a 24-hour period
○ ______ stimuli can reset the biological clock, but the effect is not immediate
■ Ex. Flying across several time zones results in jet ___
● Mismatch between circadian rhythm and local environment
88
New cards
Thermoregulation
1. Endothermy and Ectothermy
2. Variation in Body Temperature
3. Balancing Heat Loss and Gain
- Insulation
- Circulatory adaptations
- Cooling by evaporative heat loss
- Behavioral responses
- Adjusting metabolic heat production
4. Acclimatization
5. Physiological Thermostats
2. Variation in Body Temperature
3. Balancing Heat Loss and Gain
- Insulation
- Circulatory adaptations
- Cooling by evaporative heat loss
- Behavioral responses
- Adjusting metabolic heat production
4. Acclimatization
5. Physiological Thermostats
89
New cards
maintain, enzymatic, fluidity, sensitive
Thermoregulation
● the process by which animals ______ their body temperature within a normal range
● Body temperatures outside normal range can:
○ reduce the efficiency of _______ reactions
○ alter the _____ of cellular membranes
○ affect other temperature-______ biochemical processes
● the process by which animals ______ their body temperature within a normal range
● Body temperatures outside normal range can:
○ reduce the efficiency of _______ reactions
○ alter the _____ of cellular membranes
○ affect other temperature-______ biochemical processes
90
New cards
Source of heat
- Endothermy
- Ectothermy
- Ectothermy
91
New cards
Stability of body temperature
- Poikilothermy
- Homeothermy
- Homeothermy
92
New cards
exclusive
● Endothermy and ectothermy are NOT mutually _____.
93
New cards
internal
Endotherms
➔ Heat is generated by _______ metabolism
➔ can maintain a stable body temperature even if the environmental temperature fluctuates
➔ Examples include
◆ Mammals (Humans)
◆ Birds
◆ Some fishes and insects
➔ Heat is generated by _______ metabolism
➔ can maintain a stable body temperature even if the environmental temperature fluctuates
➔ Examples include
◆ Mammals (Humans)
◆ Birds
◆ Some fishes and insects
94
New cards
external, food, fluctuations
Ectotherms
➔ Heat comes from _____ sources /
environment
➔ adjust their body temperature by behavioral means (basking in the sun)
● Many nonavian reptiles
● Fishes
● Most invertebrates
➔ Generally need to consume less ____ than endotherms of same size (advantageous when resources are scarce)
➔ Tolerate larger _______ in internal temperature
➔ Effective and successful strategy as observed in the abundance and diversity of ectotherms
➔ Heat comes from _____ sources /
environment
➔ adjust their body temperature by behavioral means (basking in the sun)
● Many nonavian reptiles
● Fishes
● Most invertebrates
➔ Generally need to consume less ____ than endotherms of same size (advantageous when resources are scarce)
➔ Tolerate larger _______ in internal temperature
➔ Effective and successful strategy as observed in the abundance and diversity of ectotherms
95
New cards
source, stability
Variation in Body Temperature
● There is NO fixed relationship between the ______ of heat (endothermy/ectothermy) and the ______ of body temperature (poikilotherm/homeotherm).
● Ectotherms do NOT necessarily have low body temperatures
1. Poikilotherm
2. Homeotherm
● There is NO fixed relationship between the ______ of heat (endothermy/ectothermy) and the ______ of body temperature (poikilotherm/homeotherm).
● Ectotherms do NOT necessarily have low body temperatures
1. Poikilotherm
2. Homeotherm
96
New cards
Poikilotherm
➔ Body temperature varies with its environment (Greek poikilos = varied)
97
New cards
Homeotherm
➔ Relatively constant body temperature
98
New cards
Misconception
○ Ectotherms = “cold-blooded” &
endotherms = “warm-blooded”
(this is wrong!!)
○ Avoid the terms “cold-blooded” and “warm-blooded” because they are misleading
endotherms = “warm-blooded”
(this is wrong!!)
○ Avoid the terms “cold-blooded” and “warm-blooded” because they are misleading
99
New cards
Thermoregulation
Balancing Heat Loss and Gain
● ________ depends on an animal’s ability to control its exchange of heat with the environment through any of the four processes:
1. Radiation
2. Evaporation
3. Convection
4. Conduction
● ________ depends on an animal’s ability to control its exchange of heat with the environment through any of the four processes:
1. Radiation
2. Evaporation
3. Convection
4. Conduction
100
New cards
=, HIGH, integumentary
Balancing Heat Loss and Gain
* The goal is to have rate of heat gain __ rate of heat loss
* Heat is always transferred from ____ → LOW temperature
* Several of these mechanisms involve the _______ system, skin, hair, nails/claws/hooves
* The goal is to have rate of heat gain __ rate of heat loss
* Heat is always transferred from ____ → LOW temperature
* Several of these mechanisms involve the _______ system, skin, hair, nails/claws/hooves