Medical Records
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Parts of history and physical
Chief Complaint (CC)
History of Present Illness (HPI)
Patient History
Past Medical History, Past Surgical History, Social history, Family history, etc.
Review of Systems (ROS)
Vital Signs
Physical Examination
Inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation (IPPA)
Laboratory and imaging data
Diagnosis
Disposition
Treatment and plan
Chief Complaint
This is why the patient is seeking medical attention
▪ SUBJECTIVE (Notated in the patient's own words)
▪ Should be written in quotations as a direct quote from the patient
▪ Does not get translated intomedical terminology
For example:
▪ “I have had a bad sore throat for about a week.”
History of present illness - definition and example
Patient interview with open ended questions
Chronological narrative of SUBJECTIVE complaint(s)
Utilizes an “OPQRST” or “OLD CARTS”
Starts with “This is a *** year old *** who presents with ***”
Example:
CC= “I have had a bad sore throat for about a week.”
HPI= This is a 47 year old female who presents with a chief complaint of sore throat. Her symptoms started 1 week prior to presentation. Her sore throat is aching and now constant, worsening over the week. The pain is a 6/10 in severity and it is impacting both sides of her throat however not radiating further. Her pain is worsened when she coughs and minimally relieved by hot beverages and NSAIDs.
History of present illness - OPRQRST
Onset
provocation/palliation
quality
region&radiation
severity
time
History of Present Illness- Old Carts
Onset
Location
Duration
Character
Aggravating/ Alleviating
Radiation
Time
Severity
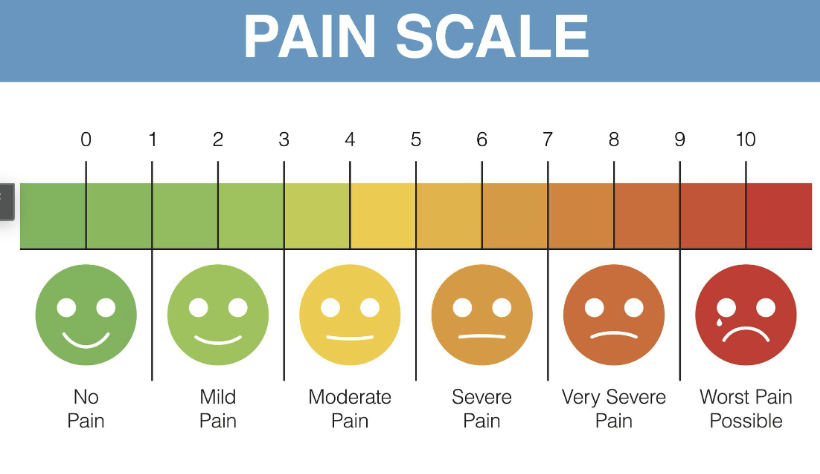
HPI Severity
Patient History Categories
Facts of the patient’s history from the following categories:
▪ Medical history: diseases/ diagnoses with date diagnosed
▪ Surgical history: procedure, location, date
▪ Medications: prescription (dose, route, frequency) and over the counter/herbal supplements
▪ Allergies: food, medication, environmental with reported reaction
▪ Vaccinations: childhood, boosters, yearly, etc.
▪ Social history: alcohol, smoking, illicit substances, occupation, living situation
▪ Family history: cancer, heart disease, inheritable conditions, etc.
Review of systems
Subjective review of each body system
highlight pertinent pos or neg responses surrounding current chief complaint or HPI
ros interview cheat sheet in bright space
Examples
general
neuro
had/ears/eyes/nose/throat
respiratory
cardio vascular
gastrointestinal
genito
muskuloskeletal
ROS Pertinent questions
Example of pertinent questions:
▪ General: any fevers/ chills? Unexpected weight changes?
▪ Neuro: Any numbness or tingling?
▪ Head/ Ears/ Eyes/ Nose/ Throat: any headache/ runny nose/ watery eyes/ swelling of throat/ difficulty swallowing?
▪ Respiratory: difficulty breathing? Cough?
▪ Cardiovascular: chest pain? Palpitations?
▪ Gastrointestinal:
▪ Genitourinary:
▪ Musculoskeletal: any muscle weakness?
Vital Signs
OBJECTIVE measurements
▪ Important to know your normal vital signs
▪ Just as important to know what abnormal vital signs signify
▪ Vital signs include:
▪ Temperature
▪ Heart rate
▪ Blood pressure
▪ Respiratory Rate
▪ Oxygenation
Vital - Temperature, associated terms
reported in celsius or Fahrenheit
measured with thermometer at specific sites such as
oral- under tongue
axillary
tympanic/ear canal
rectul
normal
37 degree c
98.6 degree F
hypothermia - low temp
normothormia - normal temp
hyperthermia - Hugh temp
thermoreg - maintenance of body temp
vital - heart rate
Heart Rate:
Reported in beats per minute
Measurements:
Pulse oximeter on distal finger tips
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
ECG/EKG can also assess rhythm
Felt & counted by hand x 1 minute at pulse sites if irregular rhythm
Auscultated & counted x 1 minute with stethoscope (apical pulse)
Normal adult heart rate: 60 - 100 beats per minute
Associated Medical Terminology:
Tachycardia: condition of fast heart rate,>100 BPM
Bradycardia; condition of slow heart rate, <60 BPM
Arrhythmia/ Dysrhythmia condition of abnormal heartrhythm
pulse sites and measurements
temporal
femoral
popliteal
posterior tibial
carotid
brachial
radial
dorsalis pedis
apical
measure by hand, document rate as well as strength
0= absent
1+= thready/weak
2+=normal
3+=bounding
heart rate related measurements
ekg
pulse oximeter
when documenting, regular or irregular
vital - blood pressure and associated terms
reported as systolic and diastolic in millimeters of mercury (mmHg)
measured with sphygmomanometer (BP cuff) most commonly at brachial site
can be taken manually with bp cuff or electronically
normal
sup = 100-140
dip = 60-90
map >65
Associated terms
hypotension = low blood pressure
hypertension = high bp
normotensive
blood pressure related measurements
bp = force exerted on atrial walls by blood
sbp = force exerted on atrial walls by blood during systole/ contraction
dbp= force exerted on atrial walls by blood during diastole (relaxation phase of heart beat)
MAP = mean arterial pressure
2(dbp+sbp)/3
vital - respiratory rate, associated terms
Respiratory Rate:
▪ Reported in breaths per minute
Measurement:
▪ observe chest rise & fall x 1 minute
▪ auscultation with stethoscope and count rate x 1 minute
▪ Can also assess rhythm (regular/ irregular) and quality (shallow/ deep)
▪ Normal adult respiratory rate:
▪ 12-20 breaths per minute
associated terms
pnea & spir/o = Breathing
Tachypneic/ tachypnea = condition of rapid breathing (>20 breaths per minute)
Bradypneic/ bradypnea = condition of slow breathing (<12 breaths per minute)
Hypoventilation/ hyperventilation = pertaining to amount of ventilation of lungs, too little or too much
Apnea= Cessation of breathing
vital - oxygenation saturation+ terms
Fraction of oxygen-saturated hemoglobin relative to total hemoglobin
▪ Reported as a percentage (%) out of 100%
▪ Important to outline if they are on oxygen while obtaining measurement
▪ Measured with a pulse oximeter on distal finger tips
▪ Normal adult oxygenation level: >94%, Can tolerate 89-92% in patient’s with chronic lung diseases like COPD
Terms
Ox/o & -oxia = Oxygen
▪ Hypoxia= Low/ deficient oxygen in the tissues
▪ Hypoxemia = Low oxygen in the blood
▪ Anoxia= Without oxygen
physical exam types
inspection
▪ First step in examine a patient or body part
▪ Your observation of the patient
▪ Continuous throughout your entire interview &exam
▪ Preliminary observations:
General appearance
Mental status
Posture
Skin color/ deformities
Body language
Gait
palpation
▪ Utilizing your sense of touch to examine characteristics of body parts
▪ Uses the pads of your fingers
▪ Can be light or deep palpation
▪ Useful to determine characteristics such as...
▪Location of organs/ structures/ masses
Size
Texture
Temperature
Tenderness
percussion
▪ Utilizing your fingers to tap a portion of the body
▪ Assess underlying tissue/ structure for the presence of fluid or air
▪ Sound differences helps you compare what medium the sound is traveling through
▪ For example, air filled organs will elicit a higher pitched percussion note than fluid filled organs
auscultation
Listening to sounds of specific body areas
▪ Examples of axreas to auscultate: Heart, Blood vessels, Lungs/ airway, Abdomen/ bowels
▪ Done by using a stethoscope (may not be necessary depending on the sound)
▪ Can help determine normal vs abnormal sounds via comparison with other areas of the organ
Nervous - ROS
ROS
▪ Changes in memory?
▪ Mood changes?
▪ Dizziness?
▪ Loss of balance?
▪ Falls?
▪ Tingling?
▪ Numbness?
▪ can ask family/ care taker if appropriate
Nervous - Physical exam
Physical Exam
▪ Level of consciousness:
▪ Alert, lethargic, unconscious
▪ Orientation:
▪ Alert and oriented x3: to person, place, & time
▪ Remote memory/ recent memory
▪ Thought content
▪ Mood
▪ Balance/ coordination
▪ Gait
cardio ros
ROS
▪ Chest pain? If yes -> OPQRST
▪ Palpitations?
▪ Leg swelling
▪ Unhealing sores/ lesions on legs?
▪ Hair loss on legs?
▪ Noticeable veins on legs?
cardio physical exam
Physical Exam
▪ Inspect for limb swelling (edema), color, venous patterns
▪ Palpation of pulses bilaterally
▪ Ex. Carotid, radial, dorsalis pedis
▪ Auscultation of heart sounds
auscultation for heart sounds
Listen for...
▪ S1 & S2
▪ Abnormal rate?
▪ Abnormal rhythm?
▪ Murmurs?
▪ Extra beats?
▪ Distant?
pulmonary ros
Pulmonary System
ROS
▪ Shortness of breath?
▪ At rest vs on exertion
▪ Pain with inspiration?
▪ Cough?
▪ Dry vs wet (productive)
▪ Wheezing?
pulmonary physical exam
Physical Exam
▪ Inspect work of breathing
▪ Posture, flaring nostrils
▪ Able to complete a full sentence?
▪ Cough?
▪ Palpation of air pockets trapped under skin
▪ Auscultate lung sounds
auscultation of lung sounds
Compare bilaterally
▪ Anatomy: R lung has 3 lobes, L lung has 2 lobes
▪ Listen for...
▪ Any decreased breath sounds?
▪ Increased breath sounds?
▪ Unequal breath sounds?
▪ Absent breath sounds?
gastrointestinal ros
▪ Abdominal pain?
▪ Heartburn?
▪ Nausea/ vomiting?
▪ Constipation/ diarrhea?
▪ Changes in stool color?
gastro physical exam
▪ Inspect abdomen size, contour, scars
▪ Auscultate bowel sounds
▪ Percuss to measure size of liver/ spleen
▪ Palpate for masses/ fluid/ tenderness
auscultation for abdominal sounds
Auscultation of abdominal sounds:
▪ Compare 4 quadrants
▪ Listen for...
▪ Any decreased sounds?
▪ Increased sounds?
▪ Unequal sounds?
▪ Absent sounds?
gastrointestinal palpation
Palpation:
▪ Light vs deep
▪ Guarding?
▪ Rebound tenderness?
genitourinary ros
▪ Changes in urine color?
▪ Changes in urine frequency?
▪ Changes in urine amount?
▪ Increased urgency?
▪ Do you get up to pee in the middle of the night?
▪ Pelvic pain? Flank pain? Lower back pain?
▪ Reproductive system assessment if appropriate
Genito urinary physical exam
Physical Exam
▪ Inspect for pelvic distension
▪ Inspect for abnormal changes to genito-urethral area
▪ Palpate flanks and lower back
▪ Percuss on back bilaterally
muskulo skeletal ros
▪ Muscle cramps?
▪ Muscle weakness?
▪ Joint pain/ stiffness?
▪ Limited mobility?
▪ Trouble walking?
▪ Injuries?
musculoskeletal physical exam
Physical Exam
▪ Inspect for swelling, deformities, symmetry, atrophy
▪ Palpate for deformities, temperature, tenderness
▪ Assess range of motion
▪ Active vs passive
integumentary ros
▪ Dry skin?
▪ Itchy skin?
▪ Rashes/ lesions/ sores/ bumps?
▪ Bruises?
▪ Provoked?
▪ Changes in mole size / characteristics?
▪ Changes in hair/ nails?
integumentary physical exam
Inspect skin throughout body for lesions, bruises, abnormalities
▪ Inspect mucous membranes
▪ Inspect nails
▪ Palpate for moisture, temperature, texture, turgor (ability for skin to return to place freely)
special senses ros
Eyes:
▪ Blurry vision/ changes in vision?
▪ Pain ?
▪ Watering/ redness/ itching ?
Ears:
▪ Ringing in your ears? (tinnitus)
▪ Changes in your hearing?
▪ Pain in your ears?
special senses physical exam
Inspect eyes
▪ Eyelids
▪ enophthalmos/ exophthalmos
▪ color of conjunctiva/ sclera
▪ pupils (equality, size, shape, reaction to light)
▪ Visual acuity
▪ Extraocular movements
Inspect ears
▪ Outer ears, middle & inner ear (via otoscope)
▪ Auditory acuity
Palpate external ears, mastoid process, tragus
▪ for tenderness, masses, bruising, swelling
enophthalmos, exophthalmos
eno = recessed or sunken
exo = protrudes
laboratory/ imaging data
Depending on the disease process that you want to work up, you may decide to
obtain labs, for example:
▪ Blood work
▪ Urine studies
Or obtain diagnostic images of certain parts of the body, for example:
▪ X-Ray
▪ Ultrasound
▪ CT scan
▪ MRI
▪ Nuclear medicine scans
laboratory blood tests
Complete Blood Count
▪ CBC
▪ Shows the makeup of your
blood components
▪ Counts the number of
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
White blood cells (leukocytes)
Platelets (thrombocyte)
Basic/ Complete Metabolic Panel
▪ BMP/ CMP
▪ Indication of your kidney &
liver function
▪ Includes:
Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, etc.)
Kidney enzymes & function
Liver enzymes & function
laboratory urine tests and urine culture
Urine Analysis: measures...
▪ pH
▪ Specific gravity (ability of the kidneys to concentrate urine)
▪ Biliribuin (liver)
▪ Glucose
▪ Ketones (sugar breakdown)
▪ Protein
▪ Blood
▪ Bacteria
▪ Nitrite (byproduct of bacterial infection)
▪ Leukocytes
▪ Etc.
Urine culture
If bacteria are present in the urine, then the culture will specify the type of bacteria as well as outline which antibiotics it is sensitive to for most effective treatment.
diagnostic imaging and related terms
Diagnostic Imaging:
▪X-Ray
▪Ultrasound
▪CT scan
▪MRI
▪Nuclear medicine scans
▪Etc.
Associated Medical Terminology:
▪ -gram = Record
▪ -graphy = Process of recording
▪ -Lucent = To shine
▪ -opaque = Obscure
▪ Scan: image of an area, organ, or tissue of body obtained by an imaging study
xray and related terms
X-Ray:
▪ 2-D view of bones & cartilage
▪ Does NOT show ligaments, tendons, etc.
▪ Views are obtained in certain positions described utilizing directional terms
▪ Common x-ray studies: Limbs, chest, abdominal
Associated Medical Terminology:
▪ Radi/o
▪ X-rays
▪ Radiolucent vs Radiopaque
Directional terms:
▪ anteroposterior (AP)
▪ posteroanterior (PA)
▪ lateral
▪ Oblique
▪ Position of body part, for example:
▪. Flexion, extension; abduction, adduction, etc.
▪ Position of body, for example:
▪ Prone, supine, recumbent, etc.
ultrasound/sonography, associated terms
Ultrasound/ Sonography:
▪ Image produced by sound waves/ vibrations as they echo off body parts
Common ultrasounds:
▪ Echocardiogram
▪ Pelvic ultrasound
▪ Transvaginal ultrasound
Associated Medical Terminology:
▪ Son/o = Sound
▪ Echo-= A repeated sound
▪ Ultra-= Beyond
ct scan
CT Scan:
▪ Computed Tomography Scan
▪An X-ray scan that works with a computer to give cross sectional images of a specific area
▪ ie a 3D X-ray that shows depth
Common CT scan sites:
Head/ brain,
neck/ cervical spine,
spinal canal sections,
chest,
abdomen/ pelvis (A/P),
limbs
Can include the use of contrast material in order to better visualize certain structures like vessels
▪ Injection of radiopaque material to show contrast w/ surrounding tissue
▪ Contrast & study examples:
▪ Barium: GI studies
▪ Iodine: angiography
mri, associated term
MRI:
▪ Magnetic Resonance Imaging
▪ Utilizes magnetic field and radio waves to produce views along planes of the body
▪ Detailed image of the soft tissues
Associated Medical Terminology:
▪ Body planes
▪ Sagittal
▪ Coronal
▪ Transverse
nuclear medicine scans
Nuclear Medicine Scans:
▪ Use of radioactive substances in the diagnosis of disease
PET & PET/CT Scan:
▪ Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
▪ Uses small amounts of radioactive isotopes, a special camera, and a computer to evaluate organ/ tissue function
▪ Pictures outline cell metabolic functions ie cells that are metabolizing quicker will be highlighted (like a tumor)
Other NM Studies Examples:
▪ Bone scan
▪ Single-photon emission CT (SPECT)
▪ Thyroid scan
▪ Thallium (TI) scan
diagnosis
Diagnosis:
▪ The identification of an illness/ disease/ problem
▪ Utilizes information from your patient’s history, subjective, and objective data to come to a conclusion
▪ Helps to guide your treatment plan and disposition
▪ Differential Diagnosis: list of possible causes/diseases/ illnesses
plan
Your plan of care for your patient
▪ Will the patient require further imaging? Further lab tests?
▪ If yes, what kind?
▪ Will the patient require treatment/ medication?
disposition
Where will this patient need to go for further medical care?
▪ For example,
▪ Follow up with primary care doctor
▪ Admit to hospital
▪ Admit to intensive care unit
▪ Etc