T8:The chemistry of the atmosphere
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the proportions of gases in the atmosphere today
80% nitrogen
20% oxygen
Why is evidence for the Earth’s early atmosphere limited?
The evidence for Earth’s early atmopshere is limited beacuse of the time scae of 4.6 billion years.
How did volcanoes form the Earth’s early atmosphere?
Volcanoes erupted releasing gases to form the early atmosphere
Which two planets would Earth’s early atmosphere have been similair to today?
Mars amd Venus.
What did Earth’s early atmosphere consist of?
Earth’s early atqmosphere consisted of mainly carbon dioxide with little or no oxygen gas.
What gases may volcanoes have produced?
Volcanoes also produced nitrogen which gradually built up in the atmosphere and there may have been small proportions of methane and ammonia.
How did the oceans form?
Water vapour condensed to form the oceans.
What happened when the oceans formed?
When the oceans formed carbon dioxide dissolved in the water and carbonates were precipitated producing sediments, reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
How did oxygen increase in Earth’s early atmosphere?
The first simple organisms such as algae and green plants photosynthesised by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen back into the atmosphere.
When did algae first produce oxygen?
2.7 billion years ago.
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
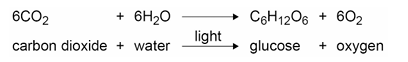
In what 2 ways did the percetages of carbon dioxide in Earth’s early atmosphere decrease?
Algae and plants decreased the percentage of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide was also decreased by the formation of sedimentary rocks and fossil fuels that contain carbon.
How was Limestone formed?
Limestone was made from the calcium carbonate deposits fro the shells and skletons of marine organisms.
How was coal formed?
From thick plant deposits.
How was oil and natural gas formed?
From deposits of plankton.
What do greenhouse gases in the atmosphere help to do?
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere maintain temperatures on Earth high enough to support life.
Name 3 greenhouse gases:
Water vapour
Carbon dioxide
Methane
How does the greenhouse effect work?
The sun emits shortwave radiation
Most of this radiation passes through the Earth's atmosphere and reaches the surface.
The Earth's surface absorbs this radiation and warms up. It then re-emits the energy as longwave radiation, primarily infrared radiation.
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb a portion of this outgoing infrared radiation.
The absorbed radiation heats the atmosphere, which in turn radiates heat back towards the Earth's surface.
What are 4 human activities that increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere?
Deforestation
Burning fossil feuls
Agricultural farming
Landfill sites
What do many scientists believe about the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere?
Many scientists believe that human activities will cause the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere to increase at the surface and that this will result in global climate change
Climate change is a very complex thing to model and that is why it leads to……….
Simplified models, speculation and opinions presented in the media that may be based on only parts of the evidence and which may be biased.
What is a major cause for climate change?
An increase in average global temperature
What are 4 possible effects of global climate change?
An increase in tempearure could lead to the polar ice caps melting causing a rise in sea levels ,increasing flooding in coastal areas and coastal erosion
Changes in rainfall patternsmay cause some regions to get too much or too little water affecting the ability of certain regions to produce food.
The frequency and serverity of storms may increase.
Changes in the temperature and amount of water available may affect wild species,leading to differences in their distribution.
What is carbon footprint?
The carbon footprint is the total amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted over the full life cycle of a product, service or event.
How can carbon footprint be reduced?
The carbon footprint can be reduced by reducing emissions of carbon dioxide and methane.
What are 2 actions which could reduce the emissions of carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere?
Using renewable energy sources instead of fossil feuls.
Governments could tax companies based on the amount of carbon dioxide they emit.
Give two reasons why action from governments could be limited to reduce carbon footprint;
A lot of money may be needed to invest into alternative technologies that lower carbon dioxide emissions
People may be reluctant to make changes to their lifestyle.
What is a major sourceof atmospheric pollutants?
The combustion of fossil fuels.
What do most fuels ,including coal, contain?
Carbon
hydrogen
sulfur.
What gases are released into the atmosphere when a fuel is burned?
carbon dioxide
water vapour
carbon monoxide
sulfur dioxide
oxides of nitrogen.
What might solid particles and hydrocarbons be released into the atmosphere in the form of?
Particles.
How is carbon monoxide and soot produced by burning fuels?
Carbon monoxide is produced
when there isn’t enough oxygen
so incomplete combustion takes place
releasing carbon monoxide and soot into the atmosphere.
How are sulfur dioxides produced by burning fuels?
Sulfur dioxide is released during the
combustion of fossil fuels
that contain sulfur impurities
causing the sulfur to become oxidised
releasing sulfur dioxides.
How are nitrogen dioxides produced by burning fuels?
Nitrogen oxides are created from a reaction between the
nitrogen and oxygen in the air
caused by the heat of burning.
What is carbon monoxide and what is its properties?
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas.
It is colourless and odourless and so is not easily detected.
What can carbon monoxide do that makes it so dangerous?
Carbon monoxide is dangerous because
it can stop the blood from carrying oxygen around the body
by binding to the haemoglobin in your red blood cells
that normally carry oxygen so less oxygen can be carried around your body.
This can lead to fainting, a coma or death.
What does sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen cause ?
Sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen cause respiratory problems in humans and cause acid rain.
what do particulates in the atmosphere cause?
Particulates cause global dimming and health problems for humans.
How do particulates cause respiratory problems?
If particulates are inhaled
they chang get stuck in the lungs
and cause damage
which causes respiratory problems.
How do particulates cause global dimming?
Particulates or the clouds they help produce
reflect sunlight back into space
so less light reaches the Earth
which causes global dimming