EXAM 4: Chapter 13 The Nervous System II: The Central Nervous System (CNS) Part 2単語カード | Quizlet
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
the limbic system
emotional brain
the limbic system
group of structures on medial aspect of each cerebral hemisphere and the diencephalon
Hippocampus and amygdaloid body
What structures of the limbic system are essential to memory consolidation?
fornix
tract of white matter that connects the hippocampus with the hypothalamus and other fiber tracks link the limbic system together
mammillary bodies
structures in the floor of the hypothalamus; concerned with feeding reflexes and behaviors
functions of limbic system
- emotional state & behavioral drives
- links the conscious, intellectual functions of the cerebral cortex with the unconscious and autonomic functions of other portions of the brain
- consolidation and retrieval of memories
Reticular fomation
group of neurons that run through the central core of the medulla, pons, and midbrain
controls AROUSAL of brain as a whole
reticular activating system (RAS)
branch of the RF that maintains consciousness and alertness
also functions in sleep - AROUSAL from sleep
- cover and protect CNS
- enclose and protect blood vessels supplying to CNS
- contain CSF
What are the functions of the meninges?
dura mater - arachnoid mater - pia mater
What are the layers of the meninges from external to internal?
dura mater
tough mother
2 layered sheet of fibrous connective tissue (periosteal layer & meningeal layer)
periosteal layer (outer) and meningeal layer (inner)
What are the 2 layers of the dura mater?
arachnoid mater
middle layer of meninges;
"spiderweb-like mother"
subdural space (cavity)
between the dura mater and the arachnpid mater; contains a film of CSF
subarachnoid space (cavity)
deep to arachnoid mater
web-like threads
- filled with CSF and blood vessels supplying to the brain
arachnoid villi
- granulations
act as valves that allow CSF to pass from subarachnoid space to dural sinuses
dura mater and arachnoid mater
two layers of the meninges that surround the brain LOOSELY
pia mater
"gentle mother"
delicate layer of CT, richly vascularized with blood vessels
CLINGS TIGHT to brain surface
Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF)
- watery fluid located in and around the brain and spinal cord
- provides cushion
- nourishes brain
- removes wastes
- transmit neurotransmitters
in the Choroid Plexuses (mainly 3rd and 4th ventricles)
Where is most of the CSF made?
a barrier that keeps the brain away from the rest of the body
What is the blood-brain-barrier?
tight junctions
What kind of junctions are a special feature of the endothelium of brain's capillaries' walls?
so that nutrients (including oxygen) and ions required by neurons can pass through the barrier
Why is the BBB not an ABSOLUTE BARRIER?
lipid soluble molecules
What kind of molecules can pass through the BBB?
Foramen magnum and ends at L1-L2
Where does the spinal cord start and end?
spinal meninges
group of specialized membranes that provides physical stability and shock absorption for the neural tissues of spinal cord
spinal dural sheath
dura mater layer but does not attach to surrounding bone; corresponds to meningeal layer only
Functions of spinal cord
- involved in sensory and motor innervation of body below the head
- 2 way conduction pathway from body to brain
- major center for REFLEXES
31 pairs
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
8 pairs
How many Cervical spinal nerves are there?
12 pairs
How many Thoracic spinal nerves are there?
5 pairs
How many Lumbar spinal nerves are there?
5 pairs
How many Sacral spinal nerves are there?
1 pair
How many Coccygeal spinal nerves are there?
epineurium - perineurium - endoneurium
What are the 3 layers covering the spinal nerve? Outer to deepest
epineurium
a sheath of dense network of collagen fibers surrounding the entire nerve
perineurium
a sheath that partitions the nerve into fascicles and forms the NERVE BLOOD BARRIER
endoneurium
a sheath of delicate CT fibers that surround individual axons of fascicles
denticulate ligaments
made up of supporting fibers (lateral from spinal cord surface) that bind the spinal pia mater and arachnoid mater TO the dura mater
- functions in preventing the spinal cord from moving side to side or slide downward
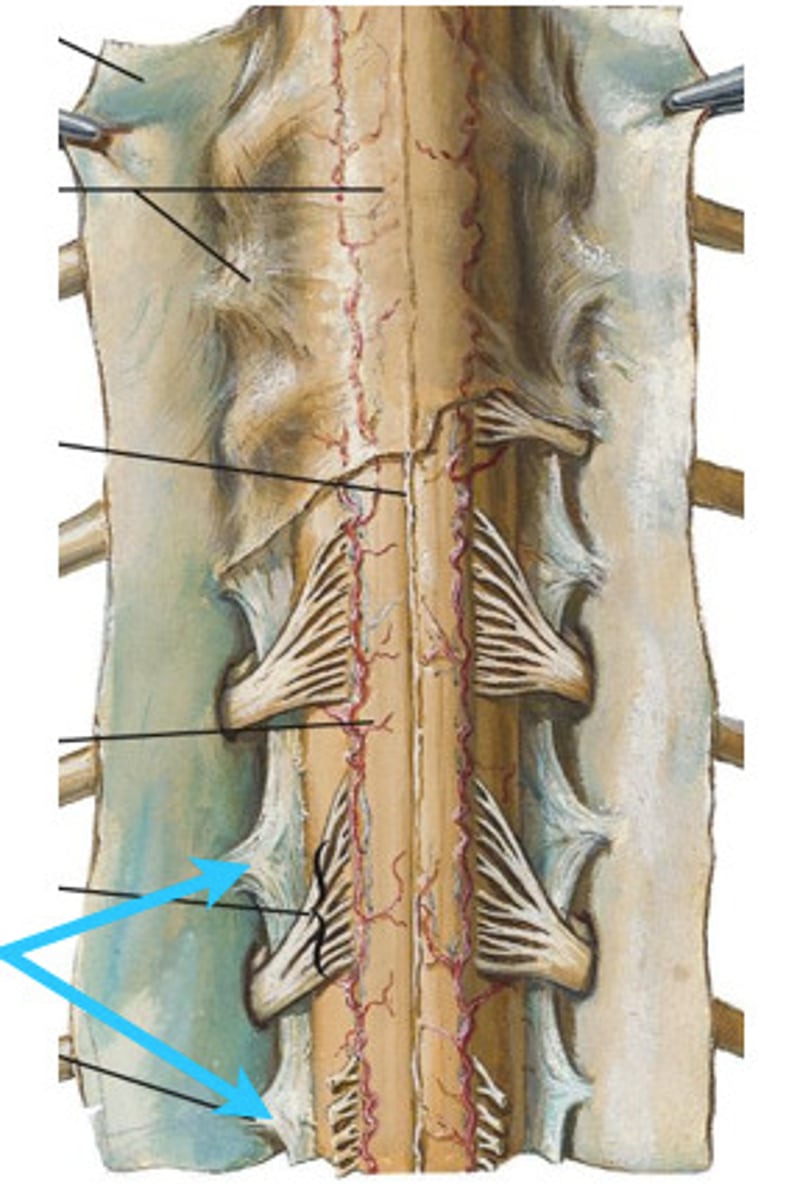
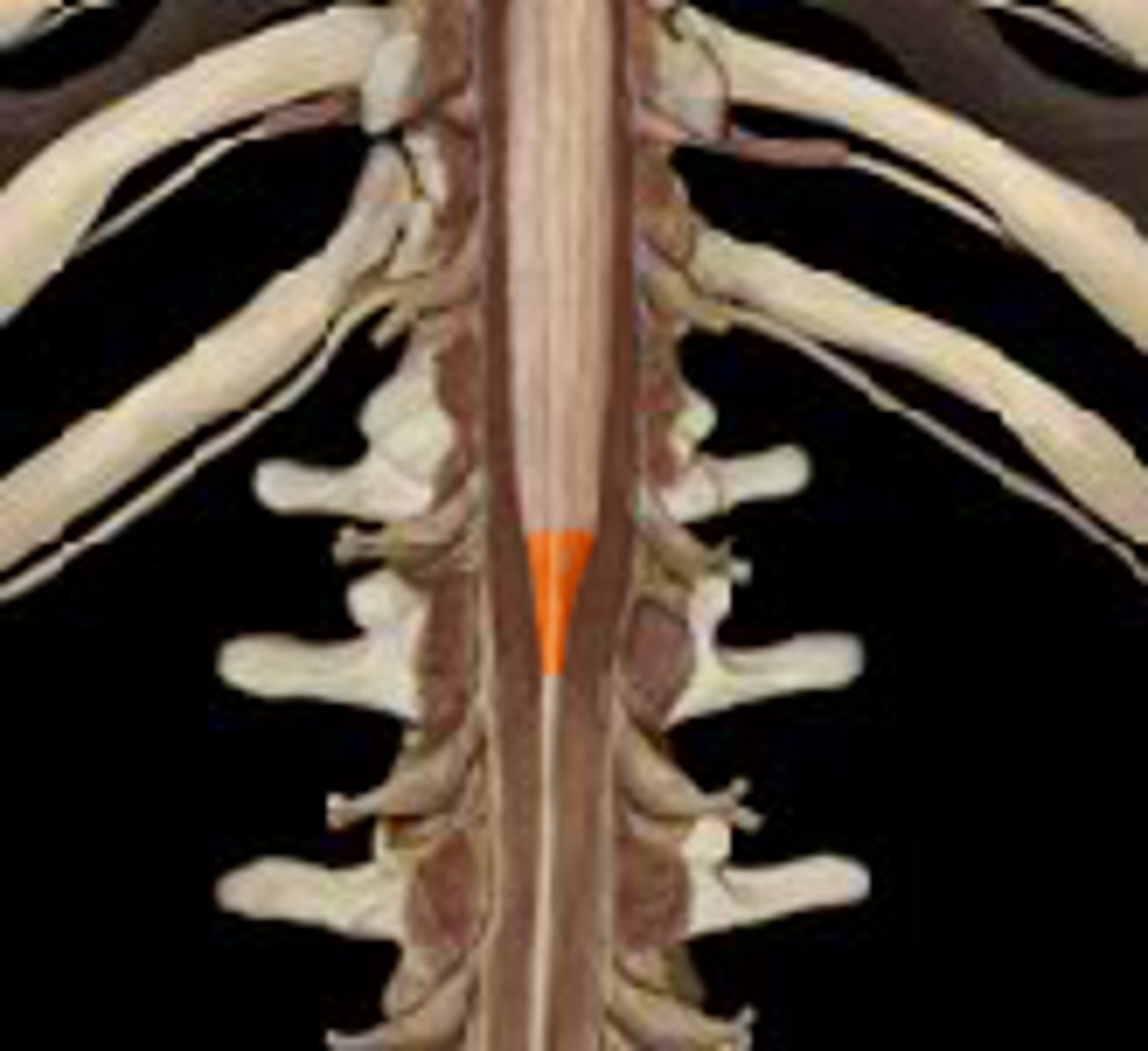
conus medullaris
tapered end of spinal cord
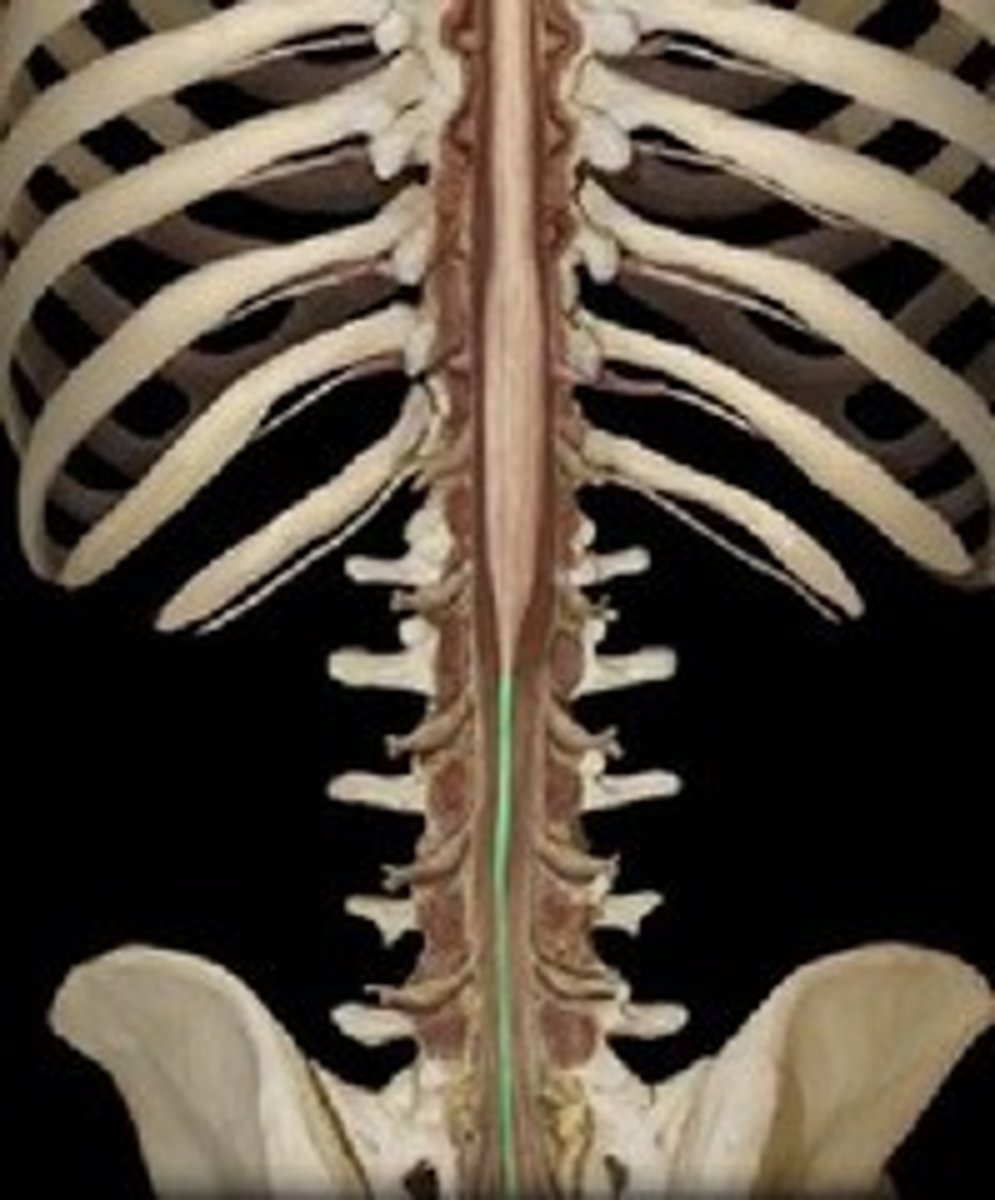
filum terminale
end of ligament
strand of fibrous CT covered with pia mater
anchors the spinal cord in place
cauda equina
"horse's tail", a fan of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
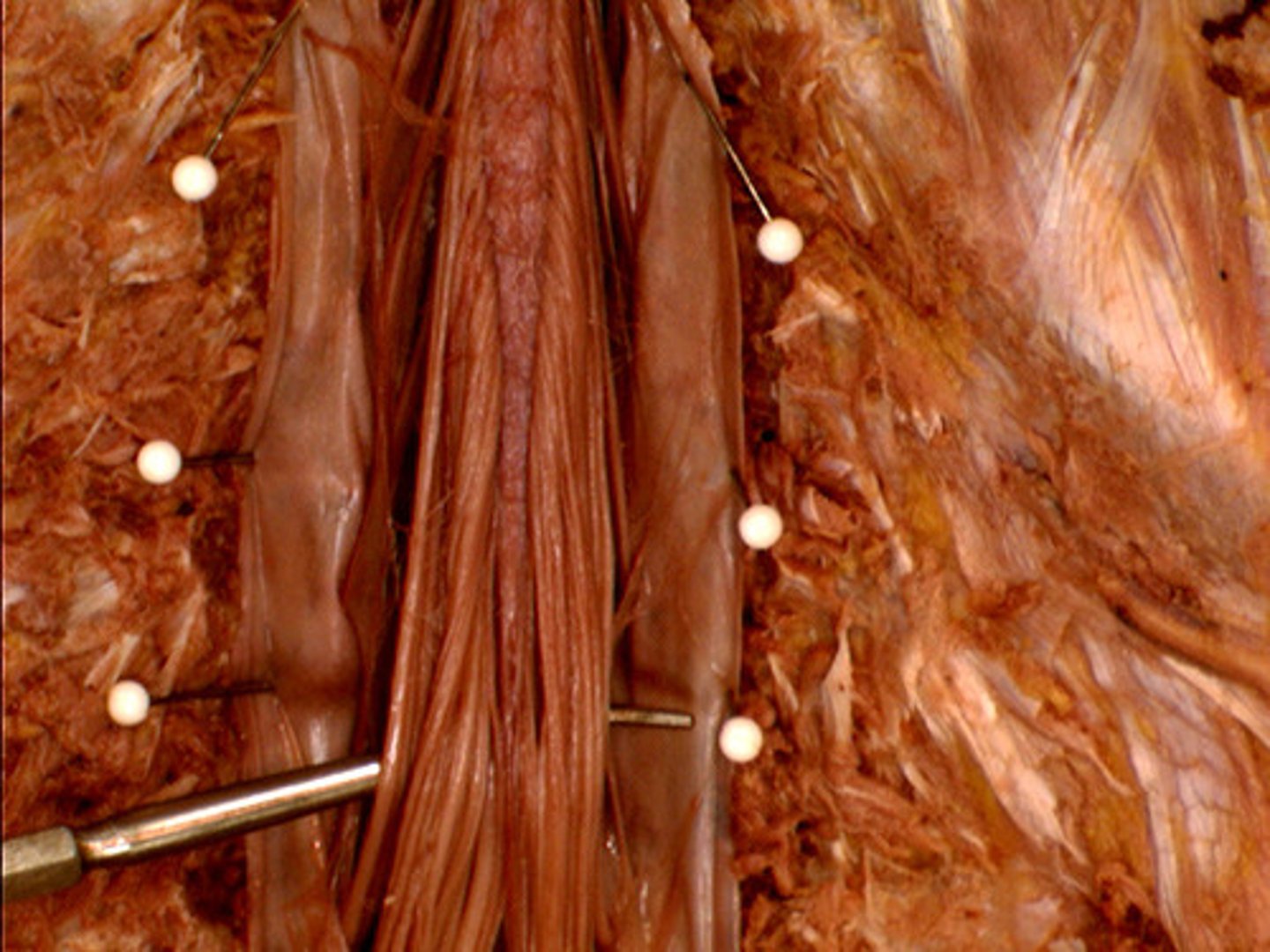
posterior median sulcus and anterior median fissure
two deep grooves that run the length of the spinal cord and partly divide with into R and L halves
inside (cross section)
Where is the gray matter of the spinal cord?
gray matter of spinal cord
mixture of motor neuron cell bodies, short unmyelinated axons and dendrites of sensory neurons, association neurons and neurolgia
gray commissure
consists of axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the spinal cord to the other side
posterior gray horns
DORSAL (SENSORY!!!!)
What parts of the spinal cord contains SOMATIC and VISCERAL SENSORY?
anterior gray horns
VENTRAL (MOTOR!!!!!!)
What parts of the spinal cord contains SOMATIC MOTOR CONTROL?
lateral gray horns
What parts of the spinal cord contains VISCERAL MOTOR NEURONS?
ascending tracts
groups of fibers that relay SENSORY INFORMATION from the spinal cord to the brain
descending tracts
groups of fibers that relay MOTOR INFORMATION from the brain to the spinal cord